Collapse Of The World Trade Center on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The collapse of the
The collapse of the
 The towers were designed as framed tube structures, which provided tenants with open floor plans uninterrupted by columns or walls. The buildings were square and on each side but had chamfered corners making the exterior of each building roughly wide. Numerous, closely spaced perimeter columns provided much of the strength to the structure, along with gravity load shared with the steel box columns of the core. Above the tenth floor, there were 59 perimeter columns along each face of the building spaced on center. While the towers were square, the interior cores were rectangular and were supported with 47 columns that ran the full height of each tower. All of the elevators and stairwells were located in the core, leaving a large column-free space between it and the perimeter that was bridged by prefabricated floor trusses. As the core was rectangular this created a long and short span distance to the perimeter columns.
The floors consisted of lightweight concrete slabs laid on a fluted steel deck. A grid of lightweight bridging trusses and main trusses supported the floors with shear connections to the concrete slab for
The towers were designed as framed tube structures, which provided tenants with open floor plans uninterrupted by columns or walls. The buildings were square and on each side but had chamfered corners making the exterior of each building roughly wide. Numerous, closely spaced perimeter columns provided much of the strength to the structure, along with gravity load shared with the steel box columns of the core. Above the tenth floor, there were 59 perimeter columns along each face of the building spaced on center. While the towers were square, the interior cores were rectangular and were supported with 47 columns that ran the full height of each tower. All of the elevators and stairwells were located in the core, leaving a large column-free space between it and the perimeter that was bridged by prefabricated floor trusses. As the core was rectangular this created a long and short span distance to the perimeter columns.
The floors consisted of lightweight concrete slabs laid on a fluted steel deck. A grid of lightweight bridging trusses and main trusses supported the floors with shear connections to the concrete slab for  The towers also incorporated a "hat truss" or "outrigger truss" located between the 107th and 110th floors, which consisted of six trusses along the long axis of core and four along the short axis. This truss system allowed optimized load redistribution of floor diaphragms between the perimeter and core, with improved performance between the different materials of flexible steel and rigid concrete allowing the moment frames to transfer sway into compression on the core, which also mostly supported the transmission tower. These trusses were installed in each building to support future transmission towers but only the north tower was ultimately fitted with one.
The towers also incorporated a "hat truss" or "outrigger truss" located between the 107th and 110th floors, which consisted of six trusses along the long axis of core and four along the short axis. This truss system allowed optimized load redistribution of floor diaphragms between the perimeter and core, with improved performance between the different materials of flexible steel and rigid concrete allowing the moment frames to transfer sway into compression on the core, which also mostly supported the transmission tower. These trusses were installed in each building to support future transmission towers but only the north tower was ultimately fitted with one.
 Though fire studies and even an analysis of the impacts of low speed jet aircraft impacts had been undertaken prior to their completion, the full scope of those studies no longer exists. Nevertheless, since fire had never before caused a skyscraper to collapse and aircraft impacts had been considered in their design, their destruction initially came as a surprise to some in the engineering community.
The structural engineers working on the World Trade Center considered the possibility that an aircraft could crash into the building. In July 1945, a B-25 bomber that was lost in the fog had crashed into the 79th floor of the Empire State Building. A year later, a C-45F Expeditor crashed into the 40 Wall Street building. Once again, fog was believed to have been the contributing factor in the collision.
Though fire studies and even an analysis of the impacts of low speed jet aircraft impacts had been undertaken prior to their completion, the full scope of those studies no longer exists. Nevertheless, since fire had never before caused a skyscraper to collapse and aircraft impacts had been considered in their design, their destruction initially came as a surprise to some in the engineering community.
The structural engineers working on the World Trade Center considered the possibility that an aircraft could crash into the building. In July 1945, a B-25 bomber that was lost in the fog had crashed into the 79th floor of the Empire State Building. A year later, a C-45F Expeditor crashed into the 40 Wall Street building. Once again, fog was believed to have been the contributing factor in the collision.
two months after the building collapses, Robertson claimed that, "with the 707, the fuel load was not considered in the design, I don't know how it could have been considered." In the interview, Robertson stated that the main difference between the design studies and the event that ultimately caused the towers to collapse was due to the velocity of the impact, which greatly increased the absorbed energy, and was never considered during the construction process.
During their investigation into the collapse, the
remarks
made by John Skilling following the 1993 WTC bombing. Without original documentation for either study, NIST said any further comments would amount to speculation. NIST 2005. pp. 305–307. In their final report on the collapses, the NIST stated that they could find no documentation that examined the impact of a high speed jet nor that of a large scale fire fueled by aviation fuel.
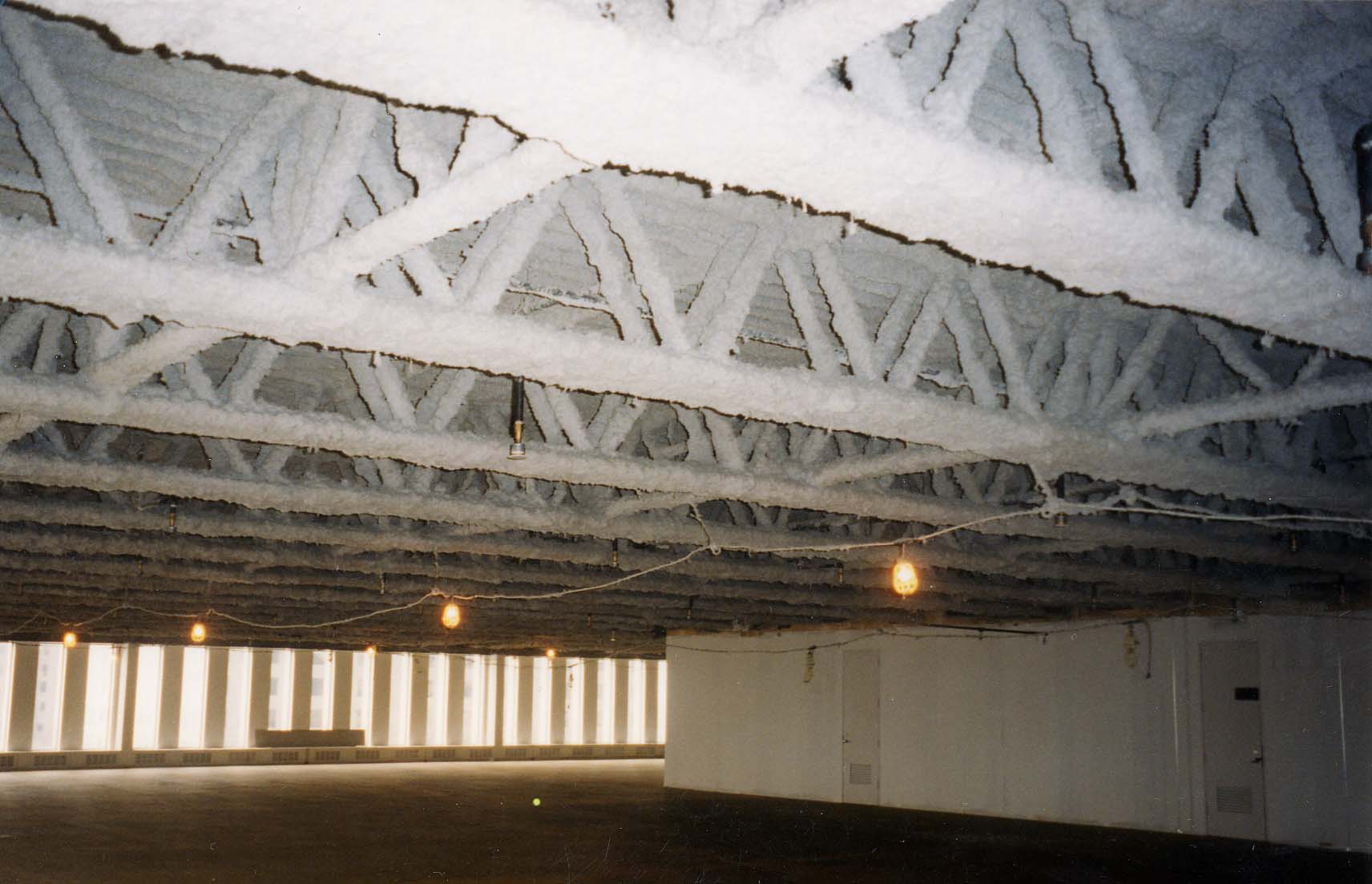 Up until the mid 1970s, the use of asbestos for
Up until the mid 1970s, the use of asbestos for
 Almost all the deaths in the Twin Towers occurred in the zones above the points of aircraft impact. As the North Tower had been struck directly midway into the structure, the three stairways in the tower core were all damaged or blocked by debris preventing escape to lower floors. In the South Tower, the impact was slightly off center to the central section of the tower and stairway A in the northwest portion of the central core was only partially blocked, and 14 to 18 civilians managed to escape from the point of aircraft impact and the floors above that. The exact numbers of who perished and where in some cases is not precisely known; however the National Institute of Standards and Technology report indicated that a total of 1,402 civilians perished at or above the impact point in the North Tower with hundreds estimated to have been killed at the moment of impact. In the South Tower, 614 civilians perished at the impacted floors and the floors above that. Fewer than 200 of the civilian fatalities occurred in the floors below the impact points but all 147 civilian passengers and crew on the two aircraft as well as all 10 terrorists perished, along with at least 18 people on the ground and in adjacent structures.
All told, emergency personnel killed as a result of the collapse included 342 members of the
Almost all the deaths in the Twin Towers occurred in the zones above the points of aircraft impact. As the North Tower had been struck directly midway into the structure, the three stairways in the tower core were all damaged or blocked by debris preventing escape to lower floors. In the South Tower, the impact was slightly off center to the central section of the tower and stairway A in the northwest portion of the central core was only partially blocked, and 14 to 18 civilians managed to escape from the point of aircraft impact and the floors above that. The exact numbers of who perished and where in some cases is not precisely known; however the National Institute of Standards and Technology report indicated that a total of 1,402 civilians perished at or above the impact point in the North Tower with hundreds estimated to have been killed at the moment of impact. In the South Tower, 614 civilians perished at the impacted floors and the floors above that. Fewer than 200 of the civilian fatalities occurred in the floors below the impact points but all 147 civilian passengers and crew on the two aircraft as well as all 10 terrorists perished, along with at least 18 people on the ground and in adjacent structures.
All told, emergency personnel killed as a result of the collapse included 342 members of the
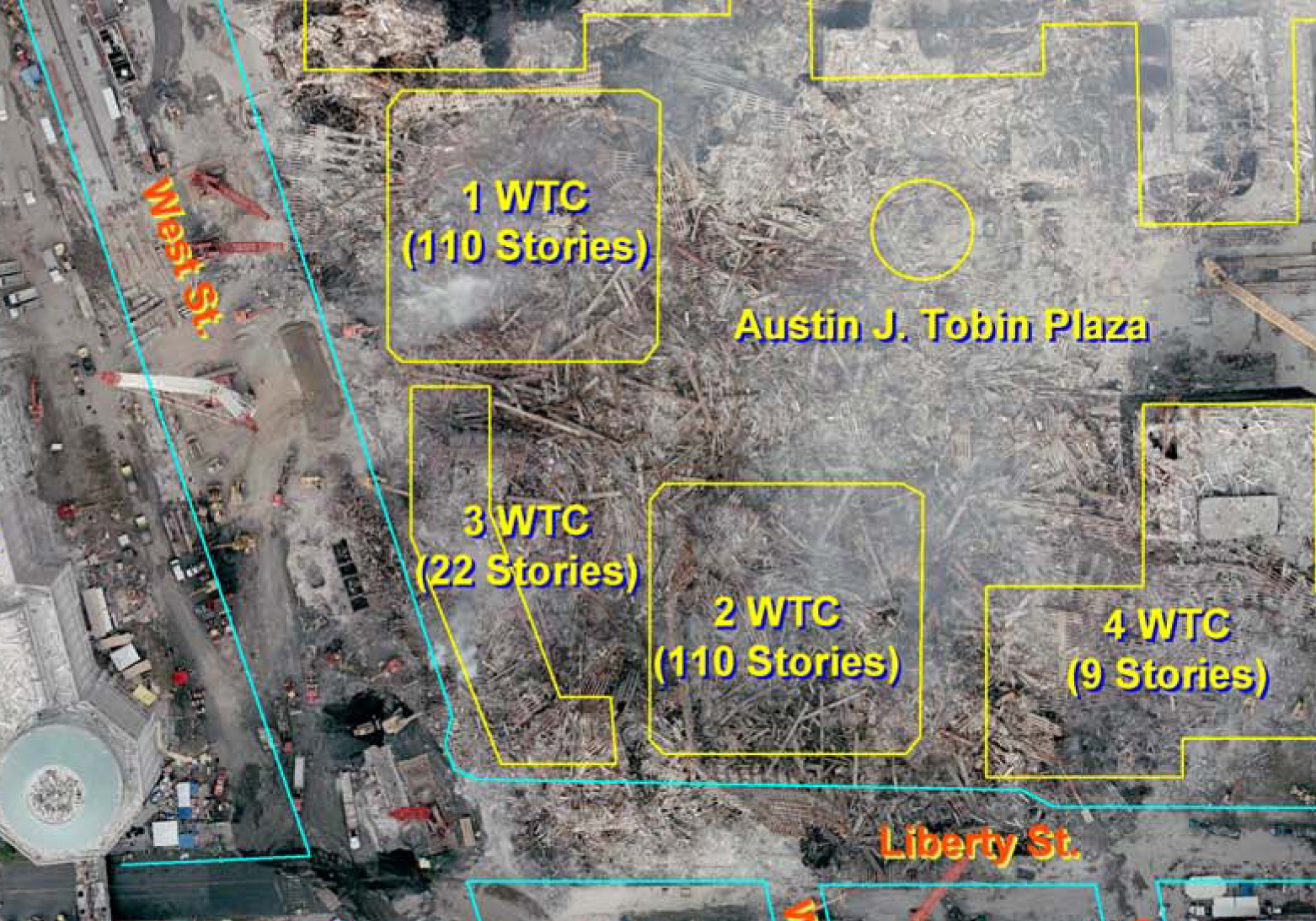
 The destruction of the Twin Towers has been called "the most infamous paradigm" of
The destruction of the Twin Towers has been called "the most infamous paradigm" of

 Aside from the structural damage, the impacts also removed fireproofing from a large part of the impact zone. As a result, the structural steel heated rapidly. This had a number of results. Core columns were weakened, and also began to shorten due to creep. The hat truss resisted this by shifting a small amount of weight to the perimeter. Meanwhile, web diagonals of the 60 foot trusses supporting the long span tenant floor area began to buckle, causing the floors to sag by more than 2 feet. This pulled in the perimeter wall. Eventually, one entire wall buckled, and the building collapsed.
WTC1 lasted almost twice as long as WTC2.  This was due to the more symmetrical impact damage to the core, and due to the fires taking more than twice as long to reach the south side of the building which had fireproofing damage.
Aside from the structural damage, the impacts also removed fireproofing from a large part of the impact zone. As a result, the structural steel heated rapidly. This had a number of results. Core columns were weakened, and also began to shorten due to creep. The hat truss resisted this by shifting a small amount of weight to the perimeter. Meanwhile, web diagonals of the 60 foot trusses supporting the long span tenant floor area began to buckle, causing the floors to sag by more than 2 feet. This pulled in the perimeter wall. Eventually, one entire wall buckled, and the building collapsed.
WTC1 lasted almost twice as long as WTC2.  This was due to the more symmetrical impact damage to the core, and due to the fires taking more than twice as long to reach the south side of the building which had fireproofing damage.
 When the columns failed, the entire building above fell onto the first intact floor beneath impact. The vertical capacity of the connections supporting an intact floor below the level of collapse was adequate to carry the load of 11 additional floors if the load was applied gradually and 6 additional floors if the load was applied suddenly (as was the case). Since the number of floors above the approximate floor of collapse initiation exceeded six in each WTC tower (12 floors in WTC 1 and 29 floors in WTC 2), the floors below the level of collapse initiation were unable to resist the suddenly applied gravitational load from the upper floors of the buildings.
When the columns failed, the entire building above fell onto the first intact floor beneath impact. The vertical capacity of the connections supporting an intact floor below the level of collapse was adequate to carry the load of 11 additional floors if the load was applied gradually and 6 additional floors if the load was applied suddenly (as was the case). Since the number of floors above the approximate floor of collapse initiation exceeded six in each WTC tower (12 floors in WTC 1 and 29 floors in WTC 2), the floors below the level of collapse initiation were unable to resist the suddenly applied gravitational load from the upper floors of the buildings.
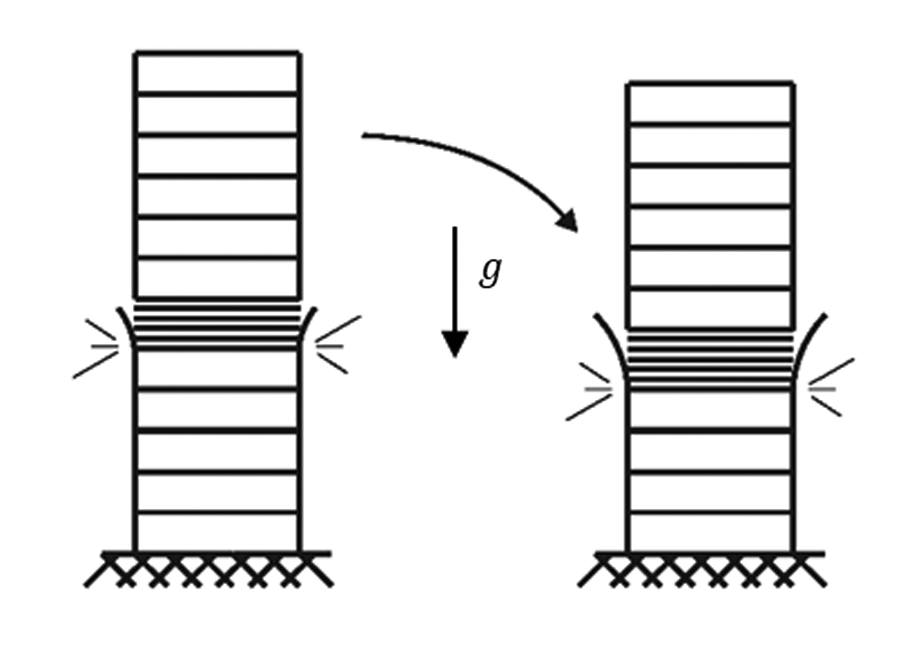 From there collapse proceeded through two phases. During the ''crush-down'' phase, the upper block destroyed the structure below in a progressive series of floor failures roughly one story at a time. Each failure began with the impact of the upper block on the floor plate of the lower section, mediated by a growing layer of rubble consisting mainly of concrete from the floor slabs. The energy from each impact was "reintroduced into the structure in hesubsequent impact, ... concentrate in the load-bearing elements directly affected by the impact." This overloaded the floor connections of the story immediately beneath the advancing destruction, causing them to detach from the perimeter and core columns. The perimeter columns peeled away and the cores were left without lateral support.
This continued until the upper block reached the ground and the ''crush-up'' phase began. Here, it was the columns that buckled one story at a time, now starting from the bottom. As each story failed, the remaining block fell through the height of the story, onto the next one, which it also crushed, until the roof finally hit the ground. The process accelerated throughout, and by the end each story was being crushed in less than a tenth of a second.
From there collapse proceeded through two phases. During the ''crush-down'' phase, the upper block destroyed the structure below in a progressive series of floor failures roughly one story at a time. Each failure began with the impact of the upper block on the floor plate of the lower section, mediated by a growing layer of rubble consisting mainly of concrete from the floor slabs. The energy from each impact was "reintroduced into the structure in hesubsequent impact, ... concentrate in the load-bearing elements directly affected by the impact." This overloaded the floor connections of the story immediately beneath the advancing destruction, causing them to detach from the perimeter and core columns. The perimeter columns peeled away and the cores were left without lateral support.
This continued until the upper block reached the ground and the ''crush-up'' phase began. Here, it was the columns that buckled one story at a time, now starting from the bottom. As each story failed, the remaining block fell through the height of the story, onto the next one, which it also crushed, until the roof finally hit the ground. The process accelerated throughout, and by the end each story was being crushed in less than a tenth of a second.
 The collapse of the South Tower shattered windows and damaged other exterior elements along the southern and eastern facades of the North Tower, although this was insufficient to contribute to the building's subsequent collapse. After the South Tower fell, NYPD helicopters relayed information about the deteriorating conditions of the North Tower. At 10:20 a.m., the NYPD aviation unit reported that "the top of the tower might be leaning", and a minute later reported that the North Tower, "is buckling on the southwest corner and leaning to the south". At 10:28 a.m., the aviation unit reported that "the roof is going to come down very shortly" and indeed, the North Tower collapsed immediately thereafter, at 10:28 a.m., after burning for 102 minutes.
After the South Tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued orders for firefighters in the North Tower to evacuate. Due to radio communications problems, firefighters inside the towers did not hear the evacuation order from their supervisors on the scene, and most were unaware that the other tower had collapsed. 342 firefighters died in the Twin Towers, as a result of the collapse of the buildings. No one was able to escape the North Tower from the impact zone or above, as all stairwells and elevator shafts on those floors were destroyed or blocked. The collapsing towers generated enormous clouds of debris and dust that enveloped lower Manhattan; light dust reached as far as the Empire State Building, located away. The debris cloud from the North Tower collapse was also larger and more widespread than the South Tower's, which would have been the result of dust from the South Tower being kicked up by the collapse of the North.
The collapse of the South Tower shattered windows and damaged other exterior elements along the southern and eastern facades of the North Tower, although this was insufficient to contribute to the building's subsequent collapse. After the South Tower fell, NYPD helicopters relayed information about the deteriorating conditions of the North Tower. At 10:20 a.m., the NYPD aviation unit reported that "the top of the tower might be leaning", and a minute later reported that the North Tower, "is buckling on the southwest corner and leaning to the south". At 10:28 a.m., the aviation unit reported that "the roof is going to come down very shortly" and indeed, the North Tower collapsed immediately thereafter, at 10:28 a.m., after burning for 102 minutes.
After the South Tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued orders for firefighters in the North Tower to evacuate. Due to radio communications problems, firefighters inside the towers did not hear the evacuation order from their supervisors on the scene, and most were unaware that the other tower had collapsed. 342 firefighters died in the Twin Towers, as a result of the collapse of the buildings. No one was able to escape the North Tower from the impact zone or above, as all stairwells and elevator shafts on those floors were destroyed or blocked. The collapsing towers generated enormous clouds of debris and dust that enveloped lower Manhattan; light dust reached as far as the Empire State Building, located away. The debris cloud from the North Tower collapse was also larger and more widespread than the South Tower's, which would have been the result of dust from the South Tower being kicked up by the collapse of the North.
NIST and the World Trade Center
The National Institute of Standards and Technology's page on the collapse of the WTC. Contains most recent developments in investigations and FAQs.
Video: The Collapse of World Trade Center 7: Why the Building Fell
(NIST)
World Trade Center – Some Engineering Aspects
Early suggestion by University of Sydney engineering instructor about how the towers might have collapsed.
contains a photo of the WTC Marriott severely damaged by the collapse of 2 WTC immediately before the collapse of 1 WTC in which the photographer was killed.
New light on 7 WTC collapse
Abdolhassan Astaneh-Asl (Principal Investigator) {{World Trade Center Building collapses in 2001 Building collapses in the United States Building fires in New York City Burned buildings and structures in the United States Environmental disasters in the United States Filmed killings September 11 attacks 2001 fires in the United States World Trade Center Commercial building fires Building collapses caused by fire 2001 in New York City
 The collapse of the
The collapse of the World Trade Center
World Trade Centers are sites recognized by the World Trade Centers Association.
World Trade Center may refer to:
Buildings
* List of World Trade Centers
* World Trade Center (2001–present), a building complex that includes five skyscrapers, a ...
occurred during the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
, after the Twin Towers were struck by two hijacked
Hijacking may refer to:
Common usage
Computing and technology
* Bluejacking, the unsolicited transmission of data via Bluetooth
* Brandjacking, the unauthorized use of a company's brand
* Browser hijacking
* Clickjacking (including ''like ...
commercial airliners. One World Trade Center
One World Trade Center (also known as One World Trade, One WTC, and formerly Freedom Tower) is the main building of the rebuilt World Trade Center complex in Lower Manhattan, New York City. Designed by David Childs of Skidmore, Owings & Mer ...
(WTC 1, or the North Tower) was hit at 8:46 a.m. Eastern time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small por ...
and collapsed at 10:28 a.m. Two World Trade Center
2 World Trade Center (2 WTC; also known as 200 Greenwich Street) is a planned skyscraper as part of the World Trade Center complex in Manhattan, New York City. It will replace the original 2 World Trade Center, which was completed in 1972 and ...
(WTC 2, or the South Tower) was hit at 9:03 a.m. and collapsed at 9:58 a.m. The resulting debris severely damaged or destroyed more than a dozen other adjacent and nearby structures, ultimately leading to the collapse of 7 World Trade Center at 5:21 p.m. A total of 2,763 people were killed in the crashes, fires, and subsequent collapses, including 2,192 civilian
Civilians under international humanitarian law are "persons who are not members of the armed forces" and they are not " combatants if they carry arms openly and respect the laws and customs of war". It is slightly different from a non-combatant ...
s, 343 firefighters, and 71 law enforcement officer
A law enforcement officer (LEO), or peace officer in North American English, is a public-sector employee whose duties primarily involve the enforcement of laws. The phrase can include campaign disclosure specialists, local police officers, ...
s as well as all the passengers and crew on the airplanes, which included 147 civilians and the 10 hijackers.
In September 2005, the National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
(NIST) published the results of its investigation into the collapse. The investigators did not find anything substandard in the design of the twin towers, noting that the severity of the attacks was beyond anything experienced in buildings in the past. They determined the fires to be the main cause of the collapses, finding that sagging floors pulled inward on the perimeter columns, causing them to bow and then to buckle. Once the upper section of the building began to move downwards, a total progressive collapse was unavoidable.
The cleanup of the World Trade Center site
The World Trade Center site, often referred to as "Ground Zero" or "the Pile" immediately after the September 11 attacks, is a 14.6-acre (5.9 ha) area in Lower Manhattan in New York City. The site is bounded by Vesey Street to the north ...
involved round-the-clock operations and cost hundreds of millions of dollars. Some surrounding structures that were not hit by the airplanes still sustained significant damage, requiring them to be torn down. Demolition of the surrounding damaged buildings continued even as new construction proceeded on the Twin Towers' replacement, the new One World Trade Center
One World Trade Center (also known as One World Trade, One WTC, and formerly Freedom Tower) is the main building of the rebuilt World Trade Center complex in Lower Manhattan, New York City. Designed by David Childs of Skidmore, Owings & Mer ...
, which was opened in November 2014.
Background
Upon completion in 1973, the Twin Towers were briefly the tallest buildings in the world, and at the time of the terrorist attacks they were still in the top five. One World Trade Center (WTC 1) the "North Tower" was, at , six feet taller than Two World Trade Center (WTC 2) the "South Tower", which stood tall. At the time of the attacks only the then recently completedPetronas Towers
The Petronas Towers, also known as the Petronas Twin Towers or KLCC Twin Towers, ( Malay: ''Menara Berkembar Petronas'') are 88-storey supertall skyscrapers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, standing at . From 1998 to 2003, they were officially desig ...
in Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = ''Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, sub ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
and the Willis Tower
The Willis Tower (originally the Sears Tower) is a 108- story, skyscraper in the Loop community area of Chicago in Illinois, United States. Designed by architect Bruce Graham and engineer Fazlur Rahman Khan of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM ...
(known then as the Sears Tower) in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
were taller. Built with a novel design that maximized interior space, the towers had a high strength to weight ratio as they utilized a new "framed tube" design that required 40 percent less steel than more traditional steel framed skyscrapers. In addition, atop WTC 1 stood a telecommunications antenna that was erected in 1978 bringing the total height of that tower to , though as a nonstructural addition, the antenna was not officially counted.
Structural design
 The towers were designed as framed tube structures, which provided tenants with open floor plans uninterrupted by columns or walls. The buildings were square and on each side but had chamfered corners making the exterior of each building roughly wide. Numerous, closely spaced perimeter columns provided much of the strength to the structure, along with gravity load shared with the steel box columns of the core. Above the tenth floor, there were 59 perimeter columns along each face of the building spaced on center. While the towers were square, the interior cores were rectangular and were supported with 47 columns that ran the full height of each tower. All of the elevators and stairwells were located in the core, leaving a large column-free space between it and the perimeter that was bridged by prefabricated floor trusses. As the core was rectangular this created a long and short span distance to the perimeter columns.
The floors consisted of lightweight concrete slabs laid on a fluted steel deck. A grid of lightweight bridging trusses and main trusses supported the floors with shear connections to the concrete slab for
The towers were designed as framed tube structures, which provided tenants with open floor plans uninterrupted by columns or walls. The buildings were square and on each side but had chamfered corners making the exterior of each building roughly wide. Numerous, closely spaced perimeter columns provided much of the strength to the structure, along with gravity load shared with the steel box columns of the core. Above the tenth floor, there were 59 perimeter columns along each face of the building spaced on center. While the towers were square, the interior cores were rectangular and were supported with 47 columns that ran the full height of each tower. All of the elevators and stairwells were located in the core, leaving a large column-free space between it and the perimeter that was bridged by prefabricated floor trusses. As the core was rectangular this created a long and short span distance to the perimeter columns.
The floors consisted of lightweight concrete slabs laid on a fluted steel deck. A grid of lightweight bridging trusses and main trusses supported the floors with shear connections to the concrete slab for composite action
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic material ...
. The trusses had a span of in the long-span areas and in the short-span area. The trusses connected to the perimeter at alternate columns, and were therefore on centers. The top chords of the trusses were bolted to seats welded to the spandrels on the perimeter side and a channel welded to interior box columns on the core side. The floors were connected to the perimeter spandrel plates with viscoelastic
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly ...
dampers, which helped reduce the amount of sway felt by building occupants.
 The towers also incorporated a "hat truss" or "outrigger truss" located between the 107th and 110th floors, which consisted of six trusses along the long axis of core and four along the short axis. This truss system allowed optimized load redistribution of floor diaphragms between the perimeter and core, with improved performance between the different materials of flexible steel and rigid concrete allowing the moment frames to transfer sway into compression on the core, which also mostly supported the transmission tower. These trusses were installed in each building to support future transmission towers but only the north tower was ultimately fitted with one.
The towers also incorporated a "hat truss" or "outrigger truss" located between the 107th and 110th floors, which consisted of six trusses along the long axis of core and four along the short axis. This truss system allowed optimized load redistribution of floor diaphragms between the perimeter and core, with improved performance between the different materials of flexible steel and rigid concrete allowing the moment frames to transfer sway into compression on the core, which also mostly supported the transmission tower. These trusses were installed in each building to support future transmission towers but only the north tower was ultimately fitted with one.
Evaluations for aircraft impact
 Though fire studies and even an analysis of the impacts of low speed jet aircraft impacts had been undertaken prior to their completion, the full scope of those studies no longer exists. Nevertheless, since fire had never before caused a skyscraper to collapse and aircraft impacts had been considered in their design, their destruction initially came as a surprise to some in the engineering community.
The structural engineers working on the World Trade Center considered the possibility that an aircraft could crash into the building. In July 1945, a B-25 bomber that was lost in the fog had crashed into the 79th floor of the Empire State Building. A year later, a C-45F Expeditor crashed into the 40 Wall Street building. Once again, fog was believed to have been the contributing factor in the collision.
Though fire studies and even an analysis of the impacts of low speed jet aircraft impacts had been undertaken prior to their completion, the full scope of those studies no longer exists. Nevertheless, since fire had never before caused a skyscraper to collapse and aircraft impacts had been considered in their design, their destruction initially came as a surprise to some in the engineering community.
The structural engineers working on the World Trade Center considered the possibility that an aircraft could crash into the building. In July 1945, a B-25 bomber that was lost in the fog had crashed into the 79th floor of the Empire State Building. A year later, a C-45F Expeditor crashed into the 40 Wall Street building. Once again, fog was believed to have been the contributing factor in the collision. Leslie Robertson
Leslie Earl Robertson (February 12, 1928 – February 11, 2021) was an American engineer. He was the lead structural engineer of the Twin Towers of the original World Trade Center in New York City, and served as structural engineer on numerous o ...
, one of the chief engineers working on the design of the World Trade Center, stated that he considered the scenario of the impact of a Boeing 707, which might be lost in the fog and flying at relatively low speeds while seeking to land at either JFK
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination i ...
or Newark Airports. In an interview with the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
(NIST) obtained a three-page white paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white pape ...
that stated the buildings would survive an aircraft-impact of a Boeing 707 or DC 8
The Douglas DC-8 (sometimes McDonnell Douglas DC-8) is a long-range narrow-body airliner built by the American Douglas Aircraft Company.
After losing the May 1954 US Air Force tanker competition to the Boeing KC-135, Douglas announced in Ju ...
flying at . In 1993, John Skilling, lead structural engineer for the WTC, during an interview conducted after the 1993 World Trade Center bombing remarked, "Our analysis indicated the biggest problem would be the fact that all the fuel (from the airplane) would dump into the building. There would be a horrendous fire. A lot of people would be killed", he said. "The building structure would still be there." In its report, NIST stated that the technical ability to perform a rigorous simulation of aircraft impact and ensuing fires is a recent development, and that the technical capability for such analysis would have been quite limited in the 1960s.The three-page white paper titled ''Salient points with regard to the structural design of The World Trade Center towers'' described an analysis of a Boeing 707 weighing and carrying of fuel striking the 80th floor of the buildings at . It is unclear whether the effect of jet fuel and aircraft contents was a consideration in the original building design, but this study is in line witremarks
made by John Skilling following the 1993 WTC bombing. Without original documentation for either study, NIST said any further comments would amount to speculation. NIST 2005. pp. 305–307. In their final report on the collapses, the NIST stated that they could find no documentation that examined the impact of a high speed jet nor that of a large scale fire fueled by aviation fuel.
Fireproofing
 Up until the mid 1970s, the use of asbestos for
Up until the mid 1970s, the use of asbestos for fireproofing
Fireproofing is rendering something (structures, materials, etc.) resistant to fire, or incombustible; or material for use in making anything fire-proof. It is a passive fire protection measure. "Fireproof" or "fireproofing" can be used as a ...
was widespread in the construction industry. However, in April 1970, the New York City Department of Air Resources ordered contractors building the World Trade Center to stop the spraying of asbestos as an insulating material.
According to NIST NCSTAR report, originally in 1969, BLAZE-SHIELD D fireproofing was used, which was a mixture of cement and asbestos fibers. When its use was discontinued, the spraying then proceeded with one of three different sprayed fire-resistive material (SFRM) insulation - BLAZE-SHIELD DC/F, BLAZE-SHIELD II or vermiculite plaster, which was coated on the trusses, perimeter columns, spandrels, and one or more surfaces of the core columns.
After the 1993 bombing, inspections found fireproofing to be deficient. Prior to the collapses, the owners of the towers, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey
The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, PANYNJ; stylized, in logo since 2020, as Port Authority NY NJ, is a joint venture between the U.S. states of New York and New Jersey, established in 1921 through an interstate compact authorize ...
, were in the process of adding fireproofing, but had only been completed on 18 floors in 1 WTC, including all the floors affected by the aircraft impact and fires, and on 13 floors in 2 WTC, although none were directly affected by the aircraft impact.
NIST concluded that the aircraft impact removed a significant portion of the fireproofing, contributing to the buildings' collapse. In WTC 1 the impact stripped the insulation off 43 of 47 core columns on more than one floor as well as floor trusses over a space of . In WTC 2 the impact removed insulation from 39 of the 47 columns on multiple floors and from floor trusses spanning an area of .
After the collapses, Leslie Robertson stated, "To the best of our knowledge, little was known about the effects of a fire from such an aircraft, and no designs were prepared for that circumstance. Indeed, at that time, no fireproofing systems were available to control the effects of such fires."
The two crashes
Aircraft impacts and resultant fires
During theSeptember 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
, four teams of al-Qaeda terrorists hijacked four different jetliners. Two of these jetliners, American Airlines Flight 11
American Airlines Flight 11 was a domestic passenger flight that was hijacked by five al-Qaeda terrorists on September 11, 2001 as part of the September 11 attacks. Lead hijacker Mohamed Atta deliberately crashed the plane into the North Towe ...
and United Airlines Flight 175
United Airlines Flight 175 was a domestic passenger flight that was hijacked by five al-Qaeda terrorists on September 11, 2001, as part of the September 11 attacks. The flight's scheduled plan was from Logan International Airport, in Boston, ...
, both Boeing 767s, were hijacked after takeoff from Boston's Logan International Airport
General Edward Lawrence Logan International Airport , also known as Boston Logan International Airport and commonly as Boston Logan, Logan Airport or simply Logan, is an international airport that is located mostly in East Boston and partial ...
. In its final moments, American Airlines Flight 11 flew south over Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
and crashed at roughly into the northern facade of the North Tower (WTC 1) at 8:46 a.m., impacting on the 93rd through 99th floors. Seventeen minutes later, United Airlines Flight 175 flew northeast, over New York Harbor, and crashed into the southern facade of the South Tower (WTC 2) at 9:03 a.m., striking between the 77th through 85th floors at .
The impacts failed the exterior columns in the regions hit by the fuselage, engines, and fuel filled wing section (34 in the North Tower and 26 in the South Tower). Damage also extended to the tips of the wings and tailfin. In addition, several core columns were either severed or heavily damaged, especially in the path of the fuselage. About one third of the fuel was consumed in the initial impact and resulting fireball.According to National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
(NIST) estimates, Flight 11 was carrying of jet fuel when it hit the North Tower. were consumed in the initial impact when the aircraft hit and a similar amount was consumed in the fireball outside the building. Approximately burnt inside the office spaces igniting combustibles. Similarly, Flight 175 was carrying around when it hit the South Tower. Up to was instantly consumed in the initial fireball and up to was consumed in the fireball outside the building. More than was burnt in the office spaces. NIST estimated that each floor of both buildings contained around four pounds per square foot (60 tons per floor) of combustibles. The fireball from Flight 175's impact was also noticeably larger than the one from Flight 11's despite the former carrying less fuel, possibly because the off-center angle of impact allowed more of the fuel to explode outwards. Some fuel from the impact traveled down at least one elevator shaft and exploded on the 78th floor of the North Tower, as well as in the main lobby. The light construction and hollow nature of the structures allowed the jet fuel to penetrate far inside the towers, igniting many large fires simultaneously over a wide area of the impacted floors. The fuel from the planes burned at most for a few minutes, but the contents of the buildings burned over the next hour or hour and a half. Despite the towers' close proximity to one another, it is unclear whether or not either tower sustained any additional minor damage from the building next to it being struck and the explosion that followed, although it is known that the major debris from Flight 11 flew past the South Tower, while the more significant pieces of wreckage from Flight 175 similarly missed the already-burning North Tower. With both cases, some of these parts landed on other nearby buildings, resulting in further destruction.
The way in which the planes hit made all the difference in determining which tower would fall sooner. Although the South Tower was the second building to be hit, more of its structural integrity was weakened by the fact that Flight 175 had struck the building faster and much lower down than Flight 11 did into the North Tower. This meant that there was far more structural weight pressing down on the damaged, burning section of the South Tower than there was in the North Tower, with a total of 25 floors above the South Tower's impact zone; by contrast, the North Tower only had 11. Not only did the North Tower collapse second, it did so after burning for 102 minutes, standing nearly twice as long as the South Tower, which only took 56 minutes to give way.
Emergency response and evacuation
 Almost all the deaths in the Twin Towers occurred in the zones above the points of aircraft impact. As the North Tower had been struck directly midway into the structure, the three stairways in the tower core were all damaged or blocked by debris preventing escape to lower floors. In the South Tower, the impact was slightly off center to the central section of the tower and stairway A in the northwest portion of the central core was only partially blocked, and 14 to 18 civilians managed to escape from the point of aircraft impact and the floors above that. The exact numbers of who perished and where in some cases is not precisely known; however the National Institute of Standards and Technology report indicated that a total of 1,402 civilians perished at or above the impact point in the North Tower with hundreds estimated to have been killed at the moment of impact. In the South Tower, 614 civilians perished at the impacted floors and the floors above that. Fewer than 200 of the civilian fatalities occurred in the floors below the impact points but all 147 civilian passengers and crew on the two aircraft as well as all 10 terrorists perished, along with at least 18 people on the ground and in adjacent structures.
All told, emergency personnel killed as a result of the collapse included 342 members of the
Almost all the deaths in the Twin Towers occurred in the zones above the points of aircraft impact. As the North Tower had been struck directly midway into the structure, the three stairways in the tower core were all damaged or blocked by debris preventing escape to lower floors. In the South Tower, the impact was slightly off center to the central section of the tower and stairway A in the northwest portion of the central core was only partially blocked, and 14 to 18 civilians managed to escape from the point of aircraft impact and the floors above that. The exact numbers of who perished and where in some cases is not precisely known; however the National Institute of Standards and Technology report indicated that a total of 1,402 civilians perished at or above the impact point in the North Tower with hundreds estimated to have been killed at the moment of impact. In the South Tower, 614 civilians perished at the impacted floors and the floors above that. Fewer than 200 of the civilian fatalities occurred in the floors below the impact points but all 147 civilian passengers and crew on the two aircraft as well as all 10 terrorists perished, along with at least 18 people on the ground and in adjacent structures.
All told, emergency personnel killed as a result of the collapse included 342 members of the New York City Fire Department
The New York City Fire Department, officially the Fire Department of the City of New York (FDNY), is an American department of the government of New York City that provides fire protection services, technical rescue/special operations services, ...
(FDNY), 71 law enforcement officers including 23 members of the New York City Police Department
The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement agency within the City of New York, the largest and one of the oldest in ...
(NYPD), 37 members of the Port Authority Police Department
The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey Police Department, or Port Authority Police Department (PAPD), is a law enforcement agency in New York and New Jersey, the duties of which are to protect and to enforce state and city laws at all t ...
(PAPD), five members of the New York State Office of Tax Enforcement
The New York State Office of Tax Enforcement (OTE) is a law enforcement entity of the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance (DTF) that conducts criminal and civil investigations, investigators employed in the office carry firearms and ...
(OTE), three officers of the New York State Office of Court Administration
The New York State Chief Administrator of the Courts (or Chief Administrative Judge of the Courts if a judge) oversees the administration and operation of the New York State Unified Court System. They are appointed by the Chief Judge of New York ...
(OCA), one fire marshal of the New York City Fire Department (FDNY) who had sworn law enforcement powers (and was also among the 343 FDNY members killed), one member of the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, ...
(FBI), and one member of the United States Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS or Secret Service) is a federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Homeland Security charged with conducting criminal investigations and protecting U.S. political leaders, their families, and ...
(USSS). The total death toll for civilian and non-civilians is estimated to be 2,606 persons.
Collapse of the Towers

 The destruction of the Twin Towers has been called "the most infamous paradigm" of
The destruction of the Twin Towers has been called "the most infamous paradigm" of progressive collapse
Progressive collapse is the process where a primary structural element fails, resulting in the failure of adjoining structural elements, which in turn causes further structural failure.
Progressive collapses may be accidental, as the result of d ...
. Precedents include the 1968 Ronan Point collapse and 1973 Skyline Plaza disaster. Each collapse began with the local failure of a few structural components and progressed to encompass the whole of the structure. Such collapses are characterized by "the separation of structural components (including non-load bearing elements), the release of gravitational energy, and the occurrence of impact forces." The vertical impact force supplies the propagating action, the principal forces are parallel, and the primary load transfer is serial. The key element in the structure that failed was constituted by the combined "vertical load-bearing members of one entire storey." Excepting the top floors of the building, which would not have released sufficient gravitational energy to bring about a total collapse, the collapses could have begun with the failure of any story.
Under these conditions, the towers collapsed symmetrically and more or less straight down, though there was some tilting of the tops of the towers and a significant amount of fallout to the sides. In both cases, the section of the building that had been damaged by the airplanes failed, which allowed the floors above the impact zone to fall freely onto the undamaged structure below. As the collapse progressed, dust and debris could be seen shooting out of the windows several floors below the advancing destruction, caused by the sudden rush of air compressed under the descending upper levels.
During each collapse, large portions of the perimeter columns and the cores were left without any lateral support, causing them to fall laterally towards the outside, pushed by the increasing pile of rubble. Consequently, the walls peeled off and separated from the buildings by a large distance – about in some cases – hitting neighboring buildings and starting fires that would later lead to the collapse of Building 7. Some connections broke as the bolts snapped, leaving many panels randomly scattered. The first fragments of the outer walls of the collapsed North Tower struck the ground 11 seconds after the collapse started, and parts of the South Tower after 9 seconds. The lower portions of both buildings' cores (60 stories of WTC 1 and 40 stories of WTC 2) remained standing for up to 25 seconds after the start of the initial collapse before they too collapsed.
Collapse initiation
 Aside from the structural damage, the impacts also removed fireproofing from a large part of the impact zone. As a result, the structural steel heated rapidly. This had a number of results. Core columns were weakened, and also began to shorten due to creep. The hat truss resisted this by shifting a small amount of weight to the perimeter. Meanwhile, web diagonals of the 60 foot trusses supporting the long span tenant floor area began to buckle, causing the floors to sag by more than 2 feet. This pulled in the perimeter wall. Eventually, one entire wall buckled, and the building collapsed.
WTC1 lasted almost twice as long as WTC2.  This was due to the more symmetrical impact damage to the core, and due to the fires taking more than twice as long to reach the south side of the building which had fireproofing damage.
Aside from the structural damage, the impacts also removed fireproofing from a large part of the impact zone. As a result, the structural steel heated rapidly. This had a number of results. Core columns were weakened, and also began to shorten due to creep. The hat truss resisted this by shifting a small amount of weight to the perimeter. Meanwhile, web diagonals of the 60 foot trusses supporting the long span tenant floor area began to buckle, causing the floors to sag by more than 2 feet. This pulled in the perimeter wall. Eventually, one entire wall buckled, and the building collapsed.
WTC1 lasted almost twice as long as WTC2.  This was due to the more symmetrical impact damage to the core, and due to the fires taking more than twice as long to reach the south side of the building which had fireproofing damage.
Total progressive collapse
 When the columns failed, the entire building above fell onto the first intact floor beneath impact. The vertical capacity of the connections supporting an intact floor below the level of collapse was adequate to carry the load of 11 additional floors if the load was applied gradually and 6 additional floors if the load was applied suddenly (as was the case). Since the number of floors above the approximate floor of collapse initiation exceeded six in each WTC tower (12 floors in WTC 1 and 29 floors in WTC 2), the floors below the level of collapse initiation were unable to resist the suddenly applied gravitational load from the upper floors of the buildings.
When the columns failed, the entire building above fell onto the first intact floor beneath impact. The vertical capacity of the connections supporting an intact floor below the level of collapse was adequate to carry the load of 11 additional floors if the load was applied gradually and 6 additional floors if the load was applied suddenly (as was the case). Since the number of floors above the approximate floor of collapse initiation exceeded six in each WTC tower (12 floors in WTC 1 and 29 floors in WTC 2), the floors below the level of collapse initiation were unable to resist the suddenly applied gravitational load from the upper floors of the buildings.
 From there collapse proceeded through two phases. During the ''crush-down'' phase, the upper block destroyed the structure below in a progressive series of floor failures roughly one story at a time. Each failure began with the impact of the upper block on the floor plate of the lower section, mediated by a growing layer of rubble consisting mainly of concrete from the floor slabs. The energy from each impact was "reintroduced into the structure in hesubsequent impact, ... concentrate in the load-bearing elements directly affected by the impact." This overloaded the floor connections of the story immediately beneath the advancing destruction, causing them to detach from the perimeter and core columns. The perimeter columns peeled away and the cores were left without lateral support.
This continued until the upper block reached the ground and the ''crush-up'' phase began. Here, it was the columns that buckled one story at a time, now starting from the bottom. As each story failed, the remaining block fell through the height of the story, onto the next one, which it also crushed, until the roof finally hit the ground. The process accelerated throughout, and by the end each story was being crushed in less than a tenth of a second.
From there collapse proceeded through two phases. During the ''crush-down'' phase, the upper block destroyed the structure below in a progressive series of floor failures roughly one story at a time. Each failure began with the impact of the upper block on the floor plate of the lower section, mediated by a growing layer of rubble consisting mainly of concrete from the floor slabs. The energy from each impact was "reintroduced into the structure in hesubsequent impact, ... concentrate in the load-bearing elements directly affected by the impact." This overloaded the floor connections of the story immediately beneath the advancing destruction, causing them to detach from the perimeter and core columns. The perimeter columns peeled away and the cores were left without lateral support.
This continued until the upper block reached the ground and the ''crush-up'' phase began. Here, it was the columns that buckled one story at a time, now starting from the bottom. As each story failed, the remaining block fell through the height of the story, onto the next one, which it also crushed, until the roof finally hit the ground. The process accelerated throughout, and by the end each story was being crushed in less than a tenth of a second.
South Tower collapse
As the fires continued to burn, occupants trapped in the upper floors of the South Tower provided information about conditions to 9-1-1 dispatchers. At 9:37 a.m., an occupant on the 105th floor of the South Tower reported that floors beneath him "in the 90-something floor" had collapsed. TheNew York City Police Department
The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement agency within the City of New York, the largest and one of the oldest in ...
aviation unit also relayed information about the deteriorating condition of the buildings to police commanders. Only 14 people escaped from the impact zone of the South Tower after it was hit (including Stanley Praimnath, who saw the plane coming at him), and only four from the floors above it. They escaped via Stairwell A, the only stairwell which had been left intact after the impact. Numerous police hotline operators who received calls from individuals inside the South Tower were not well informed of the situation as it rapidly unfolded. Many operators told callers not to descend the tower on their own, even though it is now believed that Stairwell A was most likely passable at and above the point of impact. At 9:52 a.m., the NYPD aviation unit reported over the radio that "large pieces may be falling from the top of WTC 2. Large pieces are hanging up there". With the warnings, the NYPD issued orders for its officers to evacuate. During the emergency response, there was minimal communication between the NYPD and the New York City Fire Department
The New York City Fire Department, officially the Fire Department of the City of New York (FDNY), is an American department of the government of New York City that provides fire protection services, technical rescue/special operations services, ...
(FDNY), and overwhelmed 9-1-1 dispatchers did not pass along information to FDNY commanders on-scene. At 9:58:59 a.m., the South Tower collapsed, 55 minutes after being struck.July 31, 2021, science.howstuffworks.com, Pumphrey, Clint: https://science.howstuffworks.com/engineering/structural/cause-world-trade-center-collapse.htm , Access Date July 31, 2021
North Tower collapse
 The collapse of the South Tower shattered windows and damaged other exterior elements along the southern and eastern facades of the North Tower, although this was insufficient to contribute to the building's subsequent collapse. After the South Tower fell, NYPD helicopters relayed information about the deteriorating conditions of the North Tower. At 10:20 a.m., the NYPD aviation unit reported that "the top of the tower might be leaning", and a minute later reported that the North Tower, "is buckling on the southwest corner and leaning to the south". At 10:28 a.m., the aviation unit reported that "the roof is going to come down very shortly" and indeed, the North Tower collapsed immediately thereafter, at 10:28 a.m., after burning for 102 minutes.
After the South Tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued orders for firefighters in the North Tower to evacuate. Due to radio communications problems, firefighters inside the towers did not hear the evacuation order from their supervisors on the scene, and most were unaware that the other tower had collapsed. 342 firefighters died in the Twin Towers, as a result of the collapse of the buildings. No one was able to escape the North Tower from the impact zone or above, as all stairwells and elevator shafts on those floors were destroyed or blocked. The collapsing towers generated enormous clouds of debris and dust that enveloped lower Manhattan; light dust reached as far as the Empire State Building, located away. The debris cloud from the North Tower collapse was also larger and more widespread than the South Tower's, which would have been the result of dust from the South Tower being kicked up by the collapse of the North.
The collapse of the South Tower shattered windows and damaged other exterior elements along the southern and eastern facades of the North Tower, although this was insufficient to contribute to the building's subsequent collapse. After the South Tower fell, NYPD helicopters relayed information about the deteriorating conditions of the North Tower. At 10:20 a.m., the NYPD aviation unit reported that "the top of the tower might be leaning", and a minute later reported that the North Tower, "is buckling on the southwest corner and leaning to the south". At 10:28 a.m., the aviation unit reported that "the roof is going to come down very shortly" and indeed, the North Tower collapsed immediately thereafter, at 10:28 a.m., after burning for 102 minutes.
After the South Tower collapsed, FDNY commanders issued orders for firefighters in the North Tower to evacuate. Due to radio communications problems, firefighters inside the towers did not hear the evacuation order from their supervisors on the scene, and most were unaware that the other tower had collapsed. 342 firefighters died in the Twin Towers, as a result of the collapse of the buildings. No one was able to escape the North Tower from the impact zone or above, as all stairwells and elevator shafts on those floors were destroyed or blocked. The collapsing towers generated enormous clouds of debris and dust that enveloped lower Manhattan; light dust reached as far as the Empire State Building, located away. The debris cloud from the North Tower collapse was also larger and more widespread than the South Tower's, which would have been the result of dust from the South Tower being kicked up by the collapse of the North.
Building 7 collapse
As the North Tower collapsed, heavy debris hit 7 World Trade Center, causing damage to the south face of the building and starting fires that continued to burn throughout the afternoon. Structural damage occurred to the southwest corner between Floors 7 and 17 and on the south facade between Floor 44 and the roof; other possible structural damage includes a large vertical gash near the center of the south facade between Floors 24 and 41. The building was equipped with a sprinkler system, but had many single-point vulnerabilities for failure: the sprinkler system required manual initiation of the electrical fire pumps, rather than being a fully automatic system; the floor-level controls had a single connection to the sprinkler water riser; and the sprinkler system required some power for thefire pump
A fire pump usually refers to a pressure-increasing component of the water supply for fixed-place fire suppression systems such as fire sprinklers, standpipes, and foam systems. Fire pumps are also a critical component integrated into fire tru ...
to deliver water. Also, water pressure was low, with little or no water to feed sprinklers.
Some firefighters entered 7 World Trade Center to search the building. They attempted to extinguish small pockets of fire, but low water pressure hindered their efforts. Fires burned into the afternoon on the 11th and 12th floors of 7 World Trade Center, the flames visible on the east side of the building. During the afternoon, fire was also seen on floors 6–10, 13–14, 19–22, and 29–30. In particular, the fires on floors 7 through 9 and 11 through 13 continued to burn out of control during the afternoon. At approximately 2:00 pm, firefighters noticed a bulge in the southwest corner of 7 World Trade Center between the 10th and 13th floors, a sign that the building was unstable and might cave to one side or "collapse". During the afternoon, firefighters also heard creaking sounds coming from the building and issued uncertain reports about damage in the basement. Around 3:30 pm FDNY Chief Daniel A. Nigro decided to halt rescue operations, surface removal, and searches along the surface of the debris near 7 World Trade Center and evacuate the area due to concerns for the safety of personnel. At 5:20:33 pm EDT on September 11, 2001, 7 World Trade Center started to collapse, with the crumble of the east mechanical penthouse, while at 5:21:10 pm EDT the entire building collapsed completely. There were no casualties
A casualty, as a term in military usage, is a person in military service, combatant or non-combatant, who becomes unavailable for duty due to any of several circumstances, including death, injury, illness, capture or desertion.
In civilian usag ...
associated with the collapse.
When 7 World Trade Center collapsed, debris caused substantial damage and contamination to the Borough of Manhattan Community College
The Borough of Manhattan Community College (BMCC) is a public community college in New York City. Founded in 1963 as part of the City University of New York (CUNY) system, BMCC grants associate degrees in a wide variety of vocational, busines ...
's Fiterman Hall
The Borough of Manhattan Community College (BMCC) is a public community college in New York City. Founded in 1963 as part of the City University of New York (CUNY) system, BMCC grants associate degrees in a wide variety of vocational, busines ...
building, located adjacent at 30 West Broadway, to the extent that the building was not salvageable. In August 2007, Fiterman Hall was scheduled for dismantling. A revised plan called for demolition in 2009 and completion of the new Fiterman Hall in 2012, at a cost of $325 million. The building was finally demolished in November 2009 and construction of its replacement began on December 1, 2009. The adjacent Verizon Building
The Verizon Building (also known as 100 Barclay, the Barclay–Vesey Building, and the New York Telephone Company Building) is an office and residential building at 140 West Street in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The 32-story building was ...
, an Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
building constructed in 1926, had extensive damage to its east facade from the collapse of 7 World Trade Center, though it was successfully restored at a cost of US$1.4 billion.
Other buildings
Many of the surrounding buildings were also either damaged or destroyed as the towers fell. 5 WTC endured a large fire and a partial collapse of its steel structure and was torn down. Other buildings destroyed includeSt. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church
The St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church, officially the St. Nicholas Greek Orthodox Church and National Shrine, is a church and shrine in the World Trade Center in Lower Manhattan, New York City. It is administered by the Greek Orthodox Archdi ...
, Marriott World Trade Center
The Marriott World Trade Center was a 22-story, 825-room hotel at 3 World Trade Center within the World Trade Center complex in Manhattan, New York City. It opened in April 1981 as the Vista International Hotel and was the first major hotel t ...
(Marriott Hotel 3 WTC), South Plaza (4 WTC), and U.S. Customs
The United States Customs Service was the very first federal law enforcement agency of the U.S. federal government. Established on July 31, 1789, it collected import tariffs, performed other selected border security duties, as well as conducted ...
(6 WTC). The World Financial Center buildings, 90 West Street, and 130 Cedar Street suffered fires. The Deutsche Bank Building
The Deutsche Bank Building (formerly Bankers Trust Plaza) was a 39-story office building located at 130 Liberty Street in Manhattan, New York City, adjacent to the World Trade Center site. The building opened in 1974 and closed following the ...
, the Verizon Building
The Verizon Building (also known as 100 Barclay, the Barclay–Vesey Building, and the New York Telephone Company Building) is an office and residential building at 140 West Street in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The 32-story building was ...
, and World Financial Center 3 had impact damage from the towers' collapse, as did 90 West Street. One Liberty Plaza
One Liberty Plaza, formerly the U.S. Steel Building, is a skyscraper in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is situated on a block bounded by Broadway, Liberty Street, Church Street, and Cortlandt Street, on the ...
survived structurally intact but sustained surface damage including shattered windows. 30 West Broadway was damaged by the collapse of 7 WTC. The Deutsche Bank Building, which was covered in a large black "shroud" after September 11 to cover the building's damage, was deconstructed because of water, mold, and other severe damage caused by the neighboring towers' collapse. Many works of art were destroyed in the collapse.
Investigations
Initial opinions and analysis
In the immediate aftermath of the attacks, numerous structural engineers and experts spoke to the media, describing what they thought caused the towers to collapse. Abolhassan Astaneh-Asl, a structural engineering professor at theUniversity of California at Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant uni ...
, explained that the high temperatures in the fires weakened the steel beams and columns, causing them to become "soft and mushy", and eventually they were unable to support the structure above. Astaneh-Asl also suggested that the fireproofing became dislodged during the initial aircraft impacts. He also explained that, once the initial structural failure occurred, progressive collapse
Progressive collapse is the process where a primary structural element fails, resulting in the failure of adjoining structural elements, which in turn causes further structural failure.
Progressive collapses may be accidental, as the result of d ...
of the entire structure was inevitable. César Pelli, who designed the Petronas Towers
The Petronas Towers, also known as the Petronas Twin Towers or KLCC Twin Towers, ( Malay: ''Menara Berkembar Petronas'') are 88-storey supertall skyscrapers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, standing at . From 1998 to 2003, they were officially desig ...
in Malaysia and the World Financial Center in New York, remarked, "no building is prepared for this kind of stress."
On September 13, 2001, Zdeněk P. Bažant, professor of civil engineering and materials science at Northwestern University
Northwestern University is a private research university in Evanston, Illinois. Founded in 1851, Northwestern is the oldest chartered university in Illinois and is ranked among the most prestigious academic institutions in the world.
Charte ...
, circulated a draft paper with results of a simple analysis of the World Trade Center collapse. Bažant suggested that heat from the fires was a key factor, causing steel columns in both the core and the perimeter to weaken and experience deformation before losing their carrying capacity and buckling. Once more than half of the columns on a particular floor buckled, the overhead structure could no longer be supported and complete collapse of the structures occurred. Bažant later published an expanded version of this analysis. Other analyses were conducted by MIT civil engineers Oral Buyukozturk and Franz-Josef Ulm, who also described a collapse mechanism on September 21, 2001. They later contributed to an MIT collection of papers on the WTC collapses edited by Eduardo Kausel called ''The Towers Lost and Beyond''.
Immediately following the collapses, there was some confusion about who had the authority to carry out an official investigation. While there are clear procedures for the investigation of aircraft accidents, no agency had been appointed in advance to investigate building collapses. A team was quickly assembled by the Structural Engineers Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
, led by W. Gene Corley, Senior Vice President of CTLGroup
CTLGroup is an engineering, architecture, and materials science firm that provides engineering, testing and scientific services in the following markets: Building & Facilities; Emergent Solutions; Energy & Resources; Litigation & Insurance; Materia ...
. It also involved the American Institute of Steel Construction, the American Concrete Institute
The American Concrete Institute (ACI, formerly National Association of Cement Users or NACU) is a non-profit technical society and standards developing organization. ACI was founded in January 1905 during a convention in Indianapolis. The Institu ...
, the National Fire Protection Association, and the Society of Fire Protection Engineers
The Society of Fire Protection Engineers (SFPE) is a professional society for fire protection engineering established in 1950 and incorporated as an independent organization in 1971. It is the professional society representing those practicing the ...
. ASCE ultimately invited FEMA to join the investigation, which was completed under the auspices of the latter.
The investigation was criticized by some engineers and lawmakers in the U.S. It had little funding, no authority to demand evidence, and limited access to the WTC site. One major point of contention at the time was that the cleanup of the WTC site was resulting in the destruction of the majority of the buildings' steel components. Indeed, when NIST published its final report, it noted "the scarcity of physical evidence" that it had had at its disposal to investigate the collapses. Only a fraction of a percent of the buildings remained for analysis after the cleanup was completed: some 236 individual pieces of steel, although 95% of structural beams and plates and 50% of the reinforcement bars were recovered.
FEMA published its report in May 2002. While NIST had already announced its intention to investigate the collapses in August of the same year, by September 11, 2002 (a year after the disaster), there was growing public pressure for a more thorough investigation. Congress passed the National Construction Safety Team bill in October 2002, giving NIST the authority to conduct an investigation of the World Trade Center collapses.
FEMA building performance study
FEMA suggested that fires in conjunction with damage resulting from the aircraft impacts were the key to the collapse of the towers. Thomas Eagar, Professor of Materials Engineering and Engineering Systems atMIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
, described the fires as "the most misunderstood part of the WTC collapse". This is because the fires were originally said to have "melted" the floors and columns. Jet fuel is essentially kerosene and would have served mainly to ignite very large, but not unusually hot, hydrocarbon fires. As Eagar said, "The temperature of the fire at the WTC was not unusual, and it was most definitely not capable of melting steel." This led Eagar, FEMA and others to focus on what appeared to be the weakest point of the structures, namely, the points at which the floors were attached to the building frame.
NIST report
After the FEMA report had been published, and following pressure from technical experts, industry leaders and families of victims, the Commerce Department'sNational Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
conducted a three-year, $16 million investigation into the structural failure and progressive collapse
Progressive collapse is the process where a primary structural element fails, resulting in the failure of adjoining structural elements, which in turn causes further structural failure.
Progressive collapses may be accidental, as the result of d ...
of several WTC complex structures. The study included in-house technical expertise, along with assistance from several outside private institutions, including the Structural Engineering Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
, Society of Fire Protection Engineers
The Society of Fire Protection Engineers (SFPE) is a professional society for fire protection engineering established in 1950 and incorporated as an independent organization in 1971. It is the professional society representing those practicing the ...
, National Fire Protection Association, American Institute of Steel Construction, Simpson Gumpertz & Heger Inc., Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat
The Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) is an international body in the field of tall buildings and sustainable urban design. A non-profit organization based at the Monroe Building in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States ...
, and the Structural Engineers Association of New York.
The scope of the NIST investigation was focused on identifying "the sequence of events" that triggered the collapse, and did not include detailed analysis of the collapse mechanism itself (after the point at which events made the collapse inevitable). In line with the concerns of most engineers, NIST focused on the airplane impacts and the spread and effects of the fires, modeling these using the software program Fire Dynamics Simulator. NIST developed several highly detailed structural models for specific sub-systems such as the floor trusses as well as a global model of the towers as a whole which is less detailed. These models are static
Static may refer to:
Places
*Static Nunatak, a nunatak in Antarctica
United States
* Static, Kentucky and Tennessee
*Static Peak, a mountain in Wyoming
**Static Peak Divide, a mountain pass near the peak
Science and technology Physics
*Static el ...
or quasi-static, including deformation but not the motion of structural elements after rupture as would dynamic
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' "power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics)
** Aerodynamics, the study of the motion of air
** Analytical dyna ...
models. So, the NIST models are useful for determining how the collapse was triggered, but do not shed light on events after that point.
James Quintiere, professor of fire protection engineering at the University of Maryland, called the spoliation of the steel "a gross error" that NIST should have openly criticized. He also noted that the report lacked a timeline and physical evidence to support its conclusions. Some engineers have suggested that understanding of the collapse mechanism could be improved by developing an animated sequence of the collapses based on a global dynamic model, and comparing it with the video evidence of the actual collapses. The NIST report for WTC 7 concluded that no blast sounds were heard on audio and video footage, or were reported by witnesses.
7 World Trade Center
In May 2002, FEMA issued a report on the collapse based on a preliminary investigation conducted jointly with the Structural Engineering Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers under leadership of Dr. W. Gene Corley, P.E. FEMA made preliminary findings that the collapse was not primarily caused by actual impact damage from the collapse of 1 WTC and 2 WTC but by fires on multiple stories ignited by debris from the other two towers that continued unabated due to lack of water for sprinklers or manual firefighting. The report did not reach conclusions about the cause of the collapse and called for further investigation. In response to FEMA's concerns, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) was authorized to lead an investigation into the structural failure and collapse of the World Trade Center twin towers and 7 World Trade Center. The investigation, led by Dr S. Shyam Sunder, drew not only upon in-house technical expertise, but also upon the knowledge of several outside private institutions, including the Structural Engineering Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers (SEI/ASCE), theSociety of Fire Protection Engineers
The Society of Fire Protection Engineers (SFPE) is a professional society for fire protection engineering established in 1950 and incorporated as an independent organization in 1971. It is the professional society representing those practicing the ...
(SFPE), the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat
The Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) is an international body in the field of tall buildings and sustainable urban design. A non-profit organization based at the Monroe Building in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States ...
(CTBUH), and the Structural Engineers Association of New York (SEAoNY).
The bulk of the investigation of 7 World Trade Center was delayed until after reports were completed on the collapse of the World Trade Center twin towers. In the meantime, NIST provided a preliminary report about 7 World Trade Center in June 2004, and thereafter released occasional updates on the investigation. According to NIST, the investigation of 7 World Trade Center was delayed for a number of reasons, including that NIST staff who had been working on 7 World Trade Center were assigned full-time from June 2004 to September 2005 to work on the investigation of the collapse of the twin towers. In June 2007, Shyam Sunder explained, "We are proceeding as quickly as possible while rigorously testing and evaluating a wide range of scenarios to reach the most definitive conclusion possible. The 7 WTC investigation is in some respects just as challenging, if not more so, than the study of the towers. However, the current study does benefit greatly from the significant technological advances achieved and lessons learned from our work on the towers."
In November 2008, NIST released its final report on the causes of the collapse of 7 World Trade Center. This followed their August 21, 2008 draft report which included a period for public comments. In its investigation, NIST utilized ANSYS to model events leading up to collapse initiation and LS-DYNA
LS-DYNA is an advanced general-purpose multiphysics simulation software package developed by the former Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), which was acquired by Ansys in 2019. While the package continues to contain more and more p ...
models to simulate the global response to the initiating events. NIST determined that diesel fuel did not play an important role, nor did the structural damage from the collapse of the twin towers, nor did the transfer elements (trusses, girders, and cantilever overhangs), but the lack of water to fight the fire was an important factor. The fires burned out of control during the afternoon, causing floor beams near Column 79 to expand and push a key girder off its seat, triggering the floors to fail around column 79 on Floors 8 to 14. With a loss of lateral support across nine floors, Column 79 soon buckled – pulling the East penthouse and nearby columns down with it. With the buckling of these critical columns, the collapse then progressed east-to-west across the core, ultimately overloading the perimeter support, which buckled between Floors 7 and 17, causing the entire building above to fall downward as a single unit. From collapse timing measurements taken from a video of the north face of the building, NIST observed that the building's exterior facade fell at free fall acceleration through a distance of approximately 8 stories (32 meters, or 105 feet), noting "the collapse time was approximately 40 percent longer than that of free fall for the first 18 stories of descent." The fires, fueled by office contents, along with the lack of water, were the key reasons for the collapse.
The collapse of the old 7 World Trade Center is remarkable because it was the first known instance of a tall building collapsing primarily as a result of uncontrolled fires. Based on its investigation, NIST reiterated several recommendations it had made in its earlier report on the collapse of the twin towers, and urged immediate action on a further recommendation: that fire resistance should be evaluated under the assumption that sprinklers are unavailable; and that the effects of thermal expansion on floor support systems be considered. Recognizing that current building codes are drawn to prevent loss of life rather than building collapse, the main point of NIST's recommendations is that buildings should not collapse from fire even if sprinklers are unavailable.
Other investigations
In 2003, Asif Usmani, Professor of Structural Engineering atUniversity of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 15 ...
, published a paper with two colleagues. They provisionally concluded the fires alone, without any damage from the airplanes, could have been enough to bring down the buildings. In their view, the towers were uniquely vulnerable to the effects of large fires on several floors at the same time. When the NIST report was published, Barbara Lane, with the UK engineering firm Arup, criticized its conclusion that the loss of fire proofing was a necessary factor in causing the collapses; "We have carried out computer simulations which show that the towers would have collapsed after a major fire on three floors at once, even with fireproofing in place and without any damage from plane impact." Jose L. Torero, formerly of the BRE Centre for Fire Safety Engineering
The Edinburgh Fire Research Centre (formerly the BRE Centre for Fire Safety Engineering) is the research group at The Institute of Infrastructure and Environment, University of Edinburgh conducting research in fire, structures and environment.
Th ...
at the University of Edinburgh, pursued further research into the potentially catastrophic effects of fire on real-scale buildings.
Aftermath
Cleanup
The cleanup was a massive operation coordinated by the City of New York Department of Design and Construction. On September 22, a preliminary cleanup plan was delivered byControlled Demolition, Inc.
Controlled Demolition, Inc. (CDI) is a building implosion, controlled demolition firm headquartered in Phoenix, Maryland. The firm was founded by Jack Loizeaux who used dynamite to remove tree stumps in the Baltimore, Maryland area, and moved on to ...
(CDI) of Phoenix, Maryland. Costing hundreds of millions of dollars, it involved round-the-clock operations with many contractors and subcontractors. By early November, with a third of the debris removed, officials began to reduce the number of firefighters and police officers assigned to recovering the remains of victims, in order to prioritize the removal of debris. This caused confrontations with firefighters. Despite efforts to extinguish the blaze, the large pile of debris burned for three months, until the majority of the rubble was finally removed from the site. In 2007, the demolition of the surrounding damaged buildings was still ongoing as new construction proceeded on the World Trade Center's replacement, One World Trade Center
One World Trade Center (also known as One World Trade, One WTC, and formerly Freedom Tower) is the main building of the rebuilt World Trade Center complex in Lower Manhattan, New York City. Designed by David Childs of Skidmore, Owings & Mer ...
.
Health effects
The collapse of the World Trade Center produced enormous clouds of dust that covered Manhattan for days. On September 18, 2001, theUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
(EPA) assured the public that the air in Manhattan was "safe to breathe". In 2003 the EPA's inspector general found that the agency did not at that time have sufficient data to make such a statement. Dust from the collapse seriously reduced air quality and is likely the cause of many respiratory illnesses in lower Manhattan. Asbestosis
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart d ...
is such an illness, and asbestos would have been present in the dust. Significant long term medical and psychological effects have been found among first responders including elevated levels of asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
, sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, head ...
, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
and post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats o ...
.
Health effects also extended to residents, students, and office workers of Lower Manhattan and nearby Chinatown. Several deaths have been linked to the toxic dust, and the victims' names will be included in the World Trade Center memorial
The National September 11 Memorial & Museum (also known as the 9/11 Memorial & Museum) is a memorial and museum in New York City commemorating the September 11 attacks of 2001, which killed 2,977 people, and the 1993 World Trade Center bomb ...
. More than 18,000 people have suffered from illnesses from the dust.
References
Explanatory notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
NIST and the World Trade Center
The National Institute of Standards and Technology's page on the collapse of the WTC. Contains most recent developments in investigations and FAQs.
Video: The Collapse of World Trade Center 7: Why the Building Fell
(NIST)
World Trade Center – Some Engineering Aspects
Early suggestion by University of Sydney engineering instructor about how the towers might have collapsed.
contains a photo of the WTC Marriott severely damaged by the collapse of 2 WTC immediately before the collapse of 1 WTC in which the photographer was killed.
New light on 7 WTC collapse
Abdolhassan Astaneh-Asl (Principal Investigator) {{World Trade Center Building collapses in 2001 Building collapses in the United States Building fires in New York City Burned buildings and structures in the United States Environmental disasters in the United States Filmed killings September 11 attacks 2001 fires in the United States World Trade Center Commercial building fires Building collapses caused by fire 2001 in New York City