Deep sea community on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A deep sea community is any
A deep sea community is any
PDF
Two scientists, J. Corliss and J. van Andel, first witnessed dense chemosynthetic clam beds from the submersible ''
station 225
The reported depth was 4,475
 The ocean can be conceptualized as being divided into various
The ocean can be conceptualized as being divided into various
 These animals have
These animals have
/ref>
/ref> The
 The mesopelagic zone is the upper section of the midwater zone, and extends from below
The mesopelagic zone is the upper section of the midwater zone, and extends from below
 The bathyl zone is the lower section of the midwater zone, and encompasses the depths of . Light does not reach this zone, giving it its nickname "the midnight zone"; due to the lack of light, it is less densely populated than the epipelagic zone, despite being much larger. Fish find it hard to live in this zone, as there is crushing pressure, cold temperatures of , a low level of
The bathyl zone is the lower section of the midwater zone, and encompasses the depths of . Light does not reach this zone, giving it its nickname "the midnight zone"; due to the lack of light, it is less densely populated than the epipelagic zone, despite being much larger. Fish find it hard to live in this zone, as there is crushing pressure, cold temperatures of , a low level of
 The abyssal zone remains in perpetual darkness at a depth of . The only organisms that inhabit this zone are
The abyssal zone remains in perpetual darkness at a depth of . The only organisms that inhabit this zone are



 A deep sea community is any
A deep sea community is any community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, tow ...
of organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
s associated by a shared habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
in the deep sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combin ...
. Deep sea communities remain largely unexplored, due to the technological and logistical challenges and expense involved in visiting this remote biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
. Because of the unique challenges (particularly the high barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
, extremes of temperature and absence of light), it was long believed that little life existed in this hostile environment. Since the 19th century however, research has demonstrated that significant biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
exists in the deep sea.
The three main sources of energy and nutrients for deep sea communities are marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to ...
, whale fall
A whale fall occurs when the carcass of a whale has fallen onto the ocean floor at a depth greater than , in the bathyal or abyssal zones. On the sea floor, these carcasses can create complex localized ecosystems that supply sustenance to deep-s ...
s, and chemosynthesis
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
at hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s and cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
s.
History
Prior to the 19th century scientists assumed life was sparse in the deep ocean. In the 1870sSir Charles Wyville Thomson
Sir Charles Wyville Thomson (5 March 1830 – 10 March 1882) was a Scottish natural history, natural historian and marine zoology, marine zoologist. He served as the chief scientist on the Challenger expedition; his work there revolutionized oc ...
and colleagues aboard the Challenger expedition
The ''Challenger'' expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific program that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, .
The expedition, initiated by Wil ...
discovered many deep-sea creatures of widely varying types.
The first discovery of any deep-sea chemosynthetic
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
community including higher animals was unexpectedly made at hydrothermal vents in the eastern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
during geological explorations (Corliss et al., 1979).Minerals Management Service
The Minerals Management Service (MMS) was an agency of the United States Department of the Interior that managed the nation's natural gas, oil and other mineral resources on the outer continental shelf (OCS).
Due to perceived conflict of intere ...
Gulf of Mexico OCS Region (November 2006). "Gulf of Mexico OCS Oil and Gas Lease Sales: 2007–2012. Western Planning Area Sales 204, 207, 210, 215, and 218. Central Planning Area Sales 205, 206, 208, 213, 216, and 222. Draft Environmental Impact Statement. Volume I: Chapters 1–8 and Appendices". U.S. Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, New Orleans. page 3-27Two scientists, J. Corliss and J. van Andel, first witnessed dense chemosynthetic clam beds from the submersible ''
DSV Alvin
''Alvin'' (DSV-2) is a crewed deep-ocean research submersible owned by the United States Navy and operated by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) in Woods Hole, Massachusetts. The vehicle was built by General Mills' Electronics Grou ...
'' on February 17, 1977, after their unanticipated discovery using a remote camera sled two days before.
The Challenger Deep
The Challenger Deep is the deepest-known point of the seabed of Earth, with a depth of by direct measurement from deep-diving submersibles, remotely operated underwater vehicles and benthic landers, and (sometimes) slightly more by sonar bathym ...
is the deepest surveyed point of all of Earth's oceans; it is located at the southern end of the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maximum know ...
near the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
group. The depression is named after HMS ''Challenger'', whose researchers made the first recordings of its depth on 23 March 1875 astation 225
The reported depth was 4,475
fathom
A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to , used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an International Standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally-accepted non-SI unit. Hi ...
s (8184 meters) based on two separate soundings. In 1960, Don Walsh
Don Walsh (born November 2, 1931) is an American oceanographer, explorer and marine policy specialist. He and Jacques Piccard were aboard the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' when it made a record maximum descent into the Challenger Deep on January 2 ...
and Jacques Piccard
Jacques Piccard (28 July 19221 November 2008) was a Swiss oceanographer and engineer, known for having developed underwater submarines for studying ocean currents. In the Challenger Deep, he and Lt. Don Walsh of the United States Navy were the ...
descended to the bottom of the Challenger Deep in the ''Trieste'' bathyscaphe
A bathyscaphe ( or ) is a free-diving self-propelled deep-sea submersible, consisting of a crew cabin similar to a bathysphere, but suspended below a float rather than from a surface cable, as in the classic bathysphere design.
The float is fi ...
. At this great depth a small flounder-like fish was seen moving away from the spotlight of the bathyscaphe.
The Japanese remote operated vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (technically ROUV or just ROV) is a tethered underwater mobile device, commonly called ''underwater robot''.
Definition
This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the a ...
(ROV) '' Kaiko'' became the second vessel to reach the bottom of the Challenger Deep in March 1995. ''Nereus
In Greek mythology, Nereus ( ; ) was the eldest son of Pontus (the Sea) and Gaia (the Earth), with Pontus himself being a son of Gaia. Nereus and Doris became the parents of 50 daughters (the Nereids) and a son ( Nerites), with whom Nereus liv ...
'', a hybrid remotely operated vehicle (HROV) of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI, acronym pronounced ) is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.
Established in 1930 in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, it i ...
, is the only vehicle capable of exploring ocean depths beyond 7000 meters. ''Nereus'' reached a depth of 10,902 meters at the Challenger Deep on May 31, 2009. On 1 June 2009, sonar mapping of the Challenger Deep by the Simrad EM120 multibeam sonar bathymetry system aboard the R/V ''Kilo Moana'' indicated a maximum depth of . The sonar system uses phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
* Phase space, a mathematic ...
and amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplit ...
bottom detection, with an accuracy of better than 0.2% of water depth (this is an error of about 22 meters at this depth).
Environment
Darkness
zones
Zone or The Zone may refer to:
Places Climate and altitude zones
* Death zone (originally the lethal zone), altitudes above a certain point where the amount of oxygen is insufficient to sustain human life for an extended time span
* Frigid zone, ...
, depending on depth, and presence or absence of sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
. Nearly all life forms
Life form (also spelled life-form or lifeform) is an entity that is living, such as plants (flora) and animals (fauna). It is estimated that more than 99% of all species that ever existed on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are ex ...
in the ocean depend on the photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
activities of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
Ph ...
and other marine plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s to convert carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
into organic carbon
Total organic carbon (TOC) is the amount of carbon found in an organic compound and is often used as a non-specific indicator of water quality or cleanliness of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. TOC may also refer to the amount of organic c ...
, which is the basic building block of organic matter
Organic matter, organic material, or natural organic matter refers to the large source of carbon-based compounds found within natural and engineered, terrestrial, and aquatic environments. It is matter composed of organic compounds that have c ...
. Photosynthesis in turn requires energy from sunlight to drive the chemical reactions that produce organic carbon.
The stratum of the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
up till which sunlight penetrates is referred to as the photic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
. The photic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
can be subdivided into two different vertical regions. The uppermost portion of the photic zone, where there is adequate light to support photosynthesis by phytoplankton and plants, is referred to as the euphotic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
(also referred to as the ''epipelagic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
'', or ''surface zone''). The lower portion of the photic zone, where the light intensity is insufficient for photosynthesis, is called the dysphotic zone (dysphotic means "poorly lit" in Greek). The dysphotic zone is also referred to as the ''mesopelagic zone'', or the ''twilight zone''. Its lowermost boundary is at a thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
of , which, in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
generally lies between 200 and 1000 meters.
The euphotic zone is somewhat arbitrarily defined as extending from the surface to the depth where the light intensity is approximately 0.1–1% of surface sunlight irradiance In radiometry, irradiance is the radiant flux ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area. The SI unit of irradiance is the watt per square metre (W⋅m−2). The CGS unit erg per square centimetre per second (erg⋅cm−2⋅s−1) is often used ...
, depending on season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
, latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and degree of water turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
. In the clearest ocean water, the euphotic zone may extend to a depth of about 150 meters, or rarely, up to 200 meters. Dissolved substances and solid particles absorb and scatter light, and in coastal regions the high concentration of these substances causes light to be attenuated rapidly with depth. In such areas the euphotic zone may be only a few tens of meters deep or less. The dysphotic zone, where light intensity is considerably less than 1% of surface irradiance, extends from the base of the euphotic zone to about 1000 meters. Extending from the bottom of the photic zone down to the seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
is the aphotic zone
The aphotic zone (aphotic from Greek prefix + "without light") is the portion of a lake or ocean where there is little or no sunlight. It is formally defined as the depths beyond which less than 1 percent of sunlight penetrates. Above the aphot ...
, a region of perpetual darkness.
Since the average depth of the ocean is about 4300 meters, the photic zone represents only a tiny fraction of the ocean's total volume. However, due to its capacity for photosynthesis, the photic zone has the greatest biodiversity and biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
of all oceanic zones. Nearly all primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through c ...
in the ocean occurs here. Any life forms present in the aphotic zone must either be capable of movement upwards through the water column into the photic zone for feeding, or must rely on material sinking from above, or must find another source of energy and nutrition, such as occurs in chemosynthetic
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
found near hydrothermal vent
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
s and cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
s.
Hyperbaricity
 These animals have
These animals have evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation t ...
to survive the extreme pressure of the sub-photic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
s. The pressure increases by about one atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
every ten meters. To cope with the pressure, many fish are rather small, usually not exceeding 25 cm in length. Also, scientists have discovered that the deeper these creatures live, the more gelatinous their flesh and more minimal their skeletal structure. These creatures have also eliminated all excess cavities that would collapse under the pressure, such as swim bladders.The Deep Sea at MarineBio.org – Ocean biology, Marine life, Sea creatures, Marine conservation/ref>
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
is the greatest environmental factor acting on deep-sea organisms. In the deep sea, although most of the deep sea is under pressures between 200 and 600 atm, the range of pressure is from 20 to 1,000 atm. Pressure exhibits a great role in the distribution of deep sea organisms. Until recently, people lacked detailed information on the direct effects of pressure on most deep-sea organisms, because virtually all organisms trawled from the deep sea arrived at the surface dead or dying. With the advent of traps that incorporate a special pressure-maintaining chamber, undamaged larger metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, ca ...
animals have been retrieved from the deep sea in good condition. Some of these have been maintained for experimental purposes, and we are obtaining more knowledge of the biological effects of pressure.
Temperature
The two areas of greatest and most rapidtemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
change in the oceans are the transition zone between the surface waters and the deep waters, the thermocline, and the transition between the deep-sea floor and the hot water flows at the hydrothermal vents. Thermoclines vary in thickness from a few hundred meters to nearly a thousand meters. Below the thermocline, the water mass of the deep ocean is cold and far more homogeneous. Thermoclines are strongest in the tropics, where the temperature of the epipelagic zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological proc ...
is usually above 20 °C. From the base of the epipelagic, the temperature drops over several hundred meters to 5 or 6 °C at 1,000 meters. It continues to decrease to the bottom, but the rate is much slower. Below 3,000 to 4,000 m, the water is isothermal
In thermodynamics, an isothermal process is a type of thermodynamic process in which the temperature ''T'' of a system remains constant: Δ''T'' = 0. This typically occurs when a system is in contact with an outside thermal reservoir, and a ...
. At any given depth, the temperature is practically unvarying over long periods of time. There are no seasonal temperature changes, nor are there any annual changes. No other habitat on earth has such a constant temperature.
Hydrothermal vents are the direct contrast with constant temperature. In these systems, the temperature of the water as it emerges from the "black smoker" chimneys may be as high as 400 °C (it is kept from boiling by the high hydrostatic pressure) while within a few meters it may be back down to 2–4 °C.
Salinity

Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal ...
is constant throughout the depths of the deep sea. There are two notable exceptions to this rule:
#In the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, water loss through evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidi ...
greatly exceeds input from precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
and river runoff. Because of this, salinity in the Mediterranean is higher than in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. Evaporation is especially high in its eastern half, causing the water level to decrease and salinity to increase in this area. The resulting pressure gradient pushes relatively cool, low-salinity water from the Atlantic Ocean across the basin. This water warms and becomes saltier as it travels eastward, then sinks in the region of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
and circulates westward, to spill back into the Atlantic over the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
. The net effect of this is that at the Strait of Gibraltar, there is an eastward surface current of cold water of lower salinity from the Atlantic, and a simultaneous westward current of warm saline water from the Mediterranean in the deeper zones. Once back in the Atlantic, this chemically distinct Mediterranean Intermediate Water can persist for thousands of kilometers away from its source.
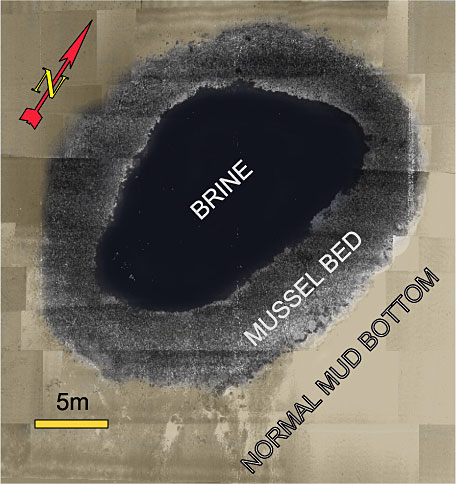
#Brine pool
A brine pool, sometimes called an underwater lake, deepwater or brine lake, is a volume of brine collected in a seafloor depression. The pools are dense bodies of water that have a salinity that is three to eight times greater than the surround ...
s are large areas of brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for br ...
on the seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
. These pools are bodies of water that have a salinity that is three to five times greater than that of the surrounding ocean. For deep sea brine pools the source of the salt is the dissolution of large salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
deposits through salt tectonics
upright=1.7
Salt tectonics, or halokinesis, or halotectonics, is concerned with the geometries and processes associated with the presence of significant thicknesses of evaporites containing rock salt within a stratigraphic sequence of rocks. This ...
. The brine often contains high concentrations of methane, providing energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
to chemosynthetic
In biochemistry, chemosynthesis is the biological conversion of one or more carbon-containing molecules (usually carbon dioxide or methane) and nutrients into organic matter using the oxidation of inorganic compounds (e.g., hydrogen gas, hydro ...
extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme temper ...
s that live in this specialized biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
. Brine pools are also known to exist on the Antarctic continental shelf The Antarctic continental shelf is a submerged piece of the Antarctic continent that underlies a portion of the Southern Ocean — the ocean which surrounds Antarctica. The shelf is generally narrow and unusually deep, its edge lying at depths avera ...
where the source of brine is salt excluded during formation of sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
. Deep sea and Antarctic brine pools can be toxic to marine animals. Brine pools are sometimes called ''seafloor lakes'' because the dense brine creates a halocline
In oceanography, a halocline (from Greek ''hals'', ''halos'' 'salt' and ''klinein'' 'to slope') is a Cline (hydrology), cline, a subtype of chemocline caused by a strong, vertical salinity gradient within a body of water. Because salinity (in c ...
which does not easily mix with overlying seawater. The high salinity raises the density of the brine, which creates a distinct surface and shoreline for the pool.NOAA exploration of a brine pool/ref> The
deep sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combin ...
, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline, at a depth of 1000 fathoms (1800 m) or more. The deepest part of the deep sea is Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maximum know ...
located in the western North Pacific. It is also the deepest point of the earth's crust. It has a maximum depth of about 10.9 km which is deeper than the height of Mount Everest
Mount Everest (; Tibetan: ''Chomolungma'' ; ) is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation (snow heig ...
. In 1960, Don Walsh
Don Walsh (born November 2, 1931) is an American oceanographer, explorer and marine policy specialist. He and Jacques Piccard were aboard the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' when it made a record maximum descent into the Challenger Deep on January 2 ...
and Jacques Piccard
Jacques Piccard (28 July 19221 November 2008) was a Swiss oceanographer and engineer, known for having developed underwater submarines for studying ocean currents. In the Challenger Deep, he and Lt. Don Walsh of the United States Navy were the ...
reached the bottom of Mariana Trench in the ''Trieste'' bathyscaphe. The pressure is about 11,318 metric tons-force per square meter (110.99 MPa
MPA or mPa may refer to:
Academia
Academic degrees
* Master of Performing Arts
* Master of Professional Accountancy
* Master of Public Administration
* Master of Public Affairs
Schools
* Mesa Preparatory Academy
* Morgan Park Academy
* Mound ...
or 16100 psi
Psi, PSI or Ψ may refer to:
Alphabetic letters
* Psi (Greek) (Ψ, ψ), the 23rd letter of the Greek alphabet
* Psi (Cyrillic) (Ѱ, ѱ), letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet, adopted from Greek
Arts and entertainment
* "Psi" as an abbreviation ...
).
Zones
Mesopelagic
 The mesopelagic zone is the upper section of the midwater zone, and extends from below
The mesopelagic zone is the upper section of the midwater zone, and extends from below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
. This is colloquially known as the "twilight zone" as light can still penetrate this layer, but it is too low to support photosynthesis. The limited amount of light, however, can still allow organisms to see, and creatures with a sensitive vision can detect prey, communicate, and orientate themselves using their sight. Organisms in this layer have large eyes to maximize the amount of light in the environment.
Most mesopelagic fish make daily vertical migrations, moving at night into the epipelagic zone, often following similar migrations of zooplankton, and returning to the depths for safety during the day. These vertical migrations often occur over a large vertical distances, and are undertaken with the assistance of a swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth w ...
. The swimbladder is inflated when the fish wants to move up, and, given the high pressures in the mesopelegic zone, this requires significant energy. As the fish ascends, the pressure in the swimbladder must adjust to prevent it from bursting. When the fish wants to return to the depths, the swimbladder is deflated. Some mesopelagic fishes make daily migrations through the thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with ...
, where the temperature changes between , thus displaying considerable tolerances for temperature change.
Mesopelagic fish usually lack defensive spines, and use colour and bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ...
to camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the ...
them from other fish. Ambush predator
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture or trap prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture prey us ...
s are dark, black or red. Since the longer, red, wavelengths of light do not reach the deep sea, red effectively functions the same as black. Migratory forms use countershaded
Countershading, or Thayer's law, is a method of camouflage in which an animal's coloration is darker on the top or upper side and lighter on the underside of the body. This pattern is found in many species of mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, and ...
silvery colours. On their bellies, they often display photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, ...
s producing low grade light. For a predator from below, looking upwards, this bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ...
camouflages the silhouette of the fish. However, some of these predators have yellow lenses that filter the (red deficient) ambient light, leaving the bioluminescence visible.
Bathyal
 The bathyl zone is the lower section of the midwater zone, and encompasses the depths of . Light does not reach this zone, giving it its nickname "the midnight zone"; due to the lack of light, it is less densely populated than the epipelagic zone, despite being much larger. Fish find it hard to live in this zone, as there is crushing pressure, cold temperatures of , a low level of
The bathyl zone is the lower section of the midwater zone, and encompasses the depths of . Light does not reach this zone, giving it its nickname "the midnight zone"; due to the lack of light, it is less densely populated than the epipelagic zone, despite being much larger. Fish find it hard to live in this zone, as there is crushing pressure, cold temperatures of , a low level of dissolved oxygen
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It ca ...
, and a lack of sufficient nutrients. What little energy is available in the bathypelagic zone filters from above in the form of detritus, faecal material, and the occasional invertebrate or mesopelagic fish. About 20% of the food that has its origins in the epipelagic zone falls down to the mesopelagic zone, but only about 5% filters down to the bathypelagic zone. The fish that do live there may have reduced or completely lost their gills, kidneys, hearts, and swimbladders, have slimy instead of scaly skin, and have a weak skeletal and muscular build. Most of the animals that live in the bathyl zone are invertebrates such as sea sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through t ...
s, cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s, and echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea ...
s. With the exception of very deep areas of the ocean, the bathyl zone usually reaches the benthic zone on the seafloor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
.
Abyssal and Hadal
 The abyssal zone remains in perpetual darkness at a depth of . The only organisms that inhabit this zone are
The abyssal zone remains in perpetual darkness at a depth of . The only organisms that inhabit this zone are chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototro ...
s and predators that can withstand immense pressures, sometimes as high as . The hadal zone (named after Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
, the Greek god
The following is a list of gods, goddesses, and many other divine and semi-divine figures from ancient Greek mythology and ancient Greek religion.
Immortals
The Greeks created images of their deities for many purposes. A temple would house the ...
of the underworld) is a zone designated for the deepest trenches
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from eros ...
in the world, reaching depths of below . The deepest point in the hadal zone is the Marianas Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maximum known ...
, which descends to and has a pressure of .
Energy sources

Marine snow
The upper photic zone of the ocean is filled with particle organic matter (POM) and is quite productive, especially in the coastal areas and the upwelling areas. However, most POM is small and light. It may take hundreds, or even thousands of years for these particles to settle through the water column into the deep ocean. This time delay is long enough for the particles to be remineralized and taken up by organisms in the food webs. Scientists at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution conducted an experiment three decades ago in deep Sargasso Sea looking at the rate of sinking. They found what became known asmarine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow (also known as "ocean dandruff") is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to ...
in which the POM are repackaged into much larger particles which sink at much greater speed, 'falling like snow'.
Because of the sparsity of food, the organisms living on and in the bottom are generally opportunistic. They have special adaptations for this extreme environment: rapid growth, effect larval dispersal mechanism and the ability to use a 'transient' food resource. One typical example is wood-boring bivalves
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bival ...
, which bore into wood and other plant remains and are fed on the organic matter from the remains.
Whale falls
For the deep-sea ecosystem, the death of awhale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
is the most important event. A dead whale can bring hundreds of tons of organic matter to the bottom. Whale fall
A whale fall occurs when the carcass of a whale has fallen onto the ocean floor at a depth greater than , in the bathyal or abyssal zones. On the sea floor, these carcasses can create complex localized ecosystems that supply sustenance to deep-s ...
community progresses through three stages:
# Mobile scavenger stage: Big and mobile deep-sea animals arrive at the site almost immediately after whales fall on the bottom. Amphipods
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far descri ...
, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
s, sleeper shark
The Somniosidae are a family of sharks in the order Squaliformes, commonly known as sleeper sharks. The common name ''"sleeper shark"'' comes from their slow swimming, low activity level, and perceived non-aggressive nature.
Distribution and hab ...
s and hagfish
Hagfish, of the class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped, slime-producing marine fish (occasionally called slime eels). They are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, a ...
are all scavengers.
# Opportunistic stage: Organisms arrive which colonize the bones and surrounding sediments that have been contaminated with organic matter from the carcass and any other tissue left by the scavengers. One genus is ''Osedax
''Osedax'' is a genus of deep-sea siboglinid polychaetes, commonly called boneworms, zombie worms, or bone-eating worms. ''Osedax'' is Latin for "bone-eater". The name alludes to how the worms bore into the bones of whale carcasses to reach en ...
'', a tube worm. The larva is born without sex. The surrounding environment determines the sex of the larva. When a larva settles on a whale bone, it turns into a female; when a larva settles on or in a female, it turns into a dwarf male. One female ''Osedax'' can carry more than 200 of these male individuals in its oviduct.
# Sulfophilic stage: Further decomposition of bones and seawater sulfate reduction happen at this stage. Bacteria create a sulphide-rich environment analogous to hydrothermal vents. Polynoids, bivalves, gastropods
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. Ther ...
and other sulphur-loving creatures move in.
Chemosynthesis
Hydrothermal vents

Hydrothermal vents
A hydrothermal vent is a fissure on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hotspot ...
were discovered in 1977 by scientists from Scripps Institution of Oceanography. So far, the discovered hydrothermal vents are all located at the boundaries of plates: East Pacific, California, Mid-Atlantic ridge, China and Japan.
New ocean basin material is being made in regions such as the Mid-Atlantic ridge as tectonic plates pull away from each other. The rate of spreading of plates is 1–5 cm/yr. Cold sea water circulates down through cracks between two plates and heats up as it passes through hot rock. Minerals and sulfides are dissolved into the water during the interaction with rock. Eventually, the hot solutions emanate from an active sub-seafloor rift, creating a hydrothermal vent.
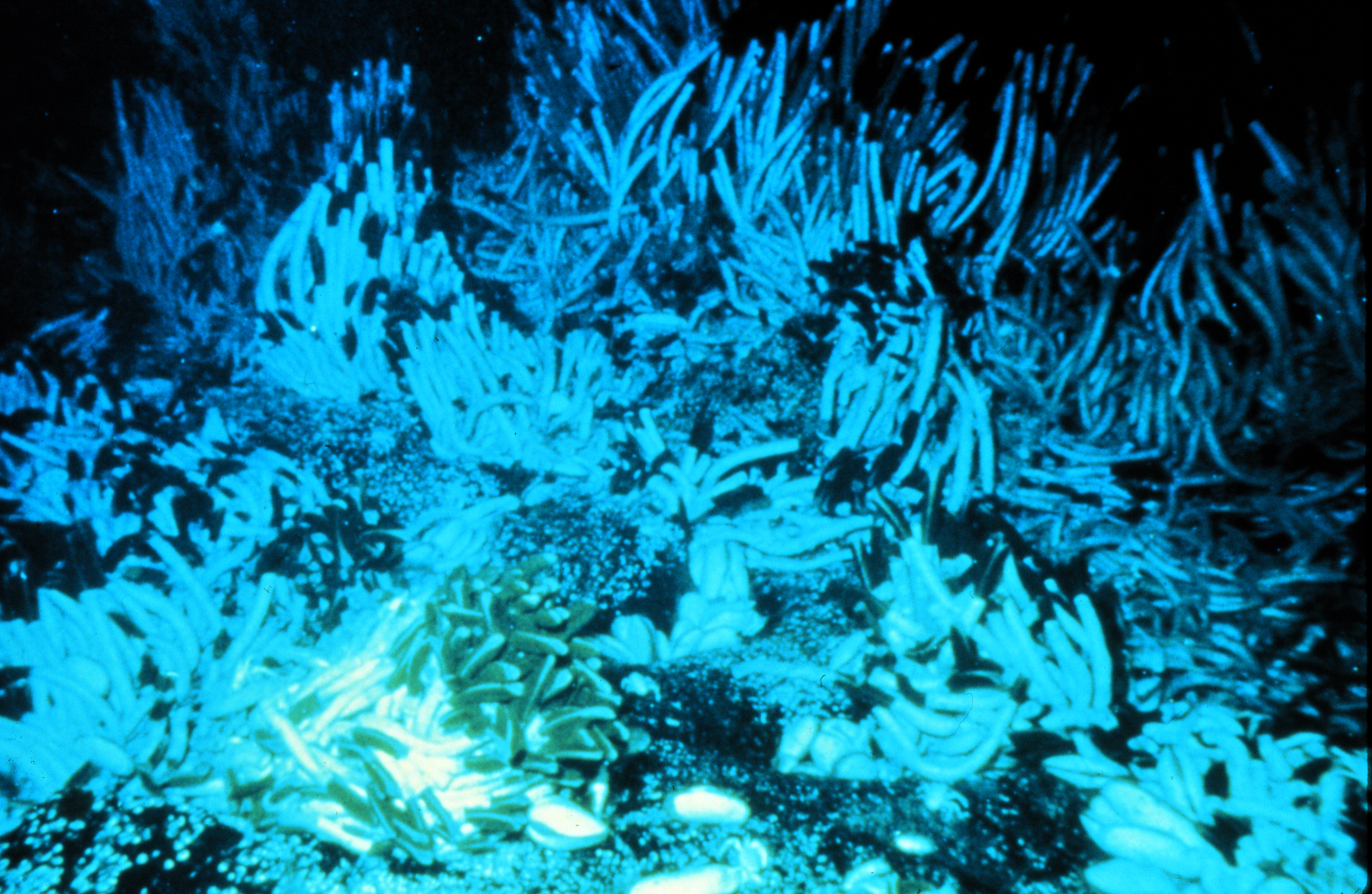
Chemosynthesis of bacteria provide the energy and organic matter for the whole food web in vent ecosystems. Giant tube worm
''Riftia pachyptila'', commonly known as the giant tube worm and less commonly known as the Giant beardworm, is a marine invertebrate in the phylum Annelida (formerly grouped in phylum Pogonophora and Vestimentifera) related to tube worms ...
s can grow to tall because of the richness of nutrients. Over 300 new species have been discovered at hydrothermal vents.
Hydrothermal vents are entire ecosystems independent from sunlight, and may be the first evidence that the earth can support life without the sun.
Cold seeps
Acold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
(sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
where hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Eart ...
and other hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool
A brine pool, sometimes called an underwater lake, deepwater or brine lake, is a volume of brine collected in a seafloor depression. The pools are dense bodies of water that have a salinity that is three to eight times greater than the surround ...
.
Ecology
Deep seafood web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one ...
s are complex, and aspects of the system are poorly understood. Typically, predator-prey interactions within the deep are compiled by direct observation (likely from remotely operated underwater vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (technically ROUV or just ROV) is a tethered underwater mobile device, commonly called ''underwater robot''.
Definition
This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the ai ...
s), analysis of stomach contents, and biochemical analysis. Stomach content analysis is the most common method used, but it is not reliable for some species.
In deep sea pelagic ecosystems off of California, the trophic web is dominated by deep sea fishes, cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s, gelatinous zooplankton
Gelatinous zooplankton are fragile animals that live in the water column in the ocean. Their delicate bodies have no hard parts and are easily damaged or destroyed. Gelatinous zooplankton are often transparent. All jellyfish are gelatinous zoopla ...
, and crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s. Between 1991 and 2016, 242 unique feeding relationships between 166 species of predators and prey demonstrated that gelatinous zooplankton have an ecological impact similar to that of large fishes and squid. Narcomedusae
Narcomedusae is an order of hydrozoans in the subclass Trachylinae. Members of this order do not normally have a polyp stage. The medusa has a dome-shaped bell with thin sides. The tentacles are attached above the lobed margin of the bell with ...
, siphonophore
Siphonophorae (from Greek ''siphōn'' 'tube' + ''pherein'' 'to bear') is an order within Hydrozoa, which is a class of marine organisms within the phylum Cnidaria. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the order contains 175 specie ...
s (of the family Physonectae
Physonectae is a suborder of siphonophores. In Japanese it is called ().
Organisms in the suborder Physonectae follow the classic Siphonophore body plan. They are almost all pelagic, and are composed of a colony of specialized zooids that ori ...
), ctenophore
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
s, and cephalopods consumed the greatest diversity of prey, in decreasing order. Cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
has been documented in squid of the genus ''Gonatus
''Gonatus'' is a genus of squid in the family Gonatidae
The Gonatidae, also known as armhook squid, are a family of moderately sized squid. The family contains about 19 species in three genera, widely distributed and plentiful in cold boreal w ...
''.
See also
*Deep sea fish
Deep-sea fish are fish that live in the darkness below the sunlit surface waters, that is below the epipelagic or photic zone of the sea. The lanternfish is, by far, the most common deep-sea fish. Other deep sea fishes include the flashlight ...
* Movile Cave
Movile Cave () is a cave near Mangalia, Constanța County, Romania discovered in 1986 by Cristian Lascu a few kilometers from the Black Sea coast. It is notable for its unique groundwater ecosystem abundant in hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxi ...
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Deep Sea Communities Oceanography