Companion Shadow on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
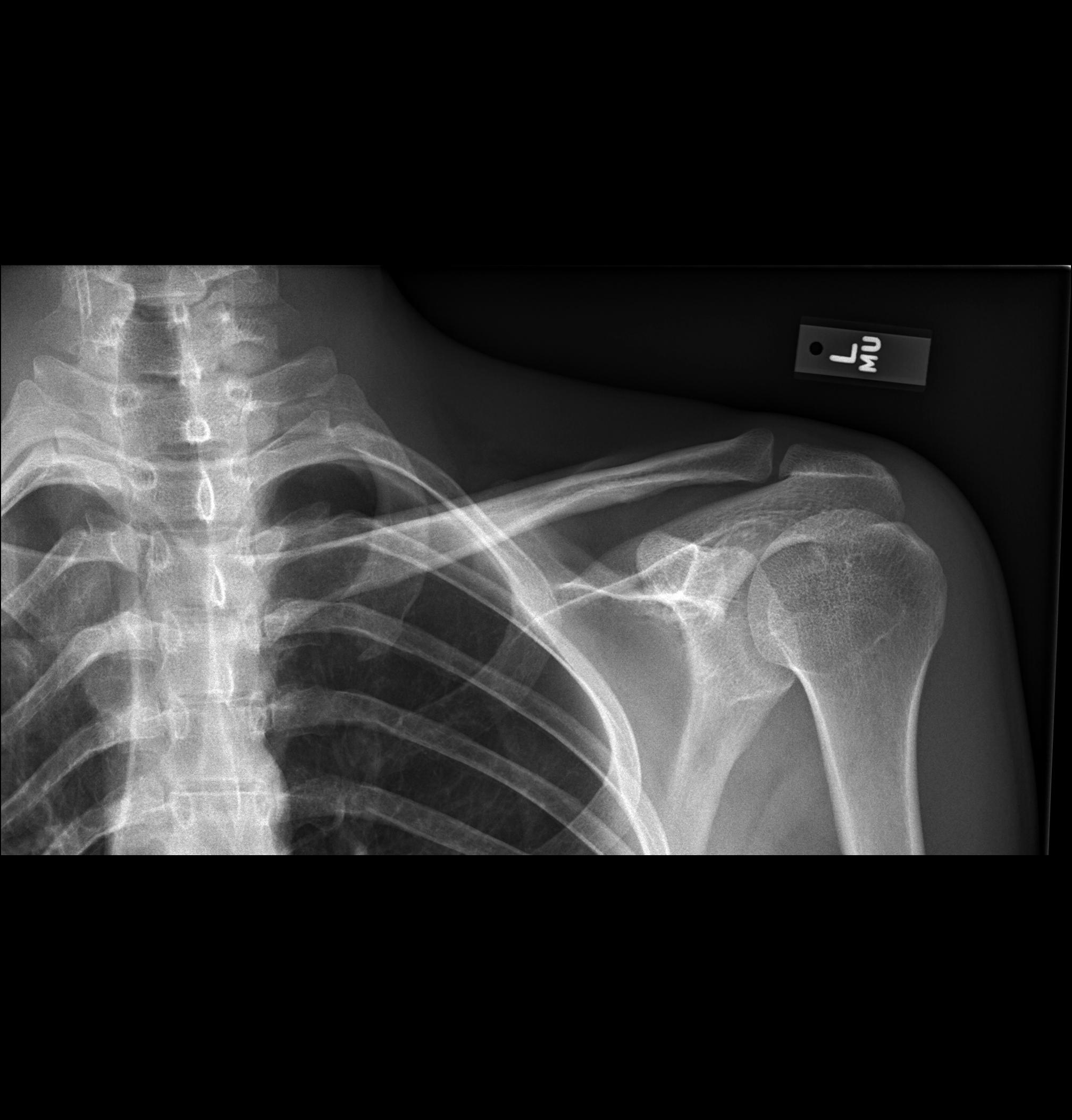 Companion shadow is a term used in describing
Companion shadow is a term used in describing
Lange S., Walsh G. Radiology of chest diseases, 2nd Edition, 1998 * Rib companion shadows parallel the
Kurihara Y., Yakushiji Y.K., Matsumoto J., Ishikawa T., Hirata K., The Ribs: Anatomic and Radiologic Considerations, January 1999 RadioGraphics, 19, 105-119. * Scapular companion shadow overlie the
Lams p.m., Jolles H., The scapula companion shadow, January 1981 Radiology, 138, 19-23.
 Companion shadow is a term used in describing
Companion shadow is a term used in describing radiographs
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnos ...
that denotes the appearance of a smooth, homogenous, radiodensity with a well-defined margin that runs parallel with a bony landmark. Companion shadows represent soft tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
that overlies the respective bony landmark in profile. They are not seen in every radiograph and can be misinterpreted as pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
.
Types of companion shadow
* Clavicular companion shadow is a thin soft-tissue stripe along the upper edge of theclavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the rig ...
.Lange S., Walsh G. Radiology of chest diseases, 2nd Edition, 1998 * Rib companion shadows parallel the
ribs
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi- ...
and measure 1–5 mm in diameter project adjacent to the inferior and inferolateral margins of the first and second ribs and the axillary portions of the lower ribs. These companion shadows of the first and second ribs occur in 35% and 31% of the population, respectively. Rib companion shadows represent the fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
and muscles
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle ...
in the intercostal space
The intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs (Lat. costa). Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.
Structures in intercostal space
* several kinds ...
. The shadows that accompany the ribs may mimic pleural
The pleural cavity, pleural space, or interpleural space is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication bet ...
and lung disease
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
.Kurihara Y., Yakushiji Y.K., Matsumoto J., Ishikawa T., Hirata K., The Ribs: Anatomic and Radiologic Considerations, January 1999 RadioGraphics, 19, 105-119. * Scapular companion shadow overlie the
scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
, with a smooth, well-defined margin parallel to the medial border of the scapula. The companion shadow results from unusual radiographic position of the scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eithe ...
, which causes a soft-tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
fold to occur along its medial border. Winging of the scapula may also be responsible for the shadow. Scapular companion shadows may be mistaken for a soft-tissue
Soft tissue is all the tissue in the body that is not hardened by the processes of ossification or calcification such as bones and teeth. Soft tissue connects, surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligam ...
or pleural lesion.Lams p.m., Jolles H., The scapula companion shadow, January 1981 Radiology, 138, 19-23.
References
{{Reflist Radiology