circular prokaryote chromosome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A circular chromosome is a chromosome in bacteria, archaea, mitochondria, and
A circular chromosome is a chromosome in bacteria, archaea, mitochondria, and
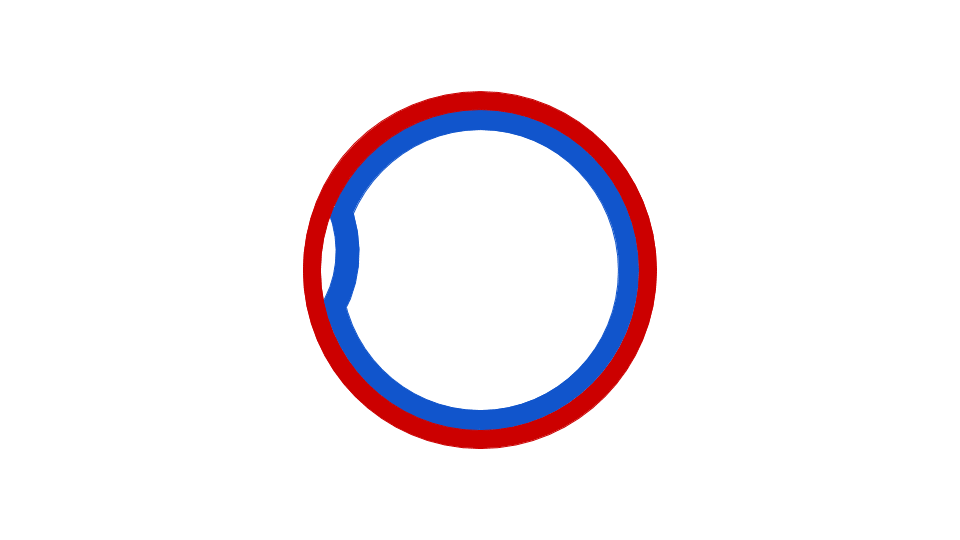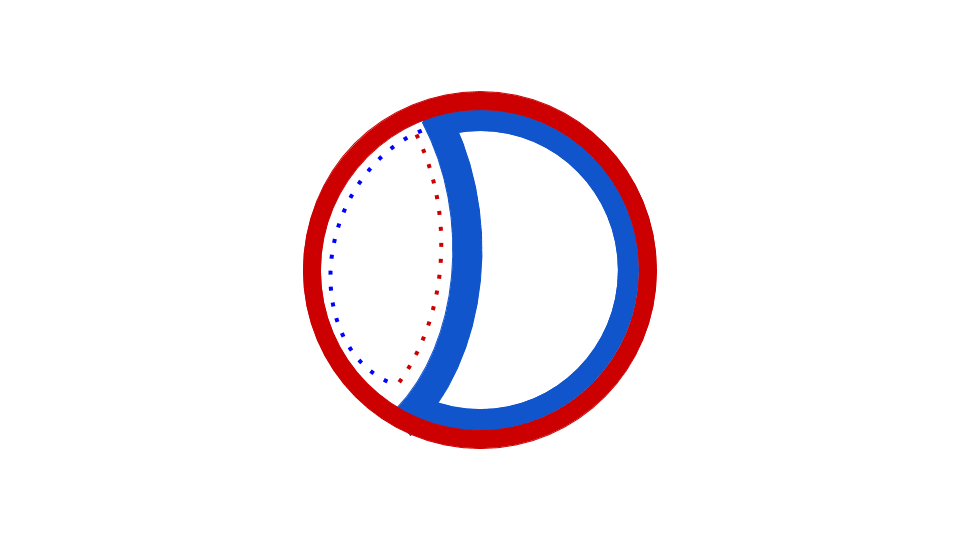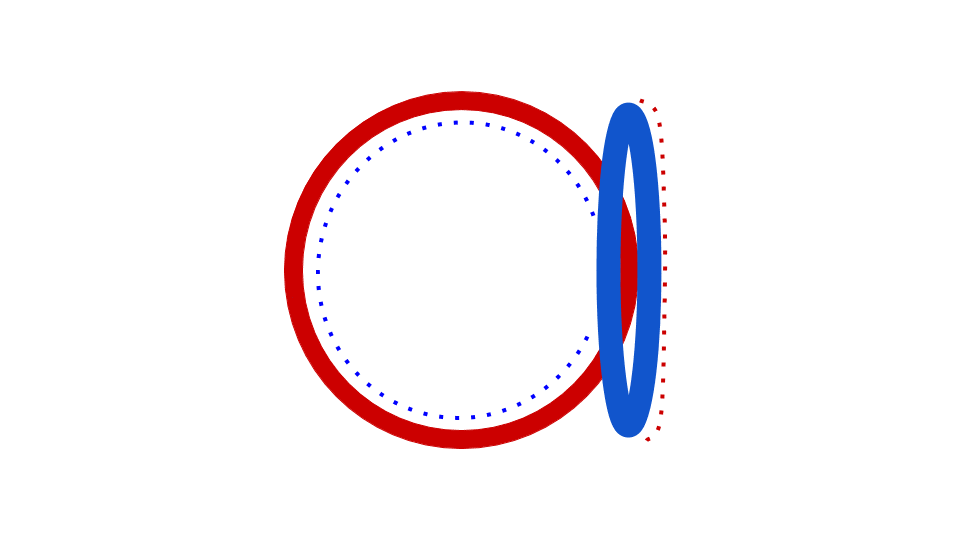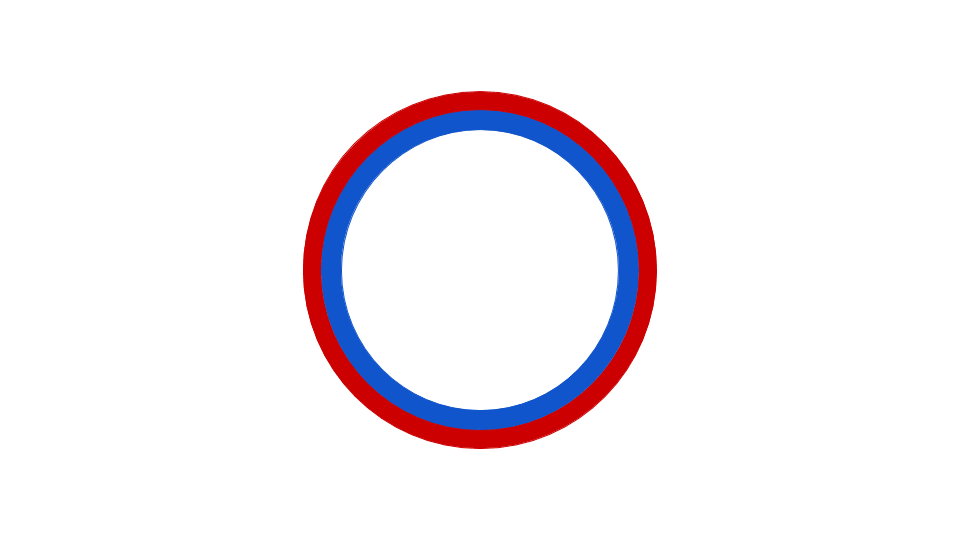 The circular bacteria chromosome replication is best understood in the well-studied bacteria ''
The circular bacteria chromosome replication is best understood in the well-studied bacteria ''
As described above, bacterial chromosomal replication occurs in a bidirectional manner. This was first demonstrated by specifically labelling replicating bacterial chromosomes with
The ''E. coli''
 Termination is the process of fusion of replication forks and disassembly of the replisomes to yield two separate and complete DNA molecules. It occurs in the terminus region, approximately opposite oriC on the chromosome (Fig 5). The terminus region contains several DNA replication terminator sites, or "Ter" sites. A special "replication terminator" protein must be bound at the Ter site for it to pause replication. Each Ter site has polarity of action, that is, it will arrest a replication fork approaching the Ter site from one direction, but will allow unimpeded fork movement through the Ter site from the other direction. The arrangement of the Ter sites forms two opposed groups that forces the two forks to meet each other within the region they span. This arrangement is called the "replication fork trap."
* See locations and sequences of the replication termini of ''E. coli.''(A) Map showing the ori and the 10 Ter sites. (B) The consensus sequence of Ter
Termination is the process of fusion of replication forks and disassembly of the replisomes to yield two separate and complete DNA molecules. It occurs in the terminus region, approximately opposite oriC on the chromosome (Fig 5). The terminus region contains several DNA replication terminator sites, or "Ter" sites. A special "replication terminator" protein must be bound at the Ter site for it to pause replication. Each Ter site has polarity of action, that is, it will arrest a replication fork approaching the Ter site from one direction, but will allow unimpeded fork movement through the Ter site from the other direction. The arrangement of the Ter sites forms two opposed groups that forces the two forks to meet each other within the region they span. This arrangement is called the "replication fork trap."
* See locations and sequences of the replication termini of ''E. coli.''(A) Map showing the ori and the 10 Ter sites. (B) The consensus sequence of Ter
The Ter sites specifically interact with the replication terminator protein called Tus protein, Tus in ''E. coli''. The Tus-Ter complex impedes the DNA unwinding activity of DnaB in an orientation-dependent manner. * The crystal structure of the Ter DNA-Tus protein complex (A) showing the nonblocking and the fork-blocking faces of Tus. (B) A cross-sectional view of the helicase-arresting surfac
Replication of the DNA separating the opposing replication forks, leaves the completed chromosomes joined as ‘
chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ...
s, in the form of a molecule of circular DNA, unlike the linear chromosome A linear chromosome is a chromosome which is linear in shape, and contains terminal ends. In most eukaryotic cells, DNA is arranged in multiple linear chromosomes. In contrast, most prokaryotic cells generally contain a singular circular chromosom ...
of most eukaryotes.
Most prokaryote chromosomes contain a circular DNA molecule – there are no free ends to the DNA. Free ends would otherwise create significant challenges to cells with respect to DNA replication and stability. Cells that do contain chromosomes with DNA ends, or telomeres (most eukaryotes), have acquired elaborate mechanisms to overcome these challenges. However, a circular chromosome can provide other challenges for cells. After replication, the two progeny circular chromosomes can sometimes remain interlinked or tangled, and they must be resolved so that each cell inherits one complete copy of the chromosome during cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there a ...
.
Replication
 The circular bacteria chromosome replication is best understood in the well-studied bacteria ''
The circular bacteria chromosome replication is best understood in the well-studied bacteria ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' and ''Bacillus subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus '' Bacillus ...
''. Chromosome replication proceeds in three major stages: initiation, elongation and termination. The initiation stage starts with the ordered assembly of "initiator" proteins at the origin region of the chromosome, called oriC. These assembly stages are regulated to ensure that chromosome replication occurs only once in each cell cycle. During the elongation phase of replication, the enzymes that were assembled at oriC during initiation proceed along each arm ("replichore The ''Escherichia coli'' chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the ...
") of the chromosome, in opposite directions away from the oriC, replicating the DNA to create two identical copies. This process is known as bidirectional replication. The entire assembly of molecules involved in DNA replication on each arm is called a "replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthe ...
." At the forefront of the replisome is a DNA helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating ...
that unwinds the two strands of DNA, creating a moving "replication fork
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritan ...
". The two unwound single strands of DNA serve as templates for DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
, which moves with the helicase (together with other proteins) to synthesise a complementary copy of each strand. In this way, two identical copies of the original DNA are created. Eventually, the two replication forks moving around the circular chromosome meet in a specific zone of the chromosome, approximately opposite oriC, called the terminus region. The elongation enzymes then disassemble, and the two "daughter" chromosomes are resolved before cell division is completed.
Initiation
The ''E. coli'' bacterial replication origin, called ''oriC'' consists of DNA sequences that are recognised by theDnaA
Introduction
Based on the Replicon Model, a positively active initiator molecule contacts with a particular spot on a circular chromosome called the replicator to start DNA replication. DnaA is a protein that activates initiation of DNA replica ...
protein, which is highly conserved amongst different bacterial species. DnaA binding to the origin initiates the regulated recruitment of other enzymes and proteins that will eventually lead to the establishment of two complete replisomes for bidirectional replication.
DNA sequence elements within ''ori''C that are important for its function include DnaA boxes, a 9-mer repeat with a highly conserved consensus sequence 5' – TTATCCACA – 3', that are recognized by the DnaA protein. DnaA protein plays a crucial role in the initiation of chromosomal DNA replication. Bound to ATP, and with the assistance of bacterial histone-like proteins UDnaA then unwinds an AT-rich region near the left boundary of ''oriC'', which carries three 13-mer motifs, and opens up the double-stranded DNA for entrance of other replication proteins.
This region also contains four “GATC” sequences that are recognized by DNA adenine methylase
DNA adenine methylase, (Dam methylase) (also site-specific DNA-methyltransferase (adenine-specific), , ''modification methylase'', ''restriction-modification system'') is an enzyme that adds a methyl group to the adenine of the sequence 5'-GATC-3' ...
(Dam), an enzyme that modifies the adenine base when this sequence is unmethylated or hemimethylated. The methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
of adenine
Adenine () (symbol A or Ade) is a nucleobase (a purine derivative). It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivativ ...
s is important as it alters the conformation of DNA to promote strand separation, and it appears that this region of ''ori''C has a natural tendency to unwind.
DnaA then recruits the replicative helicase, DnaB, from the DnaB-DnaC complex to the unwound region to form the pre-priming complex. After DnaB translocates to the apex of each replication fork, the helicase both unwinds the parental DNA and interacts momentarily with primase.
In order for DNA replication to continue, single stranded binding protein A binding protein is any protein that acts as an agent to bind two or more molecules together.
Examples include:
*DNA-binding protein
**Single-strand binding protein
** Telomere-binding protein
*RNA-binding protein
**Poly(A)-binding protein
** N ...
s are needed to prevent the single strands of DNA from forming secondary structures and to prevent them from re-annealing. In addition, DNA gyrase
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-poly ...
is needed to relieve the topological stress created by the action of DnaB helicase.
Elongation
When the replication fork moves around the circle, a structure shaped like the Greek lettertheta
Theta (, ; uppercase: Θ or ; lowercase: θ or ; grc, ''thē̂ta'' ; Modern: ''thī́ta'' ) is the eighth letter of the Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician letter Teth . In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 9.
G ...
Ө is formed. John Cairns demonstrated the theta structure
A theta structure is an intermediate structure formed during the replication of a circular DNA molecule. Two replication forks can proceed independently around the DNA ring and when viewed from above the structure resembles the Greek letter "thet ...
of E. coli chromosomal replication in 1963, using an innovative method to visualize DNA replication. In his experiment, he radioactively labeled the chromosome by growing his cultures in a medium containing 3H-thymidine
Thymidine (symbol dT or dThd), also known as deoxythymidine, deoxyribosylthymine, or thymine deoxyriboside, is a pyrimidine deoxynucleoside. Deoxythymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with deoxyadenosine (A) in double-stranded DNA. ...
. The nucleoside base was incorporated uniformly into the bacterial chromosome. He then isolated the chromosomes by lysing the cells gently and placed them on an electron micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken ...
(EM) grid which he exposed to X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
film for two months. This Experiment clearly demonstrates the theta replication model of circular bacterial chromosomes.
* See Autoradiograph of intact replicating chromosome of ''E.coli'As described above, bacterial chromosomal replication occurs in a bidirectional manner. This was first demonstrated by specifically labelling replicating bacterial chromosomes with
radioactive isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
s. The regions of DNA undergoing replication during the experiment were then visualized by using autoradiograph
An autoradiograph is an image on an X-ray film or nuclear emulsion produced by the pattern of decay emissions (e.g., beta particles or gamma rays) from a distribution of a radioactive substance. Alternatively, the autoradiograph is also available ...
y and examining the developed film microscopically. This allowed the researchers to see where replication was taking place. The first conclusive observations of bidirectional replication was from studies of B. subtilis. Shortly after, the E. coli chromosome was also shown to replicate bidirectionally.
* See Figure 4 of D. M. Prescott, and P. L. Kuempel (1972): A grain track produced by an ''E. coli'' chromosome from cells labeled for 19 min with Hthymine, followed by labelingfor 2.5 min with Hhymine and HhymidineThe ''E. coli''
DNA polymerase III holoenzyme
DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the primary enzyme complex involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. It was discovered by Thomas Kornberg (son of Arthur Kornberg) and Malcolm Gefter in 1970. The complex has high processivity (i.e. the number ...
is a 900 kD complex, possessing an essentially a dimeric structure. Each monomeric
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
unit has a catalytic core, a dimerization
A dimer () ('' di-'', "two" + ''-mer'', "parts") is an oligomer consisting of two monomers joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak, covalent or intermolecular. Dimers also have significant implications in polymer chemistry, inorganic che ...
subunit, and a processivity
In molecular biology and biochemistry, processivity is an enzyme's ability to catalyze "consecutive reactions without releasing its substrate".
For example, processivity is the average number of nucleotides added by a polymerase enzyme, such as ...
component . DNA Pol III uses one set of its core subunits to synthesize the leading strand
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
continuously, while the other set of core subunits cycles from one Okazaki fragment
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (approximately 150 to 200 base pairs long in eukaryotes) which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase to create the lagging strand during ...
to the next on the looped lagging strand. Leading strand synthesis begins with the synthesis of a short RNA primer
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohyd ...
at the replication origin by the enzyme Primase (DnaG
DnaG is a bacterial DNA primase and is encoded by the ''dnaG'' gene. The enzyme DnaG, and any other DNA primase, synthesizes short strands of RNA known as oligonucleotides during DNA replication. These oligonucleotides are known as primers b ...
protein).
Deoxynucleotides
A deoxyribonucleotide is a nucleotide that contains deoxyribose. They are the monomeric units of the informational biopolymer, deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA). Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three parts: a deoxyribose sugar (monosaccharide), a n ...
are then added to this primer by a single DNA polymerase III dimer, in an integrated complex with DnaB helicase. Leading strand synthesis then proceeds continuously, while the DNA is concurrently unwound at the replication fork. In contrast, lagging strand synthesis is accomplished in short Okazaki fragments. First, an RNA primer is synthesized by primase, and, like that in leading strand synthesis, DNA Pol III binds to the RNA primer and adds deoxyribonucleotides.
When the synthesis of an Okazaki fragment has been completed, replication halts and the core subunits of DNA Pol III dissociates from the β sliding clamp sliding clap is the processivity subunit of DNA Pol III The RNA primer is removed and replaced with DNA by DNA polymerase I
DNA polymerase I (or Pol I) is an enzyme that participates in the process of prokaryotic DNA replication. Discovered by Arthur Kornberg in 1956, it was the first known DNA polymerase (and the first known of any kind of polymerase). It was initial ...
hich_also_possesses_proofreading_exonuclease_activity.html" ;"title="exonuclease.html" ;"title="hich also possesses proofreading exonuclease">hich also possesses proofreading exonuclease activity">exonuclease.html" ;"title="hich also possesses proofreading exonuclease">hich also possesses proofreading exonuclease activityand the remaining nick is sealed by DNA ligase, which then ligates these fragments to form the lagging strand.
A substantial proportion (10-15%) of the replication forks originating at oriC encounter a DNA damage (naturally occurring), DNA damage or strand break when cells are grown under normal laboratory conditions (without an exogenous DNA damaging treatment). The encountered DNA damages are ordinarily processed by homologous recombination, recombinational repair enzymes to allow continued replication fork progression.
Termination
 Termination is the process of fusion of replication forks and disassembly of the replisomes to yield two separate and complete DNA molecules. It occurs in the terminus region, approximately opposite oriC on the chromosome (Fig 5). The terminus region contains several DNA replication terminator sites, or "Ter" sites. A special "replication terminator" protein must be bound at the Ter site for it to pause replication. Each Ter site has polarity of action, that is, it will arrest a replication fork approaching the Ter site from one direction, but will allow unimpeded fork movement through the Ter site from the other direction. The arrangement of the Ter sites forms two opposed groups that forces the two forks to meet each other within the region they span. This arrangement is called the "replication fork trap."
* See locations and sequences of the replication termini of ''E. coli.''(A) Map showing the ori and the 10 Ter sites. (B) The consensus sequence of Ter
Termination is the process of fusion of replication forks and disassembly of the replisomes to yield two separate and complete DNA molecules. It occurs in the terminus region, approximately opposite oriC on the chromosome (Fig 5). The terminus region contains several DNA replication terminator sites, or "Ter" sites. A special "replication terminator" protein must be bound at the Ter site for it to pause replication. Each Ter site has polarity of action, that is, it will arrest a replication fork approaching the Ter site from one direction, but will allow unimpeded fork movement through the Ter site from the other direction. The arrangement of the Ter sites forms two opposed groups that forces the two forks to meet each other within the region they span. This arrangement is called the "replication fork trap."
* See locations and sequences of the replication termini of ''E. coli.''(A) Map showing the ori and the 10 Ter sites. (B) The consensus sequence of TerThe Ter sites specifically interact with the replication terminator protein called Tus protein, Tus in ''E. coli''. The Tus-Ter complex impedes the DNA unwinding activity of DnaB in an orientation-dependent manner. * The crystal structure of the Ter DNA-Tus protein complex (A) showing the nonblocking and the fork-blocking faces of Tus. (B) A cross-sectional view of the helicase-arresting surfac
Replication of the DNA separating the opposing replication forks, leaves the completed chromosomes joined as ‘
catenane
In macromolecular chemistry, a catenane () is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture consisting of two or more interlocked macrocycles, i.e. a molecule containing two or more intertwined rings. The interlocked rings cannot be sepa ...
s’ or topologically interlinked circles. The circles are not covalently linked, but cannot be separated because they are interwound and each is covalently closed. The catenated circles require the action of topoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
s to separate the circles ecatanation In E.coli, DNA topoisomerase IV plays the major role in the separation of the catenated chromosomes, transiently breaking both DNA strands of one chromosome and allowing the other chromosome to pass through the break.
There has been some confusion about the role DNA gyrase
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-poly ...
plays in decatenation. To define the nomenclature, there are two types of topoisomerases: type I produces transient single-strand breaks in DNA and types II produces transient double-strand breaks. As a result, the type I enzyme removes supercoil
DNA supercoiling refers to the amount of twist in a particular DNA strand, which determines the amount of strain on it. A given strand may be "positively supercoiled" or "negatively supercoiled" (more or less tightly wound). The amount of a st ...
s from DNA one at a time, whereas the type II enzyme removes supercoils two at a time. The topo I of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the type I topoisomerase. The eukaryotic topo II, bacterial gyrase, and bacterial topo IV belong to the type II.
We often forget that DNA gyrase does in fact have topoisomerase type II activity; thus, with it being a homologue of topoisomerase IV (also having topoisomerase II activity) we expect similarity in the two proteins' functions. DNA gyrase preliminary role is to introduce negative super coils into DNA, thereby relaxing positive supercoils that come into play during DNA replication. Topoisomerase IV also relaxes positive supercoils, therefore, DNA Gyrase and topoisomerase IV play an almost identical role in removing the positive supercoils ahead of a translocating DNA polymerase, allowing DNA replication to continue unhindered by topological strain.
Confusion arises when some scientific literature
: ''For a broader class of literature, see Academic publishing.''
Scientific literature comprises scholarly publications that report original empirical and theoretical work in the natural and social sciences. Within an academic field, scienti ...
state that DNA gyrase is the sole enzyme responsible for decatanation. In an experiment conducted by Zechiedrich, Khodursky and Cozzarelli in 1997, it was found that topoisomerase IV is the only important decatenase of DNA replication intermediates in bacteria.E L Zechiedrich, A B Khodursky, N R Cozzarelli. Topoisomerase IV, not gyrase, decatenates products of site-specific recombination in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1997 Oct 1;11 (19):2580-92 9334322 In this particular experiment, when DNA gyrase alone were inhibited, most of the catenanes were unlinked. However, when Topoisomerase IV alone was inhibited, decatenation was almost completely blocked. The results obtained suggest that Topoisomerase IV is the primary decatenase '' in vivo'', and although DNA gyrase does play a role in decatenation, its function is not as essential as topoisomerase IV in the decatentation of interlinked chromosomes.
Acknowledgments
This is based on an article by Imalda Devaparanam and David Tribe made available under CC by SA licensing conditions from a University course activity at the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Melbourne, 2007.See also
*Catenane
In macromolecular chemistry, a catenane () is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture consisting of two or more interlocked macrocycles, i.e. a molecule containing two or more intertwined rings. The interlocked rings cannot be sepa ...
* Möbius strip
In mathematics, a Möbius strip, Möbius band, or Möbius loop is a surface that can be formed by attaching the ends of a strip of paper together with a half-twist. As a mathematical object, it was discovered by Johann Benedict Listing and Aug ...
* Nucleoid
The nucleoid (meaning '' nucleus-like'') is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell ...
* Plasmid
* Ribbon theory In differential geometry, a ribbon (or strip) is the combination of a smooth space curve and its corresponding normal vector. More formally, a ribbon denoted by (X,U) includes a curve X given by a three-dimensional vector X(s), depending continuousl ...
* Rolling circle replication
* Topoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
* Theta type replication
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Circular Bacterial Chromosome Chromosomes Bacteriology Cell anatomy