Collagen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Collagen () is the main structural

 A distinctive feature of collagen is the regular arrangement of
A distinctive feature of collagen is the regular arrangement of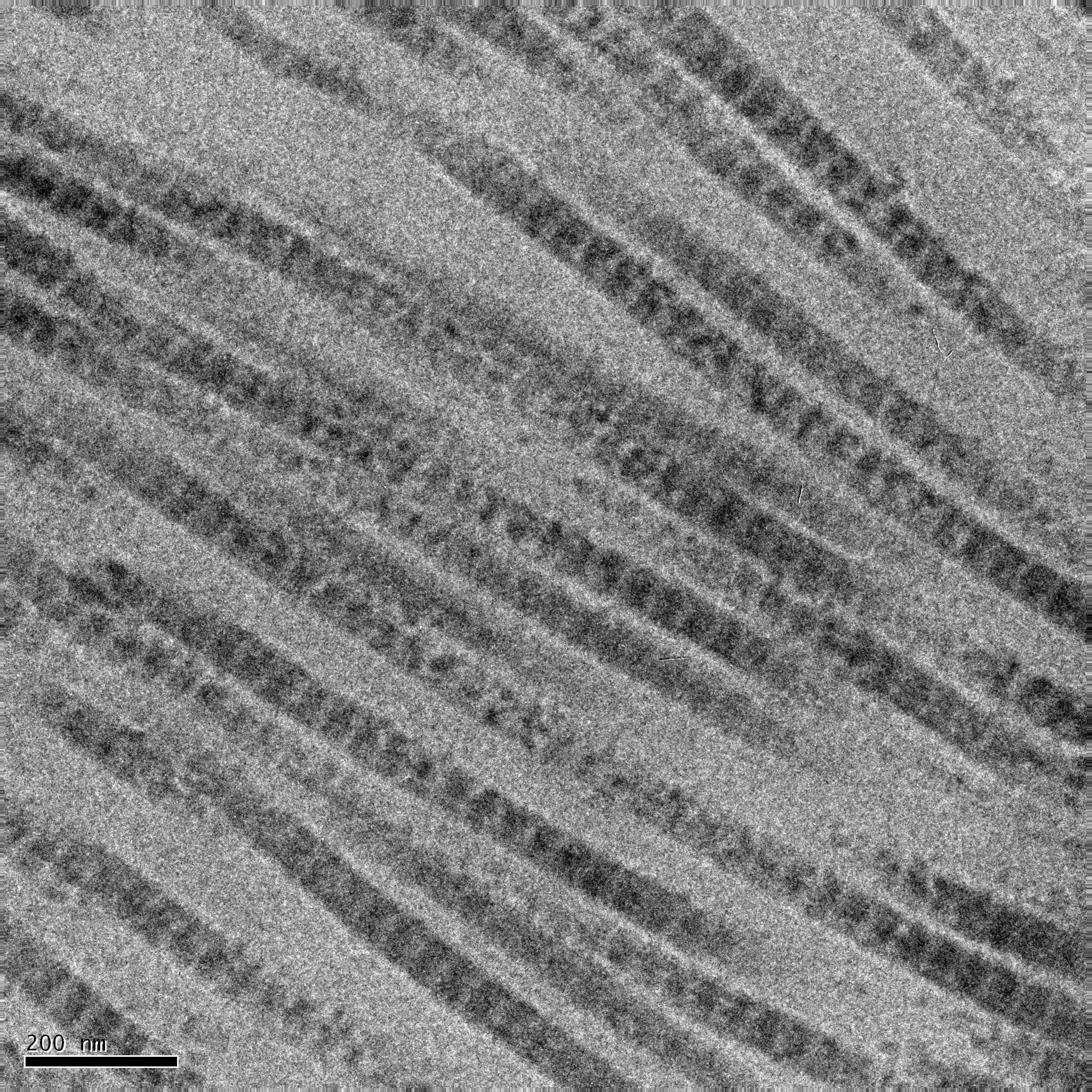  There is some
There is some
. Pharmaxchange.info. Retrieved on 21 April 2013. It strengthens
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
in the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide s ...
found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
s bound together to form a triple helix
In the fields of geometry and biochemistry, a triple helix (plural triple helices) is a set of three congruent geometrical helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. This means that each of the helices keeps the same ...
of elongated fibril
Fibrils (from the Latin ''fibra'') are structural biological materials found in nearly all living organisms. Not to be confused with fibers or filaments, fibrils tend to have diameters ranging from 10-100 nanometers (whereas fibers are micro ...
known as a collagen helix
In molecular biology, the collagen triple helix or type-2 helix is the main secondary structure of various types of fibrous collagen, including type I collagen. In 1954, Ramachandran & Kartha (13, 14) advanced a structure for the collagen tripl ...
. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s, ligaments, and skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
.
Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
s, blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue
Muscle tissue (or muscular tissue) is soft tissue that makes up the different types of muscles in most animals, and give the ability of muscles to contract. Muscle tissue is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. ...
, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that creates collagen. Gelatin, which is used in food and industry, is collagen that has been irreversibly hydrolyzed.
Etymology
The name ''collagen'' comes from the Greek κόλλα (''kólla''), meaning " glue", and suffix -γέν, ''-gen'', denoting "producing".Human types
Over 90% of the collagen in the human body istype I collagen
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It forms large, eosinophilic fibers known as collagen fibers.
It is present in scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by repair, as well as tendons, ligaments, the endomy ...
. However, as of 2011, 28 types of human collagen have been identified, described, and divided into several groups according to the structure they form. All of the types contain at least one triple helix
In the fields of geometry and biochemistry, a triple helix (plural triple helices) is a set of three congruent geometrical helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. This means that each of the helices keeps the same ...
. The number of types shows collagen's diverse functionality.
* Fibrillar (Type I, II, III, V, XI)
* Non-fibrillar
** FACIT
Facit (''Facit AB'') was an industrial corporation and manufacturer of office products including furniture. It was based in Åtvidaberg, Sweden, and founded in 1922 as ''AB Åtvidabergs Industrier''. Facit AB, a manufacturer of mechanical ca ...
(Fibril Associated Collagens with Interrupted Triple Helices) (Type IX, XII, XIV, XIX, XXI)
** Short chain (Type VIII, X)
** Basement membrane (Type IV)
** Multiplexin (Multiple Triple Helix domains with Interruptions) (Type XV, XVIII)
** MACIT (Membrane Associated Collagens with Interrupted Triple Helices) (Type XIII, XVII)
** Microfibril forming (Type VI)
** Anchoring fibrils (Type VII)
The five most common types are:
* Type I: skin, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
, vasculature, organs, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
(main component of the organic part of bone)
* Type II: cartilage (main collagenous component of cartilage)
* Type III: reticulate (main component of reticular fiber
Reticular fibers, reticular fibres or reticulin is a type of fiber in connective tissue composed of type III collagen secreted by reticular cells. Reticular fibers crosslink to form a fine meshwork (reticulin). This network acts as a supportin ...
s), commonly found alongside type I
* Type IV: forms basal lamina, the epithelium-secreted layer of the basement membrane
* Type V: cell surfaces, hair, and placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
In human biology
Cardiac
The collagenouscardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through t ...
which includes the four heart valve
A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart ...
rings, is histologically, elastically and uniquely bound to cardiac muscle. The cardiac skeleton
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through t ...
also includes the separating septa of the heart chambers – the interventricular septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backwar ...
and the atrioventricular septum. Collagen contribution to the measure of cardiac performance summarily represents a continuous torsional force opposed to the fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids ( liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them.
It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and ...
of blood pressure emitted from the heart. The collagenous structure that divides the upper chambers of the heart from the lower chambers is an impermeable membrane that excludes both blood and electrical impulses through typical physiological means. With support from collagen, atrial fibrillation never deteriorates to ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and n ...
. Collagen is layered in variable densities with smooth muscle mass. The mass, distribution, age and density of collagen all contribute to the compliance required to move blood back and forth. Individual cardiac valvular leaflets are folded into shape by specialized collagen under variable pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
. Gradual calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
deposition within collagen occurs as a natural function of aging. Calcified points within collagen matrices show contrast in a moving display of blood and muscle, enabling methods of cardiac imaging technology to arrive at ratios essentially stating blood in ( cardiac input) and blood out ( cardiac output). Pathology of the collagen underpinning of the heart is understood within the category of connective tissue disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
.
Bone grafts
As the skeleton forms the structure of the body, it is vital that it maintains its strength, even after breaks and injuries. Collagen is used in bone grafting as it has a triple helical structure, making it a very strong molecule. It is ideal for use in bones, as it does not compromise the structural integrity of the skeleton. The triple helical structure of collagen prevents it from being broken down by enzymes, it enables adhesiveness of cells and it is important for the proper assembly of the extracellular matrix.Tissue regeneration
Collagen scaffolds are used in tissue regeneration, whether in sponges, thin sheets, gels, or fibers. Collagen has favorable properties for tissue regeneration, such as pore structure, permeability, hydrophilicity, and stability in vivo. Collagen scaffolds also support deposition of cells, such as osteoblasts and fibroblasts, and once inserted, facilitate growth to proceed normally.Reconstructive surgical uses
Collagens are widely employed in the construction ofartificial skin Artificial skin is a collagen scaffold that induces regeneration of skin in mammals such as humans. The term was used in the late 1970s and early 1980s to describe a new treatment for massive burns. It was later discovered that treatment of deep ski ...
substitutes used in the management of severe burns and wounds. These collagens may be derived from bovine, equine, porcine, or even human sources; and are sometimes used in combination with silicones, glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case ...
s, fibroblasts, growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for regul ...
s and other substances.
Wound healing
Collagen is one of the body's key natural resources and a component of skin tissue that can benefit all stages ofwound healing
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue.
In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier again ...
. When collagen is made available to the wound bed, closure can occur. Wound deterioration, followed sometimes by procedures such as amputation, can thus be avoided.
Collagen is a natural product and is thus used as a natural wound dressing and has properties that artificial wound dressings do not have. It is resistant against bacteria, which is of vital importance in a wound dressing. It helps to keep the wound sterile, because of its natural ability to fight infection. When collagen is used as a burn dressing, healthy granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any siz ...
is able to form very quickly over the burn, helping it to heal rapidly.
Throughout the four phases of wound healing, collagen performs the following functions:
* Guiding function: Collagen fibers serve to guide fibroblasts. Fibroblasts migrate along a connective tissue matrix.
* Chemotactic
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + '' taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
properties: The large surface area available on collagen fibers can attract fibrogenic cells which help in healing.
* Nucleation: Collagen, in the presence of certain neutral salt molecules, can act as a nucleating agent causing formation of fibrillar structures.
* Hemostatic
An antihemorrhagic (antihæmorrhagic) agent is a substance that promotes hemostasis (stops bleeding). It may also be known as a hemostatic (also spelled haemostatic) agent.
Antihemorrhagic agents used in medicine have various mechanisms of action: ...
properties: Blood platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s interact with the collagen to make a hemostatic plug.
Cosmetic medicine
Bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship betwe ...
collagen is widely used in dermal filler
Injectable filler (injectable cosmetic filler, injectable facial filler) is a soft tissue filler injected into the skin at different depths to help fill in facial wrinkles, provide facial volume, and augment facial features: restoring a smoother ap ...
s for aesthetic correction of wrinkles and skin aging Most medical bovine collagen is derived from young beef cattle from certified BSE-free animals. Most manufacturers use donor animals from either "closed herds", or from countries which have never had a reported case of BSE, such as Australia, Brazil, and New Zealand.
Basic research
Collagen is used in laboratory studies for cell culture, studying cell behavior and cellular interactions with theextracellular environment
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
. Collagen is also widely used as a bioink for 3D bioprinting and biofabrication of 3D tissue models.
Biology
The collagen protein is composed of a triple helix, which generally consists of two identical chains (α1) and an additional chain that differs slightly in its chemical composition (α2). The amino acid composition of collagen is atypical for proteins, particularly with respect to its highhydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelati ...
content. The most common motifs in the amino acid sequence of collagen are glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid ( carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinog ...
- proline-X and glycine-X-hydroxyproline, where X is any amino acid other than glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid ( carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinog ...
, proline or hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelati ...
. The average amino acid composition for fish and mammal skin is given.
Synthesis
First, a three-dimensional stranded structure is assembled, with the amino acids glycine and proline as its principal components. This is not yet collagen but its precursor, procollagen. Procollagen is then modified by the addition ofhydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
groups to the amino acids proline and lysine. This step is important for later glycosylation and the formation of the triple helix structure of collagen. Because the hydroxylase enzymes that perform these reactions require vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) ...
as a cofactor, a long-term deficiency in this vitamin results in impaired collagen synthesis and scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding ...
. These hydroxylation reactions are catalyzed by two different enzymes: prolyl-4-hydroxylase and lysyl-hydroxylase. The reaction consumes one ascorbate molecule per hydroxylation.
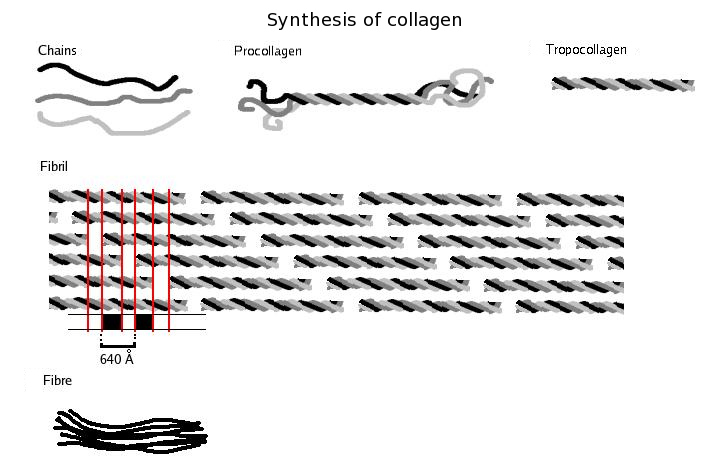
The synthesis of collagen occurs inside and outside of the cell. The formation of collagen which results in fibrillary collagen (most common form) is discussed here. Meshwork collagen, which is often involved in the formation of filtration systems, is the other form of collagen. All types of collagens are triple helices, and the differences lie in the make-up of the alpha peptides created in step 2.
# Transcription of mRNA: About 44 genes are associated with collagen formation, each coding for a specific mRNA sequence, and typically have the "''COL''" prefix. The beginning of collagen synthesis begins with turning on genes which are associated with the formation of a particular alpha peptide (typically alpha 1, 2 or 3).
# Pre-pro-peptide formation: Once the final mRNA exits from the cell nucleus and enters into the cytoplasm, it links with the ribosomal subunits and the process of translation occurs. The early/first part of the new peptide is known as the signal sequence. The signal sequence on the N-terminal of the peptide is recognized by a signal recognition particle on the endoplasmic reticulum, which will be responsible for directing the pre-pro-peptide
A protein precursor, also called a pro-protein or pro-peptide, is an inactive protein (or peptide) that can be turned into an active form by post-translational modification, such as breaking off a piece of the molecule or adding on another molecule ...
into the endoplasmic reticulum. Therefore, once the synthesis of new peptide is finished, it goes directly into the endoplasmic reticulum for post-translational processing. It is now known as preprocollagen.
# Pre-pro-peptide to pro-collagen: Three modifications of the pre-pro-peptide occur leading to the formation of the alpha peptide:
## The signal peptide on the N-terminal is removed, and the molecule is now known as ''propeptide'' (not procollagen).
## Hydroxylation of lysines and prolines on propeptide by the enzymes 'prolyl hydroxylase' and 'lysyl hydroxylase' (to produce hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine) occurs to aid cross-linking of the alpha peptides. This enzymatic step requires vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) ...
as a cofactor. In scurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding ...
, the lack of hydroxylation of prolines and lysines causes a looser triple helix (which is formed by three alpha peptides).
## Glycosylation occurs by adding either glucose or galactose monomers onto the hydroxyl groups that were placed onto lysines, but not on prolines.
## Once these modifications have taken place, three of the hydroxylated and glycosylated propeptides twist into a triple helix forming procollagen. Procollagen still has unwound ends, which will be later trimmed. At this point, the procollagen is packaged into a transfer vesicle destined for the Golgi apparatus.
# Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
modification: In the Golgi apparatus, the procollagen goes through one last post-translational modification before being secreted out of the cell. In this step, oligosaccharides (not monosaccharides as in step 3) are added, and then the procollagen is packaged into a secretory vesicle destined for the extracellular space.
# Formation of tropocollagen: Once outside the cell, membrane bound enzymes known as collagen peptidases, remove the "loose ends" of the procollagen molecule. What is left is known as tropocollagen. Defects in this step produce one of the many collagenopathies known as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This step is absent when synthesizing type III, a type of fibrillar collagen.
# Formation of the collagen fibril: lysyl oxidase, an extracellular copper-dependent enzyme, produces the final step in the collagen synthesis pathway. This enzyme acts on lysines and hydroxylysines producing aldehyde groups, which will eventually undergo covalent bonding between tropocollagen molecules. This polymer of tropocollagen is known as a collagen fibril.
Amino acids
Collagen has an unusualamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
composition and sequence:
* Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid ( carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinog ...
is found at almost every third residue
Residue may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
* An amino acid, within a peptide chain
* Crop residue, materials left after agricultural processes
* Pesticide residue, refers to the pesticides that may remain on or in food after they are applied ...
.
* Proline makes up about 17% of collagen.
* Collagen contains two uncommon derivative amino acids not directly inserted during translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
. These amino acids are found at specific locations relative to glycine and are modified post-translationally by different enzymes, both of which require vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) ...
as a cofactor.
** Hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelati ...
derived from proline
** Hydroxylysine derived from lysine – depending on the type of collagen, varying numbers of hydroxylysines are glycosylated (mostly having disaccharide
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar or ''biose'') is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are simple sugars soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, la ...
s attached).
Cortisol stimulates degradation
Degradation may refer to:
Science
* Degradation (geology), lowering of a fluvial surface by erosion
* Degradation (telecommunications), of an electronic signal
* Biodegradation of organic substances by living organisms
* Environmental degradatio ...
of (skin) collagen into amino acids.
Collagen I formation
Most collagen forms in a similar manner, but the following process is typical for type I: # Inside the cell ## Two types of alpha chains – alpha-1 and alpha 2, are formed duringtranslation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
on ribosomes along the rough endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ( ...
(RER). These peptide chains known as preprocollagen, have registration peptides on each end and a signal peptide.
## Polypeptide chains are released into the lumen of the RER.
## Signal peptides are cleaved inside the RER and the chains are now known as pro-alpha chains.
## Hydroxylation of lysine and proline amino acids occurs inside the lumen. This process is dependent on and consumes ascorbic acid (vitamin C) as a cofactor.
## Glycosylation of specific hydroxylysine residues occurs.
## Triple alpha helical structure is formed inside the endoplasmic reticulum from two alpha-1 chains and one alpha-2 chain.
## Procollagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
is shipped to the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles ...
, where it is packaged and secreted into extracellular space by exocytosis.
# Outside the cell
## Registration peptides are cleaved and tropocollagen is formed by procollagen peptidase
Procollagen peptidase (, ''procollagen N-terminus, N-terminal peptidase'', ''procollagen aminopeptidase'', ''aminoprocollagen peptidase'', ''aminoterminal procollagen peptidase'', ''procollagen aminoterminal protease'', ''procollagen N-terminal pr ...
.
## Multiple tropocollagen molecules form collagen fibrils, via covalent cross-linking (aldol reaction
The aldol reaction is a means of forming carbon–carbon bonds in organic chemistry.
Discovered independently by the Russian chemist Alexander Borodin in 1869 and by the French chemist Charles-Adolphe Wurtz in 1872, the reaction combines two c ...
) by lysyl oxidase which links hydroxylysine and lysine residues. Multiple collagen fibrils form into collagen fibers.
## Collagen may be attached to cell membranes via several types of protein, including fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collage ...
, laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins ...
, fibulin
Fibulin (FY-beau-lin) (now known as Fibulin-1 FBLN1) is the prototypic member of a multigene family, currently with seven members. Fibulin-1 is a calcium-binding glycoprotein. In vertebrates, fibulin-1 is found in blood and extracellular matr ...
and integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
.
Synthetic pathogenesis
Vitamin C deficiency causesscurvy
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding ...
, a serious and painful disease in which defective collagen prevents the formation of strong connective tissue. Gums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lin ...
deteriorate and bleed, with loss of teeth; skin discolors, and wounds do not heal. Prior to the 18th century, this condition was notorious among long-duration military, particularly naval, expeditions during which participants were deprived of foods containing vitamin C.
An autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blo ...
or rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
may attack healthy collagen fibers.
Many bacteria and viruses secrete virulence factor
Virulence factors (preferably known as pathogenicity factors or effectors in plant science) are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa) to achieve the following ...
s, such as the enzyme collagenase
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as ''Clostridium''. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of ...
, which destroys collagen or interferes with its production.
Molecular structure
A single collagen molecule, tropocollagen, is used to make up larger collagen aggregates, such as fibrils. It is approximately 300 nm long and 1.5 nm in diameter, and it is made up of three polypeptide strands (called alpha peptides, see step 2), each of which has the conformation of a left-handedhelix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helic ...
– this should not be confused with the right-handed alpha helix. These three left-handed helices are twisted together into a right-handed triple helix or "super helix", a cooperative quaternary structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also refe ...
stabilized by many hydrogen bonds. With type I collagen and possibly all fibrillar collagens, if not all collagens, each triple-helix associates into a right-handed super-super-coil referred to as the collagen microfibril. Each microfibril is interdigitated with its neighboring microfibrils to a degree that might suggest they are individually unstable, although within collagen fibrils, they are so well ordered as to be crystalline.
 A distinctive feature of collagen is the regular arrangement of
A distinctive feature of collagen is the regular arrangement of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
s in each of the three chains of these collagen subunits. The sequence often follows the pattern Gly- Pro-X or Gly-X- Hyp, where X may be any of various other amino acid residues. Proline or hydroxyproline constitute about 1/6 of the total sequence. With glycine accounting for the 1/3 of the sequence, this means approximately half of the collagen sequence is not glycine, proline or hydroxyproline, a fact often missed due to the distraction of the unusual GX1X2 character of collagen alpha-peptides. The high glycine content of collagen is important with respect to stabilization of the collagen helix as this allows the very close association of the collagen fibers within the molecule, facilitating hydrogen bonding and the formation of intermolecular cross-links. This kind of regular repetition and high glycine content is found in only a few other fibrous proteins, such as silk fibroin
Fibroin is an insoluble protein present in silk produced by numerous insects, such as the larvae of ''Bombyx mori'', and other moth genera such as '' Antheraea'', '' Cricula'', '' Samia'' and '' Gonometa''. Silk in its raw state consists of tw ...
.
Collagen is not only a structural protein. Due to its key role in the determination of cell phenotype, cell adhesion, tissue regulation, and infrastructure, many sections of its non-proline-rich regions have cell or matrix association/regulation roles. The relatively high content of proline and hydroxyproline rings, with their geometrically constrained carboxyl
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic ...
and (secondary) amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent ...
groups, along with the rich abundance of glycine, accounts for the tendency of the individual polypeptide strands to form left-handed helices spontaneously, without any intrachain hydrogen bonding.
Because glycine is the smallest amino acid with no side chain, it plays a unique role in fibrous structural proteins. In collagen, Gly is required at every third position because the assembly of the triple helix puts this residue at the interior (axis) of the helix, where there is no space for a larger side group than glycine's single hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
atom. For the same reason, the rings of the Pro and Hyp must point outward. These two amino acids help stabilize the triple helix – Hyp even more so than Pro; a lower concentration of them is required in animals such as fish, whose body temperatures are lower than most warm-blooded animals. Lower proline and hydroxyproline contents are characteristic of cold-water, but not warm-water fish; the latter tend to have similar proline and hydroxyproline contents to mammals. The lower proline and hydroxproline contents of cold-water fish and other poikilotherm
A poikilotherm () is an animal whose internal temperature varies considerably. Poikilotherms have to survive and adapt to environmental stress. One of the most important stressors is temperature change, which can lead to alterations in membrane ...
animals leads to their collagen having a lower thermal stability than mammalian collagen. This lower thermal stability means that gelatin derived from fish collagen is not suitable for many food and industrial applications.
The tropocollagen subunits spontaneously self-assemble, with regularly staggered ends, into even larger arrays in the extracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
spaces of tissues. Additional assembly of fibrils is guided by fibroblasts, which deposit fully formed fibrils from fibripositors. In the fibrillar collagens, molecules are staggered to adjacent molecules by about 67 nm (a unit that is referred to as ‘D’ and changes depending upon the hydration state of the aggregate). In each D-period repeat of the microfibril, there is a part containing five molecules in cross-section, called the "overlap", and a part containing only four molecules, called the "gap". These overlap and gap regions are retained as microfibrils assemble into fibrils, and are thus viewable using electron microscopy. The triple helical tropocollagens in the microfibrils are arranged in a quasihexagonal packing pattern.
 There is some
There is some covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms ...
crosslinking within the triple helices, and a variable amount of covalent crosslinking between tropocollagen helices forming well organized aggregates (such as fibrils). Larger fibrillar bundles are formed with the aid of several different classes of proteins (including different collagen types), glycoproteins, and proteoglycans to form the different types of mature tissues from alternate combinations of the same key players. Collagen's insolubility was a barrier to the study of monomeric collagen until it was found that tropocollagen from young animals can be extracted because it is not yet fully crosslinked. However, advances in microscopy techniques (i.e. electron microscopy (EM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM)) and X-ray diffraction have enabled researchers to obtain increasingly detailed images of collagen structure ''in situ''. These later advances are particularly important to better understanding the way in which collagen structure affects cell–cell and cell–matrix communication and how tissues are constructed in growth and repair and changed in development and disease. For example, using AFM–based nanoindentation it has been shown that a single collagen fibril is a heterogeneous material along its axial direction with significantly different mechanical properties in its gap and overlap regions, correlating with its different molecular organizations in these two regions.
Collagen fibrils/aggregates are arranged in different combinations and concentrations in various tissues to provide varying tissue properties. In bone, entire collagen triple helices lie in a parallel, staggered array. 40 nm gaps between the ends of the tropocollagen subunits (approximately equal to the gap region) probably serve as nucleation sites for the deposition of long, hard, fine crystals of the mineral component, which is hydroxylapatite (approximately) Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6. Type I collagen gives bone its tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
.
Associated disorders
Collagen-related diseases most commonly arise from genetic defects or nutritional deficiencies that affect the biosynthesis, assembly, posttranslational modification, secretion, or other processes involved in normal collagen production. In addition to the above-mentioned disorders, excessive deposition of collagen occurs inscleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas ...
.
Diseases
One thousand mutations have been identified in 12 out of more than 20 types of collagen. These mutations can lead to various diseases at the tissue level.Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other organs—may b ...
– Caused by a mutation in ''type 1 collagen'', dominant autosomal disorder, results in weak bones and irregular connective tissue, some cases can be mild while others can be lethal. Mild cases have lowered levels of collagen type 1 while severe cases have structural defects in collagen.
Chondrodysplasia
Osteochondrodysplasia is a general term for a disorder of the development (dysplasia) of bone ("osteo") and cartilage ("chondro"). Osteochondrodysplasias are rare diseases. About 1 in 5,000 babies are born with some type of skeletal dysplasia. Non ...
s – Skeletal disorder believed to be caused by a mutation in ''type 2 collagen'', further research is being conducted to confirm this.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome – Thirteen different types of this disorder, which lead to deformities in connective tissue, are known. Some of the rarer types can be lethal, leading to the rupture of arteries. Each syndrome is caused by a different mutation. For example, the vascular type (vEDS) of this disorder is caused by a mutation in ''collagen type 3''.
Alport syndrome
Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000-10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect ...
– Can be passed on genetically, usually as X-linked dominant, but also as both an autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive disorder, sufferers have problems with their kidneys and eyes, loss of hearing can also develop during the childhood or adolescent years.
Knobloch syndrome – Caused by a mutation in the COL18A1 gene that codes for the production of collagen XVIII. Patients present with protrusion of the brain tissue and degeneration of the retina; an individual who has family members suffering from the disorder is at an increased risk of developing it themselves since there is a hereditary link.
Characteristics
Collagen is one of the long, fibrous structural proteins whose functions are quite different from those ofglobular protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (formi ...
s, such as enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s. Tough bundles of collagen called ''collagen fibers'' are a major component of the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide s ...
that supports most tissues and gives cells structure from the outside, but collagen is also found inside certain cells. Collagen has great tensile strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or F_\text within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials t ...
, and is the main component of fascia, cartilage, ligaments, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
and skin. Along with elastin and soft keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
, it is responsible for skin strength and elasticity, and its degradation leads to wrinkle
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of ...
s that accompany aging.Dermal Fillers , The Ageing Skin. Pharmaxchange.info. Retrieved on 21 April 2013. It strengthens
blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s and plays a role in tissue development. It is present in the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
and lens of the eye in crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
line form. It may be one of the most abundant proteins in the fossil record, given that it appears to fossilize frequently, even in bones from the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
and Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
.
Uses
150px, A salami and the collagen casing (below) it came in Collagen has a wide variety of applications, from food to medical. In the medical industry it is used in cosmetic surgery and burn surgery. In the food sector, one usage example is in casings for sausages. If collagen is subject to sufficient denaturation, e.g. by heating, the three tropocollagen strands separate partially or completely into globular domains, containing a different secondary structure to the normal collagen polyproline II (PPII), e.g.random coil
In polymer chemistry, a random coil is a conformation of polymers where the monomer subunits are oriented randomly while still being bonded to adjacent units. It is not one specific shape, but a statistical distribution of shapes for all the ch ...
s. This process describes the formation of gelatin, which is used in many foods, including flavored gelatin dessert
Gelatin desserts (also Jelly or Jello) are desserts made with a sweetened and flavoured processed collagen product (gelatin). This kind of dessert was first recorded as jelly by Hannah Glasse in her 18th-century book ''The Art of Cookery'', a ...
s. Besides food, gelatin has been used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and photography industries. It is also used as a dietary supplement.
From the Greek for glue, ''kolla'', the word collagen means " glue producer" and refers to the early process of boiling the skin and sinews of horses and other animals to obtain glue. Collagen adhesive was used by Egyptians about 4,000 years ago, and Native Americans used it in bows about 1,500 years ago. The oldest glue in the world, carbon-dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
as more than 8,000 years old, was found to be collagen – used as a protective lining on rope baskets and embroidered
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on c ...
fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not th ...
s, to hold utensils together, and in crisscross decorations on human skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
s. Collagen normally converts to gelatin, but survived due to dry conditions. Animal glues are thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
, softening again upon reheating, so they are still used in making musical instruments such as fine violins and guitars, which may have to be reopened for repairs – an application incompatible with tough, synthetic plastic adhesives, which are permanent. Animal sinews and skins, including leather, have been used to make useful articles for millennia.
Gelatin-resorcinol
Resorcinol (or resorcin) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)2. It is one of three isomeric benzenediols, the 1,3-isomer (or '' meta''-isomer). Resorcinol crystallizes from benzene as colorless needles that are readily soluble i ...
-formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section ...
glue (and with formaldehyde replaced by less-toxic pentanedial and ethanedial) has been used to repair experimental incisions in rabbit lungs.
History
The molecular and packing structures of collagen eluded scientists over decades of research. The first evidence that it possesses a regular structure at the molecular level was presented in the mid-1930s. Research then concentrated on the conformation of the collagenmonomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; '' mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
...
, producing several competing models, although correctly dealing with the conformation of each individual peptide chain. The triple-helical "Madras" model, proposed by G. N. Ramachandran in 1955, provided an accurate model of quaternary structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also refe ...
in collagen. This model was supported by further studies of higher resolution in the late 20th century.
The packing structure of collagen has not been defined to the same degree outside of the fibrillar collagen types, although it has been long known to be hexagonal. As with its monomeric structure, several conflicting models propose either that the packing arrangement of collagen molecules is 'sheet-like', or is microfibril A microfibril is a very fine fibril, or fiber-like strand, consisting of glycoproteins and cellulose. It is usually, but not always, used as a general term in describing the structure of protein fiber, e.g. hair and sperm tail. Its most frequently ...
lar. The microfibrillar structure of collagen fibrils in tendon, cornea and cartilage was imaged directly by electron microscopy in the late 20th century and early 21st century. The microfibrillar structure of rat tail tendon was modeled as being closest to the observed structure, although it oversimplified the topological progression of neighboring collagen molecules, and so did not predict the correct conformation of the discontinuous D-periodic pentameric arrangement termed ''microfibril''.
See also
* Collagen hybridizing peptide, a peptide that can bind to denatured collagen * Hypermobility spectrum disorder * Metalloprotease inhibitor *Osteoid
In histology, osteoid is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue. Osteoblasts begin the process of forming bone tissue by secreting the osteoid as several specific proteins. When ...
, collagen-containing component of bone
References
{{Authority control * Structural proteins Edible thickening agents Aging-related proteins