Colony Of Georgia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territory, dependent territories that are Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter, not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governing colony, self-governed colonies controlled by settler colonialism, colonial settlers.
The term colony originates from the ancient rome, ancient Roman ''colonia (Roman), colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'.
Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were Greek colonisation, overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''wikt:metropolis, metropolis'' ("mother-city").
Since early-modern times, historians, administrators, and political scientists have generally used the term "colony" to refer mainly to the many different overseas territory, overseas territories of particularly European states between the 15th and 20th centuries Common Era, CE, with colonialism and decolonization as corresponding phenomena. While colonies often developed from Factory (trading post), trading outposts or territorial claims, such areas do not need to be a product of colonization, nor become colonially organized territories.
Some historians use the term ''informal colony'' to refer to a country under the ''de facto'' control of another state, although this term is often contentious.
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territory, dependent territories that are Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter, not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governing colony, self-governed colonies controlled by settler colonialism, colonial settlers.
The term colony originates from the ancient rome, ancient Roman ''colonia (Roman), colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'.
Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were Greek colonisation, overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''wikt:metropolis, metropolis'' ("mother-city").
Since early-modern times, historians, administrators, and political scientists have generally used the term "colony" to refer mainly to the many different overseas territory, overseas territories of particularly European states between the 15th and 20th centuries Common Era, CE, with colonialism and decolonization as corresponding phenomena. While colonies often developed from Factory (trading post), trading outposts or territorial claims, such areas do not need to be a product of colonization, nor become colonially organized territories.
Some historians use the term ''informal colony'' to refer to a country under the ''de facto'' control of another state, although this term is often contentious.
online free
* James, Lawrence. ''The Illustrated Rise and Fall of the British Empire'' (2000) * Kia, Mehrdad, ed. ''The Ottoman Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2017) * Page, Melvin E. ed. ''Colonialism: An International Social, Cultural, and Political Encyclopedia'' (3 vol. 2003) * Priestley, Herbert Ingram. (''France overseas;: A study of modern imperialism'' 1938) 463pp; encyclopedic coverage as of late 1930s * Tarver, H. Micheal and Emily Slape. ''The Spanish Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2 vol. 2016) * Wesseling, H.L. ''The European Colonial Empires: 1815–1919'' (2015).
Non-Self-Governing Territories Listed by the United Nations General Assembly in 2002
Non-Self-Governing Territories Listed by the United Nations General Assembly in 2012
(covers Siberia as Russian colony) {{Authority control Types of administrative division Colonialism, Articles containing video clips
 In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territory, dependent territories that are Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter, not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governing colony, self-governed colonies controlled by settler colonialism, colonial settlers.
The term colony originates from the ancient rome, ancient Roman ''colonia (Roman), colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'.
Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were Greek colonisation, overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''wikt:metropolis, metropolis'' ("mother-city").
Since early-modern times, historians, administrators, and political scientists have generally used the term "colony" to refer mainly to the many different overseas territory, overseas territories of particularly European states between the 15th and 20th centuries Common Era, CE, with colonialism and decolonization as corresponding phenomena. While colonies often developed from Factory (trading post), trading outposts or territorial claims, such areas do not need to be a product of colonization, nor become colonially organized territories.
Some historians use the term ''informal colony'' to refer to a country under the ''de facto'' control of another state, although this term is often contentious.
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolitan state'' (or "mother country"). This administrative colonial separation makes colonies neither incorporated territories nor client states. Some colonies have been organized either as dependent territory, dependent territories that are Chapter XI of the United Nations Charter, not sufficiently self-governed, or as self-governing colony, self-governed colonies controlled by settler colonialism, colonial settlers.
The term colony originates from the ancient rome, ancient Roman ''colonia (Roman), colonia'', a type of Roman settlement. Derived from ''colon-us'' (farmer, cultivator, planter, or settler), it carries with it the sense of 'farm' and 'landed estate'.
Furthermore the term was used to refer to the older Greek ''apoikia'' (), which were Greek colonisation, overseas settlements by ancient Greek city-states. The city that founded such a settlement became known as its ''wikt:metropolis, metropolis'' ("mother-city").
Since early-modern times, historians, administrators, and political scientists have generally used the term "colony" to refer mainly to the many different overseas territory, overseas territories of particularly European states between the 15th and 20th centuries Common Era, CE, with colonialism and decolonization as corresponding phenomena. While colonies often developed from Factory (trading post), trading outposts or territorial claims, such areas do not need to be a product of colonization, nor become colonially organized territories.
Some historians use the term ''informal colony'' to refer to a country under the ''de facto'' control of another state, although this term is often contentious.
Etymology
The word "colony" comes from the Latin word , used as concept for Ancient Rome, Roman military bases and eventually cities. This in turn derives from the word , which was a Roman tenant farmer. The terminology is taken from architectural analogy, where a column pillar is beneath the (often stylized) head Capital (architecture), capital, which is also a biological analog of the body as subservient beneath the controlling head (with 'capital' coming from the Latin word , meaning 'head'). So colonies are not independently self-controlled, but rather are controlled by a separate entity that serves the capital function. Roman colonies first appeared when the Roman Republic, Romans conquered neighbouring Ancient peoples of Italy, Italic peoples. These were small farming settlements that appeared when the Romans had subdued an enemy in war. Though a colony could take many forms, such as a trade outpost or a military base in enemy territory, such has not been inherently colonies. Its original definition as a settlement created by people migrating from a central region to an outlying one became the modern definition. Settlements that began as Roman colonia include cities from Cologne (which retains this history in its name), Belgrade to York. A tell-tale sign of a settlement within the Roman sphere of influence once being a Roman colony is a city centre with a grid pattern.Ancient examples
* Carthage formed as a Phoenician colony * Cadiz formed as a Phoenician colony * Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene was a colony of the Greeks of Santorini, Thera * Sicily was a Phoenician colony * Sardinia was a Phoenician colony * Marseille formed as a Ancient Greece, Greek colony * Malta was a Phoenician colony * Cologne formed as a Ancient Rome, Roman colony and its modern name refer to the Latin term "Colonia". * Kandahar formed as a Ancient Greek, Greek colony during the Hellenistic era by Alexander the Great in 330 BC.Modern historical examples
* : a colony of Portugal from the 16th century to its independence in 1975. * gained its independence from Spain in 1810. * was formed as a British Dominion in 1901 from a Federation of Australia, federation of six distinct British colonies which were founded between 1788 and 1829. * : was a colony of Great Britain important in the Atlantic slave trade. It gained its independence in 1966. * : a Colonial Brazil, colony of Portugal since the 16th century. Independent since 1822. * : was colonized first by France as New France (1534–1763) and England (in Newfoundland, 1582) then Canada under British rule, under British rule (1763–1867), before achieving Dominion status and losing "colony" designation. * : a colony of Belgium from 1908 to 1960; previously under private ownership of King Leopold II. * was an Italian colony from 1935 to 1941. Sovereignty has been reestablished after a British protectorate status in 1947. * was formed in October 1887 from Annam, Tonkin, Cochinchina (which together form modern Vietnam) and the Kingdom of Cambodia; Laos was added after the Franco-Siamese War in 1893. The federation lasted until 1954. In the four protectorates, the French formally left the local rulers in power, who were the Emperors of Vietnam, Kings of Cambodia, and Kings of Luang Prabang, but gathered all powers in their hands, the local rulers acting only as figureheads. * : Contact between Europe and Ghana (known as the Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast) began in the 15th century with the arrival of the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese. This soon led to the establishment of several colonies by European powers: Portuguese Gold Coast (1482–1642), Dutch Gold Coast (1598–1872), Swedish Gold Coast (1650–1663), Danish Gold Coast (1658–1850), Brandenburger Gold Coast, Brandenburger and Prussian Gold Coast (1685–1721) and British Gold Coast (1821–1957). In 1957, Ghana was the first African colony south of the Sahara to become independent. * was a colony of Denmark-Norway from 1721 and was a colony of Denmark from 1814 to 1953. In 1953 Greenland was made an equal part of the Danish Kingdom. Home rule was granted in 1979 and extended to self-rule in 2009. See also Danish colonization of the Americas. * : a colony of Portugal since the 15th century. Independent since 1974. * was a British colony (from 1983 British Dependent Territory) from 1841 to 1997. Is now a Special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Region of China. * India was an imperial political entity comprising present-day India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan with regions under the British Raj, direct control of the British Government of the United Kingdom from 1858 to 1947. From the 15th century until 1961, Portuguese India (Goa) was a colony of Portugal. Pondicherry and Chandernagore were part of French India from 1759 to 1954. Small Danish colonies of Tharangambadi, Serampore and the Nicobar Islands) from 1620 to 1869 were known as Danish India. * was a Dutch colony which differs in each region, but gain full independence as a whole nation in 1949. * was part of the Spanish West Indies in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. It became an English colony in 1655 and; independence in 1962. * a colony set up in 1821 by American private citizens for the migration of Free Negro, African American freedmen. Liberian Declaration of Independence from the American Colonization Society on 26 July 1847. It is the second oldest black republic in the world after Haiti. * was a Portuguese colony (from 1976 a "Chinese territory under Portuguese administration") from 1557 to 1999. In 1999, two years after Hong Kong, it became a Special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Region of China. * was colonized initially by the Portuguese Empire and captures Malacca. After 1511, where the Portuguese Empire had colonized Malaysia, Britain establishes colonies and trading ports on Malay peninsula; Penang is leased to the British East India Company. The Dutch Empire encountered Malaysia when it was looking for spices to trade with. * was a British Malta Protectorate, protectorate and later a Malta Colony, colony from the French Revolutionary Wars in 1800 to independence in 1964. * : a colony of Portugal since the 15th century. Independent since 1975. * , previously a colony of Spain from to 1898 as part of the Spanish East Indies, was a colony of the United States from 1898 to 1946. Achieved self-governing Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), Commonwealth status in 1935; independent in 1946. * was a colony of Spain from 1493 to 1898, when it passed to be a colonial possession of the United States, classified by the United States as "an unincorporated territory". In 1914, the Puerto Rican House of Delegates voted unanimously in favor of independence from the United States, but this was rejected by the U.S. Congress as "unconstitutional" and in violation of the U.S. 1900 Foraker Act. In 1952, after the US Congress approved Puerto Rico's constitution, its formal name became "Commonwealth of Puerto Rico", but its new name "did not change Puerto Rico's political, social, and economic relationship to the United States." That year, the United States advised the United Nations (UN) that the island was a self-governing territory. The United States has been "unwilling to play in public the imperial role... it has no appetite for acknowledging in a public way the contradictions implicit in frankly colonial rule." The island has been called a colony by many, including US Federal judges, US Congresspeople, the Chief Justice of the Puerto Rico Supreme Court, and numerous scholars.Angel Collado-Schwarz. ''Decolonization Models for America's Last Colony: Puerto Rico.'' Syracuse University Press. 2012. * consisted of territories and colonies by various African and European powers, including the Dutch, the British, and the Nguni. The territory consisting of the modern nation was ruled directly by the British from 1806 to 1910; became a self-governing dominion of Union of South Africa in 1910. * : a British colony from 1815 to 1948. Known as Ceylon. Was a British Dominion until 1972. Also a Portuguese Ceylon, Portuguese colony in the 16th–17th centuries, and a Dutch Ceylon, Dutch colony in the 17th–18th centuries. * was a colony of Japan from 1910 to 1945. North and South Korea were established in 1948. * has a complex history of colonial rule under various powers, including the Dutch Formosa, Dutch (1624–1662), Spanish Formosa, Spanish (1626–1642), Taiwan under Qing rule, Chinese (1683–1895), and Taiwan under Japanese rule, Japanese (1895–1945). The Prehistory of Taiwan, precolonial (pre-1624) inhabitants of Taiwan are the ethno-linguistically Austronesian languages, Austronesian Taiwanese indigenous peoples, rather than the vast majority of present-day Taiwanese people, who are mostly ethno-linguistically Han Chinese. Twice throughout history, Taiwan has served as a ''quasi'' rump state for Chinese Government in exile, governments, the first instance being the Transition from Ming to Qing, Ming-loyalist Kingdom of Tungning (1662–1683) and the second instance being the present-day Taiwan, Republic of China (ROC), which officially claims Pan-Blue Coalition, continuity or Pan-Green Coalition, succession from the Republic of China (1912–1949), having Republic of China retreat to Taiwan, retreated from mainland China to Taiwan in 1949 during the final years of the Chinese Civil War (1927–1949). The ROC, whose ''de facto'' territory consists almost entirely of the Geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan and List of islands of Taiwan, its minor satellite islands, continues to rule Taiwan as if it were a separate country from the China, People's Republic of China (consisting of mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau). * The was formed from a union of thirteen British Thirteen Colonies, colonies. The Colony of Virginia was the first of the thirteen colonies. All thirteen declared independence in July 1776 and expelled the British governors.Current colonies
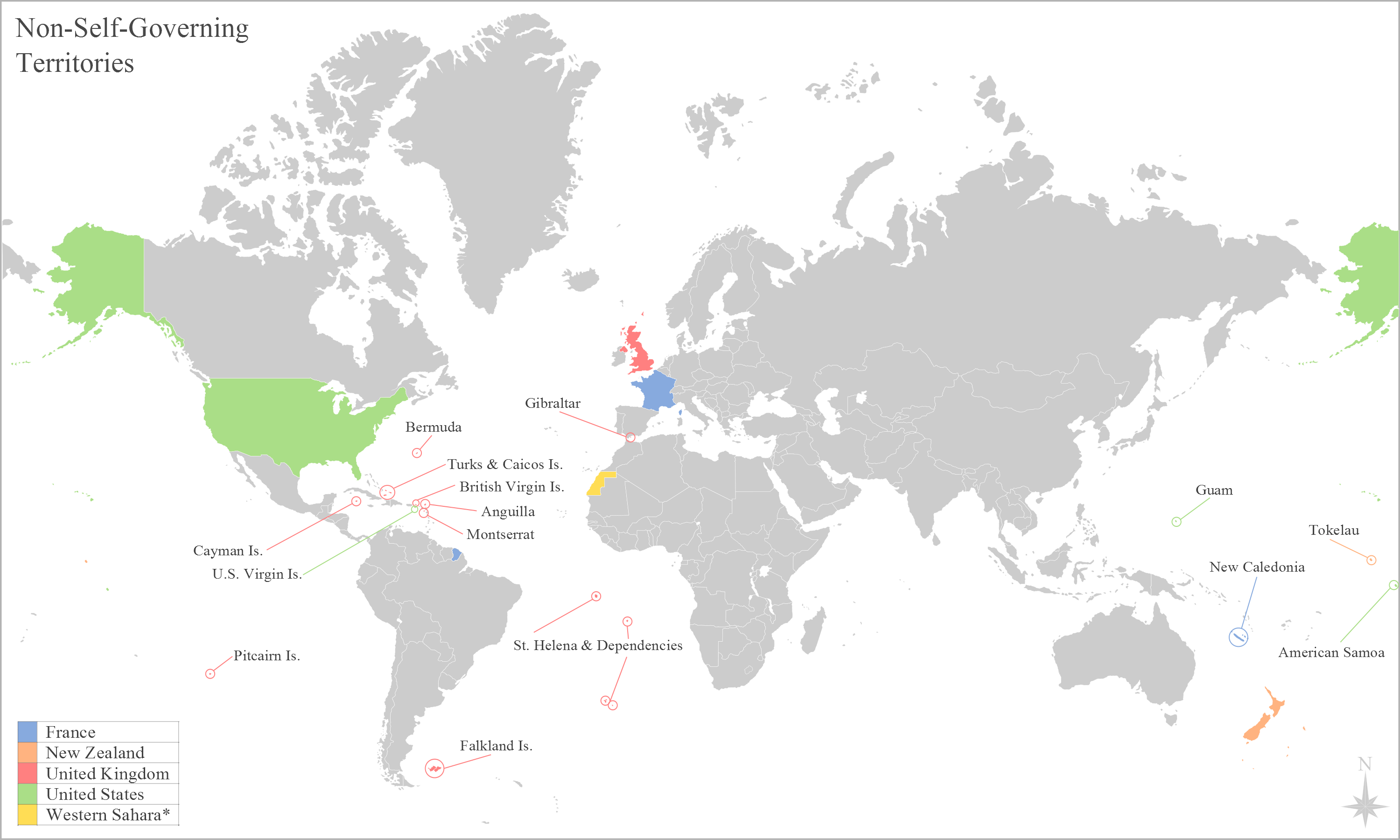
The Special Committee on Decolonization maintains the United Nations list of non-self-governing territories, which identifies areas the United Nations (though not without controversy) believes are colonies. Given that dependent territory, dependent territories have varying degrees of autonomy and political power in the affairs of the controlling state, there is disagreement over the classification of "colony".See also
* Colonialism * Colonization * Decolonization * Democracy Peace Theory * Exploitation colonialism * Scramble for Africa * Settler colonialism * United Nations list of non-self-governing territories * Development town * Spice Trade * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Further reading
* Aldrich, Robert. ''Greater France: A History of French Overseas Expansion'' (1996) * Ansprenger, Franz ed. ''The Dissolution of the Colonial Empires'' (1989) * Benjamin, Thomas, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Western Colonialism Since 1450'' (2006). * Ermatinger, James. ed. ''The Roman Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2 vol 2018) * Higham, C. S. S. ''History Of The British Empire'' (1921online free
* James, Lawrence. ''The Illustrated Rise and Fall of the British Empire'' (2000) * Kia, Mehrdad, ed. ''The Ottoman Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2017) * Page, Melvin E. ed. ''Colonialism: An International Social, Cultural, and Political Encyclopedia'' (3 vol. 2003) * Priestley, Herbert Ingram. (''France overseas;: A study of modern imperialism'' 1938) 463pp; encyclopedic coverage as of late 1930s * Tarver, H. Micheal and Emily Slape. ''The Spanish Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2 vol. 2016) * Wesseling, H.L. ''The European Colonial Empires: 1815–1919'' (2015).
External links
Non-Self-Governing Territories Listed by the United Nations General Assembly in 2002
Non-Self-Governing Territories Listed by the United Nations General Assembly in 2012
(covers Siberia as Russian colony) {{Authority control Types of administrative division Colonialism, Articles containing video clips