Combat Arms Regimental System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Combat Arms Regimental System (CARS), was the method of assigning unit designations to



units
Unit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* UNIT, a fictional military organization in the science fiction television series ''Doctor Who''
* Unit of action, a discrete piece of action (or beat) in a theatrical presentation
Music
* Unit (album), ...
of some of the combat arms
Combat arms (or fighting arms in non-American parlance) are troops within national armed forces who participate in direct tactical ground combat. In general, they are units that carry or employ weapons, such as infantry, cavalry, and artillery ...
branches of the
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land warfare, land military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight Uniformed services of the United States, U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army o ...
, including Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
, Special Forces, Field Artillery, and Armor
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or f ...
, from 1957 to 1981. Air Defense Artillery
The Air Defense Artillery Branch is the branch of the United States Army that specializes in anti-aircraft weapons (such as surface to air missiles). In the U.S. Army, these groups are composed of mainly air defense systems such as the Patrio ...
was added in 1968.
CARS was superseded by the U.S. Army Regimental System
The United States Army Regimental System (USARS) is an organizational and classification system used by the United States Army. It was established in 1981 to replace the Combat Arms Regimental System (CARS) to provide each soldier with continu ...
(USARS) in 1981, although the term "Regiment" was never appended to the official name or designation of CARS regiments, and was not added to USARS regiments until 2005.
History
Before the adoption of CARS, there was no satisfactory means of maintaining the active life of the combat arms organizations. Whenever the nation entered periods of military retrenchment, units were invariably broken up, reorganized, consolidated, or disbanded. During periods of mobilization, large numbers of new units were created. Changes in weapons and techniques of warfare produced new types of units to replace the old ones. As a result, soldiers frequently served in organizations with little or no history, while units with long combat records remained inactive. In the late 1950s requirements for maneuverable and flexible major tactical organizations demanded highly mobile divisions with greatly increased firepower. For this purpose the regiment was deemed too large and unwieldy and had to be broken up into smaller organizations. (Most artillery andarmored
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or f ...
regiments had already been broken up for flexibility and maneuverability during World War II.)
When the U.S. Army division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
was reorganized under the Pentomic
Pentomic (cf. ''Greek pent(e)-'' +''-tome'' "of five parts") was a structure for infantry and airborne divisions adopted by the US Army between 1957 and 1963, in response to the potential use of tactical nuclear weapons, on future battlefields. ...
structure in 1957, the traditional regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscript ...
al organization was eliminated, raising questions as to what the new units were to be called, how they were to be numbered, and what their relationship to former organizations was to be.
On 24 January 1957 the Secretary of the Army approved the CARS concept, as devised by the Deputy Chief of Staff for Personnel, which was designed to provide a flexible regimental structure that would permit perpetuation of unit history and tradition in the new tactical organization of divisions, without restricting the organizational trends of the future.
Units that participated in CARS
* There were 61 Regular Army infantry regiments and 18 Army Reserve infantry regiments, plus the 1st Special Forces, in the Combat Arms Regimental System. * There were 30 Regular Army armor/cavalry regiments in the Combat Arms Regimental System. The only Regular Army combat units not organized under CARS were the2nd
A second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI).
Second, Seconds or 2nd may also refer to:
Mathematics
* 2 (number), as an ordinal (also written as ''2nd'' or ''2d'')
* Second of arc, an angular measurement unit, ...
, 3rd, 6th, 11th
11 (eleven) is the natural number following 10 and preceding 12. It is the first repdigit. In English, it is the smallest positive integer whose name has three syllables.
Name
"Eleven" derives from the Old English ', which is first atteste ...
, and 14th Armored Cavalry Regiment
The 14th Cavalry Regiment is a cavalry regiment of the United States Army. It has two squadrons that provide reconnaissance, surveillance, and target acquisition for Stryker brigade combat teams. Constituted in 1901, it has served in conflicts ...
s.
* There were 82 Regular Army artillery regiments in the Combat Arms Regimental System – 58 field artillery regiments and 24 air defense artillery regiments.
* Except for the 18 Army Reserve infantry regiments, those regiments organized under CARS had elements in both the Regular Army and the Army Reserve. In the Army National Guard, each state has its own regiments. The number of CARS regiments varied as troop allotments change. The 1st Special Forces has elements in all three components – Regular Army
A regular army is the official army of a state or country (the official armed forces), contrasting with irregular forces, such as volunteer irregular militias, private armies, mercenaries, etc. A regular army usually has the following:
* a standin ...
, Army Reserve
A military reserve force is a military organization whose members have military and civilian occupations. They are not normally kept under arms, and their main role is to be available when their military requires additional manpower. Reserve ...
and Army National Guard.
The criteria for the majority of the regiments selected were two factors: age (one point for each year since original organization) and honors (two points for each campaign and American decoration). Those regiments with the most points were selected for inclusion in the system.
CARS implementation phases
* Phase I: Reorganization of Regular Army regiments (1957) * Phase II: Reorganization of Army Reserve regiments (1959) * Phase III: Reorganization of Army National Guard regiments (1959) * Phase IV: Mobilization planning (1957–present) * Phase V: Organization of regimental headquarters (subsequently suspended indefinitely)Organization
Each company, battery ortroop
A troop is a military sub-subunit, originally a small formation of cavalry, subordinate to a squadron. In many armies a troop is the equivalent element to the infantry section or platoon. Exceptions are the US Cavalry and the King's Tr ...
in the regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscript ...
(as originally organized) was reorganized as the headquarters and headquarters element of a new battle group, battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions a ...
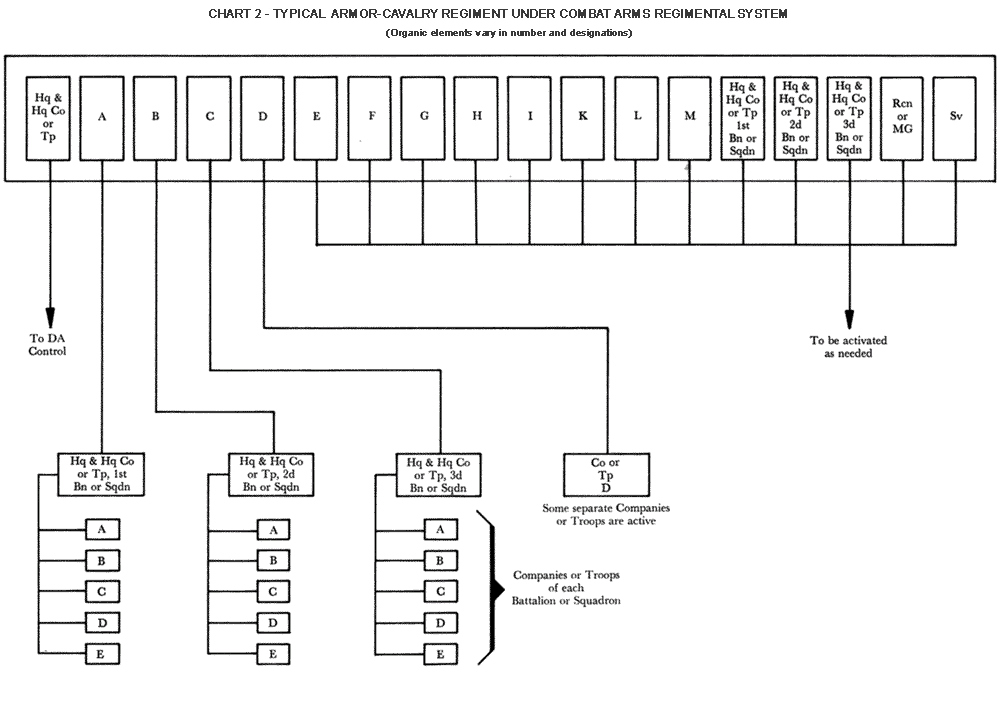
, or squadron in the new regiment. The new battle group, battalion, or squadron's organic elements (lettered elements, such as "Company A") were constituted and activated as new units. Each of the old companies, batteries, or troops of the former regiment also had the capability of becoming a separate company, battery, or troop in the new regiment. The regimental headquarters was transferred to Department of the Army control. (For detailed charts of typical regiments reorganized under CARS, see below Illustrations of organization under CARS)
The lowest numbered or lettered active element of the regiment normally has custody of the regimental properties. If, however, the lowest numbered or lettered active element is unable to care for the properties, they may be transferred to the next lowest numbered or lettered active element. If a numbered or lettered element of the regiment is activated lower than the one having custody of the regimental properties, the properties will not necessarily be transferred.
Difference between a brigade and a regiment
In a regiment not organized under CARS, there is a fixed number of organic elements organized into battalions or squadrons. For example, the infantry regiment ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
contained twelve companies A through M (minus J – not used) divided into three battalions (of four companies each), plus supporting elements such as the service company.
A brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
B ...
, on the other hand, is a flexible organization; it has no permanent elements. A brigade may have several different kinds of units assigned to it, such as: three light infantry battalions or two mechanized infantry and an armor battalion or one light, one mechanized and one armor battalion; plus support units. The usual number of maneuver battalions was three; however, this was a guideline not a rule (ex: the 173rd Airborne Brigade in Vietnam had four airborne infantry battalions).
In tactical structure, therefore, it is very similar to the Regimental Combat Team of World War II and Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
. Its maneuver (infantry and armor) elements were not required to be from the same regiment. Since they were flexible, except for the headquarters and headquarters company, no two brigades need be alike, whereas all regiments were fixed with organic elements provided for under basic tables of organization and equipment.
Battle honors
Each battalion or squadron of a CARS regiment has a replica of the regimental colors with the number of the battalion or squadron in the upper fly. The streamers attached to the colors were those for the regiment, as determined when the regiment was reorganized under CARS, plus those subsequently earned by the battalion or squadron. Those campaigns and decorations actually earned by the battalion or squadron were shown on the streamers by earned honor devices. Regimental honors were listed on the battalion or squadron Lineage and Honors Certificates, with the earned honors being marked by asterisks. Separate batteries, troops, and companies of CARS regiments display only those honors they actually earned, not the regimental ones. Campaign participation credit for these guidon-bearing units are displayed by silver bands and decorations streamers. (See ARs 672-5-1, 840-10 and 870-5 for further details.) Personnel wear the distinctive insignia for their regiment and the shoulder sleeve insignia of their division or other tactical organization to which they were assigned. (See AR 670-5 for further details.) The Adjutant General controls the designations of elements to be activated and coordinates his selections with the Center of Military History.Regiments organized under Combat Arms Regimental System
Armor
* 13th Armor * 32nd Armor * 33rd Armor * 34th Armor * 35th Armor * 37th Armor * 40th Armor * 63rd Armor * 64th Armor * 66th Armor * 67th Armor * 68th Armor * 69th Armor * 70th Armor * 72nd Armor * 73rd Armor * 77th Armor * 81st ArmorAir Defense Artillery
* 1st Air Defense Artillery * 2nd Air Defense Artillery * 3rd Air Defense Artillery * 4th Air Defense Artillery * 5th Air Defense Artillery * 6th Air Defense Artillery * 7th Air Defense Artillery * 38th Air Defense Artillery * 43rd Air Defense Artillery * 44th Air Defense Artillery * 51st Air Defense Artillery * 52nd Air Defense Artillery * 55th Air Defense Artillery * 56th Air Defense Artillery * 57th Air Defense Artillery * 59th Air Defense Artillery * 60th Air Defense Artillery * 61st Air Defense Artillery * 62nd Air Defense Artillery * 65th Air Defense Artillery * 67th Air Defense Artillery * 68th Air Defense Artillery * 71st Air Defense Artillery * 517th Air Defense Artillery * 562nd Air Defense ArtilleryCavalry
* 1st Cavalry * 4th Cavalry * 5th Cavalry * 6th Cavalry * 7th Cavalry * 8th Cavalry * 9th Cavalry * 10th Cavalry * 12th CavalryField Artillery
* 1st Field Artillery * 2nd Field Artillery * 3rd Field Artillery * 4th Field Artillery * 5th Field Artillery * 6th Field Artillery * 7th Field Artillery * 8th Field Artillery * 9th Field Artillery * 10th Field Artillery * 11th Field Artillery * 12th Field Artillery * 13th Field Artillery * 14th Field Artillery * 15th Field Artillery * 16th Field Artillery * 17th Field Artillery * 18th Field Artillery * 19th Field Artillery * 20th Field Artillery * 21st Field Artillery * 22nd Field Artillery * 25th Field Artillery * 27th Field Artillery * 29th Field Artillery * 30th Field Artillery * 31st Field Artillery * 32nd Field Artillery * 33rd Field Artillery * 34th Field Artillery * 35th Field Artillery * 36th Field Artillery * 37th Field Artillery * 38th Field Artillery * 39th Field Artillery * 40th Field Artillery * 41st Field Artillery * 42nd Field Artillery * 73rd Field Artillery * 75th Field Artillery * 76th Field Artillery * 77th Field Artillery * 78th Field Artillery * 79th Field Artillery * 80th Field Artillery * 81st Field Artillery * 82nd Field Artillery * 83rd Field Artillery * 84th Field Artillery * 92nd Field Artillery * 94th Field Artillery * 319th Field Artillery * 103rd Field Artillery * 201st Field Artillery * 320th Field Artillery * 321st Field Artillery * 333rd Field Artillery * 377th Field ArtilleryInfantry
Regular Army regiments
* 1st Infantry * 2nd Infantry * 3rd Infantry * 4th Infantry * 5th Infantry * 6th Infantry * 7th Infantry * 8th Infantry * 9th Infantry * 10th Infantry * 11th Infantry * 12th Infantry * 13th Infantry * 14th Infantry * 15th Infantry * 16th Infantry *17th Infantry
The 17th Infantry (The Loyal Regiment) was an infantry regiment of the Bengal Army, later of the united British Indian Army. It was formed at Phillour in 1858 by Major J. C. Innes from men of the 3rd, 36th and 61st Bengal Native Infantry regimen ...
* 18th Infantry
* 19th Infantry
* 20th Infantry
* 21st Infantry
* 22nd Infantry
* 23rd Infantry
* 26th Infantry
* 27th Infantry
* 28th Infantry
* 29th Infantry
* 30th Infantry
* 31st Infantry
* 32nd Infantry
* 33rd Infantry
* 34th Infantry
* 35th Infantry
* 36th Infantry
* 38th Infantry
* 39th Infantry
* 41st Infantry
* 46th Infantry
* 47th Infantry
* 48th Infantry
* 50th Infantry
* 51st Infantry
* 52nd Infantry
* 54th Infantry
* 58th Infantry
* 60th Infantry
* 61st Infantry
* 75th Infantry
* 87th Infantry
* 187th Infantry
* 188th Infantry
* 325th Infantry
* 327th Infantry
* 501st Infantry
* 502nd Infantry
* 503rd Infantry
* 504th Infantry
* 505th Infantry
* 506th Infantry
* 508th Infantry
* 509th Infantry
* 511th Infantry
Army Reserve regiments
* 59th Infantry * 305th Infantry * 306th Infantry * 307th Infantry * 314th Infantry * 315th Infantry * 322nd Infantry * 345th Infantry * 357th Infantry * 358th Infantry * 359th Infantry * 381st Infantry * 383rd Infantry * 409th Infantry * 410th Infantry * 411th Infantry * 442nd InfantrySpecial Forces Regiment
* 1st Special ForcesIllustrations of organization under CARS
Chart 1 – Typical Infantry Regiment under CARS

Chart 2 – Typical Armor/Cavalry Regiment under CARS

Chart 3 – Typical Field Artillery Regiment under CARS

Chart 4 – Typical Air Defense Artillery Regiment under CARS

Citations
{{reflistGeneral references
* John K. Mahon and Romana Danysh, CMH 60-3: ''Infantry, Part I: Regular Army, The Pentomic Concept and the Combat Arms Regimental System'' * Department of the Army RegulationsFurther reading
* Department of the Army Publications ** 672-5-1. Military Awards. 1974-06-03 ** 840-10. Flags and Guidons: Description and use of flags, guidons, tabards and automobile plates. 1962-08-23. ** 870-5 Historical Activities: Military history – responsibilities, policies and procedures. 1977-01-22. ** 870-20 Historical Activities: Historical properties and museums, 1976-09-28 ** _____. Circular 220-1. October 1960. ** _____. Pamphlet 220-1. June 1957. * "America's Pride: Famous Old Regiments to Get New Life," The Army Reservist, III (October 1957), 10–11. * "Army Studies Ways to Keep Famed Regiments on Roster," Army Times (28 April 1956), 7. * Atwood, Thomas W. "A Hard Look at CARS," Armor, LXXII (July–August 1963), 19–22. * Booth, Thomas W. "Combat Arms Regimental System," Army Information Digest, XII (August 1957) 24–31. * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "Battle Honor 'Lies' ", Army Times (10 March 1962), 13. * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "Colorful Names Would Identify Regiments," Army Times (2 August 1958), 9. * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "The Combat Regiments," Army Times (16 July 1960), 15. * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "Is Regimental Plan a Paper Exercise?" Army Times (23 March 1957). * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "The Question of CARS," Army, XI (July 1961), 23–27. * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "Regimental Plan Can Live or Die," Army Times (16 February 1957). * Bourjaily, Monte Jr. "Unit Homes in '57?" Army Times (29 December 1956), 1, 35. * "CARS Confusion," editorial, Army Times (25 July 1959), 10+. * Corbett, W.H. "New Life for Old Regiments," National Guardsman, XII (April 1958), 8, 9; (May 1958), 4, 5. * Danysh, Romana. "What’s the History of Your Unit?" Army Digest, XXII (December 1967), 12–15. * Dupuy, R. Ernest. "Our Regiments will Live Forever," Army-Navy-Air Force Register, LXXVIII (September 1957), 3. * Eliot, George Fielding. "Army’s Future Tightly Linked to 'Future of the Regiment,’ " Army Times (June 1955). * "Future of the Regiment," Army Times (4 December 1954); (11 December 1954). * Gavin, James M. "The Traditional Regiments will Live On," Army Combat Forces Journal, V (May 1955), 20–21. * Harrison, O.C. "Doubts About the Regimental System," Army, VII (July 1957), 62+. * Harrison, O.C. "The Combat Arms Regimental System," Armor, LXVI (November–December 1957), 18–21. * "Historic Regimental Designations to be Retained by the Army," Army Navy Air Force Register, LXXVII, 1. * Jones, F. P. "The Cost of Going Regimental," Army, XVII (May 1967), 47–49. * Keliher, John G. "CARS is OK. It Can Do the Job," Army, XI (May 1961), 70–71. * Kennedy, William V. "Continuity Through the Regiment," National Guardsman, XIII (February 1959), 2, 3, 31. * Lamison, K.R. and John Wike. "Combat Arms Regimental System," Army Information Digest, XIX (September 1964), 16–24. * Mahon, John K. and Romana Danysh. Infantry. ARMY LINEAGE SERIES. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1972. Pages 87–100. * McMahon, Walter L. "CARS '75; Permanent Headquarters for the Combat Arms Regimental System." US Army War College Research Paper, 31 October 1974. * Palmer, Bruce Jr. "Let’s Keep the Regiment," Army Combat Forces Journal, V (May 1955), 22–23. * "Reserves Brought into CARS," Army Times (4 April 1959). * Schmieier, Elmer. "Long Live the Regiment," Army, VII (April 1957), 25–28. * Short, James Harvey. "Young Soldiers Fade Away." Student essay, US Army War College, 13 January 1967. * Sinnreich, Richard H. and George K. Osborn. "Revive the Regiment, Rotate, and Reorganize," Army, XXV (May 1975), 12–14. * Stubbs, Mary Lee and Stanley Russell Connor. Armor-Cavalry. ARMY LINEAGE SERIES. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1969. Pages 81–83. * Tallat-Kelpsa, Algis J. "A Regiment as Home for Career Soldiers," Army, XXI (January 1971), 51–52. * Wike, John W. "Our Regimental Heritage," Army Information Digest, XIX (February 1964), 50–56. * Organizational History Branch,United States Army Center of Military History
The United States Army Center of Military History (CMH) is a directorate within the United States Army Training and Doctrine Command. The Institute of Heraldry remains within the Office of the Administrative Assistant to the Secretary of the Ar ...
U.S. Army Combat Arms Regimental System
The Combat Arms Regimental System (CARS), was the method of assigning unit designations to units of some of the combat arms branches of the
United States Army, including Infantry, Special Forces, Field Artillery, and Armor, from 1957 to 1981. ...