Darién scheme on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Darien scheme was an unsuccessful attempt, backed largely by investors of the
 In the face of opposition by English commercial interests, the Company of Scotland raised subscriptions in
In the face of opposition by English commercial interests, the Company of Scotland raised subscriptions in
 Close to the fort, the settlers began erecting the huts of the main settlement, New Edinburgh (until 2011 known as Puerto Escocés (''Scottish Harbour''), now Puerto Inabaginya, in
Close to the fort, the settlers began erecting the huts of the main settlement, New Edinburgh (until 2011 known as Puerto Escocés (''Scottish Harbour''), now Puerto Inabaginya, in
 Word of the first expedition did not reach Scotland in time to prevent a second voyage of more than 1000 people.
A new company flagship, ''The Rising Sun'', boasting 38 cannon, led the way, supported by ''The Duke of Hamilton'', the ''Hope of Bo'ness'', and a smaller vessel, the ''Hope''. They sailed from the Clyde, on the west of Scotland, cutting out the perilous round-Scotland route taken by the previous ships.Prebble, ''The Darien Disaster'', p. 238.
The expedition had the blessing of the Church of Scotland who had appointed
Word of the first expedition did not reach Scotland in time to prevent a second voyage of more than 1000 people.
A new company flagship, ''The Rising Sun'', boasting 38 cannon, led the way, supported by ''The Duke of Hamilton'', the ''Hope of Bo'ness'', and a smaller vessel, the ''Hope''. They sailed from the Clyde, on the west of Scotland, cutting out the perilous round-Scotland route taken by the previous ships.Prebble, ''The Darien Disaster'', p. 238.
The expedition had the blessing of the Church of Scotland who had appointed
The Darien Scheme
an article by Roger Moorhouse
The Darien Scheme – The Fall of Scotland
The Darien Chest
Pathfinder Pack on The Darien Scheme
Account, written in 1700, by a colonist
''
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
, to gain wealth and influence by establishing ''New Caledonia'', a colony on the Isthmus of Panama, in the late 1690s. The plan was for the colony, located on the Gulf of Darién, to establish and manage an overland route to connect the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The backers knew that the first sighting of the Pacific Ocean by Balboa was after crossing the isthmus through Darién.
The attempt at settling the area did not go well; more than 80% of participants died within a year, and the settlement was abandoned twice.Little, "The Caribbean colony ..."
There are many explanations for the disaster. Rival claims have been made suggesting that the undertaking was beset by poor planning and provisioning; by divided leadership; by a lack of demand for traded goods, owing to an English trade blockade; by devastating epidemics of tropical disease; by the successful collaboration between the English East India Company and the English government to frustrate it; and by a failure to anticipate the Spanish Empire's military response. It was finally abandoned in March 1700 after a siege by Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
forces, which also blockaded the harbour.
As the Company of Scotland was backed by approximately 20% of all the money circulating in Scotland, its failure left the entire Scottish Lowlands in financial ruin. This was an important factor in weakening their resistance to the Act of Union (completed in 1707). The land where the Darien colony was built is located in the modern territory of Guna Yala
Guna Yala, formerly known as San Blas, is a '' comarca indígena'' (indigenous province) in northeast Panama. Guna Yala is home to the indigenous people known as the Gunas. Its capital is Gaigirgordub. It is bounded on the north by the Car ...
, an autonomous indigenous territory home to the Guna people
The Guna, are an Indigenous people of Panama and Colombia. In the Guna language, they call themselves ''Dule'' or ''Tule'', meaning "people", and the name of the language is ''Dulegaya'', literally "people-mouth".
The term was in the language ...
.
The expedition also took sovereignty over 'Crab Isle' (modern day Vieques, Puerto Rico
Vieques (; ), officially Isla de Vieques, is an island and municipality of Puerto Rico, in the northeastern Caribbean, part of an island grouping sometimes known as the Spanish Virgin Islands. Vieques is part of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, ...
) in 1698, yet sovereignty was short-lived.
Origins
The late 17th century was a difficult period for Scotland, as it was for much of Europe; the years 1695-97 saw catastrophic famine in present-day Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Norway and Sweden, plus an estimated two million deaths in France and Northern Italy. The 1690s were Scotland's coldest decade in the past 750 years as documented in tree ring records. Scotland's economy was relatively small, its range of exports was limited, and it was in a weak position in relation to England, its powerful neighbour (with which it was in personal but not yetpolitical union
A political union is a type of political entity which is composed of, or created from, smaller polities, or the process which achieves this. These smaller polities are usually called federated states and federal territories in a federal govern ...
). In an era of economic rivalry in Europe, Scotland was incapable of protecting itself from the effects of English competition and legislation.Prebble, ''Darien: The Scottish Dream''. The kingdom had no reciprocal export trade and its once-thriving industries such as shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befo ...
were in deep decline; goods that were in demand had to be bought from England for sterling. Moreover, the Navigation Acts
The Navigation Acts, or more broadly the Acts of Trade and Navigation, were a long series of English laws that developed, promoted, and regulated English ships, shipping, trade, and commerce between other countries and with its own colonies. The ...
further increased economic dependence on England by limiting Scotland's shipping, and the Royal Scots Navy
The Royal Scots Navy (or Old Scots Navy) was the navy of the Kingdom of Scotland from its origins in the Middle Ages until its merger with the Kingdom of England's Royal Navy per the Acts of Union 1707. There are mentions in Medieval records of ...
was relatively small. Though the unusual cold affected much of the Northern Hemisphere, Scotland suffered disproportionately and lost 10-15% of its entire population, possibly due to its political isolation. A series of domestic conflicts, including the 1639-51 Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 B ...
and unrest related to religious differences between 1670-1690 exhausted the people and diminished their resources. The so-called "seven ill years
The Seven Ill Years, also known as the Seven Lean Years (), is the term used for a period of widespread and prolonged famine in Scotland during the 1690s, named after the Biblical famine in Egypt predicted by Joseph in the Book of Genesis
T ...
" of the 1690s saw widespread crop failures and famine, while Scotland's deteriorating economic position led to calls for a political or customs union with England. However, the stronger feeling among Scots was that the country should become a great mercantile and colonial power like England.
In response, several solutions were enacted by the Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council o ...
: in 1695
the Bank of Scotland
The Bank of Scotland plc (Scottish Gaelic: ''Banca na h-Alba'') is a commercial and clearing bank based in Scotland and is part of the Lloyds Banking Group, following the Bank of Scotland's implosion in 2008. The bank was established by th ...
was established; the Act for the Settling of Schools created a parish-based system of public education throughout Scotland; and the Company of Scotland was chartered with capital to be raised by public subscription to trade with "Africa and the Indies".Prebble, ''The Darien Disaster''.
 In the face of opposition by English commercial interests, the Company of Scotland raised subscriptions in
In the face of opposition by English commercial interests, the Company of Scotland raised subscriptions in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
, Hamburg and London for the scheme. For his part, King William II of Scotland and III of England had given only lukewarm support to the whole Scottish colonial endeavour. England was at war with France and hence did not want to offend Spain, which claimed the territory as part of New Granada.Insh, ''Papers'', p. x.
One reason for English opposition to the Scheme was the then prevalent economic theory of mercantilism, a concept as widespread and accepted then as capitalism is today. Modern economics generally assumes a constantly growing market but mercantilism viewed it as static; that meant increasing one's market share required taking it from someone else. This meant the Darien Scheme was not simply competition but an active threat to English merchants.
England was also under pressure from the London-based East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and South ...
, who were keen to maintain their monopoly over English foreign trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significant ...
. It therefore forced the English and Dutch investors to withdraw. Next, the East India Company threatened legal action on the grounds that the Scots had no authority from the king to raise funds outside the English realm, and obliged the promoters to refund subscriptions to the Hamburg investors. This left no source of finance but Scotland itself.
Returning to Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
, the Company of Scotland for Trading to Africa raised £400,000 sterling in a few weeks (equivalent to roughly £ today), with investments from every level of society, and totalling about a fifth of the wealth of Scotland.Carroll, "The Sorry Story ..." It was, for Scotland, a massive amount of capital.Prebble, ''Darien: The Scottish Dream'', p. 90.
Scottish-born trader and financier William Paterson had long promoted a plan for a colony on the Isthmus of Panama to be used as a gateway between the Atlantic and Pacific – the same principle which, much later, would lead to the construction of the Panama Railroad
The Panama Canal Railway ( es, Ferrocarril de Panamá) is a railway line linking the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean in Central America. The route stretches across the Isthmus of Panama from Colón (Atlantic) to Balboa (Pacific, near P ...
, and then the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
. Paterson was instrumental in getting the company off the ground in London. He had failed to interest several European countries in his project but, in the aftermath of the English reaction to the company, he was able to get a hearing for his ideas.
The Scots' original aim of emulating the East India Company by breaking into the lucrative trading areas of the Indies and Africa was forgotten, and the highly ambitious Darien scheme was adopted by the company. Paterson later fell from grace when a subordinate embezzled
Embezzlement is a crime that consists of withholding assets for the purpose of conversion of such assets, by one or more persons to whom the assets were entrusted, either to be held or to be used for specific purposes. Embezzlement is a type ...
funds from the company, took back Paterson's stock and expelled him from the Court of Directors; he was to have little real influence on events after this point.
First expedition (1698)
Many former officers and soldiers, who had little hope of other employment, eagerly joined the Darien project. Many of them were acquainted from serving in the army and several – Thomas Drummond, for example – were notorious for their involvement in theMassacre of Glencoe
The Massacre of Glencoe ( gd, Murt Ghlinne Comhann) took place in Glen Coe in the Highlands of Scotland
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Cultur ...
. In some eyes they appeared to be a clique
A clique ( AusE, CanE, or ), in the social sciences, is a group of individuals who interact with one another and share similar interests. Interacting with cliques is part of normative social development regardless of gender, ethnicity, or popular ...
, and this was to cause much suspicion among other members of the expedition. The first Council (appointed in July 1698), which was to govern the colony until a parliament was established, consisted of Major James Cunningham of Eickett, Daniel Mackay, James Montgomerie, William Vetch, Robert Jolly, Robert Pinkerton and Captain Robert Pennecuik (commodore of the expedition fleet).
The first expedition of five ships (''Saint Andrew'', ''Caledonia'', ''Unicorn'', ''Dolphin'', and ''Endeavour'') set sail from the east coast port of Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by ''Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
to avoid observation by English warships in July 1698, with around 1200 people on board. The journey around Scotland for those kept below deck was so traumatic that some colonists thought it comparable to the worst parts of the whole Darien experience. Their orders were "to proceed to the Bay of Darien, and make the Isle called the Golden Island ... some few leagues to the leeward of the mouth of the great River of Darien ... and there make a settlement on the mainland". The fleet called at Madeira and the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, and took possession of Crab Isle which would be taken over by the Danish after the failure of the colony. The fleet made landfall off the coast of Darien on 2 November.
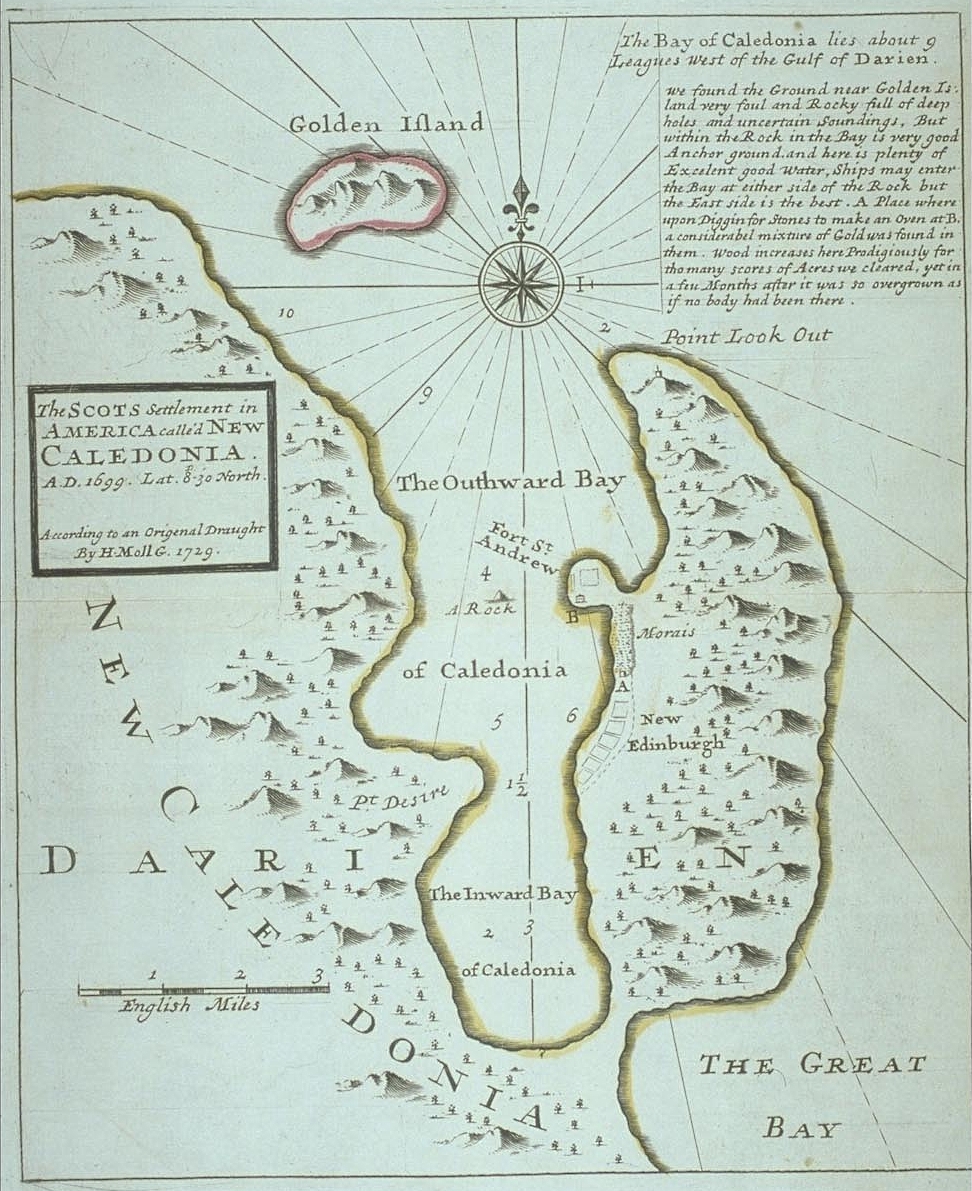
The settlers christened their new home "Caledonia" declaring "we do here settle and in the name of God establish ourselves; and in honour and for the memory of that most ancient and renowned name of our Mother Country, we do, and will from henceforward call this country by the name of Caledonia; and ourselves, successors, and associates, by the name of Caledonians". With Drummond in charge, they dug a ditch
A ditch is a small to moderate divot created to channel water. A ditch can be used for drainage, to drain water from low-lying areas, alongside roadways or fields, or to channel water from a more distant source for plant irrigation. Ditches ar ...
through the neck of land that divided one side of the harbour in Caledonia Bay from the ocean, and constructed Fort St Andrew, which was equipped with 50 cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
, but no source of fresh water. A BBC report in 2014 identified this ditch as the only identifiable remnant of Caledonia. A watchhouse on a mountain completed the fortifications. Although the harbour appeared to be a natural one, it later proved to have tides that could easily wreck a vessel trying to leave. The colony was a potential threat to the Spanish Empire by being located near routes used for silver shipments. The feasibility of the scheme, especially for a country of Scotland's limited resources, has often been considered doubtful, although some modern authorities consider that it might have possessed good prospects of success if it had been given the support of England.
The chosen site is indeed only 80km from the Pacific Ocean, but it is a highly inhospitable 80km.
New Edinburgh
 Close to the fort, the settlers began erecting the huts of the main settlement, New Edinburgh (until 2011 known as Puerto Escocés (''Scottish Harbour''), now Puerto Inabaginya, in
Close to the fort, the settlers began erecting the huts of the main settlement, New Edinburgh (until 2011 known as Puerto Escocés (''Scottish Harbour''), now Puerto Inabaginya, in Guna Yala
Guna Yala, formerly known as San Blas, is a '' comarca indígena'' (indigenous province) in northeast Panama. Guna Yala is home to the indigenous people known as the Gunas. Its capital is Gaigirgordub. It is bounded on the north by the Car ...
Province, Panama), and clearing land to plant yams and maize. Letters sent home by the expedition created a misleading impression that everything was going according to plan. This seems to have been by agreement, as certain optimistic phrases kept recurring. However, it meant the Scottish public would be completely unprepared for the coming disaster.
Agriculture proved difficult and the natives, though hostile to Spain, were unwilling to trade for the combs and other trinkets offered by the colonists. Most serious was the near-total failure to sell any goods to the few passing traders who put into the bay. With the onset of summer the following year, malaria and fever led to many deaths. Eventually, the mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
rose to ten settlers a day. Natives brought gifts of fruit and plantains
Plantain may refer to:
Plants and fruits
* Cooking banana, banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking
** True plantains, a group of cultivars of the genus ''Musa''
* ''Plantaginaceae'', a family of flowerin ...
, but these were appropriated by the leaders and sailors, who mostly remained on board ships. The only luck the settlers had was in giant turtle hunting, but fewer and fewer men were fit enough for such strenuous work. The situation was exacerbated by the lack of food, mainly due to a high rate of spoilage caused by improper stowing. At the same time, King William instructed the Dutch and English colonies in America not to supply the Scots' settlement, so as not to incur the wrath of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
. The only reward the council had to give was alcohol, and drunkenness became common, even though it sped the deaths of men already weakened by dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
, fever and the rotting, worm-infested food.
After just eight months, the colony was abandoned in July 1699, except for six men who were too weak to move. The deaths continued on the ships, and only 300 of the 1200 settlers survived. A desperate ship from the colony had called in at the Jamaican city of Port Royal, but it was refused assistance on the orders of the English government, who feared antagonising the Spanish. Those on the single ship that returned home found themselves regarded as a disgrace to their country, and were even disowned by their families. The ''Caledonia'', with 250 survivors, including William Paterson and the Drummond brothers, made a desperate passage to New York, then just a small town of 5000, landing on 10 August. Four days later, ''Unicorn'' (commanded by Captain John Anderson) limped into New York harbour. In a letter to Hugh Montgomerie, a Glasgow merchant, Robert Drummond reported that sickness and mortality continued to afflict the remnant of the colonists. When the Scots were told that two ships, the ''Olive Branch'' and ''Hopeful Beginning'', had already sailed to re-supply the now deserted colony, Thomas Drummond commissioned two sloops
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular ...
to aid their efforts in Darien.Prebble, ''The Darien Disaster'', pp. 206–207 & 220.
Re-supply (1699)
In August 1699, the ''Olive Branch'' and ''Hopeful Beginning'' with 300 settlers arrived in Darien to find ruined huts and 400 overgrown graves. Expecting a bustling town, the ship's captains debated their next move. When the ''Olive Branch'' was destroyed by an accidental fire, the survivors fled to Jamaica in the ''Hopeful Beginning'', and landed in Port Royal harbour. The Scots were not allowed ashore, and illness struck the crowded ship. On 20 September, Thomas E. Drummond set sail from New York in the sloop ''Ann of Caledonia'', (formerly the ''Anne''), picking up another fully supplied vessel (the ''Society'') on the way. They arrived in Darien to find the burnt timbers of the ''Olive Branch'' rotting on the shore.Second expedition (1699)
 Word of the first expedition did not reach Scotland in time to prevent a second voyage of more than 1000 people.
A new company flagship, ''The Rising Sun'', boasting 38 cannon, led the way, supported by ''The Duke of Hamilton'', the ''Hope of Bo'ness'', and a smaller vessel, the ''Hope''. They sailed from the Clyde, on the west of Scotland, cutting out the perilous round-Scotland route taken by the previous ships.Prebble, ''The Darien Disaster'', p. 238.
The expedition had the blessing of the Church of Scotland who had appointed
Word of the first expedition did not reach Scotland in time to prevent a second voyage of more than 1000 people.
A new company flagship, ''The Rising Sun'', boasting 38 cannon, led the way, supported by ''The Duke of Hamilton'', the ''Hope of Bo'ness'', and a smaller vessel, the ''Hope''. They sailed from the Clyde, on the west of Scotland, cutting out the perilous round-Scotland route taken by the previous ships.Prebble, ''The Darien Disaster'', p. 238.
The expedition had the blessing of the Church of Scotland who had appointed Alexander Shields
Alexander Shields or Sheilds or Sheills (January 1661 – 1700) was a Scottish, Presbyterian, nonconformist minister, activist, and author. He was imprisoned in London, in Edinburgh and on the Bass Rock for holding private worship services. A ...
as the senior of the 4 ministers (including Archibald Stobo and Francis Borland).
The second expedition arrived in Caledonia Bay on 30 November 1699 and found Thomas Drummond's New York sloops already there. Some men were sent ashore to rebuild the huts, which caused others to complain that they had come to join a settlement, not build one.Prebble, ''Darien: The Scottish Dream''
Morale was low and little progress was made. Drummond insisted there could be no discussion, and the fort must be rebuilt as a Spanish attack would surely come soon.
Drummond clashed with the merchant James Byres, who maintained that the Counsellors of the first expedition had now lost that status and had Drummond arrested. Initially bellicose, Byres began to send away all those he suspected of being offensively minded – or of being allegiant to Drummond. He outraged a kirk
Kirk is a Scottish and former Northern English word meaning "church". It is often used specifically of the Church of Scotland. Many place names and personal names are also derived from it.
Basic meaning and etymology
As a common noun, ''kirk' ...
minister by claiming it would be unlawful to resist the Spanish by force of arms, as all war was unchristian. Byres then deserted the colony in a sloop.
The colonists sank into apathy until the arrival of Alexander Campbell of Fonab, sent by the company to organise a defence. He provided the resolute leadership which had been lacking and took the initiative by driving the Spanish from their stockade at Toubacanti in January 1700. However, Fonab was wounded in the daring frontal attack and then became incapacitated with a fever.
The Spanish force – who were also suffering serious losses from fever – closed in on Fort St Andrew and besieged it for a month. Disease was still the main cause of death at this time. The Spanish commander called for the Scots to surrender and avoid a final assault, warning that if they did not, no quarter
The phrase no quarter was generally used during military conflict to imply combatants would not be taken prisoner, but killed.
According to some modern American dictionaries, a person who is given no quarter is "not treated kindly" or "treated ...
would be given.
After negotiations, the Scots were allowed to leave with their guns, and the colony was abandoned for the last time. Only a handful of those from the second expedition returned to Scotland. Of the total 2500 settlers that set off, just a few hundred survived.Little, "The Caribbean colony ..."
Reactions to the disaster
The failure of the colonisation project provoked tremendous discontent throughout Lowland Scotland, where almost every family had been affected. Some held the English responsible, and others believed that they could and should assist in yet another effort at making the scheme work. The company petitioned the king to affirm their right to the colony. However, he declined, saying that although he was sorry the company had incurred such huge losses, reclaiming Darien would mean war with Spain. The continuing futile debate on the issue served to further increase bitter feelings. An estimated 15-40% of all the actual capital in Scotland was invested in this project. Hoping to recoup some of its capital by a more conventional venture, the company sent two ships from the Clyde, the ''Speedy Return'' and the ''Continent'', to the Guinea coast laden with trade goods. Sea captain Robert Drummond was the master of the ''Speedy Return''; his brother Thomas, who had played such a large part in the second expedition, wassupercargo
A supercargo (from Spanish ''sobrecargo'') is a person employed on board a vessel by the owner of cargo carried on the ship. The duties of a supercargo are defined by admiralty law and include managing the cargo owner's trade, selling the merchand ...
on the vessel. Instead of trying to sell for gold as the company's directors intended, however, the Drummond brothers had exchanged the goods for slaves, whom they sold in Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
. Carousing with the buccaneer
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from the Restoration in 1660 until about 168 ...
s for whom the island was a refuge, the Drummonds fell in with pirate John Bowen, who offered them loot if they would lend him their ships for a raid on homeward bound Indiamen.
Drummond backed out of the agreement, only to have Bowen appropriate the ships while Drummond was ashore. Bowen burnt the ''Continent'' on the Malabar coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
when he decided she was of no use to him, and he later scuttled the ''Speedy Return'' after transferring her crew to a merchant ship that he had taken. The Drummonds apparently decided against returning to Scotland, where they would have had to explain the loss of the ships they had been entrusted with, and no more was ever heard of them.
The company sent out another ship, but she was lost at sea. Unable to afford the cost of fitting out yet another vessel, the company hired the ''Annandale'' in London to trade in the Spice Islands. However, the East India Company had the ship seized on the grounds that it was in contravention of their charter. That provoked an uproar in Scotland, greatly aided by the inflammatory rhetoric of the company's secretary, Roderick MacKenzie, a relentless enemy of the English. Fury at the country's impotence led to the scapegoating and hanging of three innocent English sailors.Prebble, ''Darien: The Scottish Dream'', pp. 1–9 & 308–315.
Hangings
In July 1704, Thomas Green, the 25-year-oldmaster
Master or masters may refer to:
Ranks or titles
* Ascended master, a term used in the Theosophical religious tradition to refer to spiritually enlightened beings who in past incarnations were ordinary humans
*Grandmaster (chess), National Master ...
of the ''Worcester'', an English merchant ship, arrived at Leith
Leith (; gd, Lìte) is a port area in the north of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, founded at the mouth of the Water of Leith. In 2021, it was ranked by ''Time Out'' as one of the top five neighbourhoods to live in the world.
The earliest ...
. Mackenzie convinced himself that the ship was an East India Company ship that should be seized in reprisal for the ''Annandale''. He succeeded in getting legal authority and Green, who had been given the command at 21, watched as his ship's cargo was impounded and the sails, guns and rudder were removed over the next three months.
In December, the crew was arrested for piracy. Although many in Scotland were delighted, it soon became clear to the directors of the Darien company that Mackenzie's charges were not supported by any proof, and it seemed the men would be released. However, Mackenzie suddenly claimed to have ascertained from the crew of the ''Worcester'' that Green had drunkenly boasted of taking the ''Speedy Return'', killing the Drummonds and burning the ship. Green and two of his crew, John Madden and James Simpson, were sent for trial in Edinburgh. Mackenzie produced several witnesses including members of Green's crew; their statements contradicted one another and none of them could accurately describe the dates, locations, or descriptions of the supposed victims of the ''Worcester''. The prosecution case, which was made in medieval Latin and legal Doric, was unintelligible to jury and accused alike. The defence advocates' objections were dismissed by court officials and they fled after the trial. Some jurors resisted bringing in a verdict of guilty, but the men were convicted and sentenced to death by hanging.
The Queen advised her 30 privy councillors in Edinburgh that the men should be pardoned, but the common people demanded for the sentence to be carried out. Nineteen councillors made excuses to stay away from the deliberations on a reprieve, fearing the wrath of a huge mob that had arrived in Edinburgh to demand the sailors be put to death. Even though they had affidavits from London by two of the crew of the ''Speedy Return'', who testified that Green and his crew had no knowledge or involvement in the fate of the ship, the remaining councillors refused to pardon the men.
Green, Madden and Simpson were subjected to derision and insults by the mob before they were hanged. Green had complete faith that as an innocent man, he would be reprieved, and he was still looking to the Edinburgh road for a messenger as the hangman placed the hood over his head. The remainder of Green's crew were quietly pardoned and released.
Consequences of failure
The failure of the Darien colonisation project has been cited as one of the motivations for the 1707 Acts of Union. According to this argument, the Scottish establishment (landed aristocracy and mercantile elites) considered that their best chance of being part of a major power would be to share the benefits of England's international trade and the growth of the English overseas possessions and so its future would have to lie in unity with England. Furthermore, Scotland's nobles were almost bankrupted by the Darien fiasco. Some Scottish nobility petitioned Westminster to wipe out the Scottish national debt and stabilise the currency. Although the first request was not met, the second was, and the Scottish shilling was given the fixed value of an English penny. Personal Scottish financial interests were also involved. Scottish commissioners had invested heavily in the Darien project and believed that they would receive compensation for their losses. The 1707 Acts of Union, Article 15, granted £398,085 10s sterling to Scotland to offset future liability towards the English national debt. This amount equates to about £100,000,000 in 2020 money.In popular culture
Novels
* ''The Rising Sun'' by Douglas Galbraith (2000). Fictional account of the Darien catastrophe, written in the style of a journal, from the perspective of a cargo-master on the ''Rising Sun''. *''Siphonophore'' by Jaimie Batchan (2021). Begins as the account of a settler from the Darien scheme who has been left behind when the surviving members of the colony return to Scotland.Stage plays
* ''Caledonia'' byAlistair Beaton
Alistair Beaton (born 1947) is a playwright and satirist, journalist, radio presenter, novelist and television writer. At one point in his career he was also a speechwriter for Gordon Brown.
Born in Glasgow, Scotland, Beaton was educated at the ...
(2010). A satire about the Royal Bank of Scotland and the Scottish colonial ambitions of the late 17th century.
* "Darien, a commonplace book of Murdo Macfarlane" by Richard Robb (2019). A musical about the Scottish attempt to settle the Darien gap imagined through the eyes of one settler Murdo Macfarlane. Presented by Bell Baxter high school.
Music
* "Dreams of Darien" by The Paul McKenna Band (2011). A Scottish folk song describing the events of the Darien Scheme and the reaction in Scotland. * The Darien Venture, a math-pop band from Glasgow, Scotland, who were active from 2008-2013. * "Darien" by Stanley Accrington, Manchester-based folk singer/songwriter (1986) included on his CD Semi Final Second Leg.Games
* ''Darien Apocalypse'', a 2018 Euro-style boardgame from British producer Ragnar Brothers where players cooperatively or competitively strive to develop the Darien trading colony and either help or hinder each other as much as possible against the depredations the original settlers faced.Installations
* ''Astro-Darien'' byKode9
Steve Goodman, known as Kode9 (born 1973) is a Scottish electronic music artist, DJ, and founder of the Hyperdub record label. He was one of the founding members of the early dubstep scene with his late collaborator The Spaceape. He has releas ...
and Lawrence Lek. An audiovisual installation that takes inspiration from the Darien Scheme, space races, and simulation games. Displayed at Corsica Studios, London in 2021.
See also
* Lionel Wafer *Gregor MacGregor
General Gregor MacGregor (24 December 1786 – 4 December 1845) was a Scottish soldier, adventurer, and confidence trickster who attempted from 1821 to 1837 to draw British and French investors and settlers to "Poyais", a fictional Central Am ...
* the Marquis de Rays
Other Scottish settlements in the Americas:
* Darien, Georgia
Darien () is a city in and the county seat of McIntosh County, Georgia, United States. It lies on Georgia's coast at the mouth of the Altamaha River, approximately south of Savannah, and is part of the Brunswick, Georgia Metropolitan Statisti ...
* Perth Amboy, New Jersey
Perth Amboy is a city in Middlesex County, New Jersey. Perth Amboy is part of the New York metropolitan area. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the city's population was 55,436. Perth Amboy has a Hispanic majority population. In the 2010 census, th ...
* Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * (fictionalisation) * * * Orr, Julie (2018), ''Scotland, Darien and the Atlantic World, 1698 - 1700'', Edinburgh University Press, *External links
The Darien Scheme
an article by Roger Moorhouse
The Darien Scheme – The Fall of Scotland
The Darien Chest
Pathfinder Pack on The Darien Scheme
Account, written in 1700, by a colonist
''
Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Ni ...
'' article regarding ''Caledonia'', a play by Alistair Beaton
Alistair Beaton (born 1947) is a playwright and satirist, journalist, radio presenter, novelist and television writer. At one point in his career he was also a speechwriter for Gordon Brown.
Born in Glasgow, Scotland, Beaton was educated at the ...
about the Darien scheme
{{DEFAULTSORT:Darien Scheme
Former Scottish colonies
1690s in Scotland
History of Panama
Political scandals in Scotland
17th century in Scotland
Settlement schemes
Former populated places in Panama
Former populated places in Central America
1690s in Central America
17th century in Central America
States and territories disestablished in the 1700s
1698 establishments in Scotland
1700 disestablishments in Scotland
1700s disestablishments in North America
Trading companies of Scotland