Cam Pha on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all

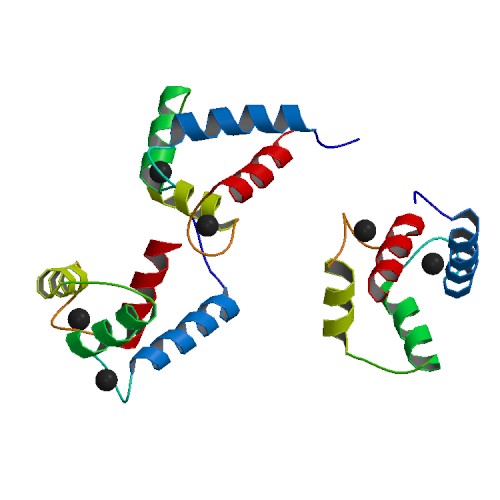 Binding of Ca2+ by the EF-hands causes an opening of the N- and C-domains, which exposes hydrophobic target-binding surfaces. These surfaces interact with complementary nonpolar segments on target proteins, typically consisting of groups of bulky hydrophobic amino acids separated by 10–16 polar and/or basic amino acids. The flexible central domain of calmodulin allows the protein to wrap around its target, although alternate modes of binding are known. "Canonical" targets of calmodulin, such as myosin light-chain kinases and
Binding of Ca2+ by the EF-hands causes an opening of the N- and C-domains, which exposes hydrophobic target-binding surfaces. These surfaces interact with complementary nonpolar segments on target proteins, typically consisting of groups of bulky hydrophobic amino acids separated by 10–16 polar and/or basic amino acids. The flexible central domain of calmodulin allows the protein to wrap around its target, although alternate modes of binding are known. "Canonical" targets of calmodulin, such as myosin light-chain kinases and
 Calmodulin plays an important role in excitation contraction (EC) coupling and the initiation of the cross-bridge cycling in smooth muscle, ultimately causing smooth muscle contraction. In order to activate contraction of smooth muscle, the head of the
Calmodulin plays an important role in excitation contraction (EC) coupling and the initiation of the cross-bridge cycling in smooth muscle, ultimately causing smooth muscle contraction. In order to activate contraction of smooth muscle, the head of the
 While yeasts have only a single CaM gene, plants and vertebrates contain an evolutionarily conserved form of CaM genes. The difference between plants and animals in Ca2+ signaling is that the plants contain an extended family of the CaM in addition to the evolutionarily conserved form. Calmodulins play an essential role in plant development and adaptation to environmental stimuli.
Calcium plays a key role in the structural integrity of the cell wall and the membrane system of the cell. However, high calcium levels can be toxic to a plant's cellular energy metabolism and, hence, the Ca2+ concentration in the cytosol is maintained at a submicromolar level by removing the cytosolic Ca2+ to either the
While yeasts have only a single CaM gene, plants and vertebrates contain an evolutionarily conserved form of CaM genes. The difference between plants and animals in Ca2+ signaling is that the plants contain an extended family of the CaM in addition to the evolutionarily conserved form. Calmodulins play an essential role in plant development and adaptation to environmental stimuli.
Calcium plays a key role in the structural integrity of the cell wall and the membrane system of the cell. However, high calcium levels can be toxic to a plant's cellular energy metabolism and, hence, the Ca2+ concentration in the cytosol is maintained at a submicromolar level by removing the cytosolic Ca2+ to either the
Calmodulin
and it
conformational change
*
 Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular ...
by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases.
Structure
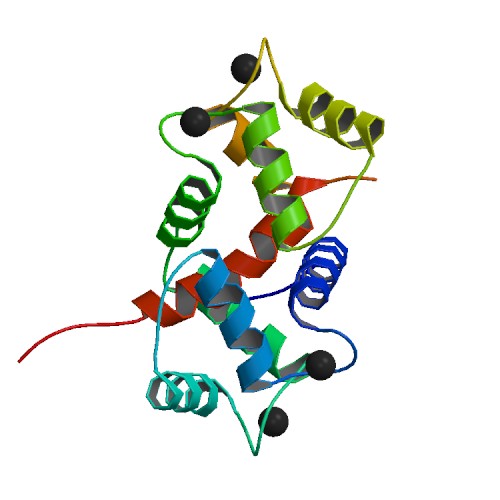
Calmodulin is a small, highly conserved protein that is 148 amino acids long (16.7 kDa). The protein has two approximately symmetrical globular domains (the N- and C- domains) each containing a pair ofEF hand
The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or ''motif'' found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins.
The EF-hand motif contains a helix–loop–helix topology, much like the spread thumb and forefinger of the human hand, i ...
motifs separated by a flexible linker region for a total of four Ca2+ binding sites, two in each globular domain. In the Ca2+-free state, the helices that form the four EF-hands are collapsed in a compact orientation, and the central linker is disordered; in the Ca2+-saturated state, the EF-hand helices adopt an open orientation roughly perpendicular to one another, and the central linker forms an extended alpha-helix in the crystal structure, but remains largely disordered in solution. The C-domain has a higher binding affinity for Ca2+ than the N-domain.
Calmodulin is structurally quite similar to troponin C
Troponin C is a protein which is part of the troponin complex. It contains four calcium-binding EF hands, although different isoforms may have fewer than four functional calcium-binding subdomains. It is a component of thin filaments, along wi ...
, another Ca2+-binding protein containing four EF-hand motifs. However, troponin C contains an additional alpha-helix at its N-terminus, and is constitutively bound to its target, troponin I
Troponin I is a cardiac and skeletal muscle protein family. It is a part of the troponin protein complex, where it binds to actin in thin myofilaments to hold the actin-tropomyosin complex in place. Troponin I prevents myosin from binding to ac ...
. It therefore does not exhibit the same diversity of target recognition as does calmodulin.
Importance of flexibility in calmodulin
Calmodulin's ability to recognize a tremendous range of target proteins is due in large part to its structural flexibility. In addition to the flexibility of the central linker domain, the N- and C-domains undergo open-closed conformational cycling in the Ca2+-bound state. Calmodulin also exhibits great structural variability, and undergoes considerable conformational fluctuations, when bound to targets. Moreover, the predominantly hydrophobic nature of binding between calmodulin and most of its targets allows for recognition of a broad range of target protein sequences. Together, these features allow calmodulin to recognize some 300 target proteins exhibiting a variety of CaM-binding sequence motifs.Mechanism

 Binding of Ca2+ by the EF-hands causes an opening of the N- and C-domains, which exposes hydrophobic target-binding surfaces. These surfaces interact with complementary nonpolar segments on target proteins, typically consisting of groups of bulky hydrophobic amino acids separated by 10–16 polar and/or basic amino acids. The flexible central domain of calmodulin allows the protein to wrap around its target, although alternate modes of binding are known. "Canonical" targets of calmodulin, such as myosin light-chain kinases and
Binding of Ca2+ by the EF-hands causes an opening of the N- and C-domains, which exposes hydrophobic target-binding surfaces. These surfaces interact with complementary nonpolar segments on target proteins, typically consisting of groups of bulky hydrophobic amino acids separated by 10–16 polar and/or basic amino acids. The flexible central domain of calmodulin allows the protein to wrap around its target, although alternate modes of binding are known. "Canonical" targets of calmodulin, such as myosin light-chain kinases and CaMKII
/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM kinase II or CaMKII) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is regulated by the /calmodulin complex. CaMKII is involved in many signaling cascades and is thought to be an important mediator ...
, bind only to the Ca2+-bound protein, whereas some proteins, such as NaV channels and IQ-motif
The IQ calmodulin-binding motif is an amino acid sequence motif containing the following sequence:
* ILVxxx Kxxx Kx ILVWY
The term "IQ" refers to the first two amino acids of the motif: isoleucine (commonly) and glutamine (invariably).
Functio ...
proteins, also bind to calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+. Binding of calmodulin induces conformational rearrangements in the target protein via "mutually induced fit", leading to changes in the target protein's function.
Calcium binding by calmodulin exhibits considerable cooperativity, making calmodulin an unusual example of a monomeric (single-chain) cooperative-binding protein. Furthermore, target binding alters the binding affinity of calmodulin toward Ca2+ ions, which allows for complex allosteric interplay between Ca2+ and target binding interactions. This influence of target binding on Ca2+ affinity is believed to allow for Ca2+ activation of proteins that are constitutively bound to calmodulin, such as small-conductance Ca2+-activated potassium (SK) channels.
Although calmodulin principally operates as a Ca2+ binding protein, it also coordinates other metal ions. For example, in the presence of typical intracellular concentrations of Mg2+ (0.5 – 1.0 mM) and resting concentrations of Ca2+ (100 nM), calmodulin's Ca2+ binding sites are at least partially saturated by Mg2+. This Mg2+ is displaced by the higher concentrations of Ca2+ generated by signaling events. Similarly, Ca2+ may itself be displaced by other metal ions, such as the trivalent lanthanides, that associate with calmodulin's binding pockets even more strongly than Ca2+. Though such ions distort calmodulin's structure and are generally not physiologically relevant due to their scarcity ''in vitro'', they have nonetheless seen wide scientific use as reporters of calmodulin structure and function.
Role in animals
Calmodulin mediates many crucial processes such asinflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
, metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
, apoptosis, smooth muscle contraction, intracellular movement, short-term and long-term memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to short-term and working memory, which persist for only about 18 to 30 seconds. Long- ...
, and the immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
. Calcium participates in an intracellular signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
system by acting as a diffusible second messenger to the initial stimuli. It does this by binding various targets in the cell including a large number of enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s, ion channels, aquaporin
Aquaporins, also called water channels, are channel proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membrane of biological cells, mainly facilitating transport of water between cells. The cell membranes of a ...
s and other proteins. Calmodulin is expressed in many cell types and can have different subcellular locations, including the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, within organelles, or associated with the plasma or organelle membranes, but it is always found intracellularly. Many of the proteins that calmodulin binds are unable to bind calcium themselves, and use calmodulin as a calcium sensor and signal transducer. Calmodulin can also make use of the calcium stores in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the sarcoplasmic reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cells. The main function of the SR is to store calcium ions (Ca2+). Calcium ion levels are ke ...
. Calmodulin can undergo post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation and proteolytic cleavage
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, ...
, each of which has potential to modulate its actions.
Specific examples
Role in smooth muscle contraction
 Calmodulin plays an important role in excitation contraction (EC) coupling and the initiation of the cross-bridge cycling in smooth muscle, ultimately causing smooth muscle contraction. In order to activate contraction of smooth muscle, the head of the
Calmodulin plays an important role in excitation contraction (EC) coupling and the initiation of the cross-bridge cycling in smooth muscle, ultimately causing smooth muscle contraction. In order to activate contraction of smooth muscle, the head of the myosin light chain
A myosin light chain is a light chain (small polypeptide subunit) of myosin. Myosin light chains were discovered by Chinese biochemist Cao Tianqin (Tien-chin Tsao) when he was a graduate student at the University of Cambridge in England.
Str ...
must be phosphorylated. This phosphorylation is done by myosin light chain (MLC) kinase. This MLC kinase is activated by a calmodulin when it is bound by calcium, thus making smooth muscle contraction dependent on the presence of calcium, through the binding of calmodulin and activation of MLC kinase.
Another way that calmodulin affects muscle contraction is by controlling the movement of Ca2+ across both the cell and sarcoplasmic reticulum
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a membrane-bound structure found within muscle cells that is similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum in other cells. The main function of the SR is to store calcium ions (Ca2+). Calcium ion levels are ke ...
membranes. The Ca2+ channels, such as the ryanodine receptor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, can be inhibited by calmodulin bound to calcium, thus affecting the overall levels of calcium in the cell. Calcium pumps take calcium out of the cytoplasm or store it in the endoplasmic reticulum and this control helps regulate many downstream processes.
This is a very important function of calmodulin because it indirectly plays a role in every physiological process that is affected by smooth muscle contraction such as digestion and contraction of arteries (which helps distribute blood and regulate blood pressure).
Role in metabolism
Calmodulin plays an important role in the activation of phosphorylase kinase, which ultimately leads toglucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
being cleaved from glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes (). Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphor ...
.
Calmodulin also plays an important role in lipid metabolism
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, involving the breakdown or storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids, such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. In anim ...
by affecting Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing th ...
. Calcitonin is a polypeptide hormone that lowers blood Ca2+ levels and activates G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...
cascades that leads to the generation of cAMP. The actions of calcitonin can be blocked by inhibiting the actions of calmodulin, suggesting that calmodulin plays a crucial role in the activation of calcitonin.
Role in short-term and long-term memory
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) plays a crucial role in a type of synaptic plasticity known aslong-term potentiation
In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons ...
(LTP) which requires the presence of calcium/calmodulin. CaMKII contributes to the phosphorylation of an AMPA receptor which increases the sensitivity of AMPA receptors. Furthermore, research shows that inhibiting CaMKII interferes with LTP.
Role in plants
 While yeasts have only a single CaM gene, plants and vertebrates contain an evolutionarily conserved form of CaM genes. The difference between plants and animals in Ca2+ signaling is that the plants contain an extended family of the CaM in addition to the evolutionarily conserved form. Calmodulins play an essential role in plant development and adaptation to environmental stimuli.
Calcium plays a key role in the structural integrity of the cell wall and the membrane system of the cell. However, high calcium levels can be toxic to a plant's cellular energy metabolism and, hence, the Ca2+ concentration in the cytosol is maintained at a submicromolar level by removing the cytosolic Ca2+ to either the
While yeasts have only a single CaM gene, plants and vertebrates contain an evolutionarily conserved form of CaM genes. The difference between plants and animals in Ca2+ signaling is that the plants contain an extended family of the CaM in addition to the evolutionarily conserved form. Calmodulins play an essential role in plant development and adaptation to environmental stimuli.
Calcium plays a key role in the structural integrity of the cell wall and the membrane system of the cell. However, high calcium levels can be toxic to a plant's cellular energy metabolism and, hence, the Ca2+ concentration in the cytosol is maintained at a submicromolar level by removing the cytosolic Ca2+ to either the apoplast
Inside a plant, the apoplast can mean the space outside of cell membranes, where material can diffuse freely; that is, the extracellular spaces.
''Apoplast '' can also refer especially to the continuum of cell walls of adjacent cells; fluid and ...
or the lumen of the intracellular organelles. Ca2+ pulses created due to increased influx and efflux act as cellular signals in response to external stimuli such as hormones, light, gravity, abiotic stress factors and also interactions with pathogens.
CMLs (CaM-related proteins)
Plants contain CaM-related proteins (CMLs) apart from the typical CaM proteins. The CMLs have about 15% amino acid similarity with the typical CaMs. '' Arabidopsis thaliana'' contains about 50 different CML genes which leads to the question of what purpose these diverse ranges of proteins serve in the cellular function. All plant species exhibit this diversity in the CML genes. The different CaMs and CMLs differ in their affinity to bind and activate the CaM-regulated enzymes ''in vivo''. The CaM or CMLs are also found to be located in different organelle compartments.Plant growth and development
In ''Arabidopsis,'' the protein DWF1 plays an enzymatic role in the biosynthesis of brassinosteroids, steroid hormones in plants that are required for growth. An interaction occurs between CaM and DWF1, and DWF1 being unable to bind CaM is unable to produce a regular growth phenotype in plants. Hence, CaM is essential for the DWF1 function in plant growth. CaM binding proteins are also known to regulate reproductive development in plants. For instance, the CaM-binding protein kinase in tobacco acts as a negative regulator of flowering. However, these CaM-binding protein kinase are also present in the shootapical meristem
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells conti ...
of tobacco and a high concentration of these kinases in the meristem causes a delayed transition to flowering in the plant.
''S''-locus receptor kinase (SRK) is another protein kinase that interacts with CaM. SRK is involved in the self-incompatibility responses involved in pollen-pistil interactions in ''Brassica
''Brassica'' () is a genus of plants in the cabbage and mustard family ( Brassicaceae). The members of the genus are informally known as cruciferous vegetables, cabbages, or mustard plants. Crops from this genus are sometimes called ''cole c ...
''.
CaM targets in ''Arabidopsis'' are also involved in pollen development and fertilization. Ca2+ transporters are essential for pollen tube growth. Hence, a constant Ca2+ gradient is maintained at the apex of pollen tube for elongation during the process of fertilization. Similarly, CaM is also essential at the pollen tube apex, where its primarily role involves the guidance of the pollen tube growth.
Interaction with microbes
Nodule formation
Ca2+ plays a important role in nodule formation in legumes. Nitrogen is an essential element required in plants and many legumes, unable to fix nitrogen independently, pair symbiotically with nitrogen-fixing bacteria that reduce nitrogen to ammonia. This legume-''Rhizobium
''Rhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. ''Rhizobium'' species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of (primarily) legumes and other flowering plants.
The bacteria colonize plant cells ...
'' interaction establishment requires the Nod factor that is produced by the ''Rhizobium'' bacteria. The Nod factor
Nod factors (nodulation factors or NF), are signaling molecules produced by soil bacteria known as rhizobia in response to flavonoid exudation from plants under nitrogen limited conditions. Nod factors initiate the establishment of a symbiotic rel ...
is recognized by the root hair cells that are involved in the nodule formation in legumes. Ca2+ responses of varied nature are characterized to be involved in the Nod factor recognition. There is a Ca2+ flux at the tip of the root hair initially followed by repetitive oscillation of Ca2+ in the cytosol and also Ca2+ spike occurs around the nucleus. DMI3, an essential gene for Nod factor signaling functions downstream of the Ca2+ spiking signature, might be recognizing the Ca2+ signature. Further, several CaM and CML genes in '' Medicago'' and ''Lotus'' are expressed in nodules.
Pathogen defense
Among the diverse range of defense strategies plants utilize against pathogens, Ca2+ signaling is very common. Free Ca2+ levels in the cytoplasm increases in response to a pathogenic infection. Ca2+ signatures of this nature usually activate the plant defense system by inducing defense-related genes and the hypersensitive cell death. CaMs, CMLs and CaM-binding proteins are some of the recently identified elements of the plant defense signaling pathways. Several CML genes intobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, bean and tomato are responsive to pathogens. CML43 is a CaM-related protein that, as isolated from APR134 gene in the disease-resistant leaves of ''Arabidopsis'' for gene expression analysis, is rapidly induced when the leaves are inoculated with ''Pseudomonas syringae
''Pseudomonas syringae'' is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from intern ...
''. These genes are also found in tomatoes (''Solanum lycopersicum''). The CML43 from the APR134 also binds to Ca2+ ions in vitro which shows that CML43 and APR134 are, hence, involved in the Ca2+-dependent signaling during the plant immune response to bacterial pathogens. The CML9 expression in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is rapidly induced by phytopathogenic bacteria, flagellin
Flagellin is a globular protein that arranges itself in a hollow cylinder to form the filament in a bacterial flagellum. It has a mass of about 30,000 to 60,000 daltons. Flagellin is the principal component of bacterial flagella, and is present ...
and salicylic acid. Expression of soybean SCaM4 and SCaM5 in transgenic ''tobacco'' and ''Arabidopsis'' causes an activation of genes related to pathogen resistance and also results in enhanced resistance to a wide spectrum of pathogen infection. The same is not true for soybean SCaM1 and SCaM2 that are highly conserved CaM isoforms. The ''At''BAG6 protein is a CaM-binding protein that binds to CaM only in the absence of Ca2+ and not in the presence of it. ''At''BAG6 is responsible for the hypersensitive response of programmed cell death in order to prevent the spread of pathogen infection or to restrict pathogen growth. Mutations in the CaM binding proteins can lead to severe effects on the defense response of the plants towards pathogen infections. Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (CNGCs) are functional protein channels in the plasma membrane that have overlapping CaM binding sites transport divalent cations such as Ca2+. However, the exact role of the positioning of the CNGCs in this pathway for plant defense is still unclear.
Abiotic stress response in plants
Change in intracellular Ca2+ levels is used as a signature for diverse responses towards mechanical stimuli, osmotic and salt treatments, and cold and heat shocks. Different root cell types show a different Ca2+ response to osmotic and salt stresses and this implies the cellular specificities of Ca2+ patterns. In response to external stress CaM activates glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) that catalyzes the conversion of -glutamate to GABA. A tight control on the GABA synthesis is important for plant development and, hence, increased GABA levels can essentially affect plant development. Therefore, external stress can affect plant growth and development and CaM are involved in that pathway controlling this effect.Plant examples
Sorghum
The plant sorghum is well established model organism and can adapt in hot and dry environments. For this reason, it is used as a model to study calmodulin's role in plants. Sorghum contains seedlings that express aglycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid ( carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinog ...
-rich RNA-binding protein
RNA-binding proteins (often abbreviated as RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes.
RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif ...
, SbGRBP. This particular protein can be modulated by using heat as a stressor. Its unique location in the cell nucleus and cytosol demonstrates interaction with calmodulin that requires the use of Ca2+. By exposing the plant to versatile stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
conditions, it can cause different proteins that enable the plant cells to tolerate environmental changes to become repressed. These modulated stress proteins are shown to interact with CaM. The ''CaMBP'' genes expressed in the sorghum are depicted as a “model crop” for researching the tolerance to heat and drought stress.
''Arabidopsis''
In an ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' study, hundreds of different proteins demonstrated the possibility to bind to CaM in plants.Family members
*Calmodulin 1
Calmodulin 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CALM1'' gene.
Function
Calmodulin 1 is the archetype of the family of calcium-modulated (calmodulin) proteins of which nearly 20 members have been found. They are identified by their ...
()
* Calmodulin 2 ()
* Calmodulin 3 ()
* calmodulin 1 pseudogene 1 ()
* Calmodulin-like 3 ()
* Calmodulin-like 4 ()
* Calmodulin-like 5 ()
* Calmodulin-like 6 ()
Other calcium-binding proteins
Calmodulin belongs to one of the two main groups of calcium-binding proteins, calledEF hand
The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or ''motif'' found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins.
The EF-hand motif contains a helix–loop–helix topology, much like the spread thumb and forefinger of the human hand, i ...
proteins. The other group, called annexin
Annexin is a common name for a group of cellular proteins. They are mostly found in eukaryotic organisms (animal, plant and fungi).
In humans, the annexins are found inside the cell. However some annexins (Annexin A1, Annexin A2, and Annexin A5) ...
s, bind calcium and phospholipids such as lipocortin
Annexin is a common name for a group of cellular proteins. They are mostly found in eukaryotic organisms (animal, plant and fungi).
In humans, the annexins are found inside the cell. However some annexins (Annexin A1, Annexin A2, and Annexin A5) ...
. Many other proteins bind calcium, although binding calcium may not be considered their principal function in the cell.
See also
*Proteopedia page foCalmodulin
and it
conformational change
*
Protein kinase
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphates to them (phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a fu ...
* Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
References
External links
* * * * * {{Nitric oxide signaling EF-hand-containing proteins Cell signaling Signal transduction Calcium signaling