Data Maintenance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling
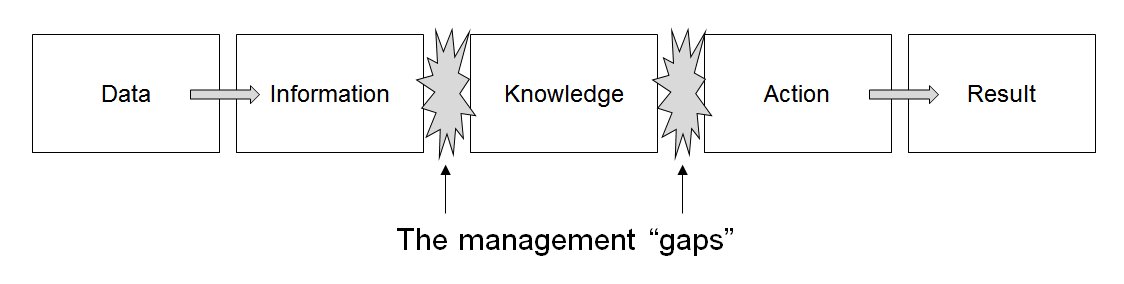 The "DIKAR" model stands for Data, Information, Knowledge, Action, and Result. It is a framework used to bridge the gap between raw data and actionable outcomes. The model emphasizes the transformation of data into information, which is then interpreted to create knowledge. This knowledge guides actions that lead to measurable results. DIKAR is widely applied in organizational strategies, helping businesses align their data management processes with decision-making and performance goals. By focusing on each stage, the model ensures that data is effectively utilized to drive informed decisions and achieve desired outcomes. It is particularly valuable in technology-driven environments.
The "information ladder" illustrates the progression from data (raw facts) to information (processed data), knowledge (interpreted information), and ultimately wisdom (applied knowledge). Each step adds value and context, enabling better decision-making. It emphasizes the transformation of unstructured inputs into meaningful insights for practical use.
The "DIKAR" model stands for Data, Information, Knowledge, Action, and Result. It is a framework used to bridge the gap between raw data and actionable outcomes. The model emphasizes the transformation of data into information, which is then interpreted to create knowledge. This knowledge guides actions that lead to measurable results. DIKAR is widely applied in organizational strategies, helping businesses align their data management processes with decision-making and performance goals. By focusing on each stage, the model ensures that data is effectively utilized to drive informed decisions and achieve desired outcomes. It is particularly valuable in technology-driven environments.
The "information ladder" illustrates the progression from data (raw facts) to information (processed data), knowledge (interpreted information), and ultimately wisdom (applied knowledge). Each step adds value and context, enabling better decision-making. It emphasizes the transformation of unstructured inputs into meaningful insights for practical use.
data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
.
Concept
The concept of data management emerged alongside the evolution of computing technology. In the 1950s, as computers became more prevalent, organizations began to grapple with the challenge of organizing and storing data efficiently. Early methods relied on punch cards and manual sorting, which were labor-intensive and prone to errors. The introduction of database management systems in the 1970s marked a significant milestone, enabling structured storage and retrieval of data. By the 1980s, relational database models revolutionized data management, emphasizing the importance of data as an asset and fostering a data-centric mindset in business. This era also saw the rise of data governance practices, which prioritized the organization and regulation of data to ensure quality and compliance. Over time, advancements in technology, such as cloud computing and big data analytics, have further refined data management, making it a cornerstone of modern business operations. , data management encompasses a wide range of practices, from data storage and security to analytics and decision-making, reflecting its critical role in driving innovation and efficiency across industries.Topics in Data Management
The Data Management Body of Knowledge, DMBoK, developed by the Data Management Association, DAMA, outlines key knowledge areas that serve as the foundation for modern data management practices. suggesting a framework for organizations to manage data as a strategicasset
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can b ...
.Data Governance
Setting policies, procedures, and accountability frameworks to ensure that data is accurate, secure, and used responsibly throughout the organization.Data Architecture
Focuses on designing the overall structure of data systems. It ensures that data flows are efficient and that systems are scalable, adaptable, and aligned with business needs.Data Modeling and Design
This area centers on creating models that logically represent data relationships. It’s essential for both designing databases and ensuring that data is structured in a way that facilitates analysis and reporting.Data Storage and Operations
Deals with the physical storage of data and its day-to-day management. This includes everything from traditional data centers to cloud-based storage solutions and ensuring efficient data processing.Data Integration and Interoperability
Ensures that data from various sources can be seamlessly shared and combined across multiple systems, which is critical for comprehensive analytics and decision-making.Document and Content Management
Focuses on managing unstructured data such as documents, multimedia, and other content, ensuring that it is stored, categorized, and easily retrievable.Data Warehousing, Business Intelligence and Data Analytics
Involves consolidating data into repositories that support analytics, reporting, and business insights.Metadata Management
Manages data about data, including definitions, origin, and usage, to enhance the understanding and usability of the organization’s data assets.Data Quality Management
Dedicated to ensuring that data remains accurate, complete, and reliable, this area emphasizes continuous monitoring and improvement practices.Reference and master data management
Reference data comprises standardized codes and values for consistent interpretation across systems. Master data management (MDM) governs and centralizes an organization’s critical data, ensuring a unified, reliable information source that supports effective decision-making and operational efficiency.Data security
Data security refers to a comprehensive set of practices and technologies designed to protect digital information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. It encompasses encryption, access controls, monitoring, and risk assessments to maintain data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.Data privacy
Data privacy involves safeguarding individuals’ personal information by ensuring its collection, storage, and use comply with consent, legal standards, and confidentiality principles. It emphasizes protecting sensitive data from misuse or unauthorized access while respecting users' rights.Data management as a foundation of information management
The distinction between data and derived value is illustrated by the "information ladder" or the DIKAR model. The "DIKAR" model stands for Data, Information, Knowledge, Action, and Result. It is a framework used to bridge the gap between raw data and actionable outcomes. The model emphasizes the transformation of data into information, which is then interpreted to create knowledge. This knowledge guides actions that lead to measurable results. DIKAR is widely applied in organizational strategies, helping businesses align their data management processes with decision-making and performance goals. By focusing on each stage, the model ensures that data is effectively utilized to drive informed decisions and achieve desired outcomes. It is particularly valuable in technology-driven environments.
The "information ladder" illustrates the progression from data (raw facts) to information (processed data), knowledge (interpreted information), and ultimately wisdom (applied knowledge). Each step adds value and context, enabling better decision-making. It emphasizes the transformation of unstructured inputs into meaningful insights for practical use.
The "DIKAR" model stands for Data, Information, Knowledge, Action, and Result. It is a framework used to bridge the gap between raw data and actionable outcomes. The model emphasizes the transformation of data into information, which is then interpreted to create knowledge. This knowledge guides actions that lead to measurable results. DIKAR is widely applied in organizational strategies, helping businesses align their data management processes with decision-making and performance goals. By focusing on each stage, the model ensures that data is effectively utilized to drive informed decisions and achieve desired outcomes. It is particularly valuable in technology-driven environments.
The "information ladder" illustrates the progression from data (raw facts) to information (processed data), knowledge (interpreted information), and ultimately wisdom (applied knowledge). Each step adds value and context, enabling better decision-making. It emphasizes the transformation of unstructured inputs into meaningful insights for practical use.
Data management in research
In research, Data management refers to the systematic process of handling data throughout its lifecycle. This includes activities such as collecting, organizing, storing, analyzing, and sharing data to ensure its accuracy, accessibility, and security. Effective data management also involves creating a data management plan, DMP, addressing issues like ethical considerations, compliance with regulatory standards, and long-term preservation. Proper management enhances research transparency, reproducibility, and the efficient use of resources, ultimately contributing to the credibility and impact of research findings. It is a critical practice across disciplines to ensure data integrity and usability both during and after a research project.Big Data
big data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
refers to the collection and analyses of massive sets of data. While big data is a recent phenomenon, the requirement for data to aid decision-making traces back to the early 1970s with the emergence of decision support systems (DSS). These systems can be considered as the initial iteration of data management for decision support.
Financial and economic outcomes
Studies indicate that customer transactions account for a 40% increase in the data collected annually, which means that financial data has a considerable impact on business decisions. Therefore, modern organizations are using big data analytics to identify 5 to 10 new data sources that can help them collect and analyze data for improved decision-making. Jonsen (2013) explains that organizations using average analytics technologies are 20% more likely to gain higher returns compared to their competitors who have not introduced any analytics capabilities in their operations. Also, IRI reported that the retail industry could experience an increase of more than $10 billion each year resulting from the implementation of modern analytics technologies. Therefore, the following hypothesis can be proposed: Economic and financial outcomes can impact how organizations use data analytics tools.See also
* Open data * Data curation * Data retentionReferences
Further reading
* *External links
* * * * * {{Data