Concentric Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

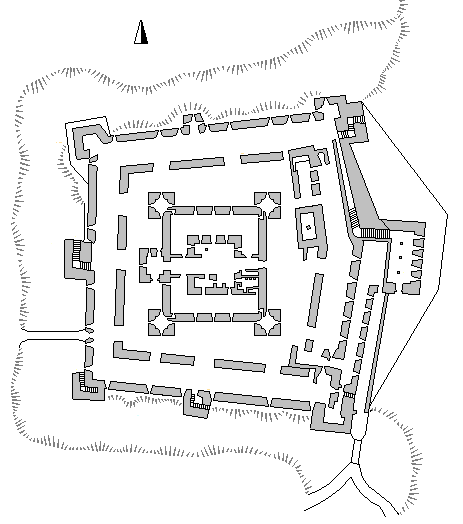 A concentric castle is a castle with two or more concentric curtain walls, such that the outer wall is lower than the inner and can be defended from it. The layout was square (at Belvoir and
A concentric castle is a castle with two or more concentric curtain walls, such that the outer wall is lower than the inner and can be defended from it. The layout was square (at Belvoir and

 Surrounding fortresses or towns with a series of defensive walls where the outer walls are lower than the inner walls is something that has been found in fortifications going back thousands of years to cultures like the Assyrians,
Surrounding fortresses or towns with a series of defensive walls where the outer walls are lower than the inner walls is something that has been found in fortifications going back thousands of years to cultures like the Assyrians,
File:Marqab-crusader-castle-donjon.jpg, Castle of Margat (Syria), 1062–
File: Belvoir fortress.JPG,

Beaumaris
Beaumaris ( ; cy, Biwmares ) is a town and community on the Isle of Anglesey in Wales, of which it is the former county town of Anglesey. It is located at the eastern entrance to the Menai Strait, the tidal waterway separating Anglesey from th ...
) where the terrain permitted, or an irregular polygon (at Krak
KMPS (910 AM) is a commercial radio station that is licensed to Hesperia, California and broadcasts to the Victor Valley area. It is owned by El Dorado Broadcasters and airs a Regional Mexican radio format with programming from La X 103.1. KMP ...
and Margat
Margat, also known as Marqab ( ar, قلعة المرقب, ''Qalaat al-Marqab'', lit=Castle of the Watchtower), is a castle near Baniyas, Syria, which was a Crusader fortress and one of the major strongholds of the Knights Hospitaller. It is lo ...
) where curtain walls of a spur castle
A spur castle is a type of medieval fortification that is sited on a spur of a hill or mountain for defensive purposes. Ideally, it would be protected on three sides by steep hillsides; the only vulnerable side being that where the spur joins the ...
followed the contours of a hill.
Concentric castles resemble one castle nested inside the other, thus creating an inner and outer ward. They are typically built without a central free-standing keep. Where the castle includes a particularly strong tower (donjon), such as at Krak or Margat, it projects from the inner enceinte
Enceinte (from Latin incinctus: girdled, surrounded) is a French term that refers to the "main defensive enclosure of a fortification". For a castle, this is the main defensive line of wall towers and curtain walls enclosing the position. Fo ...
.
Development
 Surrounding fortresses or towns with a series of defensive walls where the outer walls are lower than the inner walls is something that has been found in fortifications going back thousands of years to cultures like the Assyrians,
Surrounding fortresses or towns with a series of defensive walls where the outer walls are lower than the inner walls is something that has been found in fortifications going back thousands of years to cultures like the Assyrians, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Ancient Egyptians and Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
. The ancient city of Lachish
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. Th ...
, a place in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, was excavated and found to consist of multiple walls that were illustrated in Assyrian art documenting their successful siege of the city. The Byzantines also famously constructed the Walls of Constantinople
The Walls of Constantinople ( el, Τείχη της Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) are a series of defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (today Istanbul in Turkey) since its founding as the ...
, which featured double layers of walls through most of its perimeter and a moat. The city of ancient Babylon also featured multiple layers of fortifications
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, famously seen in the Ishtar Gate
The Ishtar Gate was the eighth gate to the inner city of Babylon (in the area of present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq). It was constructed circa 575 BCE by order of King Nebuchadnezzar II on the north side of the city. It was pa ...
. However, the relationship of the concentric castle to other forms of fortification is complex. An example of an early concentric castle is the Byzantine castle of Korykos
Corycus ( el, Κώρυκος; also transliterated Corycos or Korykos; hy, Կոռիկոս, translit=Koṙikos; tr, Kız Kalesi, lit. "maiden castle") was an ancient city in Cilicia Trachaea, Anatolia, located at the mouth of the valley calle ...
in Turkey, built in the early 11th century AD.
Historians (in particular Hugh Kennedy
Hugh Edward Kennedy (11 July 1879 – 1 December 1936) was an Irish Cumann na nGaedheal politician, barrister and judge who served as Chief Justice of Ireland from 1924 to 1936, a judge of the Supreme Court from 1924 to 1936 and Attorney Gener ...
) have argued that the concentric defence arose as a response to advances in siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
technology in the crusader state
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
s from the 12th to the 13th century. The outer wall protected the inner one from siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while oth ...
s, while the inner wall and the projecting towers provided flanking fire from crossbows
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an elastic launching device consisting of a bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock of a long fire ...
. Also, the strong towers may have served as platforms for trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weight ...
s for shooting back at the besiegers. The walls typically include tower
A tower is a tall structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures.
Towers are specifi ...
s, arrowslit
An arrowslit (often also referred to as an arrow loop, loophole or loop hole, and sometimes a balistraria) is a narrow vertical aperture in a fortification through which an archer can launch arrows or a crossbowman can launch bolts.
The interio ...
s, and wall-head defences such as crenellation
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at interva ...
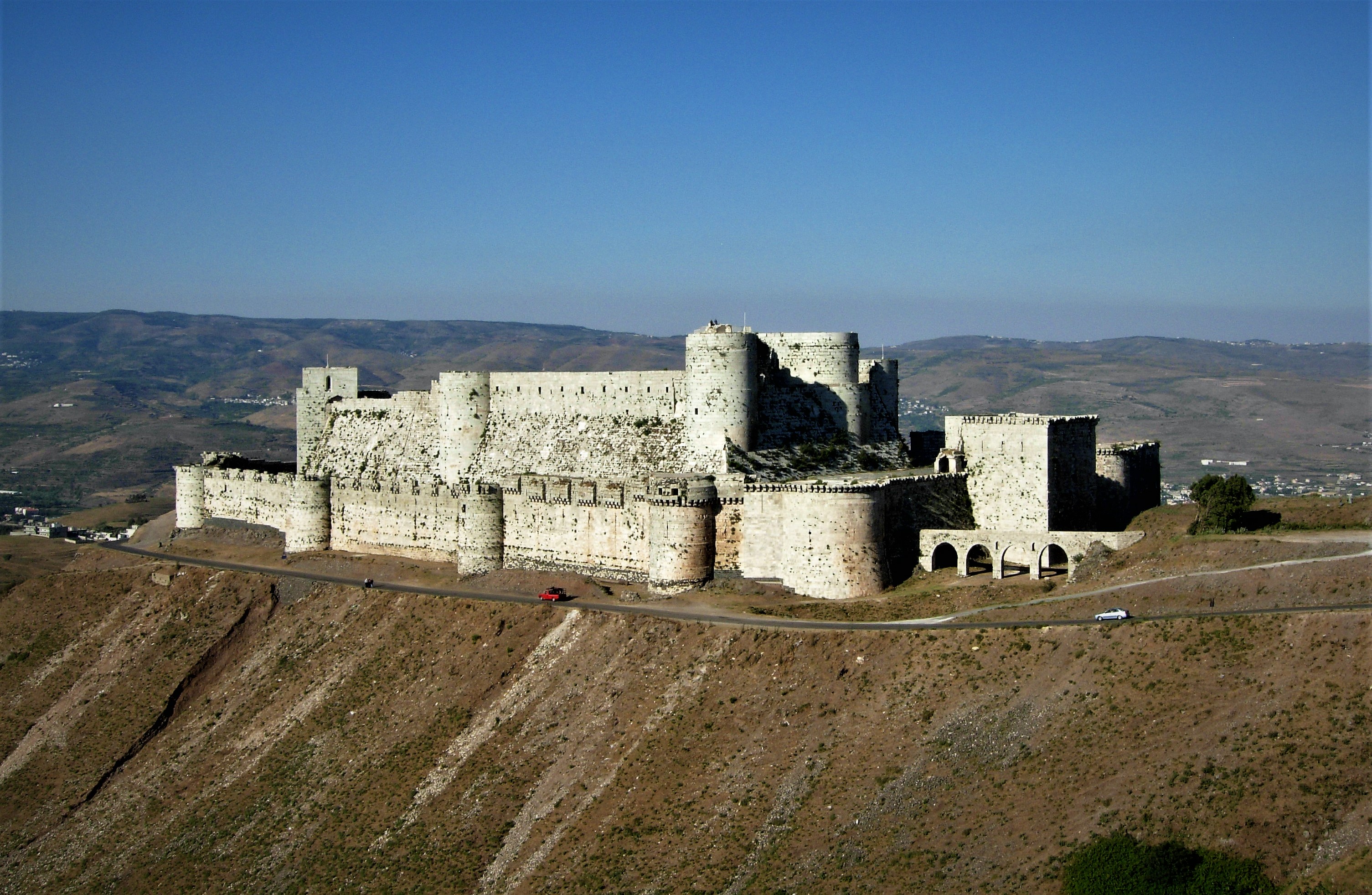
and, in more advanced cases, machicolations, all aimed at an active style of defence. The Krak des Chevaliers
Krak des Chevaliers, ar, قلعة الحصن, Qalʿat al-Ḥiṣn also called Hisn al-Akrad ( ar, حصن الأكراد, Ḥiṣn al-Akrād, rtl=yes, ) and formerly Crac de l'Ospital; Krak des Chevaliers or Crac des Chevaliers (), is a medieva ...
in Syria is the best-preserved of the concentric crusader castles. By contrast, Château Pèlerin was not a concentric castle, as the side facing the sea did not require defensive walls. However, the two walls facing the land are built on the same defensive principles as other crusader castles in the same period, rivalling the defences at Krak.
While a concentric castle has double walls and towers on all sides, the defences need not be uniform in all directions. There can still be a concentration of defences at a vulnerable point. At Krak des Chevaliers, this is the case at the southern side, where the terrain permits an attacker to deploy siege engines. Also, the gate and postern
A postern is a secondary door or gate in a fortification such as a city wall or castle curtain wall. Posterns were often located in a concealed location which allowed the occupants to come and go inconspicuously. In the event of a siege, a postern ...
s are typically strengthened using a bent entrance
A bent or indirect entrance is a defensive feature in medieval fortification.Adrian Boas, On a Necessary Vulnerability, https://www.adrianjboas.com/post/on-a-necessary-vulnerability In a castle with a bent entrance, the gate passage is narrow and ...
or flanking towers.
Concentric castles were expensive to build, so that only the powerful military orders, the Hospitallers
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic Church, Catholic Military ord ...
and Templars
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
, or powerful kings could afford to build and maintain them. It has also been pointed out that the concentric layout suited the requirements of military orders such as the Hospitallers in resembling a monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whi ...
and housing a large garrison. Such castles were beyond the means of feudal barons. Thus, concentric castles coexisted with simpler enclosure castles and tower keeps even in the crusader state
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
s.
Concentric castles appeared in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
in the 13th century, with the castles built in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
by Edward I providing some outstanding examples, in particular Beaumaris Castle
Beaumaris Castle ( ; cy, Castell Biwmares ), in Beaumaris, Anglesey, Wales, was built as part of Edward I's campaign to conquer north Wales after 1282. Plans were probably first made to construct the castle in 1284, but this was delayed d ...
, a "perfect concentric castle", albeit unfinished. As Beaumaris was built on flat terrain rather than a spur
A spur is a metal tool designed to be worn in pairs on the heels of riding boots for the purpose of directing a horse or other animal to move forward or laterally while riding. It is usually used to refine the riding aids (commands) and to ba ...
, it was both necessary and possible to build walls and towers facing in all directions, giving a very regular, almost square, floor plan to the castle. Some influence from crusader fortification has been conjectured, but the amount of technology transfer from the East and much earlier Byzantine examples remains controversial among historians.
Similar structures
In the German-speaking states of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, many castles had double curtain walls with a narrow ward between them, referred to as a . These were added at vulnerable points like the gate but were rarely as fully developed as in the concentric castles in Wales or the Crusader castles.
The principle of an outer and inner wall was also used in fortified cities, such as the Theodosian Walls
The Walls of Constantinople ( el, Τείχη της Κωνσταντινουπόλεως) are a series of defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (today Istanbul in Turkey) since its founding as the ...
of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
and the city wall of Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the Au ...
.
The concept of mutually reinforcing lines of defence with flanking fire was continued in later periods, such as the early modern fortifications of Vauban, where outer defence works were protected and overlooked by others and their capture did not destroy the integrity of the inner Citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
I ...
.
Citadels from before and during the Reconquista in Spain and Portugal also have fortifications similar to concentric castles found elsewhere in Europe. Castle of Almodóvar del Río is a good example of such a fortress along with Saint George Castle in Lisbon Portugal.
Examples of concentric castles
Belvoir Castle
Belvoir Castle ( ) is a faux historic castle and stately home in Leicestershire, England, situated west of the town of Grantham and northeast of Melton Mowbray. The Castle was first built immediately after the Norman Conquest of 1066 an ...
(Israel), 1150
File:Burg Münzenberg.jpg, Münzenberg Castle
Münzenberg Castle (German. ''Burg Münzenberg'') is a ruined hill castle in the town of the same name in the Wetteraukreis, Hesse, Germany. It dates from the 12th century. It is one of the best preserved castles from the High Middle Ages in Germ ...
(Hesse), 1162
File: Kidwelly castle whole.JPG, Kidwelly Castle, south-west Wales, 13th century
File: Castell Rhuddlan, Sir Ddinbych, Cymru 33.JPG, Rhuddlan Castle
Rhuddlan Castle ( cy, Castell Rhuddlan; ) is a castle located in Rhuddlan, Denbighshire, Wales. It was erected by Edward I in 1277, following the First Welsh War.
Much of the work was overseen by master mason James of Saint George. Rhudd ...
, north of Wales, 1277
File: Harlech Castle - Cadw photograph.jpg, Harlech Castle
Harlech Castle ( cy, Castell Harlech; ) in Harlech, Gwynedd, Wales, is a Grade I listed medieval fortification built onto a rocky knoll close to the Irish Sea. It was built by Edward I during his invasion of Wales between 1282 and 1289 at t ...
, west of Wales, 1282–
File: Beaumaris aerial.jpg, Beaumaris Castle
Beaumaris Castle ( ; cy, Castell Biwmares ), in Beaumaris, Anglesey, Wales, was built as part of Edward I's campaign to conquer north Wales after 1282. Plans were probably first made to construct the castle in 1284, but this was delayed d ...
, on the island of Anglesey at the north-west of Wales, 1295
File: Kizkalesi Korykos.JPG, The Byzantine castle of Korykos
Corycus ( el, Κώρυκος; also transliterated Corycos or Korykos; hy, Կոռիկոս, translit=Koṙikos; tr, Kız Kalesi, lit. "maiden castle") was an ancient city in Cilicia Trachaea, Anatolia, located at the mouth of the valley calle ...
from the sea c.11th cent. AD. It featured fully concentric features a century before the first examples of concentric fortifications were seen in the West
File: Caerphilly aerial.jpg, Caerphilly Castle
Caerphilly Castle ( cy, Castell Caerffili) is a medieval fortification in Caerphilly in South Wales. The castle was constructed by Gilbert de Clare in the 13th century as part of his campaign to maintain control of Glamorgan, and saw extensi ...
, south of Wales, 13th century
See also
*Buhen
Buhen ( grc, Βοὥν ''Bohón'') was an ancient Egyptian settlement situated on the West bank of the Nile below (to the North of) the Second Cataract in what is now Northern State, Sudan.
It is now submerged in Lake Nasser, Sudan; as a resu ...
(ancient Egyptian stronghold)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Concentric Castle Castles by type