Cavalier-Smith on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of
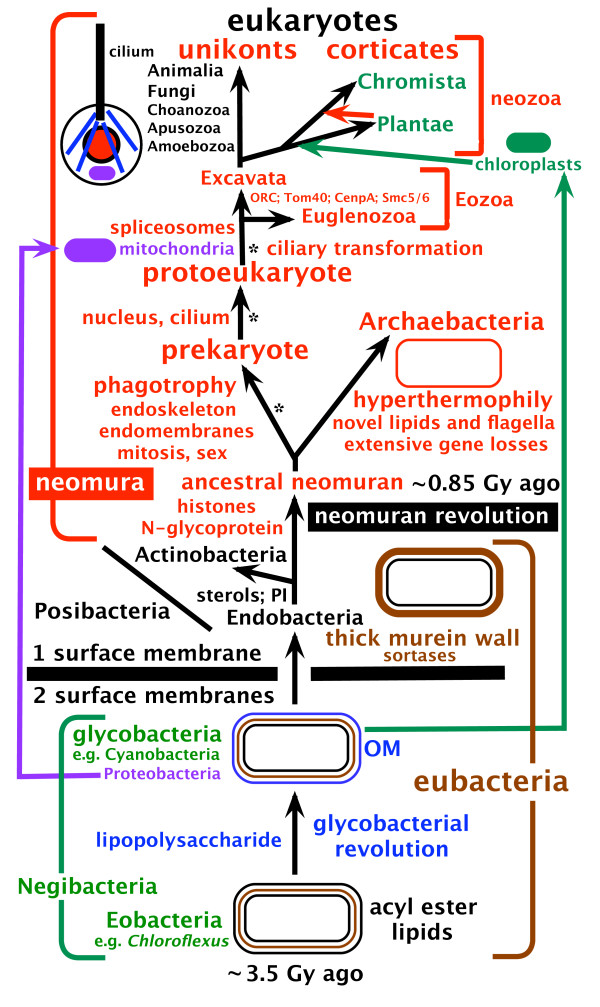 Cavalier-Smith wrote extensively on the taxonomy and classification of all life forms, but especially protists. One of his major contributions to biology was his proposal of a new
Cavalier-Smith wrote extensively on the taxonomy and classification of all life forms, but especially protists. One of his major contributions to biology was his proposal of a new
 Five of Cavalier-Smith's kingdoms are classified as eukaryotes as shown in the following scheme:
*''Eubacteria''
* Neomura
**''Archaebacteria''
**Eukaryotes
***Kingdom Protozoa
***
Five of Cavalier-Smith's kingdoms are classified as eukaryotes as shown in the following scheme:
*''Eubacteria''
* Neomura
**''Archaebacteria''
**Eukaryotes
***Kingdom Protozoa
***
evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes ( natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life ...
in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
.
His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exc ...
s) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista
Chromista is a biological kingdom consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their photosynthetic organelles ( plastids). It includes all protists whose plastids contain chlorophyll ''c'', ...
, Chromalveolata
Chromalveolata was a eukaryote supergroup present in a major classification of 2005, then regarded as one of the six major groups within the eukaryotes.
It was a refinement of the kingdom Chromista, first proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in ...
, Opisthokont
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and ...
a, Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many forami ...
, and Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free- ...
. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms.
Life and career
Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated atNorwich School
Norwich School (formally King Edward VI Grammar School, Norwich) is a selective English independent day school in the close of Norwich Cathedral, Norwich. Among the oldest schools in the United Kingdom, it has a traceable history to 1096 as a ...
, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of t ...
(MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii".
From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigator at Rockefeller University. He became Lecturer of biophysics at King's College London in 1969. He was promoted to Reader in 1982.
From the early 1980s, Smith promoted views about the taxonomic relationships among living organisms. He was prolific, drawing on a near-unparalleled wealth of information to suggest novel relationships.
In 1989 he was appointed Professor of Botany at the University of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a public research university with campuses near Vancouver and in Kelowna, British Columbia. Established in 1908, it is British Columbia's oldest university. The university ranks among the top thre ...
.
In 1999, he joined the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
, becoming Professor of evolutionary biology in 2000.
Thomas Cavalier-Smith died in March 2021 following the development of cancer.
Taxonomy
Cavalier-Smith was a prolific taxonomist, drawing on a near-unparalleled wealth of information to suggest novel relationships. His suggestions were translated into taxonomic concepts and classifications with which he associated new names, or in some cases, reused old names. Cavalier-Smith did not follow or espouse an explicit taxonomic philosophy but his approach was closest to evolutionary taxonomy. He and several other colleagues were opposed tocladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived char ...
approaches to taxonomy arguing that the goals of cladification and classification were different; his approach was similar to that of many others' broad-based treatments of protists.
The scope of Cavalier-Smith's taxonomic propositions was grand, but the numbers and composition of the components (taxa), and, often, their relations were not stable. Propositions were often ambiguous and short-lived; he frequently amended taxa without any change in the name. His approach was not universally accepted: Others attempted to underpin taxonomy of protists with a nested series of atomised, falsifiable propositions, following the philosophy of transformed cladistics. However, this approach is no longer considered defensible.
Cavalier-Smith's ideas that led to the taxonomic structures were usually first presented in the form of tables and complex, annotated diagrams. When presented at scientific meetings, they were sometimes too rich, and often written too small, for the ideas to be easily grasped. Some such diagrams made their way into publications, where careful scrutiny was possible, and where the conjectural nature of some assertions was evident. The richness of his ideas, their continuing evolution, and the transition into taxonomies that gave Cavalier-Smith's investigations into evolutionary paths (phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ...
) and the resulting classifications, its distinctive character.
Four major influences
Thomas Cavalier-Smith worked at a time when there was a pervasive presumption that classification should reflect evolutionary pathways. How this should be done had four major influences, as described in the following subsections.Prior representation
First, was a residue of the 'traditional' approach that admitted speculation and which lacked any explicit rigor as to how a particular evolutionary insight should be translated into the arrangement and ranks of taxa. Inherent to this approach were narratives about character evolution and classifications that included paraphyletic taxa, and in which degree of difference would influence the rank assigned to taxa.Popperian philosophy of science
The second influence was the philosophy as to how scientific progress was made. It had been articulated by K. Popper and had shifted the emphasis from verification of ideas to the falsification of hypotheses. Popper saw that science progressed by a process that eliminated unsound hypotheses, so whittling down of the array of possible explanations leading towards the explanations which were more likely correct. To fit into this process, hypotheses needed to be falsifiable.Cladistics
The third influence was 'cladistics' – an explicit way of presenting (and then 'falsifying', although see) evolutionary hypotheses. This was initially articulated by Willi Hennig, and was increasingly (but not universally) accepted by many as how taxonomy should be done. The justification of the cladistic approach in terms of Popperian hypothetico-deductivism was popular in the 1970-80s but is no longer considered defensible (see Sober and reviewed in Rieppel ).Genetic sequencing
Fourthly, technical advances in sequencing technology led to a massive growth of hypotheses about evolutionary relationships based on the similarities among sequences of compared organisms. Algorithms were used to analyse sequence data, with the results being usually presented in the form of dendrograms.Cavalier-Smith's narrative style
Cavalier-Smith was courageous in his adherence to the earlier traditionalist style characterized byCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
, that of relying on narratives. One example was his advocacy for the Chromista
Chromista is a biological kingdom consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their photosynthetic organelles ( plastids). It includes all protists whose plastids contain chlorophyll ''c'', ...
that united lineages that had plastids with chlorophylls a and c (primarily chrysophytes and other stramenopiles
Stramenopile is a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have be ...
, cryptophytes, and haptophytes) despite clear evidence that the group corresponded to a clade.
It was Cavalier-Smith's claim that there was a single endosymbiotic event by which chlorophyll a c containing plastids were acquired by a common ancestor of all three groups, and that the differences (such as cytological components and their arrangements) among the groups were the result of subsequent evolutionary changes. This interpretation that chromists were monophyletic also required that the heterotrophic ( protozoan) members of all three groups had arisen from ancestors with plastids.
The alternative hypothesis was that the three chromphytic lineages were not closely related (to the exclusion of other lineages) (i.e. were polyphyletic), likely that all were ancestrally without plastids, and that separate symbiotic events established the chlorophyll a/c plastids stramenopiles, cryptomonads and haptophytes. The polyphyly of the chromists has been re-asserted in subsequent studies.
Cavalier-Smith's lack of an objective and reproducible methodology that would translate evolutionary insights into taxa and hierarchical schemes, were often confusing to those who did not follow his publications closely. Many of his taxa requiring his frequent adjustment, as illustrated below. In turn this led to confusion as to the scope of taxa a taxonomic name was applied to.
Cavalier-Smith also reused familiar names (such as Protozoa) for innovative taxonomic concepts. This created confusion because Protozoa was and still is used in its old sense, alongside its use in the newer senses. Because of Cavalier-Smith's tendency to publish rapidly and to change his narratives and taxonomic summaries frequently, his approach and claims were frequently debated.
Cavalier-Smith's contributions
 Cavalier-Smith wrote extensively on the taxonomy and classification of all life forms, but especially protists. One of his major contributions to biology was his proposal of a new
Cavalier-Smith wrote extensively on the taxonomy and classification of all life forms, but especially protists. One of his major contributions to biology was his proposal of a new kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
of life: the Chromista
Chromista is a biological kingdom consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their photosynthetic organelles ( plastids). It includes all protists whose plastids contain chlorophyll ''c'', ...
, even though it is not widely accepted to be monophyletic (see above).
He also introduced new taxonomic groupings group for eukaryotes such as the Chromalveolata
Chromalveolata was a eukaryote supergroup present in a major classification of 2005, then regarded as one of the six major groups within the eukaryotes.
It was a refinement of the kingdom Chromista, first proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in ...
(1981), Opisthokonta (1987), Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many forami ...
(2002), and Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free- ...
(2002). Though well known, many of his claims have been controversial and have not gained widespread acceptance in the scientific community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many " sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional activities are als ...
. His taxonomic revisions often influenced the overall classification of all life forms.
Eight kingdoms model
Cavalier-Smith's first major classification system was the division of all organisms into eight kingdoms. In 1981, he proposed that by completely revising Robert Whittaker's Five Kingdom system, there could be eight kingdoms: Bacteria, Eufungi, Ciliofungi, Animalia, Biliphyta, Viridiplantae, Cryptophyta, and Euglenozoa. In 1983, he revised his system particularly in the light of growing evidence that Archaebacteria were a separate group from Bacteria, to include an array of lineages that had been excluded from his 1981 treatment, to deal with issues of polyphyly, and to promote new ideas of relationships. In addition, some protists lacking mitochondria were discovered. As mitochondria were known to be the result of theendosymbiosis
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within ...
of a proteobacterium, it was thought that these amitochondriate eukaryotes were primitively so, marking an important step in eukaryogenesis. As a result, these amitochondriate protists were given special status as a protozan subkingdom Archezoa Archezoa was a kingdom proposed in the 20th century by Thomas Cavalier-Smith (1942–2021), and was believed to encompass eukaryotes which did not have mitochondria (and are therefore ''amitochondriate'') or peroxisomes (e.g. '' Giardia''). The c ...
, that he later elevated to kingdom status. This was later referred to as the Archezoa hypothesis. In, 1993, the eight kingdoms became: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Archezoa, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia.
The kingdom Archezoa went through many compositional changes due to evidence of polyphyly and paraphyly before being abandoned. He assigned some former members of the kingdom Archezoa Archezoa was a kingdom proposed in the 20th century by Thomas Cavalier-Smith (1942–2021), and was believed to encompass eukaryotes which did not have mitochondria (and are therefore ''amitochondriate'') or peroxisomes (e.g. '' Giardia''). The c ...
to the phylum Amoebozoa.
Six kingdoms models
By 1998, Cavalier-Smith had reduced the total number of kingdoms from eight to six: Animalia, Protozoa,Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, Plantae
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ...
(including Glaucophyte, red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
and green algae), Chromista
Chromista is a biological kingdom consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their photosynthetic organelles ( plastids). It includes all protists whose plastids contain chlorophyll ''c'', ...
, and Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
. Nevertheless, he had already presented this simplified scheme for the first time on his 1981 paper and endorsed it in 1983.
 Five of Cavalier-Smith's kingdoms are classified as eukaryotes as shown in the following scheme:
*''Eubacteria''
* Neomura
**''Archaebacteria''
**Eukaryotes
***Kingdom Protozoa
***
Five of Cavalier-Smith's kingdoms are classified as eukaryotes as shown in the following scheme:
*''Eubacteria''
* Neomura
**''Archaebacteria''
**Eukaryotes
***Kingdom Protozoa
*** Unikont
Amorphea are members of a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungus, Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of ...
s (heterotrophs
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
)
****Kingdom Animalia
****Kingdom Fungi
*** Bikont
A bikont ("two flagella") is any of the eukaryotic organisms classified in the group Bikonta. Many single-celled members of the group, and the presumed ancestor, have two flagella.
Enzymes
Another shared trait of bikonts is the fusion of two ge ...
s (primarily photosynthetic)
****Kingdom Plantae (including red and green algae)
****Kingdom Chromista
The kingdom Animalia was divided into four subkingdoms: Radiata
Radiata or Radiates is a historical taxonomic rank that was used to classify animals with radially symmetric body plans. The term Radiata is no longer accepted, as it united several different groupings of animals that do not form a monophyletic ...
(phyla Porifera, Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
, Placozoa
The Placozoa are a basal form of marine free-living (non-parasitic) multicellular organism. They are the simplest in structure of all animals. Three genera have been found: the classical ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', '' Hoilungia hongkongensis'', a ...
, and Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
), Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. O ...
, Mesozoa
The Mesozoa are minuscule, worm-like parasites of marine invertebrates. Generally, these tiny, elusive creatures consist of a somatoderm (outer layer) of ciliated cells surrounding one or more reproductive cells.
A recent study recovered Mesoz ...
, and Bilateria (all other animal phyla).
He created three new animal phyla: Acanthognatha ( rotifers, acanthocephalans, gastrotrichs, and gnathostomulids
Gnathostomulids, or jaw worms, are a small phylum of nearly microscopic marine animals. They inhabit sand and mud beneath shallow coastal waters and can survive in relatively anoxic environments. They were first recognised and described in 1956. ...
), Brachiozoa (brachiopods
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, wh ...
and phoronids
Phoronids (scientific name Phoronida, sometimes called horseshoe worms) are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore (a "crown" of tentacles), and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies. ...
), and Lobopoda ( onychophorans and tardigrades
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär ...
)
and recognised a total of 23 animal phyla.
Cavalier-Smith's 2003 classification scheme:
* Unikont
Amorphea are members of a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungus, Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of ...
s
** protozoan phylum Amoebozoa (ancestrally uniciliate)
** opisthokonts
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and ...
*** uniciliate protozoan phylum Choanozoa
*** kingdom Fungi
*** kingdom Animalia
* Bikont
A bikont ("two flagella") is any of the eukaryotic organisms classified in the group Bikonta. Many single-celled members of the group, and the presumed ancestor, have two flagella.
Enzymes
Another shared trait of bikonts is the fusion of two ge ...
s
** protozoan infrakingdom Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many forami ...
*** phylum Cercozoa
*** phylum Retaria
Retaria is a clade within the supergroup Rhizaria containing the Foraminifera and the Radiolaria. In 2019, the Retaria were recognized as a basal Rhizaria group, as sister of the Cercozoa
Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryote ...
( Radiozoa and Foraminifera
Foraminifera (; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly ...
)
** protozoan infrakingdom Excavata
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free- ...
*** phylum Loukozoa
Loukozoa (+ Ancyromonads) (From Greek ''loukos'': groove) is a proposed taxon used in some classifications of eukaryotes, consisting of the Metamonada and Malawimonadea. Ancyromonads are closely related to this group, as sister of the entire grou ...
*** phylum Metamonada
*** phylum Euglenozoa
*** phylum Percolozoa
The Percolozoa are a group of colourless, non-photosynthetic Excavata, including many that can transform between amoeboid, flagellate, and cyst stages.
Characteristics
Most Percolozoa are found as bacterivores in soil, fresh water and occasio ...
** protozoan phylum Apusozoa ( Thecomonadea and Diphylleida)
** the chromalveolate
Chromalveolata was a eukaryote supergroup present in a major classification of 2005, then regarded as one of the six major groups within the eukaryotes.
It was a refinement of the kingdom Chromista, first proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in ...
clade
*** kingdom Chromista
Chromista is a biological kingdom consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their photosynthetic organelles ( plastids). It includes all protists whose plastids contain chlorophyll ''c'', ...
(Cryptista
Cryptista is a clade of algae-like eukaryotes. It is most likely related to Archaeplastida which includes plants and many algae, within the larger group Diaphoretickes.
Although it has sometimes placed along with Haptista in the group Hacrob ...
, Heterokonta
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which a ...
, and Haptophyta
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for '' Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae.
The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at ...
)
*** protozoan infrakingdom Alveolata
**** phylum Ciliophora
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different ...
**** phylum Miozoa ( Protalveolata, Dinozoa, and Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. Th ...
)
** kingdom Plantae
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ...
( Viridaeplantae, Rhodophyta and Glaucophyta
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of speci ...
)
Seven kingdoms model
Cavalier-Smith and his collaborators revised the classification in 2015, and published it in '' PLOS ONE''. In this scheme they reintroduced the division of prokaryotes into two kingdoms,Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
(previously 'Eubacteria') and Archaea (previously 'Archebacteria'). This is based on the consensus in the Taxonomic Outline of Bacteria and Archaea (TOBA) and the Catalogue of Life
The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic I ...
.
Proposed root of the tree of life
In 2006, Cavalier-Smith proposed that thelast universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the most recent population from which all organisms now living on Earth share common descent—the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth. This includes all cellular organisms; th ...
to all life was a non-flagellate Gram-negative bacterium ("negibacterium") with two membranes (also known as diderm bacterium).
Awards and honours
Cavalier-Smith was elected Fellow of theLinnean Society of London
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature colle ...
(FLS) in 1980, the Institute of Biology The Institute of Biology (IoB) was a professional body for biologists, primarily those working in the United Kingdom. The Institute was founded in 1950 by the Biological Council: the then umbrella body for Britain's many learned biological societie ...
(FIBiol) in 1983, the Royal Society of Arts (FRSA) in 1987, the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research
The Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) is a Canadian-based global research organization that brings together teams of top researchers from around the world to address important and complex questions. It was founded in 1982 and is s ...
(CIFAR) in 1988, the Royal Society of Canada (FRSC) in 1997, and the Royal Society of London
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in 1998.
He received the International Prize for Biology
The is an annual award for "outstanding contribution to the advancement of research in fundamental biology." The Prize, although it is not always awarded to a biologist, is one of the most prestigious honours a natural scientist can receive. Ther ...
from the Emperor of Japan in 2004, and the Linnean Medal for Zoology in 2007. He was appointed Fellow of the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) between 1998 and 2007, and Advisor of the Integrated Microbial Biodiversity of CIFAR. He won the 2007 Frink Medal
The Frink Medal for British Zoologists is awarded by the Zoological Society of London "For significant and original contributions by a professional zoologist to the development of zoology." It consists of a bronze plaque (76 by 83 millimetres), de ...
of the Zoological Society of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity devoted to the worldwide conservation of animals and their habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained the London Zoo, and since 1931 Whipsnade Park.
History
On 29 ...
.
References
External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Cavalier-Smith, Thomas English biologists Protistologists 1942 births British evolutionary biologists English humanists English microbiologists English taxonomists Fellows of the Royal Society People educated at Norwich School Alumni of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge Alumni of King's College London Academics of King's College London Academics of the University of Oxford 20th-century biologists 21st-century biologists 20th-century British scientists 21st-century British scientists 2021 deaths