Cleopatra Selene II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cleopatra Selene II (
 Cleopatra Selene was born in approximately 40 BC in
Cleopatra Selene was born in approximately 40 BC in
by Chris Bennett He was named after his mother's dynasty and her younger brother. In naming her son, Cleopatra created a distinct Greek-Egyptian tone and emphasized her role as heiress of the Ptolemies in exile. * A daughter, whose name has not survived, is mentioned in an inscription. It has been suggested that she was the Drusilla who was the first wife of
 In 25 BC, Augustus decided to confer on Juba II and Selene the newly created
In 25 BC, Augustus decided to confer on Juba II and Selene the newly created
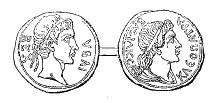 Cleopatra supported Mauretanian
Cleopatra supported Mauretanian
 The couple ruled Mauretania for almost two decades until Cleopatra's death at the age of 35. Controversy surrounds her exact date of death. The following epigram by Greek epigrammatist
The couple ruled Mauretania for almost two decades until Cleopatra's death at the age of 35. Controversy surrounds her exact date of death. The following epigram by Greek epigrammatist
''North Africa: the Roman Coast''
Chalfont St. Peter, Buckinghamshire: Bradt Travel Guides. , p. 11.
 Cleopatra was survived by her husband and their son Ptolemy, who ruled Mauretania together until Juba's death in AD 23. Ptolemy then reigned until 40, when he was executed by Emperor
Cleopatra was survived by her husband and their son Ptolemy, who ruled Mauretania together until Juba's death in AD 23. Ptolemy then reigned until 40, when he was executed by Emperor
Cleopatra's Daughter: While Antony and Cleopatra have been immortalised in history and in popular culture, their offspring have been all but forgotten. Their daughter, Cleopatra Selene, became an important ruler in her own right
. ''
Behind the Scenes of Cleopatra's Daughter
. *
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: Κλεοπάτρα Σελήνη; summer 40 BC – BC; the numeration is modern) was a Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
princess, Queen of Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
(briefly in 25 BC) and Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
(25 BC – 5 BC) and Queen of Cyrenaica (34 BC – 30 BC). She was an important royal woman in the early Augustan age.
Cleopatra Selene was the only daughter of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
Queen Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
of Egypt and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
Triumvir Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autoc ...
. In the Donations of Antioch and of Alexandria This article lists people, events and other subjects which are referred to as "of Alexandria".
of Alexandria
* Ammonius of Alexandria (3rd century AD), a Greek philosopher from Alexandria and one of the founders of Neoplatonism.
* Appian of Ale ...
, she was made queen of Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
. After Antony and Cleopatra's defeat at Actium and their suicides in Egypt in 30 BC, Selene and her brothers were brought to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and placed in the household of Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
's sister, Octavia the Younger
Octavia the Younger ( la, Octavia Minor; c. 66 BC – 11 BC) was the elder sister of the first Roman Emperor, Augustus (known also as Octavian), the half-sister of Octavia the Elder, and the fourth wife of Mark Antony. She was also the great-gran ...
, a former wife of her father.
Selene eventually married Juba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
of Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
and Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
. She had great influence in Mauretania's government decisions, especially regarding trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
and construction projects. During their reign, the country became extremely wealth
Wealth is the abundance of Value (economics), valuable financial assets or property, physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for financial transaction, transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the ...
y. The couple had a son and successor, Ptolemy of Mauretania
Ptolemy of Mauretania ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ''Ptolemaîos''; la, Gaius Iulius Ptolemaeus; 13 9BC–AD40) was the last Roman client king and ruler of Mauretania for Rome. He was the son of Juba II, the king of Numidia and a member ...
. Through their granddaughter Drusilla
Drusilla is a female given name deriving from the Roman cognomen Drusilla.
History
The name has its origin from the Latin cognomen (and later praenomen) ''Drusus'' which itself derived from the Greek ''drosos'' (dew). The diminutive "illa" t ...
, the Ptolemaic line intermarried into Roman nobility for many generations.
Early life
Childhood
 Cleopatra Selene was born in approximately 40 BC in
Cleopatra Selene was born in approximately 40 BC in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, as Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
's only daughter. Her second name ("moon" in Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
) opposes the second name of her twin
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
brother, Alexander Helios ("sun" in Ancient Greek). She was raised and highly educated in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
in a manner appropriate for a princess. The twins were formally acknowledged by their father, Triumvir Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autoc ...
, during a political meeting with their mother in 37 BC. Their younger brother, Ptolemy Philadelphos, was born a year later. Their mother most likely planned for Selene to marry her older half-brother Caesarion
Ptolemy XV Caesar). (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος ; 23 June 47 BC – August 30 BC), nicknamed Caesarion (, "Little Caesar"), was the last pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt, reigning with his mother Cleopatra from 2 September 44 BC until her de ...
, possibly the only biological son of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
, after whom he was named.
Over the next two years, Antony bestowed a great deal of land on Cleopatra and their children under his triumviral authority. In 34 BC, during the Donations of Alexandria, huge crowds assembled to witness the couple sit on golden thrones on a silver platform with Caesarion, Cleopatra Selene, Alexander Helios, and Ptolemy Philadelphus sitting on smaller ones below them. Antony declared Cleopatra to be Queen of Kings
King of Kings; grc-gre, Βασιλεὺς Βασιλέων, Basileùs Basiléōn; hy, արքայից արքա, ark'ayits ark'a; sa, महाराजाधिराज, Mahārājadhirāja; ka, მეფეთ მეფე, ''Mepet mepe'' ...
, Caesarion to be the true son of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
and King of Egypt, and proceeded to bestow kingdoms of their own upon Selene and her brothers. She was made ruler of Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
. Neither of the children were old enough to assume control of their lands, but it was clear that their parents intended they should do so in the future. This event, along with Antony's marriage to Cleopatra and divorce of Octavia Minor
Octavia the Younger ( la, Octavia Minor; c. 66 BC – 11 BC) was the elder sister of the first Roman Emperor, Augustus (known also as Octavian), the half-sister of Octavia the Elder, and the fourth wife of Mark Antony. She was also the great-gra ...
, older sister of Octavian (future Roman Emperor Caesar Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
), marked a turning point that led to the Final War of the Roman Republic
The War of Actium (32–30 BC) was the last civil war of the Roman Republic, fought between Mark Antony (assisted by Cleopatra and by extension Ptolemaic Egypt) and Octavian. In 32 BC, Octavian convinced the Roman Senate to declare war on the E ...
.
In 31 BC. during a naval battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
at Actium
Actium or Aktion ( grc, Ἄκτιον) was a town on a promontory in ancient Acarnania at the entrance of the Ambraciot Gulf, off which Octavian gained his celebrated victory, the Battle of Actium, over Antony and Cleopatra, on September 2, 31& ...
, Antony and Cleopatra were defeated by Octavian. By the time Octavian arrived in Egypt in the summer of 30 BC, the couple had sent the children away. Caesarion went to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, but en route he was betrayed by his tutor, intercepted by Roman forces and executed. Selene, Alexander, and Ptolemy Philadelphos went south to Thebes. Meanwhile, their parents committed suicide as Octavian and his army invaded Egypt. The deaths of their mother and Caesarion left Selene and Alexander nominally in charge of Egypt until the kingdom was officially annexed by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
two weeks later.
Life at Rome
Octavian captured Selene and her brothers, and took them toRome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. During his triumph
The Roman triumph (Latin triumphus) was a celebration for a victorious military commander in ancient Rome. For later imitations, in life or in art, see Trionfo. Numerous later uses of the term, up to the present, are derived directly or indirectl ...
, he paraded the twins dressed as the moon and the sun in heavy golden chains, behind an effigy
An effigy is an often life-size sculptural representation of a specific person, or a prototypical figure. The term is mostly used for the makeshift dummies used for symbolic punishment in political protests and for the figures burned in certai ...
of their mother clutching an asp to her arm. The chains were so heavy that the children were unable to walk in them, eliciting unexpected sympathy from many of the Roman onlookers.
Once Egypt had ceased to exist as an independent kingdom, there remained the question of what to do with Selene and her brothers. In the absence of any surviving relative, responsibility for the children passed to Augustus, who in turn gave the siblings to Octavia to be raised in her household on the Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; la, Collis Palatium or Mons Palatinus; it, Palatino ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." ...
. They were members of an extended family that included their half-brother Iullus Antonius
Iullus Antonius (43–2 BC) was a Roman magnate and poet. A son of Mark Antony and Fulvia, he was spared by the emperor Augustus after the civil wars of the Republic, and was married to the emperor's niece. He was later condemned as one of the l ...
(their father's son with his late wife Fulvia
Fulvia (; c. 83 BC – 40 BC) was an aristocratic Roman woman who lived during the Late Roman Republic. Fulvia's birth into an important political dynasty facilitated her relationships and, later on, marriages to Publius Clodius Pulcher, Gai ...
), their half-sisters, both called Antonia (daughters of their father with Octavia), and Octavia's older children from a previous marriage, Marcus Claudius Marcellus
Marcus Claudius Marcellus (; 270 – 208 BC), five times elected as consul of the Roman Republic, was an important Roman military leader during the Gallic War of 225 BC and the Second Punic War. Marcellus gained the most prestigious award a Roma ...
and his two sisters called Marcella. Between 26 and 20 BC, Cleopatra Selene is the only known surviving member of the Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
. Her brothers are not recorded in any known historical account and are presumed to have died, possibly from either illness or assassination.
Marriage and issue
Octavia arranged for Cleopatra Selene to marry the intellectual KingJuba II
Juba II or Juba of Mauretania (Latin: ''Gaius Iulius Iuba''; grc, Ἰóβας, Ἰóβα or ;Roller, Duane W. (2003) ''The World of Juba II and Kleopatra Selene'' "Routledge (UK)". pp. 1–3. . c. 48 BC – AD 23) was the son of Juba I and client ...
of Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
, whose father had committed suicide in 46 BC. He was sent to be raised in Caesar's household; on Caesar's death in 44 BC custody passed to Octavian, the future Augustus. The marriage likely took place in 25 BC and was commemorated in an epigram
An epigram is a brief, interesting, memorable, and sometimes surprising or satirical statement. The word is derived from the Greek "inscription" from "to write on, to inscribe", and the literary device has been employed for over two mille ...
that survives in its entirety:
The couple had two children:
* Ptolemy of Mauretania
Ptolemy of Mauretania ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ''Ptolemaîos''; la, Gaius Iulius Ptolemaeus; 13 9BC–AD40) was the last Roman client king and ruler of Mauretania for Rome. He was the son of Juba II, the king of Numidia and a member ...
born in 10 BC Cleopatra Seleneby Chris Bennett He was named after his mother's dynasty and her younger brother. In naming her son, Cleopatra created a distinct Greek-Egyptian tone and emphasized her role as heiress of the Ptolemies in exile. * A daughter, whose name has not survived, is mentioned in an inscription. It has been suggested that she was the Drusilla who was the first wife of
Antonius Felix
Antonius Felix (possibly Tiberius Claudius Antonius Felix, in Greek: ὁ Φῆλιξ; born circa 5–10) was the 4th Roman procurator of Judea Province in 52–60, in succession to Ventidius Cumanus.
Life
Felix was the younger brother of t ...
, but this woman was more likely a granddaughter through Ptolemy instead.
A hoard of Selene's coins has been dated at 17 AD. It is traditionally believed that she was alive to mint them, but this would mean that her husband married Princess Glaphyra of Cappadocia during Selene's lifetime. Historians generally assume that Juba wouldn't have taken a second wife as a thoroughly Romanized king, arguing that if he married Glaphyra before 4 AD, then his first wife must have already been dead. However, even contemporary client kings with Roman citizenship took multiple wives. It is possible that Selene and Juba separated for a time, but that their rift was mended after Juba's divorce from Glaphyra.
Queen of Mauretania
 In 25 BC, Augustus decided to confer on Juba II and Selene the newly created
In 25 BC, Augustus decided to confer on Juba II and Selene the newly created client
Client(s) or The Client may refer to:
* Client (business)
* Client (computing), hardware or software that accesses a remote service on another computer
* Customer or client, a recipient of goods or services in return for monetary or other valuabl ...
kingdom of Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
since Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
was, after a brief period of status as the Roman client kingdom under king Juba II (30 - 25 BC) once again directly annexed to the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
as the part of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. The young rulers renamed their new capital '' Caesarea'' (modern Cherchell, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
), in honor of the Emperor.
Mauretania was a vast territory, but lacked organization. Cleopatra Selene is said to have exercised great influence on the policies which Juba promoted. She imported
An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.
In international trade, the importation and exportation of goods are limited ...
many important advisers, scholars, and artists from her mother's royal court in Alexandria to serve in Caesarea. Through the couple's influence, the Mauretanian kingdom flourished.
Economy
 Cleopatra supported Mauretanian
Cleopatra supported Mauretanian trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
. The kingdom developed a significant export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ...
throughout the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
region, particularly with Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
. Their products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
included fish, grapes, pearls, figs, grain, wooden furniture and purple dye harvested from shellfish. Tingis
Tingis (Latin; grc-gre, Τίγγις ''Tíngis'') or Tingi ( Ancient Berber:), the ancient name of Tangier in Morocco, was an important Carthaginian, Moor, and Roman port on the Atlantic Ocean. It was eventually granted the status of a Roman colo ...
(modern Tangier
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the cap ...
), a town at the Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
(modern Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
), became a major trade centre. The value and quality of Mauretanian coins became recognised throughout the Roman Empire.
Building projects
Cleopatra's promotion of architecture marks a transition between the Hellenistic style and Roman. The construction and sculptural projects at Caesarea andVolubilis
Volubilis (; ar, وليلي, walīlī; ber, ⵡⵍⵉⵍⵉ, wlili) is a partly excavated Berber-Roman city in Morocco situated near the city of Meknes, and may have been the capital of the kingdom of Mauretania, at least from the time of Kin ...
display a mixture of Ancient Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
, Greek and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
architectural styles. These buildings included a lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
in the style of Pharos of Alexandria
The Lighthouse of Alexandria, sometimes called the Pharos of Alexandria (; Ancient Greek: ὁ Φάρος τῆς Ἀλεξανδρείας, contemporary Koine ), was a lighthouse built by the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, during the rei ...
in the harbour, a royal palace situated in the seafront, and numerous temples dedicated to Roman and Egyptian deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
. Her vigorous promotion of her mother's legacy stood in sharp contrast to the negative image being disseminated in contemporary Augustan poetry.
Death
 The couple ruled Mauretania for almost two decades until Cleopatra's death at the age of 35. Controversy surrounds her exact date of death. The following epigram by Greek epigrammatist
The couple ruled Mauretania for almost two decades until Cleopatra's death at the age of 35. Controversy surrounds her exact date of death. The following epigram by Greek epigrammatist Crinagoras of Mytilene
Crinagoras of Mytilene, also known as Crinogoras, sometimes spelt as Krinagorasis or Krinagoras (name in Greek: Κριναγόρας ὁ Μυτιληναῖος, 70 BC-18) was a Greek epigrammatist and ambassador, who lived in Rome as a court poet. ...
is considered to be her eulogy:
If this poem isn't simply literary license, Selene's death seems to have coincided with a lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth ...
. If so, astronomical correlation then can be used to help pinpoint the date of her death: Lunar eclipses occurred in 9, 8, 5 and 1 BC and in AD 3, 7, 10, 11 and 14. The event in 5 BC most closely resembles the description given in the eulogy. However, the date of her death is not ascertainable with any certainty. Zahi Hawass
Zahi Abass Hawass ( ar, زاهي حواس; born May 28, 1947) is an Egyptian archaeologist, Egyptologist, and former Minister of State for Antiquities Affairs, serving twice. He has also worked at archaeological sites in the Nile Delta, the Wes ...
, former Director of Egyptian Antiquities, believes Cleopatra died in 8 AD.
Selene was placed in the Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania
The Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania is a funerary monument located on the road between Cherchell and Algiers, in Tipaza Province, Algeria. The mausoleum is the tomb where the Numidian Berber King Juba II (son of Juba I of Numidia) and the Queen Cleop ...
in modern Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, built by her and Juba east of Caesarea and still visible. Juba died in 23 AD and was buried in the same tomb. There is a fragmentary inscription dedicated to the couple as the "King and Queen of Mauretania". Their remains have not been found at the site, perhaps due to tomb raids, possibly shortly after the mausoleum's construction; or because the structure was meant to serve as a memorial and not as a place of burial.Davies, Ethel (2009)''North Africa: the Roman Coast''
Chalfont St. Peter, Buckinghamshire: Bradt Travel Guides. , p. 11.
Legacy
 Cleopatra was survived by her husband and their son Ptolemy, who ruled Mauretania together until Juba's death in AD 23. Ptolemy then reigned until 40, when he was executed by Emperor
Cleopatra was survived by her husband and their son Ptolemy, who ruled Mauretania together until Juba's death in AD 23. Ptolemy then reigned until 40, when he was executed by Emperor Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germanicu ...
, his mother's great nephew, who was probably jealous of Mauretania's wealth
Wealth is the abundance of Value (economics), valuable financial assets or property, physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for financial transaction, transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the ...
. Caligula's successor, Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
, took advantage of Ptolemy's lack of heirs and assumed control of Mauretania, turning it into the Roman provinces of Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana (Latin for "Tangerine Mauretania") was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia (or Chella ...
. Thereafter, Cleopatra, Juba and Ptolemy were mostly forgotten.
One of the two satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope ...
s of the asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
(216) Kleopatra was named Cleoselene in her honor.
In fiction
* Cleopatra Selene is mentioned in the novels byRobert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was a British poet, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were both Celtic ...
, ''I, Claudius
''I, Claudius'' is a historical novel by English writer Robert Graves, published in 1934. Written in the form of an autobiography of the Roman Emperor Claudius, it tells the history of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and the early years of the Roma ...
'' and ''Claudius the God''.
* Cleopatra Selene is a significant character in Wallace Breem's historical novel ''The Legate's Daughter'' (1974), Phoenix/Orion Books Ltd.
* ''Cleopatra's Daughter'' by Andrea Ashton (1979) tells of Cleopatra Selene's early life.
*''The Memoirs of Cleopatra'' by Margaret George (1997) mentions Cleopatra Selene's birth and early life with her mother.
* ''Querida Alejandría'' by María García Esperón (Bogotá 2007: Norma, ), is a novel in the form of a letter by Cleopatra Selene to the people of Alexandria.
* ''Cleopatra's Daughter'' by Michelle Moran (2009) tells the story of Cleopatra Selene's early life, from the demise of her parents through her life in Rome until her marriage to Juba II of Numidia.
* ''Lily of the Nile'', ''Song of the Nile'', and ''Daughters of the Nile'', a trilogy by Stephanie Dray, tells the life story of Cleopatra Selene mixed with magical fantasy.
* ''Cleopatra's Moon'' by Vicky Alvear Shecter (2011) is a novel for teens about Cleopatra Selene. The book ends with Cleopatra's marriage to Juba II.
* Cleopatra Selene and her twin Alexander appear briefly in the television series ''Rome''.
* ''Selene, córka Kleopatry'' by Natalia Rolleczek is a novel about Cleopatra Selene and her brothers from the death of their parents until her marriage.
* Selene is a lead character in Michael Livingston
Michael Livingston is a historian, a professor of medieval literature, and a historical fantasy novelist. His 2015 debut novel, '' The Shards of Heaven'', was followed by two sequels.
Early life, education and career
Originally from Colorado, ...
's 2015 historical fantasy novel ''The Shards of Heaven
''The Shards of Heaven'' is a 2015 historical fantasy debut novel by Michael Livingston. It chronicles Octavian's war against Mark Antony and Cleopatra, seen from the perspective of the minor historical figures who surround them.
Plot
Years af ...
''.
* Cleopatra Selene is a major character in "The Daughters of Pallatine Hill", by Phyllis T. Smith (2016)
* Though identified simply as the daughter of the most famous Cleopatra, a character calling herself Patra appears in the third Night Huntress
''Night Huntress'' is a series of seven urban fantasy romance novels by author Jeaniene Frost. The first novel was published in 2007 by Avon and took place in a world where supernatural creatures exist but are not known to the general public at ...
book as a vampire living in modern times, and is the novel's antagonist.
See also
* Caesarea *Volubilis
Volubilis (; ar, وليلي, walīlī; ber, ⵡⵍⵉⵍⵉ, wlili) is a partly excavated Berber-Roman city in Morocco situated near the city of Meknes, and may have been the capital of the kingdom of Mauretania, at least from the time of Kin ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * *Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
– ''Roman History''
* Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
– ''Makers of Rome'' – Mark Antony
* Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; c. AD 69 – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire.
His most important surviving work is a set of biographies ...
– ''The Lives of the Twelve Caesars
''De vita Caesarum'' (Latin; "About the Life of the Caesars"), commonly known as ''The Twelve Caesars'', is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire written by Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus. The g ...
'' – Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
& Caligula
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), better known by his nickname Caligula (), was the third Roman emperor, ruling from 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the popular Roman general Germanicu ...
* Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
– Juba II
Further reading
* Draycott, Jane (22 May 2018).Cleopatra's Daughter: While Antony and Cleopatra have been immortalised in history and in popular culture, their offspring have been all but forgotten. Their daughter, Cleopatra Selene, became an important ruler in her own right
. ''
History Today
''History Today'' is an illustrated history magazine. Published monthly in London since January 1951, it presents serious and authoritative history to as wide a public as possible. The magazine covers all periods and geographical regions and pub ...
''.
* Moran, Michelle.Behind the Scenes of Cleopatra's Daughter
. *
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cleopatra Selene 40 BC births 6 BC deaths 1st-century BC Egyptian people 1st-century BC Egyptian women Kingdom of Numidia Egyptian twins Roman client rulers Roman-era Egyptians Cleopatra Selene 2 Mauretanian queens Children of Cleopatra Children of Mark Antony