Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black
liquid mixture of mainly
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
s, and is found in
geological formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exp ...
s. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and
petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil. A
fossil fuel, petroleum is formed when large quantities of dead organisms, mostly
zooplankton and
algae, are buried underneath
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
and subjected to both prolonged heat and pressure.
Petroleum is primarily recovered by
oil drilling. Drilling is carried out after studies of structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, and reservoir characterisation. Recent developments in technologies have also led to exploitation of other
unconventional reserves such as
oil sands
Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and wate ...
and
oil shale.
Once extracted, oil is refined and separated, most easily by
distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the he ...
, into innumerable products for direct use or use in manufacturing. Products include fuels such as
gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
(petrol),
diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engi ...
,
kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was re ...
and
jet fuel
Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel (ATF, also abbreviated avtur) is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial a ...
among many others;
asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
and
lubricants; chemical
reagents used to make
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adapta ...
s;
solvents,
textiles,
refrigerants
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the refrigeration cycle of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where in most cases they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulate ...
,
paint,
synthetic rubber,
fertilizers,
pesticides,
pharmaceuticals, and thousands of others. Petroleum is used in manufacturing a vast variety of materials essential for modern life,
and it is estimated that the world consumes about each day. Petroleum production can be extremely profitable and was critical to global economic development in the 20th century, with some countries, so called "
oil states
A petrostate or oil state is a nation whose economy is heavily dependent on the extraction and export of oil or natural gas. The presence alone of large oil and gas industries does not define a petrostate; countries like Norway, Canada, and the Un ...
", gaining significant economic and international power because of their control of oil production.
Petroleum exploitation and use has had significant negative environmental and social consequences.
Extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pr ...
,
refining and
burning
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
of petroleum fuels all release large quantities of
greenhouse gases, so petroleum is one of the
major contributors to climate change. Other
negative environmental effects include
oil spills, and air and water pollution. Some of these effects have direct and indirect health consequences for humans. Oil has also been a source of conflict leading to both
state-led-wars and other conflicts. Production of petroleum is speculated to reach
peak oil before 2035 as global economies lower dependencies on petroleum as part of
climate change mitigation and a transition towards
renewable energy and
electrification
Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and, in many contexts, the introduction of such power by changing over from an earlier power source.
The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology, economic histo ...
.
Etymology

The word ''petroleum'' comes from Medieval Latin (literally 'rock oil'), which comes from Latin
petra 'rock' (from Greek ) and
oleum
Oleum (Latin ''oleum'', meaning oil), or fuming sulfuric acid, is a term referring to solutions of various compositions of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid, or sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid (also known as pyrosulfuric acid). Ol ...
'oil' (from Greek ).
The term was used in the treatise ''
De Natura Fossilium'', published in 1546 by the German mineralogist
Georg Bauer, also known as Georgius Agricola. In the 19th century, the term ''petroleum'' was often used to refer to
mineral oil
Mineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of higher alkanes from a mineral source, particularly a distillate of petroleum, as distinct from usually edible vegetable oils.
The name 'mineral oil' by itself is imprecise ...
s produced by distillation from mined organic solids such as
cannel coal
Cannel coal or candle coal is a type of bituminous coal, also classified as terrestrial type oil shale. Hutton(1987) Dyni (2006), pp. 3–4 Speight (2012), pp. 6–7 Due to its physical morphology and low mineral content cannel coal is considered ...
(and later
oil shale) and refined oils produced from them; in the United Kingdom, storage (and later transport) of these oils were regulated by a series of Petroleum Acts, from the ''Petroleum Act 1863'' onwards.
History
Early

Petroleum, in one form or another, has been used since ancient times. More than 4300 years ago,
bitumen was mentioned when the Sumerians used it to make boats. Tablet of the legend of the birth of
Sargon of Akkad, mentioned a basket which was closed by straw and bitumen. More than 4000 years ago, according to
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
and
Diodorus Siculus,
asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
was used in the construction of the walls and towers of
Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
; there were oil pits near Ardericca (near Babylon), and a pitch spring on
Zacynthus.
Great quantities of it were found on the banks of the river
Issus, one of the tributaries of the
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
. Ancient
Persian tablets indicate the medicinal and lighting uses of petroleum in the upper levels of their society.
The use of petroleum in ancient China dates back to more than 2000 years ago. The ''
I Ching'', one of the earliest Chinese writings, cites that oil in its raw state, without refining, was first discovered, extracted, and used in China in the first century BCE. In addition, the Chinese were the first to record the use of petroleum as fuel as early as the fourth century BCE. By 347 CE, oil was produced from bamboo-drilled wells in China.
Crude oil was often distilled by
Persian chemists, with clear descriptions given in Arabic handbooks such as those of
Muhammad ibn Zakarīya Rāzi
Abū Bakr al-Rāzī (full name: ar, أبو بکر محمد بن زکریاء الرازي, translit=Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Zakariyyāʾ al-Rāzī, label=none), () rather than ar, زکریاء, label=none (), as for example in , or in . In m ...
(Rhazes). The streets of
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
were paved with
tar, derived from petroleum that became accessible from natural fields in the region. In the 9th century,
oil fields were exploited in the area around modern
Baku,
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
. These fields were described by the
Arab geographer
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age (variously dated between the 8th century and 16th century). Muslim scholars made advances to the map-m ...
Abu al-Hasan 'Alī al-Mas'ūdī
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus ...
in the 10th century, and by
Marco Polo in the 13th century, who described the output of those wells as hundreds of shiploads.
Arab and Persian chemists also distilled crude oil in order to produce
flammable products for military purposes. Through
Islamic Spain, distillation became available in
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
by the 12th century. It has also been present in Romania since the 13th century, being recorded as păcură.
Sophisticated oil pits, deep, were dug by the
Seneca People and other
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
in
Western Pennsylvania as early as 1415–1450. The French General
Louis-Joseph de Montcalm encountered Seneca using petroleum for ceremonial fires and as a healing lotion during a visit to Fort Duquesne in 1750.
Early British explorers to
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
documented a flourishing oil extraction industry based in
Yenangyaung that, in 1795, had hundreds of hand-dug wells under production.
Pechelbronn (Pitch fountain) is said to be the first European site where petroleum has been explored and used. The still active Erdpechquelle, a spring where petroleum appears mixed with water has been used since 1498, notably for medical purposes. Oil sands have been mined since the 18th century.
In
Wietze in lower Saxony, natural asphalt/bitumen has been explored since the 18th century. Both in Pechelbronn as in Wietze, the coal industry dominated the petroleum technologies.
Modern
Chemist
James Young noticed a natural petroleum seepage in the
Riddings colliery at
Alfreton
Alfreton ( ) is a town and civil parish in the Amber Valley district of Derbyshire, England. The town was formerly a Norman Manor and later an Urban District. The population of the Alfreton parish was 7,971 at the 2011 Census. The villages of ...
,
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the nor ...
from which he distilled a light thin oil suitable for use as lamp oil, at the same time obtaining a more viscous oil suitable for lubricating machinery. In 1848, Young set up a small business refining the crude oil.
Young eventually succeeded, by distilling
cannel coal
Cannel coal or candle coal is a type of bituminous coal, also classified as terrestrial type oil shale. Hutton(1987) Dyni (2006), pp. 3–4 Speight (2012), pp. 6–7 Due to its physical morphology and low mineral content cannel coal is considered ...
at a low heat, in creating a fluid resembling petroleum, which when treated in the same way as the seep oil gave similar products. Young found that by slow distillation he could obtain a number of useful liquids from it, one of which he named "paraffine oil" because at low temperatures it congealed into a substance resembling paraffin wax.
The production of these oils and solid
paraffin wax
Paraffin wax (or petroleum wax) is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins t ...
from coal formed the subject of his patent dated 17 October 1850. In 1850 Young & Meldrum and Edward William Binney entered into partnership under the title of E.W. Binney & Co. at
Bathgate
Bathgate ( sco, Bathket or , gd, Both Chèit) is a town in West Lothian, Scotland, west of Livingston and adjacent to the M8 motorway. Nearby towns are Armadale, Blackburn, Linlithgow, Livingston, West Calder and Whitburn. Situated south ...
in
West Lothian and E. Meldrum & Co. at Glasgow; their works at Bathgate were completed in 1851 and became the first truly commercial oil-works in the world with the first modern oil refinery.

The world's first oil refinery was built in 1856 by
Ignacy Łukasiewicz. His achievements also included the discovery of how to distill kerosene from seep oil, the invention of the modern kerosene lamp (1853), the introduction of the first modern street lamp in Europe (1853), and the construction of the world's first modern oil well (1854).
The demand for petroleum as a fuel for lighting in North America and around the world quickly grew.
Edwin Drake
Edwin Laurentine Drake (March 29, 1819 – November 9, 1880), also known as Colonel Drake, was an American businessman and the first American to successfully drill for oil.
Early life
Edwin Drake was born in Greenville, New York on March 2 ...
's
1859 well near Titusville, Pennsylvania, is popularly considered the first modern well. Already 1858 Georg Christian Konrad Hunäus had found a significant amount of petroleum while drilling for
lignite
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible, sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35%, and is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat ...
1858 in
Wietze, Germany. Wietze later provided about 80% of the German consumption in the Wilhelminian Era. The production stopped in 1963, but Wietze has hosted a Petroleum Museum since 1970.
Drake's well is probably singled out because it was drilled, not dug; because it used a steam engine; because there was a company associated with it; and because it touched off a major boom. However, there was considerable activity before Drake in various parts of the world in the mid-19th century. A group directed by Major Alexeyev of the Bakinskii Corps of Mining Engineers hand-drilled a well in the Baku region of Bibi-Heybat in 1846. There were engine-drilled wells in West Virginia in the same year as Drake's well. An early commercial well was hand dug in
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
in 1853, and another in nearby
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
in 1857. At around the same time the world's first, small, oil refinery was opened at
Jasło in Poland, with a larger one opened at
Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest.
The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Blejoi commun ...
in Romania shortly after. Romania is the first country in the world to have had its annual crude oil output officially recorded in international statistics: 275 tonnes for 1857.
The
first commercial oil well in Canada became operational in 1858 at
Oil Springs, Ontario (then
Canada West).
[Oil Museum of Canada, Black Gold: Canada's Oil Heritage, Oil Springs: Boom & Bust](_blank)
Businessman
James Miller Williams dug several wells between 1855 and 1858 before discovering a rich reserve of oil four metres below ground. Williams extracted 1.5 million litres of crude oil by 1860, refining much of it into kerosene lamp oil. Williams's well became commercially viable a year before Drake's Pennsylvania operation and could be argued to be the first commercial oil well in North America. The discovery at Oil Springs touched off an
oil boom which brought hundreds of speculators and workers to the area. Advances in drilling continued into 1862 when local driller Shaw reached a depth of 62 metres using the spring-pole drilling method. On January 16, 1862, after an explosion of
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
, Canada's first oil gusher came into production, shooting into the air at a recorded rate of per day. By the end of the 19th century the Russian Empire, particularly the
Branobel
The Petroleum Production Company Nobel Brothers, Limited, or Branobel (short for братьев Нобель "brat'yev Nobel" — "Nobel Brothers" in Russian), was an oil company set up by Ludvig Nobel and Baron Peter von Bilderling. It operated ...
company in
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, had taken the lead in production.
[Akiner(2004), p. 5]

Access to oil was and still is a major factor in several military conflicts of the twentieth century, including
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, during which oil facilities were a major strategic asset and were
extensively bombed. The
German invasion of the Soviet Union included the goal to capture the
Baku oilfields, as it would provide much needed oil-supplies for the German military which was suffering from blockades. Oil exploration in North America during the early 20th century later led to the US's becoming the leading producer by mid-century. As petroleum production in the US peaked during the 1960s, however, the United States was surpassed by Saudi Arabia and the Soviet Union.
In
1973, Saudi Arabia and other
Arab nations imposed an
oil embargo An oil embargo is an economic situation wherein entities engage in an embargo to limit the transport of petroleum to or from an area, in order to exact some desired outcome. One commentator states, " oil embargo is not a common commercial practice; ...
against the United States, United Kingdom, Japan and other Western nations which supported
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
in the
Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was an armed conflict fought from October 6 to 25, 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by E ...
of October 1973. The embargo caused an
oil crisis. This was followed by the
1979 oil crisis, which was caused by a drop in
oil production in the wake of the
Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dyna ...
and caused oil prices to more than double. The two oil price shocks had many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. In particular, they led to sustained reductions in demand as a result of substitution to other fuels (especially coal and nuclear) and improvements in energy efficiency, facilitated by government policies. High oil prices also induced investment in oil production by non-OPEC countries, including Prudhoe Bay in Alaska, the North Sea offshore fields of the United Kingdom and Norway, the Cantarell offshore field of Mexico, and oil sands in Canada.
Today, about 90 percent of vehicular fuel needs are met by oil. Petroleum also makes up 40 percent of total energy consumption in the United States, but is responsible for only 1 percent of electricity generation. Petroleum's worth as a portable, dense energy source powering the vast majority of vehicles and as the base of many industrial chemicals makes it one of the world's most important
commodities.
The top three oil producing countries are the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
,
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, and
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
.
In 2018, due in part to developments in
hydraulic fracturing and
horizontal drilling, the United States became the world's largest producer.
About 80 percent of the world's readily accessible reserves are located in the Middle East, with 62.5 percent coming from the Arab 5:
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
,
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (Middle East, The Middle East). It is ...
,
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
,
Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
and
Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
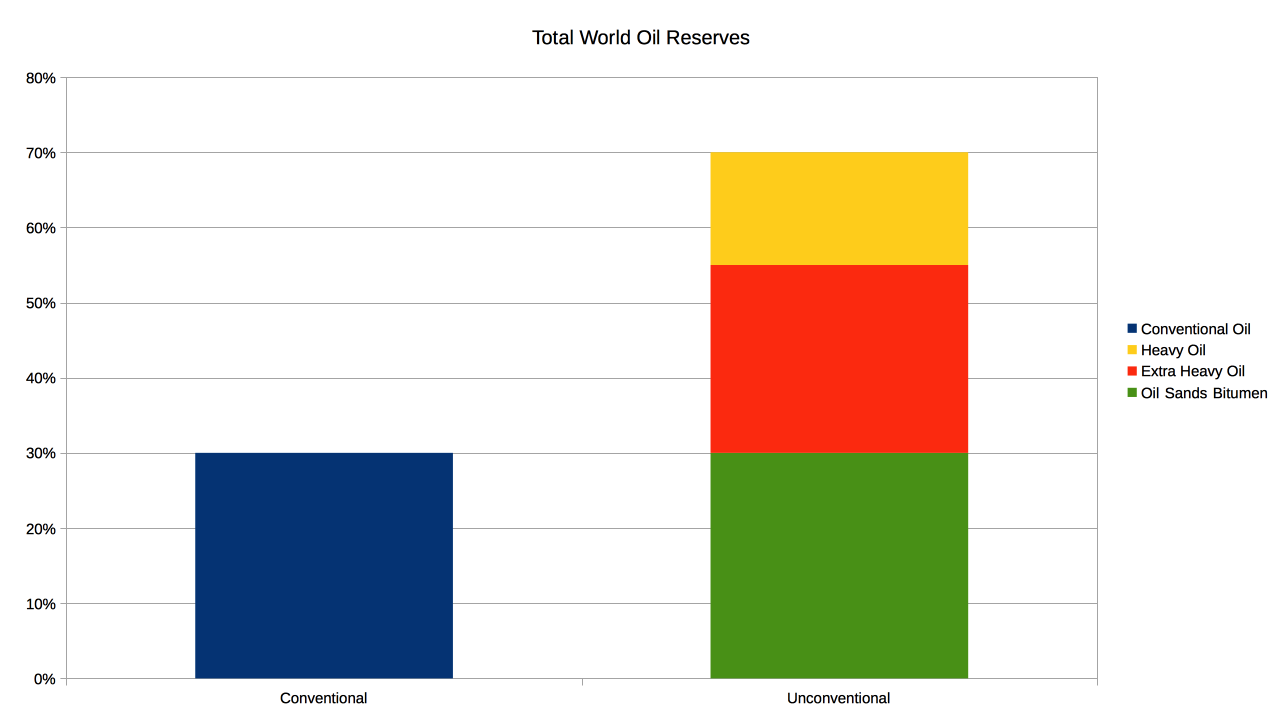
. A large portion of the world's total oil exists as unconventional sources, such as
bitumen in
Athabasca oil sands and
extra heavy oil in the
Orinoco Belt. While significant volumes of oil are extracted from oil sands, particularly in Canada, logistical and technical hurdles remain, as oil extraction requires large amounts of heat and water, making its net energy content quite low relative to conventional crude oil. Thus, Canada's oil sands are not expected to provide more than a few million barrels per day in the foreseeable future.
Composition
Petroleum includes not only crude oil, but all liquid, gaseous and solid
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
s. Under surface
pressure and temperature conditions, lighter hydrocarbons
methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
,
ethane,
propane and
butane exist as gases, while
pentane and heavier hydrocarbons are in the form of liquids or solids. However, in an underground
oil reservoir the proportions of gas, liquid, and solid depend on subsurface conditions and on the
phase diagram of the petroleum mixture.
An
oil well produces predominantly crude oil, with some natural gas
dissolved in it. Because the pressure is lower at the surface than underground, some of the gas will come out of
solution
Solution may refer to:
* Solution (chemistry), a mixture where one substance is dissolved in another
* Solution (equation), in mathematics
** Numerical solution, in numerical analysis, approximate solutions within specified error bounds
* Solutio ...
and be recovered (or burned) as ''associated gas'' or ''solution gas''. A
gas well produces predominantly
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
. However, because the underground temperature is higher than at the surface, the gas may contain heavier hydrocarbons such as pentane,
hexane
Hexane () is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and has the molecular formula C6H14.
It is a colorless liquid, odorless when pure, and with boiling points approximately . It is widely used as a cheap, relative ...
, and
heptane in the
gaseous state. At surface conditions these will
condense out of the gas to form "
natural-gas condensate
Natural-gas condensate, also called natural gas liquids, is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. Some gas species within the raw natu ...
", often shortened to ''condensate.'' Condensate resembles gasoline in appearance and is similar in composition to some
volatile light crude oils.
The proportion of light hydrocarbons in the petroleum mixture varies greatly among different
oil fields, ranging from as much as 97 percent by weight in the lighter oils to as little as 50 percent in the heavier oils and
bitumens.
The hydrocarbons in crude oil are mostly
alkanes,
cycloalkanes and various
aromatic hydrocarbons, while the other organic compounds contain
nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
,
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and
sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, and trace amounts of metals such as iron, nickel, copper and
vanadium. Many oil reservoirs contain live bacteria. The exact molecular composition of crude oil varies widely from formation to formation but the proportion of
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements canno ...
s varies over fairly narrow limits as follows:
Four different types of hydrocarbon molecules appear in crude oil. The relative percentage of each varies from oil to oil, determining the properties of each oil.
Crude oil varies greatly in appearance depending on its composition. It is usually black or dark brown (although it may be yellowish, reddish, or even greenish). In the reservoir it is usually found in association with natural gas, which being lighter forms a "gas cap" over the petroleum, and
saline water which, being heavier than most forms of crude oil, generally sinks beneath it. Crude oil may also be found in a semi-solid form mixed with sand and water, as in the
Athabasca oil sands in Canada, where it is usually referred to as crude
bitumen. In Canada, bitumen is considered a sticky, black, tar-like form of crude oil which is so thick and heavy that it must be heated or diluted before it will flow. Venezuela also has large amounts of oil in the
Orinoco oil sands
The Orinoco Belt is a territory in the southern strip of the eastern Orinoco River Basin in Venezuela which overlies the world's largest deposits of petroleum. Its local Spanish name is ''Faja Petrolífera del Orinoco'' (Orinoco Petroleum Belt).
...
, although the hydrocarbons trapped in them are more fluid than in Canada and are usually called
extra heavy oil. These oil sands resources are called
unconventional oil to distinguish them from oil which can be extracted using traditional oil well methods. Between them, Canada and
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
contain an estimated of bitumen and extra-heavy oil, about twice the volume of the world's reserves of conventional oil.
Petroleum is used mostly, by volume, for refining into
fuel oil and gasoline, both important ''
primary energy
Primary energy (PE) is an energy form found in nature that has not been subjected to any human engineered conversion process. It is energy contained in raw fuels, and other forms of energy, including waste, received as input to a system. Prim ...
'' sources. Eight-four percent by volume of the hydrocarbons present in petroleum is converted into energy-rich fuels (petroleum-based fuels), including gasoline, diesel, jet, heating, and other fuel oils, and
liquefied petroleum gas. The lighter grades of crude oil produce the best yields of these products, but as the world's reserves of light and medium oil are depleted,
oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, li ...
are increasingly having to process heavy oil and bitumen, and use more complex and expensive methods to produce the products required. Because heavier crude oils have too much carbon and not enough hydrogen, these processes generally involve removing carbon from or adding hydrogen to the molecules, and using
fluid catalytic cracking to convert the longer, more complex molecules in the oil to the shorter, simpler ones in the fuels.
Due to its high
energy density, easy transportability and
relative abundance, oil has become the world's most important source of energy since the mid-1950s. Petroleum is also the raw material for many
chemical products, including
pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
s,
solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s,
fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s,
pesticides, and plastics; the 16 percent not used for energy production is converted into these other materials. Petroleum is found in
porous rock formations in the upper
strata of some areas of the
Earth's crust. There is also petroleum in
oil sands (tar sands). Known
oil reserves are typically estimated at 190 km
3 (1.2
trillion
''Trillion'' is a number with two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000,000, i.e. one million million, or (ten to the twelfth power), as defined on the short scale. This is now the meaning in both American and British English.
* 1,000,000,000,00 ...
(short scale) barrels
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
) without oil sands, or 595 km
3 (3.74 trillion barrels) with oil sands. Consumption is currently around per day, or 4.9 km
3 per year, yielding a remaining oil supply of only about 120 years, if current demand remains static. More recent studies, however, put the number at around 50 years.
Chemistry

Petroleum is mainly a mixture of
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
s, i.e. containing only carbon and hydrogen. The most common components are
alkanes (paraffins),
cycloalkanes (
naphthenes), and
aromatic hydrocarbons. They generally have from 5 to 40 carbon atoms per molecule, although trace amounts of shorter or longer molecules may be present in the mixture.
The alkanes from
pentane (C
5H
12) to
octane (C
8H
18) are
refined into gasoline, the ones from
nonane
Nonane is a linear alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. It is a colorless, flammable liquid, occurring primarily in the component of the petroleum distillate fraction commonly called kerosene, which is used as a heating, tractor, a ...
(C
9H
20) to
hexadecane
Hexadecane (also called cetane) is an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C16H34. Hexadecane consists of a chain of 16 carbon atoms, with three hydrogen atoms bonded to the two end carbon atoms, and two hydrogens bonded to each of the 1 ...
(C
16H
34) into
diesel fuel
Diesel fuel , also called diesel oil, is any liquid fuel specifically designed for use in a diesel engine, a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignition takes place without a spark as a result of compression of the inlet air and ...
,
kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was re ...
and
jet fuel
Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel (ATF, also abbreviated avtur) is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial a ...
. Alkanes with more than 16 carbon atoms can be refined into
fuel oil and
lubricating oil. At the heavier end of the range,
paraffin wax
Paraffin wax (or petroleum wax) is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins t ...
is an alkane with approximately 25 carbon atoms, while
asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
has 35 and up, although these are usually
cracked by modern refineries into more valuable products. The shortest molecules, those with four or fewer carbon atoms, are in a gaseous state at room temperature. They are the petroleum gases. Depending on demand and the cost of recovery, these gases are either
flared off, sold as
liquefied petroleum gas under pressure, or used to power the refinery's own burners. During the winter, butane (C
4H
10), is blended into the gasoline pool at high rates, because its high vapour pressure assists with cold starts. Liquified under pressure slightly above atmospheric, it is best known for powering cigarette lighters, but it is also a main fuel source for many developing countries. Propane can be liquified under modest pressure, and is consumed for just about every application relying on petroleum for energy, from cooking to heating to transportation.
The ''aromatic hydrocarbons'' are
unsaturated hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, a ...
which have one or more planar six-carbon rings called
benzene rings, to which hydrogen atoms are attached with the formula C
nH
2n-6. They tend to burn with a sooty flame, and many have a sweet aroma. Some are
carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive sub ...
.
These different molecules are separated by
fractional distillation at an oil refinery to produce gasoline, jet fuel, kerosene, and other hydrocarbons. For example,
2,2,4-trimethylpentane (isooctane), widely used in
gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
, has a chemical formula of C
8H
18 and it reacts with oxygen
exothermically:
:2
(''l'') + 25
(''g'') → 16
(''g'') + 18
(''g'') (ΔH = −5.51 MJ/mol of octane)
The number of various molecules in an oil sample can be determined by laboratory analysis. The molecules are typically extracted in a
solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
, then separated in a
gas chromatograph
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substan ...
, and finally determined with a suitable
detector, such as a
flame ionization detector or a
mass spectrometer. Due to the large number of co-eluted hydrocarbons within oil, many cannot be resolved by traditional gas chromatography and typically appear as a hump in the chromatogram. This
Unresolved Complex Mixture (UCM) of hydrocarbons is particularly apparent when analysing weathered oils and extracts from tissues of organisms exposed to oil. Some of the components of oil will mix with water: the
water associated fraction of the oil.
Incomplete combustion of petroleum or gasoline results in production of toxic byproducts. Too little oxygen during combustion results in the formation of
carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
. Due to the high temperatures and high pressures involved, exhaust gases from gasoline combustion in car engines usually include
nitrogen oxides which are responsible for creation of
photochemical smog.
Formation
Fossil petroleum

Petroleum is a
fossil fuel derived from ancient
fossilized organic materials, such as
zooplankton and
algae.
Vast amounts of these remains settled to sea or lake bottoms where they were covered in
stagnant water
Water stagnation occurs when water stops flowing. Stagnant water can be a major environmental hazard.
Dangers
Malaria and dengue are among the main dangers of stagnant water, which can become a breeding ground for the mosquitoes that tran ...
(water with no dissolved
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
) or
sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
s such as
mud and
silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
faster than they could
decompose aerobically. Approximately 1
m below this sediment, water oxygen concentration was low, below 0.1 mg/L, and
anoxic conditions existed. Temperatures also remained constant.
As further layers settled to the sea or lake bed, intense heat and pressure built up in the lower regions. This process caused the organic matter to change, first into a waxy material known as
kerogen, found in various
oil shales around the world, and then with more heat into liquid and gaseous
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
s via a process known as
catagenesis. Formation of petroleum occurs from hydrocarbon
pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements '' ...
in a variety of mainly
endothermic
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. ...
reactions at high temperature or pressure, or both.
These phases are described in detail below.
Anaerobic decay
In the absence of plentiful oxygen,
''aerobic'' bacteria were prevented from decaying the organic matter after it was buried under a layer of sediment or water. However,
''anaerobic'' bacteria were able to reduce
sulfates and
nitrates among the matter to
H2S and
N2 respectively by using the matter as a source for other reactants. Due to such anaerobic bacteria, at first this matter began to break apart mostly via
hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
:
polysaccharides and
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s were hydrolyzed to
simple sugars and
amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s respectively. These were further anaerobically
oxidized
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
at an accelerated rate by the
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s of the bacteria: e.g., amino acids went through
oxidative deamination to
imino acids, which in turn reacted further to
ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
and
α-keto acids.
Monosaccharides in turn ultimately decayed to
CO2 and
methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
. The anaerobic decay products of amino acids, monosaccharides,
phenols and
aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl gro ...
s combined to
fulvic acid Humic substances (HS) are organic compounds that are important components of humus, the major organic fraction of soil, peat, and coal (and also a constituent of many upland streams, dystrophic lakes, and ocean water). For a long era in the 19th an ...
s.
Fats and
waxes were not extensively hydrolyzed under these mild conditions.
Kerogen formation
Some phenolic compounds produced from previous reactions worked as
bactericide
A bactericide or bacteriocide, sometimes abbreviated Bcidal, is a substance which kills bacteria. Bactericides are disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics.
However, material surfaces can also have bactericidal properties based solely on their ...
s and the
actinomycetales
The Actinomycetales is an order of Actinomycetota. A member of the order is often called an actinomycete. Actinomycetales are generally gram-positive and anaerobic and have mycelia in a filamentous and branching growth pattern. Some actinomycete ...
order of bacteria also produced antibiotic compounds (e.g.,
streptomycin). Thus the action of anaerobic bacteria ceased at about 10 m below the water or sediment. The mixture at this depth contained fulvic acids, unreacted and partially reacted fats and waxes, slightly modified
lignin, resins and other hydrocarbons.
As more layers of organic matter settled to the sea or lake bed, intense heat and pressure built up in the lower regions.
As a consequence, compounds of this mixture began to combine in poorly understood ways to
kerogen. Combination happened in a similar fashion as
phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it r ...
and
formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) ( systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
molecules react to
urea-formaldehyde resins, but kerogen formation occurred in a more complex manner due to a bigger variety of reactants. The total process of kerogen formation from the beginning of anaerobic decay is called diagenesis, a word that means a transformation of materials by dissolution and recombination of their constituents.
Transformation of kerogen into fossil fuels
Kerogen formation continued to the depth of about 1
km from the Earth's surface where temperatures may reach around 50
°C
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The d ...
. Kerogen formation represents a halfway point between organic matter and fossil fuels: kerogen can be exposed to oxygen, oxidize and thus be lost, or it could be buried deeper inside the
Earth's crust and be subjected to conditions which allow it to slowly transform into fossil fuels like petroleum. The latter happened through catagenesis in which the reactions were mostly
radical rearrangements of kerogen. These reactions took thousands to millions of years and no external reactants were involved. Due to radical nature of these reactions, kerogen reacted towards two classes of products: those with low H/C ratio (
anthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is co ...
or products similar to it) and those with high H/C ratio (
methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
or products similar to it); i.e., carbon-rich or hydrogen-rich products. Because catagenesis was closed off from external reactants, the resulting composition of the fuel mixture was dependent on the composition of the kerogen via reaction
stoichiometry
Stoichiometry refers to the relationship between the quantities of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equ ...
. Three types of kerogen exist: type I (algal), II (liptinic) and III (humic), which were formed mainly from
algae,
plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cruc ...
and
woody plants (this term includes
trees,
shrubs and
liana
A liana is a long- stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the canopy in search of direct sunlight. The word ''liana'' does not refer to a t ...
s) respectively.
Catagenesis was
pyrolytic despite the fact that it happened at relatively low temperatures (when compared to commercial pyrolysis plants) of 60 to several hundred °C. Pyrolysis was possible because of the long reaction times involved. Heat for catagenesis came from the decomposition of
radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
materials of the crust, especially
40K,
232Th,
235U and
238U. The heat varied with
geothermal gradient and was typically 10-30 °C per km of depth from the Earth's surface. Unusual
magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
intrusions, however, could have created greater localized heating.
Oil window (temperature range)
Geologists often refer to the temperature range in which oil forms as an ''"oil window"''.
Below the minimum temperature oil remains trapped in the form of kerogen. Above the maximum temperature the oil is converted to natural gas through the process of
thermal cracking. Sometimes, oil formed at extreme depths may migrate and become trapped at a much shallower level. The
Athabasca Oil Sands are one example of this.
Abiogenic petroleum
An alternative mechanism to the one described above was proposed by Russian scientists in the mid-1850s, the hypothesis of
abiogenic petroleum origin (petroleum formed by inorganic means), but this is contradicted by geological and
geochemical evidence.
Abiogenic sources of oil have been found, but never in commercially profitable amounts. "The controversy isn't over whether abiogenic oil reserves exist," said Larry Nation of the American Association of Petroleum Geologists. "The controversy is over how much they contribute to Earth's overall reserves and how much time and effort geologists should devote to seeking them out."
Reservoirs

Three conditions must be present for oil reservoirs to form:
* a
source rock
In petroleum geology, source rock is rock which has generated hydrocarbons or which could generate hydrocarbons. Source rocks are one of the necessary elements of a working petroleum system. They are organic-rich sediments that may have been depo ...
rich in
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
material buried deeply enough for subterranean heat to cook it into oil,
* a
porous and
permeable reservoir rock where it can accumulate,
* a
caprock (seal) or other mechanism to prevent the oil from escaping to the surface. Within these reservoirs, fluids will typically organize themselves like a three-layer cake with a layer of water below the oil layer and a layer of gas above it, although the different layers vary in size between reservoirs. Because most hydrocarbons are less dense than rock or
water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, they often migrate upward through adjacent rock layers until either reaching the surface or becoming trapped within porous rocks (known as
reservoirs) by impermeable rocks above. However, the process is influenced by underground water flows, causing oil to migrate hundreds of kilometres horizontally or even short distances downward before becoming trapped in a reservoir. When hydrocarbons are concentrated in a trap, an
oil field forms, from which the liquid can be extracted by
drilling and
pumping.
The reactions that produce oil and natural gas are often modeled as first order breakdown reactions, where hydrocarbons are broken down to oil and natural gas by a set of parallel reactions, and oil eventually breaks down to natural gas by another set of reactions. The latter set is regularly used in
petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewabl ...
plants and
oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, li ...
.
Petroleum has mostly been recovered by
oil drilling (natural petroleum springs are rare). Drilling is carried out after studies of structural geology (at the reservoir scale), sedimentary basin analysis, and reservoir characterisation (mainly in terms of the
porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measur ...
and
permeability of geologic reservoir structures). Recent improvements to technologies have also led to exploitation of other unconventional reserves such as
oil sands
Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and wate ...
and
oil shale. Wells are drilled into oil reservoirs to extract the crude oil. "Natural lift" production methods that rely on the natural reservoir pressure to force the oil to the surface are usually sufficient for a while after reservoirs are first tapped. In some reservoirs, such as in the Middle East, the natural pressure is sufficient over a long time. The natural pressure in most reservoirs, however, eventually dissipates. Then the oil must be extracted using "
artificial lift" means. Over time, these "primary" methods become less effective and "secondary" production methods may be used. A common secondary method is
"waterflood" or injection of water into the reservoir to increase pressure and force the oil to the drilled shaft or "wellbore." Eventually "tertiary" or "enhanced" oil recovery methods may be used to increase the oil's flow characteristics by injecting steam, carbon dioxide and other gases or chemicals into the reservoir. In the United States, primary production methods account for less than 40 percent of the oil produced on a daily basis, secondary methods account for about half, and tertiary recovery the remaining 10 percent. Extracting oil (or "bitumen") from oil/tar sand and oil shale deposits requires mining the sand or shale and heating it in a vessel or retort, or using "in-situ" methods of injecting heated liquids into the deposit and then pumping the liquid back out saturated with oil.
Unconventional oil reservoirs
Oil-eating bacteria
biodegrade oil that has escaped to the surface.
Oil sands
Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and wate ...
are reservoirs of partially biodegraded oil still in the process of escaping and being biodegraded, but they contain so much migrating oil that, although most of it has escaped, vast amounts are still present—more than can be found in conventional oil reservoirs. The lighter fractions of the crude oil are destroyed first, resulting in reservoirs containing an extremely heavy form of crude oil, called crude bitumen in Canada, or extra-heavy crude oil in
Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. These two countries have the world's largest deposits of oil sands.
On the other hand,
oil shales
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitute ...
are source rocks that have not been exposed to heat or pressure long enough to convert their trapped hydrocarbons into crude oil. Technically speaking, oil shales are not always shales and do not contain oil, but are fined-grain sedimentary rocks containing an insoluble organic solid called
kerogen. The kerogen in the rock can be converted into crude oil using heat and pressure to simulate natural processes. The method has been known for centuries and was patented in 1694 under British Crown Patent No. 330 covering, "A way to extract and make great quantities of pitch, tar, and oil out of a sort of stone." Although oil shales are found in many countries, the United States has the world's largest deposits.
Classification

The
petroleum industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The larg ...
generally classifies crude oil by the geographic location it is produced in (e.g.,
West Texas Intermediate,
Brent, or
Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
), its
API gravity
The American Petroleum Institute gravity, or API gravity, is a measure of how heavy or light a petroleum liquid is compared to water: if its API gravity is greater than 10, it is lighter and floats on water; if less than 10, it is heavier and sink ...
(an oil industry measure of density), and its sulfur content. Crude oil may be considered ''
light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
'' if it has low density, ''
heavy'' if it has high density, or ''medium'' if it has a density between that of ''light'' and ''heavy''. Additionally, it may be referred to as ''
sweet'' if it contains relatively little sulfur or ''
sour'' if it contains substantial amounts of sulfur.
The geographic location is important because it affects transportation costs to the refinery. ''Light'' crude oil is more desirable than ''heavy'' oil since it produces a higher yield of gasoline, while ''sweet'' oil commands a higher price than ''sour'' oil because it has fewer environmental problems and requires less refining to meet sulfur standards imposed on fuels in consuming countries. Each crude oil has unique molecular characteristics which are revealed by the use of
Crude oil assay analysis in petroleum laboratories.
Barrels
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
from an area in which the crude oil's molecular characteristics have been determined and the oil has been classified are used as pricing
references throughout the world. Some of the common reference crudes are:
*
West Texas Intermediate (WTI), a very high-quality, sweet, light oil delivered at
Cushing, Oklahoma for North American oil
*
Brent Blend, consisting of 15 oils from fields in the
Brent and
Ninian systems in the
East Shetland Basin of the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
. The oil is landed at
Sullom Voe
Sullom Voe is an inlet of the North Sea between the parishes of Delting and Northmavine in Shetland, Scotland. It is a location of the Sullom Voe oil terminal and Shetland Gas Plant. The word Voe is from the Old Norse ' and denotes a small b ...
terminal in
Shetland. Oil production from Europe, Africa and Middle Eastern oil flowing West tends to be priced off this oil, which forms a
benchmark
*
Dubai-Oman, used as benchmark for Middle East sour crude oil flowing to the Asia-Pacific region
*
Tapis (from
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
, used as a reference for light Far East oil)
* Minas (from
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
, used as a reference for heavy Far East oil)
* The
OPEC Reference Basket
The OPEC Reference Basket (ORB), also referred to as the OPEC Basket, is a weighted average of prices for petroleum blends produced by OPEC members. It is used as an important benchmark for crude oil prices. OPEC has often attempted to keep the p ...
, a weighted average of oil blends from various
OPEC (The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) countries
*
Midway Sunset Heavy, by which heavy oil in California is priced
*
Western Canadian Select the benchmark crude oil for emerging heavy, high TAN (acidic) crudes.
There are declining amounts of these benchmark oils being produced each year, so other oils are more commonly what is actually delivered. While the reference price may be for West Texas Intermediate delivered at Cushing, the actual oil being traded may be a discounted Canadian heavy oil—Western Canadian Select—delivered at
Hardisty,
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest T ...
, and for a Brent Blend delivered at Shetland, it may be a discounted Russian Export Blend delivered at the port of
Primorsk.
Once extracted, oil is refined and separated, most easily by
distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the he ...
, into numerous products for direct use or use in manufacturing, such as
petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
(gasoline),
diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engi ...
and
kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was re ...
to
asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
and chemical
reagents (
ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds).
Ethylene ...
,
propylene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH=CH2. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petro ...
,
butene
Butene, also known as butylene, is an alkene with the formula . The word ''butene'' may refer to any of the individual compounds. They are colourless gases that are present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for ...
,
acrylic acid,
para-xylene
''p''-Xylene ( ''para''-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The ''p-'' stands for ''para-'', indicating that the two methyl groups in ''p''-xylene occupy the diamet ...
) used to make
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adapta ...
s,
pesticides and
pharmaceuticals.
Industry
Transport
In the 1950s, shipping costs made up 33 percent of the price of oil transported from the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
to the United States,
but due to the development of
supertankers in the 1970s, the cost of shipping dropped to only 5 percent of the price of Persian oil in the US.
Due to the increase of the value of the crude oil during the last 30 years, the share of the shipping cost on the final cost of the delivered commodity was less than 3% in 2010.
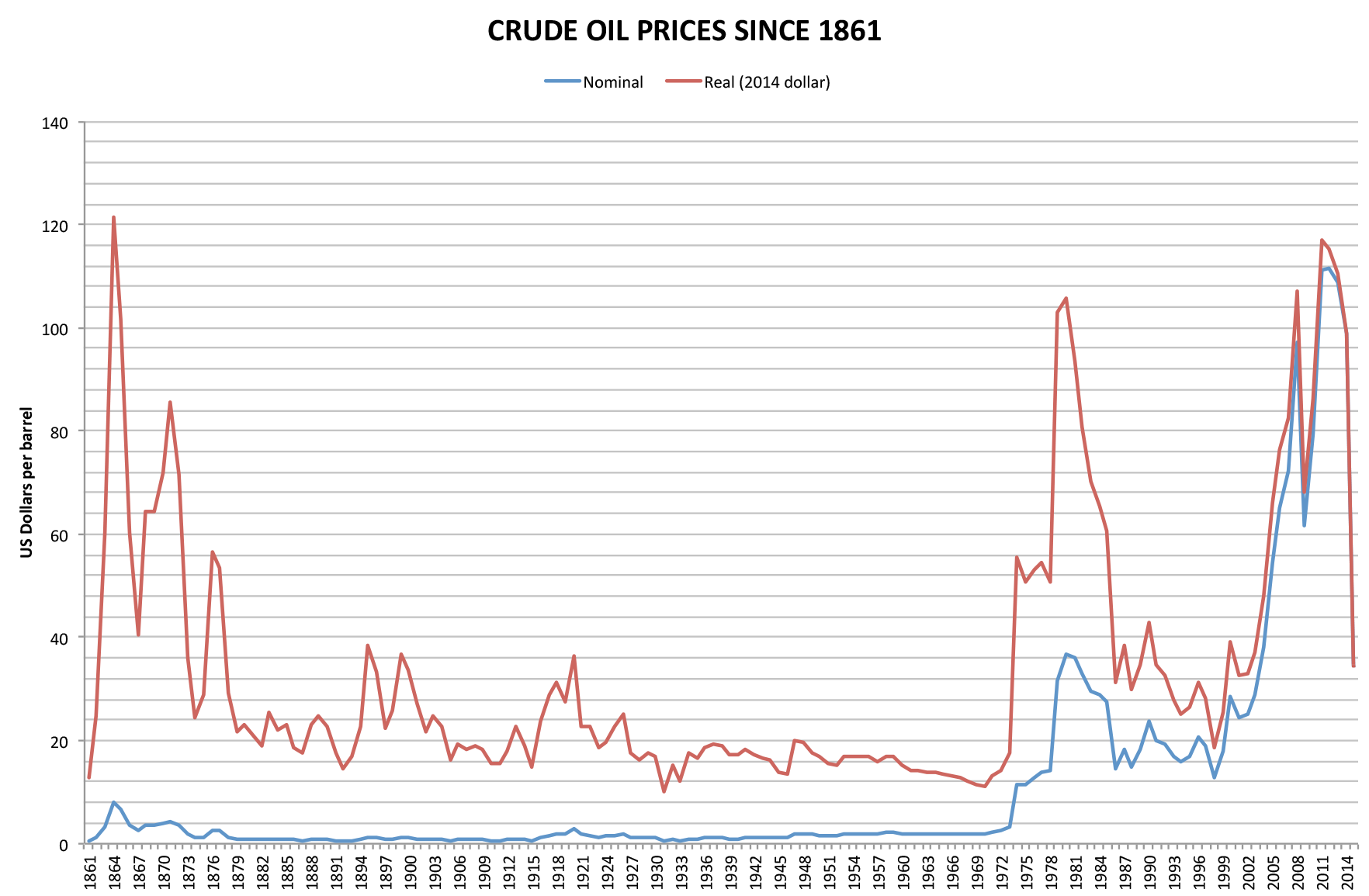
Price
Trade
Crude oil is traded as a future on the Nymex exchange. Futures contracts are agreements in which buyers and sellers agree to purchase and deliver specific amounts of physical crude oil on a given date in the future. Each contract covers 1000 barrels and can be purchased up to nine years into the future.
Below are the contract specifications for crude oil:
Uses
The chemical structure of petroleum is
heterogeneous, composed of hydrocarbon chains of different lengths. Because of this, petroleum may be taken to
oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, li ...
and the hydrocarbon chemicals separated by
distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the he ...
and treated by other
chemical processes, to be used for a variety of purposes. The total cost per plant is about 9 billion dollars.
Fuels
The most common
distillation fractions of petroleum are
fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy b ...
s. Fuels include (by increasing boiling temperature range):
Petroleum classification according to chemical composition.
Other derivatives
Certain types of resultant hydrocarbons may be mixed with other non-hydrocarbons, to create other end products:
*
Alkenes
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, a ...
(olefins), which can be manufactured into plastics or other compounds
*
Lubricants (produces light machine oils,
motor oils, and
greases, adding
viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the int ...
stabilizers as required)
*
Wax, used in the packaging of
frozen foods, among others
*
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
or
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
. These are useful industrial materials. Sulfuric acid is usually prepared as the acid precursor
oleum
Oleum (Latin ''oleum'', meaning oil), or fuming sulfuric acid, is a term referring to solutions of various compositions of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid, or sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid (also known as pyrosulfuric acid). Ol ...
, a byproduct of
sulfur removal from fuels.
* Bulk
tar
*
Asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
*
Petroleum coke
Petroleum coke, abbreviated coke or petcoke, is a final carbon-rich solid material that derives from oil refining, and is one type of the group of fuels referred to as cokes. Petcoke is the coke that, in particular, derives from a final crack ...
, used in speciality carbon products or as solid fuel
*
Paraffin wax
Paraffin wax (or petroleum wax) is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins t ...
*
Aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to satur ...
petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewabl ...
s to be used as precursors in other
chemical production
Use by country
Consumption statistics
File:Global Carbon Emissions.svg, Global fossil carbon emissions, an indicator of consumption, from 1800.
File:World energy consumption.svg, Rate of world energy usage per year from 1970.[BP]
Statistical Review of World Energy
, Workbook (xlsx), London, 2012
File:Oil consumption per day by region from 1980 to 2006.svg, Daily oil consumption from 1980 to 2006.
File:Oil consumption per day by region from 1980 to 2006 solid3.svg, Oil consumption by percentage of total per region from 1980 to 2006: .
File:World oil consumption 1980 to 2007 by region.svg, Oil consumption 1980 to 2007 by region.
Consumption
According to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) estimate for 2017, the world consumes 98.8 million barrels of oil each day.

This table orders the amount of petroleum consumed in 2011 in thousand
barrels
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
(1000 bbl) per day and in thousand cubic metres (1000 m
3) per day:
Source
US Energy Information Administration
Population Data:
1 peak production of oil already passed in this state
2 This country is not a major oil producer
Production

In petroleum industry parlance, ''production'' refers to the quantity of crude extracted from reserves, not the literal creation of the product.
Exportation

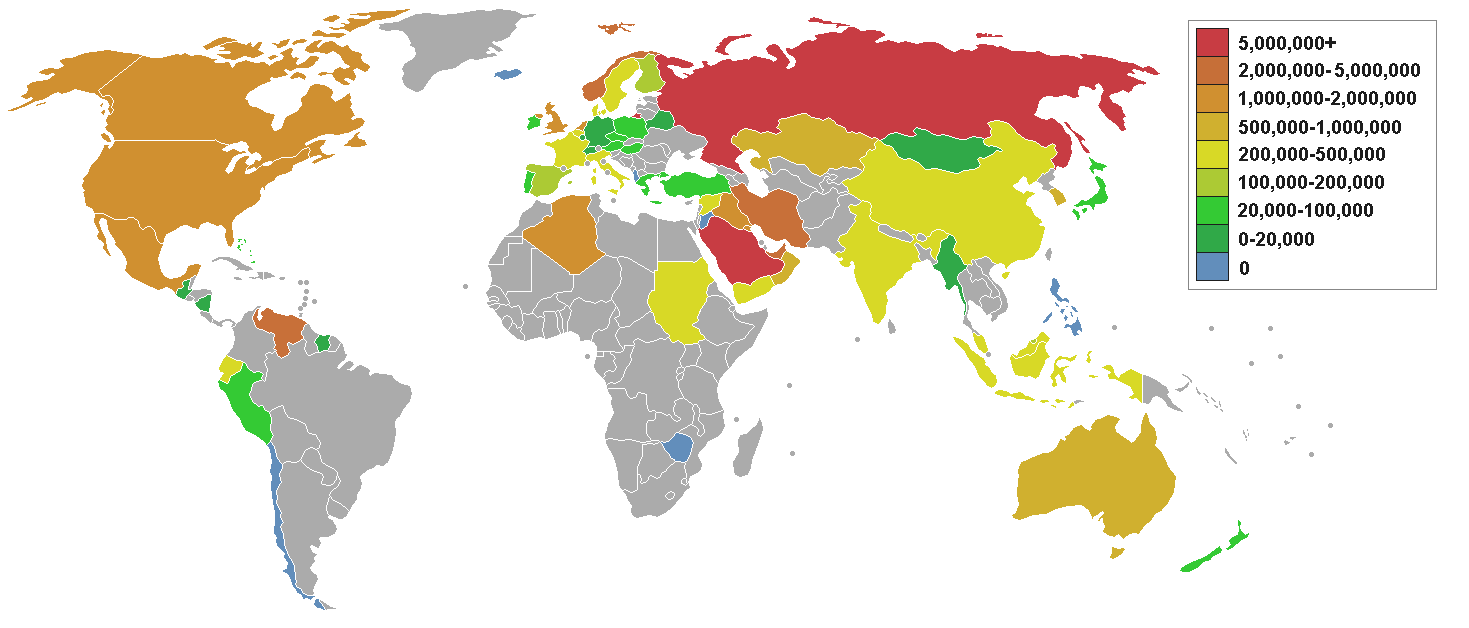
In order of net exports in 2011, 2009 and 2006 in thousand
bbl
A barrel is one of several units of volume applied in various contexts; there are dry barrels, fluid barrels (such as the U.K. beer barrel and U.S. beer barrel), oil barrels, and so forth. For historical reasons the volumes of some barrel units ...
/
d and thousand m
3/d:
Source
US Energy Information Administration
1 peak production already passed in this state
2 Canadian statistics are complicated by the fact it is both an importer and exporter of crude oil, and refines large amounts of oil for the U.S. market. It is the leading source of U.S. imports of oil and products, averaging in August 2007.
Total world production/consumption (as of 2005) is approximately .
Importation
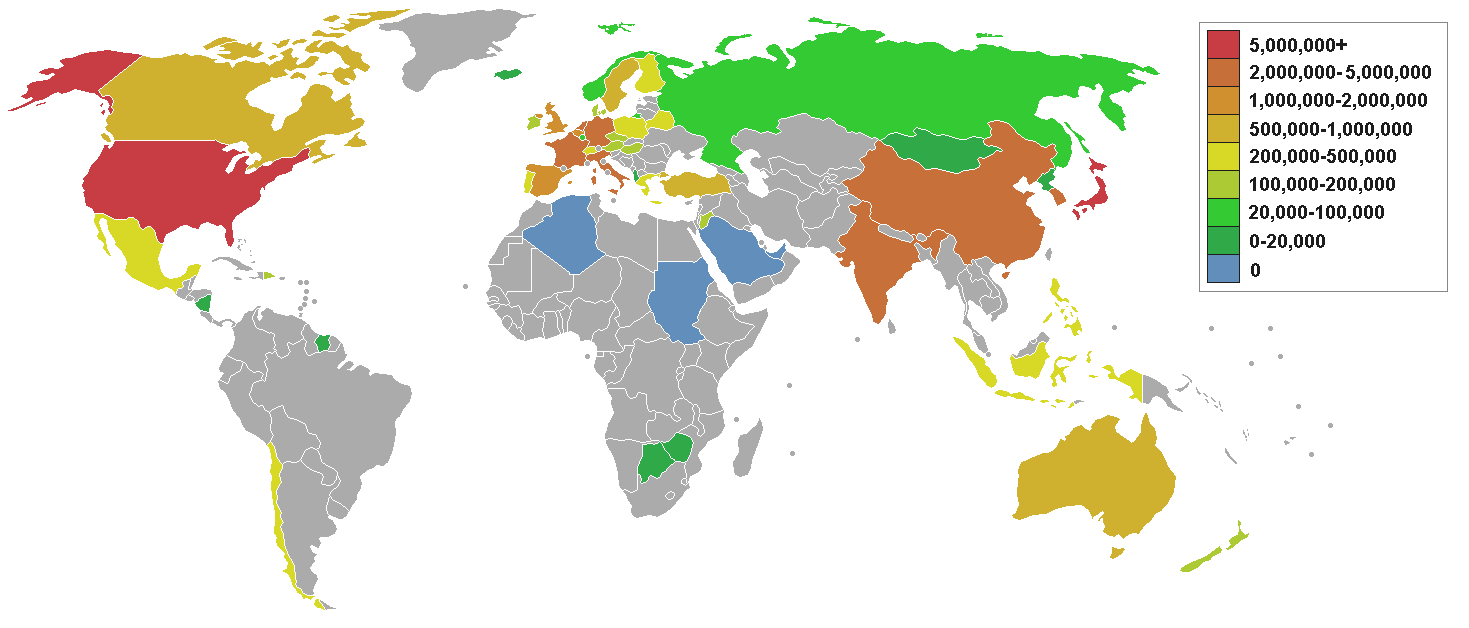
In order of net imports in 2011, 2009 and 2006 in thousand
bbl
A barrel is one of several units of volume applied in various contexts; there are dry barrels, fluid barrels (such as the U.K. beer barrel and U.S. beer barrel), oil barrels, and so forth. For historical reasons the volumes of some barrel units ...
/
d and thousand m
3/d:
Source
US Energy Information Administration
Non-producing consumers
Countries whose oil production is 10% or less of their consumption.
Source
Environmental effects

Climate change
, about a quarter of annual global
greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
is the carbon dioxide from burning petroleum (plus methane leaks from the industry). Along with the burning of coal, petroleum combustion is the largest contributor to the increase in atmospheric CO
2. Atmospheric CO
2 has risen over the last 150 years to current levels of over 415
ppmv
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they ...
, from the
180–300 ppmv of the prior 800 thousand years. The rise in Arctic temperature has reduced the minimum
Arctic ice pack to , a loss of almost half since satellite measurements started in 1979.

Ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ...
is the increase in the acidity of the Earth's oceans caused by the uptake of
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
() from the
atmosphere. This increase in acidity inhibits all marine life—having a greater impact on smaller organisms as well as shelled organisms (see
scallops).
Extraction
Oil extraction is simply the removal of oil from the reservoir (oil pool). Oil is often recovered as a water-in-oil emulsion, and
specialty chemicals
Speciality chemicals (also called specialties or effect chemicals) are particular chemical products which provide a wide variety of effects on which many other industry sectors rely. Some of the categories of speciality chemicals are adhesives, ag ...
called
demulsifiers
Demulsifiers, or emulsion breakers, are a class of specialty chemicals used to separate emulsions, for example, water in oil. They are commonly used in the processing of crude oil, which is typically produced along with significant quantities of sa ...
are used to separate the oil from water. Oil extraction is costly and often environmentally damaging. Offshore exploration and extraction of oil disturb the surrounding marine environment.
Oil spills
Crude oil and refined fuel
spills from
tanker ship
A tanker (or tank ship or tankship) is a ship designed to transport or store liquids or gases in bulk. Major types of tankship include the oil tanker, the chemical tanker, and gas carrier. Tankers also carry commodities such as vegetable oils, ...
accidents have damaged natural
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s and human livelihoods in
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U ...
, the
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
, the
Galápagos Islands
The Galápagos Islands ( Spanish: , , ) are an archipelago of volcanic islands. They are distributed on each side of the equator in the Pacific Ocean, surrounding the centre of the Western Hemisphere, and are part of the Republic of Ecuad ...
, France and many
other places.
The quantity of oil spilled during accidents has ranged from a few hundred tons to several hundred thousand tons (e.g.,
Deepwater Horizon oil spill,
SS Atlantic Empress
SS ''Atlantic Empress'' was a Greek oil tanker that in 1979 collided with the oil tanker '' Aegean Captain'' in the Caribbean, and eventually sank, having created the fifth largest oil spill on record and the largest ship-based spill having sp ...
,
Amoco Cadiz). Smaller spills have already proven to have a great impact on ecosystems, such as the
''Exxon Valdez'' oil spill.
Oil spills at sea are generally much more damaging than those on land, since they can spread for hundreds of nautical miles in a thin
oil slick which can cover beaches with a thin coating of oil. This can kill sea birds, mammals, shellfish and other organisms it coats. Oil spills on land are more readily containable if a makeshift earth dam can be rapidly
bulldozed
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large, motorized machine equipped with a metal blade to the front for pushing material: soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous tracks ...
around the spill site before most of the oil escapes, and land animals can avoid the oil more easily.
Control of oil spills is difficult, requires ad hoc methods, and often a large amount of manpower. The dropping of bombs and incendiary devices from aircraft on the wreck produced poor results; modern techniques would include pumping the oil from the wreck, like in the
''Prestige'' oil spill or the
''Erika'' oil spill.
Though crude oil is predominantly composed of various hydrocarbons, certain nitrogen heterocyclic compounds, such as
pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid w ...
,
picoline, and
quinoline are reported as contaminants associated with crude oil, as well as facilities processing oil shale or coal, and have also been found at legacy
wood treatment sites. These compounds have a very high water solubility, and thus tend to dissolve and move with water. Certain naturally occurring bacteria, such as ''
Micrococcus
''Micrococcus'' (mi’ krō kŏk’ Əs) is a genus of bacteria in the Micrococcaceae family. ''Micrococcus'' occurs in a wide range of environments, including water, dust, and soil. Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from ...
'', ''
Arthrobacter'', and ''
Rhodococcus'' have been shown to degrade these contaminants.
Because petroleum is a naturally occurring substance, its presence in the environment need not be the result of human causes such as accidents and routine activities (
seismic exploration,
drilling, extraction, refining and combustion). Phenomena such as
seeps
A petroleum seep is a place where natural liquid or gaseous hydrocarbons escape to the earth's atmosphere and surface, normally under low pressure or flow. Seeps generally occur above either terrestrial or offshore petroleum accumulation stru ...
and
tar pit
Tar pits, sometimes referred to as asphalt pits, are large asphalt deposits. They form in the presence of oil, which is created when decayed organic matter is subjected to pressure underground. If this crude oil seeps upward via fractures, cond ...
s are examples of areas that petroleum affects without man's involvement.
Tarballs
A tarball is a blob of crude oil (not to be confused with
tar, which is a man-made product derived from pine trees or refined from petroleum) which has been weathered after floating in the ocean. Tarballs are an aquatic
pollutant in most environments, although they can occur naturally, for example in the Santa Barbara Channel of California
or in the Gulf of Mexico off Texas. Their concentration and features have been used to assess the extent of
oil spills. Their composition can be used to identify their sources of origin, and tarballs themselves may be dispersed over long distances by deep sea currents.
They are slowly decomposed by bacteria, including ''
Chromobacterium violaceum'', ''
Cladosporium resinae
''Amorphotheca resinae'' is an ascomycete fungus of the family Amorphothecaceae which is known to thrive in environments containing alkanes (and water), like aviation fuel
Aviation fuels are petroleum-based fuels, or petroleum and syntheti ...
'', ''
Bacillus submarinus'', ''
Micrococcus varians'', ''
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. a ...
'', ''
Candida marina
Candida, or Cándida (Spanish), may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* ''Candida'' (fungus), a genus of yeasts
** Candidiasis, an infection by ''Candida'' organisms
* Malvasia Candida, a variety of grape
Places
* Candida, Campania, a ''comu ...
'' and ''
Saccharomyces estuari
''Saccharomyces'' is a genus of fungi that includes many species of yeasts. ''Saccharomyces'' is from Greek σάκχαρον (sugar) and μύκης (fungus) and means ''sugar fungus''. Many members of this genus are considered very important in f ...
''.
Whales
James S. Robbins has argued that the advent of petroleum-refined kerosene saved some species of great whales from
extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the Endling, last individual of the species, although the Functional ext ...
by providing an inexpensive substitute for
whale oil
Whale oil is oil obtained from the blubber of whales. Whale oil from the bowhead whale was sometimes known as train oil, which comes from the Dutch word ''traan'' (" tear" or "drop").
Sperm oil, a special kind of oil obtained from the head ...
, thus eliminating the economic imperative for open-boat
whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
, but others say that fossil fuels increased whaling with most whales being killed in the 20th century.
Alternatives
In 2018 road transport used 49% of petroleum, aviation 8%, and uses other than energy 17%.
Electric vehicles are the main alternative for road transport and
biojet for aviation. Single-use plastics have a high carbon footprint and may pollute the sea, but as of 2022 the best alternatives are unclear.
International relations
Control of petroleum production has been a significant driver of international relations during much of the 20th and 21st centuries.
Organizations like OPEC have played an outsized role in international politics. Some historians and commentators have called this the "
Age of Oil
The Age of Oil, also known as the Oil Age, the Petroleum Age, or the Oil Boom, refers to the era in human history characterised by an increased use of petroleum in products and as fuel. Though unrefined petroleum has been used for various purposes ...
"
With the rise of
renewable energy and addressing
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
some commentators expect a realignment of international power away from
petrostate
A petrostate or oil state is a nation whose economy is heavily dependent on the extraction and export of oil or natural gas. The presence alone of large oil and gas industries does not define a petrostate; countries like Norway, Canada, and the ...
s.
Corruption
"Oil rents" have been described as connected with corruption in political literature. A 2011 study suggested that increases in oil rents increased corruption in countries with heavy government involvement in the production of oil. The study found that increases in oil rents "significantly deteriorates political rights". The researchers noted oil exploitation gave politicians "an incentive to extend civil liberties but reduce political rights in the presence of oil windfalls to evade redistribution and conflict".
Conflict
Petroleum production can be linked with conflict: whether through direct aggression, trade wars such as
the 2020 Russia–Saudi Arabia oil price war, or by indirectly funding aggressors, such as the
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic ter ...
.
OPEC
Future production
 Consumption
Consumption in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries has been abundantly pushed by automobile sector growth. The
1985–2003 oil glut even fueled the sales of low fuel economy vehicles in
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
countries. The 2008 economic crisis seems to have had some impact on the sales of such vehicles; still, in 2008 oil consumption showed a small increase.
In 2016 Goldman Sachs predicted lower demand for oil due to emerging economies concerns, especially China. The
BRICS
BRICS is an acronym for five leading emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The first four were initially grouped as "BRIC" (or "the BRICs") in 2001 by Goldman Sachs economist Jim O'Neill, who coined the te ...
(Brasil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) countries might also kick in, as China briefly had the largest automobile market in December 2009. In the long term, uncertainties linger; the
OPEC believes that the OECD countries will push low consumption policies at some point in the future; when that happens, it will definitely curb oil sales, and both OPEC and the
Energy Information Administration (EIA) kept lowering their 2020 consumption estimates during the past five years. A detailed review of
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing car ...
oil projections have revealed that revisions of world oil production, price and investments have been motivated by a combination of demand and supply factors.
All together, Non-OPEC conventional projections have been fairly stable the last 15 years, while downward revisions were mainly allocated to OPEC. Recent upward revisions are primarily a result of US
tight oil.
Production will also face an increasingly complex situation; while OPEC countries still have large reserves at low production prices, newly found reservoirs often lead to higher prices; offshore giants such as
Tupi, Guara and
Tiber
The Tiber ( ; it, Tevere ; la, Tiberis) is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by th ...
demand high investments and ever-increasing technological abilities. Subsalt reservoirs such as Tupi were unknown in the twentieth century, mainly because the industry was unable to probe them.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) techniques (example:
DaQing, China) will continue to play a major role in increasing the world's recoverable oil.
The expected availability of petroleum resources has always been around 35 years or even less since the start of the modern exploration. The
oil constant, an insider pun in the German industry, refers to that effect.
A growing number of divestment campaigns from major funds pushed by newer generations who question the sustainability of petroleum may hinder the financing of future oil prospection and production.
Peak oil
Peak oil is a term applied to the projection that future petroleum production (whether for individual oil wells, entire oil fields, whole countries, or worldwide production) will eventually peak and then decline at a similar rate to the rate of increase before the peak as these reserves are exhausted. The peak of oil discoveries was in 1965, and oil production per year has surpassed oil discoveries every year since 1980. However, this does not mean that potential oil production has surpassed oil demand.
It is difficult to predict the oil peak in any given region, due to the lack of knowledge and/or transparency in accounting of global oil reserves. Based on available production data, proponents have previously predicted the peak for the world to be in years 1989, 1995, or 1995–2000. Some of these predictions date from before the recession of the early 1980s, and the consequent lowering in global consumption, the effect of which was to delay the date of any peak by several years. Just as the 1971 U.S. peak in oil production was only clearly recognized after the fact, a peak in world production will be difficult to discern until production clearly drops off.
In 2020, according to
BP's Energy Outlook 2020, peak oil had been reached, due to the changing energy landscape coupled with the
economic toll of the COVID-19 pandemic.
While there has been much focus historically on peak oil supply, focus is increasingly shifting to peak demand as more countries seek to transition to renewable energy. The GeGaLo index of geopolitical gains and losses assesses how the geopolitical position of 156 countries may change if the world fully transitions to renewable energy resources. Former oil exporters are expected to lose power, while the positions of former oil importers and countries rich in renewable energy resources is expected to strengthen.
Unconventional oil
Unconventional oil] is petroleum produced or extracted using techniques other than the conventional methods. The calculus for peak oil has changed with the introduction of
unconventional production methods. In particular, the combination of
horizontal drilling and
hydraulic fracturing has resulted in a significant increase in production from previously uneconomic plays. Analysts expected that $150 billion would be spent on further developing North American tight oil fields in 2015. The large increase in tight oil production is one of the reasons behind the price drop in late 2014. Certain rock
strata contain hydrocarbons but have low permeability and are not thick from a vertical perspective. Conventional vertical wells would be unable to economically retrieve these hydrocarbons. Horizontal drilling, extending horizontally through the strata, permits the well to access a much greater volume of the strata. Hydraulic fracturing creates greater permeability and increases hydrocarbon flow to the wellbore.
Hydrocarbons on other worlds
On
Saturn's largest moon,
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, lakes of liquid hydrocarbons comprising methane, ethane, propane and other constituents, occur naturally. Data collected by the space probe ''
Cassini–Huygens'' yield an estimate that the visible lakes and seas of Titan contain about 300 times the volume of Earth's proven oil reserves.
Drilled samples from the surface of
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
taken in 2015 by the
''Curiosity'' rover's Mars Science Laboratory have found organic molecules of
benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms ...
and
propane in 3-billion-year-old rock samples in
Gale Crater.
[
]
In fiction
See also
*
Barrel of oil equivalent
*
Filling station
A filling station, also known as a gas station () or petrol station (), is a facility that sells fuel and engine lubricants for motor vehicles. The most common fuels sold in the 2010s were gasoline (or petrol) and diesel fuel.
Ga ...
*
Gas oil ratio
*
List of oil exploration and production companies
*
List of oil fields
*
Manure-derived synthetic crude oil
*
Oil burden Oil burden is the volume of petroleum consumed, multiplied by the average price, and divided by nominal gross domestic product.
This gives the proportion of the world economy devoted to buying oil. It is a concept developed by Veronique Riches-F ...
*
Petroleum geology
*
Petroleum politics
Petroleum politics have been an increasingly important aspect of diplomacy since the rise of the petroleum industry in the Middle East in the early 20th century. As competition continues for a vital resource, the strategic calculations of major ...
*
Petrocurrency
Petrocurrency (or petrodollar) is a word used with three distinct meanings, often confused:
#Dollars paid to oil-producing nations (petrodollar recycling)—a term invented in the 1970s meaning trading surpluses of oil-producing nations.
#Currenci ...
*
Thermal depolymerization
*
Total petroleum hydrocarbon Total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) is a term used for any mixture of hydrocarbons that are found in crude oil. There are several hundred of these compounds, but not all occur in any one sample. Crude oil is used to make petroleum products, which can ...
*
Waste oil
*
Unconventional (oil & gas) reservoir
Unconventional (oil & gas) reservoirs, or unconventional resources (resource plays) are accumulations where oil & gas phases are tightly bound to the rock fabric by strong capillary forces, requiring specialised measures for evaluation and extr ...
Citations
Explanatory footnotes
General and cited references
*
* translated 1955
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Mirbabayev M.F.(2017).Brief history of the first drilled oil well;and the people involved.-"Oil-Industry History"(US),vol.18,#1, p. 25-34.
Further reading
*
Juhasz, Antonia, "The End of OIL?: The
pandemic has battered an already struggling oil industry. Whether it survives is up to us", ''
Sierra Magazine
The Sierra Club is an environmental organization with chapters in all 50 United States, Washington D.C., and Puerto Rico. The club was founded on May 28, 1892, in San Francisco, California, by Scottish-American preservationist John Muir, who ...
'', vol. 105, no. 5 (September / October 2020), pp. 36–40, 51.
*
External links
Global Fossil Infrastructure TrackerAPI – the trade association of the US oil industry.(
American Petroleum Institute
The American Petroleum Institute (API) is the largest U.S. trade association for the oil and natural gas industry. It claims to represent nearly 600 corporations involved in production, refinement, distribution, and many other aspects of the ...
)
U.S. Energy Information Administration*
*
Oil and Gas Data TransparencyU.S. National Library of Medicine: Hazardous Substances Databank – Crude OilBest Dubai Desert Safari Deals*
A Short History of Petroleum,
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
, 10 August 1878, p. 85
{{Authority control
Causes of war
Chemical mixtures
Glassforming liquids and melts
 The word ''petroleum'' comes from Medieval Latin (literally 'rock oil'), which comes from Latin petra 'rock' (from Greek ) and
The word ''petroleum'' comes from Medieval Latin (literally 'rock oil'), which comes from Latin petra 'rock' (from Greek ) and  Petroleum, in one form or another, has been used since ancient times. More than 4300 years ago, bitumen was mentioned when the Sumerians used it to make boats. Tablet of the legend of the birth of Sargon of Akkad, mentioned a basket which was closed by straw and bitumen. More than 4000 years ago, according to
Petroleum, in one form or another, has been used since ancient times. More than 4300 years ago, bitumen was mentioned when the Sumerians used it to make boats. Tablet of the legend of the birth of Sargon of Akkad, mentioned a basket which was closed by straw and bitumen. More than 4000 years ago, according to  Access to oil was and still is a major factor in several military conflicts of the twentieth century, including
Access to oil was and still is a major factor in several military conflicts of the twentieth century, including  Crude oil varies greatly in appearance depending on its composition. It is usually black or dark brown (although it may be yellowish, reddish, or even greenish). In the reservoir it is usually found in association with natural gas, which being lighter forms a "gas cap" over the petroleum, and saline water which, being heavier than most forms of crude oil, generally sinks beneath it. Crude oil may also be found in a semi-solid form mixed with sand and water, as in the Athabasca oil sands in Canada, where it is usually referred to as crude bitumen. In Canada, bitumen is considered a sticky, black, tar-like form of crude oil which is so thick and heavy that it must be heated or diluted before it will flow. Venezuela also has large amounts of oil in the
Crude oil varies greatly in appearance depending on its composition. It is usually black or dark brown (although it may be yellowish, reddish, or even greenish). In the reservoir it is usually found in association with natural gas, which being lighter forms a "gas cap" over the petroleum, and saline water which, being heavier than most forms of crude oil, generally sinks beneath it. Crude oil may also be found in a semi-solid form mixed with sand and water, as in the Athabasca oil sands in Canada, where it is usually referred to as crude bitumen. In Canada, bitumen is considered a sticky, black, tar-like form of crude oil which is so thick and heavy that it must be heated or diluted before it will flow. Venezuela also has large amounts of oil in the  Petroleum is mainly a mixture of
Petroleum is mainly a mixture of  Petroleum is a fossil fuel derived from ancient fossilized organic materials, such as zooplankton and algae. Vast amounts of these remains settled to sea or lake bottoms where they were covered in
Petroleum is a fossil fuel derived from ancient fossilized organic materials, such as zooplankton and algae. Vast amounts of these remains settled to sea or lake bottoms where they were covered in 
 This table orders the amount of petroleum consumed in 2011 in thousand
This table orders the amount of petroleum consumed in 2011 in thousand  In petroleum industry parlance, ''production'' refers to the quantity of crude extracted from reserves, not the literal creation of the product.
In petroleum industry parlance, ''production'' refers to the quantity of crude extracted from reserves, not the literal creation of the product.


 Consumption in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries has been abundantly pushed by automobile sector growth. The 1985–2003 oil glut even fueled the sales of low fuel economy vehicles in
Consumption in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries has been abundantly pushed by automobile sector growth. The 1985–2003 oil glut even fueled the sales of low fuel economy vehicles in