Department of Defense (USA) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the
 The
The
 The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is the secretary and his/her deputy's (mainly) civilian staff.
OSD is the principal staff element of the secretary of defense in the exercise of policy development, planning, resource management, fiscal and program evaluation and oversight, and interface and exchange with other U.S. government departments and agencies, foreign governments, and international organizations, through formal and informal processes. OSD also performs oversight and management of the Defense Agencies, Department of Defense Field Activities, and specialized Cross Functional Teams.
The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is the secretary and his/her deputy's (mainly) civilian staff.
OSD is the principal staff element of the secretary of defense in the exercise of policy development, planning, resource management, fiscal and program evaluation and oversight, and interface and exchange with other U.S. government departments and agencies, foreign governments, and international organizations, through formal and informal processes. OSD also performs oversight and management of the Defense Agencies, Department of Defense Field Activities, and specialized Cross Functional Teams.
File:US Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) seal (vector).svg, Defense Intelligence Agency
File:National Security Agency.svg, National Security Agency
File:US-NationalGeospatialIntelligenceAgency-2008Seal.svg, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency
File:US-NationalReconnaissanceOffice-Seal.svg, National Reconnaissance Office
 The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the Department of Defense who advise the secretary of defense, the
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the Department of Defense who advise the secretary of defense, the
File:United States Department of the Army Seal.svg,
File:Mark of the United States Army.svg, U.S. Army
File:Emblem of the United States Marine Corps.svg,
 A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad/continuing mission.
These Military Departments are responsible for equipping and training troops to fight, while the Unified Combatant Commands are responsible for military forces' actual operational command. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The Unified Commands are governed by a Unified Command PlanŌĆöa frequently updated document (produced by the DoD), which lays out the Command's mission, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the
A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad/continuing mission.
These Military Departments are responsible for equipping and training troops to fight, while the Unified Combatant Commands are responsible for military forces' actual operational command. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The Unified Commands are governed by a Unified Command PlanŌĆöa frequently updated document (produced by the DoD), which lays out the Command's mission, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the
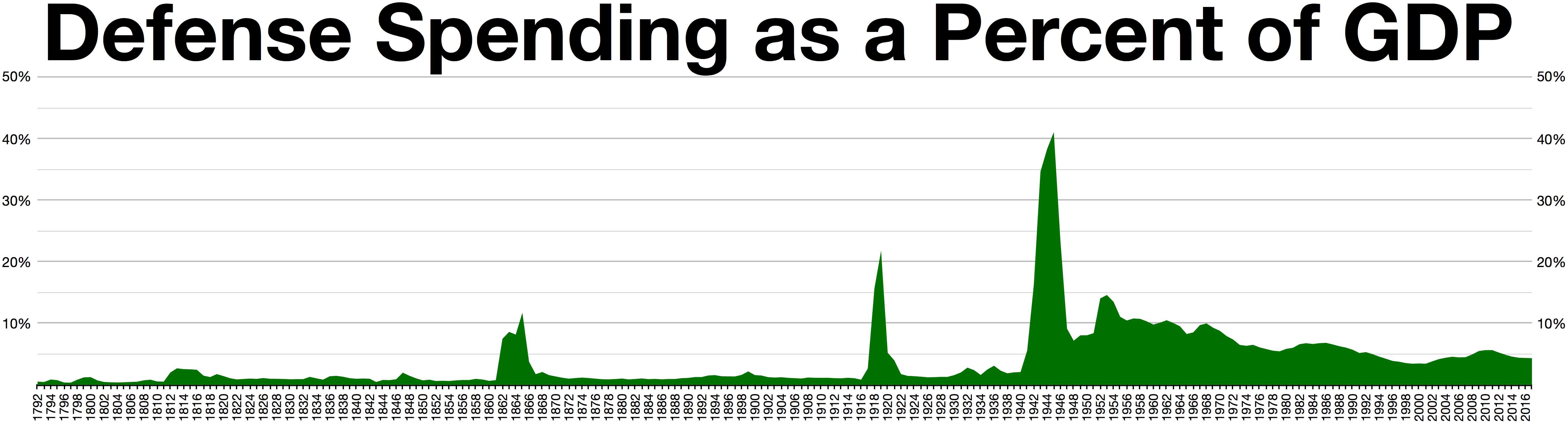 Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of budgeted global military spending ŌĆō more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget),Mackenzie Eaglen (05 February 2020) Is Army Richest Service? Navy? Air Force? AEIŌĆÖs Eaglen Peels Back Budget Onion
Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of budgeted global military spending ŌĆō more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget),Mackenzie Eaglen (05 February 2020) Is Army Richest Service? Navy? Air Force? AEIŌĆÖs Eaglen Peels Back Budget Onion
/ref> He will re-deploy to the modernization of hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and missile defense.Paul McLeary (February 05, 2020) SecDef Eyeing Moving Billions By Eliminating Offices, Legacy Systems
/ref> Beyond 2021 the 27th secretary of defense is projecting the need for yearly budget increases of 3 to 5 percent to modernize.McLeary (February 06, 2020) Flatline: SecDef Esper Says DoD Budgets Must Grow 3-5%
/ref> The Department of Defense accounts for the majority of federal discretionary spending. In FY 2017, the Department of Defense budgeted spending accounted for 15% of the U.S. federal budget, and 49% of federal discretionary spending, which represents funds not accounted for by pre-existing obligations. However, this does not include many military-related items that are outside the Defense Department budget, such as nuclear weapons research, maintenance, cleanup, and production, which is in the Department of Energy budget, Veterans Affairs, the Treasury Department's payments in pensions to military retirees and widows and their families, interest on debt incurred in past wars, or State Department financing of foreign arms sales and militarily-related development assistance. Neither does it include defense spending that is not military in nature, such as the Department of Homeland Security, counter-terrorism spending by the FBI, and intelligence-gathering spending by the NSA. In the
In the
* Numbers may not add due to rounding
Department of Defense
on
Department of Defense
in the
Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)
Budget and Financial Management Policy
Death and Taxes: 2009
ĆöA visual guide and infographic of the 2009 United States federal budget, including the Department of Defense with data provided by the Comptrollers office.
* * * {{Navboxes , list = {{United States Armed Forces {{United States intelligence agencies {{United States federal executive departments {{Authority control 1947 establishments in the United States Government agencies established in 1947 Nuclear weapons infrastructure of the United States
federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military atta ...
and the United States Armed Forces. The DoD is the largest employer in the world, with over 1.34 million active-duty service members (soldiers, marines, sailors, airmen, and guardians) as of June 2022. The DoD also maintains over 778,000 National Guard and reservists, and over 747,000 civilians bringing the total to over 2.87 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the DoD's stated mission is to provide "the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security".
The Department of Defense is headed by the secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
, a cabinet-level head who reports directly to the president of the United States. Beneath the Department of Defense are three subordinate military departments: the Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the U.S. The Department of the Army is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is org ...
, the Department of the Navy Navy Department or Department of the Navy may refer to:
* United States Department of the Navy,
* Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), in the United Kingdom, 1964-1997
* Confederate States Department of the Navy, 1861-1865
* Department of the Na ...
, and the Department of the Air Force. In addition, four national intelligence services are subordinate to the Department of Defense: the Defense Intelligence Agency ( DIA), the National Security Agency (NSA
The National Security Agency (NSA) is a national-level intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collectio ...
), the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency ( NGA), and the National Reconnaissance Office ( NRO). Other Defense agencies include the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency ( DARPA), the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA DLA may refer to: Entities and organizations
* DLA Piper, an international law firm
* DLA (TV), a Latin American television provider
* Defense Logistics Agency, United States
* Democratic Left Alliance, a Polish political party
* Dental Laborat ...
), the Missile Defense Agency (MDA
MDA, mda, or ''variation'', may refer to:
Places
* Moldova, a country in Europe with the ISO 3166-1 country code MDA Politics
* Meghalaya Democratic Alliance (2018), ruling coalition government in the Indian State of Meghalaya led by National Pe ...
), the Defense Health Agency (DHA DHA, Dha and dha may refer to:
Chemicals
* Docosahexaenoic acid, a 22:6 omega-3 fatty acid
* Dehydroandrosterone, an endogenous androgenic steroid
* Dehydroascorbic acid, an oxidized form of ascorbic acid
* Dehydroacetic acid, a pyrone derivati ...
), Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA
The Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense (DoD) for countering weapons of mass destruction (WMD; chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, and high explosives). Accord ...
), the Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency ( DCSA), the Space Development Agency ( SDA) and the Pentagon Force Protection Agency ( PFPA), all of which are subordinate to the secretary of defense. Additionally, the Defense Contract Management Agency ( DCMA) is responsible for administering contracts for the DoD. Military operations are managed by eleven regional or functional Unified combatant commands. The Department of Defense also operates several joint services schools, including the Eisenhower School
The Dwight D. Eisenhower School for National Security and Resource Strategy (Eisenhower School), formerly known as the Industrial College of the Armed Forces (ICAF), is a part of the National Defense University. It was renamed on September 6, 20 ...
(ES) and the National War College
The National War College (NWC) of the United States is a school in the National Defense University. It is housed in Roosevelt Hall on Fort Lesley J. McNair, Washington, D.C., the third-oldest Army post still active.
History
The National War Colle ...
(NWC).
History
Faced with rising tensions between the Thirteen Colonies and theBritish government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mh├▓rachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_es ...
, one of the first actions taken by the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
in September 1774 was to recommend that the colonies begin defensive military preparations. In mid-June 1775, after the outbreak of the Revolutionary War, the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
, recognizing the necessity of having a national army that could move about and fight beyond the boundaries of any particular colony, organized the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
on 14 June 1775. This momentous event is commemorated in the U.S. annually as Flag Day. Later that year, Congress would charter the Continental Navy
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United States during the American Revolutionary War and was founded October 13, 1775. The fleet cumulatively became relatively substantial through the efforts of the Continental Navy's patron John Adams ...
on 13 October, and the Continental Marines on 10 November.
The War Department and Navy Department
Upon the seating of the1st U.S. Congress
The 1st United States Congress, comprising the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met from March 4, 1789, to March 4, 1791, during the first two years of George Washington's presidency, first at Federal Hall in ...
on 4 March 1789, legislation to create a military defense force stagnated as they focused on other concerns relevant to setting up the new government. President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
went to Congress to remind them of their duty to establish a military twice during this time. Finally, on the last day of the session, 29 September 1789, Congress created the War Department. The War Department handled naval affairs until Congress created the Navy Department Navy Department or Department of the Navy may refer to:
* United States Department of the Navy,
* Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), in the United Kingdom, 1964-1997
* Confederate States Department of the Navy, 1861-1865
* Department of the Na ...
in 1798. The secretaries of each department reported directly to the president as cabinet-level advisors until 1949, when all military departments became subordinate to the Secretary of Defense.
National Military Establishment
After the end of World War II, President Harry Truman proposed the creation of a unified department of national defense. In a special message to Congress on 19 December 1945, the president cited both wasteful military spending and inter-departmental conflicts. Deliberations in Congress went on for months focusing heavily on the role of the military in society and the threat of granting too much military power to the executive. On 26 July 1947, Truman signed theNational Security Act of 1947
The National Security Act of 1947 ( Pub.L.br>80-253 61 Stat.br>495 enacted July 26, 1947) was a law enacting major restructuring of the United States government's military and intelligence agencies following World War II. The majority of the pro ...
, which set up a unified military command known as the "National Military Establishment", as well as creating the Central Intelligence Agency, the National Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
, National Security Resources Board The National Security Resources Board was a United States government agency created by the National Security Act of 1947 whose purpose was to advise the President, in times of war, on how to mobilize natural resources, manpower, and the scientific e ...
, United States Air Force (formerly the Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
) and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The act placed the National Military Establishment under the control of a single secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
. The National Military Establishment formally began operations on 18 September, the day after the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
confirmed James V. Forrestal
James Vincent Forrestal (February 15, 1892 ŌĆō May 22, 1949) was the last Cabinet-level United States Secretary of the Navy and the first United States Secretary of Defense.
Forrestal came from a very strict middle-class Irish Catholic fami ...
as the first secretary of defense. The National Military Establishment was renamed the "Department of Defense" on 10 August 1949 and absorbed the three cabinet-level military departments, in an amendment to the original 1947 law. The renaming is alleged to be due to the Establishment's abbreviation, NME, being pronounced "enemy".
Under the Department of Defense Reorganization Act
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national secur ...
of 1958 (), channels of authority within the department were streamlined while still maintaining the ordinary authority of the Military Departments to organize, train, and equip their associated forces. The Act clarified the overall decision-making authority of the secretary of defense with respect to these subordinate Military Departments and more clearly defined the operational chain of command over U.S. military forces (created by the military departments) as running from the president to the secretary of defense and then to the unified combatant commanders. Also provided in this legislation was a centralized research authority, the Advanced Research Projects Agency, eventually known as DARPA. The act was written and promoted by the Eisenhower administration and was signed into law 6 August 1958.
Financial discrepancies
A day before the September 11 attacks of 2001, Secretary of DefenseDonald Rumsfeld
Donald Henry Rumsfeld (July 9, 1932 ŌĆō June 29, 2021) was an American politician, government official and businessman who served as Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under president Gerald Ford, and again from 2001 to 2006 under Presi ...
announced that the department was unable to account for about $2.3 trillion worth of transactions. Reuters reported in 2013 that the Pentagon was the only federal agency that had not released annual audits as required by a 1992 law. According to Reuters, the Pentagon "annually reports to Congress that its books are in such disarray that an audit is impossible". In June 2016, the Office of the Inspector General released a report stating that the Army made $6.5 trillion in wrongful adjustments to its accounting entries in 2015.
Organizational structure
 The
The secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
, appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, is by federal law () the head of the Department of Defense, "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to Department of Defense", and has "authority, direction, and control over the Department of Defense". Because the Constitution vests all military authority in Congress and the president, the statutory authority of the secretary of defense is derived from their constitutional authority. Since it is impractical for either Congress or the president to participate in every piece of Department of Defense affairs, the secretary of defense and the secretary's subordinate officials generally exercise military authority.
The Department of Defense is composed of the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD OSD may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Ocean Science Discussions, the discussion and review section of the journal ''Ocean Science''
* Optimal shape design, a part of the field of optimal control theory
* Oral sedation dentistry, the oral admi ...
), the Joint Chiefs of Staff ( JCS) and the Joint Staff ( JS), Office of the Inspector General ( DODIG), the Combatant Commands
A unified combatant command (CCMD), also referred to as a combatant command, is a joint military command of the United States Department of Defense that is composed of units from two or more service branches of the United States Armed Forces, an ...
, the Military Departments (Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the U.S. The Department of the Army is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is org ...
(DA), Department of the Navy Navy Department or Department of the Navy may refer to:
* United States Department of the Navy,
* Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), in the United Kingdom, 1964-1997
* Confederate States Department of the Navy, 1861-1865
* Department of the Na ...
(DON) & Department of the Air Force (DAF)), the Defense Agencies and Department of Defense Field Activities, the National Guard Bureau
The National Guard Bureau is the federal instrument responsible for the administration of the National Guard established by the United States Congress as a joint bureau of the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force. It was cre ...
(NGB), and such other offices, agencies, activities, organizations, and commands established or designated by law, or by the president or by the secretary of defense.
Department of Defense Directive 5100.01 describes the organizational relationships within the department, and is the foundational issuance for delineating the major functions of the department. The latest version, signed by former secretary of defense Robert Gates in December 2010, is the first major re-write since 1987.
Office of the Secretary of Defense
 The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is the secretary and his/her deputy's (mainly) civilian staff.
OSD is the principal staff element of the secretary of defense in the exercise of policy development, planning, resource management, fiscal and program evaluation and oversight, and interface and exchange with other U.S. government departments and agencies, foreign governments, and international organizations, through formal and informal processes. OSD also performs oversight and management of the Defense Agencies, Department of Defense Field Activities, and specialized Cross Functional Teams.
The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is the secretary and his/her deputy's (mainly) civilian staff.
OSD is the principal staff element of the secretary of defense in the exercise of policy development, planning, resource management, fiscal and program evaluation and oversight, and interface and exchange with other U.S. government departments and agencies, foreign governments, and international organizations, through formal and informal processes. OSD also performs oversight and management of the Defense Agencies, Department of Defense Field Activities, and specialized Cross Functional Teams.
Defense agencies
OSD also supervises the following Defense Agencies:National intelligence agencies
Several defense agencies are members of the United States Intelligence Community. These are national-level intelligence services that operate under the Department of Defense jurisdiction but simultaneously fall under the authorities of thedirector of national intelligence
The director of national intelligence (DNI) is a senior, cabinet-level United States government official, required by the Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 to serve as executive head of the United States Intelligence Commu ...
. They fulfill the requirements of national policymakers and war planners, serve as Combat Support Agencies, and also assist non-Department of Defense intelligence or law enforcement services such as the Central Intelligence Agency and the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
.
The military services each have their own intelligence elements that are distinct from but subject to coordination by national intelligence agencies under the Department of Defense. Department of Defense manages the nation's coordinating authorities and assets in disciplines of signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligenceŌĆöabbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
, geospatial intelligence
In the United States, geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) is intelligence about the human activity on earth derived from the exploitation and analysis of imagery, signals, or signatures with geospatial information. GEOINT describes, assesses, and vis ...
, and measurement and signature intelligence, and also builds, launches, and operates the Intelligence Community's satellite assets. Department of Defense also has its own human intelligence service
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a pu ...
, which contributes to the CIA's human intelligence efforts while also focusing on military human intelligence priorities. These agencies are directly overseen by the Undersecretary of Defense for Intelligence
The under secretary of defense for intelligence and security or USD(I&S) is a high-ranking civilian position in the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) within the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) that acts as the principal civilian advisor a ...
.
Joint Chiefs of Staff
 The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the Department of Defense who advise the secretary of defense, the
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the Department of Defense who advise the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council
The Homeland Security Council (HSC) is an entity within the Executive Office of the President of the United States tasked with advising the President on matters relevant to Homeland Security. The current Homeland Security Advisor is Elizabeth Sh ...
, the National Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
and the president on military matters. The composition of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is defined by statute and consists of the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (CJCS) is the presiding officer of the United States Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS). The chairman is the highest-ranking and most senior military officer in the United States Armed Forces Chairman: app ...
(CJCS), vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (VJCS) is, by U.S. law, the second highest-ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces, - Vice Chairman ranking just below the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The vice chairman ...
(VCJCS), senior enlisted advisor to the chairman (SEAC), the Military Service chiefs from the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, and Space Force
A space force is a military branch of a nation's armed forces that conducts military operations in outer space and space warfare. The world's first space force was the Russian Space Forces, established in 1992 as an independent military service. ...
, in addition to the chief of National Guard Bureau
The National Guard Bureau is the federal instrument responsible for the administration of the National Guard established by the United States Congress as a joint bureau of the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force. It was cre ...
, all appointed by the president following Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
confirmation. Each of the individual Military Service Chiefs, outside their Joint Chiefs of Staff obligations, works directly for the secretary of the Military Department concerned: the secretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
, secretary of the Navy and secretary of the Air Force.
Following the GoldwaterŌĆōNichols Act
The GoldwaterŌĆōNichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of October 4, 1986 , (signed by President Ronald Reagan), made the most sweeping changes to the United States Department of Defense since the department was established in the ...
in 1986 the Joint Chiefs of Staff do not have operational command authority, neither individually nor collectively, as the chain of command goes from the president to the secretary of defense, and from the Secretary of Defense to the commanders of the Combatant Commands. GoldwaterŌĆōNichols also created the office of vice-chairman, and the chairman is now designated as the ''principal military adviser'' to the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council, the National Security Council and to the president.
The Joint Staff (JS) is a headquarters staff at the Pentagon
In geometry, a pentagon (from the Greek ŽĆ╬Ł╬ĮŽä╬Ą ''pente'' meaning ''five'' and ╬│Žē╬Į╬»╬▒ ''gonia'' meaning ''angle'') is any five-sided polygon or 5-gon. The sum of the internal angles in a simple pentagon is 540┬░.
A pentagon may be simpl ...
made up of personnel from all four services that assist the chairman and vice chairman in discharging their duties, and managed by the director of the Joint Staff (DJS) who is a lieutenant general or vice admiral.
Military Departments and Services
There are three Military Departments within the Department of Defense: # theDepartment of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the U.S. The Department of the Army is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is org ...
, within which the United States Army is organized.
# the Department of the Navy Navy Department or Department of the Navy may refer to:
* United States Department of the Navy,
* Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), in the United Kingdom, 1964-1997
* Confederate States Department of the Navy, 1861-1865
* Department of the Na ...
, within which the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps are organized.
# the Department of the Air Force, within which the United States Air Force and United States Space Force are organized.
The Military Departments are each headed by their own secretary (i.e., Secretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
, Secretary of the Navy and Secretary of the Air Force), appointed by the president, with the advice and consent of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
. They have the legal authority under Title 10 of the United States Code to conduct all the affairs of their respective departments within which the military services are organized. The secretaries of the Military Departments are (by law) subordinate to the secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
and (by SecDef delegation) to the deputy secretary of defense.
Secretaries of Military Departments, in turn, normally exercise authority over their forces by delegation through their respective service chiefs (i.e., Chief of Staff of the Army, Commandant of the Marine Corps
The commandant of the Marine Corps (CMC) is normally the highest-ranking officer in the United States Marine Corps and is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Joint Chiefs of Staff: composition; functions. The CMC reports directly to the secr ...
, Chief of Naval Operations
The chief of naval operations (CNO) is the professional head of the United States Navy. The position is a statutory office () held by an admiral who is a military adviser and deputy to the secretary of the Navy. In a separate capacity as a memb ...
, Chief of Staff of the Air Force, and Chief of Space Operations) over forces not assigned to a Combatant Command.
Secretaries of Military Departments and service chiefs do not possess operational command authority over U.S. troops (this power was stripped from them in the Defense Reorganization Act of 1958
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
), and instead, Military Departments are tasked solely with "the training, provision of equipment, and administration of troops."
Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the U.S. The Department of the Army is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is org ...
File:United States Department of the Navy Seal.svg, Department of the Navy Navy Department or Department of the Navy may refer to:
* United States Department of the Navy,
* Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), in the United Kingdom, 1964-1997
* Confederate States Department of the Navy, 1861-1865
* Department of the Na ...
File:Seal of the US Air Force.svg, Department of the Air Force
U.S. Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through comb ...
File:Emblem of the United States Navy.svg, U.S. Navy
File:Mark of the United States Air Force.svg, U.S. Air Force
File:Seal of the United States Space Force.svg, U.S. Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces, one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and the world's only independent space force. Along with its sister branch, the U.S. Air Force, the Space ...
Unified Combatant Commands
 A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad/continuing mission.
These Military Departments are responsible for equipping and training troops to fight, while the Unified Combatant Commands are responsible for military forces' actual operational command. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The Unified Commands are governed by a Unified Command PlanŌĆöa frequently updated document (produced by the DoD), which lays out the Command's mission, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the
A unified combatant command is a military command composed of personnel/equipment from at least two Military Departments, which has a broad/continuing mission.
These Military Departments are responsible for equipping and training troops to fight, while the Unified Combatant Commands are responsible for military forces' actual operational command. Almost all operational U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command. The Unified Commands are governed by a Unified Command PlanŌĆöa frequently updated document (produced by the DoD), which lays out the Command's mission, geographical/functional responsibilities, and force structure.
During military operations, the chain of command runs from the president to the secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
to the combatant commanders of the Combatant Commands.
the United States has eleven Combatant Commands, organized either on a geographical basis (known as "area of responsibility
Area of responsibility (AOR) is a pre-defined geographic region assigned to Combatant commanders of the Unified Command Plan (UCP), that are used to define an area with specific geographic boundaries where they have the authority to plan and cond ...
", AOR) or on a global, functional basis:
* U.S. Northern Command
United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) is one of eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense. The command is tasked with providing military support for non-military authorities in the U.S., and protect ...
(USNORTHCOM)
* U.S. Southern Command (USSOUTHCOM)
* U.S. Central Command
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Tas ...
(USCENTCOM)
* U.S. European Command
The United States European Command (EUCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the United States military, headquartered in Stuttgart, Germany. Its area of focus covers and 51 countries and territories, including Europe, Russia ...
(USEUCOM)
* U.S. Indo-Pacific Command
United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM) is a unified combatant command of the United States Armed Forces responsible for the Indo-Pacific region.
Formerly known as United States Pacific Command (USPACOM) since its inception in 1947, t ...
(USINDOPACOM)
* U.S. Africa Command
The United States Africa Command (USAFRICOM, U.S. AFRICOM, and AFRICOM), is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense, headquartered at Kelley Barracks, Stuttgart, Germany. It is responsible for U ...
(USAFRICOM)
* U.S. Strategic Command
United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands in the United States Department of Defense. Headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska, USSTRATCOM is responsible for strategic nuclear deterre ...
(USSTRATCOM)
* U.S. Special Operations Command
The United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM or SOCOM) is the unified combatant command charged with overseeing the various special operations component commands of the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, and Air Force of the United States Arm ...
(USSOCOM)
* U.S. Transportation Command (USTRANSCOM)
* U.S. Cyber Command
United States Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). It unifies the direction of cyberspace operations, strengthens DoD cyberspace capabilities, and integra ...
(USCYBERCOM)
* U.S. Space Command
United States Space Command (USSPACECOM or SPACECOM) is a unified combatant command of the United States Department of Defense, responsible for military operations in outer space, specifically all operations 100 kilometers (62 miles) and grea ...
(USSPACECOM)
Budget
 Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of budgeted global military spending ŌĆō more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget),Mackenzie Eaglen (05 February 2020) Is Army Richest Service? Navy? Air Force? AEIŌĆÖs Eaglen Peels Back Budget Onion
Department of Defense spending in 2017 was 3.15% of GDP and accounted for about 38% of budgeted global military spending ŌĆō more than the next 7 largest militaries combined. By 2019, the 27th secretary of defense had begun a line-by-line review of the defense budget; in 2020 the secretary identified items amounting to $5.7 billion, out of a $106 billion subtotal (the so-called "fourth estate" agencies such as missile defense, and defense intelligence, amounting to 16% of the defense budget),Mackenzie Eaglen (05 February 2020) Is Army Richest Service? Navy? Air Force? AEIŌĆÖs Eaglen Peels Back Budget Onion/ref> He will re-deploy to the modernization of hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and missile defense.Paul McLeary (February 05, 2020) SecDef Eyeing Moving Billions By Eliminating Offices, Legacy Systems
/ref> Beyond 2021 the 27th secretary of defense is projecting the need for yearly budget increases of 3 to 5 percent to modernize.McLeary (February 06, 2020) Flatline: SecDef Esper Says DoD Budgets Must Grow 3-5%
/ref> The Department of Defense accounts for the majority of federal discretionary spending. In FY 2017, the Department of Defense budgeted spending accounted for 15% of the U.S. federal budget, and 49% of federal discretionary spending, which represents funds not accounted for by pre-existing obligations. However, this does not include many military-related items that are outside the Defense Department budget, such as nuclear weapons research, maintenance, cleanup, and production, which is in the Department of Energy budget, Veterans Affairs, the Treasury Department's payments in pensions to military retirees and widows and their families, interest on debt incurred in past wars, or State Department financing of foreign arms sales and militarily-related development assistance. Neither does it include defense spending that is not military in nature, such as the Department of Homeland Security, counter-terrorism spending by the FBI, and intelligence-gathering spending by the NSA.
 In the
In the 2010 United States federal budget
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2010, titled A New Era of Responsibility: Renewing America's Promise, is a United States federal budget, spending request by President of the United States, President Barack Obama to fund governm ...
, the Department of Defense was allocated a base budget of $533.7 billion, with a further $75.5 billion adjustment in respect of 2009, and $130 billion for overseas contingencies. The subsequent 2010 Department of Defense Financial Report shows the total budgetary resources for fiscal year 2010 were $1.2 trillion. Of these resources, $1.1 trillion were obligated and $994 billion were disbursed, with the remaining resources relating to multi-year modernization projects requiring additional time to procure. After over a decade of non-compliance
In general, compliance means conforming to a rule, such as a specification, policy, standard or law. Compliance has traditionally been explained by reference to the deterrence theory, according to which punishing a behavior will decrease the viol ...
, Congress has established a deadline of Fiscal year 2017 for the Department of Defense to achieve audit readiness.
In 2015 the allocation for the Department of Defense was $585 billion, the highest level of budgetary resources among all Federal agencies, and this amounts to more than one-half of the annual Federal Expenditures in the United States federal budget discretionary budget.
On 9/28/2018, President Donald Trump signed the Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act, 2019 and Continuing Appropriations Act, 2019 (H.R.6157) into law. On 30 September 2018, the FY2018 Budget expired and the FY2019 budget came into effect.
For FY2019
The FY2019 Budget for the Department of Defense is approximately $686,074,048,000 (Including Base + Overseas Contingency Operations + Emergency Funds) in discretionary spending and $8,992,000,000 in mandatory spending totaling $695,066,000,000 Undersecretary of Defense (Comptroller)David L. Norquist
David L. Norquist (born November 24, 1966) is an American financial management professional and government official who served as the 34th United States deputy secretary of defense from 2019 to 2021. In January 2021, he served for two days as act ...
said in a hearing regarding the FY 2019 budget: "The overall number you often hear is $716 billion. That is the amount of funding for national defense, the accounting code is 050, and includes more than simply the Department of Defense. It includes, for example, the Department of Energy and others. That large a number, if you back out the $30 billion for non-defense agencies, you get to $686 billion. That is the funding for the Department of Defense, split between $617 billion in base and $69 billion in overseas contingency."
The Department of Defense budget encompasses the majority of the National Defense Budget of approximately $716.0 billion in discretionary spending and $10.8 billion in mandatory spending for a $726.8 billion total. Of the total, $708.1 billion falls under the jurisdiction of the House Committee on Armed Services and Senate Armed Services Committee and is subject to authorization by the annual National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA). The remaining $7.9 billion falls under the jurisdiction of other congressional committees.
The Department of Defense is unique because it is one of the few federal entities where the majority of its funding falls into the discretionary category. The majority of the entire federal budget is mandatory, and much of the discretionary funding in the budget consists of DoD dollars.
Budget overview
Energy use
The Department of Defense was the largest single consumer of energy in the United States in 2006. It is one of the largest carbon polluters in history, producing more carbon emissions than the total emissions of over 100 countries combined. In FY 2006, the department used almost 30,000 gigawatt hours (GWH) of electricity, at the cost of almost $2.2 billion. The department's electricity use would supply enough electricity to power more than 2.6 million average American homes. In electricity consumption, if it were a country, the department would rank 58th in the world, using slightly less than Denmark and slightly more thanSyria
Syria ( ar, ž│┘Å┘łž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Äž¦ or ž│┘Å┘łž▒┘É┘Ŗ┘Äž®, translit=S┼½riy─ü), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, ž¦┘äž¼┘ģ┘ć┘łž▒┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž©┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž│┘łž▒┘Ŗž®, al-Jumh┼½r─½yah al-╩╗Arab─½yah as-S┼½r─½yah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
(CIA World Factbook, 2006).Colonel Gregory J. Lengyel, USAF, The Brookings Institution, Department of Defense Energy Strategy, August 2007.
The Department of Defense was responsible for 93% of all US government fuel consumption in 2007 ( Department of the Air Force: 52%; Department of the Navy Navy Department or Department of the Navy may refer to:
* United States Department of the Navy,
* Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), in the United Kingdom, 1964-1997
* Confederate States Department of the Navy, 1861-1865
* Department of the Na ...
: 33%; Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the U.S. The Department of the Army is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is org ...
: 7%; other Department components: 1%). The Department of Defense uses of fuel annually, an average of of fuel per day. A large Army division may use about per day. According to the 2005 ''CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
'', if it were a country, the Department of Defense would rank 34th in the world in average daily oil use, coming in just behind Iraq and just ahead of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
. The Air Force is the largest user of fuel energy in the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
. The Air Force uses 10% of the nation's aviation fuel. ( JP-8 accounts for nearly 90% of its fuels.) This fuel usage breaks down as such: 82% jet fuel, 16% facility management and 2% ground vehicle/equipment.
Criticism
In the latestCenter for Effective Government
The Center for Effective Government, formerly OMB Watch, was a think tank and advocacy group based in Washington, D.C. It was focused on government transparency. Founded in 1983, the organization ceased operations in 2016, folding its work into th ...
analysis of 15 federal agencies which receive the most Freedom of Information Act Freedom of Information Act may refer to the following legislations in different jurisdictions which mandate the national government to disclose certain data to the general public upon request:
* Freedom of Information Act 1982, the Australian act
* ...
requests, published in 2015 (using 2012 and 2013 data, the most recent years available), the DoD earned 61 out of a possible 100 points, a DŌłÆ grade. While it had improved from a failing grade in 2013, it still had low scores in processing requests (55%) and their disclosure rules (42%).
A 2013 ''Reuters'' investigation concluded that Defense Finance & Accounting Service, the Department of DefenseŌĆÖs primary financial management arm, implements monthly ŌĆ£unsubstantiated change actionsŌĆØŌĆöillegal, inaccurate ŌĆ£plugsŌĆØŌĆöthat forcibly make DODŌĆÖs books match TreasuryŌĆÖs books. It concluded:Fudging the accounts with false entries is standard operating procedureŌĆ” Reuters has found that the Pentagon is largely incapable of keeping track of its vast stores of weapons, ammunition, and other supplies; thus it continues to spend money on new supplies it doesnŌĆÖt need and on storing others long out of date. It has amassed a backlog of more than half a trillion dollarsŌĆ” w much of that money paid for actual goods and services delivered isnŌĆÖt known.In 2015, a Pentagon consulting firm performed an audit on the Department of Defense's budget. It found that there was $125 billion in wasteful spending that could be saved over the next five years without layoffs or reduction in military personnel. In 2016, '' The Washington Post'' uncovered that rather than taking the advice of the auditing firm, senior defense officials suppressed and hid the report from the public to avoid political scrutiny. Shortly after the
2020 Baghdad International Airport airstrike
On 3 January 2020, Qasem Soleimani, an Iranian major general, was killed by a U.S. drone strike at Baghdad International Airport. The drone targeted and killed Soleimani while he was on his way to meet Iraqi Prime Minister Adil Abdul-Mahdi i ...
, the Iranian parliament
The Islamic Consultative Assembly ( fa, ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž┤┘łž▒ž¦█ī ž¦ž│┘䞦┘ģ█ī, Majles-e Showr─ü-ye Esl─üm─½), also called the Iranian Parliament, the Iranian Majles (Arabicised spelling Majlis) or ICA, is the national legislative body of Iran. The P ...
designated all of the U.S. military, including the Department of Defense, as a terrorist organization.
Related legislation
The organization and functions of the Department of Defense are in Title 10 of the United States Code. Other significant legislation related to the Department of Defense includes: * 1947:National Security Act of 1947
The National Security Act of 1947 ( Pub.L.br>80-253 61 Stat.br>495 enacted July 26, 1947) was a law enacting major restructuring of the United States government's military and intelligence agencies following World War II. The majority of the pro ...
* 1958: Department of Defense Reorganization Act,
* 1963: Department of Defense Appropriations Act,
* 1963: Military Construction Authorization Act,
* 1967: Supplemental Defense Appropriations Act,
* 1984: Department of Defense Authorization Act,
* 1986: Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1986 (Department of Defense Reorganization Act),
* 1996: Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act,
See also
* Arms industry * List of United States military bases * MilitaryŌĆōindustrial complex * Nuclear weapons * Private military company * Title 32 of the Code of Federal Regulations * United States Department of Homeland Security * United States Department of Justice * United States Department of Veterans Affairs * Warrior Games * JADE (planning system) * Global Command and Control SystemReferences
External links
*Department of Defense
on
USAspending.gov ttp://www.usaspending.gov USASpending.govis a database of spending by the United States federal government.
History
Around the time of the Act's passage, OMB Watch, a government watchdog group, was developing a site that would do essentially eve ...
Department of Defense
in the
Federal Register
The ''Federal Register'' (FR or sometimes Fed. Reg.) is the official journal of the federal government of the United States that contains government agency rules, proposed rules, and public notices. It is published every weekday, except on feder ...
Office of the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)
Budget and Financial Management Policy
Death and Taxes: 2009
ĆöA visual guide and infographic of the 2009 United States federal budget, including the Department of Defense with data provided by the Comptrollers office.
* * * {{Navboxes , list = {{United States Armed Forces {{United States intelligence agencies {{United States federal executive departments {{Authority control 1947 establishments in the United States Government agencies established in 1947 Nuclear weapons infrastructure of the United States
Defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...