demand management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Demand management is a planning methodology used to forecast, plan for and manage the
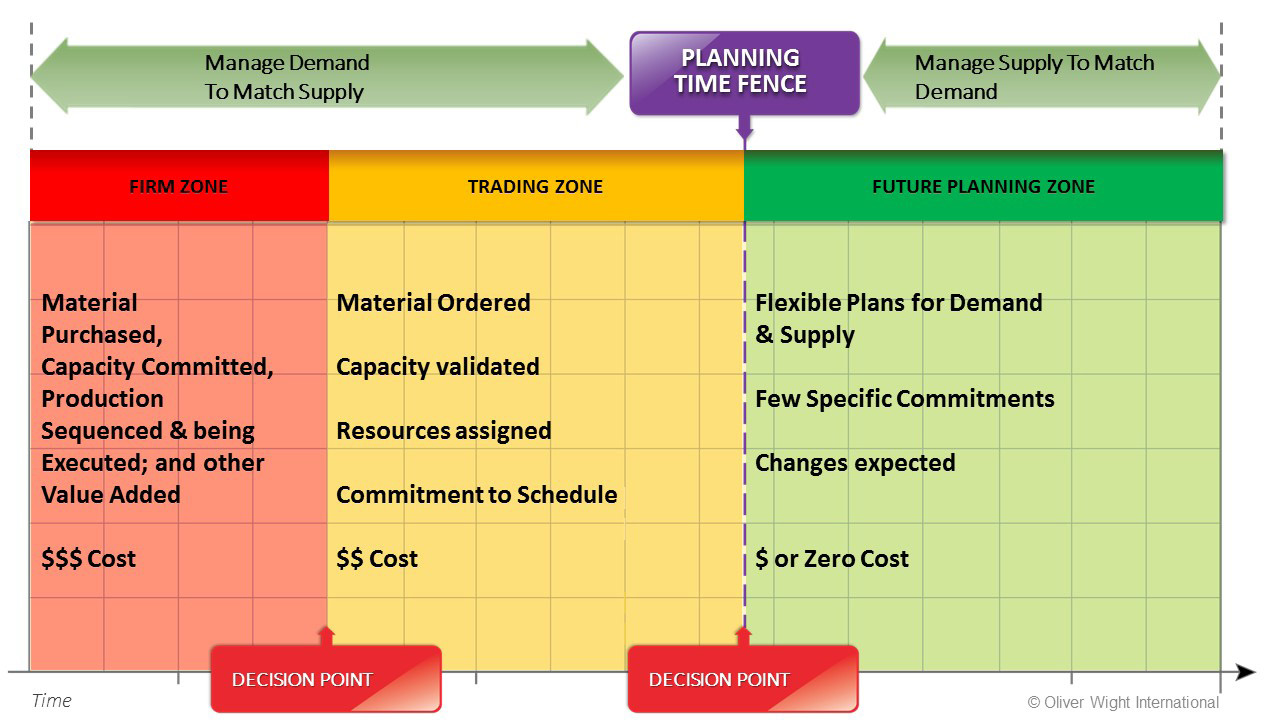 The demand control process requires that all functions agree on time fences within the planning horizon, which should be no less than a rolling 24 months based on integrated business planning
The demand control process requires that all functions agree on time fences within the planning horizon, which should be no less than a rolling 24 months based on integrated business planning
Demand Management for IT
Economic planning Demand Supply chain management
demand
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item ...
for products and services. This can be at macro-levels as in economics and at micro-levels within individual organizations. For example, at macro-levels, a government may influence interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, t ...
s to regulate financial demand. At the micro-level, a cellular service provider may provide free night and weekend use to reduce demand during peak hours.
Demand management has a defined set of processes, capabilities and recommended behaviors for companies that produce goods and services. Consumer electronics
Consumer electronics or home electronics are Electronics, electronic (Analogue electronics, analog or digital electronics, digital) equipment intended for everyday use, typically in private homes. Consumer electronics include devices used for ...
and goods companies often lead in the application of demand management practices to their demand chains; demand management outcomes are a reflection of policies and programs to influence demand as well as competition and options available to users and consumers. Effective demand management follows the concept of a "closed loop" where feedback from the results of the demand plans is fed back into the planning process to improve the predictability of outcomes. Many practices reflect elements of systems dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays.
Overview
System dynamics is a methodology and mathematical ...
. Volatility is being recognized as significant an issue as the focus on variance of demand to plans and forecasts.
In economics
Macroeconomics
In macroeconomics, ''demand management'' it is the art or science of controlling aggregate demand to avoid arecession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
.
Demand management at the macroeconomic level involves the use of discretionary policy
In macroeconomics, discretionary policy is an economic policy based on the ''ad hoc'' judgment of policymakers as opposed to policy set by predetermined rules. For instance, a central banker could make decisions on interest rates on a case-by-ca ...
and is inspired by Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ...
, though today elements of it are part of the economic mainstream. The underlying idea is for the government to use tools like interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, t ...
s, taxation
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, o ...
, and public expenditure
Public expenditure is spending made by the government of a country on collective needs and wants, such as pension, provisions, security, infrastructure, etc. Until the 19th century, public expenditure was limited as laissez faire philosophies b ...
to change key economic decisions like consumption, investment, the balance of trade
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance ...
, and public sector borrowing resulting in an 'evening out' of the business cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by exami ...
. Demand management was widely adopted in the 1950s to 1970s, and was for a time successful. It caused the stagflation of the 1970s, which is considered to have been precipitated by the supply shock
A supply shock is an event that suddenly increases or decreases the supply of a commodity or service, or of commodities and services in general. This sudden change affects the equilibrium price of the good or service or the economy's general p ...
caused by the 1973 oil crisis.
Theoretical criticisms of demand management are that it relies on a long-run Phillips Curve
The Phillips curve is an economic model, named after William Phillips (economist), William Phillips hypothesizing a correlation between reduction in unemployment and increased rates of wage rises within an economy. While Phillips himself did no ...
for which there is no evidence, and that it produces dynamic inconsistency
In economics, dynamic inconsistency or time inconsistency is a situation in which a decision-maker's preferences change over time in such a way that a preference can become inconsistent at another point in time. This can be thought of as there b ...
and can therefore be non-credible.
Today, most governments relatively limit interventions in demand management to tackling short-term crises, and rely on policies like independent central banks and fiscal policy rules to prevent long-run economic disruption.
Natural resources and environment
Innatural resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
management and environmental policy
Environmental policy is the commitment of an organization or government to the laws, regulations, and other policy mechanisms concerning environmental issues. These issues generally include air and water pollution, waste management, ecosystem ...
more generally, demand management refers to policies to control consumer demand for environmentally sensitive or harmful goods such as water and energy. Within manufacturing firms the term is used to describe the activities of demand forecasting, planning, and order fulfillment. In the environmental context demand management is increasingly taken seriously to reduce the economy's throughput of scarce resources for which market pricing does not reflect true costs. Examples include metering of municipal water, and carbon taxes on gasoline.
Welfare economics
Demand management in economics focuses on the optimal allocation resources to affectsocial welfare
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specificall ...
.
Welfare economics
Welfare economics is a branch of economics that uses microeconomic techniques to evaluate well-being (welfare) at the aggregate (economy-wide) level.
Attempting to apply the principles of welfare economics gives rise to the field of public econ ...
uses the perspective and techniques of microeconomics, but they can be aggregated to make macroeconomic conclusions. Because different "optimal" states may exist in an economy in terms of the allocation of resources, welfare economics seeks the state that will create the highest overall level of social welfare.
Some people object to the idea of wealth redistribution because it flies in the face of pure capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, pri ...
ideals, but economists suggest that greater states of overall social good might be achieved by redistributing incomes in the economy.
Because welfare economics follows the techniques of microeconomics, where demand planning is part of the process especially the redistribution of the funds through government taxes, fees and royalties to programs for societal good, such as roads, services, income support and agriculture support programs.
Demand management as a business process
Demand management is both a stand-alone process and one that is integrated intosales and operations planning Sales and operations planning (S&OP) is an integrated business management process through which the executive/leadership team continually achieves focus, alignment, and synchronization among all organization functions. The S&OP process includes an ...
(S&OP) or integrated business planning (IBP).
Demand management in its most effective form has a broad definition well beyond just developing a "forecast" based on history supplemented by "market" or customer intelligence
Customer intelligence (CI) as part of business intelligence is the process of gathering and analyzing information regarding customers, and their details and activities, to build deeper and more effective customer relationships and improve decis ...
, and often left to the supply chain organization to interpret. Philip Kotler notes two key points: 1. Demand management is the responsibility of the marketing organization (in his definition sales is subset of marketing); 2. The demand "forecast" is the result of planned marketing efforts. Those planned efforts, not only should focus on stimulating demand, more importantly influencing demand so that a business's objectives are achieved.
The components of effective demand management, identified by George Palmatier and Colleen Crum, are: 1. planning demand; 2. communicating demand; 3. influencing demand and 4. prioritizing demand.
Demand control
Demand control is a principle of the overarching demand management process found in most manufacturing businesses. Demand control focuses on alignment of supply and demand when there is a sudden, unexpected shift in the demand plan. The shifts can occur when near-term demand becomes greater than supply, or when actual orders are less than the established demand plan. The result can lead to reactive decisions, which can have a negative impact of workloads, costs, and customer satisfaction. Demand control creates synchronization across the sales, demand planning, and supply planning functions. Unlike typical monthly demand or supply planning reviews, demand control reviews occur at more frequent intervals (daily or weekly), which allows the organization to respond quickly and proactively to possible demand or supply imbalances.Time fences
 The demand control process requires that all functions agree on time fences within the planning horizon, which should be no less than a rolling 24 months based on integrated business planning
The demand control process requires that all functions agree on time fences within the planning horizon, which should be no less than a rolling 24 months based on integrated business planning Demand controller
A demand controller is established when a company implements a demand control process. Unlike a demand planner who focuses on long-term order management, the demand controller is responsible for short-term order management, focusing specifically when demand exceeds supply or demand appears to be less than planned, and engages sales management in both situations. The demand controller works across multiple functions involved in the supply and demand processes, including demand planning, supply planning, sales, and marketing.Elements
Planning demand involves a full multiple-view process or work flow; including statistical forecast as a baseline from clean "demand history" ot shipments using the most effective statistical models. Kai Trepte developed theMicrosoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for ...
add-in "Forecast X" to provide practitioners with a workstation capability to assess the best matches between data and forecast models. Increasingly "predictive forecasts" have moved from a limited use to becoming best practice for more companies. Predictive forecasts use simulation of potential future outcomes and their probabilities rather than history to form the basis for long range (5-10+ years) demand plans. Baseline forecasts are typically developed by demand planners and analysts, who may be regional or centrally located. They work under the guidance of the demand manager. Baseline forecasts are communicated to members of the demand management team. This usually includes regional sales leaders, market managers, and product managers. The team may include customer service leads who manager orders under service agreements with customers and have direct insight into customer demand. For major retailers this is often point of sale
The point of sale (POS) or point of purchase (POP) is the time and place at which a retail transaction is completed. At the point of sale, the merchant calculates the amount owed by the customer, indicates that amount, may prepare an invoice f ...
data provided to suppliers.
Information technology
Information technology and information system demand managers seek to understand in advance how to best meet the needs and expectations of customers, clients, partners, and enablers. Thus, proper forecast and sizing of demand is required in order to deliver a stable and effective technology environment.Demand management as part of project portfolio management
Romano, Grimaldi, and Colasuonno consider demand management as a harvesting activity, governed by a strategy that gives portfolios direction and a selection model intended to select the best beneficial set of activities aligned with strategic objectives. They suggest component-oriented demand management be approached proactively, with a strategy driven by business objectives, and responsibility of top management representing the chosen strategic direction.See also
* Customer demand planning *Demand chain
The term demand chain has been used in a business and management context as contrasting terminology alongside, or in place of, "supply chain". Madhani suggests that the demand chain "comprises all the demand processes necessary to understand, creat ...
*Demand modeling
In economics, demand is the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices during a given time. The relationship between price and quantity demand is also called the demand curve. Demand for a specific item ...
*Forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a company might estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual ...
* Functional finance
*Inventory control
Inventory control or stock control can be broadly defined as "the activity of checking a shop's stock". It is the process of ensuring that the right amount of supply is available within a business. However, a more focused definition takes into acco ...
*Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labo ...
*Workforce modeling {{peacock, date=January 2014
Workforce modeling is the process by which the need for skilled workers at a particular point in time (demand) is matched directly with the availability and preference of skilled workers (supply). The resulting mathemat ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Demand Management for IT
Economic planning Demand Supply chain management