Carteia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Carteia ( grc, Καρτηίᾳ) was a
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
n and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
town at the head of the Bay of Gibraltar
The Bay of Gibraltar ( es, Bahía de Algeciras), is a bay at the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula. It is around long by wide, covering an area of some , with a depth of up to in the centre of the bay. It opens to the south into the Strait ...
in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. It was established at the most northerly point of the bay, next to the town of San Roque, about halfway between the modern cities of Algeciras
Algeciras ( , ) is a municipality of Spain belonging to the province of Cádiz, Andalusia. Located in the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, near the Strait of Gibraltar, it is the largest city on the Bay of Gibraltar ( es, Bahía de Algeci ...
and Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, overlooking the sea on elevated ground at the confluence of two rivers, nowadays called Guadarranque
The Guadarranque ( es, Río Guadarranque) is a short coastal river of Spain in the Andalusian ''comarca'' of Campo de Gibraltar in the province of Cádiz. It is impounded to form the Embalse de Guadarranque. Its name is derived from the Arab '' ...
and Cachon.
According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, it was founded around 940 BC as the trading settlement of ''Kʿrt'' (meaning "city" in the Phoenician language
Phoenician ( ) is an extinct Canaanite Semitic language originally spoken in the region surrounding the cities of Tyre and Sidon. Extensive Tyro-Sidonian trade and commercial dominance led to Phoenician becoming a lingua franca of the maritim ...
; compare Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
and Cartagena). The area had much to offer a trader; the hinterland behind Carteia, in the modern south of Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
, was rich in wood, cereals, oranges, lemons, lead, iron, copper and silver. Dyes were another much sought-after commodity, especially those from the murex
''Murex'' is a genus of medium to large sized predatory tropical sea snails. These are carnivorous marine gastropod molluscs in the family Muricidae, commonly called "murexes" or "rock snails".Houart, R.; Gofas, S. (2010). Murex Linnaeus, 175 ...
shellfish, used to make the prized Tyrian purple
Tyrian purple ( grc, πορφύρα ''porphúra''; la, purpura), also known as Phoenician red, Phoenician purple, royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon. It is ...
. Strabo and Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest Roman geographer. He was born in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less ...
, mention that some believe that Carteia used to be the Tartessos
Tartessos ( es, Tarteso) is, as defined by archaeological discoveries, a historical civilization settled in the region of Southern Spain characterized by its mixture of local Paleohispanic and Phoenician traits. It had a proper writing system ...
. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
writes that Carteia was called by the Greeks Tartessos.
The town's strategic location meant that it played a significant role in the wars between Carthage and the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
in the 2nd and 3rd centuries BC. It may have been the site of Hamilcar __NOTOC__
Hamilcar ( xpu, 𐤇𐤌𐤋𐤊 , ,. or , , "Melqart is Gracious"; grc-gre, Ἁμίλκας, ''Hamílkas'';) was a common Carthaginian masculine given name. The name was particularly common among the ruling families of ancient Carthage. ...
's landing with his army and elephants in 237 BC, and in 206 BC the Carthaginian admiral Adherbal retreated there with the remnants of his fleet after being defeated by Gaius Laelius in the Battle of Carteia
The Battle of Carteia, also known by the modern name Battle of the Guadalquivir, was a battle of the Second Punic War that took place in 206 BC between the forces of Carthage and the Roman Republic. The name "Battle of the Guadalquivir" is anach ...
. Around 190 BC, the town was captured by the Romans.
Roman and medieval period

Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
records that in 171 BC, the Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in ...
was petitioned by a group of Romano-Spanish people, the sons of Roman soldiers and Spanish women. Although they were of Roman descent they were not regarded as Roman citizens, nor were they allowed to marry Roman citizens. The Senate responded by elevating Carteia to the status of a ''colonia'' (Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term '' colony''.
Character ...
) and granting around 4,000 Romano-Spanish people the right to live there and receive a grant of land on a similar basis to Roman colonists.
The existing inhabitants were permitted to remain there, while all of the inhabitants were given the right to marry Roman citizens and to carry on trade with Romans. This marked a significant innovation for Rome's overseas colonies; the Carteians were the first outside Italy to receive a civic status known as the Latin Rights
Latin rights (also Latin citizenship, Latin: ''ius Latii'' or ''ius latinum'') were a set of legal rights that were originally granted to the Latins (Latin: "Latini", the People of Latium, the land of the Latins) under Roman law in their origin ...
, halfway between being a non-citizen provincial and a full Roman citizen. Other cities in Spain were later granted a similar status.
The ''Colonia Libertinorum Carteia'' (Freedmen's Colony of Carteia) prospered for another 580 years under Roman rule. It grew to become a substantial city which served as a centre for the export of local wines, shipped in amphora
An amphora (; grc, ἀμφορεύς, ''amphoreús''; English plural: amphorae or amphoras) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storag ...
e fired in large kilns found on the site, and the manufacture of ''garum
Garum is a fermented fish sauce that was used as a condiment in the cuisines of Phoenicia, ancient Greece, Rome, Carthage and later Byzantium. Liquamen is a similar preparation, and at times they were synonymous. Although garum enjoyed its gre ...
'' fish sauce. Carteia acquired a mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaAE ...
, amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
, temples and port, and played a significant role in late Roman Republican affairs. Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
made it his western base for his campaign against Mediterranean pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
in 68 BC. His sons Gnaeus and Sextus
Sextus is an ancient Roman ''praenomen'' or "first name". Its standard abbreviation is Sex., and the feminine form would be Sexta. It is one of the numeral ''praenomina'', like Quintus ("fifth") and Decimus ("tenth"), and means "sixth". Although i ...
raised an army there in 45 BC before being defeated by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
at the Battle of Munda
The Battle of Munda (17 March 45 BC), in southern Hispania Ulterior, was the final battle of Caesar's civil war against the leaders of the Optimates. With the military victory at Munda and the deaths of Titus Labienus and Gnaeus Pompeius (elde ...
. While Gnaeus was captured and executed, Sextus escaped via Carteia's port and fled north to the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
.
Little is known of the remainder of Carteia's Roman history, but it appears to have been sacked by the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
around 409 AD, by which time it was probably already in decline. Nonetheless, archaeological evidence shows that urban life continued there into the medieval period. The foundations of an early Christian basilica have been found, a Visigothic necropolis exists near one of the Roman temples, and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
remains discovered at the site show its continued occupation when Carteia was incorporated into the Byzantine province of Spania
Spania ( la, Provincia Spaniae) was a province of the Eastern Roman Empire from 552 until 624 in the south of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. It was established by the Emperor Justinian I in an effort to restore the western prov ...
during the 6th-7th centuries.
In the 9th century, after the Umayyad conquest of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of t ...
, Islamic sources referred to the town – which was probably not much more than a village by then – as ''Qartayanna'' or Cartagena. The Marinids
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) ar ...
constructed a tower nearby, known today as the ''Torre de Cartagena'', using stones from the ruined Roman walls.
Rediscovery and current condition
The site of Carteia was rediscovered by a young British Army officer, John Conduitt, who served in Gibraltar ascommissary
A commissary is a government official charged with oversight or an ecclesiastical official who exercises in special circumstances the jurisdiction of a bishop.
In many countries, the term is used as an administrative or police title. It often c ...
to the garrison between April 1713 to early 1717. He identified the city as having stood on a hill then known as El Rocadillo, which Richard Ford
Richard Ford (born February 16, 1944) is an American novelist and short story writer. His best-known works are the novel ''The Sportswriter'' and its sequels, ''Independence Day'', ''The Lay of the Land'' and ''Let Me Be Frank With You'', and the ...
described in his ''A Handbook for Travellers in Spain
''A Handbook for Travellers in Spain'' is an 1845 work of travel literature by English writer Richard Ford. It has been described as a defining moment in the genre.
British tourists were travelling through Europe in increasing numbers and the n ...
'' (1845):
Conduitt communicated his discovery to the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in London and was invited to read a paper on Carteia on his return to the capital. He did so on 20 June 1717, with Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, Theology, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosophy, natural philosopher"), widely ...
in attendance as chair. Coincidentally, Newton was also interested in Carteia, as he was in the middle of writing his work '' The Chronology of Ancient Kingdoms'', and he invited Conduitt to his home to discuss the ancient city. It was there that Conduitt met Newton's niece, Catherine Barton. After a whirlwind courtship the two were married on 26 August 1717, though Barton was almost a decade older than Conduitt, albeit still renowned for her beauty.
An early 19th-century writer, the anonymous "Calpensis", described how he had "often walked over the site of Carteia, attracted by the rich variety of broken pieces of marble scattered over the fields. Part of the wall enclosing the farm-house was then rudely made up of broken pillars, columns and cornices, of marble of the finest workmanship."
Some of the earliest excavations were carried out at the behest of the British; in 1811–12, Vice-Admiral Charles Penrose reached agreement with the estate's owners to allow amateur antiquarians from Gibraltar to "excavate and examine any part of its ground for antiquities." The excavations found the remains of a tessellated Roman pavement, which was thought to belong to a temple, as well as foundations of Roman buildings.
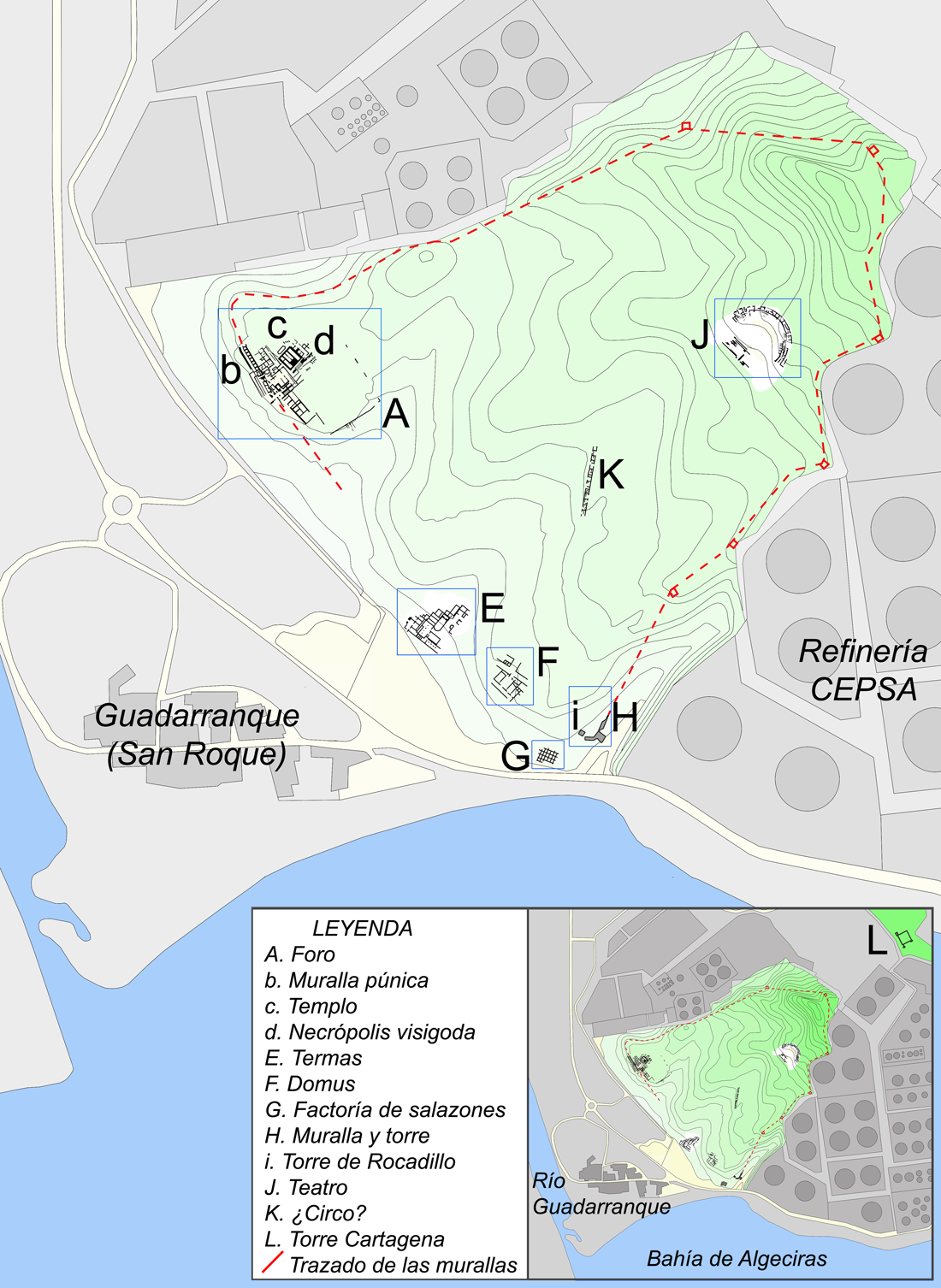
Although the area around Carteia was open farmland in the time of "Calpensis", it is now heavily industrialised. The site of Carteia is surrounded on three sides by an oil refinery. It was not given protection until as late as the 1960s, by which time the necropolis and city gates had been lost to encroaching development. However, the main urban area has been preserved and can be visited. A number of significant structures can still be seen, including the original Carthaginian city gate, a monumental sandstone flight of steps leading down to what was possibly the forum, a large temple, a number of houses and an extensive Roman baths. The 16th century ''Torre de Rocadillo'' can also be seen. From 1971 to 1974, excavations were carried out which found part of a bust of the Emperor Augustus and a headless statue of a man wearing a toga
The toga (, ), a distinctive garment of ancient Rome, was a roughly semicircular cloth, between in length, draped over the shoulders and around the body. It was usually woven from white wool, and was worn over a tunic. In Roman historical tra ...
. The Carteia Archaeological Museum in San Roque displays archaeological finds from the site.
References
{{reflist, 2 171 BC 170s BC establishments Archaeological sites in Andalusia Buildings and structures in the Province of Cádiz Coloniae (Roman) Roman sites in Spain Roman towns and cities in Spain Tourist attractions in Andalusia San Roque, Cádiz Phoenician colonies in Spain