Chloralkali process on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor
The chloralkali process (also chlor-alkali and chlor

 In the mercury-cell process, also known as the
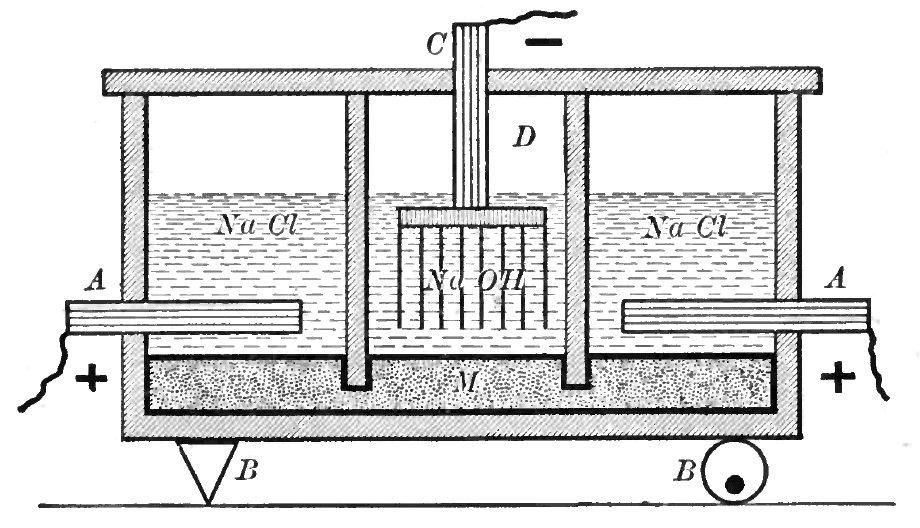
In the mercury-cell process, also known as the
"Brine Electrolysis."
''Electrochemistry Encyclopedia.'' Cleveland: Case Western Reserve University.
Animation showing the membrane cell processAnimation showing the diaphragm cell process
{{electrolysis Chemical processes Electrolysis Industrial gases
alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
) is an industrial process for the electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
of sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35. ...
(NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and al ...
(caustic soda), which are commodity chemicals required by industry. Thirty five million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in this process are widely used in the chemical industry.
Usually the process is conducted on a brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for ...
(an aqueous solution of NaCl), in which case sodium hydroxide (NaOH), hydrogen, and chlorine result. When using calcium chloride
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide.
Ca ...
or potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt ...
, the products contain calcium or potassium instead of sodium. Related processes are known that use molten NaCl to give chlorine and sodium metal or condensed hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chlorid ...
to give hydrogen and chlorine.
The process has a high energy consumption, for example around of electricity per tonne of sodium hydroxide produced. Because the process yields equivalent amounts of chlorine and sodium hydroxide (two moles of sodium hydroxide per mole of chlorine), it is necessary to find a use for these products in the same proportion. For every mole of chlorine produced, one mole of hydrogen is produced. Much of this hydrogen is used to produce hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dige ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
, hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
, or is burned for power and/or steam production.
History
The chloralkali process has been in use since the 19th century and is a primary industry in theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
. It has become the principal source of chlorine during the 20th century. The diaphragm cell process and the mercury cell process have been used for over 100 years but are environmentally unfriendly through their use of asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
and mercury, respectively. The membrane cell process, which was only developed in the past 60 years, is a superior method with its improved energy efficiency and lack of harmful chemicals.
Although the first formation of chlorine by the electrolysis of brine was attributed to chemist William Cruikshank in 1800, it was 90 years later that the electrolytic method was used successfully on a commercial scale. Industrial scale production began in 1892. In 1833, Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, ...
formulated the laws that governed the electrolysis of aqueous solutions, and patents were issued to Cook and Watt in 1851 and to Stanley in 1853 for the electrolytic production of chlorine from brine.Process systems
Three production methods are in use. While the mercury cell method produces chlorine-free sodium hydroxide, the use of several tonnes of mercury leads to serious environmental problems. In a normal production cycle a few hundred pounds of mercury per year are emitted, which accumulate in the environment. Additionally, the chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced via the mercury-cell chloralkali process are themselves contaminated with trace amounts of mercury. The membrane and diaphragm method use no mercury, but the sodium hydroxide contains chlorine, which must be removed.Membrane cell
The most common chloralkali process involves the electrolysis ofaqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be re ...
sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35. ...
(a brine) in a membrane cell
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. ...
. A membrane, such as one made from Nafion
Nafion is a brand name for a sulfonated tetrafluoroethylene based fluoropolymer-copolymer discovered in the late 1960s by Dr. Walther Grot of DuPont. Nafion is a brand of the Chemours company. It is the first of a class of synthetic polymers with ...
, Flemion or Aciplex, is used to prevent the reaction between the chlorine and hydroxide ions.
Saturated brine is passed into the first chamber of the cell where the chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride s ...
ions are oxidised
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
at the anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
, losing electrons to become chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
gas (A in figure):
:2Cl− → + 2 e−
At the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
, positive hydrogen ion
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particle ...
s pulled from water molecules are reduced by the electrons provided by the electrolytic current, to hydrogen gas, releasing hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. ...
ions into the solution (C in figure):
:2 + 2e− → H2 + 2OH−
The ion-permeable ion-exchange membrane at the center of the cell allows the sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
ions (Na+) to pass to the second chamber where they react with the hydroxide ions to produce caustic soda (NaOH) (B in figure). The overall reaction for the electrolysis of brine is thus:
:2NaCl + 2 → + + 2NaOH
Diaphragm cell
In the diaphragm cell process, there are two compartments separated by a permeable diaphragm, often made of asbestos fibers. Brine is introduced into the anode compartment and flows into the cathode compartment. Similarly to the membrane cell, chloride ions are oxidized at the anode to produce chlorine, and at the cathode, water is split into caustic soda and hydrogen. The diaphragm prevents the reaction of the caustic soda with the chlorine. A diluted caustic brine leaves the cell. The caustic soda must usually be concentrated to 50% and the salt removed. This is done using an evaporative process with about three tonnes of steam per tonne of caustic soda. The salt separated from the caustic brine can be used to saturate diluted brine. The chlorine contains oxygen and must often be purified by liquefaction and evaporation.Mercury cell
 In the mercury-cell process, also known as the
In the mercury-cell process, also known as the Castner–Kellner process
The Castner–Kellner process is a method of electrolysis on an aqueous alkali chloride solution (usually sodium chloride solution) to produce the corresponding alkali hydroxide, invented by American Hamilton Castner and Austrian Carl Kellner in ...
, a saturated brine solution floats on top of a thin layer of mercury. The mercury is the cathode, where sodium is produced and forms an amalgam with the mercury. The amalgam is continuously drawn out of the cell and reacted with water which decomposes the amalgam into sodium hydroxide, hydrogen and mercury. The mercury is recycled into the electrolytic cell. Chlorine is produced at the anode and bubbles out of the cell. Mercury cells are being phased out due to concerns about mercury poisoning
Mercury poisoning is a type of metal poisoning due to exposure to mercury. Symptoms depend upon the type, dose, method, and duration of exposure. They may include muscle weakness, poor coordination, numbness in the hands and feet, skin rashes ...
from mercury cell pollution such as occurred in Canada (see Ontario Minamata disease) and Japan (see Minamata disease
Minamata disease is a neurological disease caused by severe mercury poisoning. Signs and symptoms include ataxia, numbness in the hands and feet, general muscle weakness, loss of peripheral vision, and damage to hearing and speech. In extreme ...
).
Unpartitioned cell
The initial overall reaction produces hydroxide and also hydrogen and chlorine gases: :2 NaCl + 2 H2O → 2 NaOH + H2 + Cl2 Without a membrane, the OH− ions produced at the cathode are free to diffuse throughout the electrolyte. As the electrolyte becomes morebasic
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ...
due to the production of OH−, less Cl2 emerges from the solution as it begins to disproportionate
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can ...
to form chloride and hypochlorite
In chemistry, hypochlorite is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite (household bleach) and calcium hypochlorite (a component of ...
ions at the anode:
:Cl2 + 2 NaOH → NaCl + NaClO + H2O
The more opportunity the Cl2 has to interact with NaOH in the solution, the less Cl2 emerges at the surface of the solution and the faster the production of hypochlorite progresses. This depends on factors such as solution temperature, the amount of time the Cl2 molecule is in contact with the solution, and concentration of NaOH.
Likewise, as hypochlorite increases in concentration, chlorates are produced from them:
: 3 NaClO → NaClO3 + 2 NaCl
This reaction is accelerated at temperatures above about 60 °C. Other reactions occur, such as the self-ionization of water and the decomposition of hypochlorite at the cathode, the rate of the latter depends on factors such as diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical ...
and the surface area of the cathode in contact with the electrolyte.
If current is interrupted while the cathode is submerged, cathodes that are attacked by hypochlorites, such as those made from stainless steel, will dissolve in unpartitioned cells.
If producing hydrogen and oxygen gases is not a priority, the addition of 0.18% sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
or potassium chromate to the electrolyte will improve the efficiency of producing the other products.
Electrodes
Due to the corrosive nature of chlorine production, the anode (where the chlorine is formed) must be non-reactive and has been made from materials such asplatinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Pla ...
metal, graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
(called plumbago in Faraday's time), or platinized titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion i ...
. A mixed metal oxide clad titanium anode (also called a dimensionally stable anode) is the industrial standard today. Historically, platinum, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
, lead dioxide, manganese dioxide
Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-ce ...
, and ferrosilicon (13–15% silicon) have also been used as anodes. Platinum alloyed with iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density o ...
is more resistant to corrosion from chlorine than pure platinum. Unclad titanium cannot be used as an anode because it anodizes, forming a non-conductive oxide and passivates. Graphite will slowly disintegrate due to internal electrolytic gas production from the porous nature of the material and carbon dioxide forming due to carbon oxidation, causing fine particles of graphite to be suspended in the electrolyte that can be removed by filtration. The cathode (where hydroxide forms) can be made from unalloyed titanium, graphite, or a more easily oxidized metal such as stainless steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's r ...
or nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
.
Manufacturer associations
The interests of chloralkali product manufacturers are represented at regional, national and international levels by associations such as Euro Chlor and The World Chlorine Council.See also
* Electrochemical engineering *Gas diffusion electrode
Gas diffusion electrodes (GDE) are electrodes with a conjunction of a solid, liquid and gaseous interface, and an electrical conducting catalyst supporting an electrochemical reaction between the liquid and the gaseous phase.
Principle
GDEs are us ...
* Solvay process
The Solvay process or ammonia-soda process is the major industrial process for the production of sodium carbonate (soda ash, Na2CO3). The ammonia-soda process was developed into its modern form by the Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay during the 1860s ...
, a similar industrial method of making sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
from calcium carbonate and sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as salt (although sea salt also contains other chemical salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35. ...
References
Further reading
* Bommaraju, Tilak V.; Orosz, Paul J.; Sokol, Elizabeth A.(2007)"Brine Electrolysis."
''Electrochemistry Encyclopedia.'' Cleveland: Case Western Reserve University.
External links
*Animation showing the membrane cell process
{{electrolysis Chemical processes Electrolysis Industrial gases