Davenport Tablets on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Davenport Tablets are three inscribed slate tablets found in mounds near
The Davenport Tablets are three inscribed slate tablets found in mounds near
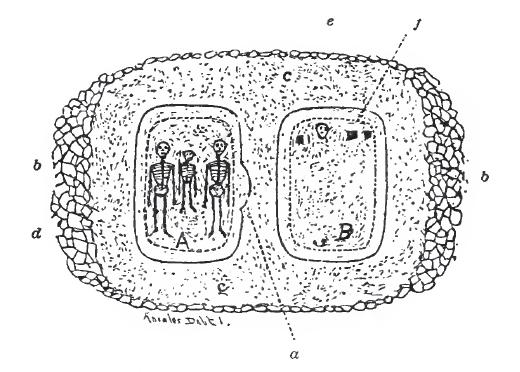 As Gass continued digging in Mound No. 3, he came across three human skeletons- two adults and one child, five copper axes wrapped in cloth, and copper beads. The child skeleton was found in between the two others 5 1/2 feet below the surface. Above the skeletons lay a thick layer of shells and a sloping layer of shells. Two years before the discovery of the tablets, Dr. Farquharson said that previously "there were no layers of stones nor shells" in the mounds .
As Gass continued digging in Mound No. 3, he came across three human skeletons- two adults and one child, five copper axes wrapped in cloth, and copper beads. The child skeleton was found in between the two others 5 1/2 feet below the surface. Above the skeletons lay a thick layer of shells and a sloping layer of shells. Two years before the discovery of the tablets, Dr. Farquharson said that previously "there were no layers of stones nor shells" in the mounds .
 The Davenport Tablets are three inscribed slate tablets found in mounds near
The Davenport Tablets are three inscribed slate tablets found in mounds near Davenport, Iowa
Davenport is a city in and the county seat of Scott County, Iowa, United States. Located along the Mississippi River on the eastern border of the state, it is the largest of the Quad Cities, a metropolitan area with a population of 384,324 and a ...
on January 10, 1877, and January 30, 1878. If these tablets were real, they would have been proof for the argument that the people who built the Native American mounds, called the Mound Builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
were built by an ancient race of settlers. The Davenport Tablets were originally considered authentic, though opinion shifted after 1885 and they are now considered a hoax.
The tablets were found in mounds along with other items such as human skeletons, copper axes, and copper beads. One tablet represents a cremation scene, the second represents a hunting scene and the last is a calendar. The tablets had a total of 74 letters, deducting 24 repetitions. However, the letters were in a random order which could not be properly interpreted.
Even as the tablets were being examined, people questioned their authenticity. The tablets appeared to be in mint condition which would not have been the case if they had been buried for a long period of time. The site where the tablets were found revealed evidence someone had dug into the mound and placed the tablets. Because if the tablets had been untouched for many years, then the soil would have solidified around them rather than remaining loose.
Discovery
The first two tablets were discovered on January 10, 1877, at the site known as Cook's Farm by local clergyman the Reverend Jacob Gass, while he was engaged in an emergency excavation due to the imminent transfer of the access rights. They were found in one of the mounds on the site, Mound No. 3. In an excavation a year later (the access rights having been restored), Charles Harrison, the president of the Davenport Academy of Natural Sciences, while excavating there with Gass, found a third tablet in Mound No. 11, which was near where the two previous tablets were discovered. They are often associated in discussions with a pipe found by Gass and anotherLutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
minister, the Reverend Ad Blumer in 1880 in a separate group of mounds, referred to as the 'elephant pipe' by Gass. Blumer gave the pipe to the academy and shortly after his donation, the academy acquired a similar pipe from Gass which he reported had been found by a farmer in Louisa County, Iowa
Louisa County ( ) is a county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 10,837. The county seat is Wapello.
Louisa County is part of the Muscatine Micropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Louisa County was ...
. Charles Putnam wrote a vindication of these artifacts in 1885.
Mound No. 3
Grave A
 As Gass continued digging in Mound No. 3, he came across three human skeletons- two adults and one child, five copper axes wrapped in cloth, and copper beads. The child skeleton was found in between the two others 5 1/2 feet below the surface. Above the skeletons lay a thick layer of shells and a sloping layer of shells. Two years before the discovery of the tablets, Dr. Farquharson said that previously "there were no layers of stones nor shells" in the mounds .
As Gass continued digging in Mound No. 3, he came across three human skeletons- two adults and one child, five copper axes wrapped in cloth, and copper beads. The child skeleton was found in between the two others 5 1/2 feet below the surface. Above the skeletons lay a thick layer of shells and a sloping layer of shells. Two years before the discovery of the tablets, Dr. Farquharson said that previously "there were no layers of stones nor shells" in the mounds .
Grave B
The first two tablets were found in Grave B. Mounds are typically constructed in layers, however the arch in this grave indicated that at some point the mound was disrupted. In the middle of the grave was a layer of stones. The grave is 6 feet wide and 10 feet long and dug about 2.5 feet in depth. This information alone suggested how easy it would be to insert the tablets at the bottom without displacing other articles in the grave. After the discovery of the tablets, Gass came back and removed some remaining articles in the grave such as scattered skeleton parts, a copper axe, copper beads, pottery fragments, and yellow pigment. Farquharson examined the tablets and noticed, based on their original smooth markings, the tablets had not been subjected to much weathering.Mound No.11
While the owners of Cooks' Farm were plowing, unusual stones were found and Gass visited the mounds again. During this excavation he discovered more stones with ancient engravings along with the last tablet. On May 15 he found five inscribed stones, two of which are in a museum and the other three were too large to remove.Debunking the Tablets
The Davenport Tablets were sent to the Bureau of American Ethnology in theSmithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
to be studied further from 1877 to 1885. Initially the authenticity of the Davenport artifacts was not questioned in informal preliminary reports and opinions by academics including Lewis H Morgan. Spencer Baird
Spencer Fullerton Baird (; February 3, 1823 – August 19, 1887) was an American naturalist, ornithologist, ichthyologist, herpetologist, and museum curator. Baird was the first curator to be named at the Smithsonian Institution. He eventually ...
, secretary of the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
, assigned the task of making a preliminary study to Dr. E. Foreman, an assistant. Foreman's preliminary response was that they were not ancient. This was followed by a nine page report which raised questions as to their authenticity such as unweathered incisions and a perfect circle probably drawn with a steel compass. A debate escalated between those at The Davenport Academy and the Smithsonian Institution regarding whether the Davenport Tablets were real or fake. From the pages of minor scholarly journals to the foremost news in the journal ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
'', eventually the tablets' authenticity fell under the criticism of the new Smithsonian spokesman, Cyrus Thomas
Cyrus Thomas (July 27, 1825 – June 26, 1910) was an American ethnologist and entomologist prominent in the late 19th century and noted for his studies of the natural history of the American West.
Biography
Thomas was born in Kingsport, ...
. Thomas lambasted them as "anomalous waifs," which had absolutely no supporting, or contextual, evidence to aide in their authenticity. University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (UI, U of I, UIowa, or simply Iowa) is a public university, public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is org ...
Professor Marshall McKusick now refers to the find and the circumstances surrounding it as "The Davenport Conspiracy". McKusick suggested the tablets were modified roof tiles stolen off the Old Slate House, a house of prostitutes.
Interpretations
In McKusick's 1991 book, ''The Davenport Conspiracy Revisited'', McKusick asserts that Gass may have been the victim of an ill-advised joke played on him by fellow Davenport Academy members, who were possibly motivated by their jealousy of a foreign-born outsider in their midst. In 1874 Gass had made important discoveries of beautiful and complex Native American art at the Cook farm, such as copper axes. The level of technical ability and artistic craftsmanship by ancient Native Americans was evident in these artifacts. At a time when archeological enthusiasts digging along theMississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
in Iowa and Illinois were turning up nothing, Gass had the luck of hitting a genuine archaeological jackpot. However, after that date it is questionable as to what the motives of his academic rivals and relatives might have been.
Another explanation for the dubious origins of the artifacts might involve the credibility of Gass himself. It is believed Gass dealt in fake Native American effigy pipes, such as the many examples illustrated in ''The Davenport Conspiracy Revisited''. Genuine effigy pipes are a testament to the creative abilities of the ancient Native American Indians, but their counterfeit
To counterfeit means to imitate something authentic, with the intent to steal, destroy, or replace the original, for use in illegal transactions, or otherwise to deceive individuals into believing that the fake is of equal or greater value tha ...
s are of poor quality. Made of shale, clay, and limestone, these frauds were often traded amongst Gass and his colleagues, many ending up in the Davenport Academy museum. However, it is possible Gass himself was not the perpetrator of these fakes, but was influenced by people jealous of his abilities and good luck in selecting excavation sites. In this case, it was his own relatives, Edwin Gass and Adolph Blumer who persuaded him to take these fakes seriously and trade them.
See also
*Cardiff Giant
The Cardiff Giant was one of the most famous archaeological hoaxes in American history. It was a , 3,000 pound purported "petrified man" uncovered on October 16, 1869, by workers digging a well behind the barn of William C. "Stub" Newell in Cardi ...
* Grave Creek Stone
* Mound Builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
* L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows ( lit. Meadows Cove) is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newfoundland in the Ca ...
* Nomans Land (Massachusetts)
Nomans Land (Wampanoag: ;; also mapped "No Man's Land," "No Mans Land," or "No Man's island"), is an uninhabited island 612 acres (248 ha) in size, located in the town of Chilmark, Dukes County, Massachusetts. It is situated about ...
* Bat Creek inscription
The Bat Creek inscription is an inscribed stone tablet found by John W. Emmert on February 14, 1889. Emmert claimed to have found the tablet in Tipton Mound 3 during an excavation of Hopewell mounds in Loudon County, Tennessee. This excavation was ...
* Turkey Mountain inscriptions
* Oklahoma runestones
* Viking Altar Rock
* Spirit Pond runestones
* Petroform
Petroforms, also known as boulder outlines or boulder mosaics, are human-made shapes and patterns made by lining up large rocks on the open ground, often on quite level areas. Petroforms in North America were originally made by various Native A ...
* Petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
* Rock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also ...
References
*Putnam, Charles E. A Vindication Of The Authenticity Of The Elephant Pipes And Inscribed Tablets In The Museum Of The Davenport Academy Of Natural Sciences, 1885. *Guthrie, James L. "The Blind Men and the Elephants: The Davenport Relics Reconsidered." NEARA Monograph, 2005. *Silverberg, Robert (1970). ''The Mound Builders''. Ohio University Press. *Williams, Stephen. ''Fantastic Archaeology.'' Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1991. *McKusick, Marshall. ''The Davenport Conspiracy Revisited.'' Ames: Iowa State University Press, 1991. {{refend * Pseudoarchaeology Hoaxes in the United States 19th-century hoaxes 1877 in science 1877 in the United States Archaeological forgeries 1877 in Iowa