Cocaine Addiction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cocaine dependence is a
/ref> The symptoms of cocaine withdrawal range from moderate to severe:
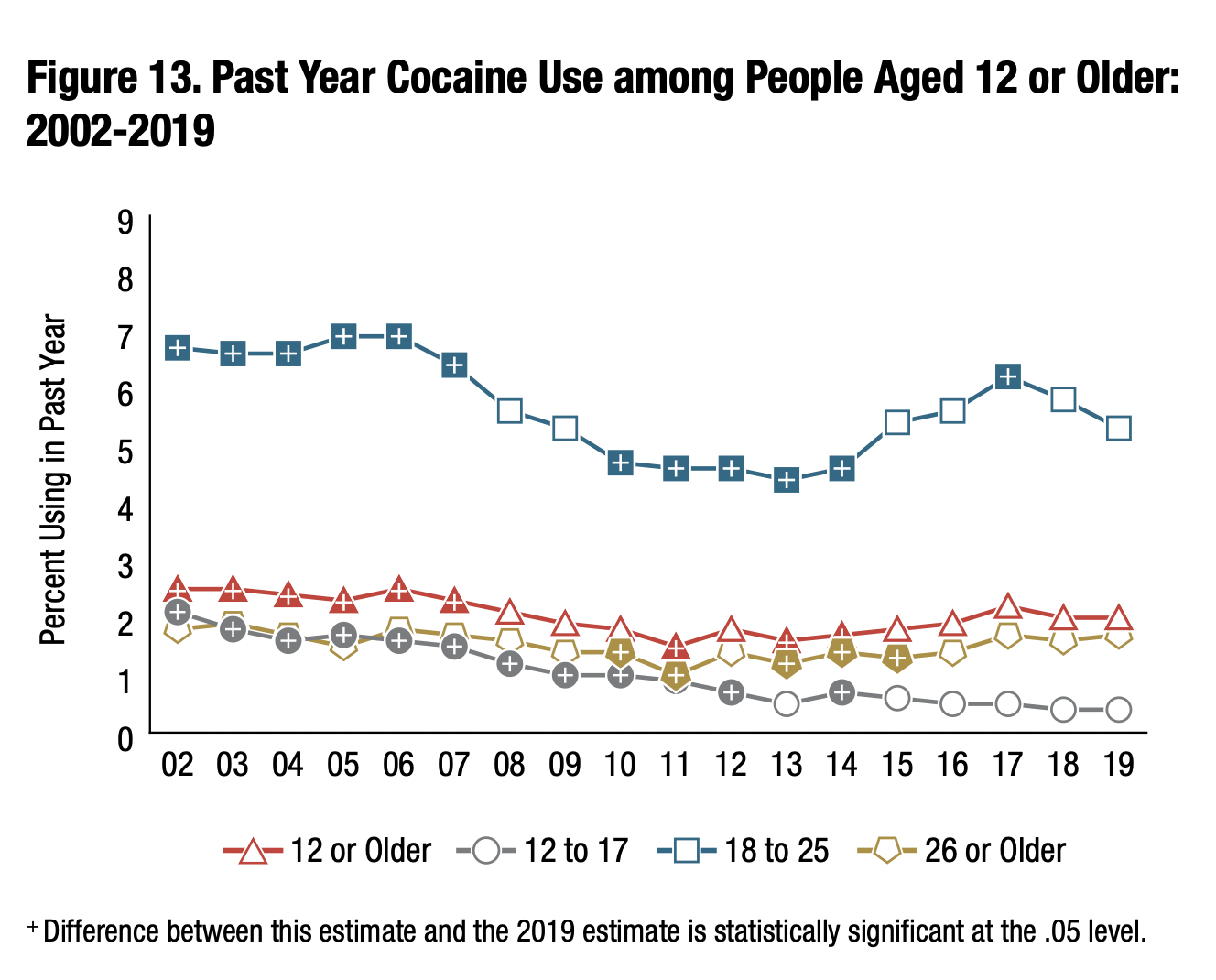 In the United States, past year cocaine users in 2019 was 5.5 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 97,000 users; ages 18–25 had 1.8 million users and ages 26 or older had 3.6 million users.
Past year cocaine users with a cocaine use disorder in 2019 was 1 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 5,000 people with a cocaine use disorder; ages 18–25 had 250,000 people with a cocaine use disorder and ages 26 or older had 756,000 people with a cocaine use disorder
In the United States, cocaine use overdose deaths have been on the rise and in 2019, the CDC reported over 16,000 deaths from cocaine overdose.
In the United States, past year cocaine users in 2019 was 5.5 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 97,000 users; ages 18–25 had 1.8 million users and ages 26 or older had 3.6 million users.
Past year cocaine users with a cocaine use disorder in 2019 was 1 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 5,000 people with a cocaine use disorder; ages 18–25 had 250,000 people with a cocaine use disorder and ages 26 or older had 756,000 people with a cocaine use disorder
In the United States, cocaine use overdose deaths have been on the rise and in 2019, the CDC reported over 16,000 deaths from cocaine overdose.
neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal ...
disorder that is characterized by withdrawal symptoms
Drug withdrawal, drug withdrawal syndrome, or substance withdrawal syndrome, is the group of symptoms that occur upon the abrupt discontinuation or decrease in the intake of pharmaceutical or recreational drugs.
In order for the symptoms of wit ...
upon cessation from cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from t ...
use. It also often coincides with cocaine addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
which is a biopsychosocial
Biopsychosocial models are a class of trans-disciplinary models which look at the interconnection between biology, psychology, and socio-environmental factors. These models specifically examine how these aspects play a role in topics ranging from ...
disorder characterized by persistent use of cocaine and/or crack despite substantial harm and adverse consequences. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed., abbreviated DSM-5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiatric ...
), classifies problematic cocaine use as a " Stimulant use disorder". The International Classification of Diseases (11th rev., abbreviated ICD-11
The ICD-11 is the eleventh revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). It replaces the ICD-10 as the global standard for recording health information and causes of death. The ICD is developed and annually updated by the World H ...
), includes "Cocaine dependence" as a classification (diagnosis) under "Disorders due to use of cocaine".
The use of cocaine creates euphoria and high amounts of energy. If taken in large doses, it is possible to cause mood swings
A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of mood. Such changes can play a positive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning, or be disruptive. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as par ...
, paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concer ...
, insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
, psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
, high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, a fast heart rate
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (su ...
, panic attacks
Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear and discomfort that may include palpitations, sweating, chest pain or chest discomfort, shortness of breath, trembling, dizziness, numbness, confusion, or a feeling of impending doom or of losing ...
, seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with l ...
that are extremely difficult to control, cognitive impairments
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities),
* specific and restricted defic ...
and drastic changes in personality. Cocaine overdose may result in cardiovascular and brain damage, such as: status epilepticus, constricting blood vessels in the brain, causing strokes and constricting arteries in the heart; causing heart attacks
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may tr ...
.Cocaine Use and Its Effects/ref> The symptoms of cocaine withdrawal range from moderate to severe:
dysphoria
Dysphoria (; ) is a profound state of unease or dissatisfaction. It is the semantic opposite of euphoria. In a psychiatric context, dysphoria may accompany depression, anxiety, or agitation.
In psychiatry
Intense states of distress and uneas ...
, depression, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, decreased libido, psychological and physical weakness, pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
, and compulsive cravings.
Signs and symptoms
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant known to make users feel energetic, cheerful, talkative, etc. In time, negative side effects include increased body temperature, irregular or rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, increased risk of heart attacks, strokes and even sudden death from cardiac arrest. Many people who habitually use cocaine develop a transient, manic-like condition similar toamphetamine psychosis
Stimulant psychosis is a mental disorder characterized by psychotic symptoms (such as hallucinations, paranoid ideation, delusions, disorganized thinking, grossly disorganized behaviour) which involves and typically occurs following an overdose or ...
and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdra ...
, whose symptoms include aggression, severe paranoia, restlessness, confusion and tactile hallucinations; which can include the feeling of something crawling under the skin ( formication), also known as "coke bugs", during binges. Different ingestion techniques have their own symptoms that accompany them. Snorting it can cause a loss of sense of smell, nose bleeds, problems swallowing and an inflamed, runny nose. Smoking it causes lung damage and injecting it puts users at risk of contracting infectious diseases like HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
and hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
. Heavy users of cocaine have also reported having thoughts of suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
, unusual weight loss, trouble maintaining relationships, and an unhealthy, pale appearance.
Withdrawal symptoms
When used habitually, cocaine, because of its highly addictive nature, can change brain structure and function. Circuits within the brain structure, that play a part in stress signals become more sensitive. When cocaine is not being used this increases an individual's displeasure and negative moods. In 1986, Gawin and Kleber led an important study on the withdrawal symptoms of cocaine users. In this study, three distinct phases were reported. These phases are the 'crash', 'withdrawal' and 'extinction'. The 'crash' phase or phase 1 occurs directly after cocaine is not being used anymore. Withdrawal symptoms for this phase are exhaustion, hypersomnia, no cravings to use,dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD), is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically a disorder primarily of mood, consisting of similar cognitive and physical problems as major depressive disorder, but with lo ...
, increased appetite, restlessness, and irritability. The second phase, or 'withdrawal' phase occurs 1–10 weeks after cocaine users quit, symptoms include: lethargy
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overwo ...
, anxiety, erratic sleep, strong craving, emotional lability, irritability, depression, poor concentration, and bowel issues. Finally the last phase or the 'extinction' phase occurs up to 28 weeks after discontinued use, symptoms include: episodic cravings and some dysphoria
Dysphoria (; ) is a profound state of unease or dissatisfaction. It is the semantic opposite of euphoria. In a psychiatric context, dysphoria may accompany depression, anxiety, or agitation.
In psychiatry
Intense states of distress and uneas ...
.
Epidemiology and prevalence rates
 In the United States, past year cocaine users in 2019 was 5.5 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 97,000 users; ages 18–25 had 1.8 million users and ages 26 or older had 3.6 million users.
Past year cocaine users with a cocaine use disorder in 2019 was 1 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 5,000 people with a cocaine use disorder; ages 18–25 had 250,000 people with a cocaine use disorder and ages 26 or older had 756,000 people with a cocaine use disorder
In the United States, cocaine use overdose deaths have been on the rise and in 2019, the CDC reported over 16,000 deaths from cocaine overdose.
In the United States, past year cocaine users in 2019 was 5.5 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 97,000 users; ages 18–25 had 1.8 million users and ages 26 or older had 3.6 million users.
Past year cocaine users with a cocaine use disorder in 2019 was 1 million for people aged 12 or older. When broken into age groups, ages 12–17 had 5,000 people with a cocaine use disorder; ages 18–25 had 250,000 people with a cocaine use disorder and ages 26 or older had 756,000 people with a cocaine use disorder
In the United States, cocaine use overdose deaths have been on the rise and in 2019, the CDC reported over 16,000 deaths from cocaine overdose.
Risk
A study consisting of 1,081 U.S. residents who had first usedcocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from t ...
within the previous 24 months was conducted. It was found that the risk of becoming dependent
A dependant is a person who relies on another as a primary source of income. A common-law spouse who is financially supported by their partner may also be included in this definition. In some jurisdictions, supporting a dependant may enabl ...
on cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from t ...
within two years of first use was 5–6%. The risk of becoming dependent within 10 years of first use increased to 15–16%. These were the aggregate rates for all types of use considered, such as smoking, snorting, and injecting. Among recent-onset users individual rates of dependency were higher for smoking (3.4 times) and much higher for injecting. Women were 3.3 times more likely to become dependent, compared with men. Users who started at ages 12 or 13 were four times as likely to become dependent compared to those who started between ages 18 and 20.
However, a study of non-deviantThe study's authors stated that they wanted to know which effects and consequences of cocaine use would become visible with persons who are mainstream citizens or as close to that social stratum as possible users in Amsterdam found a "relative absence of destructive and compulsive use patterns over a ten year period" and concluded that cocaine users can and do exercise control. "Our respondents applied two basic types of controls to themselves: 1) restricting use to certain situations and to emotional states in which cocaine's effects would be most positive, and 2) limiting mode of ingestion to snorting of modest amounts of cocaine, staying below 2.5 grams a week for some, and below 0.5 grams a week for most. Nevertheless, those whose use level exceeded 2.5 grams a week all returned to lower levels".
Treatment
Therapy
Twelve-step program
Twelve-step programs are international mutual aid programs supporting recovery from substance addictions, behavioral addictions and compulsions. Developed in the 1930s, the first twelve-step program, Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), aided its memb ...
s such as Cocaine Anonymous Cocaine Anonymous (C.A.) is a twelve-step program formed in 1982 for people who seek recovery from drug addiction. It is patterned very closely after Alcoholics Anonymous, although the two groups are unaffiliated. While many C.A. members have been ...
(modeled on Alcoholics Anonymous
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is an international mutual aid fellowship of alcoholics dedicated to abstinence-based recovery from alcoholism through its spiritually-inclined Twelve Step program. Following its Twelve Traditions, AA is non-professi ...
) have been widely used to help those with cocaine addiction. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT), and motivational interviewing (MI) can be especially powerful approaches to treating cocaine addiction. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) combined with motivational therapy Motivational therapy (or MT) is a combination of humanistic treatment and enhanced cognitive-behavioral strategies, designed to treat substance use disorders. It is similar to motivational interviewing and motivational enhancement therapy.
Method
...
(MT) have proven to be more helpful than 12 step programs in treating cocaine dependency. However, both these approaches have a fairly low success rate as research suggests that the withdrawal symptoms can last for several weeks. For instance, one of the main predictors of a successful recovery is dependent on the number of continuous days a user is able to stay off of the substance. Alternative holistic treatments such as physical exercise and Meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally cal ...
has been proven effective in reducing cocaine cravings. Other non-pharmacological treatments such as acupuncture and hypnosis have been explored, but without conclusive results.
Medications
Numerous medications have been investigated for use in cocaine dependence, but , none of them were considered to be effective.Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of b ...
s, such as carbamazepine
Carbamazepine (CBZ), sold under the trade name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other m ...
, gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain. It is a first-line medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabeti ...
, lamotrigine, and topiramate
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence. For epilepsy this includes treatment for gener ...
, do not appear to be effective as treatment. Limited evidence suggests that antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but also in a range of ...
s are also ineffective for treatment of cocaine dependence. Few studies have examined bupropion (a novel antidepressant) for cocaine dependence; however, trials performed thus far have not shown it to be an effective form of treatment for this purpose.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) is a United States federal government research institute whose mission is to "advance science on the causes and consequences of drug use and addiction and to apply that knowledge to improve individual a ...
(NIDA) of the U.S. National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
is researching modafinil, a narcolepsy drug and mild stimulant, as a potential cocaine treatment. Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a naturally occurring psychoactive substance found in plants in the family Apocynaceae such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', '' Voacanga africana'', and '' Tabernaemontana undulata''. It is a psychedelic with dissociative properties.
Pre ...
has been under investigation as a treatment for cocaine dependency and is used in clinics in Mexico, the Netherlands and Canada. It was legal for a time in Costa Rica, but has been illegal since 2018. It is illegal to use in many countries, such as Sweden, Norway, the United Kingdom, and in the United States. Other medications that have been investigated for this purpose include acetylcysteine, baclofen
Baclofen, sold under the brand name Lioresal among others, is a medication used to treat muscle spasticity such as from a spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis. It may also be used for hiccups and muscle spasms near the end of life. It is ta ...
, and vanoxerine
Vanoxerine is a piperazine derivative which is a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). Vanoxerine binds to the target site on the dopamine transporter (DAT) ~ 50 times more strongly than cocaine, but simultaneously inhibits the ...
. Medications such as phenelzine
Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil, among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class which is primarily used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic. Along with tranylcypromine an ...
, have been used to cause an "aversion reaction" when administered with cocaine.
Vaccine
TA-CD TA-CD is an active vaccine developed by the Xenova Group which is used to negate the effects of cocaine, making it suitable for use in treatment of addiction. It is created by combining norcocaine with inactivated cholera toxin.
It works in much t ...
is an active vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifie ...
developed by the Xenova Group which is used to negate the effects of cocaine, making it suitable for use in treatment of addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use o ...
. It is created by combining norcocaine
Norcocaine is a minor metabolite of cocaine. It is the only confirmed pharmacologically active metabolite of cocaine, although salicylmethylecgonine
Salicylmethylecgonine, (2′-Hydroxycocaine) is a tropane derivative drug which is both a syn ...
with inactivated cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
toxin.
Research
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse gener ...
(TMS) is being studied as a treatment for cocaine addiction, although definitive evidence for efficacy does not yet exist.
Other research on rodents has suggested that cocaine use leads to complexes of dopamine transporter
The dopamine transporter (also dopamine active transporter, DAT, SLC6A3) is a membrane-spanning protein that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synaptic cleft back into cytosol. In the cytosol, other transporters sequester the dop ...
s, which build up tolerance to the drug. It's possible that future treatment for cocaine addiction might target those complexes.
See also
* SB-277011-A – a dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, used in the study of cocaine addiction. Where cocaine reduces the threshold for brain electrical self-stimulation in rats, an indication of cocaine's rewarding effects, SB-277011-A completely reverses this effect.Notes
References
Reference notes
External links
{{Psychoactive substance use Cocaine Substance dependence de:Kokain#Kokainismus