Common Eldarin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in ''
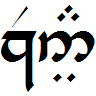 Tolkien imagined many writing systems for his Elves. The best-known is the "Tengwar of
Tolkien imagined many writing systems for his Elves. The best-known is the "Tengwar of
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship
Parma Eldalamberon
Vinyar Tengwar
Ardalambion
– Helge Fauskanger's site on Tolkien languages, with Quenya course and materials
*
Thorsten Renk's Quetin i lambë eldaiva - a Quenya Course (gz archive)
– Ales Bican examines the evidence for the shortened form of the locative (-s).
Quenya–English dictionary
{{Good article Agglutinative languages Middle-earth languages Subject–verb–object languages Middle-earth Elves Constructed languages introduced in the 1910s 1910 introductions Constructed languages
Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language
A constructed language (sometimes called a conlang) is a language whose phonology, grammar, and vocabulary, instead of having developed naturally, are consciously devised for some purpose, which may include being devised for a work of fiction. ...
, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves
An elf () is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic mythology and folklore. Elves appear especially in North Germanic mythology. They are subsequently mentioned in Snorri Sturluson's Icelandic Prose Edda. He distinguishes ...
in his Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the '' Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is ...
fiction.
Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes doma ...
several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
, and was familiar with Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
(the latter being the primary inspiration for Sindarin
Sindarin is one of the fictional languages devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for use in his fantasy stories set in Arda, primarily in Middle-earth. Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the Elves. The word is a Quenya word.
Called in E ...
, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
, particularly Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, during his development of Quenya.
A notable feature of Tolkien's Elvish languages was his development of a complex internal history of characters to speak those tongues in their own fictional universe. He felt that his languages changed and developed over time, as with the historical languages which he studied professionally—not in a vacuum, but as a result of the migrations and interactions of the peoples who spoke them.
Within Tolkien's legendarium, Quenya is one of the many Elvish languages
Elvish languages are constructed languages used by Elves in a fantasy setting. The philologist and fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien created the first of these languages, including Quenya and Sindarin.
Tolkien's Elvish languages
The philologist ...
spoken by the immortal Elves, called '' Quendi'' ('speakers') in Quenya. Quenya translates as simply "language" or, in contrast to other tongues that the Elves met later in their long history, "elf-language". After the Elves divided, Quenya originated as the speech of two clans of "High Elves" or Eldar, the Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor (also spelled Ñoldor, meaning ''those with knowledge'' in his constructed language Quenya) were a kindred of Elves who migrated west to the blessed realm of Valinor from the continent of Middle-ea ...
and the Vanyar, who left Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the '' Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is ...
to live in Eldamar
Valinor (Quenya'': Land of the Valar'') or the Blessed Realms is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to me ...
("Elvenhome"), in Valinor
Valinor (Quenya'': Land of the Valar'') or the Blessed Realms is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to ...
, the land of the immortal and God-like Valar. Of these two groups of Elves, most of the Noldor returned to Middle-earth where they met the Sindarin-speaking Grey-elves. The Noldor eventually adopted Sindarin and used Quenya primarily as a ritual or poetic language, whereas the Vanyar who stayed behind in Eldamar retained the use of Quenya.
In this way, the Quenya language was symbolic of the high status of the Elves, the firstborn of the races of Middle-earth, because of their close connection to Valinor, and its decreasing use also became symbolic of the slowly declining Elven culture in Middle-earth. In the Second Age
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the history of Arda, also called the history of Middle-earth, began when the Ainur entered Arda, following the creation events in the Ainulindalë and long ages of labour throughout Eä, the fictional uni ...
of Middle-earth's chronology the Men
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chro ...
of Númenor
Númenor, also called Elenna-nórë or Westernesse, is a fictional place in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings. It was the kingdom occupying a large island to the west of Middle-earth, the main setting of Tolkien's writings, and was the greatest civil ...
learnt the Quenya tongue. In the Third Age
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the history of Arda, also called the history of Middle-earth, began when the Ainur entered Arda, following the creation events in the Ainulindalë and long ages of labour throughout Eä, the fictional un ...
, the time of the setting of ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'', Quenya was learnt as a second language
A person's second language, or L2, is a language that is not the native language ( first language or L1) of the speaker, but is learned later. A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a ...
by all Elves of Noldorin origin, and it continued to be used in spoken and written form, but their mother-tongue
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
was the Sindarin of the Grey-elves. As the Noldor remained in Middle-earth, their Noldorin dialect of Quenya also gradually diverged from the Vanyarin dialect spoken in Valinor, undergoing both sound changes and grammatical changes.
The Quenya language featured prominently in Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings'', as well as in his posthumously published history of Middle-earth ''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
''. The longest text in Quenya published by Tolkien during his lifetime is the poem "Namárië
"Namárië" () is a poem by J. R. R. Tolkien written in Quenya, a constructed language, and published in ''The Lord of the Rings''. It is subtitled "Galadriel's Lament in Lórien", which in Quenya is ''Altariello nainië Lóriendessë''. The ...
"; other published texts are no longer than a few sentences. At his death, Tolkien left behind a number of unpublished writings on Quenya, and later Tolkien scholars have prepared his notes and unpublished manuscripts for publication in the journals ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' and ''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'', also publishing scholarly and linguistic analyses of the language. Tolkien never created enough vocabulary to make it possible to converse in Quenya, although fans have been writing poetry and prose in Quenya since the 1970s. This has required conjecture and the need to devise new words, in effect developing a kind of neo-Quenya language.
External history
J. R. R. Tolkien began to construct his first Elven tongue c. 1910–1911 while he was at theKing Edward's School, Birmingham
King Edward's School (KES) is an independent day school for boys in the British public school tradition, located in Edgbaston, Birmingham. Founded by King Edward VI in 1552, it is part of the Foundation of the Schools of King Edward VI in Bir ...
. He later called it ''Qenya'' (c. 1915), and later changed the spelling to ''Quenya''. He was then already familiar with Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, and several ancient Germanic languages, such as Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
, and Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
.Letter #163, ''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien
''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien'' is a selection of J. R. R. Tolkien's letters published in 1981, edited by Tolkien's biographer Humphrey Carpenter assisted by Christopher Tolkien. The selection from a large mass of materials contains 354 lett ...
''. He had invented several cryptographic codes, and two or three constructed languages. Tolkien took an interest in the Finnish mythology of the Kalevala
The ''Kalevala'' ( fi, Kalevala, ) is a 19th-century work of epic poetry compiled by Elias Lönnrot from Karelian and Finnish oral folklore and mythology, telling an epic story about the Creation of the Earth, describing the controversies and ...
, then became acquainted with Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
, which he found to provide an aesthetically pleasing inspiration for his High-elven language. Many years later, he wrote: "It was like discovering a complete wine-cellar filled with bottles of an amazing wine of a kind and flavour never tasted before. It quite intoxicated me." Regarding the inspiration for Quenya, Tolkien wrote that:
Tolkien never intended Quenya or any of his constructed languages to be used in everyday life as an international auxiliary language
An international auxiliary language (sometimes acronymized as IAL or contracted as auxlang) is a language meant for communication between people from all different nations, who do not share a common first language. An auxiliary language is primaril ...
, although he was in favour of the idea of Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communic ...
as an auxiliary language within Europe. With his Quenya, Tolkien pursued a double aesthetic goal: "classical and inflected". This urge, in fact, was the motivation for his creation of a 'mythology'. While the language developed, Tolkien felt that it needed speakers, including their own history and mythology, which he thought would give a language its 'individual flavour'. Tolkien, J. R. R. ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'' "Foreword to the Second Edition". ''The Lord of the Rings'', according to Tolkien, "was primarily linguistic in inspiration and was begun in order to provide the necessary background of 'history' for Elvish tongues". This process of first inventing a language and then creating a background setting for its fictional speakers has been described as unique. Dimitra Fimi
Dimitra Fimi (born 2 June 1978) is a Scottish academic and writer and since 2020 the Senior Lecturer in Fantasy and Children's Literature at the University of Glasgow. Her research includes that of the writings of J. R. R. Tolkien and children's ...
, a Tolkien scholar, argues that Tolkien's invention of Qenya started as a quest for the ideal language, to match the moral and aesthetic objectives that were part of his project of creating "a mythology for England". Fimi argues that Tolkien deliberately used sound symbolism
In linguistics, sound symbolism is the resemblance between sound and meaning. It is a form of linguistic iconicity. For example, the English word ''ding'' may sound similar to the actual sound of a bell. Linguistic sound may be perceived as simi ...
to unify sound and meaning and make the language appear as an ideal language, fit to be spoken in the utopian
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imaginary community or society that possesses highly desirable or nearly perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia'', describing a fictional island socie ...
realm of the Elves and fairies of Valinor. Tolkien considered Quenya to be "the one language which has been designed to give play to my own most normal phonetic taste". Tolkien, J. R. R. 1997. ''The Monsters and the Critics, and Other Essays
''The Monsters and the Critics, and Other Essays'' is a collection of J. R. R. Tolkien's scholarly linguistic essays edited by his son Christopher and published posthumously in 1983.
All of them were initially delivered as lectures to academics ...
''. p. 212
From the onset, Tolkien used comparative philology
Comparative linguistics, or comparative-historical linguistics (formerly comparative philology) is a branch of historical linguistics that is concerned with comparing languages to establish their historical relatedness.
Genetic relatedness ...
and the tree model
In historical linguistics, the tree model (also Stammbaum, genetic, or cladistic model) is a model of the evolution of languages analogous to the concept of a family tree, particularly a phylogenetic tree in the biological evolution of species. ...
as his major tools in his constructed languages. He usually started with the phonological system of the proto-language
In the tree model of historical linguistics, a proto-language is a postulated ancestral language from which a number of attested languages are believed to have descended by evolution, forming a language family. Proto-languages are usually unattes ...
and then proceeded by inventing for each daughter language
In historical linguistics, a daughter language, also known as descendant language, is a language descended from another language, its mother language, through a process of genetic descent. If more than one language has developed from the same pr ...
the necessary sequence of sound change
A sound change, in historical linguistics, is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic chan ...
s. "I find the construction and the interrelation of the languages an aesthetic pleasure in itself, quite apart from ''The Lord of the Rings'', of which it was/is in fact independent." J. R. R. Tolkien, letter to a reader, ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 61.
Development
In his lifetime, Tolkien experimented ceaselessly with his constructed languages, and they were subjected to many revisions. Quenya had many grammars with substantial differences between the different stages of its development. During the first conceptual stage of ''early Quenya'' c. 1910 to c. 1920, the language was called ''Elfin'' in English and ''Eldarissa'' in Qenya proper. While its development was a continuous process, Quenya underwent a number of major revisions in its grammar, mostly inconjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
* Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change ...
and the pronominal system. The vocabulary, however, was not subject to sudden or extreme change. Tolkien sometimes changed the meaning of a word, but he almost never discarded it once invented, and he kept on refining its meaning, and countlessly forged new synonyms. Moreover, Elvish etymology was in constant flux. Tolkien delighted in inventing new etymons for his Quenya vocabulary. But after the publication of ''The Lord of the Rings'' (finished c. 1949–1950, published in 1954–1955), the grammar rules of Quenya went through very few changes and this version was then defined as ''late Quenya'' (c. 1950–1973).
The spelling ''Qenya'' is sometimes used to distinguish ''early Quenya'' from later versions. Qenya differs from late Quenya by having different internal history, vocabulary, and grammar rules as described in the "Qenyaqetsa". Examples include a different accusative or the abolition of final consonant clusters in later Quenya. Fimi suggests that Qenya as it appears in the "Qenyaqetsa" was supposed to be a mystic language, as the Lexicon contains a number of words with clear Christian religious connotations, such as ''anatarwesta'' "crucifixion" and ''evandilyon'' "gospel" – these words were not part of late Quenya.
In the early 1930s, Tolkien decided that the proto-language of the Elves was Valarin
The Valar (; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are "angelic powers" or "gods", #154 to Naomi Mitchison, September 1954 subordinate to the one God (Eru Ilúvatar). The Ainulindalë describes how those of the ...
, the tongue of the gods or Valar as he called them: "The language of the Elves derived in the beginning from the Valar, but they changed it even in the learning, and moreover modified and enriched it constantly at all times by their own invention." In the ''Comparative Tables'', ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, pp. 18–28 the mechanisms of sound change were described by Tolkien for the following daughter languages: ''Qenya, Lindarin'' (a dialect of Qenya), ''Telerin, Old Noldorin'' (or ''Fëanorian''), ''Noldorin'' (or ''Gondolinian''), ''Ilkorin'' (especially of Doriath), ''Danian of Ossiriand, East Danian, Taliska
Gothic is an extinct East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the '' Codex Argenteus'', a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text ...
, West Lemberin, North Lemberin, and East Lemberin''. For this proto-language of the Elves, Tolkien appears to have borrowed the five-part plosive
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or simply a stop, is a pulmonic consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases.
The occlusion may be made with the tongue tip or blade (, ), tongue body (, ), lip ...
system of Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
, the ancestor of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
, Greek, Latin, and others; namely, one labial, one coronal, and three velar plosives (palatal, plain, and labial). The first table below provides some of the "Primary Initial Combinations" from the ''Comparative Tables''.
Another characteristic of Quenya reminiscent of ancient natural languages like Old Greek, Old English or Sanskrit is the dual grammatical number which is used in addition to singular and plural. It has been suggested that Tolkien used the dual to give Quenya an "archaic feel" in its role as an ancient language of the Elves.
About ten years later, Tolkien changed his mind about the origin of the Elvish proto-language. Instead of learning from the Valar, the Elves had created an original language Quenderin which had become the proto-language of the Elven language family.J. R. R. Tolkien, "Lambion Ontale: Descent of Tongues", Tengwesta Qenderinwa 2, ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (18), p. 71: "The Elves began to make in the beginning of their being languageand it is one with their being, since it was of their nature and the first of all their gift to devise names and words." For this new language, Tolkien kept the many roots he had invented for Valarin in the 1930s, which then became "Quenderin roots". The Eldarin family of languages comprises Quenya, Telerin, Sindarin and Nandorin. The evolution in Quenya and Telerin of the nasalised initial groups of Quenderin is described thus in Tolkien's ''Outline of Phonology'':
In contrast to early Qenya, the grammar of Quenya was influenced by Finnish, an agglutinative language
An agglutinative language is a type of synthetic language with morphology that primarily uses agglutination. Words may contain different morphemes to determine their meanings, but all of these morphemes (including stems and affixes) tend to rem ...
, but much more by Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, a synthetic Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Science
* Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis
* Synthetic ...
and fusional language
Fusional languages or inflected languages are a type of synthetic language, distinguished from agglutinative languages by their tendency to use a single inflectional morpheme to denote multiple grammatical, syntactic, or semantic features.
...
, and also Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
,Tolkien wrote about Quenya: "It might be said to be composed on a Latin basis with two other (main) ingredients that happen to give me 'phonaesthetic' pleasure: Finnish, and Greek". Letter No. 144. ''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien''. from which he probably took the idea of the diglossia
In linguistics, diglossia () is a situation in which two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled ...
of Quenya with its highly codified variety: the Parmaquesta, used only in certain situations such as literature. The phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
of Quenya was also inspired by certain aspects of Finnish, but this is not easily recognised.
Tolkien almost never borrowed words directly from real languages into Quenya. The major exception is the name Earendel/Eärendil, which he found in an Old English poem by Cynewulf
Cynewulf (, ; also spelled Cynwulf or Kynewulf) is one of twelve Old English poets known by name, and one of four whose work is known to survive today. He presumably flourished in the 9th century, with possible dates extending into the late 8th ...
. Yet the Finnish influence extended sometimes also to the vocabulary. A few Quenya words, such as ''tul-'' "come" and ''anta-'' "give", clearly have a Finnish origin. Other forms that appear to have been borrowed are actually coincidental, such as Finnish ''kirja'' "book", and Quenya ''cirya'' "ship". Tolkien invented the Valarin/Quenderin root ''kir-'' from which sprang his Quenya word ''cirya''. The Latin ''aure'' "dawn", and Quenya ''aure'' "moment of special meaning, special day, festival day" are unrelated. Instead, Quenya ''aurë'' comes from the Valarin/Quenderin root ur-. Germanic influence can more be seen in grammar (the -r nominative plural ending is reminiscent of the Scandinavian languages
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages—a sub-family of the Indo-European languages—along with the West Germanic languages and the extinct East Germanic languages. The language group is als ...
) or phonology, than in words: ''Arda
Arda or ARDA may refer to:
Places
*Arda (Maritsa), a river in Bulgaria and Greece
* Arda (Italy), a river in Italy
* Arda (Douro), a river in Portugal
*Arda, Bulgaria, a village in southern Bulgaria
* Arda, County Fermanagh, a townland in County ...
'', the Quenya name for "region", just happened to resemble Germanic ''Erde'' "earth", while it actually comes from the Valarin/Quenderin root ''gar-''. According to Tom DuBois and Scott Mellor, the name of Quenya itself may have been influenced by the name Kven
KVEN (1520 AM, "La Voz 1520 AM & 96.3 FM") is a commercial radio station that is licensed to Port Hueneme, California and serves the Ventura County area. The station is owned by Gold Coast Broadcasting and broadcasts a Spanish-language news/ta ...
, a language closely related to Finnish, but Tolkien never mentioned this.
Some linguists have argued that Quenya can be understood as an example of a particular kind of artificial language that helps to create a fictional world. Other such languages would include Robert Jordan
James Oliver Rigney Jr. (October 17, 1948 – September 16, 2007), better known by his pen name Robert Jordan," Robert Jordan" was the name of the protagonist in the 1940 Hemingway novel ''For Whom the Bell Tolls'', though this is not how the n ...
's Old Tongue and the Klingon language
The Klingon language ( tlh, tlhIngan Hol, links=no, '' '': , ) is the constructed language spoken by a fictional alien race called the Klingons, in the ''Star Trek'' universe.
Described in the 1985 book '' The Klingon Dictionary'' by Marc Ok ...
of the ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the eponymous 1960s television series and quickly became a worldwide pop-culture phenomenon. The franchise has expanded into vari ...
'' series invented by Marc Okrand. It was observed that they form "a sociolinguistic context within which group and individual identities can be created."
Publication of linguistic papers
Two journals, ''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' from issue No. 39 (July 1998), and ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' from issue No. 11 (1995), are today exclusively devoted to the editing and publishing of Tolkien's mass of unpublished linguistic papers. Important grammatical texts, alluded to in the ''History of Middle-earth
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the history of Arda, also called the history of Middle-earth, began when the Ainur entered Arda, following the creation events in the Ainulindalë and long ages of labour throughout Eä, the fictional uni ...
'' series and described as almost unreadable or quite incomprehensible, have been published in these two journals. The "Early Qenya Grammar", written by Tolkien c. 1925, was edited and published in ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 14.''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 14.
An analysis of Quenya's prosodic structure was published by Alexander Stainton in 2022.
Use of Quenya
Attempts by fans to write in Quenya began in the 1970s, when the total corpus of published Elvish comprised only a few hundred words. Since then, the use of Elvish has flourished in poems and texts, phrases and names, and even tattoos. But Tolkien himself never made his languages complete enough for conversation. As a result, newly invented Elvish texts require conjecture and sometimes the coinage of new words. The use of Quenya has expanded over the years as new words have been created, forming a Neo-Quenya language that is based on Tolkien's original Quenya but incorporates many new elements.Internal history
The Elvish languages are afamily
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
of several related languages and dialects. The following is a brief overview of the fictional internal history of late Quenya as conceived by Tolkien. Tolkien imagined an Elven society with a vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
language for every-day use, ''Tarquesta'', and a more educated language for use in ceremonies and lore, ''Parmaquesta''.
The Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger Verlyn Flieger (born 1933) is an author, editor, and Professor Emerita in the Department of English at the University of Maryland at College Park, where she taught courses in comparative mythology, medieval literature, and the works of J. R. R. Tol ...
observed that the "degree of proximity" to the light of the Valar affected the development of both languages in terms of phonology, morphology and semantics. The division between Light Elves and Dark Elves that took place during the Sundering of the Elves
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Seconds) and Nelyar ...
is reflected in their respective languages.
Primitive Quendian
The Elves at first shared a common language, Primitive Quendian, called ''Quenderin'' in Quenya. Among the Eldar, i.e. those Elves who undertook the Great March toValinor
Valinor (Quenya'': Land of the Valar'') or the Blessed Realms is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to ...
and Eldamar
Valinor (Quenya'': Land of the Valar'') or the Blessed Realms is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to me ...
, Primitive Quendian developed into Common Eldarin. Some of the Eldar remained in Beleriand
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional legendarium, Beleriand was a region in northwestern Middle-earth during the First Age. Events in Beleriand are described chiefly in his work ''The Silmarillion'', which tells the story of the early ages of Middle ...
and became the Grey Elves
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Seconds) and Nelyar ...
; their language developed into Sindarin
Sindarin is one of the fictional languages devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for use in his fantasy stories set in Arda, primarily in Middle-earth. Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the Elves. The word is a Quenya word.
Called in E ...
. Most of the other Eldar continued to Eldamar ('Elvenhome') in Aman and founded the great city of Tirion, where they developed Quenya. J. R. R. Tolkien, ''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
'', ch. 6 "Of Feanor and the Unchaining of Melkor", see also "Quenya" in the annotated Index p. 346 J. R. R. Tolkien, "Tengwesta Qenderinwa", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' 18, p. 72. "The most ancient structure of the tongue common to all the ''Qendelie'' lvish raceis ... not known to the Elves, through some things may be guessed or discovered by those who will compare one with another the written forms of Eldarin languages of Valinor, together with such records of the Avari as we here in Eressëa have set down in these later days.", p. 421.
Quenya's older form, first recorded in the sarati of Rúmil, is called Old or Ancient Quenya (''Yára-Quenya'' in Quenya). In Eldamar, the Noldor and Vanyar spoke two slightly different though mutually intelligible dialects of Tarquesta: ''Noldorin Quenya'' and ''Vanyarin Quenya''. J. R. R. Tolkien, "Tengwesta Qenderinwa 2", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (18), p. 75. Later Noldorin Quenya became ''Exilic Quenya'', when most of the Noldor Elves followed their leader Fëanor
Fëanor () is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's '' The Silmarillion''. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel. As a great loremaster and creator, he improved the Sarati alphabet, inventing ...
into exile from Eldamar and back to Middle-earth, where the immortal Elves first awoke. J. R. R. Tolkien, "Words, Phrases and Passages", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' 17, p. 128.
Use by Elves, Valar, and Men
Quenya was used by the godlike Valar. The Elves derived someloanwords
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because th ...
from the Valar's language, which was called Valarin in Quenya, although these were more numerous in the Vanyarin dialect than in Noldorin. This was probably because of the enduringly close relationship the Vanyarin Elves had with the Valar. The Quenya as used by the Vanyar also incorporated several words from Valarin that were not found in the Noldorin dialect, such as ''tulka'' ("yellow", from Valarin ''tulukha(n)''), ''ulban'' ("blue", presumably from the same root as Valarin ''ul(l)u'' meaning "water"), and ''nasar'' ("red", original Valarin not given)., "Part Four. Quendi and Eldar: Appendix D. *Kwen, Quenya, and the Elvish (especially Ñoldorin) words for 'Language': Note on the 'Language of the Valar'", p. 398
According to "Quendi and Eldar: Essekenta Eldarinwa", ''Quendya'' was the usual Vanyarin name given to the Quenya language, since in Vanyarin, the consonant groups ''ndy'' and ''ny'' remained quite distinct., p. 361. In Noldorin, ''ndy'' eventually became ''ny''. Tolkien explained that "the word ''Quenya'' itself has been cited as an exempla (e.g. by Ælfwine), but this is a mistake due to supposition that ''kwenya'' was properly ''kwendya'' and directly derived from the name ''Quendi'' 'Elves'. This appears not to be the case. The word is ''Quenya'' in Vanyarin, and always so in Parmaquesta.", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 93.
The Elves of the Third Clan, or Teleri
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elf (Middle-earth), Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Se ...
, who reached Eldamar later than the Noldor and the Vanyar, spoke a different but closely related tongue, usually called Telerin
J. R. R. Tolkien constructed many Elvish languages; the best known are Quenya and Sindarin. These were the various languages spoken by the Elves of Middle-earth as they developed as a society throughout the Ages. In his pursuit for realism and i ...
. It was seen by some Elves to be just another dialect of Quenya. This was not the case with the Teleri for whom their tongue was distinct from Quenya. After the Vanyar left the city of Túna, Telerin and Noldorin Quenya grew closer.
The rebellious Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor (also spelled Ñoldor, meaning ''those with knowledge'' in his constructed language Quenya) were a kindred of Elves who migrated west to the blessed realm of Valinor from the continent of Middle-ea ...
, who followed their leader Fëanor to Middle-earth, spoke only Quenya. But Elu Thingol, King of the Sindar
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Seconds) and Nelya ...
of Beleriand, forbade the use of Quenya in his realm when he learned of the slaying of Telerin Elves by the Noldor.''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
'', chapter 15 By doing so, he both restricted the possibility of the Sindar to enhance and brighten their language with influences from Quenya and accelerated the "dimininution and spiritual impoverishment" of the Noldorin culture. The Noldor at this time had fully mastered Sindarin, while the Sindar were slow to learn Quenya. Quenya in Middle-earth became known as ''Exilic Quenya'' when the Noldor eventually adopted the Sindarin language as their native speech after Thingol's ruling. It differed from Amanian Quenya mostly in vocabulary, having some loanwords from Sindarin. It differed also in pronunciation, representing the recognition of sound-changes which had begun among the Noldor before the exile and had caused Noldorin Quenya to diverge from Vanyarin Quenya. The change of ''z'' (< old intervocalic ''s'') to ''r'' was the latest in Noldorin, belonging to early Exilic Quenya. The grammatical changes were only small though since the features of their "old language" were carefully taught.''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 129.
From the Second Age
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the history of Arda, also called the history of Middle-earth, began when the Ainur entered Arda, following the creation events in the Ainulindalë and long ages of labour throughout Eä, the fictional uni ...
on, Quenya was used ceremonially by the Men
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chro ...
of Númenor
Númenor, also called Elenna-nórë or Westernesse, is a fictional place in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings. It was the kingdom occupying a large island to the west of Middle-earth, the main setting of Tolkien's writings, and was the greatest civil ...
and their descendants in Gondor
Gondor is a fictional kingdom in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, described as the greatest realm of Men in the west of Middle-earth at the end of the Third Age. The third volume of ''The Lord of the Rings'', ''The Return of the King'', is largely ...
and Arnor for the official names of kings and queens; this practice was resumed by Aragorn
Aragorn is a fictional character and a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings''. Aragorn was a Ranger of the North, first introduced with the name Strider and later revealed to be the heir of Isildur, an ancient King of Ar ...
when he took the crown as Elessar Telcontar. Quenya in the Third Age had almost the same status as the Latin language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of ...
had in medieval Europe, and was called ''Elven-latin'' by Tolkien. J. R. R. Tolkien, ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'', Appendix F: "Of the Elves".
Phonology
Tolkien described the pronunciation of the Elvish languages by Elves, Men and Hobbits has been described in a variety of sources. The documentation about late Quenya phonology is contained in the Appendix E of the ''Lord of the Rings'' and the "Outline of Phonology", one of Tolkien's texts, published in ''Parma Eldalamberon'' No. 19., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, pages 68-107
Tolkien based Quenya pronunciation more on Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
than on Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
. Thus, Quenya lacks the vowel harmony
In phonology, vowel harmony is an assimilatory process in which the vowels of a given domain – typically a phonological word – have to be members of the same natural class (thus "in harmony"). Vowel harmony is typically long distance, me ...
and consonant gradation
Consonant gradation is a type of consonant mutation (mostly lenition but also assimilation) found in some Uralic languages, more specifically in the Finnic, Samic and Samoyedic branches. It originally arose as an allophonic alternation betw ...
present in Finnish, and accent is not always on the first syllable of a word. Typical Finnish elements like the front vowels ''ö'', ''ä'' and ''y'' are lacking in Quenya, but phonological similarities include the absence of aspirated unvoiced stops or the development of the syllables ''ti'' > ''si'' in both languages. The combination of a Latin basis with Finnish phonological rules resulted in a product that resembles Italian in many respects, which was Tolkien's favourite modern Romance language.''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien
''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien'' is a selection of J. R. R. Tolkien's letters published in 1981, edited by Tolkien's biographer Humphrey Carpenter assisted by Christopher Tolkien. The selection from a large mass of materials contains 354 lett ...
'', #223: "I remain in love with Italian, and feel quite lorn without a chance of trying to speak it."
The tables below list the consonants (Q. ''ólamar'') and vowels of late colloquial Noldorin Quenya, i.e. Quenya as spoken among the Exiled Noldor in Middle-earth. They are written using the International Phonetic Alphabet, unless otherwise noted.
Consonants
The Quenya consonant system has 6 major places of articulation: Labial consonant, labial (involving the lips), Dental consonant, dental (involving the tongue and the back of the teeth), Alveolar consonant, alveolar (involving the tongue and the alveolar ridge of the jaw), Palatal consonant, palatal (involving the tongue and the middle part of the roof of the mouth), Velar consonant, velar (involving the back of the tongue and the back part of the roof of the mouth), and Glottal consonant, glottal (involving the vocal folds). The dental Fricative consonant, fricative () and the voiced alveolar fricative () occur in the Vanyarin varieties, but were gradually replaced with and respectively in Noldorin Quenya. Notably, voiced Stop consonant, plosives only occur after Nasal consonant, nasals and Liquid consonant, liquids, i.e. there is no simple but only the clusters , and these occur only between vowels. (This may not be true in Vanyarin Quenya, given the word ''Aldudénië'', the name of a lament for the death of the Two Trees of Valinor composed by Elemmírë of the Vanyar.) Prenasalized consonant, Prenasalised consonants are prominent in Quenya, and include their own ''tengwar''. The following table presents the inventory of classic Noldorin consonants. Grouping of consonants occurs only in the central parts of a word, except for combinations with the semivowels and . : Quenya orthography (using the Latin script) follows the IPA, but uses as an alternative to , writes not followed by another velar as (in early Quenya when this still can occur, as in ''Ñoldor''; otherwise it is written ), and represents the consonants using the digraphs . Similarly, the digraphs may represent palatal stop allophones of , namely , although they are not independent phonemes. In addition, in the cluster represents after or and after other vowels. In some instances was used for the combination as in ''Helcaraxë''.Morphophonemics and allophony
Some consonants are realised differently when they occur in clusters with certain other consonants. This particularly concerns clusters that involve the approximants or the glottal fricative . Clusters where the second consonant was are realised as palatalised consonants, and clusters where the second consonant was are realised as labialised. Consonant clusters where the initial consonant is are realised as preaspirated and devoiced.Palatal clusters
The pronunciation of the consonant cluster is in Noldorin Quenya, which is a "strong voiceless y, similar to, but more frictional than the initial sound in English ''huge''"., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 75 In Vanyarin Quenya, is pronounced .
According to Tolkien, the cluster is pronounced as "a 'front explosive' [c], as e.g. Hungarian ''ty'', but it is followed by an appreciable partly unvoiced y-offglide". J. R. R. Tolkien, "Quenya Consonants", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (22), p. 66.
Tolkien stated that the cluster is pronounced as in English "new" ., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 74. In the Vanyarin dialect, , , and were realised as , , and respectively. Tolkien wrote about : "In Vanyarin Quenya and among some Ñoldor the cluster was sounded with voiceless ''y'', sc. as , which later in Vanyarin became ";, ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 86. cf. Hungarian phonology, Hungarian ''lopj'' 'steal'.
Labial clusters
The cluster is realised as , a "Fricative consonant, spirantal voiceless ''w''. It has more tense with closer lip-aperture and more friction than the voiceless ''wh'' of English". According to Tolkien, the graph or is pronounced as "a lip-rounded 'k' followed by a partly unvoiced w-offglide", that is .Glottal clusters
The clusters and are realised as Voiceless dental and alveolar lateral fricatives, and Voiceless alveolar trill, , the same as and in Sindarin. These, like their Sindarin equivalents, derived from Primitive Elvish ''sl-'' and ''sr-''. The primitive consonant clusters ''sm-'' and ''sn-'' came out in Quenya as and ; it has been suggested that there was an intermediate stage of and , the voiceless versions and , in Common Eldarin; these soon merged with the voiced and . Voiceless ''hl'' and ''hr'' have a complex history which Tolkien describes thus: "Among the Noldor hr, hl became voiced to r, l before the Exile, and the use of r, l in these cases was normal in Tarquesta, as spoken, tho' the spelling was usually maintained. Since later the Exiles were familiar with voiceless ''hr'', ''hl'' in their Sindarin speech many of them restored this sound in Tarquesta, according to the traditional spelling. The learned had, of course, at all times retained hr, hl in reading or reciting Parmaquesta.", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 79.
Simplification of clusters
In the late Ancient Quenya period, when vowels were lost in long compound words, the clusters thus created, or the consonants that became final, were as a rule changed or reduced: :-m > -n; :all stops > -t; :-d > -r; :-th > -t; :-nd > -n; :-mb, -ng > -n; :-ñ > -n; :any combination with s (as ''-ts, -st, -ss'') > -s; :any combination with -ht > -t.Vowels
Quenya has five vowels (Quenya ''ómar''), and a distinction of Vowel length, length. The short vowels are/a, e, i, o, u/ and the long ones are written with an acute accent as/á, é, í, ó, ú/. The precise quality of the vowels is not known, but their pronunciation is likely closer to the "pure" vowels of Italian and Spanish than to the diphthongised English ones. According to Pesch, for the vowels /a, i, u/ the short and long forms have the same vowel quality, similar to the vowels of Finnish or Polish. But for the vowels/e, o/, the short vowels are pronounced slightly lower and closer to and , respectively, whereas the long ones are pronounced as high-mid vowels and . This interpretation is based on a statement by Tolkien, saying that é and ó, when correctly pronounced by Elves, were just a little "Raised (phonetics), tenser and 'closer'" than their short counterparts: "neither very tense and close, nor very slack and open"., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 106. This interpretation results in a vowel system with 7 different vowel qualities and a length distinction in the high and low vowels only; this system is depicted in table 3.
Late Noldorin Quenya has 6 diphthongs (Quenya ''ohloni''):/iu, eu, ai, au, oi, ui/. All of these are Diphthong#Falling and rising, falling, except for/iu/ () which is rising. In Old Quenya, all diphthongs were falling. Tolkien wrote: "It is probable that before the Exile Vanyarin and Noldorin [Quenya] in common shifted ''iu, ui'' to rising diphthongs,, ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 107. (...) but only is reported as a Diphthong#Types of diphthongs, rising diphthong similar to the beginning of English ''yule'' . On the other hand, ''ui'' remained in Exilic Quenya a falling diphthong as reported".
Syllables and stress
In Quenya, the stressing of a syllable is predictable and non-phonemic (i.e. the meaning of a word never changes depending on the stress), but it is partly determined by syllable weight. Words of two syllables are stressed on the first syllable. In words of three or more syllables, the stress is on the penult, penultimate syllable if this is heavy, otherwise on the antepenult, antepenultimate syllable, i.e. the third-to-last syllable. This stress rule is the same as the Latin phonology and orthography#Stress rule, stress-pattern found in Latin. In Quenya, heavy syllables are syllables that contain either a long vowel, a diphthong, or a final consonant (thus an intervocalic consonant cluster: ''ll, ld, mm, ss,'' ''ny'', ''ry'', etc.). Medially ''hy'' and ''hw'' close a syllable in Parmaquesta, but not colloquially in Tarquesta. Quenya has also a secondary accent. The placement of stress and the distinction between heavy and light syllables is important in Quenya verse., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 88.
Phonotactics
Tolkien also devised phonotactics, phonotactical rules for late Quenya, governing the way in which the sounds could be combined to form words: *Only the following consonants have phonemically Gemination, geminated forms, i.e. elongated consonants: ::''pp, tt, cc, mm, nn, ss, ll, rr''. (However, Quenya for "death" is ''effírië'', featuring a geminated ''f''.) :These occur only medially., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 81. The geminated occlusives ''pp, tt, cc'' are aspirated.
* Tolkien wrote that in Common Eldarin as final consonants only the "dentals ''t, s, d, th, n, r, l'' (all frequent except ''th'') and the labial nasal ''m'' (frequent). In addition the combination ''-nt'' (though usually a coalescence of more than one inflexional element) seems also to have been permitted; possibly also ''st''. No other consonant groups were tolerated. ''y, w'' are not included, since they naturally took the syllabic forms i, u as suffixed elements.", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 80. These evolved from Common Eldarin to Quenya Tolkien explains on the same page thus: ''m > n'' ; ''t, n, r'' and ''s'' remained without change ; final C.E. ''th'' became Quenya ''t'' and final ''d > r'', and so: "the list of 'permissible finals':
::''n, r, l, s, t, nt''
:remained constant in Quenya speech-feeling".
* Quenya tolerates only the following initial consonants:
::''p, t, c, f, s, h, hy, hw, m, n, ñ, v, l, hl, r, hr, y, w''., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 103.
* Quenya tolerates only the following initial groups:
::''x, ps, ty, ny, ly, qu, ñw'' (became ''nw'' in Noldorin Quenya)
* Quenya tolerates only the following medial biconsonantal groups (those especially common are bolded):
::''ht, lc, ld, lf, lm, lp, lqu, lt, lv, lw, ly, mb, mn, mp, my, nc, nd, ng, nt, nw ''(''ñw'' initial only), ''ny, ps, pt, qu, rc, rd, rm, rn, rp, rt, rs, rv, rw, ry, sc, st, sw, ts, tw, ty, x''.
* Quenya does not tolerate triconsonantal (or longer) combinations, except ''c, h, g'' followed by ''w'', or ''h, t, d'' followed by ''y''. So, Quenya permits the following 12 triconsonantal groups only:
::''nqu'', lqu, ''rqu'', ''squ'', ''ngw'', ''rhw'', ''nty'', ''lty'', ''hty'', ''rty'', ''sty'', ''lhy''.
:Differences in triconsonant pronunciation:
::''hty'' in Noldorin Quenya, in Vanyarin Quenya,, ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 84.
::''sty'' in Noldorin Quenya, in Vanyarin Quenya (cf. ''ść'' vs. ''szcz'' in Polish language, Polish),, ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 87.
::In all other cases ''y'', and ''w'' became syllabic ''i, u'' after the consonant groups., ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' No. 19, p. 82.
* Quenya does not tolerate the combination of two different occlusives. "Where these anciently occurred, as in ''pt, ct'', one of the two, or both, became opened and spirantal."
* As in Sindarin, the combination ''ft'' is avoided.
Grammar
The grammar of Quenya is agglutinative and mostly suffixing, i.e. different word particles are joined by appending them. It has basic word classes of verbs, nouns and pronouns/determiners, adjectives and prepositions. Nouns are Inflection, inflected for case and number. Verbs are inflected for tense and aspect, and for agreement with subject and object. In early Quenya, adjectives agree with the noun they modify in case and number, but not in later Quenya, where this agreement disappears. The basic word order is subject–verb–object. Unless otherwise noted, samples in this section refer to Late Quenya as conceived by Tolkien after 1951.Nouns
Quenya nouns can have up to four numbers: singular, general plural ("plural 1"), particular/partitive plural ("plural 2"), and dual. In late Quenya Tarquesta, the plural is formed by a suffix to the subjective form of the noun: for ''plural 1'' the suffix is ''-i'' or ''-r''; for ''plural 2'' the suffix is ''-li''. J. R. R. Tolkien, "Words, Phrases and Passages in Various Tongues in ''The Lord of the Rings''", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 135. Quenya nouns are declension, declined for Grammatical case, case. Parmaquesta Quenya has ten Declension, cases. These include the four primary cases: Nominative case, nominative, Accusative case, accusative, Genitive case, genitive, and Instrumental case, instrumental; three adverbial cases: Allative case, allative (of which the Dative case, dative is a shortened form), Locative case, locative (also with a shortened form), and Ablative case, ablative; and a possessive or adjectival case. The accusative was however only used for Parmaquesta and had been replaced by nominative in late colloquial Quenya.
Adjectives
In late Quenya, the singular endings are ''-a, -ë, -ëa'', and a rare form ''-in'' that may be seen as a shortened form of ''-ina''. The corresponding plural forms are ''-ë, ,-i, ië'', and possibly ''-inë''. The latter version is however not attested. Quenya adjectives may be freely used as nouns,J. R. R. Tolkien, "Early Qenya Grammar", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (14), p. 77, in which case they are also inflected like a noun: e.g. ''vinya'', "new", may be used as ''vinyar'', "news".
Prepositions and adverbs
In Quenya, there are many similarities in form between prepositions and adverbs since the grammatical case already determines the relation of verb and object. Thus: :''an i falmali ''='' i falmalinna(r)'' "upon the many waves" The preposition ''an'' is related to the ''-nna'' case ending.Pronouns
As with all parts of Quenya grammar, the pronominal system was subject to many revisions throughout Tolkien's life, and the available corpus was not systematic until a list of endings was published in ''Vinyar Tengwar'' No. 49 in 2007. In late Quenya, pronouns have both separate or independent forms, and suffix forms."Quenya Pronominal Elements", ''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' (49), p. 51.''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 57.
The separate pronouns have both a short and long form that are used for intensive pronouns, emphatic and normal pronouns respectively. Examples of the emphatic form include: , , (1st to 3rd person plural). Such emphatic disjunctive pronouns, were already present in early Quenya but differed from the later versions (e.g. plural: , , ).
"I love him" (or "her") can be expressed in Quenya as or .''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' (49), p. 15. "I love them" would be then or (these two forms are reconstructed).
If a pronoun is the subject of a sentence, it becomes tied to the verb either as separate word directly before the verb, or as a suffix after the inflected verb. In the suffixed form, an (singular) and a (plural and dual) may be added to the long subjective pronouns as objectives of the 3rd person:J. R. R. Tolkien, "Words, Phrases and Passages in Various Tongues in ''The Lord of the Rings''", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 110.
:, literally "have found-I-it", "I have found it" ( Aragorn
Aragorn is a fictional character and a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's ''The Lord of the Rings''. Aragorn was a Ranger of the North, first introduced with the name Strider and later revealed to be the heir of Isildur, an ancient King of Ar ...
's outcry when he finds the sapling of the White Tree of Gondor, White Tree. J. R. R. Tolkien, ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'', ''The Return of the King'', "The Steward and the King".)
:, "You have found it/him/her".
:, "You have found them".
It is debated whether certain attested special male and female pronouns that were exclusively used for the description of persons are still applicable to late Quenya as found in ''The Lord of the Rings''.
Possessive determiners
The possessive determiners (analogous to English ''my'', ''his'', etc.) are used to indicate the possessor of the noun they determine. They mark the person and number of the possessor, and are inflected to agree with the noun they are attached in number and case. While the English language distinguishes between masculine and feminine singular possessors (''his'' vs. ''her''), late Quenya generally does not. "Since by Quenya idiom in describing the parts of body of several persons the number proper to each individual is used, the plural of parts existing in pairs (as hands, eyes, ears, feet) is seldom required. Thus "their hand" would be used, (they raised) their hands (one each), , (they raised) their hands (each both), and could not occur".''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 161.
: "They raised their hands."
: "They raised their hands."
: "Varda has uplifted her (two) hands."From the "Namárië
"Namárië" () is a poem by J. R. R. Tolkien written in Quenya, a constructed language, and published in ''The Lord of the Rings''. It is subtitled "Galadriel's Lament in Lórien", which in Quenya is ''Altariello nainië Lóriendessë''. The ...
" poem by J. R. R. Tolkien.
The usual plural ending is , , "my heirs".
Demonstrative
The demonstrative makes a three-way distinction between entities the speaker is referring to: :, "this"; :, "that (over there)"; :, "that (over there, away from both of us)".Verbs
According to Tolkien, "the inflections of [Qenya] verbs are always pretty regular",J. R. R. Tolkien, "Early Qenya Grammar", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (14), p. 56. and Quenya verbs are either in a ''personal form'' or an ''impersonal form''. Usually in linguistics, an ''impersonal verb'' is a verb that cannot take a true subject, because it does not represent an action, occurrence, or state-of-being of any specific person, place, or thing. This is not how Tolkien intended the use of "impersonal." An ''impersonal verb'' form is a verb to which no pronoun has been attached, as () or (); , "I do (habitually)", is a personal form (with , a short suffix for "I, me"). As explained by Tolkien, verbs in Quenya are negated by using a "negative verb" in front of the proper verb in the impersonal tense form.''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 144.
Tolkien noted that "when the emphatic pronoun is used separately the verb has no inflexion (save for number)."''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'', (17), p. 76.
: "Finwë is making (right now)."
: "The Elves are making."
: "I am making."
: "We are making."
: "He/She is (really) making."
: "We are (really) making."
Late Quenya verbs have also a dual agreement morpheme :
: "May two stars shine."''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' (49), p. 43.
In the imperative mood, plurality and duality are not expressed. ''There is no agreement.'' The verb stays singular. J. R. R. Tolkien, "Words, Phrases and Passages in Various Tongues in ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
''", ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), pp. 93–94.
The Copula (linguistics), copula in late Quenya is the verb . Tolkien stated that it was used only in joining adjectives, nouns, and pronouns in statements (or wishes) asserting (or desiring) a thing to have certain quality, or to be same as another, and also that the copula was not used when the meaning was clear.''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' (49), p. 9. Otherwise, the copula is zero copula, left out, which may provide for ambiguous tenses when there is no further context:
:, can be translated in English either as "Elves are ambidexters", or "Elves were ambidexters".''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' (49), p. 7.
:. "A is good", or "A was good".
Syntax
Quenya allows for a flexible word order because it is an inflectional language like Latin. Nevertheless, it has word order rules. The usual syntax structure is subject-verb-object. The adjective can be placed before or after the noun that it modifies.Vocabulary
Because many of Tolkien's writings on the Elvish languages remain unpublished it is difficult to know how large a vocabulary he devised. By 2008, about 25,000 Elvish words had been published.Proper nouns
Quenya's proper nouns are names of people and things in Middle-earth.''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
'', "Index" (annotated by Christopher Tolkien as a glossary), pp. 313-365
: "Rest"; "Bride"; "He who Arises in Might"; "Youth"; "Sublime"; "Steadfast one."
: "Fell Fire"; "Most Bright Lady"; "Cunning Man"; "Spirit of Fire"; "(?)Dreamer"; "The Abhorred."
: "Music of the Ainur"; "Home of the Eldar"; "Jaws of Ice"; "Father of All"; "Ever Snow-white Peak"; "Rock of Song"; "Master of Doom"; "land of the Vali", sc. Valar; "Foam-flower"; "Giver of fruits."
: "Land under the Waves"; "Lofty Tower of the Elvish-people"; "Tale of the Silmarils."
Some prepositions and adverbs
* : [place] beyond; [time] after. * : up(wards). * : towards, upon. * : forth, out of [with the complement noun in ablative case] * : [static] far beyond. * : far, far off, far away. * : [addition] beyond ; over and above, in addition to. * : [not touching] beneath, under. * : 1. under. 2. upon. 3. after (of place), behind. * : under, beneath. * : 1. in front of, ahead, before [in all relation but time]. 2, after [of time only].Greetings
The word used as a form of polite address to an Elf (male or female) is: Tar. Among the Númenoreans it became "King/Queen" and used as a form of address for a superior, especially a King or a Queen; cf. ''Tarinya'', used by Prince Aldarion to address his father, King Tar-Meneldur.''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
'', "Appendix: Elements in Quenya and Sindarin Names", ''tar-''.
* ''Namárië'' is a reduced form of Quenya , literally "be well". It is a formula used in Tarquesta for greetings and also for farewell.''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' (17), p. 162.
* The most usual formula used by the Noldor for greeting each other is "(Stay) in happiness!"
::In ''The Lord of the Rings'', the hobbit Frodo Baggins used another address of welcome: , corrected by Tolkien in the Second Edition to This was a traditional formula in an elevated style, used between people going on crossing paths: "A star shines upon the hour of the meeting of our ways"., p. 367.
* The most usual formula used by the Noldor in farewells is "Go happily!", or "To happiness!".
Numerals
According to Christopher Tolkien, "the Eldar used two systems of numerals one of sixes (or twelves), and one of fives. (or tens)." That is a duodecimal counting (base 12), and a decimal system. The Quenya word made by J. R. R. Tolkien for the 'decimal system of counting' is ''maquanotië'' - "hand counting". J. R. R. Tolkien "HFN – The words for 'hand' – The fingers", ''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'', n° 47, p. 10.
The known numbers for 1–20 are presented below; those from early Quenya ("Early Qenya Grammar") are in bold.
Other attested number words include ''esta'' and ''inga'' for 'first'. Tolkien was dissatisfied with ''esta'', the definition is marked with a query in the "Etymologies". J. R. R. Tolkien, "The Etymologies" in ''The Lost Road'', p. 356. ''Maqua'' means specifically a ''group of five'' objects, like the English word "pentad"; similarly ''maquat'' "pair of fives" refers to a group of ten objects. The word ''yunquenta'' for thirteen literally means "12 and one more". J. R. R. Tolkien, "NKE: manuscript text on neter 9, kanat 4, and enek 6", ''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' n° 47, p. 15.
"Qenya" numerals above twenty show that the smaller units come first, "21" being "one-twenty", and also reflects in how it's written in Tengwar.Omentielva: Arda Philology 2 http://www.omentielva.com/ardaph2.htm
Writing systems
Most of the time, Tolkien wrote his invented languages using the Latin script, but he devised Tolkien's scripts, his own writing systems to match the internal histories of his languages.Elvish writing systems
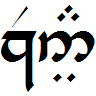 Tolkien imagined many writing systems for his Elves. The best-known is the "Tengwar of
Tolkien imagined many writing systems for his Elves. The best-known is the "Tengwar of Fëanor
Fëanor () is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's '' The Silmarillion''. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel. As a great loremaster and creator, he improved the Sarati alphabet, inventing ...
" but the first one he created c. 1919 was the "Tengwar of Rumil", also called the sarati. He decided that, prior to their Exile, the Noldorin Elves first used the sarati of Rúmil to record Ancient Quenya. In Middle-earth, Quenya appears to have been rarely written using the "Elvish runes" or cirth, named ''certar'' in Quenya.
Latin script
Tolkien's spelling in Latin script of Quenya was largely phonemic, with each letter corresponding to a specific phoneme in the language. However, the vowels varied in pronunciation depending upon their length. Specific rules for consonants were provided in Appendix E of ''The Lord of the Rings,'' e.g. the letter ''c'' is always pronounced ''k'', ''qu'' stands for ''kw'', J. R. R. Tolkien, ''The Lord of the Rings
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's bo ...
'', Appendix E, part I. ''Orqui'' is ''Orkwi''. Tolkien's standard orthography for Quenya uses all the letters of the Latin script except ''j'', ''k'', and ''z'', together with the acute accent, acute and diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis diacritic, marks on vowels; the letters ''ñ'', ''þ'' and ''z'' only appear in early Quenya. Occasionally, Tolkien wrote Quenya with a "Finnish-style" orthography (rather than the standard Latin-Romance version), in which ''c'' is replaced by ''k'', ''y'' with ''j'', and long vowels written double. The acute accent marks long vowels, while the diaeresis indicates that a vowel is not part of a diphthong, for example in ''ëa'' or ''ëo'', while final ''e'' is marked with a diaeresis to remind English-speakers that it is not silent.
Corpus
The poem "" is the longest piece of Quenya found in ''The Lord of the Rings'', yet the first sentence in Quenya is uttered by a Hobbit; namely Frodo's greeting to the Elves: . Other examples include Elendil's words spoken upon reaching Middle-earth, and repeated by Aragorn at his coronation: "Out of the Great Sea to Middle-earth I am come. In this place I will abide, and my heirs, unto the ending of the world!" Treebeard's greeting to Celeborn and Galadriel is also spoken in Quenya: "O beautiful ones, parents of beautiful children".''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien
''The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien'' is a selection of J. R. R. Tolkien's letters published in 1981, edited by Tolkien's biographer Humphrey Carpenter assisted by Christopher Tolkien. The selection from a large mass of materials contains 354 lett ...
'', #230. Another fragment is Sam Gamgee, Sam's cry when he uses Galadriel's phial against Shelob: "Hail Eärendil, brightest of stars!"The Return of the King, ch. 1 And in ''The Silmarillion'', the phrase "The day has come! Behold, people of the Eldar and Fathers of Men, the day has come!", is cried by Fingon before the Battle of Unnumbered Tears. J. R. R. Tolkien, ''The Silmarillion
''The Silmarillion'' () is a collection of myths and stories in varying styles by the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien. It was edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, assisted by the fantasy author Guy Gavri ...
'', chapter 20
Other Quenya poems spoken by Tolkien in public but never published in his lifetime are ("The Last Ark"), , and in his lecture ''A Secret Vice'', and published in 1983 in ''The Monsters and the Critics''. A faulty fragment of the poem "Narqelion", written in early Quenya or Elfin between November 1915 and March 1916, was published by Humphrey Carpenter in his ''Biography''. A facsimile of the entire poem was published only in 1999.''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' No. 40, April 1999
See also
* Calendar of Imladris * Elvish languages (Middle-earth) * Languages constructed by J. R. R. Tolkien * Sarati *Sindarin
Sindarin is one of the fictional languages devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for use in his fantasy stories set in Arda, primarily in Middle-earth. Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the Elves. The word is a Quenya word.
Called in E ...
References
Primary
:''This list identifies each item's location in Tolkien's writings.'' The entries in the journals ''Parma Eldalamberon
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second mos ...
'' and ''Vinyar Tengwar
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship (E. L. F.) is a "Special Interest Group" of the Mythopoeic Society devoted to the study of the constructed languages of J. R. R. Tolkien, today headed by the computer scientist Carl F. Hostetter. It was founded by ...
'' contain Tolkien's previously-unpublished accounts of the language, annotated by scholars, so these are not purely primary sources.
Secondary
Sources
* * * * * * *Further reading
* Appleyard, Anthony (1992). "Quenya Grammar Re-Examined". ''Quettar'' 43, pp. 3–21. * Derzhanski, Ivan A. (1997). "E man i yulma oi enquanta men?" ''Vinyar Tengwar'' 38, pp. 14–18. * Robert Foster (author), Foster, Robert and Glen GoodKnight (1971). "Sindarin and Quenya Phonology". ''Mythcon I: Proceedings'', 54–56. Los Angeles: Mythopoeic Society. * Gilson, Christopher and Carl F. Hostetter (1994). "The entu, ensi, enta Declension: A Preliminary Analysis". ''Vinyar Tengwar'' 36, pp. 7–29. * Gilson, Christopher and Patrick Wynne (1991). "The Elves at Koivienéni: A New Quenya Sentence". ''Mythlore'' 17(3), pp. 23–30. * Carl F. Hostetter, Hostetter, Carl F. (1992). ""Si man i-yulmar n(g)win enquatuva": A Newly-Discovered Tengwar Inscription". ''Vinyar Tengwar'' 21, pp. 6–10. * * Kloczko, Edward (1995). ''Dictionnaire des langues elfiques, volume 1 (Quenya-Français-Anglais/Quenya-French-English)''. Toulon: Tamise. * * Welden, Bill (2001). "Negation in Quenya". ''Vinyar Tengwar'' 42, pp. 32–34. * Wynne, Patrick H. and Christopher Gilson (1993). "Trees of Silver and of Gold: A Guide to the Koiveinéni Manuscript". ''Vinyar Tengwar'' 27, pp. 7–42.External links
The Elvish Linguistic Fellowship
Parma Eldalamberon
Vinyar Tengwar
Ardalambion
– Helge Fauskanger's site on Tolkien languages, with Quenya course and materials
*
Thorsten Renk's Quetin i lambë eldaiva - a Quenya Course (gz archive)
– Ales Bican examines the evidence for the shortened form of the locative (-s).
Quenya–English dictionary
{{Good article Agglutinative languages Middle-earth languages Subject–verb–object languages Middle-earth Elves Constructed languages introduced in the 1910s 1910 introductions Constructed languages