Delta Pictoris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Delta Pictoris, Latinized from δ Pictoris, is a binary star system in the southern constellation 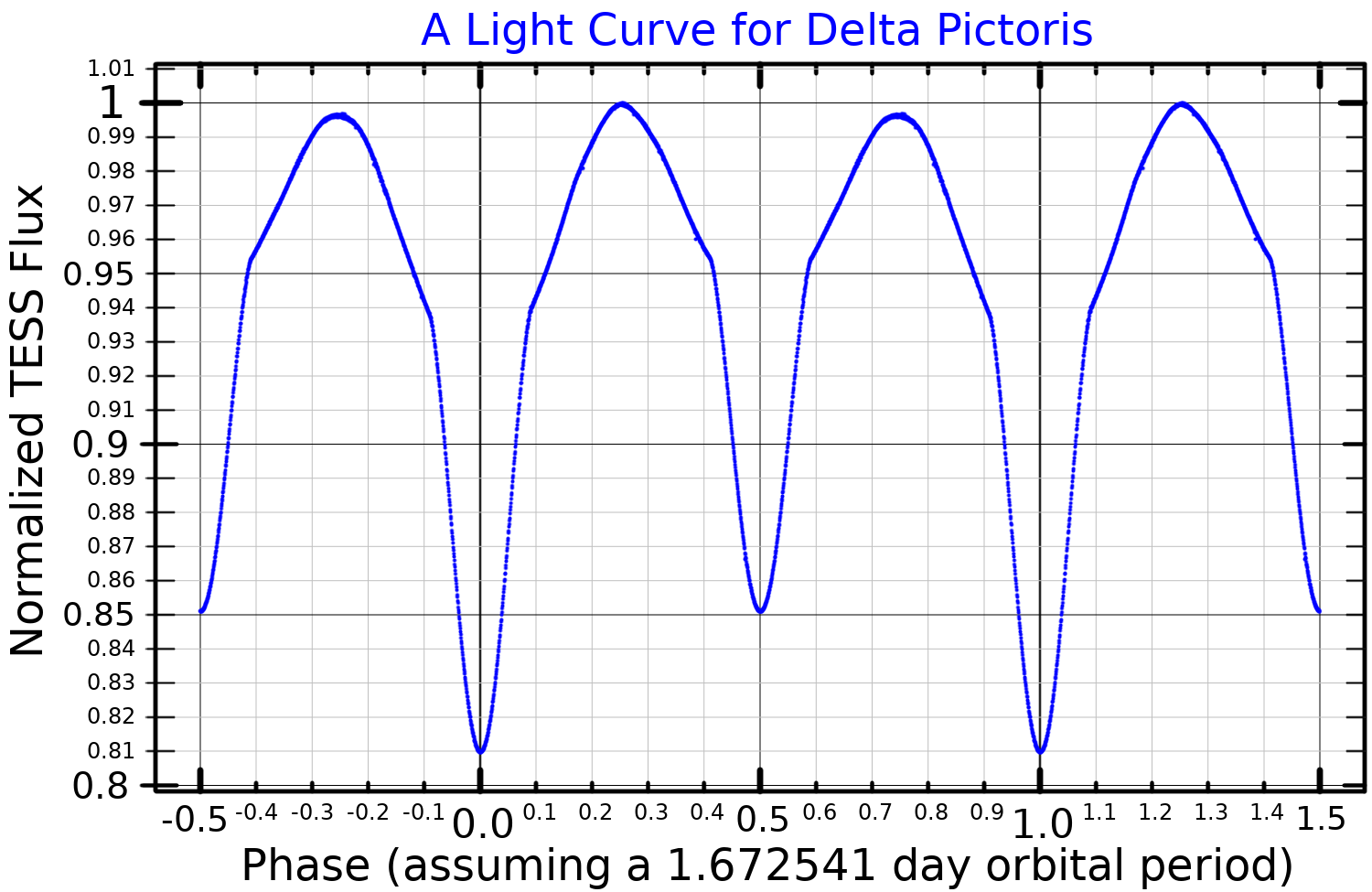 The binary nature of this system was discovered by R. E. Wilson in 1914, then it was found to be
The binary nature of this system was discovered by R. E. Wilson in 1914, then it was found to be
Pictor
Pictor is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, located between the star Canopus and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Its name is Latin for painter, and is an abbreviation of the older name Equuleus Pictoris (the "painter's easel ...
. It is visible to the naked with a combined apparent visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
of 4.72. The system is located at a distance of approximately 1,300 light years from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of ~31 km/s. It is a runaway star
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the Observational astronomy, observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space.
Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar Velocity, velocities in the Milky W ...
system that is generating a bow shock
In astrophysics, a bow shock occurs when the magnetosphere of an astrophysical object interacts with the nearby flowing ambient plasma such as the solar wind. For Earth and other magnetized planets, it is the boundary at which the speed of th ...
as it moves through the interstellar medium.
 The binary nature of this system was discovered by R. E. Wilson in 1914, then it was found to be
The binary nature of this system was discovered by R. E. Wilson in 1914, then it was found to be variable
Variable may refer to:
* Variable (computer science), a symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed
* Variable (mathematics), a symbol that represents a quantity in a mathematical expression, as used in many ...
by A. W. J. Cousins in 1951. A. D. A. Thackeray published orbital elements for the pair in 1966, showing they form an eclipsing double-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of 1.67 days in essentially a circular orbit. The low inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Eart ...
of the orbital plane
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) an ...
results in shallow eclipses. The system is classified as a likely Beta Lyrae-type eclipsing binary with a peak magnitude of 4.65, which drops to 4.90 during the primary eclipse and 4.83 in the secondary eclipse. It is probably a detached binary system with no circumstellar material being found.
Both components of this system are massive main sequence stars with a combined stellar classification of B1/2(III)n. One member of the pair displays β Cep type pulsational behavior. Mass estimates give a primary with 16.3 times the mass of the Sun and a secondary with about half that.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Delta Pictoris B-type main-sequence stars Spectroscopic binaries Beta Lyrae variables Beta Cephei variables Pictor Pictoris, Delta Durchmusterung objects 042933 029276 2212