Croats on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian
 Much uncertainty revolves around the exact circumstances of their appearance given the scarcity of literary sources during the 7th and 8th century
Much uncertainty revolves around the exact circumstances of their appearance given the scarcity of literary sources during the 7th and 8th century
 Other, distinct polities also existed near the Croat duchy. These included the Guduscans (based in Liburnia),
Other, distinct polities also existed near the Croat duchy. These included the Guduscans (based in Liburnia),
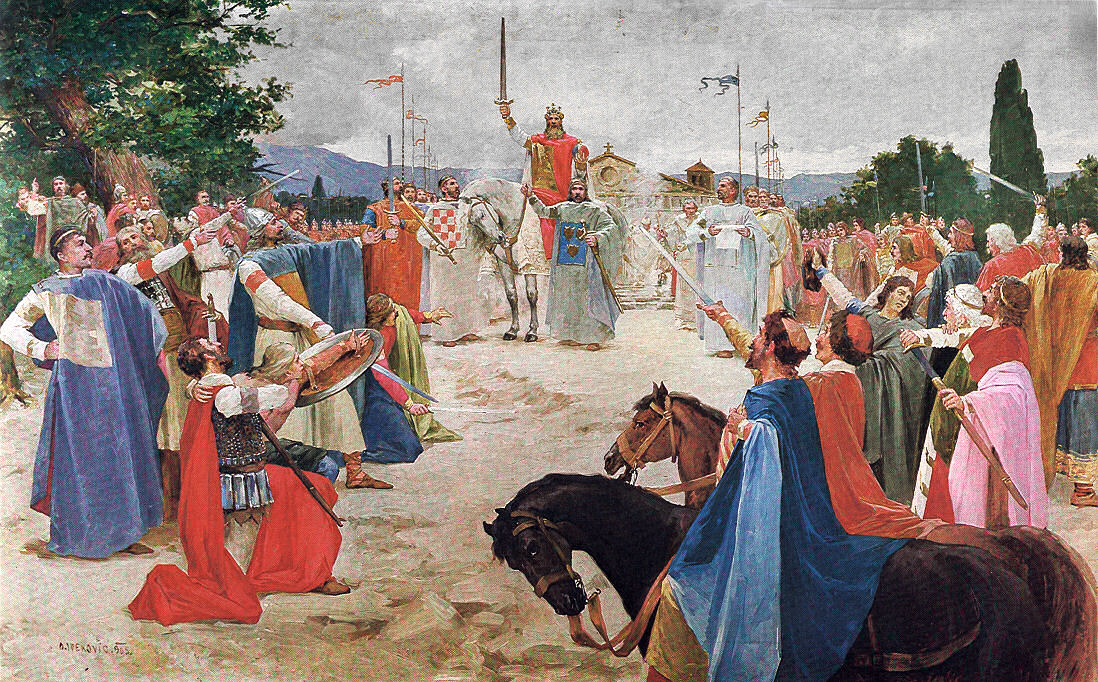 Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav (910–928) became king of Croatia by 925. The chief piece of evidence that Tomislav was crowned king comes in the form of a letter dated 925, surviving only in 16th-century copies, from Pope John X calling Tomislav ''King of Croatia, rex Chroatorum''. According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', Tomislav's army and navy could have consisted approximately 100,000 infantry units, 60,000 cavaliers, and 80 larger (''sagina'') and 100 smaller warships (''Kondura (ship), condura''), but generally isn't taken as credible. According to the Palaeography, palaeographic analysis of the original manuscript of ''De Administrando Imperio'', an estimation of the number of inhabitants in medieval Croatia between 440 and 880 thousand people, and military numbers of Franks and Byzantines – the Croatian military force was most probably composed of 20,000–100,000 infantrymen, and 3,000–24,000 horsemen organized in 60 allagions. The Croatian Kingdom as an ally of Byzantine Empire was in conflict with the rising First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire ruled by Tsar Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I. In 923, due to a deal of Pope John X and a Patriarch of Constantinopole, the sovereignty of Byzantine Dalmatia (theme), coastal cities in Dalmatia came under Tomislav's Governancy. The war escalated on 27 May 927, in the Croatian–Bulgarian battle of 927, battle of the Bosnian Highlands, after Serbs were conquered and some fled to the Croatian Kingdom. There Croats under leadership of their king Tomislav completely defeated the Bulgarian army led by military commander Alogobotur, and stopped Simeon's extension westwards.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki" The central town in the Duvno field was named Tomislavgrad ("Tomislav's town") in his honour in the 20th century.
Tomislav was succeeded by Trpimir II of Croatia, Trpimir II (928–935), and Krešimir I of Croatia, Krešimir I (935–945), this period, on the whole, however, is obscure. Miroslav of Croatia, Miroslav (945–949) was killed by his ban Pribina during an internal power struggle, losing part of islands and coastal cities. Mihajlo Krešimir II, Krešimir II (949–969) kept particularly good relations with the Dalmatian cities, while his son Stjepan Držislav (969–997) established better relations with the Byzantine Empire and received a formal authority over Dalmatian cities. His three sons, Svetoslav Suronja, Svetoslav (997–1000), Krešimir III of Croatia, Krešimir III (1000–1030) and Gojslav of Croatia, Gojslav (1000–1020), opened a violent contest for the throne, weakening the state and further losing control. Krešimir III and his brother Gojslav co-ruled from 1000 until 1020, and attempted to restore control over lost Dalmatian cities now under Venetian control. Krešimir was succeeded by his son Stjepan I of Croatia, Stjepan I (1030–1058), who tried to reinforce the alliance with the Byzantines when he sent a segment of his naval fleet in war against the Arabs in 1032, in favour for their tolerance about conquering Zadar another Byzantine ally, from Venice. He did conquer it, but the circumstances changed later and lost it.
Petar Krešimir IV of Croatia, Krešimir IV (1058–1074) managed to get the Byzantine Empire to confirm him as the supreme ruler of the Dalmatian cities. Croatia under Krešimir IV was composed of twelve counties and was slightly larger than in Tomislav's time, and included the closest southern Dalmatian duchy of Pagania. From the outset, he continued the policies of his father, but was immediately commanded by Pope Nicholas II first in 1059 and then in 1060 to reform the Croatian church in accordance with the Roman rite. This was especially significant to the papacy in the aftermath of the Great Schism of 1054.
Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav (910–928) became king of Croatia by 925. The chief piece of evidence that Tomislav was crowned king comes in the form of a letter dated 925, surviving only in 16th-century copies, from Pope John X calling Tomislav ''King of Croatia, rex Chroatorum''. According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', Tomislav's army and navy could have consisted approximately 100,000 infantry units, 60,000 cavaliers, and 80 larger (''sagina'') and 100 smaller warships (''Kondura (ship), condura''), but generally isn't taken as credible. According to the Palaeography, palaeographic analysis of the original manuscript of ''De Administrando Imperio'', an estimation of the number of inhabitants in medieval Croatia between 440 and 880 thousand people, and military numbers of Franks and Byzantines – the Croatian military force was most probably composed of 20,000–100,000 infantrymen, and 3,000–24,000 horsemen organized in 60 allagions. The Croatian Kingdom as an ally of Byzantine Empire was in conflict with the rising First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire ruled by Tsar Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I. In 923, due to a deal of Pope John X and a Patriarch of Constantinopole, the sovereignty of Byzantine Dalmatia (theme), coastal cities in Dalmatia came under Tomislav's Governancy. The war escalated on 27 May 927, in the Croatian–Bulgarian battle of 927, battle of the Bosnian Highlands, after Serbs were conquered and some fled to the Croatian Kingdom. There Croats under leadership of their king Tomislav completely defeated the Bulgarian army led by military commander Alogobotur, and stopped Simeon's extension westwards.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki" The central town in the Duvno field was named Tomislavgrad ("Tomislav's town") in his honour in the 20th century.
Tomislav was succeeded by Trpimir II of Croatia, Trpimir II (928–935), and Krešimir I of Croatia, Krešimir I (935–945), this period, on the whole, however, is obscure. Miroslav of Croatia, Miroslav (945–949) was killed by his ban Pribina during an internal power struggle, losing part of islands and coastal cities. Mihajlo Krešimir II, Krešimir II (949–969) kept particularly good relations with the Dalmatian cities, while his son Stjepan Držislav (969–997) established better relations with the Byzantine Empire and received a formal authority over Dalmatian cities. His three sons, Svetoslav Suronja, Svetoslav (997–1000), Krešimir III of Croatia, Krešimir III (1000–1030) and Gojslav of Croatia, Gojslav (1000–1020), opened a violent contest for the throne, weakening the state and further losing control. Krešimir III and his brother Gojslav co-ruled from 1000 until 1020, and attempted to restore control over lost Dalmatian cities now under Venetian control. Krešimir was succeeded by his son Stjepan I of Croatia, Stjepan I (1030–1058), who tried to reinforce the alliance with the Byzantines when he sent a segment of his naval fleet in war against the Arabs in 1032, in favour for their tolerance about conquering Zadar another Byzantine ally, from Venice. He did conquer it, but the circumstances changed later and lost it.
Petar Krešimir IV of Croatia, Krešimir IV (1058–1074) managed to get the Byzantine Empire to confirm him as the supreme ruler of the Dalmatian cities. Croatia under Krešimir IV was composed of twelve counties and was slightly larger than in Tomislav's time, and included the closest southern Dalmatian duchy of Pagania. From the outset, he continued the policies of his father, but was immediately commanded by Pope Nicholas II first in 1059 and then in 1060 to reform the Croatian church in accordance with the Roman rite. This was especially significant to the papacy in the aftermath of the Great Schism of 1054.
 He was succeeded by Demetrius Zvonimir of Croatia, Dmitar Zvonimir, who was of the Svetoslavić branch of the House of Trpimirović, and a Ban of Slavonia (1064–1075). He was Crown of Zvonimir, crowned on 8 October 1076Dominik Mandić, Rasprave i prilozi iz stare hrvatske povijesti, Institute of Croatian history, Rome, 1963., page 315., 438. at Solin, Croatia, Solin in the Hollow Church, Basilica of Saint Peter and Moses (known today as ''Hollow Church'') by a representative of Pope Gregory VII.
He was in conflict with dukes of Istria, while historical records ''Annales Carinthiæ'' and ''Chronica Hungarorum'' note he invaded Carinthia (state), Carinthia to aid Hungary in war during 1079/83, but this is disputed. Unlike Petar Krešimir IV, he was also an ally of the Normans, with whom he joined in wars against Byzantium. He married in 1063 Helena of Hungary, Queen of Croatia, Helen of Hungary, the daughter of King Bela I of the Hungarian Árpád dynasty, and the sister of the future King Ladislaus I of Hungary, Ladislaus I. As King Zvonimir died in 1089 in unknown circumstances, with no direct heir to succeed him, Stjepan II of Croatia, Stjepan II ( 1089–1091) last of the main Trpimirović line came to the throne at an old age and reigned for two years.
After his death civil war and unrest broke out shortly afterward as northern nobles decided Ladislaus I for the Croatian King. In 1093, southern nobles elected a new ruler, King Petar Svačić ( 1093–1097), who managed to unify the Kingdom around his capital of Knin. His army resisted repelling Hungarian assaults, and restored Croatian rule up to the river
He was succeeded by Demetrius Zvonimir of Croatia, Dmitar Zvonimir, who was of the Svetoslavić branch of the House of Trpimirović, and a Ban of Slavonia (1064–1075). He was Crown of Zvonimir, crowned on 8 October 1076Dominik Mandić, Rasprave i prilozi iz stare hrvatske povijesti, Institute of Croatian history, Rome, 1963., page 315., 438. at Solin, Croatia, Solin in the Hollow Church, Basilica of Saint Peter and Moses (known today as ''Hollow Church'') by a representative of Pope Gregory VII.
He was in conflict with dukes of Istria, while historical records ''Annales Carinthiæ'' and ''Chronica Hungarorum'' note he invaded Carinthia (state), Carinthia to aid Hungary in war during 1079/83, but this is disputed. Unlike Petar Krešimir IV, he was also an ally of the Normans, with whom he joined in wars against Byzantium. He married in 1063 Helena of Hungary, Queen of Croatia, Helen of Hungary, the daughter of King Bela I of the Hungarian Árpád dynasty, and the sister of the future King Ladislaus I of Hungary, Ladislaus I. As King Zvonimir died in 1089 in unknown circumstances, with no direct heir to succeed him, Stjepan II of Croatia, Stjepan II ( 1089–1091) last of the main Trpimirović line came to the throne at an old age and reigned for two years.
After his death civil war and unrest broke out shortly afterward as northern nobles decided Ladislaus I for the Croatian King. In 1093, southern nobles elected a new ruler, King Petar Svačić ( 1093–1097), who managed to unify the Kingdom around his capital of Knin. His army resisted repelling Hungarian assaults, and restored Croatian rule up to the river
 In the union with Hungary, institutions of separate Croatian statehood were maintained through the Sabor (an assembly of Croatian nobles) and the ban (viceroy). In addition, the Croatian nobles retained their lands and titles. Coloman retained the institution of the Sabor and relieved the Croatians of taxes on their land. Coloman's successors continued to crown themselves as Kings of Croatia separately in Biograd na Moru. The Hungarian king also introduced a variant of the feudal system. Large fiefs were granted to individuals who would defend them against outside incursions thereby creating a system for the defence of the entire state. However, by enabling the nobility to seize more economic and military power, the kingdom itself lost influence to the powerful noble families. In Croatia the House of Šubić, Šubić were one of the oldest Croatian noble families and would become particularly influential and important, ruling the area between Zrmanja and the Krka (Croatia), Krka rivers. The local noble family from Krk island (who later took the surname House of Frankopan, Frankopan) is often considered the second most important medieval family, as ruled over northern Adriatic and is responsible for the adoption of one of oldest European statutes, Law codex of Vinodol (1288). Both families gave many native bans of Croatia. Other powerful families were House of Nelipić, Nelipić from Zagora (Croatia), Dalmatian Zagora (14th–15th centuries); Kačić who ruled over
In the union with Hungary, institutions of separate Croatian statehood were maintained through the Sabor (an assembly of Croatian nobles) and the ban (viceroy). In addition, the Croatian nobles retained their lands and titles. Coloman retained the institution of the Sabor and relieved the Croatians of taxes on their land. Coloman's successors continued to crown themselves as Kings of Croatia separately in Biograd na Moru. The Hungarian king also introduced a variant of the feudal system. Large fiefs were granted to individuals who would defend them against outside incursions thereby creating a system for the defence of the entire state. However, by enabling the nobility to seize more economic and military power, the kingdom itself lost influence to the powerful noble families. In Croatia the House of Šubić, Šubić were one of the oldest Croatian noble families and would become particularly influential and important, ruling the area between Zrmanja and the Krka (Croatia), Krka rivers. The local noble family from Krk island (who later took the surname House of Frankopan, Frankopan) is often considered the second most important medieval family, as ruled over northern Adriatic and is responsible for the adoption of one of oldest European statutes, Law codex of Vinodol (1288). Both families gave many native bans of Croatia. Other powerful families were House of Nelipić, Nelipić from Zagora (Croatia), Dalmatian Zagora (14th–15th centuries); Kačić who ruled over  As the Ottoman wars in Europe, Turkish incursion into Europe started, Croatia once again became a border area between two major forces in the
As the Ottoman wars in Europe, Turkish incursion into Europe started, Croatia once again became a border area between two major forces in the  The Battle of Mohács (1526) and the death of King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II ended the Hungarian-Croatian union. In 1526, the Hungarian parliament elected two separate kings János Szapolyai and Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I Habsburg, but the choice of the Croatian sabor Parliament on Cetin, at Cetin prevailed on the side of Ferdinand I, as they elected him as the new king of Croatia on 1 January 1527, uniting both lands under Habsburg rule. In return they were promised the historic rights, freedoms, laws and defence of Croatian Kingdom.
However, the Hungarian-Croatian Kingdom was not enough well prepared and organized and the Ottoman Empire expanded further in the 16th century to include most of Slavonia, western Bosnia and Lika. For the sake of stopping the Ottoman conquering and possible assault on the capital of Vienna, the large areas of Croatia and Slavonia (even Hungary and Romania) bordering the Ottoman Empire were organized as a Military Frontier which was ruled directly from Vienna military headquarters. The invasion caused migration of Croats, and the area which became deserted was subsequently settled by Serbs, Vlachs, Ethnic German, Germans and others. The negative effects of feudalism escalated in 1573 when the peasants in northern Croatia and Slovenia Croatian and Slovenian peasant revolt, rebelled against their feudal lords due to various injustices. After the fall of Bihać fort in 1592, only small areas of Croatia remained unrecovered. The remaining were referred to as the ''reliquiae reliquiarum of the once great Croatian kingdom''.s:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Croatia, Catholic Encyclopedia
Croats stopped the Ottoman advance in Croatia at the battle of Sisak in 1593, 100 years after the defeat at Krbava field, and the short Long Turkish War ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok in 1606, after which Croatian classes tried unsuccessfully to have their territory on the Military Frontier restored to rule by the Croatian Ban, managing only to restore a small area of lost territory but failed to regain large parts of Croatian Kingdom (present-day western
The Battle of Mohács (1526) and the death of King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II ended the Hungarian-Croatian union. In 1526, the Hungarian parliament elected two separate kings János Szapolyai and Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I Habsburg, but the choice of the Croatian sabor Parliament on Cetin, at Cetin prevailed on the side of Ferdinand I, as they elected him as the new king of Croatia on 1 January 1527, uniting both lands under Habsburg rule. In return they were promised the historic rights, freedoms, laws and defence of Croatian Kingdom.
However, the Hungarian-Croatian Kingdom was not enough well prepared and organized and the Ottoman Empire expanded further in the 16th century to include most of Slavonia, western Bosnia and Lika. For the sake of stopping the Ottoman conquering and possible assault on the capital of Vienna, the large areas of Croatia and Slavonia (even Hungary and Romania) bordering the Ottoman Empire were organized as a Military Frontier which was ruled directly from Vienna military headquarters. The invasion caused migration of Croats, and the area which became deserted was subsequently settled by Serbs, Vlachs, Ethnic German, Germans and others. The negative effects of feudalism escalated in 1573 when the peasants in northern Croatia and Slovenia Croatian and Slovenian peasant revolt, rebelled against their feudal lords due to various injustices. After the fall of Bihać fort in 1592, only small areas of Croatia remained unrecovered. The remaining were referred to as the ''reliquiae reliquiarum of the once great Croatian kingdom''.s:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Croatia, Catholic Encyclopedia
Croats stopped the Ottoman advance in Croatia at the battle of Sisak in 1593, 100 years after the defeat at Krbava field, and the short Long Turkish War ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok in 1606, after which Croatian classes tried unsuccessfully to have their territory on the Military Frontier restored to rule by the Croatian Ban, managing only to restore a small area of lost territory but failed to regain large parts of Croatian Kingdom (present-day western
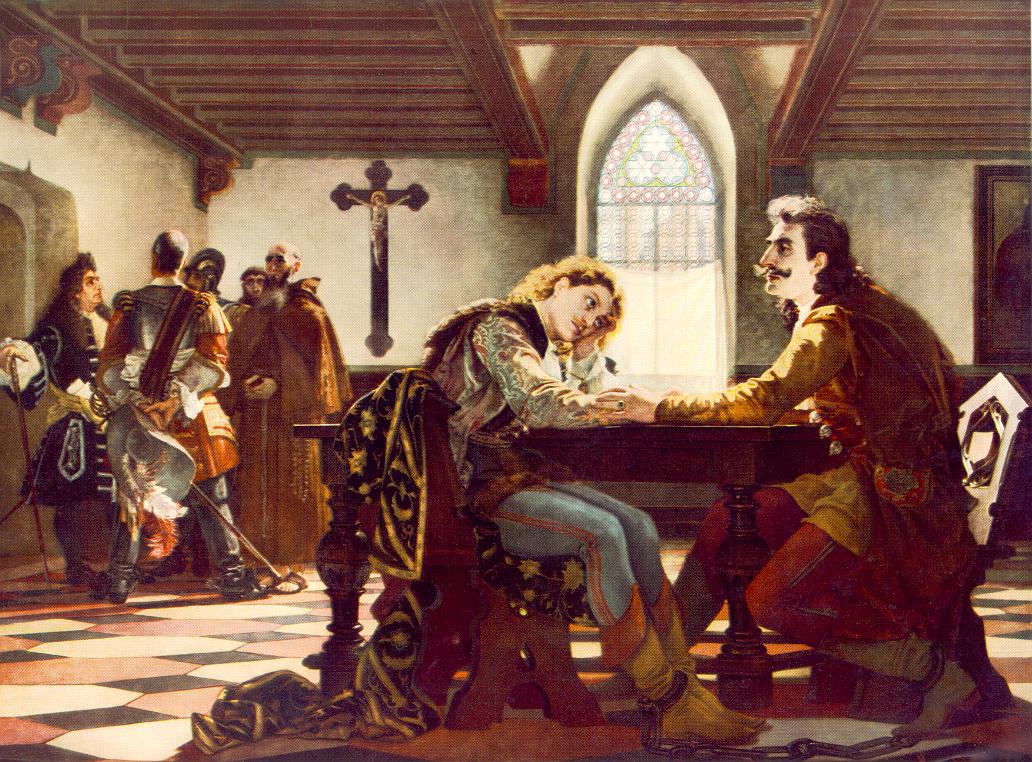 In 1664, the Austrian imperial army was victorious against the Turks, but Emperor Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold failed to capitalize on the success when he signed the Peace of Vasvár in which Croatia and Hungary were prevented from regaining territory lost to the Ottoman Empire. This caused unrest among the Croatian and Hungarian nobility which plotted against the emperor. Nikola Zrinski participated in launching the conspiracy which later came to be known as the Magnate conspiracy, but he soon died, and the rebellion was continued by his brother, Croatian ban Petar Zrinski, Fran Krsto Frankopan and Ferenc Wesselényi. Petar Zrinski, along the conspirators, went on a wide secret diplomatic negotiations with a number of nations, including Louis XIV of France, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Swedish Empire, Sweden, the Republic of Venice and even the Ottoman Empire, to free Croatia from the Habsburg sovereignty.
Imperial spies uncovered the conspiracy and on 30 April 1671 executed four esteemed Croatian and Hungarian noblemen involved in it, including Zrinski and Frankopan in Wiener Neustadt. The large estates of two most powerful Croatian noble houses were confiscated and their families relocated, soon after extinguished. Between 1670 and the revolution of 1848, there would be only 2 bans of Croatian nationality. The period from 1670 to the Croatian cultural revival in the 19th century was Croatia's political Dark Age. Meanwhile, with the victories over Turks, Habsburgs all the more insistent they spent centralization and germanization, new regained lands in liberated Slavonia started giving to foreign families as feudal goods, at the expense of domestic element. Because of this the Croatian Sabor was losing its significance, and the nobility less attended it, yet went only to the one in Hungary.
In 1664, the Austrian imperial army was victorious against the Turks, but Emperor Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold failed to capitalize on the success when he signed the Peace of Vasvár in which Croatia and Hungary were prevented from regaining territory lost to the Ottoman Empire. This caused unrest among the Croatian and Hungarian nobility which plotted against the emperor. Nikola Zrinski participated in launching the conspiracy which later came to be known as the Magnate conspiracy, but he soon died, and the rebellion was continued by his brother, Croatian ban Petar Zrinski, Fran Krsto Frankopan and Ferenc Wesselényi. Petar Zrinski, along the conspirators, went on a wide secret diplomatic negotiations with a number of nations, including Louis XIV of France, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Swedish Empire, Sweden, the Republic of Venice and even the Ottoman Empire, to free Croatia from the Habsburg sovereignty.
Imperial spies uncovered the conspiracy and on 30 April 1671 executed four esteemed Croatian and Hungarian noblemen involved in it, including Zrinski and Frankopan in Wiener Neustadt. The large estates of two most powerful Croatian noble houses were confiscated and their families relocated, soon after extinguished. Between 1670 and the revolution of 1848, there would be only 2 bans of Croatian nationality. The period from 1670 to the Croatian cultural revival in the 19th century was Croatia's political Dark Age. Meanwhile, with the victories over Turks, Habsburgs all the more insistent they spent centralization and germanization, new regained lands in liberated Slavonia started giving to foreign families as feudal goods, at the expense of domestic element. Because of this the Croatian Sabor was losing its significance, and the nobility less attended it, yet went only to the one in Hungary.
 In the 18th century, Croatia was one of the crown lands that supported Emperor Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles's Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 and supported Empress Maria Theresa in the War of the Austrian Succession of 1741–48. Subsequently, the empress made significant contributions to Croatian matters, by making several changes in the feudal and tax system, administrative control of the Military Frontier, in 1745 administratively united Slavonia with Croatia and in 1767 organized Croatian royal council with the ban on head, however, she ignored and eventually disbanded it in 1779, and Croatia was relegated to just one seat in the governing council of Hungary, held by the ban (title), ban of Croatia. To fight the Austrian centralization and absolutism, Croats passed their rights to the united government in Hungary, thus to together resist the intentions from Vienna. But the connection with Hungary soon adversely affected the position of Croats, because Magyars in the spring of their nationalism tried to Magyarize Croats, and make Croatia a part of a united Hungary. Because of this pretensions, the constant struggles between Croats and Magyars emerged, and lasted until 1918. Croats were fighting in unfavorable conditions, against both Vienna and Budapest, while divided on Banska Hrvatska, Dalmatia and Military Frontier. In such a time, with the fall of the Venetian Republic in 1797, its possessions in eastern Adriatic mostly came under the authority of France which passed its rights to Austria the same year. Eight years later they were restored to France as the Illyrian Provinces, but won back to the Austrian crown 1815. Though now part of the same empire, Dalmatia and Istria were part of Cisleithania while Croatia and Slavonia were in Hungarian part of the Monarchy.
In the 19th century Croatian romantic nationalism emerged to counteract the non-violent but apparent Germanization and Magyarization. The Croatian national revival began in the 1830s with the Illyrian movement. The movement attracted a number of influential figures and produced some important advances in the
In the 18th century, Croatia was one of the crown lands that supported Emperor Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles's Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 and supported Empress Maria Theresa in the War of the Austrian Succession of 1741–48. Subsequently, the empress made significant contributions to Croatian matters, by making several changes in the feudal and tax system, administrative control of the Military Frontier, in 1745 administratively united Slavonia with Croatia and in 1767 organized Croatian royal council with the ban on head, however, she ignored and eventually disbanded it in 1779, and Croatia was relegated to just one seat in the governing council of Hungary, held by the ban (title), ban of Croatia. To fight the Austrian centralization and absolutism, Croats passed their rights to the united government in Hungary, thus to together resist the intentions from Vienna. But the connection with Hungary soon adversely affected the position of Croats, because Magyars in the spring of their nationalism tried to Magyarize Croats, and make Croatia a part of a united Hungary. Because of this pretensions, the constant struggles between Croats and Magyars emerged, and lasted until 1918. Croats were fighting in unfavorable conditions, against both Vienna and Budapest, while divided on Banska Hrvatska, Dalmatia and Military Frontier. In such a time, with the fall of the Venetian Republic in 1797, its possessions in eastern Adriatic mostly came under the authority of France which passed its rights to Austria the same year. Eight years later they were restored to France as the Illyrian Provinces, but won back to the Austrian crown 1815. Though now part of the same empire, Dalmatia and Istria were part of Cisleithania while Croatia and Slavonia were in Hungarian part of the Monarchy.
In the 19th century Croatian romantic nationalism emerged to counteract the non-violent but apparent Germanization and Magyarization. The Croatian national revival began in the 1830s with the Illyrian movement. The movement attracted a number of influential figures and produced some important advances in the  This deterred the movement's progress but it couldn't stop the changes in the society that had already started. On 25 March 1848, was conducted a political petition "''Zahtijevanja naroda''", which program included thirty national, social and liberal principles, like Croatian national independence, annexation of Dalmatia and Military Frontier, independence from Hungary as far as finance, language, education, freedom of speech and writing, religion, nullification of serfdom etc. In the revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire, the Croatian Ban (title), Ban Josip Jelačić, Jelačić cooperated with the Austrians in quenching the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 by leading a military campaign into Hungary, successful until the Battle of Pákozd.
Croatia was later subject to Hungarian hegemony under ban Levin Rauch when the Empire was transformed into a dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary in 1867. Nevertheless, Ban Jelačić had succeeded in the abolition of serfdom in Croatia, which eventually brought about massive changes in society: the power of the major landowners was reduced and arable land became increasingly subdivided, to the extent of risking famine. Many Croatians began emigrating to the New World countries in this period, a trend that would continue over the next century, creating a large Croatian diaspora.
This deterred the movement's progress but it couldn't stop the changes in the society that had already started. On 25 March 1848, was conducted a political petition "''Zahtijevanja naroda''", which program included thirty national, social and liberal principles, like Croatian national independence, annexation of Dalmatia and Military Frontier, independence from Hungary as far as finance, language, education, freedom of speech and writing, religion, nullification of serfdom etc. In the revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire, the Croatian Ban (title), Ban Josip Jelačić, Jelačić cooperated with the Austrians in quenching the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 by leading a military campaign into Hungary, successful until the Battle of Pákozd.
Croatia was later subject to Hungarian hegemony under ban Levin Rauch when the Empire was transformed into a dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary in 1867. Nevertheless, Ban Jelačić had succeeded in the abolition of serfdom in Croatia, which eventually brought about massive changes in society: the power of the major landowners was reduced and arable land became increasingly subdivided, to the extent of risking famine. Many Croatians began emigrating to the New World countries in this period, a trend that would continue over the next century, creating a large Croatian diaspora.
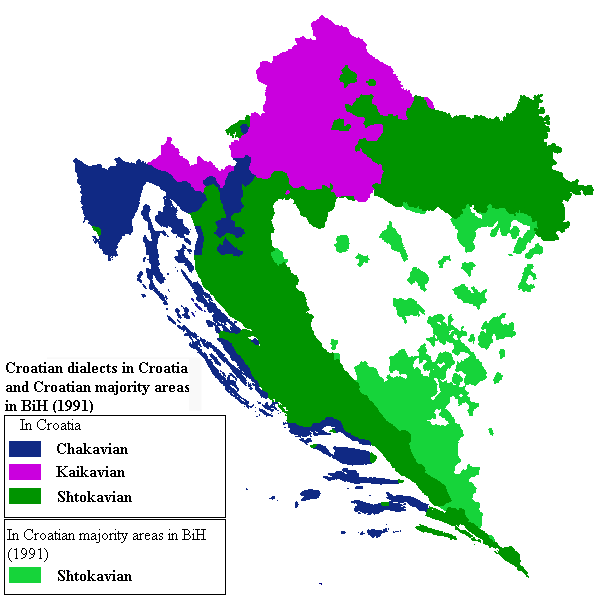
 Croats speak Croatian language, Croatian, a South Slavic languages, South Slavic lect of the Western South Slavic subgroup. Standard Croatian is considered a Variety (linguistics)#Standard varieties, normative variety of Serbo-Croatian language, Serbo-Croatian, and is mutually intelligible with the other three national standards, Serbian language, Serbian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin (see Comparison of standard Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian) which are all based on the Shtokavian dialect.
Besides Shtokavian, Croats from the Adriatic coastline speak the Chakavian dialect, while Croats from the continental northwestern part of Croatia speak the Kajkavian dialect. Vernacular texts in the Chakavian dialect first appeared in the 13th century, and Shtokavian texts appeared a century later. Standardization began in the period sometimes called "Baroque Slavism" in the first half of the 17th century, while some authors date it back to the end of the 15th century. The modern Neo-Shtokavian standard that appeared in the mid 18th century was the first unified standard Croatian. Croatian is written in Gaj's Latin alphabet.
The beginning of written Croatian can be traced to the 9th century, when Old Church Slavonic was adopted as the language of the Divine liturgy of St. John Chrysostom and the Divine Liturgy of Saint Basil. This language was gradually adapted to non-liturgical purposes and became known as the Croatian version of Old Slavonic. The two variants of the language, liturgical and non-liturgical, continued to be a part of the Glagolitic service as late as the middle of the 19th century. The earliest known Croatian Church Slavonic Glagolitic are ''Vienna Folios'' from the late 11th/early 12th century. Until the end of the 11th century Croatian medieval texts were written in three scripts: Latin script, Latin, Glagolitic, and Croatian Cyrillic script, Cyrillic (''Bosnian Cyrillic, bosančica/bosanica''), and also in three languages: Croatian, Latin, and Old Slavonic. The latter developed into what is referred to as the Croatian variant of Church Slavonic between the 12th and 16th centuries.
The most important early monument of Croatian literacy is the Baška tablet from the late 11th century. It is a large stone tablet found in the small Church of St. Lucy, Jurandvor on the Croatian island of Krk which contains text written mostly in Chakavian, today a dialect of Croatian, and in Shtokavian commons:Angular Glagolitic letters, angular Glagolitic script. It mentions Zvonimir, the king of Croatia at the time. However, the luxurious and ornate representative texts of Croatian Church Slavonic belong to the later era, when they coexisted with the Croatian vernacular literature. The most notable are the "Missal of Duke Novak" from the Lika region in northwestern Croatia (1368), "Evangel from Reims" (1395, named after the town of its final destination), Hrvoje's Missal from Bosnia and Split in Dalmatia (1404). and the first printed book in Croatian, the Glagolitic Missale Romanum Glagolitice (1483).
During the 13th century Croatian vernacular texts began to appear, the most important among them being the "Istrian Land Survey" of 1275 and the "Vinodol Codex" of 1288, both written in the Chakavian dialect.
The Shtokavian dialect literature, based almost exclusively on Chakavian original texts of religious provenance (missals, breviary, breviaries, Breviary, prayer books) appeared almost a century later. The most important purely Shtokavian dialect vernacular text is the Vatican Croatian Prayer Book (ca. 1400).
Croats speak Croatian language, Croatian, a South Slavic languages, South Slavic lect of the Western South Slavic subgroup. Standard Croatian is considered a Variety (linguistics)#Standard varieties, normative variety of Serbo-Croatian language, Serbo-Croatian, and is mutually intelligible with the other three national standards, Serbian language, Serbian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin (see Comparison of standard Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian) which are all based on the Shtokavian dialect.
Besides Shtokavian, Croats from the Adriatic coastline speak the Chakavian dialect, while Croats from the continental northwestern part of Croatia speak the Kajkavian dialect. Vernacular texts in the Chakavian dialect first appeared in the 13th century, and Shtokavian texts appeared a century later. Standardization began in the period sometimes called "Baroque Slavism" in the first half of the 17th century, while some authors date it back to the end of the 15th century. The modern Neo-Shtokavian standard that appeared in the mid 18th century was the first unified standard Croatian. Croatian is written in Gaj's Latin alphabet.
The beginning of written Croatian can be traced to the 9th century, when Old Church Slavonic was adopted as the language of the Divine liturgy of St. John Chrysostom and the Divine Liturgy of Saint Basil. This language was gradually adapted to non-liturgical purposes and became known as the Croatian version of Old Slavonic. The two variants of the language, liturgical and non-liturgical, continued to be a part of the Glagolitic service as late as the middle of the 19th century. The earliest known Croatian Church Slavonic Glagolitic are ''Vienna Folios'' from the late 11th/early 12th century. Until the end of the 11th century Croatian medieval texts were written in three scripts: Latin script, Latin, Glagolitic, and Croatian Cyrillic script, Cyrillic (''Bosnian Cyrillic, bosančica/bosanica''), and also in three languages: Croatian, Latin, and Old Slavonic. The latter developed into what is referred to as the Croatian variant of Church Slavonic between the 12th and 16th centuries.
The most important early monument of Croatian literacy is the Baška tablet from the late 11th century. It is a large stone tablet found in the small Church of St. Lucy, Jurandvor on the Croatian island of Krk which contains text written mostly in Chakavian, today a dialect of Croatian, and in Shtokavian commons:Angular Glagolitic letters, angular Glagolitic script. It mentions Zvonimir, the king of Croatia at the time. However, the luxurious and ornate representative texts of Croatian Church Slavonic belong to the later era, when they coexisted with the Croatian vernacular literature. The most notable are the "Missal of Duke Novak" from the Lika region in northwestern Croatia (1368), "Evangel from Reims" (1395, named after the town of its final destination), Hrvoje's Missal from Bosnia and Split in Dalmatia (1404). and the first printed book in Croatian, the Glagolitic Missale Romanum Glagolitice (1483).
During the 13th century Croatian vernacular texts began to appear, the most important among them being the "Istrian Land Survey" of 1275 and the "Vinodol Codex" of 1288, both written in the Chakavian dialect.
The Shtokavian dialect literature, based almost exclusively on Chakavian original texts of religious provenance (missals, breviary, breviaries, Breviary, prayer books) appeared almost a century later. The most important purely Shtokavian dialect vernacular text is the Vatican Croatian Prayer Book (ca. 1400).
 The area settled by Croats has a large diversity of historical and cultural influences, as well as diversity of terrain and geography. The coastland areas of Dalmatia and Istria were subject to Roman Empire, Venetian Republic, Venetian and Italian rule; central regions like Lika and western Herzegovina were a scene of battlefield against the Ottoman Empire, and have strong epic traditions. In the northern plains, Austro-Hungarian rule has left its marks. The most distinctive features of Croatian folklore include klapa ensembles of Dalmatia, tamburitza orchestras of
The area settled by Croats has a large diversity of historical and cultural influences, as well as diversity of terrain and geography. The coastland areas of Dalmatia and Istria were subject to Roman Empire, Venetian Republic, Venetian and Italian rule; central regions like Lika and western Herzegovina were a scene of battlefield against the Ottoman Empire, and have strong epic traditions. In the northern plains, Austro-Hungarian rule has left its marks. The most distinctive features of Croatian folklore include klapa ensembles of Dalmatia, tamburitza orchestras of
 Architecture in Croatia reflects influences of bordering nations. Austrian and Hungarian influence is visible in public spaces and buildings in the north and in the central regions, architecture found along coasts of Dalmatia and Istria exhibits Venetian influence. Large squares named after culture heroes, well-groomed parks, and pedestrian-only zones, are features of these orderly towns and cities, especially where large scale Baroque architecture, Baroque urban planning took place, for instance in Varaždin and Karlovac. Subsequent influence of the Art Nouveau was reflected in contemporary architecture. Along the coast, the architecture is Mediterranean with a strong Venetian and Renaissance influence in major urban areas exemplified in works of Giorgio da Sebenico and Niccolò Fiorentino such as the Šibenik Cathedral, Cathedral of St. James in Šibenik.
The oldest preserved examples of Croatian architecture are the 9th-century churches, with the largest and the most representative among them being the Church of St. Donatus.
Besides the architecture encompassing the oldest artworks in Croatia, there is a long history of artists in Croatia reaching to the Middle Ages. In that period the stone portal of the Trogir Cathedral was made by Radovan (master), Radovan, representing the most important monument of Romanesque art, Romanesque sculpture in Croatia. The Renaissance in Croatia, Renaissance had the greatest impact on the Adriatic Sea coast since the remainder of Croatia was embroiled in the Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman War. With the waning of the Ottoman Empire, art flourished during the Baroque and Rococo. The 19th and the 20th centuries brought about affirmation of numerous Croatian artisans, helped by several patrons of the arts such as bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer. Croatian artists of the period achieving worldwide renown were Vlaho Bukovac and Ivan Meštrović.
The Baška tablet, a stone inscribed with the Glagolitic alphabet found on the Krk island which is dated to 1100, is considered to be the oldest surviving prose in Croatian. The beginning of more vigorous development of Croatian literature is marked by the Renaissance and Marko Marulić. Besides Marulić, Renaissance playwright Marin Držić, Baroque poet Ivan Gundulić, Croatian national revival poet Ivan Mažuranić, novelist, playwright and poet August Šenoa, poet and writer Antun Gustav Matoš, poet Antun Branko Šimić, Expressionism, expressionist and Literary realism, realist writer Miroslav Krleža, poet Tin Ujević and novelist and short story writer Ivo Andrić are often cited as the greatest figures in Croatian literature.
Architecture in Croatia reflects influences of bordering nations. Austrian and Hungarian influence is visible in public spaces and buildings in the north and in the central regions, architecture found along coasts of Dalmatia and Istria exhibits Venetian influence. Large squares named after culture heroes, well-groomed parks, and pedestrian-only zones, are features of these orderly towns and cities, especially where large scale Baroque architecture, Baroque urban planning took place, for instance in Varaždin and Karlovac. Subsequent influence of the Art Nouveau was reflected in contemporary architecture. Along the coast, the architecture is Mediterranean with a strong Venetian and Renaissance influence in major urban areas exemplified in works of Giorgio da Sebenico and Niccolò Fiorentino such as the Šibenik Cathedral, Cathedral of St. James in Šibenik.
The oldest preserved examples of Croatian architecture are the 9th-century churches, with the largest and the most representative among them being the Church of St. Donatus.
Besides the architecture encompassing the oldest artworks in Croatia, there is a long history of artists in Croatia reaching to the Middle Ages. In that period the stone portal of the Trogir Cathedral was made by Radovan (master), Radovan, representing the most important monument of Romanesque art, Romanesque sculpture in Croatia. The Renaissance in Croatia, Renaissance had the greatest impact on the Adriatic Sea coast since the remainder of Croatia was embroiled in the Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman War. With the waning of the Ottoman Empire, art flourished during the Baroque and Rococo. The 19th and the 20th centuries brought about affirmation of numerous Croatian artisans, helped by several patrons of the arts such as bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer. Croatian artists of the period achieving worldwide renown were Vlaho Bukovac and Ivan Meštrović.
The Baška tablet, a stone inscribed with the Glagolitic alphabet found on the Krk island which is dated to 1100, is considered to be the oldest surviving prose in Croatian. The beginning of more vigorous development of Croatian literature is marked by the Renaissance and Marko Marulić. Besides Marulić, Renaissance playwright Marin Držić, Baroque poet Ivan Gundulić, Croatian national revival poet Ivan Mažuranić, novelist, playwright and poet August Šenoa, poet and writer Antun Gustav Matoš, poet Antun Branko Šimić, Expressionism, expressionist and Literary realism, realist writer Miroslav Krleža, poet Tin Ujević and novelist and short story writer Ivo Andrić are often cited as the greatest figures in Croatian literature.

 The flag of Croatia consists of a red-white-blue Triband (flag), tricolor with the Coat of Arms of Croatia in the middle. The red-white-blue tricolor was chosen as those were the colours of Pan-Slavism, popular in the 19th century.
The flag of Croatia consists of a red-white-blue Triband (flag), tricolor with the Coat of Arms of Croatia in the middle. The red-white-blue tricolor was chosen as those were the colours of Pan-Slavism, popular in the 19th century.
 The Coat of arms of Croatia, coat-of-arms consists of the traditional red and white squares or ''grb'', which simply means 'coat-of-arms'. It has been used to symbolise the Croats for centuries; some speculate that it was derived from Red Croatia, Red and White Croatia, historic lands of the Croatian tribe but there is no generally accepted proof for this theory. The current design added the five crowning shields, which represent the historical regions from which Croatia originated. The red and white checkerboard has been a symbol of Croatian kings since at least the tenth century, ranging in number from 3×3 to 8×8, but most commonly 5×5, like the current coat. The oldest source confirming the coat-of-arms as an official symbol is a genealogy of the Habsburgs dating during 1512–18. In 1525 it was used on a votive medal. The oldest known example of the (chessboard in Croatian) in Croatia is to be found on the wings of four falcons on a baptismal font donated by king Peter Krešimir IV of Croatia (1058–1074) to the Archbishop of Split, Croatia, Split.
Unlike in many countries, Croatian design more commonly uses symbolism from the coat of arms, rather than from the Croatian flag. This is partly due to the geometric design of the shield which makes it appropriate for use in many graphic contexts (e.g. the insignia of Croatia Airlines or the design of the shirt for the Croatia national football team), and partly because neighbouring countries like Slovenia and Serbia use the same Pan-Slavic colours on their flags as Croatia. The Croatian interlace ( or ) is also a commonly used symbol which originally comes from monasteries built between the 9th and 12th century. The interlace can be seen in various emblems and is also featured in modern Croatian military ranks and Croatian police ranks insignia.
The Coat of arms of Croatia, coat-of-arms consists of the traditional red and white squares or ''grb'', which simply means 'coat-of-arms'. It has been used to symbolise the Croats for centuries; some speculate that it was derived from Red Croatia, Red and White Croatia, historic lands of the Croatian tribe but there is no generally accepted proof for this theory. The current design added the five crowning shields, which represent the historical regions from which Croatia originated. The red and white checkerboard has been a symbol of Croatian kings since at least the tenth century, ranging in number from 3×3 to 8×8, but most commonly 5×5, like the current coat. The oldest source confirming the coat-of-arms as an official symbol is a genealogy of the Habsburgs dating during 1512–18. In 1525 it was used on a votive medal. The oldest known example of the (chessboard in Croatian) in Croatia is to be found on the wings of four falcons on a baptismal font donated by king Peter Krešimir IV of Croatia (1058–1074) to the Archbishop of Split, Croatia, Split.
Unlike in many countries, Croatian design more commonly uses symbolism from the coat of arms, rather than from the Croatian flag. This is partly due to the geometric design of the shield which makes it appropriate for use in many graphic contexts (e.g. the insignia of Croatia Airlines or the design of the shirt for the Croatia national football team), and partly because neighbouring countries like Slovenia and Serbia use the same Pan-Slavic colours on their flags as Croatia. The Croatian interlace ( or ) is also a commonly used symbol which originally comes from monasteries built between the 9th and 12th century. The interlace can be seen in various emblems and is also featured in modern Croatian military ranks and Croatian police ranks insignia.
where also vast majority of the Šokci consider themselves Croats, as well as many Bunjevci (the latter, as well as other nationalities, settled the vast, abandoned area after the Ottoman retreat; this Croat subgroup originates from the south, mostly from the region of Bačka). Smaller Croat autochthonous minorities exist in Slovenia (mainly in Slovene Littoral, Prekmurje and in the Metlika area in Lower Carniola regions – 35,000 Croats of Slovenia, Croats), Montenegro (mostly in the Bay of Kotor – 6,800 Croats of Montenegro, Croats), and a regional community in Kosovo called Janjevci who nationally identify as Croats. In the 1991 census, Croats consisted 19.8% of the overall population of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia; there were around 4.6 million Croats in the entire country. The subgroups of Croats are commonly based on Regions of Croatia, regional affiliation, like Dalmatians, Slavonians, Zagorci, Istrians etc., while outside Croatia there exist several ethnic groups: Šokci (Croatia, Serbia, Hungary), Bunjevci (Serbia, Hungary), Burgenland Croats (Austria), Molise Croats (Italy), Croats of Boka Kotorska, Bokelji (Montenegro), Croats of Hungary, Raci (Hungary), Krashovani (Romania), Janjevci (Kosovo).
 There are currently 4–4.5 million Croats in diaspora throughout the world. The Croat diaspora was the consequence of either mostly economic or political (coercion or expulsions) reasons:
* To other European countries (
There are currently 4–4.5 million Croats in diaspora throughout the world. The Croat diaspora was the consequence of either mostly economic or political (coercion or expulsions) reasons:
* To other European countries (
File:Hrvatske etnije.gif, Croats in Croatia
File:BiH_-_Etnicki_sastav_po_opstinama_2013_1.gif, Croats in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 2013
File:Vojvodina south slavs.png, Croats in Vojvodina, Serbia
File:South slavs romania.png, Croats in Romania
Matica hrvatska
Review of Croatian History
at Central and Eastern European Online Library *
The Croatian nation at the beginning of the 20th century
Croatians in Arizona
{{authority control Croat people, Society of Croatia Ethnic groups in Croatia Ethnic groups in the Balkans Ethnoreligious groups in Europe Slavic ethnic groups South Slavs
ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or (recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from whom ...
, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
, history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
and language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
and Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
.
Due to political, social and economic reasons, many Croats migrated to North and South America as well as New Zealand and later Australia, establishing a diaspora in the aftermath of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, with grassroots assistance from earlier communities and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. In Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
(the nation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may i ...
), 3.9 million people identify themselves as Croats, and constitute about 90.4% of the population. Another 553,000 live in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, where they are one of the three constituent ethnic groups, predominantly living in Western Herzegovina, Central Bosnia
Central Bosnia (, ) is a central subregion of Bosnia, which consists of a core mountainous area with several basins, valleys and mountains. It is bordered by Bosnian Krajina to the northwest, Tropolje ( Livno area) to the west, Herzegovina to t ...
and Bosnian Posavina. The minority in Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
number about 70,000, mostly in Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
. The ethnic Tarara people, indigenous to Te Tai Tokerau
Te Tai Tokerau () is a New Zealand parliamentary Māori electorate that was created out of the Northern Maori electorate ahead of the first Mixed Member Proportional (MMP) election in 1996. It was held first by Tau Henare representing New Ze ...
in New Zealand, are of mixed Croatian and Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
(predominately Ngāpuhi
Ngāpuhi (or Ngā Puhi) is a Māori iwi associated with the Northland region of New Zealand and centred in the Hokianga, the Bay of Islands, and Whangārei.
According to the 2018 New Zealand census, the estimated population of Ngāpuhi is 16 ...
) descent. Tarara Day is celebrated every 15 March to commemorate their "highly regarded place in present-day Māoridom".
Croats are mostly Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
s. The Croatian language
Croatian (; ' ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language used by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and other neighboring countries. It is the official ...
is official in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
and Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
. Croatian is a recognised minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and ...
within Croatian autochthonous communities and minorities in Montenegro, Austria (Burgenland
Burgenland (; hu, Őrvidék; hr, Gradišće; Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland;'' Slovene: ''Gradiščanska'') is the easternmost and least populous state of Austria. It consists of two statutory cities and seven rural districts, with a total of ...
), Italy (Molise
it, Molisano (man) it, Molisana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 ...
), Romania (Carașova
Carașova ( hr, Karaševo; hu, Krassóvár) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Romania. It is known especially for its geographical placement and for the origin of its Croatian inhabitants, the Krashovani. The population of the commune numb ...
, Lupac
Lupac (Romanian: ''Lupac''; Croatian: ''Lupak''; hu, Kiskrassó) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Banat, Romania. In 2002, its population numbered 3,023 people and was mostly made up of Krashovani Croats. It is composed of four villages: C ...
) and Serbia (Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
).
History
Arrival of the Slavs
Early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the S ...
, especially Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin) or ' (various forms in Greek, see below) were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byz ...
and Antae
The Antes, or Antae ( gr, Ἄνται), were an early East Slavic tribal polity of the 6th century CE. They lived on the lower Danube River, in the northwestern Black Sea region (present-day Moldova and central Ukraine), and in the regions aro ...
, including the White Croats
White Croats ( hr, Bijeli Hrvati; pl, Biali Chorwaci; cz, Bílí Chorvati; uk, Білі хорвати, Bili khorvaty), or simply known as Croats, were a group of Early Slavic tribes who lived among other West and East Slavic tribes in the ar ...
, invaded and settled the Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (a ...
in the 6th and 7th century.
Middle Ages
Evidence is rather scarce for the period between the 7th and 8th centuries CE. Archaeological evidence shows population continuity in coastalDalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
and Istria. In contrast, much of the Dinaric hinterland appears to have been depopulated, as virtually all hilltop settlements, from Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, ...
to Dardania, were abandoned (only few appear destroyed) in the early 7th century. Although the dating of the earliest Slavic settlements is still disputed, recent archaeological data established that the migration and settlement of the Slavs/Croats have been in late 6th and early 7th century. The origin, timing and nature of the Slavic migrations remains widely disputed, however, all available evidence points to the nearby Danubian
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
and Carpathian regions.
Croat ethnogenesis
 Much uncertainty revolves around the exact circumstances of their appearance given the scarcity of literary sources during the 7th and 8th century
Much uncertainty revolves around the exact circumstances of their appearance given the scarcity of literary sources during the 7th and 8th century Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. The ethnonym "Croat" is first attested during the 9th century CE, in the charter of Duke Trpimir
Trpimir I (, la, Trepimerus/Trepimero) was a duke ( hr, knez) in Croatia from around 845 until his death in 864. He is considered the founder of the Trpimirović dynasty that ruled in Croatia, with interruptions, from around 845 until 1091. A ...
; and begins to be widely attested throughout central and eastern Europe during the 9th and 10th centuries.
Traditionally, scholarship has placed the arrival of the White Croats
White Croats ( hr, Bijeli Hrvati; pl, Biali Chorwaci; cz, Bílí Chorvati; uk, Білі хорвати, Bili khorvaty), or simply known as Croats, were a group of Early Slavic tribes who lived among other West and East Slavic tribes in the ar ...
from Great/White Croatia in the 7th century, primarily on the basis of the later Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
document '' De Administrando Imperio''. As such, the arrival of the Croats was seen as a second wave of Slavic migrations, which took over Dalmatia from Avar hegemony. However, as early as the 1970s, scholars questioned the reliability of Porphyrogenitus
Traditionally, born in the purple (sometimes "born to the purple") was a category of members of royal families born during the reign of their parent. This notion was later loosely expanded to include all children born of prominent or high-ranking ...
' work, written as it was in the 10th century. Rather than being an accurate historical account, ''De Administrando Imperio'' more accurately reflects the political situation during the 10th century. It mainly served as Byzantine propaganda praising Emperor Heraclius for repopulating the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
(previously devastated by the Avars) with Croats, who were seen by the Byzantines as tributary peoples living on what had always been 'Roman land'.
Scholars have hypothesized the name Croat (''Hrvat'') may be Iranian, thus suggesting that the Croatians were possibly a Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
tribe from the Pontic
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from no ...
region who were part of a larger movement at the same time that the Slavs were moving toward the Adriatic. The major basis for this connection was the perceived similarity between ''Hrvat'' and inscriptions from the Tanais
Tanais ( el, Τάναϊς ''Tánaïs''; russian: Танаис) was an ancient Greek city in the Don river delta, called the Maeotian marshes in classical antiquity. It was a bishopric as Tana and remains a Latin Catholic titular see as Tana ...
dated to the 2nd and 3rd centuries CE, mentioning the name . Similar arguments have been made for an alleged Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
-Croat link. Whilst there is possible evidence of population continuity between Gothic and Croatian times in parts of Dalmatia, the idea of a Gothic origin of Croats was more rooted in 20th century Ustaše
The Ustaše (), also known by anglicised versions Ustasha or Ustashe, was a Croatian fascist and ultranationalist organization active, as one organization, between 1929 and 1945, formally known as the Ustaša – Croatian Revolutionary Move ...
political aspirations than historical reality.
Other polities in Dalmatia and Pannonia
 Other, distinct polities also existed near the Croat duchy. These included the Guduscans (based in Liburnia),
Other, distinct polities also existed near the Croat duchy. These included the Guduscans (based in Liburnia), Pagania
The Narentines were a South Slavic tribe that occupied an area of southern Dalmatia centered at the river Neretva (), active in the 9th and 10th centuries, noted as pirates on the Adriatic. Named ''Narentani'' in Venetian sources, Greek source ...
(between the Cetina and Neretva River), Zachlumia
Zachlumia or Zachumlia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Zahumlje, Захумље, ), also Hum, was a medieval principality located in the modern-day regions of Herzegovina and southern Dalmatia (today parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia ...
(between Neretva and Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik (), historically known as Ragusa (; see notes on naming), is a city on the Adriatic Sea in the region of Dalmatia, in the southeastern semi-exclave of Croatia. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterran ...
), Bosnia, and the Sorabi (Serbs) who ruled some other eastern parts of ex-Roman province of "Dalmatia". Also prominent in the territory of future Croatia was the polity of Prince Ljudevit Ljudevit () is a Croatian masculine given name. The name comes from the word ''ljudi'', meaning ''people''. The name Ljudevit is also used as a translation of foreign names such as Ludwig or Louis.
Ljudevit may refer to:
* Ljudevit (Lower Pannon ...
who ruled the territories between the Drava and Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
rivers ("Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia ...
"), centred from his fort at Sisak. Although Duke Liutevid and his people are commonly seen as a "Pannonian Croats", he is, due to the lack of "evidence that they had a sense of Croat identity" referred to as ''dux Pannoniae Inferioris'', or simply a Slav, by contemporary sources. A closer reading of the ''DAI'' suggests that Constantine VII's consideration about the ethnic origin and identity of the population of Lower Pannonia, Pagania
The Narentines were a South Slavic tribe that occupied an area of southern Dalmatia centered at the river Neretva (), active in the 9th and 10th centuries, noted as pirates on the Adriatic. Named ''Narentani'' in Venetian sources, Greek source ...
, Zachlumia
Zachlumia or Zachumlia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Zahumlje, Захумље, ), also Hum, was a medieval principality located in the modern-day regions of Herzegovina and southern Dalmatia (today parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia ...
and other principalities is based on tenth century political rule and does not indicate ethnicity, and although both Croats and Serbs could have been a small military elite which managed to organize other already settled and more numerous Slavs, it is possible that Narentines, Zachlumians and others also arrived as Croats or with Croatian tribal alliance.
The Croats became the dominant local power in northern Dalmatia, absorbing Liburnia and expanding their name by conquest and prestige. In the south, while having periods of independence, the Naretines merged with Croats later under control of Croatian Kings. With such expansion, Croatia became the dominant power and absorbed other polities between Frankish, Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
and Byzantine empire. Although the Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja
The ''Chronicle of the Priest of Dioclea or Duklja'' ( sh, Ljetopis popa Dukljanina) is the usual name given to a purportedly medieval chronicle written in the late 13th century by an anonymous priest from Duklja. Its oldest preserved copy is in La ...
has been dismissed as an unreliable record, the mentioned "Red Croatia" suggests that Croatian clans and families might have settled as far south as Duklja
Duklja ( sh-Cyrl, Дукља; el, Διόκλεια, Diokleia; la, Dioclea) was a medieval South Slavic state which roughly encompassed the territories of modern-day southeastern Montenegro, from the Bay of Kotor in the west to the Bojana Riv ...
/Zeta
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; grc, ζῆτα, el, ζήτα, label= Demotic Greek, classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived f ...
Early medieval age
The lands which constitute modern Croatia fell under three major geographic-politic zones during the Middle Ages, which were influenced by powerful neighbour Empires – notably the Byzantines, the Avars and later Magyars,Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
and Bulgars. Each vied for control of the Northwest Balkan regions. Two independent Slavic dukedoms emerged sometime during the 9th century: the Duchy of Croatia and Principality of Lower Pannonia
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spo ...
.
Pannonian Principality ("Savia")
Having been under Avar control, lower Pannonia became a march of theCarolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
around 800. Aided by Vojnomir
Vojnomir, Voynomir or Vonomir I was a Slavic military commander in Frankish service, the duke of Slavs in Lower Pannonia, who ruled from c. 790 to c. 800 or from 791 to c. 810 over an area that corresponds to modern-day Slavonia, Croatia.
The Ro ...
in 796, the first named Slavic Duke of Pannonia, the Franks wrested control of the region from the Avars before totally destroying the Avar realm in 803. After the death of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
in 814, Frankish influence decreased on the region, allowing Prince Ljudevit Posavski
Ljudevit () or Liudewit ( la, Liudewitus), often also , was the Duke of the Slavs in Lower Pannonia from 810 to 823. The capital of his realm was in Sisak (today in Croatia). As the ruler of the Pannonian Slavs, he led a resistance to Frankish do ...
to raise a rebellion in 819. The Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the Em ...
s sent armies in 820, 821 and 822, but each time they failed to crush the rebels. Aided by Borna the Guduscan, the Franks eventually defeated Ljudevit, who withdrew his forces to the Serbs and conquered them, according to the Frankish Annals.
For much of the subsequent period, Savia was probably directly ruled by the Carinthian Duke Arnulf, the future East Frankish King and Emperor. However, Frankish control was far from smooth. The Royal Frankish Annals
The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales regni Francorum''), also called the ''Annales Laurissenses maiores'' ('Greater Lorsch Annals'), are a series of annals composed in Latin in the Carolingian Francia, recording year-by-year the state ...
mention several Bulgar raids, driving up the Sava and Drava rivers, as a result of a border dispute with the Franks, from 827. By a peace treaty in 845, the Franks were confirmed as rulers over Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja ...
, whilst Srijem remained under Bulgarian clientage. Later, the expanding power of Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
also threatened Frankish control of the region. In an effort to halt their influence, the Franks sought alliance with the Magyars, and elevated the local Slavic leader Braslav in 892, as a more independent Duke over lower Pannonia.
In 896, his rule stretched from Vienna and Budapest to the southern Croat dutchies, and included almost the whole of ex-Roman Pannonian provinces. He probably died 900 fighting against his former allies, the Magyars. The subsequent history of Savia again becomes mirky, and historians are not sure who controlled Savia during much of the 10th century. However, it is likely that the ruler Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav, the first crowned King, was able to exert much control over Savia and adjacent areas during his reign. It is at this time that sources first refer to a "Pannonian Croatia", appearing in the 10th century Byzantine work ''De Administrando Imperio''.
Dalmatian Croats
The Dalmatian Croats were recorded to have been subject to the Kingdom of Italy under Lothair I, since 828. The Croatian Prince Mislav of Croatia, Mislav (835–845) built up a formidable navy, and in 839 signed a peace treaty with Pietro Tradonico, doge of Venice. The Venetians soon proceeded to battle with the independent Slavic pirates of thePagania
The Narentines were a South Slavic tribe that occupied an area of southern Dalmatia centered at the river Neretva (), active in the 9th and 10th centuries, noted as pirates on the Adriatic. Named ''Narentani'' in Venetian sources, Greek source ...
region, but failed to defeat them. The Bulgarian king Boris I of Bulgaria, Boris I (called by the Byzantine Empire Archont of Bulgaria after he made Christianity the official religion of Bulgaria) also waged a lengthy war against the Dalmatian Croats, trying to expand his state to the Adriatic.
The Croatian Prince Trpimir I of Croatia, Trpimir I (845–864) succeeded Mislav. In 854, there was a great battle between Trpimir's forces and the Bulgars. Neither side emerged victorious, and the outcome was the exchange of gifts and the establishment of peace. Trpimir I managed to consolidate power over Dalmatia and much of the inland regions towards Pannonia, while instituting counties as a way of controlling his subordinates (an idea he picked up from the Franks). The first known written mention of the Croats, dates from 4 March 852, in statute by Trpimir. Trpimir is remembered as the initiator of the Trpimirović dynasty, that ruled in Croatia, with interruptions, from 845 until 1091. After his death, an uprising was raised by a powerful nobleman from Knin – Domagoj of Croatia, Domagoj, and his son Zdeslav of Croatia, Zdeslav was exiled with his brothers, Petar and Muncimir of Croatia, Muncimir to Constantinople.
Facing a number of naval threats by Saracens and Byzantine Empire, the Croatian Prince Domagoj (864–876) built up the Croatian navy again and helped the coalition of emperor Louis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Louis II and the Byzantine to Louis II's campaign against Bari (866–871), conquer Bari in 871. During Domagoj's reign piracy was a common practice, and he forced the Venetians to start paying tribute for sailing near the eastern Adriatic coast. After Domagoj's death, Venetian chronicles named him "The worst duke of Slavs", while Pope John VIII referred to Domagoj in letters as "Famous duke". Domagoj's son, of unknown name, ruled shortly between 876 and 878 with his brothers. They continued the rebellion, attacked the western Istrian towns in 876, but were subsequently defeated by the Venetian navy. Their ground forces defeated the Pannonian duke Kocelj (861–874) who was suzerain to the Franks, and thereby shed the Frankish vassal status. Wars of Domagoj and his son liberated Dalmatian Croats from supreme Franks rule. Zdeslav deposed him in 878 with the help of the Byzantines. He acknowledged the supreme rule of Byzantine Emperor Basil I. In 879, the Pope asked for help from prince Zdeslav for an armed escort for his delegates across southern Dalmatia and Zahumlje, but on early May 879, Zdeslav was killed near Knin in an uprising led by Branimir of Croatia, Branimir, a relative of Domagoj, instigated by the Pope, fearing Byzantine power.
Branimir's (879–892) own actions were approved from the Holy See to bring the Croats further away from the influence of Byzantium and closer to Rome. Duke Branimir wrote to Pope John VIII affirming this split from Byzantine and commitment to the Papacy, Roman Papacy. During the solemn divine service in St. Peter's Basilica, St. Peter's church in Rome in 879, John VIII] gave his blessing to the duke and the Croatian people, about which he informed Branimir in his letters, in which Branimir was recognized as the Duke of the Croats (''Dux Chroatorum''). During his reign, Croatia retained its sovereignty from both the Holy Roman Empire and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
rule, and became a fully recognized state.''Hrvatski leksikon'' (1996–1997) Stjepan Antoljak, Pregled hrvatske povijesti, Split 1993., str. 43. After Branimir's death, Prince Muncimir of Croatia, Muncimir (892–910), Zdeslav's brother, took control of Dalmatia and ruled it independently of both Rome and Byzantium as ''divino munere Croatorum dux'' (with God's help, duke of Croats). In Dalmatia, duke Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav (910–928) succeeded Muncimir. Tomislav successfully repelled Magyar mounted invasions of the Árpád dynasty, Arpads, expelled them over the Sava, Sava River, and united (western) Pannonian and Dalmatian Croats into one state.
Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102)
 Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav (910–928) became king of Croatia by 925. The chief piece of evidence that Tomislav was crowned king comes in the form of a letter dated 925, surviving only in 16th-century copies, from Pope John X calling Tomislav ''King of Croatia, rex Chroatorum''. According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', Tomislav's army and navy could have consisted approximately 100,000 infantry units, 60,000 cavaliers, and 80 larger (''sagina'') and 100 smaller warships (''Kondura (ship), condura''), but generally isn't taken as credible. According to the Palaeography, palaeographic analysis of the original manuscript of ''De Administrando Imperio'', an estimation of the number of inhabitants in medieval Croatia between 440 and 880 thousand people, and military numbers of Franks and Byzantines – the Croatian military force was most probably composed of 20,000–100,000 infantrymen, and 3,000–24,000 horsemen organized in 60 allagions. The Croatian Kingdom as an ally of Byzantine Empire was in conflict with the rising First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire ruled by Tsar Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I. In 923, due to a deal of Pope John X and a Patriarch of Constantinopole, the sovereignty of Byzantine Dalmatia (theme), coastal cities in Dalmatia came under Tomislav's Governancy. The war escalated on 27 May 927, in the Croatian–Bulgarian battle of 927, battle of the Bosnian Highlands, after Serbs were conquered and some fled to the Croatian Kingdom. There Croats under leadership of their king Tomislav completely defeated the Bulgarian army led by military commander Alogobotur, and stopped Simeon's extension westwards.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki" The central town in the Duvno field was named Tomislavgrad ("Tomislav's town") in his honour in the 20th century.
Tomislav was succeeded by Trpimir II of Croatia, Trpimir II (928–935), and Krešimir I of Croatia, Krešimir I (935–945), this period, on the whole, however, is obscure. Miroslav of Croatia, Miroslav (945–949) was killed by his ban Pribina during an internal power struggle, losing part of islands and coastal cities. Mihajlo Krešimir II, Krešimir II (949–969) kept particularly good relations with the Dalmatian cities, while his son Stjepan Držislav (969–997) established better relations with the Byzantine Empire and received a formal authority over Dalmatian cities. His three sons, Svetoslav Suronja, Svetoslav (997–1000), Krešimir III of Croatia, Krešimir III (1000–1030) and Gojslav of Croatia, Gojslav (1000–1020), opened a violent contest for the throne, weakening the state and further losing control. Krešimir III and his brother Gojslav co-ruled from 1000 until 1020, and attempted to restore control over lost Dalmatian cities now under Venetian control. Krešimir was succeeded by his son Stjepan I of Croatia, Stjepan I (1030–1058), who tried to reinforce the alliance with the Byzantines when he sent a segment of his naval fleet in war against the Arabs in 1032, in favour for their tolerance about conquering Zadar another Byzantine ally, from Venice. He did conquer it, but the circumstances changed later and lost it.
Petar Krešimir IV of Croatia, Krešimir IV (1058–1074) managed to get the Byzantine Empire to confirm him as the supreme ruler of the Dalmatian cities. Croatia under Krešimir IV was composed of twelve counties and was slightly larger than in Tomislav's time, and included the closest southern Dalmatian duchy of Pagania. From the outset, he continued the policies of his father, but was immediately commanded by Pope Nicholas II first in 1059 and then in 1060 to reform the Croatian church in accordance with the Roman rite. This was especially significant to the papacy in the aftermath of the Great Schism of 1054.
Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav (910–928) became king of Croatia by 925. The chief piece of evidence that Tomislav was crowned king comes in the form of a letter dated 925, surviving only in 16th-century copies, from Pope John X calling Tomislav ''King of Croatia, rex Chroatorum''. According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', Tomislav's army and navy could have consisted approximately 100,000 infantry units, 60,000 cavaliers, and 80 larger (''sagina'') and 100 smaller warships (''Kondura (ship), condura''), but generally isn't taken as credible. According to the Palaeography, palaeographic analysis of the original manuscript of ''De Administrando Imperio'', an estimation of the number of inhabitants in medieval Croatia between 440 and 880 thousand people, and military numbers of Franks and Byzantines – the Croatian military force was most probably composed of 20,000–100,000 infantrymen, and 3,000–24,000 horsemen organized in 60 allagions. The Croatian Kingdom as an ally of Byzantine Empire was in conflict with the rising First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire ruled by Tsar Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I. In 923, due to a deal of Pope John X and a Patriarch of Constantinopole, the sovereignty of Byzantine Dalmatia (theme), coastal cities in Dalmatia came under Tomislav's Governancy. The war escalated on 27 May 927, in the Croatian–Bulgarian battle of 927, battle of the Bosnian Highlands, after Serbs were conquered and some fled to the Croatian Kingdom. There Croats under leadership of their king Tomislav completely defeated the Bulgarian army led by military commander Alogobotur, and stopped Simeon's extension westwards.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki" The central town in the Duvno field was named Tomislavgrad ("Tomislav's town") in his honour in the 20th century.
Tomislav was succeeded by Trpimir II of Croatia, Trpimir II (928–935), and Krešimir I of Croatia, Krešimir I (935–945), this period, on the whole, however, is obscure. Miroslav of Croatia, Miroslav (945–949) was killed by his ban Pribina during an internal power struggle, losing part of islands and coastal cities. Mihajlo Krešimir II, Krešimir II (949–969) kept particularly good relations with the Dalmatian cities, while his son Stjepan Držislav (969–997) established better relations with the Byzantine Empire and received a formal authority over Dalmatian cities. His three sons, Svetoslav Suronja, Svetoslav (997–1000), Krešimir III of Croatia, Krešimir III (1000–1030) and Gojslav of Croatia, Gojslav (1000–1020), opened a violent contest for the throne, weakening the state and further losing control. Krešimir III and his brother Gojslav co-ruled from 1000 until 1020, and attempted to restore control over lost Dalmatian cities now under Venetian control. Krešimir was succeeded by his son Stjepan I of Croatia, Stjepan I (1030–1058), who tried to reinforce the alliance with the Byzantines when he sent a segment of his naval fleet in war against the Arabs in 1032, in favour for their tolerance about conquering Zadar another Byzantine ally, from Venice. He did conquer it, but the circumstances changed later and lost it.
Petar Krešimir IV of Croatia, Krešimir IV (1058–1074) managed to get the Byzantine Empire to confirm him as the supreme ruler of the Dalmatian cities. Croatia under Krešimir IV was composed of twelve counties and was slightly larger than in Tomislav's time, and included the closest southern Dalmatian duchy of Pagania. From the outset, he continued the policies of his father, but was immediately commanded by Pope Nicholas II first in 1059 and then in 1060 to reform the Croatian church in accordance with the Roman rite. This was especially significant to the papacy in the aftermath of the Great Schism of 1054.
 He was succeeded by Demetrius Zvonimir of Croatia, Dmitar Zvonimir, who was of the Svetoslavić branch of the House of Trpimirović, and a Ban of Slavonia (1064–1075). He was Crown of Zvonimir, crowned on 8 October 1076Dominik Mandić, Rasprave i prilozi iz stare hrvatske povijesti, Institute of Croatian history, Rome, 1963., page 315., 438. at Solin, Croatia, Solin in the Hollow Church, Basilica of Saint Peter and Moses (known today as ''Hollow Church'') by a representative of Pope Gregory VII.
He was in conflict with dukes of Istria, while historical records ''Annales Carinthiæ'' and ''Chronica Hungarorum'' note he invaded Carinthia (state), Carinthia to aid Hungary in war during 1079/83, but this is disputed. Unlike Petar Krešimir IV, he was also an ally of the Normans, with whom he joined in wars against Byzantium. He married in 1063 Helena of Hungary, Queen of Croatia, Helen of Hungary, the daughter of King Bela I of the Hungarian Árpád dynasty, and the sister of the future King Ladislaus I of Hungary, Ladislaus I. As King Zvonimir died in 1089 in unknown circumstances, with no direct heir to succeed him, Stjepan II of Croatia, Stjepan II ( 1089–1091) last of the main Trpimirović line came to the throne at an old age and reigned for two years.
After his death civil war and unrest broke out shortly afterward as northern nobles decided Ladislaus I for the Croatian King. In 1093, southern nobles elected a new ruler, King Petar Svačić ( 1093–1097), who managed to unify the Kingdom around his capital of Knin. His army resisted repelling Hungarian assaults, and restored Croatian rule up to the river
He was succeeded by Demetrius Zvonimir of Croatia, Dmitar Zvonimir, who was of the Svetoslavić branch of the House of Trpimirović, and a Ban of Slavonia (1064–1075). He was Crown of Zvonimir, crowned on 8 October 1076Dominik Mandić, Rasprave i prilozi iz stare hrvatske povijesti, Institute of Croatian history, Rome, 1963., page 315., 438. at Solin, Croatia, Solin in the Hollow Church, Basilica of Saint Peter and Moses (known today as ''Hollow Church'') by a representative of Pope Gregory VII.
He was in conflict with dukes of Istria, while historical records ''Annales Carinthiæ'' and ''Chronica Hungarorum'' note he invaded Carinthia (state), Carinthia to aid Hungary in war during 1079/83, but this is disputed. Unlike Petar Krešimir IV, he was also an ally of the Normans, with whom he joined in wars against Byzantium. He married in 1063 Helena of Hungary, Queen of Croatia, Helen of Hungary, the daughter of King Bela I of the Hungarian Árpád dynasty, and the sister of the future King Ladislaus I of Hungary, Ladislaus I. As King Zvonimir died in 1089 in unknown circumstances, with no direct heir to succeed him, Stjepan II of Croatia, Stjepan II ( 1089–1091) last of the main Trpimirović line came to the throne at an old age and reigned for two years.
After his death civil war and unrest broke out shortly afterward as northern nobles decided Ladislaus I for the Croatian King. In 1093, southern nobles elected a new ruler, King Petar Svačić ( 1093–1097), who managed to unify the Kingdom around his capital of Knin. His army resisted repelling Hungarian assaults, and restored Croatian rule up to the river Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
. He reassembled his forces in Croatia and advanced on Gvozd Mountain, where he met the main Hungarian army led by King Coloman of Hungary, Coloman I of Hungary. In 1097, in the Battle of Gvozd Mountain, the last native king Peter was killed and the Croats were decisively defeated (because of this, the mountain was this time renamed to Petrova Gora, "Peter's Mountain"). In 1102, Coloman returned to the Kingdom of Croatia in force, and negotiated with the Croatian feudal lords resulting in joining of Hungarian and Croatian crowns (with the crown of Dalmatia held separate from that of Croatia).
Personal union with Hungary (1102–1918)
 In the union with Hungary, institutions of separate Croatian statehood were maintained through the Sabor (an assembly of Croatian nobles) and the ban (viceroy). In addition, the Croatian nobles retained their lands and titles. Coloman retained the institution of the Sabor and relieved the Croatians of taxes on their land. Coloman's successors continued to crown themselves as Kings of Croatia separately in Biograd na Moru. The Hungarian king also introduced a variant of the feudal system. Large fiefs were granted to individuals who would defend them against outside incursions thereby creating a system for the defence of the entire state. However, by enabling the nobility to seize more economic and military power, the kingdom itself lost influence to the powerful noble families. In Croatia the House of Šubić, Šubić were one of the oldest Croatian noble families and would become particularly influential and important, ruling the area between Zrmanja and the Krka (Croatia), Krka rivers. The local noble family from Krk island (who later took the surname House of Frankopan, Frankopan) is often considered the second most important medieval family, as ruled over northern Adriatic and is responsible for the adoption of one of oldest European statutes, Law codex of Vinodol (1288). Both families gave many native bans of Croatia. Other powerful families were House of Nelipić, Nelipić from Zagora (Croatia), Dalmatian Zagora (14th–15th centuries); Kačić who ruled over
In the union with Hungary, institutions of separate Croatian statehood were maintained through the Sabor (an assembly of Croatian nobles) and the ban (viceroy). In addition, the Croatian nobles retained their lands and titles. Coloman retained the institution of the Sabor and relieved the Croatians of taxes on their land. Coloman's successors continued to crown themselves as Kings of Croatia separately in Biograd na Moru. The Hungarian king also introduced a variant of the feudal system. Large fiefs were granted to individuals who would defend them against outside incursions thereby creating a system for the defence of the entire state. However, by enabling the nobility to seize more economic and military power, the kingdom itself lost influence to the powerful noble families. In Croatia the House of Šubić, Šubić were one of the oldest Croatian noble families and would become particularly influential and important, ruling the area between Zrmanja and the Krka (Croatia), Krka rivers. The local noble family from Krk island (who later took the surname House of Frankopan, Frankopan) is often considered the second most important medieval family, as ruled over northern Adriatic and is responsible for the adoption of one of oldest European statutes, Law codex of Vinodol (1288). Both families gave many native bans of Croatia. Other powerful families were House of Nelipić, Nelipić from Zagora (Croatia), Dalmatian Zagora (14th–15th centuries); Kačić who ruled over Pagania
The Narentines were a South Slavic tribe that occupied an area of southern Dalmatia centered at the river Neretva (), active in the 9th and 10th centuries, noted as pirates on the Adriatic. Named ''Narentani'' in Venetian sources, Greek source ...
and were famous for piracy and wars against Venice (12th–13th centuries); Kurjaković family, a branch of the old Croatian noble family Gusić from Krbava (14th–16th centuries); House of Babonić, Babonići who ruled from western Kupa to eastern Vrbas (river), Vrbas and Bosna (river), Bosna rivers, and were bans of Slavonia (13th–14th centuries); House of Iločki, Iločki family who ruled over Slavonian stronghold-cities, and in the 15th century rose to power. During this period, the Knights Templar and the Knights Hospitaller also acquired considerable property and assets in Croatia.
In the second half of the 13th century, during the Árpád dynasty, Árpád and Capetian House of Anjou, Anjou dynasty struggle, the Šubić family became hugely powerful under Paul I Šubić of Bribir, who was the longest Croatian Ban (1274–1312), conquering Bosnia and declaring himself "Lord of all of Bosnia" (1299–1312). He appointed his brother Mladen I Šubić of Bribir, Mladen I Šubić as Ban of Bosnia (1299–1304), and helped Charles I of Hungary, Charles I from House of Anjou to be the King of Hungary. After his death in 1312, his son Mladen II Šubić of Bribir, Mladen II Šubić was the Ban of Bosnia (1304–1322) and Ban of Croatia (1312–1322). The kings from House of Anjou intended to strengthen the kingdom by uniting their power and control, but to do so they had to diminish the power of the higher nobility. Charles I had already tried to crash the aristocratic privileges, intention finished by his son Louis I of Hungary, Louis the Great (1342–1382), relying on the lower nobility and towns. Both kings ruled without the Parliament, and inner nobility struggles only helped them in their intentions. This led to Mladen's defeat at the battle of Bliska in 1322 by a coalition of several Croatian noblemen and Dalmatian coastal towns with support of the King himself, in exchange of Šubić's castle of Ostrovica, Croatia, Ostrovica for Zrin Castle in Central Croatia (thus this branch was named House of Zrinski, Zrinski) in 1347. Eventually, the Babonić and Nelipić families also succumbed to the king's offensive against nobility, but with the increasing process of power centralization, Louis managed to force Venice by the Treaty of Zadar in 1358 to give up their possessions in Dalmatia. When King Louis died without successor, the question of succession remained open. The kingdom once again entered the time of internal unrest. Besides King Louis's daughter Mary, Queen of Hungary, Mary, Charles III of Naples was the closest king male relative with claims to the throne. In February 1386, two months after his coronation, he was assassinated by order of the queen Elizabeth of Bosnia. His supporters, bans John of Palisna, John Horvat and Stjepan Lacković planned a rebellion, and managed to capture and imprison Elizabeth and Mary. By orders of John of Palisna, Elizabeth was strangled. In retaliation, Magyars crowned Mary's husband Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Sigismund of Luxembourg.
King Sigismund's army was catastrophically defeated at the Battle of Nicopolis (1396) as the Rise of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman invasion was getting closer to the borders of the Hungarian-Croatian kingdom. Without news about the king after the battle, the then ruling Croatian ban House of Lacković, Stjepan Lacković and nobles invited Charles III's son Ladislaus of Naples to be the new king. This resulted with Bloody Sabor of Križevci in 1397, lose of interest for the crown by Ladislaus and selling of Dalmatia to Venice in 1403, and spreading of Croatian name to the north, while of Slavonia to the east. The dynastic struggle didn't finish, and with the Ottoman invasion on Bosnia started the first short raids in Croatian territory, defended only by local nobles.
 As the Ottoman wars in Europe, Turkish incursion into Europe started, Croatia once again became a border area between two major forces in the
As the Ottoman wars in Europe, Turkish incursion into Europe started, Croatia once again became a border area between two major forces in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. Croatian military troops fought in many battles under command of Italian Franciscans, Franciscan priest friar, fra Giovanni da Capistrano, John Capistrano, the Hungarian Generalissimus, Generalissimo János Hunyadi, John Hunyadi, and Hungarian King Matthias Corvinus, like in the Hunyadi's long campaign (1443–1444), battle of Varna (1444), second battle of Kosovo (1448), and contributed to the Christian victories over the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in the siege of Belgrade (1456) and Siege of Jajce (1463). At the time they suffered a major defeat in the battle of Krbava field (Lika, Croatia) in 1493 and gradually lost increasing amounts of territory to the Ottoman Empire. Pope Leo X called Croatia the ''forefront of Christianity (Antemurale Christianitatis)'' in 1519, given that several Croatian soldiers made significant contributions to the struggle against the Ottoman Turks. Among them there were ban (title), ban Petar Berislavić who won a victory at Dubica, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Dubica on the Una (Sava), Una river in 1513, the captain of Senj and prince of Klis Petar Kružić, who defended the Klis Fortress for almost 25 years, captain Nikola Jurišić who deterred by a magnitude larger Turkish force on their way to Vienna in 1532, or ban Nikola Šubić Zrinski who helped save Pest (city), Pest from occupation in 1542 and fought in the Battle of Szigetvar in 1566. During the Ottoman conquest tens of thousands of Croats were taken in Turkey, where they became slaves.
 The Battle of Mohács (1526) and the death of King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II ended the Hungarian-Croatian union. In 1526, the Hungarian parliament elected two separate kings János Szapolyai and Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I Habsburg, but the choice of the Croatian sabor Parliament on Cetin, at Cetin prevailed on the side of Ferdinand I, as they elected him as the new king of Croatia on 1 January 1527, uniting both lands under Habsburg rule. In return they were promised the historic rights, freedoms, laws and defence of Croatian Kingdom.
However, the Hungarian-Croatian Kingdom was not enough well prepared and organized and the Ottoman Empire expanded further in the 16th century to include most of Slavonia, western Bosnia and Lika. For the sake of stopping the Ottoman conquering and possible assault on the capital of Vienna, the large areas of Croatia and Slavonia (even Hungary and Romania) bordering the Ottoman Empire were organized as a Military Frontier which was ruled directly from Vienna military headquarters. The invasion caused migration of Croats, and the area which became deserted was subsequently settled by Serbs, Vlachs, Ethnic German, Germans and others. The negative effects of feudalism escalated in 1573 when the peasants in northern Croatia and Slovenia Croatian and Slovenian peasant revolt, rebelled against their feudal lords due to various injustices. After the fall of Bihać fort in 1592, only small areas of Croatia remained unrecovered. The remaining were referred to as the ''reliquiae reliquiarum of the once great Croatian kingdom''.s:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Croatia, Catholic Encyclopedia
Croats stopped the Ottoman advance in Croatia at the battle of Sisak in 1593, 100 years after the defeat at Krbava field, and the short Long Turkish War ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok in 1606, after which Croatian classes tried unsuccessfully to have their territory on the Military Frontier restored to rule by the Croatian Ban, managing only to restore a small area of lost territory but failed to regain large parts of Croatian Kingdom (present-day western
The Battle of Mohács (1526) and the death of King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II ended the Hungarian-Croatian union. In 1526, the Hungarian parliament elected two separate kings János Szapolyai and Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand I Habsburg, but the choice of the Croatian sabor Parliament on Cetin, at Cetin prevailed on the side of Ferdinand I, as they elected him as the new king of Croatia on 1 January 1527, uniting both lands under Habsburg rule. In return they were promised the historic rights, freedoms, laws and defence of Croatian Kingdom.
However, the Hungarian-Croatian Kingdom was not enough well prepared and organized and the Ottoman Empire expanded further in the 16th century to include most of Slavonia, western Bosnia and Lika. For the sake of stopping the Ottoman conquering and possible assault on the capital of Vienna, the large areas of Croatia and Slavonia (even Hungary and Romania) bordering the Ottoman Empire were organized as a Military Frontier which was ruled directly from Vienna military headquarters. The invasion caused migration of Croats, and the area which became deserted was subsequently settled by Serbs, Vlachs, Ethnic German, Germans and others. The negative effects of feudalism escalated in 1573 when the peasants in northern Croatia and Slovenia Croatian and Slovenian peasant revolt, rebelled against their feudal lords due to various injustices. After the fall of Bihać fort in 1592, only small areas of Croatia remained unrecovered. The remaining were referred to as the ''reliquiae reliquiarum of the once great Croatian kingdom''.s:Catholic Encyclopedia (1913)/Croatia, Catholic Encyclopedia
Croats stopped the Ottoman advance in Croatia at the battle of Sisak in 1593, 100 years after the defeat at Krbava field, and the short Long Turkish War ended with the Peace of Zsitvatorok in 1606, after which Croatian classes tried unsuccessfully to have their territory on the Military Frontier restored to rule by the Croatian Ban, managing only to restore a small area of lost territory but failed to regain large parts of Croatian Kingdom (present-day western Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
), as the present-day border between the two countries is a remnant of this outcome.
Croatian national revival (1593–1918)
In the first half of the 17th century, Croats fought in the Thirty Years' War on the side of Holy Roman Empire, mostly as light cavalry under command of imperial generalissimo Albrecht von Wallenstein. Croatian Ban, Juraj V Zrinski, also fought in the war, but died in a military camp near Bratislava, Slovakia, as he was poisoned by von Wallenstein after a verbal duel. His son, future ban and captain-general of Croatia, Miklós Zrínyi, Nikola Zrinski, participated during the closing stages of the war. In 1664, the Austrian imperial army was victorious against the Turks, but Emperor Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold failed to capitalize on the success when he signed the Peace of Vasvár in which Croatia and Hungary were prevented from regaining territory lost to the Ottoman Empire. This caused unrest among the Croatian and Hungarian nobility which plotted against the emperor. Nikola Zrinski participated in launching the conspiracy which later came to be known as the Magnate conspiracy, but he soon died, and the rebellion was continued by his brother, Croatian ban Petar Zrinski, Fran Krsto Frankopan and Ferenc Wesselényi. Petar Zrinski, along the conspirators, went on a wide secret diplomatic negotiations with a number of nations, including Louis XIV of France, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Swedish Empire, Sweden, the Republic of Venice and even the Ottoman Empire, to free Croatia from the Habsburg sovereignty.
Imperial spies uncovered the conspiracy and on 30 April 1671 executed four esteemed Croatian and Hungarian noblemen involved in it, including Zrinski and Frankopan in Wiener Neustadt. The large estates of two most powerful Croatian noble houses were confiscated and their families relocated, soon after extinguished. Between 1670 and the revolution of 1848, there would be only 2 bans of Croatian nationality. The period from 1670 to the Croatian cultural revival in the 19th century was Croatia's political Dark Age. Meanwhile, with the victories over Turks, Habsburgs all the more insistent they spent centralization and germanization, new regained lands in liberated Slavonia started giving to foreign families as feudal goods, at the expense of domestic element. Because of this the Croatian Sabor was losing its significance, and the nobility less attended it, yet went only to the one in Hungary.
In 1664, the Austrian imperial army was victorious against the Turks, but Emperor Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Leopold failed to capitalize on the success when he signed the Peace of Vasvár in which Croatia and Hungary were prevented from regaining territory lost to the Ottoman Empire. This caused unrest among the Croatian and Hungarian nobility which plotted against the emperor. Nikola Zrinski participated in launching the conspiracy which later came to be known as the Magnate conspiracy, but he soon died, and the rebellion was continued by his brother, Croatian ban Petar Zrinski, Fran Krsto Frankopan and Ferenc Wesselényi. Petar Zrinski, along the conspirators, went on a wide secret diplomatic negotiations with a number of nations, including Louis XIV of France, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Swedish Empire, Sweden, the Republic of Venice and even the Ottoman Empire, to free Croatia from the Habsburg sovereignty.
Imperial spies uncovered the conspiracy and on 30 April 1671 executed four esteemed Croatian and Hungarian noblemen involved in it, including Zrinski and Frankopan in Wiener Neustadt. The large estates of two most powerful Croatian noble houses were confiscated and their families relocated, soon after extinguished. Between 1670 and the revolution of 1848, there would be only 2 bans of Croatian nationality. The period from 1670 to the Croatian cultural revival in the 19th century was Croatia's political Dark Age. Meanwhile, with the victories over Turks, Habsburgs all the more insistent they spent centralization and germanization, new regained lands in liberated Slavonia started giving to foreign families as feudal goods, at the expense of domestic element. Because of this the Croatian Sabor was losing its significance, and the nobility less attended it, yet went only to the one in Hungary.
 In the 18th century, Croatia was one of the crown lands that supported Emperor Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles's Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 and supported Empress Maria Theresa in the War of the Austrian Succession of 1741–48. Subsequently, the empress made significant contributions to Croatian matters, by making several changes in the feudal and tax system, administrative control of the Military Frontier, in 1745 administratively united Slavonia with Croatia and in 1767 organized Croatian royal council with the ban on head, however, she ignored and eventually disbanded it in 1779, and Croatia was relegated to just one seat in the governing council of Hungary, held by the ban (title), ban of Croatia. To fight the Austrian centralization and absolutism, Croats passed their rights to the united government in Hungary, thus to together resist the intentions from Vienna. But the connection with Hungary soon adversely affected the position of Croats, because Magyars in the spring of their nationalism tried to Magyarize Croats, and make Croatia a part of a united Hungary. Because of this pretensions, the constant struggles between Croats and Magyars emerged, and lasted until 1918. Croats were fighting in unfavorable conditions, against both Vienna and Budapest, while divided on Banska Hrvatska, Dalmatia and Military Frontier. In such a time, with the fall of the Venetian Republic in 1797, its possessions in eastern Adriatic mostly came under the authority of France which passed its rights to Austria the same year. Eight years later they were restored to France as the Illyrian Provinces, but won back to the Austrian crown 1815. Though now part of the same empire, Dalmatia and Istria were part of Cisleithania while Croatia and Slavonia were in Hungarian part of the Monarchy.
In the 19th century Croatian romantic nationalism emerged to counteract the non-violent but apparent Germanization and Magyarization. The Croatian national revival began in the 1830s with the Illyrian movement. The movement attracted a number of influential figures and produced some important advances in the
In the 18th century, Croatia was one of the crown lands that supported Emperor Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles's Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 and supported Empress Maria Theresa in the War of the Austrian Succession of 1741–48. Subsequently, the empress made significant contributions to Croatian matters, by making several changes in the feudal and tax system, administrative control of the Military Frontier, in 1745 administratively united Slavonia with Croatia and in 1767 organized Croatian royal council with the ban on head, however, she ignored and eventually disbanded it in 1779, and Croatia was relegated to just one seat in the governing council of Hungary, held by the ban (title), ban of Croatia. To fight the Austrian centralization and absolutism, Croats passed their rights to the united government in Hungary, thus to together resist the intentions from Vienna. But the connection with Hungary soon adversely affected the position of Croats, because Magyars in the spring of their nationalism tried to Magyarize Croats, and make Croatia a part of a united Hungary. Because of this pretensions, the constant struggles between Croats and Magyars emerged, and lasted until 1918. Croats were fighting in unfavorable conditions, against both Vienna and Budapest, while divided on Banska Hrvatska, Dalmatia and Military Frontier. In such a time, with the fall of the Venetian Republic in 1797, its possessions in eastern Adriatic mostly came under the authority of France which passed its rights to Austria the same year. Eight years later they were restored to France as the Illyrian Provinces, but won back to the Austrian crown 1815. Though now part of the same empire, Dalmatia and Istria were part of Cisleithania while Croatia and Slavonia were in Hungarian part of the Monarchy.
In the 19th century Croatian romantic nationalism emerged to counteract the non-violent but apparent Germanization and Magyarization. The Croatian national revival began in the 1830s with the Illyrian movement. The movement attracted a number of influential figures and produced some important advances in the Croatian language
Croatian (; ' ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language used by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and other neighboring countries. It is the official ...
and culture. The champion of the Illyrian movement was Ljudevit Gaj who also reformed and standardized Croatian. The official language in Croatia had been Latin until 1847, when it became Croatian. The movement relied on a South Slavic and Panslavistic conception, and its national, political and social ideas were advanced at the time.
By the 1840s, the movement had moved from cultural goals to resisting Hungarian political demands. By the royal order of 11 January 1843, originating from the chancellor Klemens von Metternich, Metternich, the use of the Illyrian name and insignia in public was forbidden.  This deterred the movement's progress but it couldn't stop the changes in the society that had already started. On 25 March 1848, was conducted a political petition "''Zahtijevanja naroda''", which program included thirty national, social and liberal principles, like Croatian national independence, annexation of Dalmatia and Military Frontier, independence from Hungary as far as finance, language, education, freedom of speech and writing, religion, nullification of serfdom etc. In the revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire, the Croatian Ban (title), Ban Josip Jelačić, Jelačić cooperated with the Austrians in quenching the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 by leading a military campaign into Hungary, successful until the Battle of Pákozd.
Croatia was later subject to Hungarian hegemony under ban Levin Rauch when the Empire was transformed into a dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary in 1867. Nevertheless, Ban Jelačić had succeeded in the abolition of serfdom in Croatia, which eventually brought about massive changes in society: the power of the major landowners was reduced and arable land became increasingly subdivided, to the extent of risking famine. Many Croatians began emigrating to the New World countries in this period, a trend that would continue over the next century, creating a large Croatian diaspora.
This deterred the movement's progress but it couldn't stop the changes in the society that had already started. On 25 March 1848, was conducted a political petition "''Zahtijevanja naroda''", which program included thirty national, social and liberal principles, like Croatian national independence, annexation of Dalmatia and Military Frontier, independence from Hungary as far as finance, language, education, freedom of speech and writing, religion, nullification of serfdom etc. In the revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire, the Croatian Ban (title), Ban Josip Jelačić, Jelačić cooperated with the Austrians in quenching the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 by leading a military campaign into Hungary, successful until the Battle of Pákozd.
Croatia was later subject to Hungarian hegemony under ban Levin Rauch when the Empire was transformed into a dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary in 1867. Nevertheless, Ban Jelačić had succeeded in the abolition of serfdom in Croatia, which eventually brought about massive changes in society: the power of the major landowners was reduced and arable land became increasingly subdivided, to the extent of risking famine. Many Croatians began emigrating to the New World countries in this period, a trend that would continue over the next century, creating a large Croatian diaspora.
Modern history (1918–present)
After the World War I, First World War and dissolution of Austria-Hungary, most Croats were united within the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, created by unification of the short-lived State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, State of SHS with the Kingdom of Serbia. Croats became one of the constituent nations of the new kingdom. The state was transformed into the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929 and the Croats were united in the new nation with their neighbors – the South Slavs-Yugoslavs. In 1939, the Croats received a high degree of autonomy when the Banovina of Croatia was created, which united almost all ethnic Croatian territories within the Kingdom. In the World War II, Second World War, the Axis forces created the Independent State of Croatia led by theUstaše
The Ustaše (), also known by anglicised versions Ustasha or Ustashe, was a Croatian fascist and ultranationalist organization active, as one organization, between 1929 and 1945, formally known as the Ustaša – Croatian Revolutionary Move ...
movement which sought to create an ethnically pure Croatian state on the territory corresponding to present-day countries of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Post-WWII Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia became a federation consisting of 6 republics, and Croats became one of two ''constituent peoples'' of two – Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Croats in the Serbian autonomous province of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
are one of six main ethnic groups composing this region.
Following the democratization of society, accompanied with ethnic tensions that emerged ten years after the death of Josip Broz Tito, the Republic of Croatia declared independence, which was followed by Croatian War of Independence, war. In the first years of the war, over 200,000 Croats were displaced from their homes as a result of the military actions. In the peak of the fighting, around 550,000 ethnic Croats were displaced altogether during the Yugoslav wars.
Post-war government's policy of easing the immigration of ethnic Croats from abroad encouraged a number of Croatian descendants to return to Croatia. The influx was increased by the arrival of Croatian refugees from Bosnia and Herzegovina. After the war's end in 1995, most Croatian refugees returned to their previous homes, while some (mostly Croat refugees from Bosnia and Herzegovina and Janjevci from Kosovo) moved into the formerly-held Serbian housing.
Genetics
Genetics, Genetically, on the Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, Y-chromosome DNA line, a majority (75%) of male Croats from Croatia belongs to haplogroups Haplogroup I (Y-DNA), I (38%–43%), Haplogroup R1a (Y-DNA), R1a (22%–25%) and Haplogroup R1b (Y-DNA), R1b (8%–9%), while a minority (25%) mostly belongs to haplogroup Haplogroup E (Y-DNA), E (10%), and others to haplogroups Haplogroup J (Y-DNA), J (7%–10%), Haplogroup G (Y-DNA), G (2%–4%), Haplogroup H (Y-DNA), H (0.3–1.8%), and Haplogroup N (Y-DNA), N (<1%). The distribution, variance and frequency of the I2 and R1a subclades (>60%) among Croats are related to the medieval Slavic expansion, most probably from the territory of present-day Ukraine and Southeastern Poland. Genetically, on the maternal Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, mitochondrial DNA line, a majority (>65%) of Croats from Croatia (mainland and coast) belong to three of the eleven major European mtDNA haplogroups – Haplogroup H (mtDNA), H (45%), Haplogroup U (mtDNA), U (17.8–20.8%), Haplogroup J (mtDNA), J (3–11%), while a large minority (>35%) belongs to many other smaller haplogroups. Based on Autosome, autosomal Identity by descent, IBD survey the speakers of Croatian share a very high number of common ancestors dated to the migration period approximately 1,500 years ago with Poland and Romania-Bulgaria clusters among others in Eastern Europe. It was caused by the Slavic expansion, a small population which expanded into vast regions of "low population density beginning in the sixth century". Other IBD and Genetic admixture, admixture studies also found even patterns of admixture events among South, East and West Slavs at the time and area of Slavic expansion, and that the shared ancestral Balto-Slavic component among South Slavs is between 55 and 70%.Language
Bunjevac dialect
The Bunjevac dialect () or Bunjevac speech () is a Shtokavian–Younger Ikavian dialect of the Serbo-Croatian pluricentric language, used by members of the Bunjevci, Bunjevac community. It is an integral part of the cultural heritage of the Bunjevac Croats in northernSerbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
(Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
) and parts of southern Hungary. Their accent is purely Ikavian, with /i/ for the Common Slavic vowels ''yat''. Its speakers largely use the Gaj's Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet. In Serbia, it is officially recognized as a standardized minority dialect since 2018. There have been three meritorious people who preserved the Bunjevac dialect in two separate dictionaries: Grgo Bačlija and Marko Peić with "''Ričnik bački Bunjevaca''" (editions 1990, 2018), and Ante Sekulić with "''Rječnik govora bačkih Hrvata''" (2005).
Popularly, the Bunjevac dialect is often referred to as "Bunjevac language" or Bunjevac mother tongue. At the political level, depending on goal and content of the political lobby, the general confusion concerning the definition of the terms language, dialect, speech, mother tongue, is cleverly exploited, resulting in an inconsistent use of the terms.
The Institute of Croatian Language and Linguistics launched a proposal, in March 2021, to the Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Croatia, to add Bunjevac dialect to the List of Protected Intangible Cultural Heritage of the Republic of Croatia.
Religion
Croats are predominantly Roman Catholic, and before Christianity they adhered to Slavic paganism or Roman paganism. The earliest record of contact between the Pope and the Croats dates from a mid-7th century entry in the ''Liber Pontificalis''. Pope John IV (John the Dalmatian, 640–642) sent an abbot named Martin toDalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
and Istria in order to pay ransom for some prisoners and for the remains of old Christian martyrs. This abbot is recorded to have travelled through Dalmatia with the help of the Croatian leaders, and he established the foundation for the future relations between the Pope and the Croats.
The beginnings of the Christianization are also disputed in the historical texts: the Byzantine texts talk of duke Porin who started this at the incentive of emperor Heraclius (610–641), then of Duke Porga who mainly Christianized his people after the influence of missionaries from Rome, while the national tradition recalls Christianization during the rule of Dalmatian Duke Borna of Croatia, Borna (810–821). It is possible that these are all renditions of the same ruler's name. The earliest known Croatian autographs from the 8th century are found in the Latin Gospel of Cividale.
Croats were never obliged to use Latin—rather, they held mass (liturgy), masses in their own language and used the Glagolitic alphabet. In 1886 it arrived to the Principality of Montenegro, followed by the Kingdom of Serbia in 1914, and the History of Czechoslovakia (1918-38), Republic of Czechoslovakia in 1920, but only for feast days of the main patron saints. The 1935 concordat with the Kingdom of Yugoslavia anticipated the introduction of the Church Slavonic for all Croatian regions and throughout the entire state.
Smaller groups of Croats adhere to other religions, like Eastern Orthodoxy in Croatia, Eastern Orthodoxy, Protestantism and Croat Muslims, Islam. According to an official population census of Croatia by ethnicity and religion, roughly 16,600 ethnic Croats adhered to Orthodoxy, roughly 8,000 were Protestants, roughly 10,500 described themselves as "other" Christians, and roughly 9,600 were followers of Islam.
Culture
Tradition
 The area settled by Croats has a large diversity of historical and cultural influences, as well as diversity of terrain and geography. The coastland areas of Dalmatia and Istria were subject to Roman Empire, Venetian Republic, Venetian and Italian rule; central regions like Lika and western Herzegovina were a scene of battlefield against the Ottoman Empire, and have strong epic traditions. In the northern plains, Austro-Hungarian rule has left its marks. The most distinctive features of Croatian folklore include klapa ensembles of Dalmatia, tamburitza orchestras of
The area settled by Croats has a large diversity of historical and cultural influences, as well as diversity of terrain and geography. The coastland areas of Dalmatia and Istria were subject to Roman Empire, Venetian Republic, Venetian and Italian rule; central regions like Lika and western Herzegovina were a scene of battlefield against the Ottoman Empire, and have strong epic traditions. In the northern plains, Austro-Hungarian rule has left its marks. The most distinctive features of Croatian folklore include klapa ensembles of Dalmatia, tamburitza orchestras of Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja ...
. Folk arts are performed at special events and festivals, perhaps the most distinctive being Sinjska alka, Alka of Senj, a traditional knights' competition celebrating the victory against Ottoman Turks. The epic tradition is also preserved in epic songs sung with gusle. Various types of Kolo (dance), kolo circular dance are also encountered throughout Croatia.
UNESCO , Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in Croatia
* "Bećarac singing and playing from Eastern Croatia"; * "Festivity of Saint Blaise, the patron of Dubrovnik"; * "Gingerbread craft from Northern Croatia"; * "Klapa multipart singing of Dalmatia, southern Croatia"; * "Lacemaking in Croatia"; * "Međimurska popevka, a folksong from Međimurje"; * "Nijemo Kolo, silent circle dance of the Dalmatian hinterland"; * "Procession Za Križen ('following the cross')"; * "Spring procession of Ljelje/Kraljice (queens) from Gorjani"; * "Traditional manufacturing of children's wooden toys of Hrvatsko Zagorje"; * "Two-part singing and playing in the Istrian scale"; * "Zvončari, annual carnival bell ringers' pageant from the Kastav area."Arts
 Architecture in Croatia reflects influences of bordering nations. Austrian and Hungarian influence is visible in public spaces and buildings in the north and in the central regions, architecture found along coasts of Dalmatia and Istria exhibits Venetian influence. Large squares named after culture heroes, well-groomed parks, and pedestrian-only zones, are features of these orderly towns and cities, especially where large scale Baroque architecture, Baroque urban planning took place, for instance in Varaždin and Karlovac. Subsequent influence of the Art Nouveau was reflected in contemporary architecture. Along the coast, the architecture is Mediterranean with a strong Venetian and Renaissance influence in major urban areas exemplified in works of Giorgio da Sebenico and Niccolò Fiorentino such as the Šibenik Cathedral, Cathedral of St. James in Šibenik.
The oldest preserved examples of Croatian architecture are the 9th-century churches, with the largest and the most representative among them being the Church of St. Donatus.
Besides the architecture encompassing the oldest artworks in Croatia, there is a long history of artists in Croatia reaching to the Middle Ages. In that period the stone portal of the Trogir Cathedral was made by Radovan (master), Radovan, representing the most important monument of Romanesque art, Romanesque sculpture in Croatia. The Renaissance in Croatia, Renaissance had the greatest impact on the Adriatic Sea coast since the remainder of Croatia was embroiled in the Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman War. With the waning of the Ottoman Empire, art flourished during the Baroque and Rococo. The 19th and the 20th centuries brought about affirmation of numerous Croatian artisans, helped by several patrons of the arts such as bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer. Croatian artists of the period achieving worldwide renown were Vlaho Bukovac and Ivan Meštrović.
The Baška tablet, a stone inscribed with the Glagolitic alphabet found on the Krk island which is dated to 1100, is considered to be the oldest surviving prose in Croatian. The beginning of more vigorous development of Croatian literature is marked by the Renaissance and Marko Marulić. Besides Marulić, Renaissance playwright Marin Držić, Baroque poet Ivan Gundulić, Croatian national revival poet Ivan Mažuranić, novelist, playwright and poet August Šenoa, poet and writer Antun Gustav Matoš, poet Antun Branko Šimić, Expressionism, expressionist and Literary realism, realist writer Miroslav Krleža, poet Tin Ujević and novelist and short story writer Ivo Andrić are often cited as the greatest figures in Croatian literature.
Architecture in Croatia reflects influences of bordering nations. Austrian and Hungarian influence is visible in public spaces and buildings in the north and in the central regions, architecture found along coasts of Dalmatia and Istria exhibits Venetian influence. Large squares named after culture heroes, well-groomed parks, and pedestrian-only zones, are features of these orderly towns and cities, especially where large scale Baroque architecture, Baroque urban planning took place, for instance in Varaždin and Karlovac. Subsequent influence of the Art Nouveau was reflected in contemporary architecture. Along the coast, the architecture is Mediterranean with a strong Venetian and Renaissance influence in major urban areas exemplified in works of Giorgio da Sebenico and Niccolò Fiorentino such as the Šibenik Cathedral, Cathedral of St. James in Šibenik.
The oldest preserved examples of Croatian architecture are the 9th-century churches, with the largest and the most representative among them being the Church of St. Donatus.
Besides the architecture encompassing the oldest artworks in Croatia, there is a long history of artists in Croatia reaching to the Middle Ages. In that period the stone portal of the Trogir Cathedral was made by Radovan (master), Radovan, representing the most important monument of Romanesque art, Romanesque sculpture in Croatia. The Renaissance in Croatia, Renaissance had the greatest impact on the Adriatic Sea coast since the remainder of Croatia was embroiled in the Hundred Years' Croatian–Ottoman War. With the waning of the Ottoman Empire, art flourished during the Baroque and Rococo. The 19th and the 20th centuries brought about affirmation of numerous Croatian artisans, helped by several patrons of the arts such as bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer. Croatian artists of the period achieving worldwide renown were Vlaho Bukovac and Ivan Meštrović.
The Baška tablet, a stone inscribed with the Glagolitic alphabet found on the Krk island which is dated to 1100, is considered to be the oldest surviving prose in Croatian. The beginning of more vigorous development of Croatian literature is marked by the Renaissance and Marko Marulić. Besides Marulić, Renaissance playwright Marin Držić, Baroque poet Ivan Gundulić, Croatian national revival poet Ivan Mažuranić, novelist, playwright and poet August Šenoa, poet and writer Antun Gustav Matoš, poet Antun Branko Šimić, Expressionism, expressionist and Literary realism, realist writer Miroslav Krleža, poet Tin Ujević and novelist and short story writer Ivo Andrić are often cited as the greatest figures in Croatian literature.
Symbols
Communities
In Croatia (thenation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may i ...
), 3.9 million people identify themselves as Croats, and constitute about 90.4% of the population. Another 553,000 live in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, where they are one of the three constituent ethnic groups, predominantly living in Western Herzegovina, Central Bosnia
Central Bosnia (, ) is a central subregion of Bosnia, which consists of a core mountainous area with several basins, valleys and mountains. It is bordered by Bosnian Krajina to the northwest, Tropolje ( Livno area) to the west, Herzegovina to t ...
and Bosnian Posavina. The minority in Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
number about 70,000, mostly in Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
,Влада Аутономне Покрајине Војводинеwhere also vast majority of the Šokci consider themselves Croats, as well as many Bunjevci (the latter, as well as other nationalities, settled the vast, abandoned area after the Ottoman retreat; this Croat subgroup originates from the south, mostly from the region of Bačka). Smaller Croat autochthonous minorities exist in Slovenia (mainly in Slovene Littoral, Prekmurje and in the Metlika area in Lower Carniola regions – 35,000 Croats of Slovenia, Croats), Montenegro (mostly in the Bay of Kotor – 6,800 Croats of Montenegro, Croats), and a regional community in Kosovo called Janjevci who nationally identify as Croats. In the 1991 census, Croats consisted 19.8% of the overall population of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia; there were around 4.6 million Croats in the entire country. The subgroups of Croats are commonly based on Regions of Croatia, regional affiliation, like Dalmatians, Slavonians, Zagorci, Istrians etc., while outside Croatia there exist several ethnic groups: Šokci (Croatia, Serbia, Hungary), Bunjevci (Serbia, Hungary), Burgenland Croats (Austria), Molise Croats (Italy), Croats of Boka Kotorska, Bokelji (Montenegro), Croats of Hungary, Raci (Hungary), Krashovani (Romania), Janjevci (Kosovo).
Autochthonous communities
* Croatia is the nation-state of Croats. * InBosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, Croats are one of three Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constitute ethnic groups, numbering around 544,780 people or 15.43% of population. The entity of Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to majority (495,000 or about little under 90%) of Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian and Herzegovinian Croats.
* In Montenegro, the Bay of Kotor, Croats of Montenegro, Croats are a national minority, numbering 6,021 people or 0.97% of population.
* In Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
, Croats of Serbia, Croats are a national minority, numbering 57,900 people or 0.80% of population. They mostly live in the region of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
, where Croatian is official (along with five other languages), and the national capital city of Belgrade.
* In Slovenia, Croats of Slovenia, Croats are not recognized as a minority, numbering 35,642 people or 1.81% of population. They mostly live in Slovene Littoral, Prekmurje and in the Metlika area in Lower Carniola regions.
Croatian communities with minority status
* In Austria, Croats are an ethnic minority, numbering around 30,000 people inBurgenland
Burgenland (; hu, Őrvidék; hr, Gradišće; Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland;'' Slovene: ''Gradiščanska'') is the easternmost and least populous state of Austria. It consists of two statutory cities and seven rural districts, with a total of ...
(Burgenland Croats), the eastern part of Austria, and around 15,000 people in the capital city of Vienna.
* In the Czech Republic, Croats in the Czech Republic, Croats are a national minority, numbering 850–2,000 people, forming a portion of the 29% minority (as "Others"). They mostly live in the region of Moravia, in the villages of Jevišovka, Dobré Pole and Nový Přerov.
* In Hungary, Croats of Hungary, Croats are an ethnic minority, numbering 25,730 people or 0.26% of population.
* In Italy, Croats of Italy, Croats are a Molise Croatian, linguistic, and ethnic minority, numbering 23,880 people, of which 2,801 people belong to ethnic minority of Molise Croats from the region of Molise
it, Molisano (man) it, Molisana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 ...
.
* In Romania, Croats of Romania, Croats are a national minority, numbering 6,786 people. They mostly live in the Caraș-Severin County, in communes of Romania, communes of Lupac
Lupac (Romanian: ''Lupac''; Croatian: ''Lupak''; hu, Kiskrassó) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Banat, Romania. In 2002, its population numbered 3,023 people and was mostly made up of Krashovani Croats. It is composed of four villages: C ...
(90.7%) and Carașova
Carașova ( hr, Karaševo; hu, Krassóvár) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Romania. It is known especially for its geographical placement and for the origin of its Croatian inhabitants, the Krashovani. The population of the commune numb ...
(78.28%).
* In Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
, Croats of Serbia, Croats (including Bunjevci and Šokci) are a national minority.
* In Slovakia, Croats in Slovakia, Croats are an ethnic and national minority, numbering around 850 people. They mostly live in the area around Bratislava, in the villages of Chorvátsky Grob, Čunovo, Devínska Nová Ves, Rusovce and Jarovce.
Croatian minorities exist in the following regions
* In Bulgaria, there exists a small Croatian community, a branch of Janjevci, Croats from Kosovo. * In New Zealand, the mixed Croatian and Māori Tarara (Māori Croatian ethnic mix), Tarara people have their own culture, traditions and customs, and live inTe Tai Tokerau
Te Tai Tokerau () is a New Zealand parliamentary Māori electorate that was created out of the Northern Maori electorate ahead of the first Mixed Member Proportional (MMP) election in 1996. It was held first by Tau Henare representing New Ze ...
, New Zealand's northernmost region. March 15 is Tarara Day to celebrate their heritage.
* In Kosovo, Croats or Janjevci (Letničani), as they inhabited mostly the town of Janjevo, before 1991 numbered 8,062 people, but after the war many fled, and number only 270 people.
* In North Macedonia, Croats in North Macedonia, Croats number 2,686 people or 0.1% of population, mostly living in the capital city of Skopje, the city of Bitola and around the Lake Ohrid.
Diaspora
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, Croatians in Austria, Austria, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
), caused by the conquering of Ottoman Turks, when Croats as Christianity in the Ottoman Empire, Roman Catholics were oppressed.
* To the Americas (largely to Croatian Canadians, Canada, the Croatian Americans, United States of America, Croatian Chileans, Chile, and Croatian Argentines, Argentina, with smaller communities in Croatian Brazilians, Brazil, Croatian Peruvians, Peru, and Croatian Ecuadorians, Ecuador) in the end of 19th and early 20th century, large numbers of Croats emigrated particularly for economic reasons.
* To New Zealand, predominately Te Tai Tokerau
Te Tai Tokerau () is a New Zealand parliamentary Māori electorate that was created out of the Northern Maori electorate ahead of the first Mixed Member Proportional (MMP) election in 1996. It was held first by Tau Henare representing New Ze ...
, to work on Kauri gum plantations.
* A further, larger wave of emigration, this time for political reasons, took place after the end of the World War II in Yugoslavia. At this time, both collaborators of the Ustaše, Ustasha regime and those who did not want to live under a League of Communists of Yugoslavia, communist regime fled the country, to the Americas and Oceania once more.
* As immigrant workers, particularly to Germany, Austria, and Croats of Switzerland, Switzerland in the 1960s and 1970s. In addition, some emigrants left for political reasons. This migration made it possible for communist Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia to achieve lower unemployment and at the same time the money sent home by emigrants to their families provided an enormous source of foreign exchange income.
* The last large wave of Croat emigration occurred during and after the Yugoslav Wars (1991–1995). Migrant communities already established in the Americas, Oceania, and across Europe grew as a result.
The count for diaspora is approximate because of incomplete statistical records and naturalization. Overseas, the United States contains the largest Croatian Americans, Croatian emigrant group (414,714 according to the 2010 census), mostly in Ohio, Pennsylvania, Illinois and California, with a sizable community in Alaska, followed by Croatian Australians, Australia (133,268 according to the 2016 census, with concentrations in Sydney, Melbourne and Perth) and Canada (133,965 according to the 2016 census, mainly in Southern Ontario, British Columbia and Alberta).
Various estimations put the total number of Americans and Canadians with at least some Croatian ancestry at 2 million, many of whom do not identify as such in the countries' censuses.
Croats have also emigrated in several waves to Latin America, mostly to South America: chiefly Croatian Chileans, Chile, Croatian Argentines, Argentina, and Croatian Brazilians, Brazil; estimates of their number vary wildly, from 150,000 up to 500,000.
There are also smaller groups of Croatian descendants in the Brazil, Croatian Ecuadorians, Ecuador, Croatian Peruvians, Peru, South Africa, Mexico, and South Korea. The most important organisations of the Croatian diaspora are the Croatian Fraternal Union, Croatian Heritage Foundation and the Croatian World Congress.
Maps
Historiography
See also
*Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, nation-state of Croats
* Demographics of Croatia
* Timeline of Croatian history
* List of Croats
* List of rulers of Croatia
* Genetic studies on Croats
* Origin hypotheses of the Croats
* Slavs; List of Medieval Slavic tribes, Medieval Slav tribes; South Slavs
* Persians, Iranians
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*Matica hrvatska
Review of Croatian History
at Central and Eastern European Online Library *
The Croatian nation at the beginning of the 20th century
Croatians in Arizona
{{authority control Croat people, Society of Croatia Ethnic groups in Croatia Ethnic groups in the Balkans Ethnoreligious groups in Europe Slavic ethnic groups South Slavs