Demethylated on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a
 Demethylation is relevant to
Demethylation is relevant to
 Another classical (but, again, harsh) method for the removal of the methyl group of an aryl methyl ether is to heat the ether in a solution of
Another classical (but, again, harsh) method for the removal of the methyl group of an aryl methyl ether is to heat the ether in a solution of 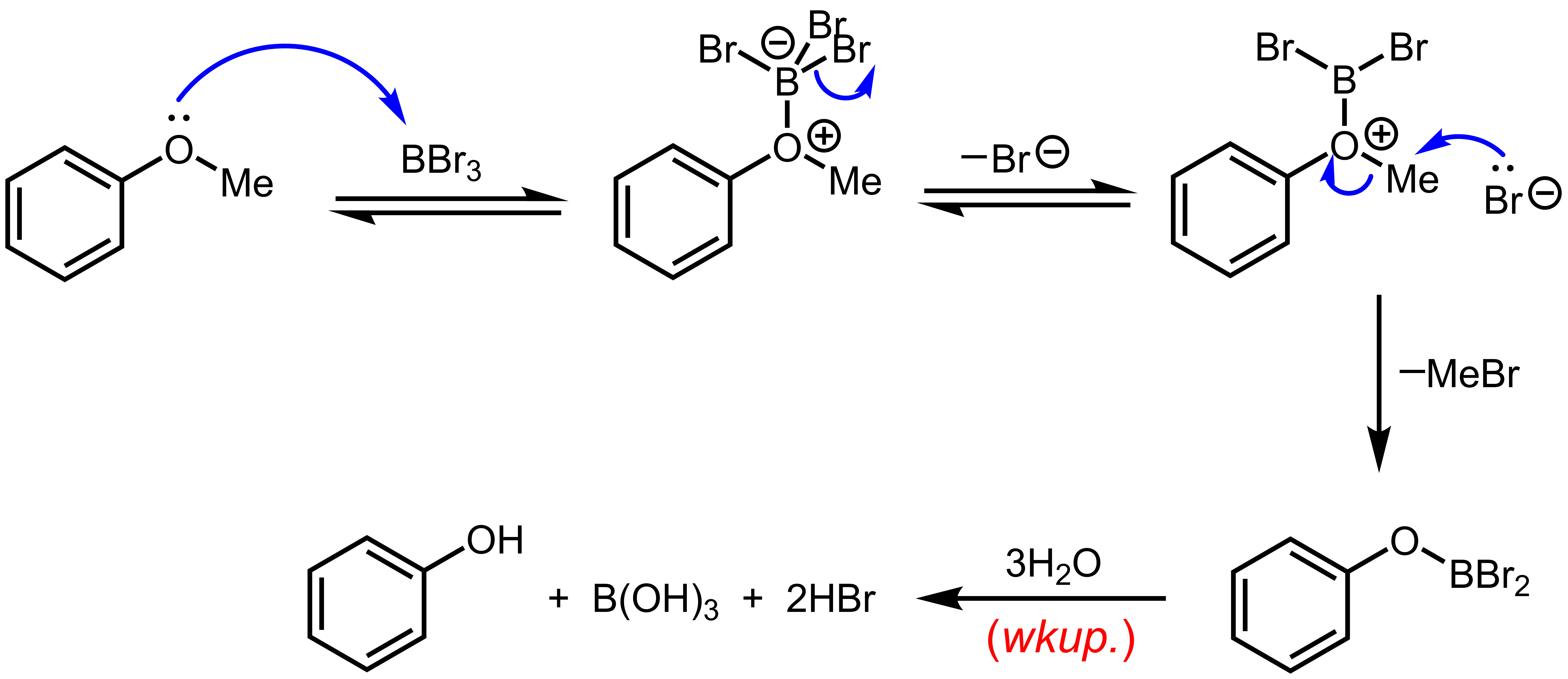 Stronger nucleophiles such as diorganophosphides (LiPPh2) also cleave aryl ethers, sometimes under mild conditions. Other strong nucleophiles that have been employed include thiolate salts like EtSNa.
Aromatic methyl ethers, particularly those with an adjacent carbonyl group, can be regioselectively demethylated using magnesium iodide etherate. An example of this being used is in the synthesis of the natural product Calphostin A, as seen below.
Stronger nucleophiles such as diorganophosphides (LiPPh2) also cleave aryl ethers, sometimes under mild conditions. Other strong nucleophiles that have been employed include thiolate salts like EtSNa.
Aromatic methyl ethers, particularly those with an adjacent carbonyl group, can be regioselectively demethylated using magnesium iodide etherate. An example of this being used is in the synthesis of the natural product Calphostin A, as seen below.
 Methyl esters also are susceptible to demethylation, which is usually achieved by
Methyl esters also are susceptible to demethylation, which is usually achieved by  A mixture of
A mixture of
methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...
(CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
The counterpart of demethylation is methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replac ...
.
In biochemistry
:epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
s. Demethylation of DNA is catalyzed by demethylase
Demethylases are enzymes that remove methyl (CH3) groups from nucleic acids, proteins (particularly histones), and other molecules. Demethylases are important epigenetics, epigenetic proteins, as they are responsible for transcriptional regulation ...
s. These enzymes oxidize
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
N-methyl groups, which occur in histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaeal phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes ...
s, in lysine derivatives, and in some forms of DNA.
:R2N-CH3 + O → R2N-H + CH2O
One family of such oxidative enzymes is the cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for examp ...
. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are a major class of non-heme iron proteins that catalyse a wide range of reactions. These reactions include hydroxylation reactions, demethylations, ring expansions, ring closures, and desaturations. Func ...
s are also active for demethylation of DNA, operating by a similar stoichiometry. These reactions, which proceed via hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation refers to the installation of a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound. Hydroxylations generate alcohols and phenols, which are very common functional groups. Hydroxylation confers some degree of water-solubility ...
, exploit the slightly weakened C-H bonds of methylamine
Methylamine, also known as methanamine, is an organic compound with a formula of . This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
Methylamine is sold ...
s and methyl ethers.
Demethylation of some sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on ...
s are steps in the biosynthesis of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
. Methyl groups are lost as formate
Formate (IUPAC name: methanoate) is the conjugate base of formic acid. Formate is an anion () or its derivatives such as ester of formic acid. The salts and esters are generally colorless.
Fundamentals
When dissolved in water, formic acid co ...
.
Biomass processing
Methoxy groups heavily decorate the biopolymerlignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
. Much interest has been shown in converting this abundant form of biomass into useful chemicals (aside from fuel). One step in such processing is demethylation.
The demethylation of vanillin
Vanillin is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a phenolic aldehyde. Its functional groups include aldehyde, hydroxyl, and ether. It is the primary component of the ethanolic extract of the vanilla bean. Synthetic vanillin ...
, a derivative of lignin, requires and strong base. Pulp and paper industry
The pulp and paper industry comprises companies that use wood, specifically pulpwood, as raw material and produce pulp, paper, paperboard, and other cellulose-based products.
Manufacturing process
In the manufacturing process, pulp is intr ...
digests lignin using aqueous sodium sulfide
Sodium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2 S, or more commonly its hydrate Na2S·9 H2O. Both the anhydrous and the hydrated salts are colorless solids, although technical grades of sodium sulfide are generally yellow to brick red ...
, which partially depolymerizes the lignin. Delignification is accompanied by extensive O-demethylation, yielding methanethiol
Methanethiol (also known as methyl mercaptan) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula . It is a colorless gas with a distinctive putrid smell. In small amounts, it is pervasive in nature and found in certain foods, such as some n ...
, which is emitted by paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
s as an air pollutant.
In organic chemistry
Demethylation often refers to cleavage ofethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R′ r ...
, especially aryl ethers.
Historically, aryl methyl ethers, including natural products such as codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
(''O''-methylmorphine), have been demethylated by heating the substance in molten pyridine hydrochloride (melting point ) at , sometimes with excess hydrogen chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hyd ...
, in a process known as the ''Zeisel–Prey ether cleavage''. Quantitative analysis for aromatic methyl ethers can be performed by argentometric determination of the ''N''-methylpyridinium chloride formed. The mechanism of this reaction starts with proton transfer from pyridinium ion to the aryl methyl ether, a highly unfavorable step (''K'' < 10−11) that accounts for the harsh conditions required, given the much weaker acidity of pyridinium ( p''K''a = 5.2) compared to the protonated aryl methyl ether (an arylmethyloxonium ion, p''K''a = –6.7 for aryl = Ph). This is followed by SN2 attack of the arylmethyloxonium ion at the methyl group by either pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weak ...
or chloride ion (depending on the substrate) to give the free phenol and, ultimately, ''N''-methylpyridinium chloride, either directly or by subsequent methyl transfer from methyl chloride to pyridine. Another classical (but, again, harsh) method for the removal of the methyl group of an aryl methyl ether is to heat the ether in a solution of
Another classical (but, again, harsh) method for the removal of the methyl group of an aryl methyl ether is to heat the ether in a solution of hydrogen bromide
Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temper ...
or hydrogen iodide
Hydrogen iodide (HI) is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas und ...
sometimes also with acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
. The cleavage of ethers by hydrobromic or hydroiodic acid proceeds by protonation of the ether, followed by displacement by bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retard ...
or iodide
An iodide ion is I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency ...
. A slightly milder set of conditions uses cyclohexyl iodide (CyI, 10.0 equiv) in ''N'',''N''-dimethylformamide to generate a small amount of hydrogen iodide ''in situ
is a Latin phrase meaning 'in place' or 'on site', derived from ' ('in') and ' ( ablative of ''situs'', ). The term typically refers to the examination or occurrence of a process within its original context, without relocation. The term is use ...
''.
Boron tribromide
Boron tribromide, BBr3, is a colorless, fuming liquid compound containing boron and bromine. Commercial samples usually are amber to red/brown, due to weak bromine contamination. It is decomposed by water and alcohols.
Chemical properties
Boron ...
, which can be used at room temperature or below, is a more specialized reagent for the demethylation of aryl methyl ethers. The mechanism of ether dealkylation proceeds via the initial reversible formation of a Lewis acid-base adduct between the strongly Lewis acidic BBr3 and the Lewis basic ether. This Lewis adduct can reversibly dissociate to give a dibromoboryl oxonium cation and Br–. Rupture of the ether linkage occurs through the subsequent nucleophilic attack on the oxonium species by Br– to yield an aryloxydibromoborane and methyl bromide. Upon completion of the reaction, the phenol is liberated along with boric acid (H3BO3) and hydrobromic acid (aq. HBr) upon hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of the dibromoborane derivative during aqueous workup.
 Stronger nucleophiles such as diorganophosphides (LiPPh2) also cleave aryl ethers, sometimes under mild conditions. Other strong nucleophiles that have been employed include thiolate salts like EtSNa.
Aromatic methyl ethers, particularly those with an adjacent carbonyl group, can be regioselectively demethylated using magnesium iodide etherate. An example of this being used is in the synthesis of the natural product Calphostin A, as seen below.
Stronger nucleophiles such as diorganophosphides (LiPPh2) also cleave aryl ethers, sometimes under mild conditions. Other strong nucleophiles that have been employed include thiolate salts like EtSNa.
Aromatic methyl ethers, particularly those with an adjacent carbonyl group, can be regioselectively demethylated using magnesium iodide etherate. An example of this being used is in the synthesis of the natural product Calphostin A, as seen below.
saponification
Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. It is an important type of alkaline hydrolysis. When the ...
. Highly specialized demethylations are abundant, such as the Krapcho decarboxylation:
:anethole
Anethole (also known as anise camphor) is an organic compound that is widely used as a flavoring substance. It is a derivative of the aromatic compound allylbenzene and occurs widely in the essential oils of plants. It is in the class of phenylpr ...
, KOH, and alcohol was heated in an autoclave. Although the product of this reaction was the expected anol
Anol, also known as ''p''-hydroxypropenylbenzene, is a simple phenol that was derived via demethylation from anethole, an estrogenic constituent of anise and fennel, by Sir Charles Dodds in 1937. It was reported to possess extremely potent e ...
, a highly reactive dimerization product in the mother liquors called dianol was also discovered by Charles Dodds
Sir Edward Charles Dodds, 1st Baronet (13 October 1899 – 16 December 1973) was a British biochemist.
Personal life
He was born in Liverpool in 1899, the only child of Ralph Edward Dodds, a shoe retailer, and Jane (née Pack) Dodds. The family s ...
.
''N''-demethylation
''N''-demethylation of 3° amines is by the von Braun reaction, which uses BrCN as thereagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a ...
to give the corresponding '' nor-'' derivatives. A modern variation of the von Braun reaction was developed, where BrCN was superseded by ethyl chloroformate. The preparation of Paxil from arecoline
Arecoline is a cholinergic agent, stimulant, and natural product, naturally occurring alkaloid found in areca nut, areca (betel) nuts of the areca palm (''Areca catechu'') found in South Asia, South and Southeast Asia. Its effects, depending on ...
is an application of this reaction, as well as the synthesis of GSK-372,475, for example.
The ''N''-demethylation of imipramine
Imipramine, sold under the brand name Tofranil, among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) mainly used in the treatment of depression. It is also effective in treating anxiety and panic disorder. Imipramine is taken by mouth.
Common s ...
gives desipramine.
See also
*Methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replac ...
, the addition of a methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...
to a substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (aquatic environment), the earthy material that exi ...
References
{{Reflist, 30em Gene expression Organic reactions