Cassiel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cassiel ( he, קַצְפִּיאֵל ''Qaṣpīʾēl'', "God is my wrath"; also known as קַפְצִיאֵל ''Qap̄ṣīʾēl'', "God is my leap"; ar, كسفيائيل, '), is an
 Qafsiel is invoked in an ancient Hebrew charm to tell if an enemy is running away. Gustav Davidson writes that Qafsiel is described as the ruler of the seventh heaven in 3 Enoch, citing Odeberg's edition. However, Odeberg's edition only states in a footnote that Qafsiel is "(one of) the guardian(s) of the door of the seventh Hall" in ''Hekhalot Rabbati''. In turn, Qaspiel is described in ''Hekhalot Rabbati'' as a guardian of the ''sixth'' palace, armed with a lightning-dripping sword (which shouts "Ruin!") as well as a bow, tempests, light, and powerful winds—weapons which he uses against anyone not fit to see God. Qaspiel is later described in the same work as one of three "guardians of the entrance of the seventh palace," alongside Dumiel and
Qafsiel is invoked in an ancient Hebrew charm to tell if an enemy is running away. Gustav Davidson writes that Qafsiel is described as the ruler of the seventh heaven in 3 Enoch, citing Odeberg's edition. However, Odeberg's edition only states in a footnote that Qafsiel is "(one of) the guardian(s) of the door of the seventh Hall" in ''Hekhalot Rabbati''. In turn, Qaspiel is described in ''Hekhalot Rabbati'' as a guardian of the ''sixth'' palace, armed with a lightning-dripping sword (which shouts "Ruin!") as well as a bow, tempests, light, and powerful winds—weapons which he uses against anyone not fit to see God. Qaspiel is later described in the same work as one of three "guardians of the entrance of the seventh palace," alongside Dumiel and
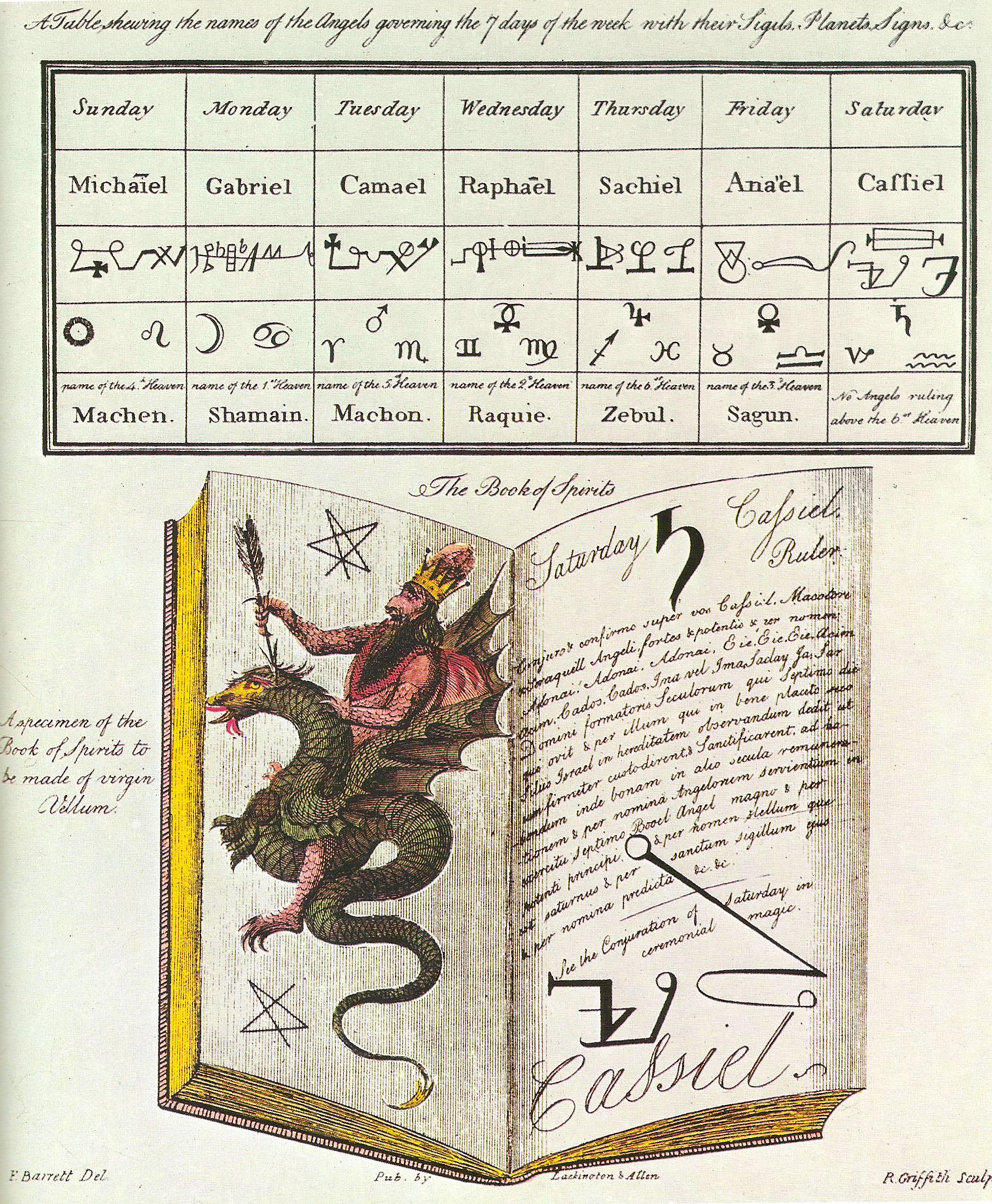 Cassiel is listed in the related works ''
Cassiel is listed in the related works ''
angel
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles ...
appearing in extracanonical Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
, and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
ic mystical
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
and magical works, often as one of the Seven Archangels
The concept of Seven Archangels is found in some works of early Jewish literature and in Christianity. In those texts, they are referenced as the angels who serve God directly.
Bible
The term ''archangel'' itself is not found in the Hebrew Bib ...
, the angel of Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, and in other roles.
In Jewish mystical literature
 Qafsiel is invoked in an ancient Hebrew charm to tell if an enemy is running away. Gustav Davidson writes that Qafsiel is described as the ruler of the seventh heaven in 3 Enoch, citing Odeberg's edition. However, Odeberg's edition only states in a footnote that Qafsiel is "(one of) the guardian(s) of the door of the seventh Hall" in ''Hekhalot Rabbati''. In turn, Qaspiel is described in ''Hekhalot Rabbati'' as a guardian of the ''sixth'' palace, armed with a lightning-dripping sword (which shouts "Ruin!") as well as a bow, tempests, light, and powerful winds—weapons which he uses against anyone not fit to see God. Qaspiel is later described in the same work as one of three "guardians of the entrance of the seventh palace," alongside Dumiel and
Qafsiel is invoked in an ancient Hebrew charm to tell if an enemy is running away. Gustav Davidson writes that Qafsiel is described as the ruler of the seventh heaven in 3 Enoch, citing Odeberg's edition. However, Odeberg's edition only states in a footnote that Qafsiel is "(one of) the guardian(s) of the door of the seventh Hall" in ''Hekhalot Rabbati''. In turn, Qaspiel is described in ''Hekhalot Rabbati'' as a guardian of the ''sixth'' palace, armed with a lightning-dripping sword (which shouts "Ruin!") as well as a bow, tempests, light, and powerful winds—weapons which he uses against anyone not fit to see God. Qaspiel is later described in the same work as one of three "guardians of the entrance of the seventh palace," alongside Dumiel and Gabriel
In Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብ� ...
. Qaspiel is also listed in ''Ma'aseh Merkavah'' as a guardian of the ''second'' palace. ''Sefer Raziel'' lists Qafsiel as the prince of Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
. The Zohar
The ''Zohar'' ( he, , ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work in the literature of Jewish mystical thought known as Kabbalah. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah (the five ...
describes Qafsiel as one of the two chief aides (alongside Hizqiel) to Gabriel. Qaspiel is also described as one of the angels of death in Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
; specifically the angel
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God.
Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles ...
who presides over the deaths of young men.
In western occult literature
 Cassiel is listed in the related works ''
Cassiel is listed in the related works ''The Sworn Book of Honorius
''The Sworn Book of Honorius'' ( la, Liber juratus Honorii, also ''Liber sacer'', ''sacratus'' or ''consecratus'') is a medieval grimoire purportedly written by Honorius of Thebes. The Latin word "juratus", which is typically translated to "swor ...
'' and in (pseudo)- Peter de Abano's ''Heptameron'' (the latter also influenced by ''Sefer Raziel''). Cassiel's presence in ''Honorius'' may also be a result of Greek influence, as he is likewise listed in a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
exorcism
Exorcism () is the religious or spiritual practice of evicting demons, jinns, or other malevolent spiritual entities from a person, or an area, that is believed to be possessed. Depending on the spiritual beliefs of the exorcist, this may be ...
manual (as Kasiel). In these works, he is, as usual, listed as the angel of Saturn but also as the angel of the North and as one of the angels named in the Sigillum Dei
The Sigillum Dei (seal of God, or signum dei vivi, symbol of the living God, called by John Dee the Sigillum Dei Aemeth) is a magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, two heptagons, and one heptagram, and is labeled with the name ...
. Following Honorius and the Heptameron, Cassiel appears in the ''Liber de Angelis'' as Cassael (again the angel over Saturn), then in various editions of the ''Key of Solomon
The ''Key of Solomon'' ( la, Clavicula Salomonis; he, מפתח שלמה []) (Also known as "The Greater Key of Solomon") is a pseudepigraphical grimoire (also known as a book of spells) attributed to Solomon, King Solomon. It probably dates b ...
'' as Cassiel or Cassael, angel (sometimes archangel) over Saturn or Saturday, and once again in the Sigillum Dei. Cassiel is depicted in Francis Barrett's '' The Magus'' as a dragon-riding Djinn with a beard, again as the angel over Saturn.
Other works
Cassiel is sometimes described as the angel of tears and the angel of temperance. As Qafsiel, he is sometimes regarded as the ruler of themoon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
instead of Saturn.
Averroes
Ibn Rushd ( ar, ; full name in ; 14 April 112611 December 1198), often Latinized as Averroes ( ), was an
Andalusian polymath and jurist who wrote about many subjects, including philosophy, theology, medicine, astronomy, physics, psy ...
and Ibn Arabi
Ibn ʿArabī ( ar, ابن عربي, ; full name: , ; 1165–1240), nicknamed al-Qushayrī (, ) and Sulṭān al-ʿĀrifīn (, , ' Sultan of the Knowers'), was an Arab Andalusian Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher, extremely influen ...
likewise listed Saturn as the planetary counterpart of the archangel Kafziel.
Ahmad al-Buni listed Kasfiyail as one of eight angels, among whom each has its own hierarchy of spirits under command.
In popular culture
*Cassiel is the main protagonist in '' The Outcast Season'' series by Rachel Caine. *Cassiel appears inWim Wenders
Ernst Wilhelm "Wim" Wenders (; born 14 August 1945) is a German filmmaker, playwright, author, and photographer. He is a major figure in New German Cinema. Among many honors, he has received three nominations for the Academy Award for Best Docu ...
's film ''Wings of Desire
''Wings of Desire'' (, ; ) is a 1987 romantic fantasy film written by Wim Wenders, Peter Handke and Richard Reitinger, and directed by Wenders. The film is about invisible, immortal angels who populate Berlin and listen to the thoughts of it ...
'', as well as the U.S. remake, '' City of Angels''. Wenders found the name in an encyclopedia about angels. Cassiel, played by Otto Sander
Otto Sander (; 30 June 1941 – 12 September 2013) was a German film, theater, and voice actor.
Life
Education and early career
Sander grew up in Kassel, where he graduated in 1961 from the Friedrichgymnasium. After leaving school he s ...
in the original and Andre Braugher
Andre Keith Braugher (; born July 1, 1962) is an American actor. He is best known for his roles as Detective Frank Pembleton in the police drama series '' Homicide: Life on the Street'' (1993–1999), used car salesman Owen Thoreau Jr. in the com ...
in the remake, watches with considerable ambivalence as his friend becomes human. In the sequel ''Faraway, So Close!
''Faraway, So Close!'' (german: In weiter Ferne, so nah!) is a 1993 German fantasy film directed by Wim Wenders. The screenplay is by Wenders, Richard Reitinger and Ulrich Zieger. It is a sequel to Wenders' 1987 film ''Wings of Desire''. Actors ...
'', Cassiel himself becomes human. Nick Cave
Nicholas Edward Cave (born 22 September 1957) is an Australian singer, songwriter, poet, lyricist, author, screenwriter, composer and occasional actor. Known for his baritone voice and for fronting the rock band Nick Cave and the Bad Seeds, ...
wrote "Cassiel's Song" as part of the music for that film.
See also
* List of angels in theology *Zaphkiel
Zaphkiel ( he, צַפְקִיאֵל ''Ṣafqīʾēl''), also written as Tzaphqiel, Tzaphkiel, Zafkiel, Zafchial, Zaphchial, Zaphiel, or Zelel, is an archangel. He is sometimes equated with Jophiel/Zophiel, but other times considered to be a diff ...
References
{{Angels in Abrahamic Religions Archangels Archangels in Christianity Archangel in Judaism Angels in Islam Individual angels