Capture of Jericho on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Capture of Jericho occurred between 19 and 21 February 1918 to the east of
 The advance from
The advance from
 The country on the eastern side of the
The country on the eastern side of the
 The plan was for the 60th (London) Division to advance to Mukhmas north-north-east of Jerusalem, then advance forward east through El Muntar Iraq Ibrahim and Ras et Tawil. Their left flank was to be covered the 53rd (Welsh) Division, which was to capture the high ground at Rammun north of Mukhmas while their right was covered by the Anzac Mounted Division.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 304 The second stage required the 60th (London) Division to advance to a point yet to be decided, in three brigade columns: the right to Jebil Ekteif south of the main Jericho road, the centre to Talat ed Dumm, and the left column moving along the "Ancient Road" running east from Mukhmas. Their final advance would take them to the edge of the ridge overlooking Jericho and the Jordan Valley; there was no plan for them to enter the valley. Each infantry column was to be supported by a 60-pounder or 6-inch artillery battery, a
The plan was for the 60th (London) Division to advance to Mukhmas north-north-east of Jerusalem, then advance forward east through El Muntar Iraq Ibrahim and Ras et Tawil. Their left flank was to be covered the 53rd (Welsh) Division, which was to capture the high ground at Rammun north of Mukhmas while their right was covered by the Anzac Mounted Division.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 304 The second stage required the 60th (London) Division to advance to a point yet to be decided, in three brigade columns: the right to Jebil Ekteif south of the main Jericho road, the centre to Talat ed Dumm, and the left column moving along the "Ancient Road" running east from Mukhmas. Their final advance would take them to the edge of the ridge overlooking Jericho and the Jordan Valley; there was no plan for them to enter the valley. Each infantry column was to be supported by a 60-pounder or 6-inch artillery battery, a
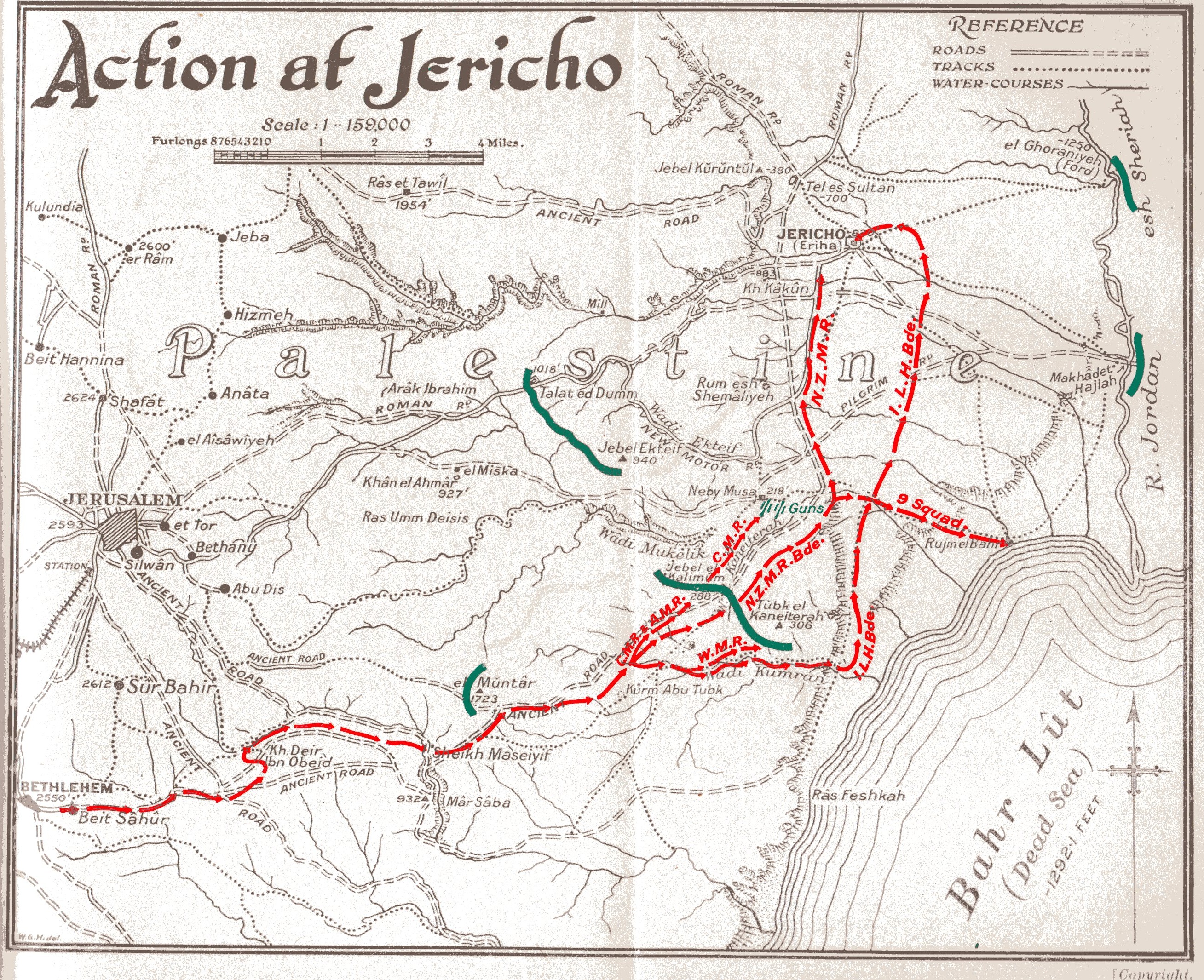 Meanwhile, the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade (with the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment which had returned from the 179th Brigade) led the 1st Light Horse Brigade at 03:30 in their advanced on El Muntar.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 308 The advance guard formed by the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment moved from Bethlehem along an ancient road down the Wadi en Nar to the valley near El Muntar hill, followed by their brigade and the 1st Light Horse Brigade. They zig-zagged down to the valley floor while Ottoman soldiers on the height of El Muntar above watched their approach. Because of the terrain they moved in single file: the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was strung out from five to eight miles (8.0–13 km), and it was hours before the long column could deploy for the attack.
Meanwhile, the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade (with the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment which had returned from the 179th Brigade) led the 1st Light Horse Brigade at 03:30 in their advanced on El Muntar.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 308 The advance guard formed by the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment moved from Bethlehem along an ancient road down the Wadi en Nar to the valley near El Muntar hill, followed by their brigade and the 1st Light Horse Brigade. They zig-zagged down to the valley floor while Ottoman soldiers on the height of El Muntar above watched their approach. Because of the terrain they moved in single file: the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was strung out from five to eight miles (8.0–13 km), and it was hours before the long column could deploy for the attack.
 By 06:00 all the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was in the valley; the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment was attacking Hill 306 while the Canterbury and Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiments attacked Hill 288. Shortly after 12:00 a mounted advance by an Auckland squadron took Hill 288, and Hill 306 was captured soon after. They attacked Ottoman positions from Tibq el Quneitra to Jebel el Kahmum astride the Mar Saba–Jericho road. These were both occupied soon after 14:00, forcing the Ottoman defenders to fall back to Nebi Musa. But Nebi Musa was strongly held by entrenched Ottoman soldiers supported by artillery, which made it impossible to move on: the attack was postponed until the next day.
Meanwhile, at dusk, the 1st Light Horse Brigade began its descent. They moved down the Wadi Qumran to the Jordan Valley, following a goat track which fell in to get into position to attack Nebi Musa from the rear. This journey was successfully completed by midnight.
By 06:00 all the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was in the valley; the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment was attacking Hill 306 while the Canterbury and Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiments attacked Hill 288. Shortly after 12:00 a mounted advance by an Auckland squadron took Hill 288, and Hill 306 was captured soon after. They attacked Ottoman positions from Tibq el Quneitra to Jebel el Kahmum astride the Mar Saba–Jericho road. These were both occupied soon after 14:00, forcing the Ottoman defenders to fall back to Nebi Musa. But Nebi Musa was strongly held by entrenched Ottoman soldiers supported by artillery, which made it impossible to move on: the attack was postponed until the next day.
Meanwhile, at dusk, the 1st Light Horse Brigade began its descent. They moved down the Wadi Qumran to the Jordan Valley, following a goat track which fell in to get into position to attack Nebi Musa from the rear. This journey was successfully completed by midnight.
 On 22 February the 60th (London) Division withdrew its main line to Jebel Ekteif – Talat ed Dumm – Ras et Tawil, leaving outposts on the cliffs above the Jordan Valley and the Anzac Mounted Division started their journey back to Richon LeZion via Bethlehem. The Anzac Mounted Division left behind in the Jordan Valley the Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiment with a subsection of machine guns and an artillery battery (under orders of the 60th Division) in a strong position where the road from Jerusalem falls into the Jordan Valley.
Ottoman troops on the western bank of the Jordan River were holding a strong bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh, protecting the old stone bridge on the main Jerusalem to Es Salt road. There was also a smaller detachment down stream, covering the ford at Makhadet Hijlah (the traditional site of Christ's baptism).Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 309
The Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment patrolled the Jordan River and valley area under enemy observation, attracting artillery shelling from Ottoman field guns. The patrols monitored the Ottoman positions at Ghoraniyeh and Makhadet Hajlah ("Partridge Ford"; cf. Deir Hijla) until 25 February when all Ottoman troops, guns and a pontoon bridge were found to have been removed to the east bank of the river. At the same time Shunet Nimrin was rapidly entrenched by the Ottoman Seventh Army and was soon held in force.
On 22 February the 60th (London) Division withdrew its main line to Jebel Ekteif – Talat ed Dumm – Ras et Tawil, leaving outposts on the cliffs above the Jordan Valley and the Anzac Mounted Division started their journey back to Richon LeZion via Bethlehem. The Anzac Mounted Division left behind in the Jordan Valley the Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiment with a subsection of machine guns and an artillery battery (under orders of the 60th Division) in a strong position where the road from Jerusalem falls into the Jordan Valley.
Ottoman troops on the western bank of the Jordan River were holding a strong bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh, protecting the old stone bridge on the main Jerusalem to Es Salt road. There was also a smaller detachment down stream, covering the ford at Makhadet Hijlah (the traditional site of Christ's baptism).Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 309
The Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment patrolled the Jordan River and valley area under enemy observation, attracting artillery shelling from Ottoman field guns. The patrols monitored the Ottoman positions at Ghoraniyeh and Makhadet Hajlah ("Partridge Ford"; cf. Deir Hijla) until 25 February when all Ottoman troops, guns and a pontoon bridge were found to have been removed to the east bank of the river. At the same time Shunet Nimrin was rapidly entrenched by the Ottoman Seventh Army and was soon held in force.
 Ottoman army garrisons continued to hold the Hedjaz railway from Deraa to
Ottoman army garrisons continued to hold the Hedjaz railway from Deraa to
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
beginning the Occupation of the Jordan Valley
The occupation of the Jordan Valley by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) began in February 1918 during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I. After the Capture of Jericho in February the Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment began pa ...
during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighti ...
. Fighting took place in an area bordered by the Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital of ...
–Nablus
Nablus ( ; ar, نابلس, Nābulus ; he, שכם, Šəḵem, ISO 259-3: ; Samaritan Hebrew: , romanized: ; el, Νεάπολις, Νeápolis) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a populati ...
road in the west, the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
in the east, and north of a line from Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
to the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank t ...
. Here a British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
force attacked Ottoman positions, forcing them back to Jericho
Jericho ( ; ar, أريحا ; he, יְרִיחוֹ ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank. It is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It is the administrative seat of the Jericho Gover ...
and eventually across the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
.
Winter rains put an end to campaigning after the advance from the Gaza–Beersheba
Beersheba or Beer Sheva, officially Be'er-Sheva ( he, בְּאֵר שֶׁבַע, ''Bəʾēr Ševaʿ'', ; ar, بئر السبع, Biʾr as-Sabʿ, Well of the Oath or Well of the Seven), is the largest city in the Negev desert of southern Israel. ...
line to the capture of Jerusalem in December 1917. This lull in the fighting offered the opportunity for the captured territories to be consolidated. Extensive developments were also required along the lines of communication
A line of communication (or communications) is the route that connects an operating military unit with its supply base. Supplies and reinforcements are transported along the line of communication. Therefore, a secure and open line of communicati ...
to ensure that front-line
A front line (alternatively front-line or frontline) in military terminology is the position(s) closest to the area of conflict of an armed force's personnel and equipment, usually referring to land forces. When a front (an intentional or uninte ...
troops were adequately supplied, approximately from their main bases at Moascar and Kantara on the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
.
General Edmund Allenby
Field Marshal Edmund Henry Hynman Allenby, 1st Viscount Allenby, (23 April 1861 – 14 May 1936) was a senior British Army officer and Imperial Governor. He fought in the Second Boer War and also in the First World War, in which he led th ...
's initial strategic plans focused on his open right flank. If attacked with sufficiently large forces, he could be outflanked by an attack from the east—unlike his left flank which rested securely on the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
to the west. His aim was to capture the territory east of Jerusalem stretching to the Dead Sea, where his right flank could be more secure. The area was garrisoned by Ottoman troops entrenched on hill-tops which the British infantry, Australian light horse
Australian Light Horse were mounted troops with characteristics of both cavalry and mounted infantry, who served in the Second Boer War and World War I. During the inter-war years, a number of regiments were raised as part of Australia's part-t ...
and New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade
The New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was a brigade of the New Zealand Army during the First World War. Raised in 1914 as part of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force, it was one of the first New Zealand units to sail for service overseas.
Th ...
s attacked. The infantry captured Talat ed Dumm on the main Jerusalem to Jericho road, while the light horse and mounted rifle brigades captured Jericho and the area to the south bordered by the Jordan River and the Dead Sea.
Background
 The advance from
The advance from Beersheba
Beersheba or Beer Sheva, officially Be'er-Sheva ( he, בְּאֵר שֶׁבַע, ''Bəʾēr Ševaʿ'', ; ar, بئر السبع, Biʾr as-Sabʿ, Well of the Oath or Well of the Seven), is the largest city in the Negev desert of southern Israel. ...
came to a halt in December.Bou 2009, p. 185 On 14 December Allenby reported to the War Cabinet
A war cabinet is a committee formed by a government in a time of war to efficiently and effectively conduct that war. It is usually a subset of the full executive cabinet of ministers, although it is quite common for a war cabinet to have senior ...
that the rainy season would prevent any further operations, after Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
was secured, for at least two months. At this time, the Egyptian Expeditionary Force
The Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) was a British Empire military formation, formed on 10 March 1916 under the command of General Archibald Murray from the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force and the Force in Egypt (1914–15), at the beginning ...
was paralysed by a breakdown in logistics
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics manages the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of ...
forcing Allenby to send the Anzac
The Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) was a First World War army corps of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force. It was formed in Egypt in December 1914, and operated during the Gallipoli campaign. General William Birdwood comman ...
and the Australian Mounted Division
The Australian Mounted Division originally formed as the Imperial Mounted Division in January 1917, was a mounted infantry, light horse and yeomanry division. The division was formed in Egypt, and along with the Anzac Mounted Division formed pa ...
s, along with the Imperial Camel Corps Brigade
The Imperial Camel Corps Brigade (ICCB) was a camel-mounted infantry brigade that the British Empire raised in December 1916 during the First World War for service in the Middle East.
From a small beginning the unit eventually grew to a brig ...
south of Gaza to shorten their lines of communication. He wrote: "I can't feed them, with certainty, and even now, a fortnight's heavy rain would bring me near starvation." On 1 January, the 5th Mounted Brigade
The 1st South Midland Mounted Brigade (later numbered as the 5th Mounted Brigade) was a yeomanry brigade of the British Army, formed as part of the Territorial Force in 1908.
It served dismounted in the Gallipoli Campaign before being remount ...
began moving back through the rain and slush followed by the 4th Light Horse Brigades Field Ambulance, beginning the Australian Mounted Division's journey back to Deir el Belah south of Gaza. The Anzac Mounted Division did not move back quite so far; the 1st
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
and possibly 2nd Light Horse Brigades moved back to Esdud while the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade
The New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was a brigade of the New Zealand Army during the First World War. Raised in 1914 as part of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force, it was one of the first New Zealand units to sail for service overseas.
Th ...
bivouacked near Ayun Kara (also known as Rishon LeZion
Rishon LeZion ( he, רִאשׁוֹן לְצִיּוֹן , ''lit.'' First to Zion, Arabic: راشون لتسيون) is a city in Israel, located along the central Israeli coastal plain south of Tel Aviv. It is part of the Gush Dan metropolitan ar ...
) not far from Jaffa.
Allenby wrote on 25 January: "I want to extend my right, to include Jericho and the N rthof the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank t ...
." This advance would remove the more serious threat to his right by pushing all the enemy across the Jordan River and securing the Jordan River crossings. It would also prevent raids into the country to the west of the Dead Sea and provide a narrow starting point for operations against the Hedjaz Railway.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 303
General Jan Christiaan Smuts
Field Marshal Jan Christian Smuts, (24 May 1870 11 September 1950) was a South African statesman, military leader and philosopher. In addition to holding various military and cabinet posts, he served as prime minister of the Union of South Af ...
, a member of the Imperial War Cabinet
The Imperial War Cabinet (IWC) was the British Empire's wartime coordinating body. It met over three sessions, the first from 20 March to 2 May 1917, the second from 11 June to late July 1918, and the third from 20 or 25 November 1918 to early Jan ...
, was sent to confer with Allenby regarding the implementation of a French qualification to the War Office
The War Office was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, when its functions were transferred to the new Ministry of Defence (MoD). This article contains text from t ...
's Joint Note No. 12—that no troops from France could be redeployed to the Egyptian Expeditionary Force. Smuts was on his way back to London in February when the first step was taken to accomplish his suggestion of crossing the Jordan River and capturing the Hedjaz Railway, and the front line was extended eastwards with the successful capture of Jericho.
Prelude
 The country on the eastern side of the
The country on the eastern side of the Judean Hills
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel wh ...
falls into the Jordan Valley in a confused mass of rocky ridges and deep narrow valleys.Wavell 1968 pp. 177–8 All the main wadis run from west to east; often with steep high banks, while the tributaries joined from all directions, breaking up the ridges making the hills, almost impossible to cross. Most tracks ran along the narrow beds of ravines where progress had to be made in single file. Further north at Jebel Kuruntul (also known as Jebel Quruntul, the Mount of Temptation
Mount of Temptation, in Palestinian Arabic ( ar, جبل لقرنطل), is a mountain over the town of Jericho in the Judean Desert, in the West Bank. Ancient Christian tradition identifies it as the location of the temptation of Jesus described ...
and Mount Quarantania) the mountains end abruptly in a 1,000-foot (300 m) cliff.Blenkinsop 1925, p. 223Cutlack 1941, p. 103 Sometimes the attacking parties had to haul themselves and each other over abrupt cliffs to be in a position to fight at close quarters at the top.Cutlack 1941, pp. 102–3 Yet, in early Spring, the area was covered by wild flowers including cyclamen, anemones, poppies and tulips.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 305
Defending force
Three Ottoman armies were deployed to defend their front line: the Eighth Army (headquartered at Tul Keram) defended the Mediterranean section, the Seventh Army (headquartered at Nablus) defended the Judean Hills sector, and the Fourth Army (headquartered at Amman) defended the eastern Transjordan section of the line. Between 3,000 and 5,000 Ottoman troops from the 26th and 53rd Infantry Divisions XX Corps defended the area on the western edge of the Jordan Valley. They garrisoned a series of hill-tops from Tubk el Kaneiterah, near the Dead Sea, through Talat ed Dumm to the Wadi Fara. Here the XX Corps was entrenched at Ras um Deisis and El Muntar Iraq Ibrahim astride the Jericho road.Erickson 2001 p. 193 There was also at least one regiment in the Jordan Valley near the Wadi el Auja.Mounted and infantry attacking force
By February, logistics had sufficiently developed to support the advance towards Jericho, and Allenby ordered Lieutenant GeneralPhilip Chetwode
Field Marshal Philip Walhouse Chetwode, 1st Baron Chetwode, 7th Baronet of Oakley, (21 September 1869 – 6 July 1950), was a senior British Army officer. He saw action during the Second Boer War, during which he was present at the Siege of Ladys ...
to capture Jericho as soon as the weather cleared. While the remainder of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force held the front line and garrisoned the captured territories in southern Palestine, Chetwode's XX Corps the 60th (2/2nd London) Division
The 60th (2/2nd London) Division was an infantry division of the British Army raised during the First World War. It was the second line-formation of the 47th (1/2nd London) Division, and was the second of two such Territorial Force divisions fo ...
was to make the attack towards Jericho, supported by his 53rd (Welsh) Division and one infantry brigade from the 74th (Yeomanry) Division
The 74th (Yeomanry) Division was a Territorial Force infantry division formed in Palestine in early 1917 from three dismounted yeomanry brigades. It served in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War, mostly as part of XX Corps. ...
on the left. They were to move towards the Wadi el Auja, which flowed eastwards into the Jordan River (not to be confused with the Wadi el Auja which flowed westwards into the Mediterranean Sea from the same watershed). At the same time, Chauvel's Desert Mounted Corps
The Desert Mounted Corps was an army corps of the British Army during the First World War, of three mounted divisions renamed in August 1917 by General Edmund Allenby, from Desert Column. These divisions which served in the Sinai and Palestin ...
, mounted force formed by the 1st Light Horse Brigade
The 1st Light Horse Brigade was a mounted infantry brigade of the Australian Imperial Force (AIF), which served in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I. The brigade was initially formed as a part-time militia formation in the early 1900s in ...
and the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade
The New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was a brigade of the New Zealand Army during the First World War. Raised in 1914 as part of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force, it was one of the first New Zealand units to sail for service overseas.
Th ...
(both brigades from the Anzac Mounted Division), was to cover the right flank of Chetwode's infantry and advance towards Rujm el Bahr on the Dead Sea.Cutlack 1941, p. 102The 2nd Light Horse Brigade remained on the maritime plain, near the Mediterranean Sea, holding a portion of the front line. owles 1922 p. 173/ref>
 The plan was for the 60th (London) Division to advance to Mukhmas north-north-east of Jerusalem, then advance forward east through El Muntar Iraq Ibrahim and Ras et Tawil. Their left flank was to be covered the 53rd (Welsh) Division, which was to capture the high ground at Rammun north of Mukhmas while their right was covered by the Anzac Mounted Division.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 304 The second stage required the 60th (London) Division to advance to a point yet to be decided, in three brigade columns: the right to Jebil Ekteif south of the main Jericho road, the centre to Talat ed Dumm, and the left column moving along the "Ancient Road" running east from Mukhmas. Their final advance would take them to the edge of the ridge overlooking Jericho and the Jordan Valley; there was no plan for them to enter the valley. Each infantry column was to be supported by a 60-pounder or 6-inch artillery battery, a
The plan was for the 60th (London) Division to advance to Mukhmas north-north-east of Jerusalem, then advance forward east through El Muntar Iraq Ibrahim and Ras et Tawil. Their left flank was to be covered the 53rd (Welsh) Division, which was to capture the high ground at Rammun north of Mukhmas while their right was covered by the Anzac Mounted Division.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 304 The second stage required the 60th (London) Division to advance to a point yet to be decided, in three brigade columns: the right to Jebil Ekteif south of the main Jericho road, the centre to Talat ed Dumm, and the left column moving along the "Ancient Road" running east from Mukhmas. Their final advance would take them to the edge of the ridge overlooking Jericho and the Jordan Valley; there was no plan for them to enter the valley. Each infantry column was to be supported by a 60-pounder or 6-inch artillery battery, a Field artillery
Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support army, armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement.
Until the ear ...
brigade and a field company of Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the '' Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is head ...
.
On 14 February, preliminary operations were carried out by the XX Corps; the 60th (London) Division which advanced to Mukhmas north-north-east of Jerusalem, while on their left flank the 53rd (Welsh) Division captured the village of Deir Diwan.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 306 At this time the 1st Light Horse and New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigades were at Ayun Kara; they marched out for Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital of ...
arriving there on 17 and 18 February. While the infantry attacks were progressing along the road between Jerusalem and Jericho on 19 February, the two brigades of the Anzac Mounted Division were to move in a flanking movement towards Nebi Musa. They were to make their way down into the Jordan Valley towards Rujm el Bahr to cut off enemy retreat from Jericho, and drive the remaining Ottoman defenders to the eastern side of the Jordan River.Downes 1938 pp. 679–81
Air support
On 3 January, two Australian aircraft discovered boats carrying corn and hay moving from Ghor el Hadit (behind Point Costigan) and Rujm el Bahr at the northern end of the Dead Sea. These were bombed and sprayed with bullets repeatedly until the boat service stopped. On 10 January, as part of the preparations for the attack on Jericho, six aircraft dropped 48 bombs on Amman and Kissir, a Hedjaz railway station to the south, resulting in several direct hits on rolling stock, station buildings and troops. Aircraft patrols were then directed to fly over Jericho and Shunet Nimrin on the western and eastern sectors of the Jordan Valley on alternate days. These patrols closely watched and reported tactical details, including the number of tents and camps, the state of supply dumps, the conditions of roads and tracks, and traffic on the railway.Battle
Infantry attack on 19 February
The 60th (London) Division advanced with their 180th Brigade in the centre, their 181st Brigade on the left, and their 179th Brigade with the Wellington Mounted Rifle Regiment covering their right flank. At Ras et Tawil, the 2/23rd Battalion, London Regiment (181st Brigade) suffered 50 casualties in attacking some 300 entrenched Ottomans, capturing 25 prisoners and two machine guns; the Ottomans abandoned their position soon after. To the north-east of El Muntar Iraq Ibrahim, during a further advance by the 2/20th Battalion, London Regiment along a narrow ridge on the south bank of the Wadi Fara, they captured the high ground suffering 66 casualties. Meanwhile, on the left flank of the 60th (London) Division, the 160th Brigade of the 53rd (Welsh) Division captured Rammun, where the 2/10th BattalionMiddlesex Regiment
The Middlesex Regiment (Duke of Cambridge's Own) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 until 1966. The regiment was formed, as the Duke of Cambridge's Own (Middlesex Regiment), in 1881 as part of the Childers Re ...
had some hard fighting, and the heights to the south. The Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment moved from Bethlehem to the Greek monastery of Mar Saba and onto the El Buqeia plateau, where Ottoman forces were entrenched astride the Mar Saba to Jericho road south of Nebi Musa.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 307 The remainder of the 1st Light Horse and New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigades moved from Bethlehem towards El Muntar.
Chetwode and Chauvel watched these operations begin from the Mount of Olives more than above sea level; by the time the light horse and mounted rifles brigades reached Jericho on 21 February they were nearly below sea level.Hill 1978, p. 142
20 February
Infantry attack
The three infantry columns advanced: the column in the centre, the 180th Brigade, captured their objective of Talat ed Dumm on the main road from Jerusalem to Jericho. This infantry brigade moved along the Jerusalem to Jericho road towards Talat ed Dumm; they were supported by the 10th Heavy Battery and one 6-inch Howitzer of the 383rd Siege Battery. The village was captured after an hour's bombardment. On the left, the 181st Brigade was slowed in their advance by small rearguards which showed skills in manoeuvre. The brigade was only able to advance to be about halfway between Ras et Tawil and Jebel Qruntul (also known as Jebel Kuruntul, the Mount of Temptation and Mount Quarantania) by nightfall, with the 231st Brigade of the 74th (Yeomanry) Division forming a reserve. On the right, the 179th Brigade column marched towards Jebel Ekteif (to the south of Talat ed Dumm); their 2/13th Battalion, London Regiment, however, faced a sheer drop of over and had to proceed across intervening ridges into parallel wadis, arriving too late for the attack. Meanwhile, two companies of the 2/16th Battalion, London Regiment from the 179th Brigade, of the 60th (London) Division were ordered to support an attack on Jebel Ekteif by the 2/15th Battalion, London Regiment. By 08:15 they had captured the advanced trenches, three companies, and fought their way up into the firing line on the summit of the hill. At 10:00 the British infantry were reported to have captured this dominating position on the Jerusalem–Jericho road, but a strong counter-attack drove them off. Jebel Ektief was finally captured at about 12:30 when heavy artillery helped the desperate attackers secure their objective.Powles 1922, p. 178Falls states it was captured at 11:25. alls 1930 Vol. 2 Part II p. 307/ref>Mounted attack
 Meanwhile, the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade (with the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment which had returned from the 179th Brigade) led the 1st Light Horse Brigade at 03:30 in their advanced on El Muntar.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 308 The advance guard formed by the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment moved from Bethlehem along an ancient road down the Wadi en Nar to the valley near El Muntar hill, followed by their brigade and the 1st Light Horse Brigade. They zig-zagged down to the valley floor while Ottoman soldiers on the height of El Muntar above watched their approach. Because of the terrain they moved in single file: the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was strung out from five to eight miles (8.0–13 km), and it was hours before the long column could deploy for the attack.
Meanwhile, the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade (with the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment which had returned from the 179th Brigade) led the 1st Light Horse Brigade at 03:30 in their advanced on El Muntar.Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 308 The advance guard formed by the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment moved from Bethlehem along an ancient road down the Wadi en Nar to the valley near El Muntar hill, followed by their brigade and the 1st Light Horse Brigade. They zig-zagged down to the valley floor while Ottoman soldiers on the height of El Muntar above watched their approach. Because of the terrain they moved in single file: the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was strung out from five to eight miles (8.0–13 km), and it was hours before the long column could deploy for the attack.
 By 06:00 all the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was in the valley; the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment was attacking Hill 306 while the Canterbury and Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiments attacked Hill 288. Shortly after 12:00 a mounted advance by an Auckland squadron took Hill 288, and Hill 306 was captured soon after. They attacked Ottoman positions from Tibq el Quneitra to Jebel el Kahmum astride the Mar Saba–Jericho road. These were both occupied soon after 14:00, forcing the Ottoman defenders to fall back to Nebi Musa. But Nebi Musa was strongly held by entrenched Ottoman soldiers supported by artillery, which made it impossible to move on: the attack was postponed until the next day.
Meanwhile, at dusk, the 1st Light Horse Brigade began its descent. They moved down the Wadi Qumran to the Jordan Valley, following a goat track which fell in to get into position to attack Nebi Musa from the rear. This journey was successfully completed by midnight.
By 06:00 all the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade was in the valley; the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment was attacking Hill 306 while the Canterbury and Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiments attacked Hill 288. Shortly after 12:00 a mounted advance by an Auckland squadron took Hill 288, and Hill 306 was captured soon after. They attacked Ottoman positions from Tibq el Quneitra to Jebel el Kahmum astride the Mar Saba–Jericho road. These were both occupied soon after 14:00, forcing the Ottoman defenders to fall back to Nebi Musa. But Nebi Musa was strongly held by entrenched Ottoman soldiers supported by artillery, which made it impossible to move on: the attack was postponed until the next day.
Meanwhile, at dusk, the 1st Light Horse Brigade began its descent. They moved down the Wadi Qumran to the Jordan Valley, following a goat track which fell in to get into position to attack Nebi Musa from the rear. This journey was successfully completed by midnight.
21 February
Under cover of darkness, the New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade advanced north along a very rough track and by daylight had reached just east of the Neby Musa position. They made a dismounted attack while British infantry attacked Neby Musa from the rear.Moore 1921, p. 101 The Canterbury Mounted Rifles Regiment occupied Neby Musa at daylight after crossing the gorge on foot to find the Ottoman garrison had withdrawn with their guns.Powles 1922, p. 179 When the 1st Light Horse Brigade reached the floor of the Jordan Valley near the Dead Sea, below sea level, it turned north towards Jericho. A single troop of 3rd Light Horse Regiment entered Jericho at about 08:00 to find the Ottoman garrison had withdrawn. The remainder of the brigade advanced up the Jordan Valley as far as the Wadi el Auja, while the Wellington Mounted Rifles Regiment (New Zealand Mounted Rifles Brigade) occupied Rujm el Bahr on the north shore of the Dead Sea. Meanwhile, the 60th (London) Division moved to the top of the cliff overlooking Jericho and the Jordan Valley from Neby Musa to Jebel Qruntul. Divisional Headquarters Staff set up their report centre about behind Jericho; when they were sitting down to a morning cup of tea, Chetwode and Chauvel joined them. Chaytor was sitting on the step of his car when shells fired from the other side of the Jordan River started to explode. One hit the front of his car and he narrowly escaped injury. This gun continued shelling the area at a range of over ; the British 13-pounders could get no further than . Chetwode's force of infantry and mounted units suffered 510 casualties during these operations.Air support
During these three days of operations No. 1 Squadron's aircraft completely dominated all enemy aircraft, bombing and machine-gunning Ottoman positions, and reporting to headquarters on progress and estimates of Ottoman dispositions and strength. Messages were also dropped on troops in the front line with urgent news. Considerable Ottoman reinforcements were seen to arrive at Shunet Nimrin on the eastern side of the Jordan River, and an aerial raiding formation from No. 1 Squadron bombed troop tents, marquees and a supply dump in the area.Aftermath
 On 22 February the 60th (London) Division withdrew its main line to Jebel Ekteif – Talat ed Dumm – Ras et Tawil, leaving outposts on the cliffs above the Jordan Valley and the Anzac Mounted Division started their journey back to Richon LeZion via Bethlehem. The Anzac Mounted Division left behind in the Jordan Valley the Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiment with a subsection of machine guns and an artillery battery (under orders of the 60th Division) in a strong position where the road from Jerusalem falls into the Jordan Valley.
Ottoman troops on the western bank of the Jordan River were holding a strong bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh, protecting the old stone bridge on the main Jerusalem to Es Salt road. There was also a smaller detachment down stream, covering the ford at Makhadet Hijlah (the traditional site of Christ's baptism).Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 309
The Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment patrolled the Jordan River and valley area under enemy observation, attracting artillery shelling from Ottoman field guns. The patrols monitored the Ottoman positions at Ghoraniyeh and Makhadet Hajlah ("Partridge Ford"; cf. Deir Hijla) until 25 February when all Ottoman troops, guns and a pontoon bridge were found to have been removed to the east bank of the river. At the same time Shunet Nimrin was rapidly entrenched by the Ottoman Seventh Army and was soon held in force.
On 22 February the 60th (London) Division withdrew its main line to Jebel Ekteif – Talat ed Dumm – Ras et Tawil, leaving outposts on the cliffs above the Jordan Valley and the Anzac Mounted Division started their journey back to Richon LeZion via Bethlehem. The Anzac Mounted Division left behind in the Jordan Valley the Auckland Mounted Rifles Regiment with a subsection of machine guns and an artillery battery (under orders of the 60th Division) in a strong position where the road from Jerusalem falls into the Jordan Valley.
Ottoman troops on the western bank of the Jordan River were holding a strong bridgehead at Ghoraniyeh, protecting the old stone bridge on the main Jerusalem to Es Salt road. There was also a smaller detachment down stream, covering the ford at Makhadet Hijlah (the traditional site of Christ's baptism).Falls 1930 Vol. 2 p. 309
The Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment patrolled the Jordan River and valley area under enemy observation, attracting artillery shelling from Ottoman field guns. The patrols monitored the Ottoman positions at Ghoraniyeh and Makhadet Hajlah ("Partridge Ford"; cf. Deir Hijla) until 25 February when all Ottoman troops, guns and a pontoon bridge were found to have been removed to the east bank of the river. At the same time Shunet Nimrin was rapidly entrenched by the Ottoman Seventh Army and was soon held in force.
 Ottoman army garrisons continued to hold the Hedjaz railway from Deraa to
Ottoman army garrisons continued to hold the Hedjaz railway from Deraa to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
(although the line was harassed and cut by insurgent Arab units) and Cemal's VIII and XII Corps 12th Corps, Twelfth Corps, or XII Corps may refer to:
* 12th Army Corps (France)
* XII Corps (Grande Armée), a corps of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XII (1st Royal Saxon) Corps, a unit of the Imperial German Army
* XII ...
guarded the northern Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
ine coast with four infantry divisions. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's War Minister, Enver Pasa, had lost confidence in the commander of the Ottoman forces in Palestine, German General von Falkenhayn, and on 1 March 1918 replaced him with General Otto Liman von Sanders
Otto Viktor Karl Liman von Sanders (; 17 February 1855 – 22 August 1929) was an Imperial German Army general who served as a military adviser to the Ottoman Army during the First World War. In 1918 he commanded an Ottoman army during the Sin ...
.
On 6 March the War Cabinet
A war cabinet is a committee formed by a government in a time of war to efficiently and effectively conduct that war. It is usually a subset of the full executive cabinet of ministers, although it is quite common for a war cabinet to have senior ...
gave Allenby leave to advance "to the maximum extent possible, consistent with the safety of the force under his orders". He decided to create a third infantry corps called the XXII, commanded by Barrow with Wavell as his chief of staff.This corps was not formed because the Spring Offensive had drained Allenby's force. On 21 March an attempt to cut the Hedjaz railway at Amman began; this coincided with the launch of the German spring offensive by Ludendorff against the Allies on the Western Front.Woodward 2006 p. 162Bruce claims that although the occupation of Jericho protected Jerusalem from Ottoman attack from the east, it did not provide the hoped-for secure base to mount operations on the Hedjaz railway. ruce 2002, p. 188/ref>
Notes
;Footnotes ;CitationsReferences
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Jericho, Capture of 1918 Conflicts in 1918 1918 in British-administered Palestine Battles of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign Battles of World War I involving Australia Battles of World War I involving New Zealand Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom Battles of World War I involving the Ottoman Empire Battles of World War I involving Germany February 1918 events