DM Geminorum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 DM Geminorum also known as Nova Geminorum 1903 was a
DM Geminorum also known as Nova Geminorum 1903 was a
 DM Geminorum also known as Nova Geminorum 1903 was a
DM Geminorum also known as Nova Geminorum 1903 was a nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
which erupted in the constellation Gemini
Gemini may refer to:
Space
* Gemini (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
** Gemini in Chinese astronomy
* Project Gemini, the second U.S. crewed spaceflight program
* Gemini Observatory, consisting of telescopes in the Northern ...
in 1903. It was discovered by Herbert Hall Turner
Herbert Hall Turner (13 August 1861 – 20 August 1930) was a British astronomer and seismologist.
Biography
Herbert Hall Turner was educated at the Leeds Modern School, Clifton College, Bristol and Trinity College, Cambridge. In 1884 h ...
at the Greenwich Observatory
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich (ROG; known as the Old Royal Observatory from 1957 to 1998, when the working Royal Greenwich Observatory, RGO, temporarily moved south from Greenwich to Herstmonceux) is an observatory situated on a hill in ...
on a Carte du Ciel
The Carte du Ciel (literally, 'Map of the Sky') and the Astrographic Catalogue (or Astrographic Chart) were two distinct but connected components of a massive international astronomical project, initiated in the late 19th century, to catalogue an ...
photographic plate
Photographic plates preceded photographic film as a capture medium in photography, and were still used in some communities up until the late 20th century. The light-sensitive emulsion of silver salts was coated on a glass plate, typically thinn ...
taken on 16 March 1903. Post-discovery examination of earlier photographs of the region taken at the Harvard College Observatory
The Harvard College Observatory (HCO) is an institution managing a complex of buildings and multiple instruments used for astronomical research by the Harvard University Department of Astronomy. It is located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United St ...
showed that the star was fainter than apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
9 on 2 March 1903, and magnitude 5.1 on 6 March 1903, making it visible to the naked eye at that time. It had a conspicuous red color due to strong Hα
H-alpha (Hα) is a specific deep-red visible spectral line in the Balmer series with a wavelength of 656.28 nm in air and 656.46 nm in vacuum; it occurs when a hydrogen electron falls from its third to second lowest energy level. H-alpha ...
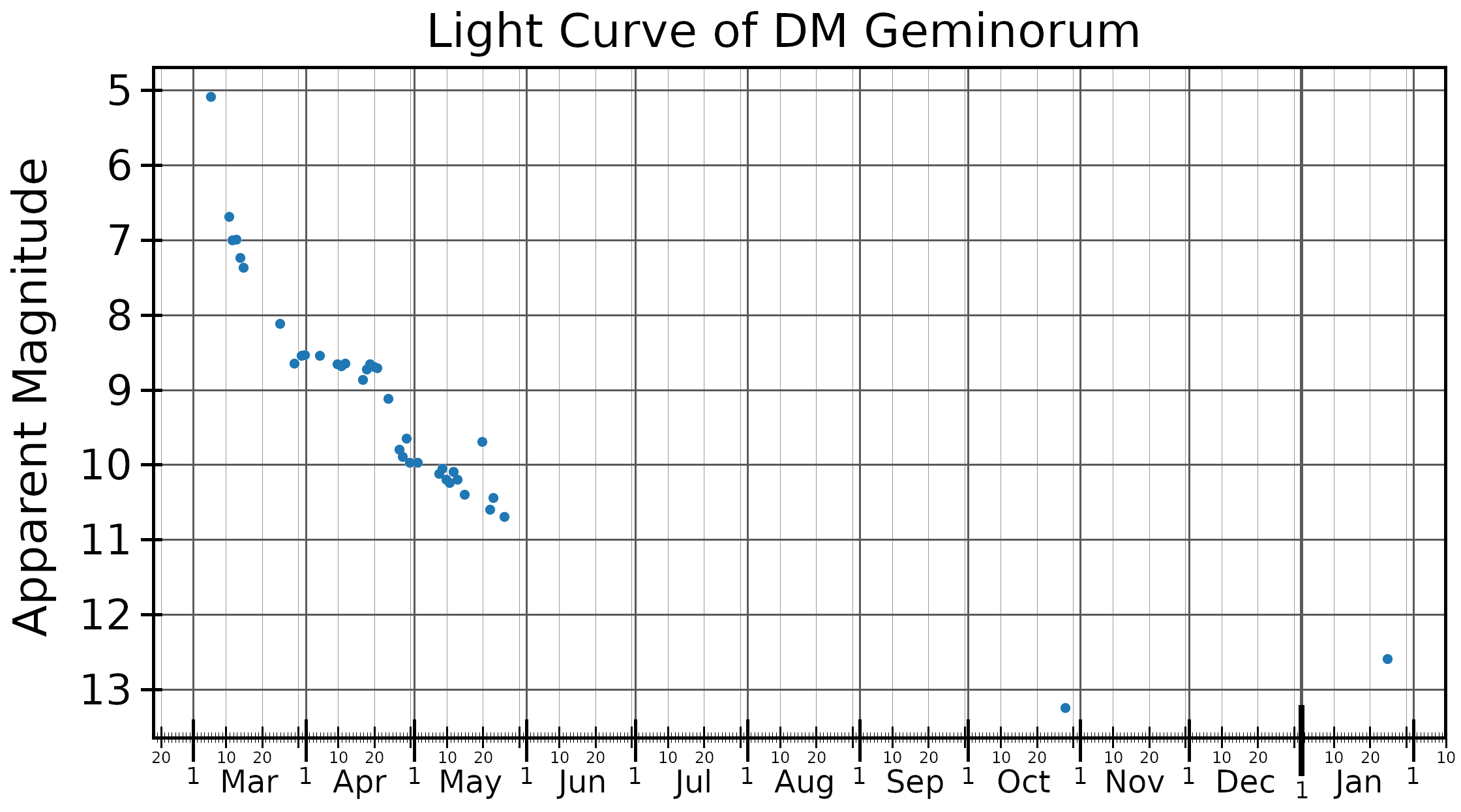
line emission. By 1 April 1903 it had faded to magnitude 8.5. By 1989 it had reached visual magnitude 17.38.
DM Geminorum faded from peak brightness by 2 magnitudes in just 6 days, making it a "very fast nova".
All novae are binary stars, with a "donor" star orbiting a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes fro ...
. The two stars are so close together that matter is transferred from the donor to the white dwarf. High speed photometry Photometry can refer to:
* Photometry (optics), the science of measurement of visible light in terms of its perceived brightness to human vision
* Photometry (astronomy), the measurement of the flux or intensity of an astronomical object's electrom ...
done with the 1.2 meter telescope at the Whipple Observatory show a small amplitude (0.25 magnitude peak-to-peak) oscillation with a period of 2 hours and 57 minutes, which is probably the orbital period of the binary system. In addition, brightness variations with a period of 22 minutes are also seen in this star's light curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequ ...
. The star's spectrum and brightness variations are similar to what is seen in intermediate polars
In astronomy, an intermediate polar (also called a DQ Herculis Star) is a type of cataclysmic variable, binary star system with a white dwarf and a cool main-sequence secondary star. In most cataclysmic variables, matter from the companion star ...
.
References
Novae Gemini (constellation) 1903 in science Geminorum, DM 048328 {{var-star-stub