Deir Al-Balah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Deir al-Balah or Deir al Balah ( ar, دير البلح, , Monastery of the Date Palm) is a Palestinian city in the central
14
/ref> The mosque in Deir al-Balah which bears his name is traditionally believed by locals to contain his tomb. Up until the later Ottoman era, Deir al-Balah was referred to in Arabic as "Darum" or "Darun" which derived from the settlement's Crusader-era Latin name "Darom" or "Doron." That name was explained by the Crusader chronicler
12
/ref> Throughout early Muslim Arab rule and until the arrival of the
11
/ref> The exact date of the fort's construction is unknown, although it was likely erected after 1153 following Amalric's capture of Ascalon to the north from the Fatimid Caliphate. As described by William of Tyre, the fort was small, ''tantum spatium intra se continens quantum est jactus lapidis'' (containing inside as much space as a stone's throw) and square-shaped with four towers, one of which was larger than the others. Amalric used Darom as a launching point for several unsuccessful military campaigns against Fatimid Egypt.Sharon, 2004, p
13
/ref> In addition to its role as a frontier fort on the border of Egypt, Darom also served as an administrative center charged with collecting taxes from the southern areas of the kingdom and customs from caravans and travelers coming from Egypt. It was deemed a permanent threat by the rulers of Egypt. Not long after its construction, a small suburb or village with a church was established by local farmers and traders just outside the fort. According to medieval chronicler
140
It hosted a garrison commanded by the
42
/ref> The first Ottoman tax census in 1525 revealed Deir al-Balah was a relatively large village with a religiously mixed population of 87 Christian families and 56 Muslim families. In 1596 it was part of Gaza Sanjak (District of Gaza) and had a Muslim majority with 175 Muslim families and 125 Christian families.Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 144. With an estimated population of 1,500, it was one of eight villages at the time to have between 1,000 and 2,000 inhabitants. Annual tax revenue from the town amounted to 17,300 akces.Petersen, 2005, p
134
/ref>
118
/ref> A substantial part of Deir al-Balah's inhabitants died in 1862 because of stagnant drinking water originating from the town's swamps. The swamps were seasonal, forming each winter as a result of flooding which failed to breach the sandstone ridge. A year later, on 29 May 1863, French explorer
223
In 1878, the

 Deir al-Balah was captured by the
Deir al-Balah was captured by the  In the 1945 statistics, Deir al-Balah had a population of 2,560; 40 Christians and 2,520 Muslims, with 14,735 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p
In the 1945 statistics, Deir al-Balah had a population of 2,560; 40 Christians and 2,520 Muslims, with 14,735 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p
45
/ref> Of this, 327 dunams were for citrus and bananas, 472 plantations and irrigable land, 14,438 used for cereals, while 39 dunams were built-up land. In the lead-up to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, residents of Deir al-Balah participated in a local attack against the nearby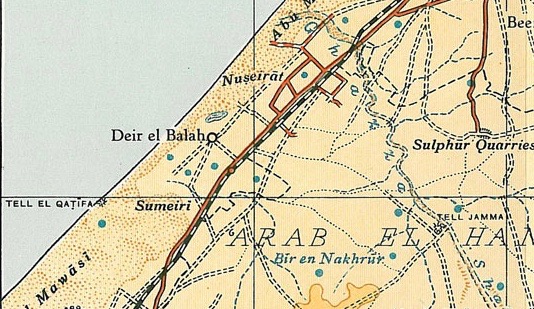 During the
During the
247
��248
53
* * * * * * * * * * *
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 19
IAAWikimedia commons
Laborers in Deir al-Balah Governorate
Map of the Deir-al Balah Governorate
{{Authority control Populated coastal places in Palestinian territories Populated places of the Byzantine Empire Cities in the Gaza Strip Cities in ancient Egypt Bronze Age sites in the State of Palestine Philistines Date palm orchards Municipalities of the State of Palestine
Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza. ...
and the administrative capital of the Deir el-Balah Governorate
The Deir el-Balah Governorate ( ar, محافظة دير البلح '), also referred to as Central Gaza Governorate ( ar, محافظة الوسطى) is one of 16 Governorates of Palestine in the central Gaza Strip which is administered by Palest ...
. It is located over south of Gaza City. The city had a population of 54,439 in 2007.Table 14: Localities in Deir al Balah Governorate by Type of Locality and Selected Indicators, 2007Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ar, الجهاز المركزي للإحصاء الفلسطيني) is the official
statistical institution of the State of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures a ...
(PCBS). 2009. p. 62. The city is known for its date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Ea ...
s, after which it is named.
Deir al-Balah dates back to the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
when it served as a fortified outpost for the New Kingdom of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radioc ...
. A monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whic ...
was built there by the Christian monk Hilarion in the mid-4th century AD and is currently believed to be the site of a mosque dedicated to Saint George
Saint George (Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
, known locally as al-Khidr. During the Crusader- Ayyubid wars, Deir al-Balah was the site of a strategic coastal fortress known as "Darum" which was continuously contested, dismantled and rebuilt by both sides until its final demolition in 1196. Afterward, the site grew to become a large village on the postal route of the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16t ...
(13th-15th centuries). It served as an episcopal see of the Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem, el, Πατριαρχεῖον Ἱεροσολύμων, ''Patriarcheîon Hierosolýmōn;'' he, הפטריארכיה היוונית-אורתודוקסית של ירושלים; ar, كنيسة الرو� ...
in Ottoman times until the late 19th century.
Under Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
ian control Deir al-Balah, whose population tripled through the influx of refugees
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
from the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, was a prosperous agricultural town until its capture by Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
in the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
. After 27 years of Israeli occupation, Deir al-Balah became the first city to come under Palestinian self-rule in 1994. Since the outbreak of the Second Intifada
The Second Intifada ( ar, الانتفاضة الثانية, ; he, האינתיפאדה השנייה, ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada ( ar, انتفاضة الأقصى, label=none, '), was a major Palestinians, Palestinian uprising a ...
in 2000, it has witnessed frequent incursions by the Israeli Army with the stated aim of stopping Qassam rocket
The Qassam rocket ( ar, صاروخ القسام ''Ṣārūkh al-Qassām''; also ''Kassam'') is a simple, steel artillery rocket developed and deployed by the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, the military arm of Hamas. These rockets cannot be fired ...
fire into Israel... Ahmad Kurd
Ahmad Kurd ( ar, أحمد كرد; 13 September 1949 – 9 May 2020) was a Palestinian politician, who served as the mayor of Deir al-Balah located in the central Gaza Strip. He was elected as mayor in 2005 as the candidate for the political party ...
, a Hamas
Hamas (, ; , ; an acronym of , "Islamic Resistance Movement") is a Palestinian Sunni-Islamic fundamentalist, militant, and nationalist organization. It has a social service wing, Dawah, and a military wing, the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Bri ...
member, was elected mayor in late January 2005.
Etymology
"Deir al-Balah," which inArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
translates as the "Monastery of the Date Palm," was named after the grove of date palms that laid west of the city. Its name dates back to the late 19th century, before which the city was locally known as "Deir Mar Jiryis" or "Deir al-Khidr" and "Deir Darum" in Ottoman records. "Mar Jiryis" translates as "Saint George
Saint George (Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
" while in Islamic tradition al-Khidr could either refer to Saint George or Elijah
Elijah ( ; he, אֵלִיָּהוּ, ʾĒlīyyāhū, meaning "My God is Yahweh/ YHWH"; Greek form: Elias, ''Elías''; syr, ܐܸܠܝܼܵܐ, ''Elyāe''; Arabic: إلياس or إليا, ''Ilyās'' or ''Ilyā''. ) was, according to the Books ...
. The inhabitants of Deir al-Balah associated al-Khidr with Saint George. The town had been named after al-Khidr, the most venerated saintly person throughout Palestine.Sharon, 2004, p14
/ref> The mosque in Deir al-Balah which bears his name is traditionally believed by locals to contain his tomb. Up until the later Ottoman era, Deir al-Balah was referred to in Arabic as "Darum" or "Darun" which derived from the settlement's Crusader-era Latin name "Darom" or "Doron." That name was explained by the Crusader chronicler
William of Tyre
William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a forme ...
as a corruption of ''domus Graecorum'', "house of the Greeks" (''dar ar-rum''). More recently, the eighteenth century scholar Albert Schultens
Albert Schultens (; 168626 January 1750) was a Dutch philologist.
Biography
He was born at Groningen, where he studied for the church. He went on to the University of Leiden, applying himself specially to Hebrew and the cognate tongues. His thesi ...
supposed its roots are the Ancient Hebrew Ancient Hebrew (ISO 639-3 code ) is a blanket term for pre-modern varieties of the Hebrew language:
* Paleo-Hebrew (such as the Siloam inscription), a variant of the Phoenician alphabet
* Biblical Hebrew (including the use of Tiberian vocalization ...
name "Darom" or "Droma", from the Hebrew root for "south", which referred to the area south of Lydda, i.e. the southern parts of the coastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Co ...
and Judean foothills together with the northern Negev Desert
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
. During early Arab rule, "ad-Darum" or "ad-Dairan" was the name of the southern subdistrict of Bayt Jibrin
Bayt Jibrin or Beit Jibrin ( ar, بيت جبرين; he, בית גוברין, translit=Beit Gubrin) was a Palestinian village located northwest of the city of Hebron. The village had a total land area of 56,185 dunams or , of which we ...
.
History
Ancient period
Deir al-Balah's history dates back to the mid-14th century BC, during theLate Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
. At that time it served as an outpost in the New Kingdom of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radioc ...
on its frontier with Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
.Bunson, 2002, p. 96. During the reign of King Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded a ...
(1303–1213 BC), Deir al-Balah became the easternmost of six garrisoned fortresses in the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to comm ...
.Morkot, 2003, p.91. The string of fortresses began with the Sinai fort in the west, and continued through the "Way of Horus" military road to Canaan.Bunson, 2002, p. 97. The square-shaped fortress of Deir al-Balah had four towers at each corner and a reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
. Archaeological findings in Deir al-Balah revealed a large ancient Egyptian cemetery with graves containing jewelry and other personal belongings. The inhabitants of the fortress employed traditional Egyptian techniques and artistic designs in their architectural works. The cosmopolitan aspect of the frontier site is proven by the rich Cypriot
Cypriot (in older sources often "Cypriote") refers to someone or something of, from, or related to the country of Cyprus.
* Cypriot people, or of Cypriot descent; this includes:
** Armenian Cypriots
** Greek Cypriots
** Maronite Cypriots
** Tur ...
, Mycenaean and Minoan findings.
Deir al-Balah remained in Egyptian hands until around 1150 BC when the Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (Septuagint, LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 6 ...
conquered the southern coastal area of Canaan. The Philistine settlement is thought to have been situated southwest of the excavation site; its remains are hidden under large sand dunes. Five pits dug into the Late Bronze Age layers and containing Philistine pottery are among the few findings from that period.
The archaeological excavations at the Egyptian-period site were executed between 1972 and 1982, during Israel's occupation, and headed by Trude Dothan. After the conclusion of the excavations the area was used for farming purposes and is now covered by vegetable gardens and fruit orchards while the main findings can be seen in Israeli museums like the Israel Museum
The Israel Museum ( he, מוזיאון ישראל, ''Muze'on Yisrael'') is an art and archaeological museum in Jerusalem. It was established in 1965 as Israel's largest and foremost cultural institution, and one of the world’s leading encyclopa ...
in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and the Hecht Museum
The Reuben and Edith Hecht Museum is a museum located on the grounds of the University of Haifa, Israel.
History
The Hecht Museum was established in 1984 by Reuben Hecht, director of Dagon Silos and a founding member of the University of Ha ...
in Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropoli ...
.
Similar cultural development is also attested at Tall al-Ajjul at that time, also in the Gaza strip.
Byzantine period
DuringByzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
rule, the first hermitage in Palestine was established by the early Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
monk Hilarion at the site of modern-day Deir al-Balah. Hilarion initially built a small hut there, but during the reign of Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic ...
(337–361) he set up the hermitage. Towards the end of his life, the monastery grew and began to attract numerous visitors. Hilarion resided at the monastery for a total of 22 years until his departure for Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
where he died in 371 AD. The hermitage was divided into several small cells constructed of mud brick and palm tree branches.Bitton-Ashkelony and Kofsky, 2004, p. 68. According to local tradition and observations from Western travelers in the 19th century, the prayer hall of the Monastery of Hilarion is currently occupied by the Mosque of al-Khidr. French explorer Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Min ...
noted that two marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
columns in the mosque were possibly parts of the Byzantine-era monastery.Bitton-Askhelony and Kofsky, 2004, p. 69.
Early Islamic period
In 632, during the early period of Islamic rule inArabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, the Muslim commander Usama ibn Zayd launched a raid against Byzantine-held Darum, which referred not to Deir al-Balah specifically, but to the area south of Lydda which included modern-day Deir al-Balah.Schick, 1995, p. 280 The site was one of the first places in Palestine to be annexed by the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after hi ...
following the conquest of Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip Lebanon
* Ghazzeh, a village in ...
by Amr ibn al-'As
( ar, عمرو بن العاص السهمي; 664) was the Arab commander who led the Muslim conquest of Egypt and served as its governor in 640–646 and 658–664. The son of a wealthy Qurayshite, Amr embraced Islam in and was assigned impor ...
in 634.Sharon, 2004, p12
/ref> Throughout early Muslim Arab rule and until the arrival of the
Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
in the late 11th century, "Darum" normally referred to the southern district of Jund Filastin whose capital fluctuated between the towns of Bayt Jibrin
Bayt Jibrin or Beit Jibrin ( ar, بيت جبرين; he, בית גוברין, translit=Beit Gubrin) was a Palestinian village located northwest of the city of Hebron. The village had a total land area of 56,185 dunams or , of which we ...
or Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies Above mean sea level, above sea level. The second-lar ...
.
The Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muh ...
caliph al-Aziz Billah (r. 975-996) granted his favored vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called '' katib'' (secretary), who was ...
, Yaqub ibn Killis, a fief in modern-day Deir al-Balah, as testified by an inscription dating to the 980s located in the city's al-Khidr Mosque. The fief included a large estate with date palms.
Crusader and Ayyubid rule
Deir al-Balah was built on the ruins of the Crusader fort of Darom (also referred to as "Doron") which was built by King Amalric I.Sharon, 2004, p11
/ref> The exact date of the fort's construction is unknown, although it was likely erected after 1153 following Amalric's capture of Ascalon to the north from the Fatimid Caliphate. As described by William of Tyre, the fort was small, ''tantum spatium intra se continens quantum est jactus lapidis'' (containing inside as much space as a stone's throw) and square-shaped with four towers, one of which was larger than the others. Amalric used Darom as a launching point for several unsuccessful military campaigns against Fatimid Egypt.Sharon, 2004, p
13
/ref> In addition to its role as a frontier fort on the border of Egypt, Darom also served as an administrative center charged with collecting taxes from the southern areas of the kingdom and customs from caravans and travelers coming from Egypt. It was deemed a permanent threat by the rulers of Egypt. Not long after its construction, a small suburb or village with a church was established by local farmers and traders just outside the fort. According to medieval chronicler
William of Tyre
William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a forme ...
, "it was a pleasant spot where conditions of life for people of the lower ranks were better than in cities". The population of the village consisted of indigenous Eastern Orthodox Christians
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
allied to and protected by the Crusader administration and garrison based in the fort. The inhabitants were considered lower-class, but integral members of society by the Crusaders of European or mixed descent. Because Darom was absent of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
bishops, in 1168 Pope Alexander III gave the Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem direct jurisdiction over the dioceses
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, putting the largely Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
inhabitants under the authority of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.
Following Amalric's withdrawal from his fifth offensive against Egypt in 1170, Muslim general Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
, fighting on behalf of the Fatimids, attacked and besieged the fortress as part of his foray into the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
. Despite initial gains, Darom was not captured or destroyed. It later became a stronghold of the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon ( la, Pauperes commilitones Christi Templique Salomonici), also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar, or simply the Templars, was a Catholic military order, o ...
and the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headq ...
from Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, led by King Baldwin III.Shahin, 2005, pp. 421–423. After the Muslim army defeated the Crusaders in the decisive Battle of Hattin in 1187, their leader Saladin, by then the independent sultan of the Ayyubid dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladi ...
, advanced south and captured both Ascalon and Darom by 1188. His first order was the fort's demolition, but he later decided against destroying it. Instead, the fortress was substantially expanded and strengthened. "Darum", which is what the Muslims called the fortress village, was encased by a wall with 17 strong towers protected by a deep moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
with stone-paved sides.Ellenblum, 2003, p140
It hosted a garrison commanded by the
emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
(commander) Alam ad-Din Qaysar and served as a store for supplies and ammunition.
The Crusaders recaptured the fortress on 24 May 1191 after a short siege commanded by King Richard the Lionheart. Authority over Darum was assigned to Count Henry I of Champagne, but Richard later had the fortress demolished in July 1193 prior to withdrawing his forces from Ascalon. The Ayyubids rebuilt the fortress soon after in order to use it as a bridgehead to reconquer territories lost in Palestine during the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity ( Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
. Nonetheless, in 1196, Sultan al-Aziz Uthman decided to have it demolished in case of its capture by the Crusaders. According to 15th-century historian al-Maqrizi
Al-Maqrīzī or Maḳrīzī (Arabic: ), whose full name was Taqī al-Dīn Abū al-'Abbās Aḥmad ibn 'Alī ibn 'Abd al-Qādir ibn Muḥammad al-Maqrīzī (Arabic: ) (1364–1442) was a medieval Egyptian Arab historian during the Mamluk era, kno ...
, this decision resulted in public resentment since travelers and merchants had significantly benefited from the fort's protection. In 1226, Syrian geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) ( ar, ياقوت الحموي الرومي) was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine Greek ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th-13th centuries). He is known for ...
visited Darum and noted it was one of the cities of Lot and contained a ruined castle.
Mamluk rule
Following its demolition, it is not known how long Darum remained deserted, but it was eventually resettled duringMamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') i ...
rule which began in 1250. For much of the Mamluk era, the town came under the administration of the politically important Niyabah of Gaza (Province of Gaza), part of the larger Mamlaka of Damascus (Kingdom of Damascus.)Ziadeh, 1953, p. 24. Along with Karatiyya
Karatiyya ( ar, كرتيا) was a Palestinian Arab village of 1,370, located northeast of Gaza, situated in a flat area with an elevation of along the coastal plain of Palestine and crossed by Wadi al-Mufrid.
History
Byzantine ceramics have b ...
and Beit Jibrin, Darum was an ''amal'' (district) of the Province of Gaza with its own ''wali
A wali (''wali'' ar, وَلِيّ, '; plural , '), the Arabic word which has been variously translated "master", "authority", "custodian", "protector", is most commonly used by Muslims to indicate an Islamic saint, otherwise referred to by t ...
'' (governor).
It became a halting post along the newly introduced regular mail routes connecting Damascus and Cairo, which were run by horse-mounted messengers with colored sashes. Syrian historian Ibn Fadlallah al-Umari did not mention Darum in his list of the route's stopping points in 1349, instead noting that al-Salqah was the only post between Rafah
Rafah ( ar, رفح, Rafaḥ) is a Palestinian city in the southern Gaza Strip. It is the district capital of the Rafah Governorate, located south of Gaza City. Rafah's population of 152,950 (2014) is overwhelmingly made up of former Palesti ...
and Gaza, suggesting that Darum was not a major settlement at the time. However, 14th-century Egyptian historian Ahmad al-Qalqashandi counters al-Umari's account, writing that Darum was the last halting post before Gaza. Roads, bridges, postal stations and a ''khan'' (caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes coverin ...
) were built in the town to accommodate the messengers. Pigeon mail service was introduced for which towers were built. Produce available in Darum during this time period included barley, wheat, grapes and grape leaves, olives, raspberries, lemons, figs, sweet melons, pomegranates and dates. Surrounding the town were the encampments of the Batn Jarm, an Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
clan that also lived around Gaza.
Ottoman era
Sometime prior to the Ottoman conquest of Palestine in 1516 or in the beginning years of Ottoman rule, Darum gained the additional name of "Deir" as in "Deir Darum" after its Byzantine-era monastery. The village continued to thrive during the early Ottoman era in Palestine which is attributed to the urban infrastructure originally established by the Crusaders. Its continued importance also stemmed from its close proximity to Gaza and its position on the former Via Maris trade route.Petersen, 2005, p42
/ref> The first Ottoman tax census in 1525 revealed Deir al-Balah was a relatively large village with a religiously mixed population of 87 Christian families and 56 Muslim families. In 1596 it was part of Gaza Sanjak (District of Gaza) and had a Muslim majority with 175 Muslim families and 125 Christian families.Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 144. With an estimated population of 1,500, it was one of eight villages at the time to have between 1,000 and 2,000 inhabitants. Annual tax revenue from the town amounted to 17,300 akces.Petersen, 2005, p
134
/ref>
Pierre Jacotin
Pierre Jacotin (1765–1827) was the director of the survey for the '' Carte de l'Égypte (Description de l'Égypte)'', the first triangulation-based map of Egypt, Syria and Palestine.
The maps were surveyed in 1799-1800 during the campaign in ...
named the village ''Deir K Helleh'' on his map from 1799. In 1838, ''Deir el-Belah'' was noted as a Muslim village in the Gaza district.Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p118
/ref> A substantial part of Deir al-Balah's inhabitants died in 1862 because of stagnant drinking water originating from the town's swamps. The swamps were seasonal, forming each winter as a result of flooding which failed to breach the sandstone ridge. A year later, on 29 May 1863, French explorer
Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Min ...
wrote that Deir al-Balah was a small, partly ruined village with a population of 350. Date farming was the principal economic activity that the inhabitants engaged in.Guerin 1869223
In 1878, the
PEF PEF, PeF, or Pef may stand for the following abbreviations:
* Palestine Exploration Fund
* Peak expiratory flow
* PEF Private University of Management Vienna
* Pentax raw file (see Raw image format)
* Perpetual Education Fund
* Perpetual Emigratio ...
's '' Survey of Western Palestine'' noted Deir al-Balah had grown to become a large village of mud houses "with wells and a small tower". At the time, it served as a see of the Greek Orthodox Church of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem, el, Πατριαρχεῖον Ἱεροσολύμων, ''Patriarcheîon Hierosolýmōn;'' he, הפטריארכיה היוונית-אורתודוקסית של ירושלים; ar, كنيسة الرو� ...
.
Modern era

 Deir al-Balah was captured by the
Deir al-Balah was captured by the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gur ...
following the surrender of Khan Yunis on 28 February 1917. By April an aerodrome
An aerodrome (Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for publ ...
and an army camp were established there and Deir al-Balah became a launching point for British forces against Ottoman-held Gaza and Beersheba
Beersheba or Beer Sheva, officially Be'er-Sheva ( he, בְּאֵר שֶׁבַע, ''Bəʾēr Ševaʿ'', ; ar, بئر السبع, Biʾr as-Sabʿ, Well of the Oath or Well of the Seven), is the largest city in the Negev desert of southern Israel. ...
to the north and northeast, respectively. Of the 25 British war cemeteries dating from World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, one of the six largest was built in Deir al-Balah in March 1917. It continued to be used until March 1918 and contains a total of 724 graves. Deir al-Balah became a part of the British Mandate of Palestine starting in 1922. A municipal council to administer the town was established by the British authorities in 1946, but it had limited jurisdiction over civil affairs and provided a few basic services.
 In the 1945 statistics, Deir al-Balah had a population of 2,560; 40 Christians and 2,520 Muslims, with 14,735 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p
In the 1945 statistics, Deir al-Balah had a population of 2,560; 40 Christians and 2,520 Muslims, with 14,735 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p45
/ref> Of this, 327 dunams were for citrus and bananas, 472 plantations and irrigable land, 14,438 used for cereals, while 39 dunams were built-up land. In the lead-up to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, residents of Deir al-Balah participated in a local attack against the nearby
kibbutz
A kibbutz ( he, קִבּוּץ / , lit. "gathering, clustering"; plural: kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1909, was Degania. Today, farming h ...
of Kfar Darom, despite being discouraged by Egyptian Army officers, but they were repelled and suffered casualties. During the war, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
captured the town along with other towns in an area that became known as the Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza. ...
. The Egyptians later established a sharia court system that held jurisdiction over personal affairs. Egyptian rule introduced relative prosperity to Deir al-Balah. The town witnessed a booming citrus industry made possible by the discovery of a substantial reservoir of ground water in the vicinity.
 During the
During the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
in June 1967, Deir al-Balah's mayor Sulaiman al-Azayiza briefly led local resistance against the incoming Israeli Army until formally surrendering the city shortly thereafter. The Israeli authorities took control of the springs, an important irrigation source. This move combined with increasing competition from Israeli citrus farmers, damaged the local citrus industry. In 1982 the mayor was dismissed and the municipal council of Deir al-Balah was disbanded and replaced by an Israeli military-appointed administration.Mattar, 2005, p. 171. During the course of the Israeli occupation, Deir al-Balah's urban areas extended into lands designated for agriculture, largely as a result of building restrictions which hindered organized expansion.
When the First Intifada
The First Intifada, or First Palestinian Intifada (also known simply as the intifada or intifadah),The word '' intifada'' () is an Arabic word meaning " uprising". Its strict Arabic transliteration is '. was a sustained series of Palestini ...
broke out in 1987, Deir al-Balah's residents participated in the uprising against Israeli rule. Around 30 residents were killed during the uprising, which formally ended in 1993 with the Oslo Accords
The Oslo Accords are a pair of agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO): the Oslo I Accord, signed in Washington, D.C., in 1993;
between the Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, منظمة التحرير الفلسطينية, ') is a Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establishing Arab unity and st ...
(PLO) and Israel. In 1994 Deir al-Balah was the first city to officially come under the control of the Palestinian National Authority
The Palestinian National Authority (PA or PNA; ar, السلطة الوطنية الفلسطينية '), commonly known as the Palestinian Authority and officially the State of Palestine,
as a result of the Gaza–Jericho Agreement
The Gaza–Jericho Agreement, officially called Agreement on the Gaza Strip and the Jericho Area, was a follow-up treaty to the Oslo I Accord in which details of Palestinian autonomy were concluded. The agreement is commonly known as the 1994 Cairo ...
.
The city has been frequently targeted in Israeli military incursions since the Second Intifada
The Second Intifada ( ar, الانتفاضة الثانية, ; he, האינתיפאדה השנייה, ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada ( ar, انتفاضة الأقصى, label=none, '), was a major Palestinians, Palestinian uprising a ...
in 2000, in part due to Qassam rocket
The Qassam rocket ( ar, صاروخ القسام ''Ṣārūkh al-Qassām''; also ''Kassam'') is a simple, steel artillery rocket developed and deployed by the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, the military arm of Hamas. These rockets cannot be fired ...
-strikes by Palestinian militants. The areas surrounding the city have also been frequent targets of razing. On 4 January 2004, Israeli authorities bulldozed around 50 dunams (5 hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100- metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is ...
s) of land in the Abu al-Ajen area east of Deir al-Balah's center. Later on 7 January, the Applied Research Institute-Jerusalem (ARIJ) reported that "Israeli bulldozers staged into al-Hikr area south of Deir el-Balah city under heavy barrage of gunfire and razed 70 dunams (7 hectares) of land planted with guava and orange groves owned by the Abu Holy and Abu Reziq families."
During factional clashes across the Gaza Strip in June 2007 which ended with Hamas
Hamas (, ; , ; an acronym of , "Islamic Resistance Movement") is a Palestinian Sunni-Islamic fundamentalist, militant, and nationalist organization. It has a social service wing, Dawah, and a military wing, the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Bri ...
gaining control over that territory, at least four paramilitaries from Hamas and Fatah
Fatah ( ar, فتح '), formerly the Palestinian National Liberation Movement, is a Palestinian nationalist social democratic political party and the largest faction of the Confederation, confederated multi-party Palestine Liberation Organizati ...
were killed in Deir al-Balah. On 2 January 2009, Deir al-Balah was shelled by the Israeli Army as part of its month-long offensive Operation Cast Lead.
Geography
Deir al-Balah is situated in the central Gaza Strip, along the coastline of the easternMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. Its city center is about east of the coast while the ancient site of Darum was uncovered to the south of central Deir al-Balah. While the city's municipal borders stretch eastward toward the border with Israel, its urban area does not extend beyond the main Salah al-Din Highway to the east.
Nearby localities include Nuseirat Camp and Bureij Camp to the north, Maghazi Camp to the northeast and Wadi as-Salqa
Wadi as-Salqa ( ar, وادي السلقا) is a Palestinian agricultural town in the Deir al-Balah Governorate, located south of Deir al-Balah. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS), the municipality had a population of 6 ...
to the south. Khan Yunis is to Deir al-Balah's south and Gaza City is located to the north.
The city has absorbed the coastal Deir al-Balah Refugee Camp, although it remains outside of Deir al-Balah's municipal administration. While the total land area was recorded as 14,735 dunams (14.7 km² or 1,473.5 hectares) in 1997, the total built-up areas of the city consist of between 7,000 and 8,000 dunams (7–8 km² or 700-800 hectares.) Deir al-Balah is divided into 29 administrative areas.
Archaeology
White marble pillar shafts were built into the walls of some houses in old Deir al-Balah. They resembled the medieval-era pillars in theTemple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites an ...
("Haram ash-Sharif") in Jerusalem.Conder and Kitchener, 1883, SWP III, pp247
��248
Mosque of al-Khidr
The Mosque of al-Khidr (also called "Maqam
MAQAM is a US-based production company specializing in Arabic and Middle Eastern media. The company was established by a small group of Arabic music and culture lovers, later becoming a division of 3B Media Inc. "MAQAM" is an Arabic word meaning ...
al-Khader") is by and was built on the site of a Byzantine monastery. The northern and southern walls were buttressed and the eastern wall has three apses. The ''Survey of Western Palestine'' related in 1875 that there were Greek inscriptions on one of the steps leading to the door at the southern wall while on the floor was a broken stone slab marked by two Maltese cross
The Maltese cross is a cross symbol, consisting of four " V" or arrowhead shaped concave quadrilaterals converging at a central vertex at right angles, two tips pointing outward symmetrically.
It is a heraldic cross variant which develop ...
es, apparently resembling a tombstone. Further slabs and Greek inscriptions were found in the eastern part of the mosque and in the courtyard. In the center is a tomb made of modern masonry that tradition claims is the tomb of Saint George ("Mar Jirjis") or al-Khidr, as he is known in Arabic.
Prior to the predominance of orthodox Islam in Palestine, the region contained numerous domed structures dedicated to Muslim patron saints, among which was the Mosque of al-Khidr in Deir al-Balah. In March 2016, the Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities in the Gaza Strip began the restoration of the Mosque of al-Khidr with financial support from UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
and the Nawa Foundation. The project aims to convert the mosque-tomb into a children's cultural library.
Demographics
According to acensus
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses in ...
conducted in 1922 by the British Mandate authorities, Deir al-Balah had a population of 916 inhabitants, consisting of 893 Muslims, 22 Jews and 1 Christians.
With a population of 2,560 in 1945, Deir al-Balah was a relatively large village. The influx of Palestinian refugee
Palestinian refugees are citizens of Mandatory Palestine, and their descendants, who fled or were expelled from their country over the course of the 1947–49 Palestine war (1948 Palestinian exodus) and the Six-Day War (1967 Palestinian exodus ...
s from nearby areas captured by Israel during the 1948 War drastically increased the population thereafter. In the 1997 census by the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ar, الجهاز المركزي للإحصاء الفلسطيني) is the official
statistical institution of the State of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures a ...
(PCBS) Deir al-Balah's population was recorded as 42,839, a figure which included the adjacent Deir al-Balah Camp (the smallest refugee camp in the Gaza Strip.) Nearly 75% of the population were below the age of 30.
In 2004 the PCBS estimated the population to be 46,159. In the 2007 census by the PCBS, the population of Deir al-Balah city alone was 54,439, making it the largest municipality in the Deir al-Balah Governorate. The camp's population was 6,438. However, Nuseirat
Nuseirat ( ar, مخيّم النصيرات) is a Palestinian refugee camp located five kilometers north-east of Deir al-Balah. The refugee camp is in the Deir al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statist ...
combined with its refugee camp has a larger population than Deir al-Balah combined with its camp. There were a total of 8,395 households and the average family size consisted of between six and seven members. The gender distribution in the city was 50.3% male and 49.7% female.
Deir al-Balah's entire population is Muslim. A sizable Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
Christian population existed until the mid-19th century. In the 1931 British census of Palestine, there were only 10 Christians in Deir al-Balah out of a population of 1,587. Today, refugees make up the majority of the population, accounting for over 66% of the city's inhabitants in 1997. However, this figure also included the Deir al-Balah Camp.
Economy
The Deir al-Balah Governorate's principal economic activity is services, accounting for 67.4% of the labor force. Commerce, hospitality and retail account for 12.9%, agriculture and fishing 10.1%, transportation and communication 5.4% and manufacturing 3.4%. In 2009 the unemployment rate in the governorate was 35.2% while the labor force participation rate was 38.7%. In 2007 there were 1,108 business establishments in the city.Agriculture and fishing
Deir al-Balah is well known for growingdate palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Ea ...
s, an estimated 20,000 of which covered the landscape south and west of the city in the 1990s. However, some 3,550 trees were uprooted or bulldozed by the Israeli Army in the early years of the Second Intifada beginning in 2000. There were an estimated 16,500 palms in Deir al-Balah in 2003. In addition to being a local delicacy, date cultivation constitutes one of the principal sources of income for many of Deir al-Balah's residents. The particular type of date that is cultivated in the area is known as "Hayani." It has a distinctly red color. Other leading agricultural products cultivated in Deir al-Balah include citrus, almonds, pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall.
The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean re ...
s and grapes.
The city has a small fishing industry and is the site of one of four wharf
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more Berth (moorings), berths ...
s in the Gaza Strip. In 2007 there were about 76 active fishing vessels employed by 550 fishermen. From 2000 to 2006, during the Second Intifada, income from fishing was halved. In order to alleviate losses resulting from a fishing limit off the coast imposed by the Israeli Navy
The Israeli Navy ( he, חיל הים הישראלי, ''Ḥeil HaYam HaYisraeli'' (English: The Israeli Sea Corps); ar, البحرية الإسرائيلية) is the naval warfare service arm of the Israel Defense Forces, operating primarily i ...
following Hamas's victory in the 2006 parliamentary elections, the Palestinian Authority Department of Fisheries has sought to construct eight artificial reefs in both Deir al-Balah and Gaza City.
Education
According to the 1997 PCBS census, 87.7% of residents in Deir al-Balah over the age of 10 were literate. The number of people who finished elementary education was 5,740, while 5,964 finished primary education and 5,289 completed secondary school. In higher education, 1,763 people attained associate degrees, 1,336 attained bachelor's degrees and 97 attained higher degrees. Educational services in Deir al-Balah are under the jurisdiction of the Khan Yunis Directorate of Higher Education. There were a total of 85 schools in the Deir al-Balah Governorate in 2007-08 according to the PNA's Ministry of Education and Higher Education. The Palestinian government operated 39 school while four were privately owned. The remainder were run by UNRWA and were mostly located in refugee camps in Deir al-Balah's vicinity. The total number of students in the governorate was 67,693, of which 50.3% were male 49.7% female. ThePalestine Technical College The Palestine Technical College is a university technical college in Deir El-Balah, Gaza Strip, Palestine. The college offers bachelor degree programs and 2-year associate degrees in technical education at the post-secondary level, as well as prog ...
, a vocational and technical college founded in 1992, is located in Deir al-Balah. A library was added to the campus in 1998.
Government
Deir al-Balah's firstvillage council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
was established in 1946 and an elected local government continued to administer the city until 1982 when the Israeli military authorities dissolved the council and appointed a mayor. In 1994 Deir al-Balah gained the status of a city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be de ...
by the Palestinian Authority (PNA). The Palestinian president, Yasser Arafat
Mohammed Abdel Rahman Abdel Raouf al-Qudwa al-Husseini (4 / 24 August 1929 – 11 November 2004), popularly known as Yasser Arafat ( , ; ar, محمد ياسر عبد الرحمن عبد الرؤوف عرفات القدوة الحسيني, Mu ...
, appointed Samir Mohammed Azayiza as mayor until 2000 when he replaced him with Sami Abu Salim, a wealthy businessman from the city. The services and functions of the municipality include city planning, infrastructure maintenance and repair, providing utilities, school administration and garbage collection.
A 15-member municipal council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural coun ...
currently administers Deir al-Balah. Although thought to be a stronghold of Fatah
Fatah ( ar, فتح '), formerly the Palestinian National Liberation Movement, is a Palestinian nationalist social democratic political party and the largest faction of the Confederation, confederated multi-party Palestine Liberation Organizati ...
, Hamas members defeated Fatah's candidates in the 2005 Palestinian municipal elections by a large margin, taking 13 seats. Despite their political affiliations, all candidates ran as Independents. Two female candidates also gained seats. Local sheikh, school operator and Hamas member Ahmad Harb Kurd garnered the most votes making him the current head of the municipality.
Mayors
* Sulaiman al-'Azayiza (at least 1967–1982)Lesch, 1980 p. 98. * Israeli Military Governor (1982–1994) * Samir Mohammed 'Azayiza (1994–2000) * Sami Abu Salim (2000–2005) *Ahmad Kurd
Ahmad Kurd ( ar, أحمد كرد; 13 September 1949 – 9 May 2020) was a Palestinian politician, who served as the mayor of Deir al-Balah located in the central Gaza Strip. He was elected as mayor in 2005 as the candidate for the political party ...
(2005–)
See also
*Hanajira
Al-Hanajira (also Arab al-Hanajira, al-Hanajra or el-Hanajreh) was one of the five principal Bedouin tribes inhabiting the Negev Desert prior to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. Its territory stretched north-south between Deir al-Balah and Gaza and e ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (p53
* * * * * * * * * * *
External links
*Survey of Western Palestine, Map 19
IAA
Laborers in Deir al-Balah Governorate
Map of the Deir-al Balah Governorate
{{Authority control Populated coastal places in Palestinian territories Populated places of the Byzantine Empire Cities in the Gaza Strip Cities in ancient Egypt Bronze Age sites in the State of Palestine Philistines Date palm orchards Municipalities of the State of Palestine