Communications-based Train Control on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Communications-based train control (CBTC) is a
(Accessed at January 14, 2019).
Bruno Gillaumin, International Railway Journal, May 2001. Retrieved by findarticles.com in June 2011. As a result, Bombardier Transportation, Bombardier opened the world's first radio-based CBTC system at
As a result, Bombardier Transportation, Bombardier opened the world's first radio-based CBTC system at
www.tsd.org/cbtc/projects, 2005. Accessed June 2011.CBTC radios: What to do? Which way to go
Tom Sullivan, 2005. www.tsd.org. Accessed May 2011. However, there have been relevant improvements since then, and currently the reliability of the radio-based communication systems has grown significantly. Moreover, it is important to highlight that not all the systems using
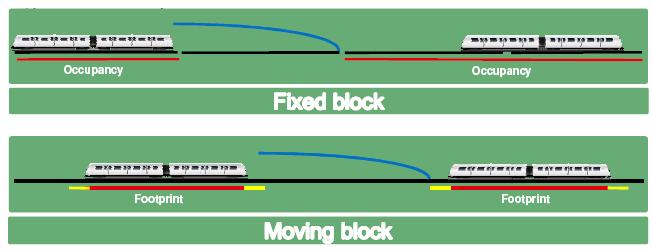 From the signalling system perspective, the first figure shows the total occupancy of the leading train by including the whole blocks which the train is located on. This is due to the fact that it is impossible for the system to know exactly where the train actually is within these blocks. Therefore, the fixed block system only allows the following train to move up to the last unoccupied block's border.
In a moving block system as shown in the second figure, the train position and its
From the signalling system perspective, the first figure shows the total occupancy of the leading train by including the whole blocks which the train is located on. This is due to the fact that it is impossible for the system to know exactly where the train actually is within these blocks. Therefore, the fixed block system only allows the following train to move up to the last unoccupied block's border.
In a moving block system as shown in the second figure, the train position and its
IEC, 2006. Accessed February 2014 In fact, CBTC is not a synonym for " Automatic train operation, driverless" or "automated trains" although it is considered as a basic enabler technology for this purpose. The grades of automation available range from a manual protected operation, GoA 1 (usually applied as a fallback operation mode) to the fully automated operation, GoA 4 (Unattended Train Operation, UTO). Intermediate operation modes comprise semi-automated GoA 2 (Semi-automated Operation Mode, STO) or driverless GoA 3 (Driverless Train Operation, DTO).Semi-automatic, driverless, and unattended operation of train
IRSE-ITC, 2010. Accessed through www.irse-itc.net in June 2011 The latter operates without a driver in the cabin, but requires an attendant to face degraded modes of operation as well as guide the passengers in the case of emergencies. The higher the GoA, the higher the safety, functionality and performance levels must be.
Bombardier Transportation Rail Control Solutions, 2010. Accessed June 2011 Of course, in the case of upgrading existing lines the design, installation, test and commissioning stages are much more critical. This is mainly due to the challenge of deploying the overlying system without disrupting the
in International Railway Journal, Keith Barrow, 2010. Accessed through goliath.ecnext.com in June 2011
Comunidad de Madrid, www.madrig.org, 2010. Accessed June 2011 Finally, it is important to mention that the CBTC systems have proven to be more energy efficient than traditional manually driven systems. The use of new functionalities, such as automatic driving strategies or a better adaptation of the transport offer to the actual demand, allows significant energy savings reducing the power consumption.
Global Transport Forum. Accessed December 2011 In principle, CBTC systems may be designed with centralized supervision systems in order to improve maintainability and reduce installation costs. If so, there is an increased risk of a single point of failure that could disrupt service over an entire system or line. Fixed block systems usually work with distributed logic that are normally more resistant to such outages. Therefore, a careful analysis of the benefits and risks of a given CBTC architecture (centralized vs. distributed) must be done during system design. When CBTC is applied to systems that previously ran under complete human control with operators working on sight it may actually result in a reduction in capacity (albeit with an increase in safety). This is because CBTC operates with less positional certainty than human sight and also with greater margin of error, margins for error as worst-case train parameters are applied for the design (e.g. guaranteed emergency brake rate vs. nominal brake rate). For instance, CBTC introduction in Philly's Center City trolley tunnel resulted initially in a marked increase in travel time and corresponding decrease in capacity when compared with the unprotected manual driving. This was the offset to finally eradicate vehicle collisions which on-sight driving cannot avoid and showcases the usual conflicts between operation and safety.
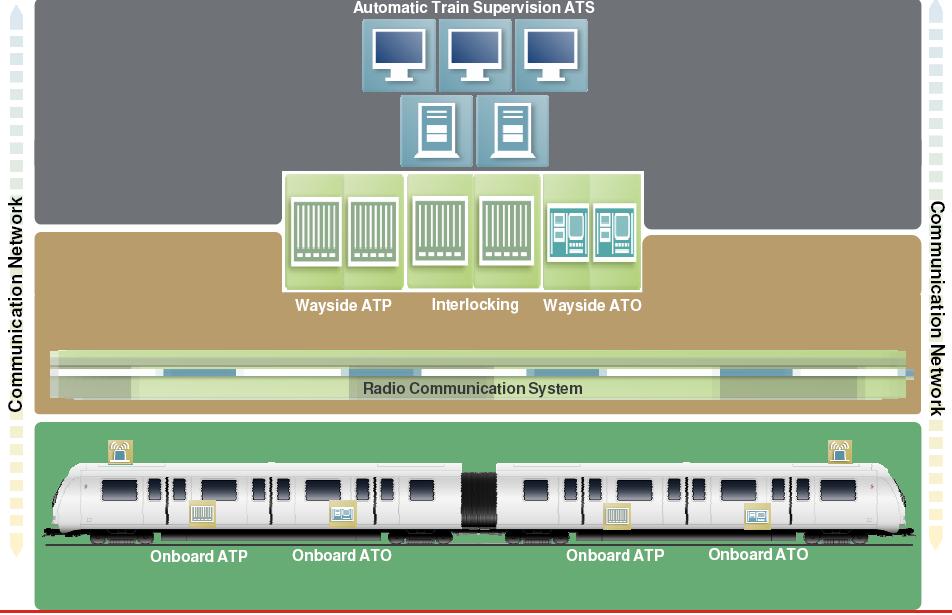 The typical architecture of a modern CBTC system comprises the following main subsystems:
# Wayside equipment, which includes the
The typical architecture of a modern CBTC system comprises the following main subsystems:
# Wayside equipment, which includes the
Press release, Bombardier Transportation Media Center, 2011. Accessed June 2011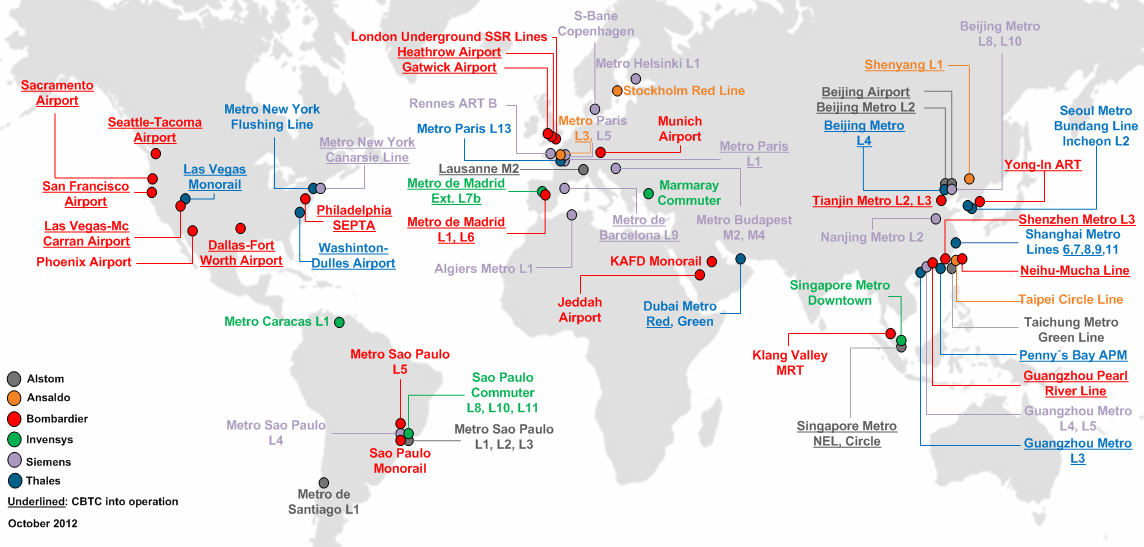
Despite the difficulty, the table below tries to summarize and reference the main radio-based CBTC systems deployed around the world as well as those ongoing projects being developed. Besides, the table distinguishes between the implementations performed over existing and operative systems ( Brownfield (software development), brownfield) and those undertaken on completely new lines (
Argenia Railway Technologies SafeNet CBTC
Thales SelTrac(R) CBTC
{{Railwaysignalling Train protection systems Telematics Railway signalling block systems
railway signaling
Railway signalling (), also called railroad signaling (), is a system used to control the movement of railway traffic. Trains move on fixed rails, making them uniquely susceptible to collision. This susceptibility is exacerbated by the enorm ...
system that uses telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that ...
between the train
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often ...
and track equipment for traffic management and infrastructure control. CBTC allows a train's position to be known more accurately than with traditional signaling systems. This makes railway traffic management safer and more efficient. Metros (and other railway systems) are able to reduce headways while maintaining or even improving safety.
A CBTC system is a "continuous, automatic train control system utilizing high-resolution train location determination, independent from track circuits; continuous, high-capacity, bidirectional train-to-wayside data communications; and trainborne and wayside processors
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, a ...
capable of implementing automatic train protection
Automatic train protection (ATP) is a type of train protection system which continually checks that the speed of a train is compatible with the permitted speed allowed by signalling, including automatic stop at certain signal aspects. If it i ...
(ATP) functions, as well as optional automatic train operation (ATO) and automatic train supervision (ATS) functions," as defined in the IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operati ...
1474 standard.1474.1–1999 – IEEE Standard for Communications-Based Train Control (CBTC) Performance and Functional Requirement(Accessed at January 14, 2019).
Background and origin
The main objective of CBTC is to increase track Headway#Capacity, capacity by reducing the time interval (headway
Headway is the distance or duration between vehicles in a transit system measured in space or time. The ''minimum headway'' is the shortest such distance or time achievable by a system without a reduction in the speed of vehicles. The precise defi ...
) between trains.
Traditional signalling systems detect trains in discrete sections of the track called ' blocks', each protected by signals that prevent a train entering an occupied block. Since every block is a fixed section of track, these systems are referred to as fixed block systems.
In a moving block CBTC system the protected section for each train is a "block" that moves with and trails behind it, and provides continuous communication of the train's exact position via radio, inductive loop, etc.Digital radio shows great potential for RaiBruno Gillaumin, International Railway Journal, May 2001. Retrieved by findarticles.com in June 2011.
 As a result, Bombardier Transportation, Bombardier opened the world's first radio-based CBTC system at
As a result, Bombardier Transportation, Bombardier opened the world's first radio-based CBTC system at San Francisco airport
San Francisco International Airport is an international airport in an unincorporated area of San Mateo County, south of Downtown San Francisco. It has flights to points throughout North America and is a major gateway to Europe, the Middle E ...
's automated people mover (APM) in February 2003. A few months later, in June 2003, Alstom
Alstom SA is a French multinational corporation, multinational rolling stock manufacturer operating worldwide in rail transport markets, active in the fields of passenger transportation, signalling, and locomotives, with products including the A ...
introduced the railway application of its radio technology on the Singapore North East line. Previously, CBTC has its former origins in the loop based systems developed by Alcatel SEL (now Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regarded ...
) for the Bombardier Automated Rapid Transit (ART) systems in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
during the mid-1980s.
These systems, which were also referred to as transmission-based train control (TBTC), made use of inductive loop
An induction or inductive loop is an electromagnetic communication or detection system which uses a moving magnet or an alternating current to induce an electric current in a nearby wire. Induction loops are used for transmission and reception ...
transmission techniques for track to train communication, introducing an alternative to track circuit
A track circuit is an electrical device used to prove the absence of a train on rail tracks to signallers and control relevant signals. An alternative to track circuits are axle counters.
Principles and operation
The basic principle behind ...
based communication. This technology, operating in the 30–60 kHz frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
range to communicate trains and wayside equipment, was widely adopted by the metro operators in spite of some electromagnetic compatibility
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy whic ...
(EMC) issues, as well as other installation and maintenance concerns (see SelTrac
SelTrac is a digital railway signalling technology used to automatically control the movements of rail vehicles. It was the first fully automatic moving-block signalling system to be commercially implemented.
What is now branded as SelTrac was ...
for further information regarding Transmission-Based-Train-Control).
As with new application of any technology, some problems arose at the beginning mainly due to compatibility and interoperability aspects.CBTC Projectswww.tsd.org/cbtc/projects, 2005. Accessed June 2011.CBTC radios: What to do? Which way to go
Tom Sullivan, 2005. www.tsd.org. Accessed May 2011. However, there have been relevant improvements since then, and currently the reliability of the radio-based communication systems has grown significantly. Moreover, it is important to highlight that not all the systems using
radio communication
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a trans ...
technology are considered to be CBTC systems. So, for clarity and to keep in line with the state-of-the-art
The state of the art (sometimes cutting edge or leading edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contexts it can also refer to a level ...
solutions for operator's requirements, this article only covers the latest moving block principle based (either true moving block or virtual block, so not dependent on track-based detection of the trains) CBTC solutions that make use of the radio communications
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
.
Main features
CBTC and moving block
CBTC systems are modern railway signaling systems that can mainly be used in urban railway lines (eitherlight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
or heavy
Heavy may refer to:
Measures
* Heavy (aeronautics), a term used by pilots and air traffic controllers to refer to aircraft capable of 300,000 lbs or more takeoff weight
* Heavy, a characterization of objects with substantial weight
* Heavy, ...
) and APMs, although it could also be deployed on commuter lines. For main lines, a similar system might be the European Railway Traffic Management System ERTMS Level 3 (not yet fully defined ).
In the modern CBTC systems the trains continuously calculate and communicate their status via radio to the wayside equipment distributed along the line. This status includes, among other parameters, the exact position, speed, travel direction and braking distance.
This information allows calculation of the area potentially occupied by the train on the track. It also enables the wayside equipment to define the points on the line that must never be passed by the other trains on the same track. These points are communicated to make the trains automatically and continuously adjust their speed while maintaining the safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly di ...
and comfort ( jerk) requirements. So, the trains continuously receive information regarding the distance to the preceding train and are then able to adjust their safety distance accordingly.
 From the signalling system perspective, the first figure shows the total occupancy of the leading train by including the whole blocks which the train is located on. This is due to the fact that it is impossible for the system to know exactly where the train actually is within these blocks. Therefore, the fixed block system only allows the following train to move up to the last unoccupied block's border.
In a moving block system as shown in the second figure, the train position and its
From the signalling system perspective, the first figure shows the total occupancy of the leading train by including the whole blocks which the train is located on. This is due to the fact that it is impossible for the system to know exactly where the train actually is within these blocks. Therefore, the fixed block system only allows the following train to move up to the last unoccupied block's border.
In a moving block system as shown in the second figure, the train position and its braking curve
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
Backgroun ...
is continuously calculated by the trains, and then communicated via radio to the wayside equipment. Thus, the wayside equipment is able to establish protected areas, each one called Limit of Movement Authority (LMA), up to the nearest obstacle (in the figure the tail of the train in front). Movement Authority (MA) is the permission for a train to move to a specific location within the constraints of the infrastructure and with supervision of speed.
End of Authority is the location to which the train is permitted to proceed and where target speed is equal to zero. End of Movement is the location to which the train is permitted to proceed according to an MA. When transmitting a MA, it is the end of the last section given in the MA.
It is important to mention that the occupancy calculated in these systems must include a safety margin for location uncertainty (in yellow in the figure) added to the length of the train. Both of them form what is usually called 'Footprint'. This safety margin depends on the accuracy of the odometry system in the train.
CBTC systems based on moving block allows the reduction of the safety distance between two consecutive trains. This distance is varying according to the continuous updates of the train location and speed, maintaining the safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly di ...
requirements. This results in a reduced headway
Headway is the distance or duration between vehicles in a transit system measured in space or time. The ''minimum headway'' is the shortest such distance or time achievable by a system without a reduction in the speed of vehicles. The precise defi ...
between consecutive trains and an increased transport capacity.
Grades of automation
Modern CBTC systems allow different levels of automation or Grades of Automation (GoA), as defined and classified in theIEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
62290-1.IEC 62290-1, Railway applications – Urban guided transport management and command/control systems – Part 1: System principles and fundamental conceptIEC, 2006. Accessed February 2014 In fact, CBTC is not a synonym for " Automatic train operation, driverless" or "automated trains" although it is considered as a basic enabler technology for this purpose. The grades of automation available range from a manual protected operation, GoA 1 (usually applied as a fallback operation mode) to the fully automated operation, GoA 4 (Unattended Train Operation, UTO). Intermediate operation modes comprise semi-automated GoA 2 (Semi-automated Operation Mode, STO) or driverless GoA 3 (Driverless Train Operation, DTO).Semi-automatic, driverless, and unattended operation of train
IRSE-ITC, 2010. Accessed through www.irse-itc.net in June 2011 The latter operates without a driver in the cabin, but requires an attendant to face degraded modes of operation as well as guide the passengers in the case of emergencies. The higher the GoA, the higher the safety, functionality and performance levels must be.
Main applications
CBTC systems allow optimal use of the railway infrastructure as well as achieving maximum capacity and minimumheadway
Headway is the distance or duration between vehicles in a transit system measured in space or time. The ''minimum headway'' is the shortest such distance or time achievable by a system without a reduction in the speed of vehicles. The precise defi ...
between operating trains, while maintaining the safety
Safety is the state of being "safe", the condition of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
There are two slightly di ...
requirements. These systems are suitable for the new highly demanding urban lines, but also to be overlaid on existing lines in order to improve their performance.''CITYFLO'' 650 Metro de Madrid, Solving the capacity challengBombardier Transportation Rail Control Solutions, 2010. Accessed June 2011 Of course, in the case of upgrading existing lines the design, installation, test and commissioning stages are much more critical. This is mainly due to the challenge of deploying the overlying system without disrupting the
revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive rev ...
service.Madrid's silent revolutioin International Railway Journal, Keith Barrow, 2010. Accessed through goliath.ecnext.com in June 2011
Main benefits
The evolution of the technology and the experience gained in operation over the last 30 years means that modern CBTC systems are more reliable and less prone to failure than older train control systems. CBTC systems normally have less wayside equipment and their diagnostic and monitoring tools have been improved, which makes them easier to implement and, more importantly, easier to maintain. CBTC technology is evolving, making use of the latest techniques and components to offer more compact systems and simpler architectures. For instance, with the advent of modern electronics it has been possible to build in redundancy so that single failures do not adversely impact operational availability. Moreover, these systems offer complete flexibility in terms of operational schedules or timetables, enabling urban rail operators to respond to the specific traffic demand more swiftly and efficiently and to solve traffic congestion problems. In fact, automatic operation systems have the potential to significantly reduce theheadway
Headway is the distance or duration between vehicles in a transit system measured in space or time. The ''minimum headway'' is the shortest such distance or time achievable by a system without a reduction in the speed of vehicles. The precise defi ...
and improve the headway#Capacity, traffic capacity compared to manual driving systems.CBTC: más trenes en hora puntComunidad de Madrid, www.madrig.org, 2010. Accessed June 2011 Finally, it is important to mention that the CBTC systems have proven to be more energy efficient than traditional manually driven systems. The use of new functionalities, such as automatic driving strategies or a better adaptation of the transport offer to the actual demand, allows significant energy savings reducing the power consumption.
Risks
The primary risk of an electronic train control system is that if the communications link between any of the trains is disrupted then all or part of the system might have to enter afailsafe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent saf ...
state until the problem is remedied. Depending on the severity of the communication loss, this state can range from vehicles temporarily reducing speed, coming to a halt or operating in a degraded mode until communications are re-established. If communication outage is permanent some sort of contingency operation must be implemented which may consist of manual operation using absolute block or, in the worst case, the substitution of an alternative form of transportation.
As a result, high availability of CBTC systems is crucial for proper operation, especially if such systems are used to increase transport capacity and reduce headway. System redundancy and recovery mechanisms must then be thoroughly checked to achieve a high robustness in operation.
With the increased availability of the CBTC system, there is also a need for extensive training and periodical refresh of system operators on the recovery procedures. In fact, one of the major system hazards in CBTC systems is the probability of human error and improper application of recovery procedures if the system becomes unavailable.
Communications failures can result from equipment malfunction, electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), also called radio-frequency interference (RFI) when in the radio frequency spectrum, is a disturbance generated by an external source that affects an electrical circuit by electromagnetic induction, electrost ...
, weak signal strength or saturation of the communications medium. In this case, an interruption can result in a service brake or emergency brake application as real time situational awareness is a critical safety requirement for CBTC and if these interruptions are frequent enough it could seriously impact service. This is the reason why, historically, CBTC systems first implemented radio communication systems in 2003, when the required technology was mature enough for critical applications.
In systems with poor line of sight or spectrum/bandwidth limitations a larger than anticipated number of transponders may be required to enhance the service. This is usually more of an issue with applying CBTC to existing transit systems in tunnels that were not designed from the outset to support it. An alternate method to improve system availability in tunnels is the use of leaky feeder cable that, while having higher initial costs (material + installation) achieves a more reliable radio link.
With the emerging services over open ISM radio bands (i.e. 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz) and the potential disruption over critical CBTC services, there is an increasing pressure in the international community (ref. report 676 of UITP organization, Reservation of a Frequency Spectrum for Critical Safety Applications dedicated to Urban Rail Systems) to reserve a frequency band specifically for radio-based urban rail systems. Such decision would help standardize CBTC systems across the market (a growing demand from most operators) and ensure availability for those critical systems.
As a CBTC system is required to have high availability
High availability (HA) is a characteristic of a system which aims to ensure an agreed level of operational performance, usually uptime, for a higher than normal period.
Modernization has resulted in an increased reliance on these systems. F ...
and particularly, allow for a graceful degradation, a secondary method of signaling might be provided to ensure some level of non-degraded service upon partial or complete CBTC unavailability. This is particularly relevant for brownfield implementations (lines with an already existing signalling system) where the infrastructure design cannot be controlled and coexistence with legacy systems is required, at least, temporarily.
For example, the New York City Canarsie Line
The BMT Canarsie Line (sometimes referred to as the 14th Street–Eastern Line) is a rapid transit line of the B Division of the New York City Subway system, named after its terminus in the Canarsie neighborhood of Brooklyn. It is served by the ...
was outfitted with a backup automatic block signaling system capable of supporting 12 trains per hour (tph), compared with the 26 tph of the CBTC system. Although this is a rather common architecture for resignalling projects, it can negate some of the cost savings of CBTC if applied to new lines. This is still a key point in the CBTC development (and is still being discussed), since some providers and operators argue that a fully redundant architecture of the CBTC system may however achieve high availability values by itself.CBTC World Congress Presentations, Stockholm, November 201Global Transport Forum. Accessed December 2011 In principle, CBTC systems may be designed with centralized supervision systems in order to improve maintainability and reduce installation costs. If so, there is an increased risk of a single point of failure that could disrupt service over an entire system or line. Fixed block systems usually work with distributed logic that are normally more resistant to such outages. Therefore, a careful analysis of the benefits and risks of a given CBTC architecture (centralized vs. distributed) must be done during system design. When CBTC is applied to systems that previously ran under complete human control with operators working on sight it may actually result in a reduction in capacity (albeit with an increase in safety). This is because CBTC operates with less positional certainty than human sight and also with greater margin of error, margins for error as worst-case train parameters are applied for the design (e.g. guaranteed emergency brake rate vs. nominal brake rate). For instance, CBTC introduction in Philly's Center City trolley tunnel resulted initially in a marked increase in travel time and corresponding decrease in capacity when compared with the unprotected manual driving. This was the offset to finally eradicate vehicle collisions which on-sight driving cannot avoid and showcases the usual conflicts between operation and safety.
Architecture
 The typical architecture of a modern CBTC system comprises the following main subsystems:
# Wayside equipment, which includes the
The typical architecture of a modern CBTC system comprises the following main subsystems:
# Wayside equipment, which includes the interlocking
In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. The signalling appliances and tracks are sometimes collectively re ...
and the subsystems controlling every zone in the line or network (typically containing the wayside ATP and ATO ATO may refer to:
Technology
*Abort to Orbit, an intact abort procedure for Space Shuttle launches
* Arsenic trioxide a potent chemotherapeutic agent for acute promyelocytic leukemia
* ATO fuse
* Automatic train operation
* Assisted take off
Mil ...
functionalities). Depending on the suppliers, the architectures may be centralized or distributed. The control of the system is performed from a central command ATS, though local control subsystems may be also included as a fallback.
# CBTC onboard equipment, including ATP and ATO ATO may refer to:
Technology
*Abort to Orbit, an intact abort procedure for Space Shuttle launches
* Arsenic trioxide a potent chemotherapeutic agent for acute promyelocytic leukemia
* ATO fuse
* Automatic train operation
* Assisted take off
Mil ...
subsystems in the vehicles.
# Train to wayside communication subsystem, currently based on radio links.
Thus, although a CBTC architecture is always depending on the supplier and its technical approach, the following logical components may be found generally in a typical CBTC architecture:
*Onboard ETCS system. This subsystem is in charge of the continuous control of the train speed according to the safety profile, and applying the brake if it is necessary. It is also in charge of the communication with the wayside ATP subsystem in order to exchange the information needed for a safe operation (sending speed and braking distance, and receiving the limit of movement authority for a safe operation).
*Onboard ATO system. It is responsible for the automatic control of the traction and braking effort in order to keep the train under the threshold established by the ATP subsystem. Its main task is either to facilitate the driver or attendant functions, or even to operate the train in a fully automatic mode while maintaining the traffic regulation targets and passenger comfort. It also allows the selection of different automatic driving strategies to adapt the runtime or even reduce the power consumption.
*Wayside ETCS system. This subsystem undertakes the management of all the communications with the trains in its area. Additionally, it calculates the limits of movement authority that every train must respect while operating in the mentioned area. This task is therefore critical for the operation safety.
*Wayside ATO system. It is in charge of controlling the destination and regulation targets of every train. The wayside ATO functionality provides all the trains in the system with their destination as well as with other data such as the dwell time in the stations. Additionally, it may also perform auxiliary and non-safety related tasks including for instance alarm/event communication and management, or handling skip/hold station commands.
*Communication system. The CBTC systems integrate a digital networked radio system by means of antennas or leaky feeder cable for the bi-directional communication between the track equipment and the trains. The 2,4 GHz band is commonly used in these systems (same as WiFi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio wa ...
), though other alternative frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is e ...
such as 900 MHz ( US), 5.8 GHz or other licensed bands may be used as well.
*ATS system. The ATS system is commonly integrated within most of the CBTC solutions. Its main task is to act as the interface between the operator and the system, managing the traffic according to the specific regulation criteria. Other tasks may include the event and alarm management as well as acting as the interface with external systems.
*Interlocking
In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. The signalling appliances and tracks are sometimes collectively re ...
system. When needed as an independent subsystem (for instance as a fallback system), it will be in charge of the vital control of the trackside objects such as switches or signals, as well as other related functionality. In the case of simpler networks or lines, the functionality of the interlocking may be integrated into the wayside ATP system.
Projects
CBTC technology has been (and is being) successfully implemented for a variety of applications as shown in the figure below (mid 2011). They range from some implementations with short track, limited numbers of vehicles and few operating modes (such as the airport APMs inSan Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
or Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
), to complex overlays on existing railway networks carrying more than a million passengers each day and with more than 100 trains (such as lines 1 and 6 in Madrid Metro
The Madrid Metro ( Spanish: ''Metro de Madrid'') is a rapid transit system serving the city of Madrid, capital of Spain. The system is the 14th longest rapid transit system in the world, with a total length of 293 km (182 mi). Its gr ...
, line 3 in Shenzhen Metro, some lines in Paris Metro, New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October ...
and Beijing Subway
The Beijing Subway is the rapid transit system of Beijing Municipality that consists of 25 lines including 20 rapid transit lines, two airport rail links, one maglev line and 2 light rail lines, and 463 stations. The rail network extends ...
, or the Sub-Surface network in London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The ...
).Bombardier to Deliver Major London Underground SignallinPress release, Bombardier Transportation Media Center, 2011. Accessed June 2011
Despite the difficulty, the table below tries to summarize and reference the main radio-based CBTC systems deployed around the world as well as those ongoing projects being developed. Besides, the table distinguishes between the implementations performed over existing and operative systems ( Brownfield (software development), brownfield) and those undertaken on completely new lines (
Greenfield
Greenfield or Greenfields may refer to:
Engineering and Business
* Greenfield agreement, an employment agreement for a new organisation
* Greenfield investment, the investment in a structure in an area where no previous facilities exist
* Greenf ...
).
List
Notes and references
Notes
References
Further reading
Argenia Railway Technologies SafeNet CBTC
Thales SelTrac(R) CBTC
{{Railwaysignalling Train protection systems Telematics Railway signalling block systems