D-Glucose on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Glucose is a simple
 Glucose is usually present in solid form as a
Glucose is usually present in solid form as a
 The other open-chain isomer -glucose similarly gives rise to four distinct cyclic forms of -glucose, each the mirror image of the corresponding -glucose.
The glucopyranose ring (α or β) can assume several non-planar shapes, analogous to the "chair" and "boat" conformations of
The other open-chain isomer -glucose similarly gives rise to four distinct cyclic forms of -glucose, each the mirror image of the corresponding -glucose.
The glucopyranose ring (α or β) can assume several non-planar shapes, analogous to the "chair" and "boat" conformations of
 Mutarotation consists of a temporary reversal of the ring-forming reaction, resulting in the open-chain form, followed by a reforming of the ring. The ring closure step may use a different group than the one recreated by the opening step (thus switching between pyranose and furanose forms), or the new hemiacetal group created on C-1 may have the same or opposite handedness as the original one (thus switching between the α and β forms). Thus, though the open-chain form is barely detectable in solution, it is an essential component of the equilibrium.
The open-chain form is thermodynamically unstable, and it spontaneously
Mutarotation consists of a temporary reversal of the ring-forming reaction, resulting in the open-chain form, followed by a reforming of the ring. The ring closure step may use a different group than the one recreated by the opening step (thus switching between pyranose and furanose forms), or the new hemiacetal group created on C-1 may have the same or opposite handedness as the original one (thus switching between the α and β forms). Thus, though the open-chain form is barely detectable in solution, it is an essential component of the equilibrium.
The open-chain form is thermodynamically unstable, and it spontaneously
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
with the molecular formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ...
. Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek ''monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
They are usually colorless, water-solub ...
, a subcategory of carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
s. Glucose is mainly made by plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
and most algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
during photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
in cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mech ...
s, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world.
In energy metabolism
Bioenergetics is a field in biochemistry and cell biology that concerns energy flow through living systems. This is an active area of biological research that includes the study of the transformation of energy in living organisms and the study of ...
, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
s. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
, in plants mainly as starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
and amylopectin Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose.
Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amylopl ...
, and in animals as glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. Glucose is naturally occurring and is found in its free state in fruits and other parts of plants. In animals, glucose is released from the breakdown of glycogen in a process known as glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanism
The ...
.
Glucose, as intravenous sugar solution
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
, is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health ...
. It is also on the list in combination with sodium chloride.
The name glucose is derived from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
(, "wine, must"), from (, "sweet"). The suffix "-ose
The suffix -ose ( or ) is used in biochemistry to form the names of sugars. This Latin suffix means "full of", "abounding in", "given to", or "like". Numerous systems exist to name specific sugars more descriptively.
Monosaccharides, the simplest ...
" is a chemical classifier, denoting a sugar.
History
Glucose was first isolated fromraisin
A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the d ...
s in 1747 by the German chemist Andreas Marggraf. Glucose was discovered in grapes by another German chemistJohann Tobias Lowitz
Johann Tobias Lowitz (russian: Товий Егорович Ловиц 25 April 1757 – 7 December 1804) was a German-Russian chemist and pharmacist. He was among the first to notice the clarification of liquids by the use of charcoal for adsorpti ...
in 1792, and distinguished as being different from cane sugar (sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
). Glucose is the term coined by Jean Baptiste Dumas
Jean Baptiste André Dumas (14 July 180010 April 1884) was a French chemist, best known for his works on organic analysis and synthesis, as well as the determination of atomic weights (relative atomic masses) and molecular weights by measuring v ...
in 1838, which has prevailed in the chemical literature. Friedrich August Kekulé Friedrich may refer to:
Names
* Friedrich (surname), people with the surname ''Friedrich''
* Friedrich (given name), people with the given name ''Friedrich''
Other
* Friedrich (board game), a board game about Frederick the Great and the Seven Year ...
proposed the term dextrose (from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, meaning "right"), because in aqueous solution of glucose, the plane of linearly polarized light is turned to the right. In contrast, -fructose (a ketohexose) and -glucose turn linearly polarized light to the left. The earlier notation according to the rotation of the plane of linearly polarized light (''d'' and ''l''-nomenclature) was later abandoned in favor of the - and -notation, which refers to the absolute configuration of the asymmetric center farthest from the carbonyl group, and in concordance with the configuration of - or -glyceraldehyde.John F. Robyt: ''Essentials of Carbohydrate Chemistry.'' Springer Science & Business Media, 2012, . p. 7.
Since glucose is a basic necessity of many organisms, a correct understanding of its chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
makeup and structure contributed greatly to a general advancement in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; ...
. This understanding occurred largely as a result of the investigations of Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fischer projection, a symbolic way of dra ...
, a German chemist who received the 1902 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
for his findings. The synthesis of glucose established the structure of organic material and consequently formed the first definitive validation of Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff's theories of chemical kinetics and the arrangements of chemical bonds in carbon-bearing molecules. Between 1891 and 1894, Fischer established the stereochemical configuration of all the known sugars and correctly predicted the possible isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Iso ...
s, applying Van 't Hoff's theory of asymmetrical carbon atoms. The names initially referred to the natural substances. Their enantiomers were given the same name with the introduction of systematic nomenclatures, taking into account absolute stereochemistry (e.g. Fischer nomenclature, / nomenclature).
For the discovery of the metabolism of glucose Otto Meyerhof
Otto Fritz Meyerhof (; April 12, 1884 – October 6, 1951) was a German physician and biochemist who won the 1922 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine.
Biography
Otto Fritz Meyerhof was born in Hannover, at Theaterplatz 16A (now:Rathenaustrasse ...
received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
in 1922. Hans von Euler-Chelpin
Hans Karl August Simon von Euler-Chelpin (15 February 1873 – 6 November 1964) was a German-born Swedish biochemist. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1929 with Arthur Harden for their investigations on the fermentation of sugar and enz ...
was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry along with Arthur Harden
Sir Arthur Harden, FRS (12 October 1865 – 17 June 1940) was a British biochemist. He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1929 with Hans Karl August Simon von Euler-Chelpin for their investigations into the fermentation of sugar and ferment ...
in 1929 for their "research on the fermentation of sugar and their share of enzymes in this process". In 1947, Bernardo Houssay
Bernardo Alberto Houssay (April 10, 1887 – September 21, 1971) was an Argentine physiologist. Houssay was a co-recipient of the 1947 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for discovering the role played by pituitary hormones in regulating th ...
(for his discovery of the role of the pituitary gland in the metabolism of glucose and the derived carbohydrates) as well as Carl Carl may refer to:
*Carl, Georgia, city in USA
*Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
* Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name
*Carl², a TV series
* "Carl", an episode of te ...
and Gerty Cori
Gerty Theresa Cori (; August 15, 1896 – October 26, 1957) was an Austro-Hungarian and American biochemist who in 1947 was the third woman to win a Nobel Prize in science, and the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Me ...
(for their discovery of the conversion of glycogen from glucose) received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. In 1970, Luis Leloir
Luis Federico Leloir (September 6, 1906 – December 2, 1987) was an Argentine physician and biochemist who received the 1970 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his discovery of the metabolic pathways in lactose. Although born in France, Leloir r ...
was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of glucose-derived sugar nucleotides in the biosynthesis of carbohydrates.
Chemical and physical properties
Glucose forms white or colorless solids that are highlysoluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
in water and acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
but poorly soluble in methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl ...
. They melt at (''α'') and (''β''), and decompose
Decomposition or rot is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ...
starting at with release of various volatile products, ultimately leaving a residue of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
.Wenyue Kang and Zhijun Zhang (2020): "Selective Production of Acetic Acid via Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Hexoses over Potassium Salts", ''Catalysts'', volume 10, pages 502-515. Glucose has a pK value of 12.16 at in water.
With six carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
, a subcategory of the monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek ''monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
They are usually colorless, water-solub ...
s. -Glucose is one of the sixteen aldohexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
stereoisomer
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in ...
s. The -isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Iso ...
, -glucose, also known as ''dextrose'', occurs widely in nature, but the -isomer, -glucose, does not. Glucose can be obtained by hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of carbohydrates such as milk sugar (lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix '' - ...
), cane sugar (sucrose), maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two- ...
, cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
, etc. Dextrose is commonly commercially manufactured from cornstarch in the US and Japan, from potato and wheat starch in Europe, and from tapioca starch
Tapioca (; ) is a starch extracted from the storage roots of the cassava plant (''Manihot esculenta,'' also known as manioc), a species native to the North and Northeast regions of Brazil, but whose use is now spread throughout South America. ...
in tropical areas. The manufacturing process uses hydrolysis via pressurized steaming at controlled pH in a jet followed by further enzymatic depolymerization. Unbonded glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
.
Structure and nomenclature
 Glucose is usually present in solid form as a
Glucose is usually present in solid form as a monohydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was underst ...
with a closed pyran
In chemistry, pyran, or oxine, is a six-membered heterocyclic, non-aromatic ring, consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom and containing two double bonds. The molecular formula is C5H6O. There are two isomers of pyran that differ by the ...
ring (dextrose hydrate). In aqueous solution, on the other hand, it is an open-chain to a small extent and is present predominantly as α- or β-pyranose Pyranose is a collective term for saccharides that have a chemical structure that includes a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. There may be other carbons external to the ring. The name derives from its similarity ...
, which interconvert. From aqueous solutions, the three known forms can be crystallized: α-glucopyranose, β-glucopyranose and β-glucopyranose hydrate. Glucose is a building block of the disaccharides lactose and sucrose (cane or beet sugar), of oligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (/ˌɑlɪgoʊˈsækəˌɹaɪd/; from the Greek ὀλίγος ''olígos'', "a few", and σάκχαρ ''sácchar'', "sugar") is a saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically two to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sugar ...
s such as raffinose
Raffinose is a trisaccharide composed of galactose, glucose, and fructose. It can be found in beans, cabbage, brussels sprouts, broccoli, asparagus, other vegetables, and whole grains. Raffinose can be hydrolyzed to D-galactose and sucrose by ...
and of polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
s such as starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
, amylopectin Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose.
Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amylopl ...
, glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
, and cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
. The glass transition temperature
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubb ...
of glucose is and the Gordon–Taylor constant (an experimentally determined constant for the prediction of the glass transition temperature for different mass fractions of a mixture of two substances) is 4.5.Benjamin Caballero, Paul Finglas, Fidel Toldrá: ''Encyclopedia of Food and Health''. Academic Press (2016). , Volume 1, p. 76.
Open-chain form
The open-chain form of glucose makes up less than 0.02% of the glucose molecules in an aqueous solution. The rest is one of two cyclic hemiacetal forms. In itsopen-chain
In chemistry, an open-chain compound (also spelled as open chain compound) or acyclic compound (Greek prefix "α", ''without'' and "κύκλος", ''cycle'') is a compound with a linear structure, rather than a cyclic one.
An open-chain compound h ...
form, the glucose molecule has an open (as opposed to cyclic
Cycle, cycles, or cyclic may refer to:
Anthropology and social sciences
* Cyclic history, a theory of history
* Cyclical theory, a theory of American political history associated with Arthur Schlesinger, Sr.
* Social cycle, various cycles in soc ...
) unbranched backbone of six carbon atoms, where C-1 is part of an aldehyde group
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group ...
. Therefore, glucose is also classified as an aldose
An aldose is a monosaccharide (a simple sugar) with a carbon backbone chain with a carbonyl group on the endmost carbon atom, making it an aldehyde, and hydroxyl groups connected to all the other carbon atoms. Aldoses can be distinguished from keto ...
, or an aldohexose
In chemistry, a hexose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with six carbon atoms. The chemical formula for all hexoses is C6H12O6, and their molecular weight is 180.156 g/mol.
Hexoses exist in two forms, open-chain or cyclic, that easily convert ...
. The aldehyde group makes glucose a reducing sugar
A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent. In an alkaline solution, a reducing sugar forms some aldehyde or ketone, which allows it to act as a reducing agent, for example in Benedict's reagent. In such a react ...
giving a positive reaction with the Fehling test
In organic chemistry, Fehling's solution is a chemical reagent used to differentiate between water-soluble carbohydrate and ketone () functional groups, and as a test for reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars, supplementary to the Tollens' r ...
.
Cyclic forms
In solutions, the open-chain form of glucose (either "-" or "-") exists in equilibrium with several cyclic isomers, each containing a ring of carbons closed by one oxygen atom. In aqueous solution, however, more than 99% of glucose molecules exist aspyranose Pyranose is a collective term for saccharides that have a chemical structure that includes a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. There may be other carbons external to the ring. The name derives from its similarity ...
forms. The open-chain form is limited to about 0.25%, and furanose
A furanose is a collective term for carbohydrates that have a chemical structure that includes a five-membered ring system consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The name derives from its similarity to the oxygen heterocycle furan, bu ...
forms exist in negligible amounts. The terms "glucose" and "-glucose" are generally used for these cyclic forms as well. The ring arises from the open-chain form by an intramolecular nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions di ...
reaction between the aldehyde group (at C-1) and either the C-4 or C-5 hydroxyl group, forming a hemiacetal
A hemiacetal or a hemiketal has the general formula R1R2C(OH)OR, where R1 or R2 is hydrogen or an organic substituent. They generally result from the addition of an alcohol to an aldehyde or a ketone, although the latter are sometimes called hemike ...
linkage, .
The reaction between C-1 and C-5 yields a six-membered heterocyclic
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and ...
system called a pyranose, which is a monosaccharide sugar (hence "-ose") containing a derivatised pyran
In chemistry, pyran, or oxine, is a six-membered heterocyclic, non-aromatic ring, consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom and containing two double bonds. The molecular formula is C5H6O. There are two isomers of pyran that differ by the ...
skeleton. The (much rarer) reaction between C-1 and C-4 yields a five-membered furanose ring, named after the cyclic ether furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly ...
. In either case, each carbon in the ring has one hydrogen and one hydroxyl attached, except for the last carbon (C-4 or C-5) where the hydroxyl is replaced by the remainder of the open molecule (which is or respectively).
The ring-closing reaction can give two products, denoted "α-" and "β-". When a glucopyranose molecule is drawn in the Haworth projection
In chemistry, a Haworth projection is a common way of writing a structural formula to represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides with a simple three-dimensional perspective. Haworth projection approximate the shapes of the actual mole ...
, the designation "α-" means that the hydroxyl group attached to C-1 and the group at C-5 lies on opposite sides of the ring's plane (a '' trans'' arrangement), while "β-" means that they are on the same side of the plane (a '' cis'' arrangement). Therefore, the open-chain isomer -glucose gives rise to four distinct cyclic isomers: α--glucopyranose, β--glucopyranose, α--glucofuranose, and β--glucofuranose. These five structures exist in equilibrium and interconvert, and the interconversion is much more rapid with acid catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
.
 The other open-chain isomer -glucose similarly gives rise to four distinct cyclic forms of -glucose, each the mirror image of the corresponding -glucose.
The glucopyranose ring (α or β) can assume several non-planar shapes, analogous to the "chair" and "boat" conformations of
The other open-chain isomer -glucose similarly gives rise to four distinct cyclic forms of -glucose, each the mirror image of the corresponding -glucose.
The glucopyranose ring (α or β) can assume several non-planar shapes, analogous to the "chair" and "boat" conformations of cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexan ...
. Similarly, the glucofuranose ring may assume several shapes, analogous to the "envelope" conformations of cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occur ...
.
In the solid state, only the glucopyranose forms are observed.
Some derivatives of glucofuranose, such as 1,2-''O''-isopropylidene--glucofuranose are stable and can be obtained pure as crystalline solids. For example, reaction of α-D-glucose with ''para''-tolylboronic acid reforms the normal pyranose ring to yield the 4-fold ester α-D-glucofuranose-1,2:3,5-bis(''p''-tolylboronate).
Mutarotation
 Mutarotation consists of a temporary reversal of the ring-forming reaction, resulting in the open-chain form, followed by a reforming of the ring. The ring closure step may use a different group than the one recreated by the opening step (thus switching between pyranose and furanose forms), or the new hemiacetal group created on C-1 may have the same or opposite handedness as the original one (thus switching between the α and β forms). Thus, though the open-chain form is barely detectable in solution, it is an essential component of the equilibrium.
The open-chain form is thermodynamically unstable, and it spontaneously
Mutarotation consists of a temporary reversal of the ring-forming reaction, resulting in the open-chain form, followed by a reforming of the ring. The ring closure step may use a different group than the one recreated by the opening step (thus switching between pyranose and furanose forms), or the new hemiacetal group created on C-1 may have the same or opposite handedness as the original one (thus switching between the α and β forms). Thus, though the open-chain form is barely detectable in solution, it is an essential component of the equilibrium.
The open-chain form is thermodynamically unstable, and it spontaneously isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Iso ...
izes to the cyclic forms. (Although the ring closure reaction could in theory create four- or three-atom rings, these would be highly strained, and are not observed in practice.) In solutions at room temperature
Colloquially, "room temperature" is a range of air temperatures that most people prefer for indoor settings. It feels comfortable to a person when they are wearing typical indoor clothing. Human comfort can extend beyond this range depending on ...
, the four cyclic isomers interconvert over a time scale of hours, in a process called mutarotation Mutarotation is the change in the ''optical rotation'' because of the change in the equilibrium between two anomers, when the corresponding stereocenters interconvert. Cyclic sugars show mutarotation as α and β anomeric forms interconvert.
The op ...
. Starting from any proportions, the mixture converges to a stable ratio of α:β 36:64. The ratio would be α:β 11:89 if it were not for the influence of the anomeric effect
In organic chemistry, the anomeric effect or Edward-Lemieux effect is a stereoelectronic effect that describes the tendency of heteroatomic substituents adjacent to a heteroatom within a cyclohexane ring to prefer the ''axial'' orientation instead ...
. Mutarotation is considerably slower at temperatures close to .
Optical activity
Whether in water or the solid form, -(+)-glucose isdextrorotatory
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circul ...
, meaning it will rotate the direction of polarized light
Polarization (also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the ...
clockwise as seen looking toward the light source. The effect is due to the chirality
Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable from ...
of the molecules, and indeed the mirror-image isomer, -(−)-glucose, is levorotatory
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circul ...
(rotates polarized light counterclockwise) by the same amount. The strength of the effect is different for each of the five tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydr ...
s.
Note that the - prefix does not refer directly to the optical properties of the compound. It indicates that the C-5 chiral centre has the same handedness as that of -glyceraldehyde (which was so labelled because it is dextrorotatory). The fact that -glucose is dextrorotatory is a combined effect of its four chiral centres, not just of C-5; and indeed some of the other -aldohexoses are levorotatory.
The conversion between the two anomers can be observed in a polarimeter
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance.Manfred Hesse, Herbert Meier, Bernd Zeeh, Stefan Bienz, Laurent Bigler, Thomas Fox: ''Spektroskopische Methoden in der organischen Chemie''. 8th revised Edition. Georg Thieme, 2011, , p. 34 (in German). When equilibrium has been reached after a certain time due to mutarotation, the angle of rotation is +52.7° mL/(dm·g). By adding acid or base, this transformation is much accelerated. The equilibration takes place via the open-chain aldehyde form.
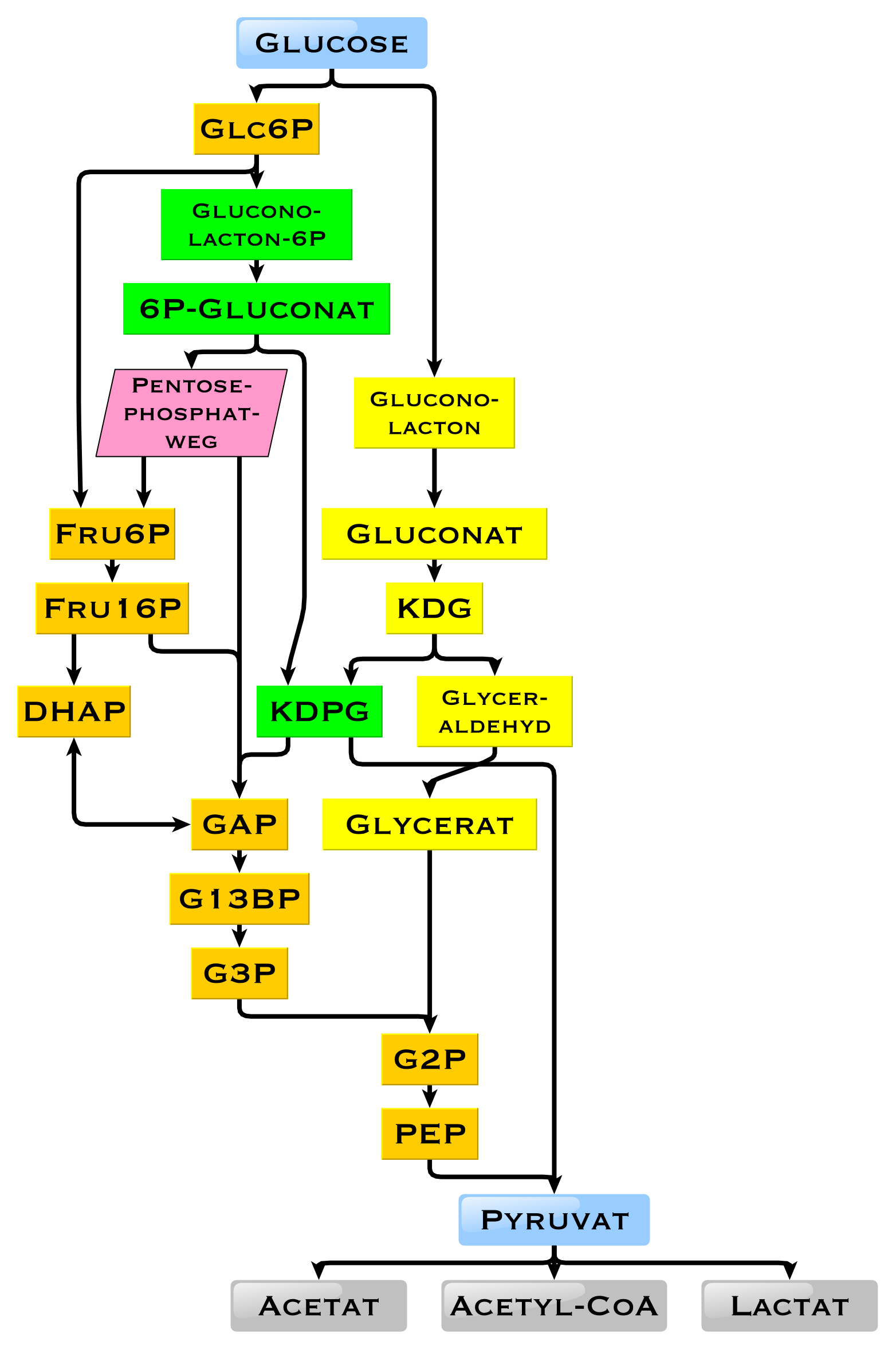
 In humans, glucose is metabolized by glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway.H. Robert Horton, Laurence A. Moran, K. Gray Scrimgeour, Marc D. Perry, J. David Rawn: ''Biochemie''. Pearson Studium; 4. aktualisierte Auflage 2008; ; p. 490–496. (german) Glycolysis is used by all living organisms,Brian K. Hall: ''Strickberger's Evolution.'' Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 2013, , p. 164. with small variations, and all organisms generate energy from the breakdown of monosaccharides. In the further course of the metabolism, it can be completely degraded via
In humans, glucose is metabolized by glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway.H. Robert Horton, Laurence A. Moran, K. Gray Scrimgeour, Marc D. Perry, J. David Rawn: ''Biochemie''. Pearson Studium; 4. aktualisierte Auflage 2008; ; p. 490–496. (german) Glycolysis is used by all living organisms,Brian K. Hall: ''Strickberger's Evolution.'' Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 2013, , p. 164. with small variations, and all organisms generate energy from the breakdown of monosaccharides. In the further course of the metabolism, it can be completely degraded via
 Glucose is a ubiquitous fuel in
Glucose is a ubiquitous fuel in
 Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in
Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in
 Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey. Glucose is extremely abundant and has been isolated from a variety of natural sources across the world, including male cones of the coniferous tree ''Wollemia nobilis'' in Rome, the roots of ''Ilex asprella'' plants in China, and straws from rice in California.
The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber".
Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey. Glucose is extremely abundant and has been isolated from a variety of natural sources across the world, including male cones of the coniferous tree ''Wollemia nobilis'' in Rome, the roots of ''Ilex asprella'' plants in China, and straws from rice in California.
The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber".
 Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. In foods, it is used as a sweetener,
Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. In foods, it is used as a sweetener,
wayback=20100331071121 ''Anlagen zum Positionspapier der Fachgruppe Nuklearchemie''
, February 2000. where it is by far the most commonly used diagnostic agent.
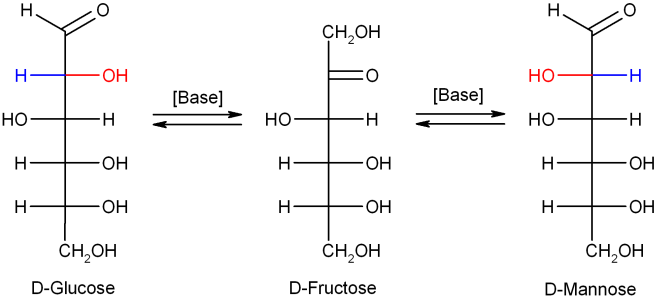
Isomerisation
In dilutesodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
or other dilute bases, the monosaccharides mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation ...
, glucose and fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
interconvert (via a Lobry de Bruyn–Alberda–Van Ekenstein transformation), so that a balance between these isomers is formed. This reaction proceeds via an enediol
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene (olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). The ter ...
:

Biochemical properties
Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide. Glucose is also the most widely used aldohexose in most living organisms. One possible explanation for this is that glucose has a lower tendency than other aldohexoses to react nonspecifically with theamine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
groups of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s. This reaction—glycation
Glycation (sometimes called non-enzymatic glycosylation) is the covalent attachment of a sugar to a protein or lipid. Typical sugars that participate in glycation are glucose, fructose, and their derivatives. Glycation is the non-enzymatic proces ...
—impairs or destroys the function of many proteins, e.g. in glycated hemoglobin
Glycated hemoglobin, also known as HbA1c, glycohemoglobin, hemoglobin A1c, A1C, is a form of hemoglobin (Hb) that is chemically linked to a sugar. Most monosaccharides, including glucose, galactose and fructose, spontaneously (i.e. non-enzymatic ...
. Glucose's low rate of glycation can be attributed to its having a more stable cyclic form
Cyclic form is a technique of musical construction, involving multiple sections or movements, in which a theme, melody, or thematic material occurs in more than one movement as a unifying device. Sometimes a theme may occur at the beginning and e ...
compared to other aldohexoses, which means it spends less time than they do in its reactive open-chain form. The reason for glucose having the most stable cyclic form of all the aldohexoses is that its hydroxy group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
s (with the exception of the hydroxy group on the anomeric carbon of -glucose) are in the equatorial position. Presumably, glucose is the most abundant natural monosaccharide because it is less glycated with proteins than other monosaccharides.Jeremy M. Berg: ''Stryer Biochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2017, , p. 531. (german) Another hypothesis is that glucose, being the only -aldohexose that has all five hydroxy substituents in the equatorial Equatorial may refer to something related to:
*Earth's equator
**the tropics, the Earth's equatorial region
**tropical climate
*the Celestial equator
** equatorial orbit
**equatorial coordinate system
** equatorial mount, of telescopes
* equatorial ...
position in the form of β--glucose, is more readily accessible to chemical reactions, for example, for esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
or acetal
In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity . Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments no ...
formation. For this reason, -glucose is also a highly preferred building block in natural polysaccharides (glycans). Polysaccharides that are composed solely of glucose are termed glucan
A glucan is a polysaccharide derived from D-glucose, linked by glycosidic bonds. Glucans are noted in two forms: alpha glucans and beta glucans. Many beta-glucans are medically important. They represent a drug target for antifungal medications of ...
s.
Glucose is produced by plants through photosynthesis using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide and can be used by all living organisms as an energy and carbon source. However, most glucose does not occur in its free form, but in the form of its polymers, i.e. lactose, sucrose, starch and others which are energy reserve substances, and cellulose and chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, which are components of the cell wall in plants or fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
and arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s, respectively. These polymers, when consumed by animals, fungi and bacteria, are degraded to glucose using enzymes. All animals are also able to produce glucose themselves from certain precursors as the need arises. Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s, cells of the renal medulla
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries whi ...
and erythrocytes
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
depend on glucose for their energy production.Peter C. Heinrich: ''Löffler/Petrides Biochemie und Pathobiochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2014, , p. 195. (german) In adult humans, there is about of glucose,U. Satyanarayana: ''Biochemistry.'' Elsevier Health Sciences, 2014, . p. 674. of which about is present in the blood. Approximately of glucose is produced in the liver of an adult in 24 hours.
Many of the long-term complications of diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
(e.g., blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
, kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as eit ...
, and peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or or ...
) are probably due to the glycation of proteins or lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
s. In contrast, enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
-regulated addition of sugars to protein is called glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not al ...
and is essential for the function of many proteins.
Uptake
Ingested glucose initially binds to the receptor for sweet taste on the tongue in humans. This complex of the proteinsT1R2
Taste receptor type 1 member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAS1R2'' gene.
The sweet taste receptor is predominantly formed as a dimer of T1R2 and T1R3 by which different organisms sense this taste. In songbirds, however, the T1 ...
and T1R3
Taste receptor type 1 member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAS1R3'' gene. The ''TAS1R3'' gene encodes the human homolog of mouse Sac taste receptor, a major determinant of differences between sweet-sensitive and -insensitive mo ...
makes it possible to identify glucose-containing food sources. Glucose mainly comes from food—about per day is produced by conversion of food,Peter C. Heinrich: ''Löffler/Petrides Biochemie und Pathobiochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2014, , p. 404. but it is also synthesized from other metabolites in the body's cells. In humans, the breakdown of glucose-containing polysaccharides happens in part already during chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
by means of amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of ...
, which is contained in saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
, as well as by maltase
Maltase (, ''alpha-glucosidase'', ''glucoinvertase'', ''glucosidosucrase'', ''maltase-glucoamylase'', ''alpha-glucopyranosidase'', ''glucosidoinvertase'', ''alpha-D-glucosidase'', ''alpha-glucoside hydrolase'', ''alpha-1,4-glucosidase'', ''alp ...
, lactase
Lactase is an enzyme produced by many organisms. It is located in the brush border of the small intestine of humans and other mammals. Lactase is essential to the complete digestion of whole milk; it breaks down lactose, a sugar which gives m ...
, and sucrase Sucrase is a digestive enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose to its subunits fructose and glucose. One form, sucrase-isomaltase, is secreted in the small intestine on the brush border. The sucrase enzyme invertase, which occurs more commo ...
on the brush border
A brush border (striated border or brush border membrane) is the microvilli-covered surface of simple cuboidal and simple columnar epithelium found in different parts of the body. Microvilli are approximately 100 nanometers in diameter and the ...
of the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
. Glucose is a building block of many carbohydrates and can be split off from them using certain enzymes. Glucosidases
Glucosidases are the glycoside hydrolase enzymes categorized under the EC number 3.2.1.
Function
Alpha-glucosidases are enzymes involved in breaking down complex carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen into their monomers.
They catalyze the ...
, a subgroup of the glycosidases, first catalyze the hydrolysis of long-chain glucose-containing polysaccharides, removing terminal glucose. In turn, disaccharides are mostly degraded by specific glycosidases to glucose. The names of the degrading enzymes are often derived from the particular poly- and disaccharide; inter alia, for the degradation of polysaccharide chains there are amylases (named after amylose, a component of starch), cellulases (named after cellulose), chitinases (named after chitin), and more. Furthermore, for the cleavage of disaccharides, there are maltase, lactase, sucrase, trehalase
The enzyme Trehalase is a glycoside hydrolase, produced by cells in the brush border of the small intestine, which catalyzes the conversion of trehalose to glucose. It is found in most animals.
The non-reducing disaccharide trehalose (α-D-glucop ...
, and others. In humans, about 70 genes are known that code for glycosidases. They have functions in the digestion and degradation of glycogen, sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because ...
s, mucopolysaccharides
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case ...
, and poly(ADP-ribose
Adenosine diphosphate ribose (ADPR) is an ester molecule formed into chains by the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase. ADPR is created from cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) by the CD38 enzyme using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a cofactor.
...
). Humans do not produce cellulases, chitinases, or trehalases, but the bacteria in the gut microbiota
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut m ...
do.
In order to get into or out of cell membranes of cells and membranes of cell compartments, glucose requires special transport proteins from the major facilitator superfamily
The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) is a superfamily of membrane transport proteins that facilitate movement of small solutes across cell membranes in response to chemiosmotic gradients.
Function
The major facilitator superfamily (MFS) are ...
. In the small intestine (more precisely, in the jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previous ...
),Harold A. Harper: ''Medizinische Biochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2013, , p. 641. glucose is taken up into the intestinal epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
with the help of glucose transporter
Glucose transporters are a wide group of membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of glucose across the plasma membrane, a process known as facilitated diffusion. Because glucose is a vital source of energy for all life, these transporter ...
s via a secondary active transport
In cellular biology, ''active transport'' is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellul ...
mechanism called sodium ion-glucose symport
A symporter is an integral membrane protein that is involved in the transport of two (or more) different molecules across the cell membrane in the same direction. The symporter works in the plasma membrane and molecules are transported across the ...
via sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1). Further transfer occurs on the basolateral
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
side of the intestinal epithelial cells via the glucose transporter GLUT2
Glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) also known as solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 2 (SLC2A2) is a transmembrane carrier protein that enables protein facilitated glucose movement across cell membranes. It is the principa ...
, as well uptake into liver cells
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, bi ...
, kidney cells, cells of the islets of Langerhans
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of ...
, neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s, astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
s, and tanycyte
Tanycytes are special ependymal cells found in the third ventricle of the brain, and on the floor of the fourth ventricle and have processes extending deep into the hypothalamus. It is possible that their function is to transfer chemical signals f ...
s. Glucose enters the liver via the portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approxima ...
and is stored there as a cellular glycogen. In the liver cell, it is phosphorylated
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, whi ...
by glucokinase
Glucokinase () is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in ...
at position 6 to form glucose 6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
, which cannot leave the cell. Glucose 6-phosphatase
The enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.9, G6Pase; systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate phosphohydrolase) catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucose 6-phosphate, resulting in the creation of a phosphate group and free glucose:
: D-glucose 6-phos ...
can convert glucose 6-phosphate back into glucose exclusively in the liver, so the body can maintain a sufficient blood glucose concentration. In other cells, uptake happens by passive transport through one of the 14 GLUT proteins. In the other cell types, phosphorylation occurs through a hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokina ...
, whereupon glucose can no longer diffuse out of the cell.
The glucose transporter GLUT1
Glucose transporter 1 (or GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC2A1'' gene. GLUT1 facilitates the transport of glucose across ...
is produced by most cell types and is of particular importance for nerve cells and pancreatic β-cells. GLUT3
Glucose transporter 3 (or GLUT3), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 3 (SLC2A3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC2A3'' gene. GLUT3 facilitates the transport of glucose across the plas ...
is highly expressed in nerve cells. Glucose from the bloodstream is taken up by GLUT4
Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4, is a protein encoded, in humans, by the ''SLC2A4'' gene. GLUT4 is the insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adi ...
from muscle cell
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscl ...
s (of the skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
and heart muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle tha ...
) and fat cell
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. I ...
s. GLUT14
Solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC2A14 gene.
Members of the glucose transporter (GLUT) family, including SLC2A14, are highly conserved integral membrane proteins ...
is expressed exclusively in testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
s. Excess glucose is broken down and converted into fatty acids, which are stored as triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as w ...
s. In the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
s, glucose in the urine is absorbed via SGLT1 and SGLT2
The sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the (solute carrier family 5 (sodium/glucose cotransporter)) gene.
Function
SGLT2 is a member of the sodium glucose cotransporter family, which are sodium-d ...
in the apical cell membranes and transmitted via GLUT2 in the basolateral cell membranes. About 90% of kidney glucose reabsorption is via SGLT2 and about 3% via SGLT1.
Biosynthesis
In plants and someprokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
s, glucose is a product of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
. Glucose is also formed by the breakdown of polymeric forms of glucose like glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
Glycogen functions as one o ...
(in animals and mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is t ...
s) or starch (in plants). The cleavage of glycogen is termed glycogenolysis, the cleavage of starch is called starch degradation.
The metabolic pathway that begins with molecules containing two to four carbon atoms (C) and ends in the glucose molecule containing six carbon atoms is called gluconeogenesis and occurs in all living organisms. The smaller starting materials are the result of other metabolic pathways. Ultimately almost all biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include large ...
s come from the assimilation of carbon dioxide in plants and microbes during photosynthesis. The free energy of formation of α--glucose is 917.2 kilojoules per mole. In humans, gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver and kidney,Leszek Szablewski: ''Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Resistance.'' Bentham Science Publishers, 2011, , p. 46. but also in other cell types. In the liver about of glycogen are stored, in skeletal muscle about .Peter C. Heinrich: ''Löffler/Petrides Biochemie und Pathobiochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2014, , p. 389. However, the glucose released in muscle cells upon cleavage of the glycogen can not be delivered to the circulation because glucose is phosphorylated by the hexokinase, and a glucose-6-phosphatase is not expressed to remove the phosphate group. Unlike for glucose, there is no transport protein for glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
. Gluconeogenesis allows the organism to build up glucose from other metabolites, including lactate or certain amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s, while consuming energy. The renal tubular cell
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a Nephron#Renal tubule, renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillary, capillaries called a glomeru ...
s can also produce glucose.
Glucose also can be found outside of living organisms in the ambient environment. Glucose concentrations in the atmosphere are detected via collection of samples by aircraft and are known to vary from location to location. For example, glucose concentrations in atmospheric air from inland China range from 0.8-20.1 pg/L, whereas east coastal China glucose concentrations range from 10.3-142 pg/L.
Glucose degradation
oxidative decarboxylation
Oxidative decarboxylation is a decarboxylation reaction caused by oxidation. Most are accompanied by α- Ketoglutarate α- Decarboxylation caused by dehydrogenation of hydroxyl carboxylic acids such as carbonyl carboxylic acid, malic acid, isocitr ...
, the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins ...
(synonym ''Krebs cycle'') and the respiratory chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
to water and carbon dioxide. If there is not enough oxygen available for this, the glucose degradation in animals occurs anaerobic to lactate via lactic acid fermentation and releases much less energy. Muscular lactate enters the liver through the bloodstream in mammals, where gluconeogenesis occurs (Cori cycle
The Cori cycle (also known as the lactic acid cycle), named after its discoverers, Carl Ferdinand Cori and Gerty Cori, is a metabolic pathway in which lactate, produced by anaerobic glycolysis in muscles, is transported to the liver and converte ...
). With a high supply of glucose, the metabolite acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
from the Krebs cycle can also be used for fatty acid synthesis
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is conve ...
. Glucose is also used to replenish the body's glycogen stores, which are mainly found in liver and skeletal muscle. These processes are hormonally
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required fo ...
regulated.
In other living organisms, other forms of fermentation can occur. The bacterium ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'' can grow on nutrient media containing glucose as the sole carbon source. In some bacteria and, in modified form, also in archaea, glucose is degraded via the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Use of glucose as an energy source in cells is by either aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, or fermentation. The first step of glycolysis is the phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
of glucose by a hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokina ...
to form glucose 6-phosphate
Glucose 6-phosphate (G6P, sometimes called the Robison ester) is a glucose sugar phosphorylated at the hydroxy group on carbon 6. This dianion is very common in cells as the majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this wa ...
. The main reason for the immediate phosphorylation of glucose is to prevent its diffusion out of the cell as the charged phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
group prevents glucose 6-phosphate from easily crossing the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
. Furthermore, addition of the high-energy phosphate group activates glucose for subsequent breakdown in later steps of glycolysis. At physiological condition
Physiological condition or, more often "physiological conditions" is a term used in biology, biochemistry, and medicine. It refers to conditions of the external or internal milieu that may occur in nature for that organism or cell system, in contr ...
s, this initial reaction is irreversible.
In anaerobic respiration, one glucose molecule produces a net gain of two ATP molecules (four ATP molecules are produced during glycolysis through substrate-level phosphorylation, but two are required by enzymes used during the process). In aerobic respiration, a molecule of glucose is much more profitable in that a maximum net production of 30 or 32 ATP molecules (depending on the organism) is generated,.
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
cells often grow comparatively quickly and consume an above-average amount of glucose by glycolysis, which leads to the formation of lactate, the end product of fermentation in mammals, even in the presence of oxygen. This is called the Warburg effect. For the increased uptake of glucose in tumors various SGLT and GLUT are overly produced.
In yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ...
, ethanol is fermented at high glucose concentrations, even in the presence of oxygen (which normally leads to respiration rather than fermentation). This is called the Crabtree effect
The Crabtree effect, named after the English biochemist Herbert Grace Crabtree, describes the phenomenon whereby the yeast, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', produces ethanol (alcohol) in aerobic conditions at high external glucose concentrations rath ...
.
Glucose can also degrade to form carbon dioxide through abiotic means. This has been demonstrated to occur experimentally via oxidation and hydrolysis at 22˚C and a pH of 2.5.
Energy source
 Glucose is a ubiquitous fuel in
Glucose is a ubiquitous fuel in biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
. It is used as an energy source in organisms, from bacteria to humans, through either aerobic respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be des ...
, anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain.
In aerobic organisms undergoing re ...
(in bacteria), or fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
. Glucose is the human body's key source of energy, through aerobic respiration, providing about 3.75 kilocalorie
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of on ...
s (16 kilojoule
The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force applied. ...
s) of food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals (including humans) derive from their food to sustain their metabolism, including their muscle, muscular activity.
Most animals derive most of their energy from aerobic respiration, namely combining the ...
per gram. Breakdown of carbohydrates (e.g., starch) yields mono-
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
and disaccharide
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar or ''biose'') is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are simple sugars soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, lact ...
s, most of which is glucose. Through glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH ...
and later in the reactions of the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins ...
and oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (UK , US ) or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine tri ...
, glucose is oxidize
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
d to eventually form carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
and water, yielding energy mostly in the form of ATP. The insulin reaction, and other mechanisms, regulate the concentration of glucose in the blood. The physiological caloric value of glucose, depending on the source, is 16.2 kilojoules per gramGeorg Schwedt: ''Zuckersüße Chemie.'' John Wiley & Sons, 2012, , p. 100 . or 15.7 kJ/g (3.74 kcal/g). The high availability of carbohydrates from plant biomass has led to a variety of methods during evolution, especially in microorganisms, to utilize glucose for energy and carbon storage. Differences exist in which end product can no longer be used for energy production. The presence of individual genes, and their gene products, the enzymes, determine which reactions are possible. The metabolic pathway of glycolysis is used by almost all living beings. An essential difference in the use of glycolysis is the recovery of NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
as a reductant for anabolism
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct molecules from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-do ...
that would otherwise have to be generated indirectly.
Glucose and oxygen supply almost all the energy for the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
, so its availability influences psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
processes. When glucose is low, psychological processes requiring mental effort (e.g., self-control
Self-control, an aspect of inhibitory control, is the ability to regulate one's emotions, thoughts, and behavior in the face of temptations and impulses. As an executive function, it is a cognitive process that is necessary for regulating one's b ...
, effortful decision-making) are impaired. In the brain, which is dependent on glucose and oxygen as the major source of energy, the glucose concentration is usually 4 to 6 mM (5 mM equals 90 mg/dL), but decreases to 2 to 3 mM when fasting. Confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
occurs below 1 mM and coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
at lower levels.
The glucose in the blood is called blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
. Blood sugar level
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
s are regulated by glucose-binding nerve cells in the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamu ...
. In addition, glucose in the brain binds to glucose receptors of the reward system
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and class ...
in the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypotha ...
. The binding of glucose to the sweet receptor on the tongue induces a release of various hormones of energy metabolism, either through glucose or through other sugars, leading to an increased cellular uptake and lower blood sugar levels. Artificial sweetener
A sugar substitute is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie () or low-calorie sweetener. Artificial sweeteners may be d ...
s do not lower blood sugar levels.
The blood sugar content of a healthy person in the short-time fasting state, e.g. after overnight fasting, is about 70 to 100 mg/dL of blood (4 to 5.5 mM). In blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intra ...
, the measured values are about 10–15% higher. In addition, the values in the arterial
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pul ...
blood are higher than the concentrations in the venous
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated b ...
blood since glucose is absorbed into the tissue during the passage of the capillary bed
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
. Also in the capillary blood, which is often used for blood sugar determination, the values are sometimes higher than in the venous blood. The glucose content of the blood is regulated by the hormones insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
, incretin
Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans by a blood-gl ...
and glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a Glucagon (medicati ...
. Insulin lowers the glucose level, glucagon increases it. Furthermore, the hormones adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
, thyroxine
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
rect 66 216 386 25 ...
, glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
s, somatotropin
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in h ...
and adrenocorticotropin
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important co ...
lead to an increase in the glucose level. There is also a hormone-independent regulation, which is referred to as glucose autoregulation
Glucose is a simple sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis f ...
. After food intake the blood sugar concentration increases. Values over 180 mg/dL in venous whole blood are pathological and are termed hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
, values below 40 mg/dL are termed hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
. When needed, glucose is released into the bloodstream by glucose-6-phosphatase from glucose-6-phosphate originating from liver and kidney glycogen, thereby regulating the homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physics, physical, and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. Thi ...
of blood glucose concentration. In ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...
s, the blood glucose concentration is lower (60 mg/dL in cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
and 40 mg/dL in sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated s ...
), because the carbohydrates are converted more by their gut microbiota into short-chain fatty acid Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are fatty acids with fewer than six carbon atoms. Derived from intestinal microbial fermentation of indigestible foods, SCFAs are the main energy source of colonocytes, making them crucial to gastrointestinal health. ...
s.Harold A. Harper: ''Medizinische Biochemie''. Springer-Verlag, 2013, , p. 294.
Some glucose is converted to lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natu ...
by astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
s, which is then utilized as an energy source by brain cells
Brain cells make up the functional tissue of the brain. The rest of the brain tissue is structural or connective called the stroma which includes blood vessels. The two main types of cells in the brain are neurons, also known as nerve cells, an ...
; some glucose is used by intestinal cells and red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s, while the rest reaches the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
, adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular e ...
and muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
cells, where it is absorbed and stored as glycogen (under the influence of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
). Liver cell glycogen can be converted to glucose and returned to the blood when insulin is low or absent; muscle cell glycogen is not returned to the blood because of a lack of enzymes. In fat cells
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. I ...
, glucose is used to power reactions that synthesize some fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
types and have other purposes. Glycogen is the body's "glucose energy storage" mechanism, because it is much more "space efficient" and less reactive than glucose itself.
As a result of its importance in human health, glucose is an analyte in glucose test
Many types of glucose tests exist and they can be used to estimate blood sugar levels at a given time or, over a longer period of time, to obtain average levels or to see how fast body is able to normalize changed glucose levels. Eating food for e ...
s that are common medical blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
s. Eating or fasting prior to taking a blood sample has an effect on analyses for glucose in the blood; a high fasting glucose blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
level may be a sign of prediabetes
Prediabetes is a component of the metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms but people with prediabetes often have obesit ...
or diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
.
The glycemic index
The glycemic (glycaemic) index (GI; ) is a number from 0 to 100 assigned to a food, with pure glucose arbitrarily given the value of 100, which represents the relative rise in the blood glucose level two hours after consuming that food. The GI of ...
is an indicator of the speed of resorption and conversion to blood glucose levels from ingested carbohydrates, measured as the area under the curve
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with ...
of blood glucose levels after consumption in comparison to glucose (glucose is defined as 100).Richard A. Harvey, Denise R. Ferrier: ''Biochemistry''. 5th Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2011, , p. 366. The clinical importance of the glycemic index is controversial,U Satyanarayana: ''Biochemistry''. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2014, , p. 508. as foods with high fat contents slow the resorption of carbohydrates and lower the glycemic index, e.g. ice cream. An alternative indicator is the insulin index The insulin index of food represents how much it elevates the concentration of insulin in the blood during the two-hour period after the food is ingested. The index is similar to the glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL), but rather than relyi ...
, measured as the impact of carbohydrate consumption on the blood insulin levels. The glycemic load
The glycemic load (GL) of food is a number that estimates how much the food will raise a person's blood glucose level after eating it. One unit of glycemic load approximates the effect of eating one gram of glucose. Glycemic load accounts for how m ...
is an indicator for the amount of glucose added to blood glucose levels after consumption, based on the glycemic index and the amount of consumed food.
Precursor
Organisms use glucose as a precursor for the synthesis of several important substances. Starch,cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
, and glycogen ("animal starch") are common glucose polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s (polysaccharides). Some of these polymers (starch or glycogen) serve as energy stores, while others (cellulose and chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, which is made from a derivative of glucose) have structural roles. Oligosaccharides of glucose combined with other sugars serve as important energy stores. These include lactose, the predominant sugar in milk, which is a glucose-galactose disaccharide, and sucrose, another disaccharide which is composed of glucose and fructose. Glucose is also added onto certain proteins and lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
s in a process called glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not al ...
. This is often critical for their functioning. The enzymes that join glucose to other molecules usually use phosphorylated
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, whi ...
glucose to power the formation of the new bond by coupling it with the breaking of the glucose-phosphate bond.
Other than its direct use as a monomer, glucose can be broken down to synthesize a wide variety of other biomolecules. This is important, as glucose serves both as a primary store of energy and as a source of organic carbon. Glucose can be broken down and converted into lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
s. It is also a precursor for the synthesis of other important molecules such as vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
(ascorbic acid). In living organisms, glucose is converted to several other chemical compounds that are the starting material for various metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
s. Among them, all other monosaccharidesPeter C. Heinrich: ''Löffler/Petrides Biochemie und Pathobiochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2014, , p. 27. such as fructose (via the polyol pathway The polyol pathway is a two-step process that converts glucose to fructose. In this pathway glucose is reduced to sorbitol, which is subsequently oxidized to fructose. It is also called the sorbitol-aldose reductase pathway.
The pathway is implic ...
),Peter C. Heinrich: ''Löffler/Petrides Biochemie und Pathobiochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2014, , p. 199, 200. mannose (the epimer of glucose at position 2), galactose (the epimer at position 4), fucose, various uronic acids and the amino sugar
In organic chemistry, an amino sugar (or more technically a 2-amino-2-deoxysugar) is a sugar molecule in which a hydroxyl group has been replaced with an amine group. More than 60 amino sugars are known, with one of the most abundant being ''N'' ...
s are produced from glucose.Peter C. Heinrich: ''Löffler/Petrides Biochemie und Pathobiochemie.'' Springer-Verlag, 2014, , p. 214. In addition to the phosphorylation to glucose-6-phosphate, which is part of the glycolysis, glucose can be oxidized during its degradation to glucono-1,5-lactone. Glucose is used in some bacteria as a building block in the trehalose
Trehalose (from Turkish '' tıgala'' – a sugar derived from insect cocoons + -ose) is a sugar consisting of two molecules of glucose. It is also known as mycose or tremalose. Some bacteria, fungi, plants and invertebrate animals synthesize it ...
or the dextran
Dextran is a complex branched glucan (polysaccharide derived from the condensation of glucose), originally derived from wine. IUPAC defines dextrans as "Branched poly-α-d-glucosides of microbial origin having glycosidic bonds predominantly C-1 ...
biosynthesis and in animals as a building block of glycogen. Glucose can also be converted from bacterial xylose isomerase
In enzymology, a xylose isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of
D-xylose and D-xylulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketos ...
to fructose. In addition, glucose metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
s produce all nonessential amino acids, sugar alcohol
Sugar alcohols (also called polyhydric alcohols, polyalcohols, alditols or glycitols) are organic compounds, typically derived from sugars, containing one hydroxyl group (–OH) attached to each carbon atom. They are white, water-soluble solids ...
s such as mannitol
Mannitol is a type of sugar alcohol used as a sweetener and medication. It is used as a low calorie sweetener as it is poorly absorbed by the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, as in glaucoma, and to lower ...
and sorbitol
Sorbitol (), less commonly known as glucitol (), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alcohol g ...
, fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s, cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell mem ...
and nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
s. Finally, glucose is used as a building block in the glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not al ...
of proteins to glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
s, glycolipid
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connec ...
s, peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ...
s, glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. ...
s and other substances (catalyzed by glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferases (GTFs, Gtfs) are enzymes ( EC 2.4) that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze the transfer of saccharide moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar (also known as the "glycosyl donor") to a nucleophilic glycos ...
s) and can be cleaved from them by glycosidase
Glycoside hydrolases (also called glycosidases or glycosyl hydrolases) catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cel ...
s.
Pathology
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
is a metabolic disorder where the body is unable to regulate levels of glucose in the blood either because of a lack of insulin in the body or the failure, by cells in the body, to respond properly to insulin. Each of these situations can be caused by persistently high elevations of blood glucose levels, through pancreatic burnout and insulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cell (biology), cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood gluco ...
. The pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an end ...
is the organ responsible for the secretion of the hormones insulin and glucagon. Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose levels, allowing the body's cells to absorb and use glucose. Without it, glucose cannot enter the cell and therefore cannot be used as fuel for the body's functions. If the pancreas is exposed to persistently high elevations of blood glucose levels, the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas could be damaged, causing a lack of insulin in the body. Insulin resistance occurs when the pancreas tries to produce more and more insulin in response to persistently elevated blood glucose levels. Eventually, the rest of the body becomes resistant to the insulin that the pancreas is producing, thereby requiring more insulin to achieve the same blood glucose-lowering effect, and forcing the pancreas to produce even more insulin to compete with the resistance. This negative spiral contributes to pancreatic burnout, and the disease progression of diabetes.
To monitor the body's response to blood glucose-lowering therapy, glucose levels can be measured. Blood glucose monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring is the use of a glucose meter for testing the concentration of glucose in the blood ( glycemia). Particularly important in diabetes management, a blood glucose test is typically performed by piercing the skin (typically, ...
can be performed by multiple methods, such as the fasting glucose test which measures the level of glucose in the blood after 8 hours of fasting. Another test is the 2-hour glucose tolerance test (GTT)for this test, the person has a fasting glucose test done, then drinks a 75-gram glucose drink and is retested. This test measures the ability of the person's body to process glucose. Over time the blood glucose levels should decrease as insulin allows it to be taken up by cells and exit the blood stream.
Hypoglycemia management
 Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in
Individuals with diabetes or other conditions that result in low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose belo ...
often carry small amounts of sugar in various forms. One sugar commonly used is glucose, often in the form of glucose tablets (glucose pressed into a tablet shape sometimes with one or more other ingredients as a binder), hard candy
A hard candy (American English), or boiled sweet (British English), is a sugar candy prepared from one or more sugar-based syrups that is heated to a temperature of 160 °C (320 °F) to make candy. Among the many hard candy varietie ...
, or sugar packet
A sugar packet is a delivery method for one serving of sugar or other sweetener. Sugar packets are commonly supplied in restaurants, coffeehouses, and tea houses, where they are preferred to sugar bowls or sugar dispensers for reasons of neatness, ...
.
Sources
 Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey. Glucose is extremely abundant and has been isolated from a variety of natural sources across the world, including male cones of the coniferous tree ''Wollemia nobilis'' in Rome, the roots of ''Ilex asprella'' plants in China, and straws from rice in California.
The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber".
Most dietary carbohydrates contain glucose, either as their only building block (as in the polysaccharides starch and glycogen), or together with another monosaccharide (as in the hetero-polysaccharides sucrose and lactose). Unbound glucose is one of the main ingredients of honey. Glucose is extremely abundant and has been isolated from a variety of natural sources across the world, including male cones of the coniferous tree ''Wollemia nobilis'' in Rome, the roots of ''Ilex asprella'' plants in China, and straws from rice in California.
The carbohydrate value is calculated in the USDA database and does not always correspond to the sum of the sugars, the starch, and the "dietary fiber".
Commercial production
Glucose is produced industrially from starch byenzymatic
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
using glucose amylase or by the use of acids
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
. Enzymatic hydrolysis has largely displaced acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reactions.P. J. Fellows: ''Food Processing Technology. Woodhead Publishing'', 2016, , p. 197. The result is glucose syrup (enzymatically with more than 90% glucose in the dry matter) with an annual worldwide production volume of 20 million tonnes (as of 2011).Thomas Becker, Dietmar Breithaupt, Horst Werner Doelle, Armin Fiechter, Günther Schlegel, Sakayu Shimizu, Hideaki Yamada: ''Biotechnology'', in: ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 7th Edition, Wiley-VCH, 2011. . Volume 6, p. 48. This is the reason for the former common name "starch sugar". The amylases most often come from ''Bacillus licheniformis
''Bacillus licheniformis'' is a bacterium commonly found in the soil. It is found on bird feathers, especially chest and back plumage, and most often in ground-dwelling birds (like sparrows) and aquatic species (like ducks).
It is a gram-posit ...
''The Amylase Research Society of Japan: ''Handbook of Amylases and Related Enzymes.'' Elsevier, 2014, , p. 195. or ''Bacillus subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillu ...
'' (strain MN-385), which are more thermostable than the originally used enzymes. Starting in 1982, pullulanase
Pullulanase (, ''limit dextrinase'', ''amylopectin 6-glucanohydrolase'', ''bacterial debranching enzyme'', ''debranching enzyme'', ''alpha-dextrin endo-1,6-alpha-glucosidase'', ''R-enzyme'', ''pullulan alpha-1,6-glucanohydrolase'') is a specific ki ...
s from ''Aspergillus niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on de ...
'' were used in the production of glucose syrup to convert amylopectin to starch (amylose), thereby increasing the yield of glucose. The reaction is carried out at a pH = 4.6–5.2 and a temperature of 55–60 °C. Corn syrup
Corn syrup is a food syrup which is made from the starch of corn (called maize in many countries) and contains varying amounts of sugars: glucose, maltose and higher oligosaccharides, depending on the grade. Corn syrup is used in foods to softe ...
has between 20% and 95% glucose in the dry matter. The Japanese form of the glucose syrup, Mizuame
is a sweetener from Japan. A clear, thick, sticky liquid, it is made by converting starch to sugars. is added to to give them a sheen, eaten in ways similar to honey, and can be a main ingredient in sweets. Some are produced in a very simila ...
, is made from sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
or rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
starch. Maltodextrin
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide that is used as a food ingredient. It is produced from vegetable starch by partial hydrolysis and is usually found as a white hygroscopic spray-dried powder. Maltodextrin is easily digestible, being absorbed as r ...
contains about 20% glucose.
Many crops can be used as the source of starch. Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, rice, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively ...
, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
, sweet potato,Alan Davidson: ''The Oxford Companion to Food''. OUP Oxford, 2014, , p. 527. corn husk
Husk (or hull) in botany is the outer shell or coating of a seed. In the United States, the term husk often refers to the leafy outer covering of an ear of maize (corn) as it grows on the plant. Literally, a husk or hull includes the protective ...
and sago
Sago () is a starch extracted from the pith, or spongy core tissue, of various tropical palm stems, especially those of ''Metroxylon sagu''. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands, where it is ...
are all used in various parts of the world. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, corn starch
Corn starch, maize starch, or cornflour (British English) is the starch derived from corn (maize) grain. The starch is obtained from the endosperm of the kernel. Corn starch is a common food ingredient, often used to thicken sauces or sou ...
(from maize) is used almost exclusively. Some commercial glucose occurs as a component of invert sugar
Inverted sugar syrup, also called invert syrup, invert sugar, simple syrup, sugar syrup, sugar water, bar syrup, syrup USP, or sucrose inversion, is a syrup mixture of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose, that is made by hydrolytic sacch ...
, a roughly 1:1 mixture of glucose and fructose that is produced from sucrose. In principle, cellulose could be hydrolyzed to glucose, but this process is not yet commercially practical.
Conversion to fructose
In the US, almost exclusively corn (more precisely, corn syrup) is used as glucose source for the production of isoglucose, which is a mixture of glucose and fructose, since fructose has a higher sweetening powerwith same physiological calorific value of 374 kilocalories per 100 g. The annual world production of isoglucose is 8 million tonnes (as of 2011). When made from corn syrup, the final product ishigh-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzym ...
(HFCS).
Commercial usage
 Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. In foods, it is used as a sweetener,
Glucose is mainly used for the production of fructose and of glucose-containing foods. In foods, it is used as a sweetener, humectant
A humectant is a hygroscopic (water-absorbing) substance used to keep things moist. They are used in many products, including food, cosmetics, medicines and pesticides. When used as a food additive, a humectant has the effect of keeping moisture ...
, to increase the volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The de ...
and to create a softer mouthfeel
Mouthfeel refers to the physical sensations in the mouth caused by food or drink, making it distinct from taste. It is a fundamental sensory attribute which, along with taste and smell, determines the overall flavor of a food item. Mouthfeel is ...
.
Various sources of glucose, such as grape juice (for wine) or malt (for beer), are used for fermentation to ethanol during the production of alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The c ...
s. Most soft drinks in the US use HFCS-55 (with a fructose content of 55% in the dry mass), while most other HFCS-sweetened foods in the US use HFCS-42 (with a fructose content of 42% in the dry mass). In Mexico, on the other hand, soft drinks are sweetened by cane sugar, which has a higher sweetening power. In addition, glucose syrup is used, inter alia, in the production of confectionery
Confectionery is the art of making confections, which are food items that are rich in sugar and carbohydrates. Exact definitions are difficult. In general, however, confectionery is divided into two broad and somewhat overlapping categories ...
such as candies, toffee
Toffee is a confection made by caramelizing sugar or molasses (creating inverted sugar) along with butter, and occasionally flour. The mixture is heated until its temperature reaches the hard crack stage of . While being prepared, toffee is ...
and fondant
Fondant is a mixture of sugar and water used as a confection, filling, or icing. Sometimes gelatin and glycerine are used as softeners or stabilizers.
There are numerous varieties of fondant, with the most basic being poured fondant. Others in ...
.Steve T. Beckett: ''Beckett's Industrial Chocolate Manufacture and Use''. John Wiley & Sons, 2017, , p. 82. Typical chemical reactions of glucose when heated under water-free conditions are caramelization
Caramelization is a process of browning of sugar used extensively in cooking for the resulting sweet nutty flavor and brown color. The brown colors are produced by three groups of polymers: caramelans (C24H36O18), caramelens (C36H50O25), and c ...
and, in presence of amino acids, the Maillard reaction
The Maillard reaction ( ; ) is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Seared steaks, fried dumplings, cookies and other kinds of biscuits, breads, toasted marshmallows, and man ...
.
In addition, various organic acids can be biotechnologically produced from glucose, for example by fermentation with ''Clostridium thermoaceticum
''Moorella thermoacetica'', previously known as ''Clostridium thermoaceticum'', is an acetogenic, thermophilic, strictly anaerobic, endospore-forming, bacterium belonging to the phylum Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phy ...
'' to produce acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, with ''Penicillium notatum
''Penicillium chrysogenum'' (formerly known as ''Penicillium notatum'') is a species of fungus in the genus ''Penicillium''. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in in ...
'' for the production of araboascorbic acid, with ''Rhizopus delemar
''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and t ...
'' for the production of fumaric acid
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297.
The salts and esters are known as fu ...
, with ''Aspergillus niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on de ...
'' for the production of gluconic acid
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4COOH. It is one of the 16 stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoic acid.
In aqueous solution at neutral pH, gluconic acid fo ...
, with ''Candida brumptii
Candida, or Cándida (Spanish), may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* ''Candida'' (fungus), a genus of yeasts
** Candidiasis, an infection by ''Candida'' organisms
* Malvasia Candida, a variety of grape
Places
* Candida, Campania, a ''comu ...
'' to produce isocitric acid
Isocitric acid is a structural isomer of citric acid. Since citric acid and isocitric acid are structural isomers, they share similar physical and chemical properties. Due to these similar properties, it is difficult to separate the isomers. Salts ...
, with ''Aspergillus terreus
''Aspergillus terreus'', also known as ''Aspergillus terrestris'', is a fungus (mold) found worldwide in soil. Although thought to be strictly asexual until recently, ''A. terreus'' is now known to be capable of sexual reproduction. This saprotr ...
'' for the production of itaconic acid
Itaconic acid, or methylidenesuccinic acid, is an organic compound. This dicarboxylic acid is a white solid that is soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone. Historically, itaconic acid was obtained by the distillation of citric acid, but currently ...
, with ''Pseudomonas fluorescens
''Pseudomonas fluorescens'' is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the ''Pseudomonas'' genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed ''P. fluorescens'' in the ''P. fluorescens'' group within the genu ...
'' for the production of 2-ketogluconic acid, with ''Gluconobacter suboxydans
''Gluconobacter'' is a genus of bacteria in the acetic acid bacteria family. They prefer sugar-rich environments, so are sometimes found as a spoilage organism in beer. They are not known to be pathogenic but can cause rot in apples and pear ...
'' for the production of 5-ketogluconic acid, with ''Aspergillus oryzae
''Aspergillus oryzae'', also known as , is a filamentous fungus (a mold) used in East Asia to saccharify rice, sweet potato, and barley in the making of alcoholic beverages such as ''sake'' and '' shōchū'', and also to ferment soybeans for m ...
'' for the production of kojic acid
Kojic acid is a chelation agent produced by several species of fungi, especially ''Aspergillus oryzae'', which has the Japanese common name ''koji''. Kojic acid is a by-product in the fermentation process of malting rice, for use in the manufactur ...
, with ''Lactobacillus delbrueckii
''Lactobacillus delbrueckii'' is a species of bacteria in the family Lactobacillaceae. It is part of the microbiota of the lower reproductive tract of women.
History
Naming
The species carries the name of Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henn ...
'' for the production of lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natu ...
, with ''Lactobacillus brevis
''Levilactobacillus brevis'' is a gram-positive, rod shaped species of lactic acid bacteria which is heterofermentative, creating CO2, lactic acid and acetic acid or ethanol during fermentation. ''L. brevis'' is the type species of the genus ''Le ...
'' for the production of malic acid
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms ...
, with ''Propionibacter shermanii
''Propionibacterium freudenreichii'' is a gram-positive, non-motile bacterium that plays an important role in the creation of Emmental cheese, and to some extent, Jarlsberg cheese, Leerdammer and Maasdam cheese. Its concentration in Swiss-type ch ...
'' for the production of propionic acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2CO2H. It is a liq ...
, with ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerugi ...
'' for the production of pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic aci ...
and with ''Gluconobacter suboxydans
''Gluconobacter'' is a genus of bacteria in the acetic acid bacteria family. They prefer sugar-rich environments, so are sometimes found as a spoilage organism in beer. They are not known to be pathogenic but can cause rot in apples and pear ...
'' for the production of tartaric acid
Tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes, but also in bananas, tamarinds, and citrus. Its salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, develops naturally i ...
.James A. Kent: ''Riegel's Handbook of Industrial Chemistry''. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013, , p. 938. Potent, bioactive natural products like triptolide that inhibit mammalian transcription via inhibition of the XPB subunit of the general transcription factor TFIIH has been recently reported as a glucose conjugate for targeting hypoxic cancer cells with increased glucose transporter expression. Recently, glucose has been gaining commercial use as a key component of "kits" containing lactic acid and insulin intended to induce hypoglycemia and hyperlactatemia to combat different cancers and infections.
Analysis
When a glucose molecule is to be detected at a certain position in a larger molecule,nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic fiel ...
, X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
analysis or lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in rec ...
immunostaining
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by A ...
is performed with concanavalin A
Concanavalin A (ConA) is a lectin (carbohydrate-binding protein) originally extracted from the jack-bean (''Canavalia ensiformis''). It is a member of the legume lectin family. It binds specifically to certain structures found in various sugars, ...
reporter enzyme conjugate, which binds only glucose or mannose.
Classical qualitative detection reactions
These reactions have only historical significance:Fehling test
TheFehling test
In organic chemistry, Fehling's solution is a chemical reagent used to differentiate between water-soluble carbohydrate and ketone () functional groups, and as a test for reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars, supplementary to the Tollens' r ...
is a classic method for the detection of aldoses.H. Fehling: ''Quantitative Bestimmung des Zuckers im Harn''. In: ''Archiv für physiologische Heilkunde
Archiv Produktion is a classical music record label of German origin. It originated in 1949 as a classical label for the Deutsche Grammophon Gesellschaft (DGG), and in 1958 Archiv was established as a subsidiary of DGG, specialising in recording ...
'' (1848), volume 7, p. 64–73 (in German). Due to mutarotation, glucose is always present to a small extent as an open-chain aldehyde. By adding the Fehling reagents (Fehling (I) solution and Fehling (II) solution), the aldehyde group is oxidized to a carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
, while the Cu2+ tartrate complex is reduced to Cu+ and forms a brick red precipitate (Cu2O).
Tollens test
In theTollens test
Tollens' reagent (chemical formula Ag(NH3)2OH) is a chemical reagent used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones along with some alpha-hydroxy ketones which can tautomerize into aldehydes. The reagent consists of a solution of silver nitr ...
, after addition of ammoniacal AgNO3 to the sample solution, glucose reduces Ag+ to elemental silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
.
Barfoed test
InBarfoed's test
Barfoed's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of copper(II) acetate to copper(I) oxide (Cu2O), which forms a brick-red precipitate.
::RCHO + 2Cu2+ + 2H2O → RCOOH + Cu2O↓ ...
, a solution of dissolved copper acetate
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-or ...
, sodium acetate
Sodium acetate, CH3COONa, also abbreviated Na O Ac, is the sodium salt of acetic acid. This colorless deliquescent salt has a wide range of uses.
Applications
Biotechnological
Sodium acetate is used as the carbon source for culturing bacteria ...
and acetic acid is added to the solution of the sugar to be tested and subsequently heated in a water bath for a few minutes. Glucose and other monosaccharides rapidly produce a reddish color and reddish brown copper(I) oxide
Copper(I) oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O. It is one of the principal oxides of copper, the other being or copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide (CuO). This red-coloured solid is a component of some antifoulin ...
(Cu2O).
Nylander's test
As a reducing sugar, glucose reacts in the Nylander's test.Other tests
Upon heating a dilutepotassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
solution with glucose to 100 °C, a strong reddish browning and a caramel-like odor develops.Georg Schwedt: ''Zuckersüße Chemie''. John Wiley & Sons, 2012, , p. 102 (in German). Concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
dissolves dry glucose without blackening at room temperature forming sugar sulfuric acid. In a yeast solution, alcoholic fermentation produces carbon dioxide in the ratio of 2.0454 molecules of glucose to one molecule of CO2. Glucose forms a black mass with stannous chloride
Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula . It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot. SnCl2 is widely used as a reducing agent (in acid ...
. In an ammoniacal silver solution, glucose (as well as lactose and dextrin) leads to the deposition of silver. In an ammoniacal lead acetate Lead acetate can refer to:
* Lead subacetate (Basic lead acetate), Pb3(OH)4(CH3COO)2
* Lead(IV) acetate (plumbic acetate), Pb(CH3COO)4
* Lead(II) acetate
Lead(II) acetate (Pb(CH3COO)2), also known as lead acetate, lead diacetate, plumbous acetat ...
solution, white lead glycoside
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
is formed in the presence of glucose, which becomes less soluble on cooking and turns brown. In an ammoniacal copper solution, yellow copper oxide Copper oxide is a compound from the two elements copper and oxygen.
Copper oxide may refer to:
* Copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide, Cu2O)
* Copper(II) oxide (cupric oxide, CuO)
* Copper peroxide (CuO2)
* Copper(III) oxide (Cu2O3)
* Copper(IV) oxide
...
hydrate is formed with glucose at room temperature, while red copper oxide is formed during boiling (same with dextrin, except for with an ammoniacal copper acetate solution). With Hager's reagent, glucose forms mercury oxide Mercury oxide can refer to:
* Mercury(I) oxide (mercurous oxide), Hg2O
* Mercury(II) oxide
Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Hg O. It has a red or orange color. Mer ...
during boiling. An alkaline bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental ...
solution is used to precipitate elemental, black-brown bismuth with glucose. Glucose boiled in an ammonium molybdate Ammonium molybdate can refer to:
*Ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH4)2MoO4
*Ammonium heptamolybdate, (NH4)6Mo7O24, usually encountered as the tetrahydrate
* Ammonium phosphomolybdate, (NH4)3PMo12O40
*Ammonium tetrathiomolybdate, (NH4)2MoS4 this chemical ...
solution turns the solution blue. A solution with indigo carmine
Indigo carmine, or 5,5′-indigodisulfonic acid sodium salt, is an organic salt derived from indigo by aromatic sulfonation, which renders the compound soluble in water. It is approved for use as a food colorant in the U.S and E.U. to produce a ...
and sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
destains when boiled with glucose.
Instrumental quantification
Refractometry and polarimetry
In concentrated solutions of glucose with a low proportion of other carbohydrates, its concentration can be determined with a polarimeter. For sugar mixtures, the concentration can be determined with arefractometer
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an Refractive index, index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index ...
, for example in the Oechsle determination in the course of the production of wine.
Photometric enzymatic methods in solution
The enzyme glucose oxidase (GOx) converts glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide while consuming oxygen. Another enzyme, peroxidase, catalyzes a chromogenic reaction (Trinder reaction) ofphenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it req ...
with 4-aminoantipyrine to a purple dye.
Photometric test-strip method
The test-strip method employs the above-mentioned enzymatic conversion of glucose to gluconic acid to form hydrogen peroxide. The reagents are immobilised on a polymer matrix, the so-called test strip, which assumes a more or less intense color. This can be measured reflectometrically at 510 nm with the aid of an LED-based handheld photometer. This allows routine blood sugar determination by nonscientists. In addition to the reaction of phenol with 4-aminoantipyrine, new chromogenic reactions have been developed that allow photometry at higher wavelengths (550 nm, 750 nm).Amperometric glucose sensor
The electroanalysis of glucose is also based on the enzymatic reaction mentioned above. The produced hydrogen peroxide can be amperometrically quantified by anodic oxidation at a potential of 600 mV. The GOx is immobilized on the electrode surface or in a membrane placed close to the electrode. Precious metals such as platinum or gold are used in electrodes, as well as carbon nanotube electrodes, which e.g. are doped with boron. Cu–CuO nanowires are also used as enzyme-free amperometric electrodes, reaching a detection limit of 50 μmol/L. A particularly promising method is the so-called "enzyme wiring", where the electron flowing during the oxidation is transferred via a molecular wire directly from the enzyme to the electrode.Other sensory methods
There are a variety of other chemical sensors for measuring glucose. Given the importance of glucose analysis in the life sciences, numerous optical probes have also been developed for saccharides based on the use of boronic acids, which are particularly useful for intracellular sensory applications where other (optical) methods are not or only conditionally usable. In addition to the organic boronic acid derivatives, which often bind highly specifically to the 1,2-diol groups of sugars, there are also other probe concepts classified by functional mechanisms which use selective glucose-binding proteins (e.g. concanavalin A) as a receptor. Furthermore, methods were developed which indirectly detect the glucose concentration via the concentration of metabolized products, e.g. by the consumption of oxygen using fluorescence-optical sensors. Finally, there are enzyme-based concepts that use the intrinsic absorbance or fluorescence of (fluorescence-labeled) enzymes as reporters.Copper iodometry
Glucose can be quantified by copper iodometry.Chromatographic methods
In particular, for the analysis of complex mixtures containing glucose, e.g. in honey, chromatographic methods such ashigh performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to pa ...
and gas chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, ...
are often used in combination with mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is use ...
. Taking into account the isotope ratios, it is also possible to reliably detect honey adulteration by added sugars with these methods. Derivatization using silylation reagents is commonly used. Also, the proportions of di- and trisaccharides can be quantified.
In vivo analysis
Glucose uptake in cells of organisms is measured with2-deoxy-D-glucose
2-Deoxy--glucose is a glucose molecule which has the 2-hydroxyl group replaced by hydrogen, so that it cannot undergo further glycolysis. As such; it acts to competitively inhibit the production of glucose-6-phosphate from glucose at the phospho ...
or fluorodeoxyglucose
18F.html" ;"title="sup>18F">sup>18Fluorodeoxyglucose (INN), or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 (USAN and USP), also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated 18F.html" ;"title="sup>18F">sup>18FDG, 2- 18F.html" ;"title="sup>18F">sup>18FDG or F ...
.Donard Dwyer: ''Glucose Metabolism in the Brain.'' Academic Press, 2002, , p. XIII. (18F)fluorodeoxyglucose is used as a tracer in positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including bl ...
in oncology and neurology,Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker
The German Chemical Society (German: ', GDCh) is a learned society and professional association founded in 1949 to represent the interests of German chemists in local, national and international contexts. GDCh "brings together people working in che ...
wayback=20100331071121 ''Anlagen zum Positionspapier der Fachgruppe Nuklearchemie''
, February 2000. where it is by far the most commonly used diagnostic agent.
References
External links
* * {{portal bar, Chemistry, Medicine Chemical pathology Nutrition World Health Organization essential medicines Pyranoses Glycolysis