Compromise Of 1850 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the
 The independent
The independent
 California was part of the Mexican Cession. After the Mexican War, California was essentially run by military governors. President
California was part of the Mexican Cession. After the Mexican War, California was essentially run by military governors. President
 The problem of what to do with the territories became the leading issue in Congress. So began the most famous debates in the history of Congress. At the head were the three titans of Congress: Henry Clay,
The problem of what to do with the territories became the leading issue in Congress. So began the most famous debates in the history of Congress. At the head were the three titans of Congress: Henry Clay,
 On April 17, a "Committee of Thirteen" agreed on the border of Texas as part of Clay's plan. The dimensions were later changed. That same day, during debates on the measures in the Senate, Vice President Fillmore and Senator Benton verbally sparred, with Fillmore charging that the Missourian was "out of order." During the heated debates, Compromise floor leader
On April 17, a "Committee of Thirteen" agreed on the border of Texas as part of Clay's plan. The dimensions were later changed. That same day, during debates on the measures in the Senate, Vice President Fillmore and Senator Benton verbally sparred, with Fillmore charging that the Missourian was "out of order." During the heated debates, Compromise floor leader
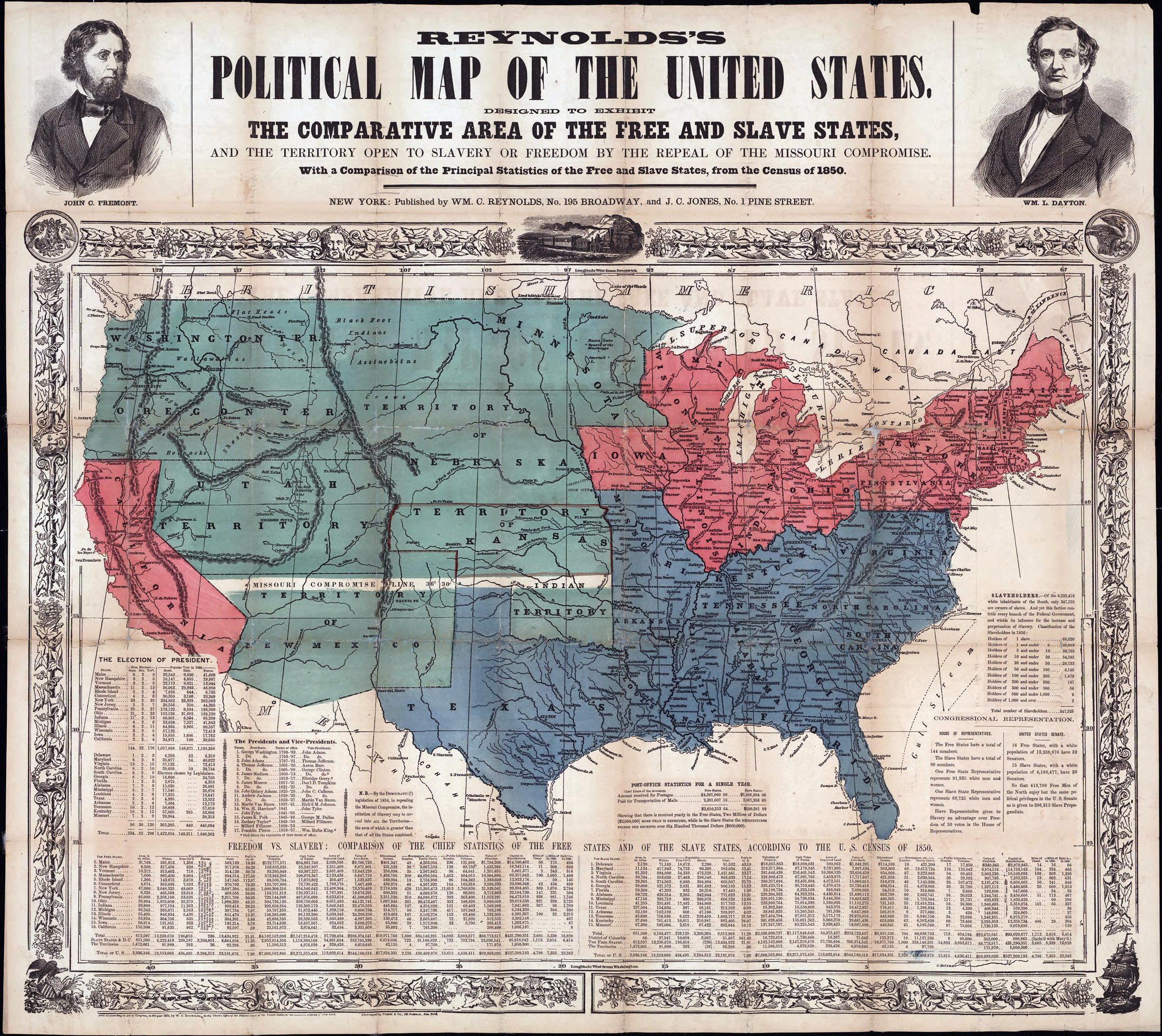 Passage of the Compromise of 1850, as it came to be known, caused celebration in Washington and elsewhere, with crowds shouting, "The Union is saved!" Fillmore himself described the Compromise of 1850 as a "final settlement" of sectional issues, though the future of slavery in New Mexico and Utah remained unclear. The admission of new states, or the organization of territories in the remaining unorganized portion of the Louisiana Purchase, could also potentially reopen the polarizing debate over slavery. Not all accepted the Compromise of 1850; a South Carolina newspaper wrote, "the Rubicon is passed ... and the Southern States are now vassals in this Confederacy." Many Northerners, meanwhile, were displeased by the Fugitive Slave Act. The debate over slavery in the territories would be re-opened in 1854 through the
Passage of the Compromise of 1850, as it came to be known, caused celebration in Washington and elsewhere, with crowds shouting, "The Union is saved!" Fillmore himself described the Compromise of 1850 as a "final settlement" of sectional issues, though the future of slavery in New Mexico and Utah remained unclear. The admission of new states, or the organization of territories in the remaining unorganized portion of the Louisiana Purchase, could also potentially reopen the polarizing debate over slavery. Not all accepted the Compromise of 1850; a South Carolina newspaper wrote, "the Rubicon is passed ... and the Southern States are now vassals in this Confederacy." Many Northerners, meanwhile, were displeased by the Fugitive Slave Act. The debate over slavery in the territories would be re-opened in 1854 through the
complegte text online
* Rozwenc, Edwin C. ed. ''The Compromise of 1850.'' (1957) convenient collection of primary and secondary documents; 102 pp. * * Sewell, Richard H. ''Ballots for Freedom: Antislavery Politics in the United States 1837–1860'' New York: Oxford University Press, 1976. * * * Waugh, John C. ''On the Brink of Civil War: The Compromise of 1850 and How It Changed the Course of American History'' (2003) * Wiltse, Charles M. ''John C. Calhoun, Sectionalist, 1840–1850'' (1951)
Compromise of 1850
from the Library of Congress
Texas Library and Archive Commission Page on 1850 Boundary Act
*
Map of North America at the time of the Compromise of 1850 at omniatlas.com
{{DEFAULTSORT:Compromise Of 1850 31st United States Congress 1850 in American politics 1850 in California 1850 in New Mexico Territory 1850 in Texas 1850 in Utah Territory 1850 in American law History of United States expansionism Presidency of Millard Fillmore Pre-statehood history of California New Mexico Territory United States slavery law United States federal territory and statehood legislation Utah Territory September 1850 events Origins of the American Civil War Political compromises in the United States Expansion of slavery in the United States
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
. It also set Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
' western and northern borders and included provisions addressing fugitive slaves
In the United States, fugitive slaves or runaway slaves were terms used in the 18th and 19th century to describe people who fled slavery. The term also refers to the federal Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Such people are also called free ...
and the slave trade. The compromise was designed by Whig senator Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, al ...
and Democratic senator Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas (April 23, 1813 – June 3, 1861) was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. A senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party for president in the 1860 presidential election, which wa ...
, with the support of President Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
.
The component acts:
* approved California’s request to enter the Union as a free state
* strengthened fugitive slave laws with the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850
The Fugitive Slave Act or Fugitive Slave Law was passed by the United States Congress on September 18, 1850, as part of the Compromise of 1850 between Southern interests in slavery and Northern Free-Soilers.
The Act was one of the most co ...
* banned the slave trade in Washington, D.C. (while still allowing slavery itself there)
* defined northern and western borders for Texas while establishing a territorial government for the Territory of New Mexico, with no restrictions on whether any future state from this territory would be free or slave
* established a territorial government for the Territory of Utah, with no restrictions on whether any future state from this territory would be free or slave
A debate over slavery in the territories had erupted during the Mexican–American War, as many Southerners sought to expand slavery to the newly-acquired lands and many Northerners opposed any such expansion. The debate was further complicated by Texas's claim to all former Mexican territory north and east of the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
, including areas it had never effectively controlled. These issues prevented the passage of organic act
In United States law, an organic act is an act of the United States Congress that establishes a territory of the United States and specifies how it is to be governed, or an agency to manage certain federal lands. In the absence of an organ ...
s to create organized territorial governments for the land acquired in the Mexican–American War. In early 1850, Clay proposed a package of eight bills that would settle most of the pressing issues before Congress. Clay's proposal was opposed by President Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military leader who served as the 12th president of the United States from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States Army, rising to th ...
, anti-slavery Whigs like William Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
, and pro-slavery Democrats like John C. Calhoun, and congressional debate over the territories continued. The debates over the bill were the most famous in Congressional history, and the divisions devolved into fistfights and drawn guns on the floor of Congress.
After Taylor died and was succeeded by Fillmore, Douglas took the lead in passing Clay's compromise through Congress as five separate bills. Under the compromise, Texas surrendered its claims to present-day New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
and other states in return for federal assumption of Texas's public debt. California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
was admitted as a free state, while the remaining portions of the Mexican Cession were organized into New Mexico Territory
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of ''Santa Fe de Nuevo México ...
and Utah Territory
The Territory of Utah was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from September 9, 1850, until January 4, 1896, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Utah, the 45th state. ...
. Under the concept of popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
, the people of each territory would decide whether or not slavery would be permitted. The compromise also included a more stringent Fugitive Slave Law
The fugitive slave laws were laws passed by the United States Congress in 1793 and 1850 to provide for the return of enslaved people who escaped from one state into another state or territory. The idea of the fugitive slave law was derived from ...
and banned the slave trade in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
The issue of slavery in the territories would be re-opened by the Kansas–Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
, but the Compromise of 1850 played a major role in postponing the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
.
Background
TheRepublic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
declared its independence from Mexico following the Texas Revolution of 1836, and, partly because Texas had been settled by a large number of Americans, there was a strong sentiment in both Texas and the United States for the annexation of Texas by the United States.Merry, pg. 120–124 In December 1845, President James K. Polk
James Knox Polk (November 2, 1795 – June 15, 1849) was the 11th president of the United States, serving from 1845 to 1849. He previously was the 13th speaker of the House of Representatives (1835–1839) and ninth governor of Tennessee (183 ...
signed a resolution annexing Texas, and Texas became the 28th state in the union. Polk sought further expansion through the acquisition of the Mexican province of Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
, which represented new lands to settle as well as a potential gateway to trade in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. His administration attempted to purchase California from Mexico, but the annexation of Texas stoked tensions between Mexico and the United States. Relations between the two countries were further complicated by Texas's claim to all land north of the Rio Grande; Mexico argued that the more northern Nueces River
The Nueces River is a river in the U.S. state of Texas, about long. It drains a region in central and southern Texas southeastward into the Gulf of Mexico. It is the southernmost major river in Texas northeast of the Rio Grande. ''Nueces'' ...
was the proper Texan border.Merry, pg. 187
In March 1846, a skirmish
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They are usually deployed in a skirmish line, an i ...
broke out on the northern side of the Rio Grande, ending in the death or capture of dozens of American soldiers. Shortly thereafter, the United States declared war on Mexico, beginning the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
.Merry, pg. 246–247 In August 1846, Polk asked Congress for an appropriation that he hoped to use as a down payment for the purchase of California in a treaty with Mexico, igniting a debate over the status of future territories.Merry, pg. 283–285 A freshman Democratic Congressman, David Wilmot
David Wilmot (January 20, 1814 – March 16, 1868) was an American politician and judge. He served as Representative and a Senator for Pennsylvania and as a judge of the Court of Claims. He is best known for being the prime sponsor and epon ...
of Pennsylvania, offered an amendment known as the Wilmot Proviso
The Wilmot Proviso was an unsuccessful 1846 proposal in the United States Congress to ban slavery in territory acquired from Mexico in the Mexican–American War. The conflict over the Wilmot Proviso was one of the major events leading to the ...
that would ban slavery in any newly acquired lands.Merry, pg. 286–289 The Wilmot Proviso was defeated in the Senate, but it injected the slavery debate into national politics.
In September 1847, an American army under General Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
captured the Mexican capital in the Battle for Mexico City
The Battle for Mexico City refers to the series of engagements from September 8 to September 15, 1847, in the general vicinity of Mexico City during the Mexican–American War. Included are major actions at the battles of Molino del Rey and Ch ...
.Merry, pg. 387–388 Several months later, Mexican and American negotiators agreed to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
, under which Mexico agreed to recognize the Rio Grande as Texas's southern border and to cede Alta California and New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
.Merry, pg. 424–425 The Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was a federal legislation of the United States that balanced desires of northern states to prevent expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a slave state and ...
had settled the issue of the geographic reach of slavery within the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
territories by prohibiting slavery in states north of 36°30′ latitude, and Polk sought to extend this line into the newly acquired territory.Merry, pp. 452–453 However, the divisive issue of slavery blocked any such legislation. As his term came to a close, Polk signed the lone territorial bill passed by Congress, which established the Territory of Oregon and banned slavery in it. Polk declined to seek re-election in the 1848 presidential election,Merry, pg. 376–377 and the 1848 election was won by the Whig ticket of Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military leader who served as the 12th president of the United States from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States Army, rising to th ...
and Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
.Merry, pg. 447–448
Prophetically, Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
quipped that "Mexico will poison us", referring to the ensuing divisions around whether the newly conquered lands would be slave or free. As of the 1848 election of Taylor, the issue was not yet apparent. Taylor was both a Whig and a slaveholder; though Whigs were increasingly anti-slavery, Taylor's slaveholding had reassured the South, and he won handily. Taylor made a key electoral promise that he would not veto any congressional resolution on slavery. Much to the horror of Southerners, however, Taylor indicated that true to his promise, he would not even veto the Wilmot Proviso if it were passed. Tensions accelerated quickly into the fall of 1849. Midterm elections worsened matters, as the Free Soil Party
The Free Soil Party was a short-lived coalition political party in the United States active from 1848 to 1854, when it merged into the Republican Party. The party was largely focused on the single issue of opposing the expansion of slavery int ...
had gained 12 seats, which gave them a king-maker position in the closely divided House: 105 Whigs to 112 Democrats. After three weeks and 62 ballots, the House could not elect a speaker; the main issue was slavery in the new territories. The tumult of that period was severe, with a loaded revolver drawn on the floor of Congress, several fistfights between Northerners and Southerners, and then Senator Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a ...
challenging an Illinois congressman to a duel. Southern congressmen increasingly bandied around the idea of secession. Finally, the House adopted a resolution that allowed a speaker to be elected with a plurality, and elected Howell Cobb
Howell Cobb (September 7, 1815 – October 9, 1868) was an American and later Confederate political figure. A southern Democrat, Cobb was a five-term member of the United States House of Representatives and the speaker of the House from 184 ...
on the 63rd ballot. As James McPherson puts it: "It was an inauspicious start to the 1850's."
Issues
Three major types of issues were addressed by the Compromise of 1850: a variety of boundary issues, the status of territory issues, and the issue of slavery. While capable of analytical distinction, the boundary and territory issues were included in the overarching issue of slavery. Pro-slavery and anti-slavery interests were each concerned with both the amount of land on which slavery was permitted and with the number of States in the slave or free camps. Since Texas was a slave state, not only the residents of that state but also both camps on a national scale had an interest in the size of Texas.Texas
Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
won the decisive Battle of San Jacinto
The Battle of San Jacinto ( es, Batalla de San Jacinto), fought on April 21, 1836, in present-day La Porte and Pasadena, Texas, was the final and decisive battle of the Texas Revolution. Led by General Samuel Houston, the Texan Army engaged ...
(April 21, 1836) against Mexico and captured Mexican president Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna
Antonio is a masculine given name of Etruscan origin deriving from the root name Antonius. It is a common name among Romance language-speaking populations as well as the Balkans and Lusophone Africa. It has been among the top 400 most popular mal ...
. He signed the Treaties of Velasco
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
, which recognized the Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
as the boundary of the Republic of Texas. The treaties were then repudiated by the government of Mexico, which insisted that Mexico remained sovereign over Texas since Santa Anna had signed the treaty under coercion, and promised to reclaim the lost territories. To the extent that there was a ''de facto'' recognition, Mexico treated the Nueces River
The Nueces River is a river in the U.S. state of Texas, about long. It drains a region in central and southern Texas southeastward into the Gulf of Mexico. It is the southernmost major river in Texas northeast of the Rio Grande. ''Nueces'' ...
as its northern boundary control. A vast, largely-unsettled area lay between the two rivers. Neither Mexico nor the Republic of Texas had the military strength to assert its territorial claim. On December 29, 1845, the Republic of Texas was annexed to the United States and became the 28th state. Texas was staunchly committed to slavery, with its constitution making it illegal for the legislature to free slaves.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo made no mention of the claims of the Republic of Texas; Mexico simply agreed to a Mexico–United States border
The Mexico–United States border ( es, frontera Estados Unidos–México) is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traver ...
south of both the "Mexican Cession" and the Republic of Texas claims. After the end of the Mexican–American War, Texas continued to claim a large stretch of disputed land that it had never effectively controlled in present-day eastern New Mexico. New Mexico had long prohibited slavery, a fact that affected the debate over its territorial status, but many New Mexican leaders opposed joining Texas primarily because Texas's capital lay hundreds of miles away and because Texas and New Mexico had a history of conflict dating back to the 1841 Santa Fe Expedition
The Texan Santa Fe Expedition was a commercial and military expedition to secure the Republic of Texas's claims to parts of Northern New Mexico for Texas in 1841. The expedition was unofficially initiated by the then-President of Texas, Mirabeau B ...
. Outside of Texas, many Southern leaders supported Texas's claims to New Mexico to secure as much territory as possible for the expansion of slavery.
Another issue that would affect the compromise was Texas's debt; it had approximately $10 million in debt left over from its time as an independent nation, and that debt would become a factor in the debates over the territories.
California
 California was part of the Mexican Cession. After the Mexican War, California was essentially run by military governors. President
California was part of the Mexican Cession. After the Mexican War, California was essentially run by military governors. President James K. Polk
James Knox Polk (November 2, 1795 – June 15, 1849) was the 11th president of the United States, serving from 1845 to 1849. He previously was the 13th speaker of the House of Representatives (1835–1839) and ninth governor of Tennessee (183 ...
tried to get Congress to establish a territorial government in California officially, but the increasingly sectional debates prevented that. The South wanted to extend slave territory to Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most po ...
and to the Pacific Coast, but the North did not. The issue of whether it would be free or slave might well have gone undecided for years, as it had already after the end of the Mexican American war, if not for the finding of natural riches.
Near the end of Polk's term in 1848, incredible news reached Washington: gold had been discovered in California. So began the California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
, which transformed California from a sleepy and almost forgotten land into a burgeoning hub with a population bigger than Delaware or Florida. The mostly lawless land found itself in desperate need of governance. Californians wanted to be made into a territory or state promptly. In response to growing demand for a better more representative government, a Constitutional Convention was held in 1849. The delegates unanimously outlawed slavery. They had no interest in extending the Missouri Compromise Line through California and splitting the state; the lightly populated southern half never had slavery and was heavily Hispanic. The issue of California would play a central role in the exhausting 1849 speaker dispute.
Other issues
Aside from the disposition of the territories, other issues had risen to prominence during the Taylor years. The Washington, D.C. slave trade angered many in the North, who viewed the presence of slavery in the capital as a blemish on the nation. Disputes aroundfugitive slaves
In the United States, fugitive slaves or runaway slaves were terms used in the 18th and 19th century to describe people who fled slavery. The term also refers to the federal Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Such people are also called free ...
had grown since 1830 in part due to improving means of transportation, as the enslaved used roads, railroads, and ships to escape. The Fugitive Slave Act of 1793
The Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 was an Act of the United States Congress to give effect to the Fugitive Slave Clause of the US Constitution ( Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3), which was later superseded by the Thirteenth Amendment, and to also gi ...
had granted jurisdiction to all state and federal judges over cases regarding fugitive slaves, but several Northern states, dissatisfied by the lack of due process
Due process of law is application by state of all legal rules and principles pertaining to the case so all legal rights that are owed to the person are respected. Due process balances the power of law of the land and protects the individual pers ...
in these cases, had passed personal liberty laws
In the context of slavery in the United States, the personal liberty laws were laws passed by several U.S. states in the North to counter the Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Different laws did this in different ways, including allowing j ...
that made it more difficult to return alleged fugitive slaves to the South. Congress also faced the issue of Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, which like California and New Mexico, had been ceded by Mexico. Utah was inhabited largely by Mormons, whose practice of polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married ...
was unpopular elsewhere in the United States.
Passage
Taylor takes office
When Taylor took office, the issue of slavery in the Mexican Cession remained unresolved. While a Southern slaveowner himself, Taylor believed that slavery was economically infeasible in the Mexican Cession, and as such he opposed slavery in those territories as a needless source of controversy. In Taylor's view, the best way forward was to admit California as a state rather than a federal territory, as it would leave the slavery question out of Congress's hands. The timing for statehood was in Taylor's favor, as theGold Rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Z ...
was well underway at the time of his inauguration, and California's population was exploding. In October 1849, a California constitutional convention unanimously agreed to join the Union—and to ban slavery within their borders. In his December 1849 State of the Union report, Taylor endorsed California's and New Mexico's applications for statehood, and recommended that Congress approve them as written and "should abstain from the introduction of those exciting topics of a sectional character".
Main figures
 The problem of what to do with the territories became the leading issue in Congress. So began the most famous debates in the history of Congress. At the head were the three titans of Congress: Henry Clay,
The problem of what to do with the territories became the leading issue in Congress. So began the most famous debates in the history of Congress. At the head were the three titans of Congress: Henry Clay, Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison, ...
, and John C. Calhoun. All had been born during the American Revolution, and had carried the torch of the Founding Fathers. This represented their last and greatest act in politics. The nationalist Clay and Webster sought compromise, while Southern sectionalist Calhoun warned of imminent disaster. The triumvirate would be broken before long as Calhoun would die of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
. In March, shortly before his death, his final speech was delivered by his friend the Virginia Senator James M. Mason, as the blanket-wrapped Calhoun sat nearby, too weak to do it himself. He provided a prescient warning that the South perceived the balance between North and South as broken, and that any further imbalance might lead to war. The situation was severe.
Other players included a variety of rising politicians who would play key roles in the Civil War, such as the staunch anti-slavery William H. Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
and Salmon P. Chase
Salmon Portland Chase (January 13, 1808May 7, 1873) was an American politician and jurist who served as the sixth chief justice of the United States. He also served as the 23rd governor of Ohio, represented Ohio in the United States Senate, a ...
, who would be in Lincoln's cabinet; the future president of the Confederacy, Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a ...
; and rival to Abraham Lincoln, Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas (April 23, 1813 – June 3, 1861) was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. A senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party for president in the 1860 presidential election, which wa ...
.
Clay proposes compromise
On January 29, 1850, Senator Henry Clay introduced a plan which combined the major subjects under discussion. His legislative package of eight bills included the admission of California as a free state, thecession
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdictio ...
by Texas of some of its northern and western territorial claims in return for debt relief, the establishment of New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
and Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
territories, a ban on the importation of slaves into the District of Columbia for sale, and a more stringent fugitive slave law. Clay had originally favored voting on each of his proposals separately, but Senator Henry S. Foote
Henry Stuart Foote (February 28, 1804May 19, 1880) was a United States Senator from Mississippi and the chairman of the United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations from 1847 to 1852. He was a Unionist Governor of Mississippi from 1852 to ...
of Mississippi convinced him to combine the proposals regarding California's admission and the disposition of Texas's borders into one bill. Clay hoped that this combination of measures would convince congressmen from both North and South to support the overall package of laws even if they objected to specific provisions. Clay's proposal attracted the support of some Northern Democrats and Southern Whigs, but it lacked the backing necessary to win passage, and debate over the bill continued. Seven months of agonizing politicking lay ahead.
Opposition
President Taylor opposed the compromise and continued to call for immediate statehood for both California and New Mexico. Senator Calhoun and some other Southern leaders argued that the compromise was biased against the South because it would lead to the creation of new free states. Most Northern Whigs, led byWilliam Henry Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
, who delivered his famous "Higher Law" speech during the controversy, opposed the Compromise as well because it would apply the Wilmot Proviso to the western territories and because of the pressing of ordinary citizens into duty on slave-hunting patrols. That provision was inserted by Democratic Virginia Senator James M. Mason to entice border-state Whigs, who faced the greatest danger of losing slaves as fugitives but were lukewarm on general sectional issues related to the South on Texas's land claims.
Debate and results
 On April 17, a "Committee of Thirteen" agreed on the border of Texas as part of Clay's plan. The dimensions were later changed. That same day, during debates on the measures in the Senate, Vice President Fillmore and Senator Benton verbally sparred, with Fillmore charging that the Missourian was "out of order." During the heated debates, Compromise floor leader
On April 17, a "Committee of Thirteen" agreed on the border of Texas as part of Clay's plan. The dimensions were later changed. That same day, during debates on the measures in the Senate, Vice President Fillmore and Senator Benton verbally sparred, with Fillmore charging that the Missourian was "out of order." During the heated debates, Compromise floor leader Henry S. Foote
Henry Stuart Foote (February 28, 1804May 19, 1880) was a United States Senator from Mississippi and the chairman of the United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations from 1847 to 1852. He was a Unionist Governor of Mississippi from 1852 to ...
of Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
drew a pistol on Benton.
In early June, nine slaveholding Southern states sent delegates to the Nashville Convention {{Events leading to US Civil War
The Nashville Convention was a political meeting held in Nashville, Tennessee, on June 3–11, 1850. Delegates from nine slave states met to consider secession, if the United States Congress decided to ban slavery ...
to determine their course of action if the compromise passed. While some delegates preached secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
, the moderates ruled and proposed a series of compromises, including extending the dividing line designated by the Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was a federal legislation of the United States that balanced desires of northern states to prevent expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a slave state and ...
of 1820 to the Pacific Coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
.
Taylor died in July 1850, and was succeeded by Vice President Fillmore, who had privately come to support Clay's proposal. The various bills were initially combined into one "omnibus" bill. Despite Clay's efforts, it failed in a crucial vote on July 31, opposed by southern Democrats and by northern Whigs. He announced on the Senate floor the next day that he intended to pass each part of the bill. The 73-year-old Clay, however, was physically exhausted as the effects of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
, which would eventually kill him, began to take their toll. Clay left the Senate to recuperate in Newport, Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, and Senator Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas (April 23, 1813 – June 3, 1861) was an American politician and lawyer from Illinois. A senator, he was one of two nominees of the badly split Democratic Party for president in the 1860 presidential election, which wa ...
took the lead in attempting to pass Clay's proposals through the Senate.
Fillmore, anxious to find a quick solution to the conflict in Texas over the border with New Mexico, which threatened to become an armed conflict between Texas militia and the federal soldiers, reversed the administration's position late in July and threw its support to the compromise measures. At the same time, Fillmore denied Texas's claims to New Mexico, asserting that the United States had promised to protect the territorial integrity of New Mexico in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Fillmore's forceful response helped convince Texas's U.S. Senators, Sam Houston
Samuel Houston (, ; March 2, 1793 – July 26, 1863) was an American general and statesman who played an important role in the Texas Revolution. He served as the first and third president of the Republic of Texas and was one of the first two i ...
and Thomas Jefferson Rusk
Thomas Jefferson Rusk (December 5, 1803July 29, 1857) was an early political and military leader of the Republic of Texas, serving as its first Secretary of War as well as a general at the Battle of San Jacinto. He was later a US politician and ...
, to support Stephen Douglas's compromise. With their support, a Senate bill providing for a final settlement of Texas's borders won passage days after Fillmore delivered his message. Under the terms of the bill, the U.S. would assume Texas's debts, while Texas's northern border was set at the 36° 30' parallel north (the Missouri Compromise line) and much of its western border followed the 103rd meridian. The bill attracted the support of a bipartisan coalition of Whigs and Democrats from both sections, though most opposition to the bill came from the South. The Senate quickly moved on to the other major issues, passing bills that provided for the admission of California, the organization of New Mexico Territory, and the establishment of a new fugitive slave law.
The debate then moved to the House of Representatives, where Fillmore, Senator Daniel Webster, Douglas, Congressman Linn Boyd
Linn Boyd (November 22, 1800 – December 17, 1859) (also spelled "Lynn") was a prominent US politician of the 1840s and 1850s, and served as Speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 1851 to 1855. Boyd was elected to the Hou ...
, and Speaker of the House Howell Cobb
Howell Cobb (September 7, 1815 – October 9, 1868) was an American and later Confederate political figure. A southern Democrat, Cobb was a five-term member of the United States House of Representatives and the speaker of the House from 184 ...
took the lead in convincing members to support the compromise bills that had been passed in the Senate. The Senate's proposed settlement of the Texas-New Mexico boundary faced intense opposition from many Southerners, as well as from some Northerners who believed that Texas did not deserve monetary compensation. After a series of close votes that nearly delayed consideration of the issue, the House voted to approve a Texas bill similar to that which had been passed by the Senate. Following that vote, the House and the Senate quickly agreed on each of the major issues, including the banning of the slave trade in Washington. The president quickly signed each bill into law save for the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850
The Fugitive Slave Act or Fugitive Slave Law was passed by the United States Congress on September 18, 1850, as part of the Compromise of 1850 between Southern interests in slavery and Northern Free-Soilers.
The Act was one of the most co ...
; he ultimately signed that law as well after Attorney General Crittenden assured him that the law was constitutional. Though some in Texas still favored sending a military expedition into New Mexico, in November 1850 the state legislature voted to accept the compromise.
Provisions
The general solution that was adopted by the Compromise of 1850 was to transfer a considerable part of the territory claimed by Texas state to the federal government; to organize two new territories formally, theTerritory of New Mexico
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of '' Nuevo México'' becoming ...
and the Territory of Utah
The Territory of Utah was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from September 9, 1850, until January 4, 1896, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Utah, the 45th state ...
, which expressly would be allowed to locally determine whether they would become slave or free territories, to add another free state to the Union (California), to adopt a severe measure to recover slaves who had escaped to a free state or free territory (the Fugitive Slave Law); and to abolish the slave trade in the District of Columbia. A key provision of each of the laws respectively organizing the Territory of New Mexico and the Territory of Utah was that slavery would be decided by local option, called popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
. That was an important repudiation of the idea behind the failure to prohibit slavery in any territory acquired from Mexico. However, the admission of California as a free state meant that Southerners were giving up their goal of a coast-to-coast belt of slave states.
Settlement of borders
Texas was allowed to keep the following portions of the disputed land: south of the 32nd parallel and south of the 36°30' parallel north and east of the 103rd meridian west. The rest of the disputed land was transferred to the Federal Government. The final border was designed to keep the frontier settlement ofEl Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
in Texas, since despite that settlement's geographic, historic, and economic ties to New Mexico, Texas had recently established a county government in El Paso and thus successfully claimed it as an integral part of Texas. A similar attempt to keep Santa Fe in Texas failed, and Santa Fe became part of the New Mexico territory.''El Paso, A Borderlands History'', by W.H. Timmons, pp. 117-125 The United States Constitution (Article IV, Section 3) does not permit Congress unilaterally to reduce the territory of any state, so the first part of the Compromise of 1850 had to take the form of an offer to the Texas State Legislature
The Texas Legislature is the state legislature of the US state of Texas. It is a bicameral body composed of a 31-member Senate and a 150-member House of Representatives. The state legislature meets at the Capitol in Austin. It is a powerful arm ...
, rather than a unilateral enactment. This ratified the bargain and, in due course, the transfer of a broad swath of land from the state of Texas to the federal government was accomplished. In return for giving up this land, the United States assumed the debts of Texas.
From the Mexican Cession, the New Mexico Territory received most of the present-day state of Arizona, most of the western part of the present-day state of New Mexico, and the southern tip of present-day Nevada (south of the 37th parallel). The territory also received most of present-day eastern New Mexico, a portion of present-day Colorado (east of the crest of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
, west of the 103rd meridian, and south of the 38th parallel); all of this land had been claimed by Texas.
From the Mexican Cession, the Utah Territory received present-day Utah, most of present-day Nevada (everything north of the 37th parallel), a major part of present-day Colorado (everything west of the crest of the Rocky Mountains), and a small part of present-day Wyoming. That included the newly-founded colony at Salt Lake, of Brigham Young
Brigham Young (; June 1, 1801August 29, 1877) was an American religious leader and politician. He was the second President of the Church (LDS Church), president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), from 1847 until his ...
. The Utah Territory also received some land that had been claimed by Texas; this land is now part of present-day Colorado that is east of the crest of the Rocky Mountains.
Fugitive Slave Act
Perhaps the most important part of the Compromise received the least attention during debates. Enacted September 18, 1850, it is informally known as the Fugitive Slave Law, or theFugitive Slave Act
A fugitive (or runaway) is a person who is fleeing from custody, whether it be from jail, a government arrest, government or non-government questioning, vigilante violence, or outraged private individuals. A fugitive from justice, also kno ...
. It bolstered the Fugitive Slave Act of 1793
The Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 was an Act of the United States Congress to give effect to the Fugitive Slave Clause of the US Constitution ( Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3), which was later superseded by the Thirteenth Amendment, and to also gi ...
. The new version of the Fugitive Slave Law now required federal judicial officials in all states and federal territories, including free states, to assist with the return of escaped slaves to their masters in slave states. Any federal marshal
The United States Marshals Service (USMS) is a federal law enforcement agency in the United States. The USMS is a bureau within the U.S. Department of Justice, operating under the direction of the Attorney General, but serves as the enforcem ...
or other official who did not arrest an alleged runaway slave was liable to a fine of $1,000 (). Law enforcement everywhere in the US now had a duty to arrest anyone suspected of being a fugitive slave
In the United States, fugitive slaves or runaway slaves were terms used in the 18th and 19th century to describe people who fled slavery. The term also refers to the federal Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Such people are also called free ...
on no more evidence than a claimant's sworn testimony of ownership. Suspected slaves could neither ask for a jury trial nor testify on their own behalf. Also, aiding a runaway slave by providing food or shelter was now a crime nationwide, punished by six months' imprisonment and a $1,000 fine. Officers capturing a fugitive slave were entitled to a fee for their work, and this expense was to be paid by the Federal Government.
The law was so completely pro-slavery as to prohibit the admission of the testimony of a person accused of being an escaped slave into evidence at the judicial hearing to determine the status of the accused escaped slave. Thus, if free Blacks were claimed to be escaped slaves, they could not resist their return to slavery (or enslavement for the first time) by truthfully telling their actual history. Furthermore, the federal commissioners overseeing the hearings were paid $5 for ruling a person was free, but were paid $10 for determining they were a slave, thus providing a financial incentive to always rule in favor of slavery regardless of the evidence. The law further exacerbated the problem of free Blacks being kidnapped and sold as slaves.
The Fugitive Slave Act was essential to meet Southern demands. In terms of public opinion in the North, the critical provision was that ordinary citizens were required to aid slave catchers, and made it a crime to assist a fugitive. Many Northerners deeply resented these requirements. Resentment towards the Act further heightened tensions between the North and South, which were then inflamed further by abolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
such as Harriet Beecher Stowe
Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe (; June 14, 1811 – July 1, 1896) was an American author and abolitionist. She came from the religious Beecher family and became best known for her novel ''Uncle Tom's Cabin'' (1852), which depicts the harsh ...
. Her novel, ''Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U. ...
'', stressed the horrors of recapturing escaped slaves and outraged Southerners.
End of slave trade in District of Columbia
A statute enacted as part of the compromise prohibited the slave trade in Washington, D.C., but not slave ownership. Southerners in Congress, alarmed and outraged, were unanimous in opposing the provision, seen as a concession to theabolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The Britis ...
and a bad precedent, but they were outvoted. However, Washington's residents could still easily buy and sell slaves in the nearby states of Virginia and Maryland.
Implications
 Passage of the Compromise of 1850, as it came to be known, caused celebration in Washington and elsewhere, with crowds shouting, "The Union is saved!" Fillmore himself described the Compromise of 1850 as a "final settlement" of sectional issues, though the future of slavery in New Mexico and Utah remained unclear. The admission of new states, or the organization of territories in the remaining unorganized portion of the Louisiana Purchase, could also potentially reopen the polarizing debate over slavery. Not all accepted the Compromise of 1850; a South Carolina newspaper wrote, "the Rubicon is passed ... and the Southern States are now vassals in this Confederacy." Many Northerners, meanwhile, were displeased by the Fugitive Slave Act. The debate over slavery in the territories would be re-opened in 1854 through the
Passage of the Compromise of 1850, as it came to be known, caused celebration in Washington and elsewhere, with crowds shouting, "The Union is saved!" Fillmore himself described the Compromise of 1850 as a "final settlement" of sectional issues, though the future of slavery in New Mexico and Utah remained unclear. The admission of new states, or the organization of territories in the remaining unorganized portion of the Louisiana Purchase, could also potentially reopen the polarizing debate over slavery. Not all accepted the Compromise of 1850; a South Carolina newspaper wrote, "the Rubicon is passed ... and the Southern States are now vassals in this Confederacy." Many Northerners, meanwhile, were displeased by the Fugitive Slave Act. The debate over slavery in the territories would be re-opened in 1854 through the Kansas–Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
.
In hindsight, the Compromise merely postponed the American Civil War for a decade, contrary to the expectations of many at the time, who felt the issue of slavery had finally been settled. During that decade, the Whig Party completely broke down, to be replaced with the new Republican Party dominant in the North, while Democrats reigned in the South.
Others argue that the Compromise only made more obvious the pre-existing sectional divisions, and laid the groundwork for future conflict. They view the Fugitive Slave Law as helping to polarize the US, as shown in the enormous reaction to Harriet Beecher Stowe
Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe (; June 14, 1811 – July 1, 1896) was an American author and abolitionist. She came from the religious Beecher family and became best known for her novel ''Uncle Tom's Cabin'' (1852), which depicts the harsh ...
's novel ''Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U. ...
''. The passage of the Fugitive Slave Law aroused feelings of bitterness in the North. Furthermore, the Compromise of 1850 led to a breakdown in the spirit of compromise in the Antebellum period
In the history of the Southern United States, the Antebellum Period (from la, ante bellum, lit= before the war) spanned the end of the War of 1812 to the start of the American Civil War in 1861. The Antebellum South was characterized by ...
. The Compromise exemplifies that spirit, but the deaths of influential senators who worked on the compromise, primarily Henry Clay and Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison, ...
, contributed to the feeling of increasing disparity between the North and South.
The delay of hostilities for ten years allowed the Northern states to continue to industrialize. The Southern states, largely based on slave labor and cash crop production, lacked the ability to industrialize heavily.
According to historian Mark Stegmaier, "The Fugitive Slave Act, the abolition of the slave trade in the District of Columbia, the admission of California as a free state, and even the application of the formula of popular sovereignty to the territories were all less important than the least remembered component of the Compromise of 1850—the statute by which Texas relinquished its claims to much of New Mexico in return for federal assumption of the debts."
Other proposals
Proposals in 1846 to 1850 on the division of the Southwest included the following (some of which are not mutually exclusive): * TheWilmot Proviso
The Wilmot Proviso was an unsuccessful 1846 proposal in the United States Congress to ban slavery in territory acquired from Mexico in the Mexican–American War. The conflict over the Wilmot Proviso was one of the major events leading to the ...
banning slavery in any new territory to be acquired from Mexico, not including Texas, which had been annexed the previous year. It passed the House in August 1846 and February 1847 but not the Senate. Later, an effort failed to attach the proviso to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
.
* The Extension of the Missouri Compromise line was proposed by failed amendments to the Wilmot Proviso by William W. Wick
William W. Wick (February 23, 1796 – May 19, 1868) was a U.S. Representative from Indiana and Secretary of State of Indiana. He was a lawyer and over his career he was a judge for 15 years. President Franklin Pierce appointed him Postmaster of ...
and then Stephen Douglas to extend the Missouri Compromise line ( 36°30' parallel north) west to the Pacific (south of Carmel-by-the-Sea, California
Carmel-by-the-Sea (), often simply called Carmel, is a city in Monterey County, California, United States, founded in 1902 and incorporated on October 31, 1916. Situated on the Monterey Peninsula, Carmel is known for its natural scenery and ric ...
) to allow the possibility of slavery in most of present-day New Mexico and Arizona, and southern California. That line was again proposed by the Nashville Convention {{Events leading to US Civil War
The Nashville Convention was a political meeting held in Nashville, Tennessee, on June 3–11, 1850. Delegates from nine slave states met to consider secession, if the United States Congress decided to ban slavery ...
of June 1850.
* Popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
, developed by Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass (October 9, 1782June 17, 1866) was an American military officer, politician, and statesman. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He w ...
and Stephen Douglas as the position of the Democratic Party, was to let the (white male) residents of each territory decide by vote whether to allow slavery. It was implemented in the Kansas–Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 () was a territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. It was drafted by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas, passed by the 33rd United States Congress, and signed into law by ...
of 1854, giving rise to the violence of the "Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the ...
" period.
* William L. Yancey
William Lowndes Yancey (August 10, 1814July 27, 1863) was an American journalist, politician, orator, diplomat and an American leader of the Southern secession movement. A member of the group known as the Fire-Eaters, Yancey was one of the mo ...
's "Alabama Platform", endorsed by the Alabama and the Georgia legislatures and by Democratic state conventions in Florida and Virginia, called for no restrictions on slavery in the territories by the federal government or territorial governments before statehood, opposition to any candidates supporting either the Wilmot Proviso or popular sovereignty, and federal legislation to overrule Mexican anti-slavery laws.
* Two free states were proposed by Zachary Taylor
Zachary Taylor (November 24, 1784 – July 9, 1850) was an American military leader who served as the 12th president of the United States from 1849 until his death in 1850. Taylor was a career officer in the United States Army, rising to th ...
, who served as President from March 1849 to July 1850. As President, he proposed that the entire area become two free states, called California and New Mexico but much larger than the ones today. None of the area would be left as an unorganized or organized territory
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sover ...
, which would avoid the question of slavery in the territories.
* Changing Texas's borders was proposed by Senator Thomas Hart Benton in December 1849 or January 1850. Texas's western and northern boundaries would be the 102nd meridian west and the 34th parallel north.
* Two southern states were proposed by Senator John Bell (Tennessee politician), John Bell, with the assent of Texas, in February 1850. New Mexico would get all Texas land north of the 34th parallel north, including today's Texas Panhandle, while the area to the south, including the southeastern part of today's New Mexico, would be divided at the Colorado River of Texas into two Southern states, balancing the admission of California and New Mexico as free states.
* The first draft of the compromise of 1850 had Texas's northwestern boundary be a straight, diagonal line from the Rio Grande 20 miles north of El Paso, Texas, El Paso to the Red River of the South, Red River (Mississippi watershed) at the 100th meridian west, the southwestern corner of today's Oklahoma.
See also
* Timeline of events leading to the American Civil WarReferences
Bibliography
* * Bell, John Frederick. "Poetry's Place in the Crisis and Compromise of 1850." ''Journal of the Civil War Era'' 5#3 (2015): 399–421. * * * * * Hamilton, Holman. ''Prologue to Conflict: The Crisis and Compromise of 1850'' (1964), the standard historical study * * Holman Hamilton. ''Zachary Taylor, Soldier in the White House'' (1951). * Heidler, David S., and Jeanne T. Heidler. ''Henry Clay: The Essential American'' (2010), major scholarly biography; 624 pp. * * Holt, Michael F. ''The Political Crisis of the 1850s'' (1978). * Holt, Michael F. ''The Fate of Their Country: Politicians, Slavery Extension, and the Coming of the Civil War'' (2005). * Johannsen, Robert W. ''Stephen A. Douglas'' (1973) * * Knupfer, Peter B. "Compromise and Statesmanship: Henry Clay's Union." in Knupfer, ''The Union As It Is: Constitutional Unionism and Sectional Compromise, 1787–1861'' (1991), pp. 119–57. * * * * Morrison, Michael A. ''Slavery and the American West: The Eclipse of Manifest Destiny and the Coming of the Civil War'' (1997) * Nevins, Allan. ''Ordeal of the Union'' (1947) v 2, highly detailed narrative * Potter, David M. ''The Impending Crisis, 1848–1861'' (1977), pp. 90–120; Pulitzer Prize * Remini, Robert. ''Henry Clay: Statesman for the Union'' (1991) * Remini, Robert. ''At the Edge of the Precipice: Henry Clay and the Compromise That Saved the Union'' (2010) 184 pages; the Compromise of 1850 * Rhodes, James Ford. ''History of the United States from the Compromise of 1850'', vol. i. (1896)complegte text online
* Rozwenc, Edwin C. ed. ''The Compromise of 1850.'' (1957) convenient collection of primary and secondary documents; 102 pp. * * Sewell, Richard H. ''Ballots for Freedom: Antislavery Politics in the United States 1837–1860'' New York: Oxford University Press, 1976. * * * Waugh, John C. ''On the Brink of Civil War: The Compromise of 1850 and How It Changed the Course of American History'' (2003) * Wiltse, Charles M. ''John C. Calhoun, Sectionalist, 1840–1850'' (1951)
External links
Compromise of 1850
from the Library of Congress
Texas Library and Archive Commission Page on 1850 Boundary Act
*
Map of North America at the time of the Compromise of 1850 at omniatlas.com
{{DEFAULTSORT:Compromise Of 1850 31st United States Congress 1850 in American politics 1850 in California 1850 in New Mexico Territory 1850 in Texas 1850 in Utah Territory 1850 in American law History of United States expansionism Presidency of Millard Fillmore Pre-statehood history of California New Mexico Territory United States slavery law United States federal territory and statehood legislation Utah Territory September 1850 events Origins of the American Civil War Political compromises in the United States Expansion of slavery in the United States