Cross-industry standard process for data mining on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cross-industry standard process for data mining, known as CRISP-DM,Shearer C., ''The CRISP-DM model: the new blueprint for data mining'', J Data Warehousing (2000); 5:13—22. is an
''The CRISP-DM User Guide''
and published as a step-by-step data mining guide later that year.Pete Chapman, Julian Clinton, Randy Kerber, Thomas Khabaza, Thomas Reinartz, Colin Shearer, and Rüdiger Wirth (2000); ''The CRISP-DM User Guide''
entry on semantic scholar, including links to PDFs
,
PDF version with high-resolution graphics
. Between 2006 and 2008 a CRISP-DM 2.0 SIG was formed and there were discussions about updating the CRISP-DM process model.Colin Shearer (2006)
/ref> The current status of these efforts is not known. However, the original crisp-dm.org website cited in the reviews, and the CRISP-DM 2.0 SIG website are both no longer active. While many non-IBM data mining practitioners use CRISP-DM, IBM is the primary corporation that currently uses the CRISP-DM process model. It makes some of the old CRISP-DM documents available for download and it has incorporated it into its
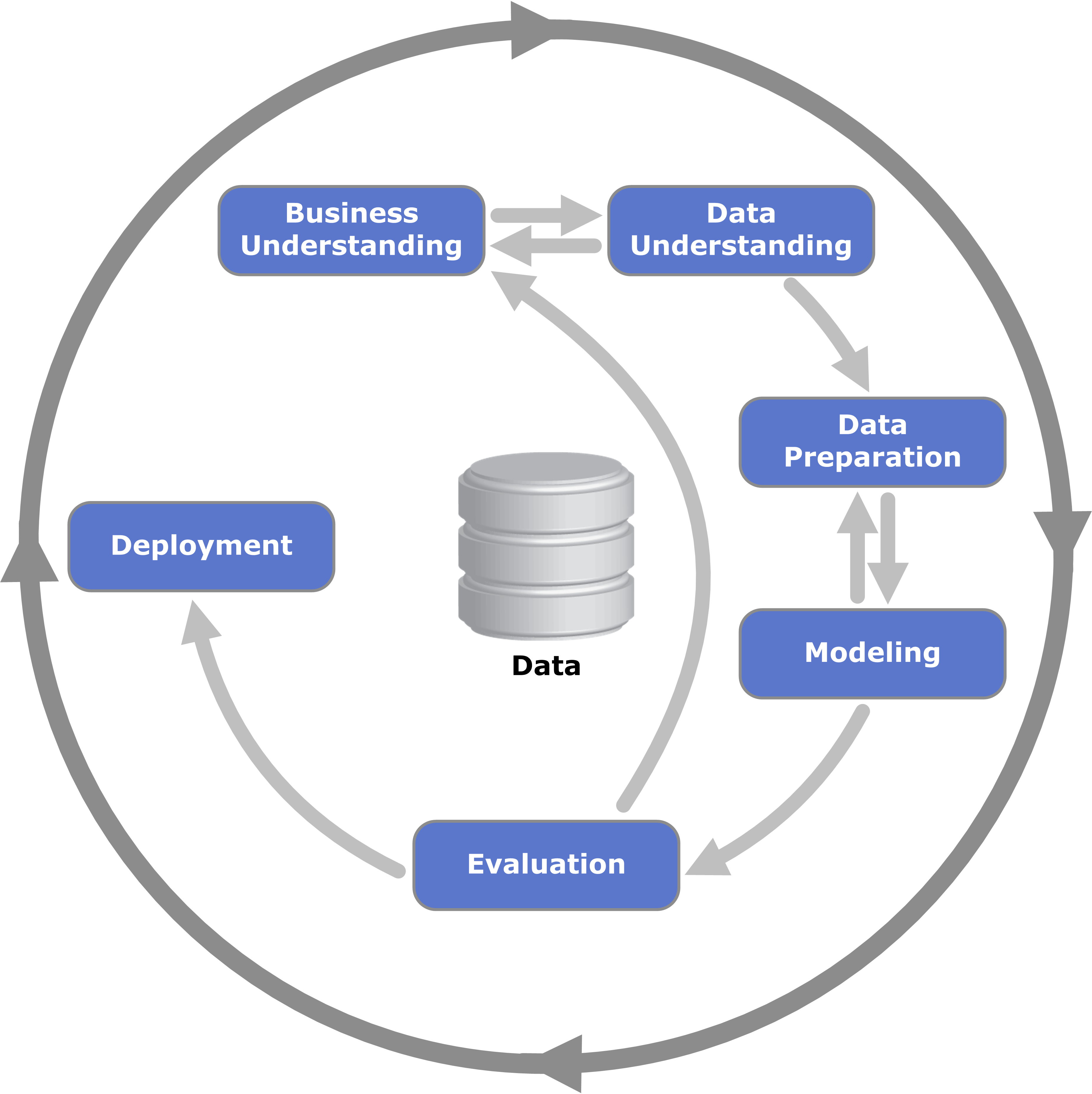 CRISP-DM breaks the process of data mining into six major phases:
* Business Understanding
* Data Understanding
* Data Preparation
* Modeling
* Evaluation
* Deployment
The sequence of the phases is not strict and moving back and forth between different phases is usually required. The arrows in the process diagram indicate the most important and frequent dependencies between phases. The outer circle in the diagram symbolizes the cyclic nature of data mining itself. A data mining process continues after a solution has been deployed. The lessons learned during the process can trigger new, often more focused business questions, and subsequent data mining processes will benefit from the experiences of previous ones.
CRISP-DM breaks the process of data mining into six major phases:
* Business Understanding
* Data Understanding
* Data Preparation
* Modeling
* Evaluation
* Deployment
The sequence of the phases is not strict and moving back and forth between different phases is usually required. The arrows in the process diagram indicate the most important and frequent dependencies between phases. The outer circle in the diagram symbolizes the cyclic nature of data mining itself. A data mining process continues after a solution has been deployed. The lessons learned during the process can trigger new, often more focused business questions, and subsequent data mining processes will benefit from the experiences of previous ones.
''KDnuggets Methodology Poll''
/ref>Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2004)
/ref>Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2007)
/ref>Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2014)
/ref> The only other data mining approach named in these polls was SEMMA. However, SAS Institute clearly states that SEMMA is not a data mining methodology, but rather a "logical organization of the functional toolset of SAS Enterprise Miner." A review and critique of data mining process models in 2009 called the CRISP-DM the "de facto standard for developing data mining and knowledge discovery projects." Other reviews of CRISP-DM and data mining process models include Kurgan and Musilek's 2006 review,Lukasz Kurgan and Petr Musilek (2006)
''A survey of Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining process models''
The Knowledge Engineering Review. Volume 21 Issue 1, March 2006, pp 1–24, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA doi: 10.1017/S0269888906000737. and Azevedo and Santos' 2008 comparison of CRISP-DM and SEMMA.Azevedo, A. and Santos, M. F. (2008)
KDD, SEMMA and CRISP-DM: a parallel overview
In Proceedings of the IADIS European Conference on Data Mining 2008, pp 182–185. Efforts to update the methodology started in 2006, but have, as of June 2015, not led to a new version, and the "Special Interest Group" (SIG) responsible along with the website has long disappeared (see History of CRISP-DM).
open standard
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a prerequisite to use open license, non-discrimination and extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in the development. There is no single definitio ...
process model that describes common approaches used by data mining experts. It is the most widely-used analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data. It also entails applying data patterns toward effective decision-making. It ...
model.
In 2015, IBM released a new methodology called '' Analytics Solutions Unified Method for Data Mining/Predictive Analytics'' (also known as ASUM-DM) which refines and extends CRISP-DM.
History
CRISP-DM was conceived in 1996 and became a European Union project under theESPRIT
Esprit or L'Esprit may refer to:
* the French for Spirit; as a loanword:
** Enthusiasm, intense interest or motivation
** Morale, motivation and readiness
** Geist "mind/spirit; intellect"
* Esprit (name), a given name and surname
* ''Esprit'' (m ...
funding initiative in 1997. The project was led by five companies: Integral Solutions Ltd (ISL), Teradata
Teradata Corporation is an American software company that provides cloud database and analytics-related software, products, and services. The company was formed in 1979 in Brentwood, California, as a collaboration between researchers at Caltech ...
, Daimler AG
The Mercedes-Benz Group AG (previously named Daimler-Benz, DaimlerChrysler and Daimler) is a German multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of the world's leading car manufactu ...
, NCR Corporation
NCR Corporation, previously known as National Cash Register, is an American software, consulting and technology company providing several professional services and electronic products. It manufactures self-service kiosks, point-of-sale termin ...
and OHRA, an insurance company.
This core consortium brought different experiences to the project: ISL, later acquired and merged into SPSS
SPSS Statistics is a statistical software suite developed by IBM for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, and criminal investigation. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. C ...
. The computer giant NCR Corporation produced the Teradata data warehouse and its own data mining software. Daimler-Benz had a significant data mining team. OHRA was just starting to explore the potential use of data mining.
The first version of the methodology was presented at the 4th CRISP-DM SIG Workshop in Brussels in March 1999,Pete Chapman (1999)''The CRISP-DM User Guide''
and published as a step-by-step data mining guide later that year.Pete Chapman, Julian Clinton, Randy Kerber, Thomas Khabaza, Thomas Reinartz, Colin Shearer, and Rüdiger Wirth (2000); ''The CRISP-DM User Guide''
entry on semantic scholar, including links to PDFs
,
PDF version with high-resolution graphics
. Between 2006 and 2008 a CRISP-DM 2.0 SIG was formed and there were discussions about updating the CRISP-DM process model.Colin Shearer (2006)
/ref> The current status of these efforts is not known. However, the original crisp-dm.org website cited in the reviews, and the CRISP-DM 2.0 SIG website are both no longer active. While many non-IBM data mining practitioners use CRISP-DM, IBM is the primary corporation that currently uses the CRISP-DM process model. It makes some of the old CRISP-DM documents available for download and it has incorporated it into its
SPSS Modeler
IBM SPSS Modeler is a data mining and text analytics software application from IBM. It is used to build predictive models and conduct other analytic tasks. It has a visual interface which allows users to leverage statistical and data mining a ...
product.
Based on current research CRISP-DM is the most widely used form of data-mining model because of its various advantages which solved the existing problems in the data mining industries. Some of the drawbacks of this model is that it does not perform project management activities. The fact behind the success of CRISP-DM is that it is industry, tool, and application neutral.
Major phases
 CRISP-DM breaks the process of data mining into six major phases:
* Business Understanding
* Data Understanding
* Data Preparation
* Modeling
* Evaluation
* Deployment
The sequence of the phases is not strict and moving back and forth between different phases is usually required. The arrows in the process diagram indicate the most important and frequent dependencies between phases. The outer circle in the diagram symbolizes the cyclic nature of data mining itself. A data mining process continues after a solution has been deployed. The lessons learned during the process can trigger new, often more focused business questions, and subsequent data mining processes will benefit from the experiences of previous ones.
CRISP-DM breaks the process of data mining into six major phases:
* Business Understanding
* Data Understanding
* Data Preparation
* Modeling
* Evaluation
* Deployment
The sequence of the phases is not strict and moving back and forth between different phases is usually required. The arrows in the process diagram indicate the most important and frequent dependencies between phases. The outer circle in the diagram symbolizes the cyclic nature of data mining itself. A data mining process continues after a solution has been deployed. The lessons learned during the process can trigger new, often more focused business questions, and subsequent data mining processes will benefit from the experiences of previous ones.
Polls
Polls conducted at the same website (KDNuggets) in 2002, 2004, 2007 and 2014 show that it was the leading methodology used by industry data miners who decided to respond to the survey.Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2002)''KDnuggets Methodology Poll''
/ref>Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2004)
/ref>Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2007)
/ref>Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro (2014)
/ref> The only other data mining approach named in these polls was SEMMA. However, SAS Institute clearly states that SEMMA is not a data mining methodology, but rather a "logical organization of the functional toolset of SAS Enterprise Miner." A review and critique of data mining process models in 2009 called the CRISP-DM the "de facto standard for developing data mining and knowledge discovery projects." Other reviews of CRISP-DM and data mining process models include Kurgan and Musilek's 2006 review,Lukasz Kurgan and Petr Musilek (2006)
''A survey of Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining process models''
The Knowledge Engineering Review. Volume 21 Issue 1, March 2006, pp 1–24, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA doi: 10.1017/S0269888906000737. and Azevedo and Santos' 2008 comparison of CRISP-DM and SEMMA.Azevedo, A. and Santos, M. F. (2008)
KDD, SEMMA and CRISP-DM: a parallel overview
In Proceedings of the IADIS European Conference on Data Mining 2008, pp 182–185. Efforts to update the methodology started in 2006, but have, as of June 2015, not led to a new version, and the "Special Interest Group" (SIG) responsible along with the website has long disappeared (see History of CRISP-DM).
References
{{Reflist Applied data mining