Demand destruction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Demand destruction is a permanent downward shift on the demand curve in the direction of lower demand of a commodity, such as energy products, induced by a prolonged period of high prices or constrained supply. In the context of the
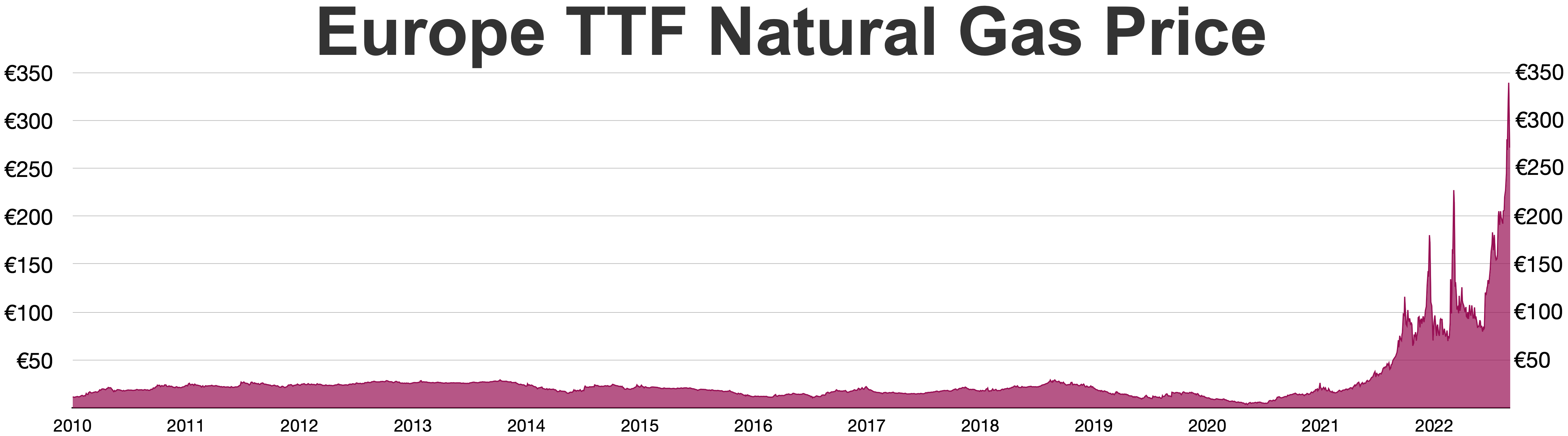 During the 1000% price increase of natural gas in Europe in 2021-2022, up to 70% of Europe's
During the 1000% price increase of natural gas in Europe in 2021-2022, up to 70% of Europe's
oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
industry, "demand" generally refers to the quantity consumed (see for example the output of any major industry organization such as the International Energy Agency), rather than any measure of a demand curve as used in mainstream economics. In economics, demand destruction refers to a permanent or sustained decline in the demand for a certain good in response to persistent high prices or limited supply. Because of persistent high prices, consumers may decide that it is not worth purchasing as much of that good, or seek out alternatives as substitutes.
Usage
The term came to some prominence in tandem with the peak oil theory, where demand destruction is the reduction of demand for oil and oil-derived products. The term is used byMatthew Simmons
Matthew Roy Simmons (April 7, 1943 – August 8, 2010) was founder and chairman emeritus of Simmons & Company International, and was a prominent figure in the field of peak oil. Simmons was motivated by the 1973 energy crisis to create an invest ...
, Mike Ruppert and other prominent proponents of the theory. It is also used in other resource
Resource refers to all the materials available in our environment which are technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and wants. Resources can broadly be classified upon their ...
industries, such as mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
.
Examples
A familiar illustration of demand destruction is the effect of high gasoline prices on automobile sales. It has been widely observed that when gasoline prices are high enough, consumers tend to begin buying smaller and more efficient cars, gradually reducing per-capita demand for gasoline. If the price rise were caused by a temporary lack of supply, and the price then subsequently goes back down as supply returns to normal, the quantity of gas consumed in this case does not immediately go back to its previous level, since the smaller cars that had been sold remain in the fleet for some time. Demand thereby has been "destroyed", shifting the demand curve. The expectation of future prices and their long-term maintenance at non-economic levels for a certain quantity of consumption also affects vehicle decisions. If the price of fuel is so high that marginal consumers cannot afford the same mileage without switching to a more efficient car, then they are forced to sell the less efficient one. An increase of the quantity of such vehicles causes the used market value to fall, which then increases the depreciation expected of a new vehicle, which increases the total cost of ownership of such vehicles, making them less popular. The coal reserves in some regions are regarded as astranded asset
Stranded assets are "assets that have suffered from unanticipated or premature write-downs, devaluations or conversion to liabilities". Stranded assets can be caused by a variety of factors and are a phenomenon inherent in the 'creative destructi ...
that may be permanently left in the ground. Competition from low priced natural gas, reduced demand for coal due to emission restrictions and uneconomic export situations each play a part. Environmental legislation that prevents fracking
Fracking (also known as hydraulic fracturing, hydrofracturing, or hydrofracking) is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of bedrock formations by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of "frac ...
strands potential natural gas reserves.
 During the 1000% price increase of natural gas in Europe in 2021-2022, up to 70% of Europe's
During the 1000% price increase of natural gas in Europe in 2021-2022, up to 70% of Europe's nitrogen fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
production was shut down on various occasions, as gas is the main part of the production cost.
See also
*Oil price increases since 2003
:''This article is a chronology of events affecting the oil market. For a discussion of the energy crisis of the same period, see 2000s energy crisis. For current fuel prices, see Gasoline usage and pricing.''
From the mid-1980s to September 20 ...
* Population growth
* Supply and demand
References
Demand Energy economics Peak resource production Scarcity {{economics-stub