Calorimeter (particle Physics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
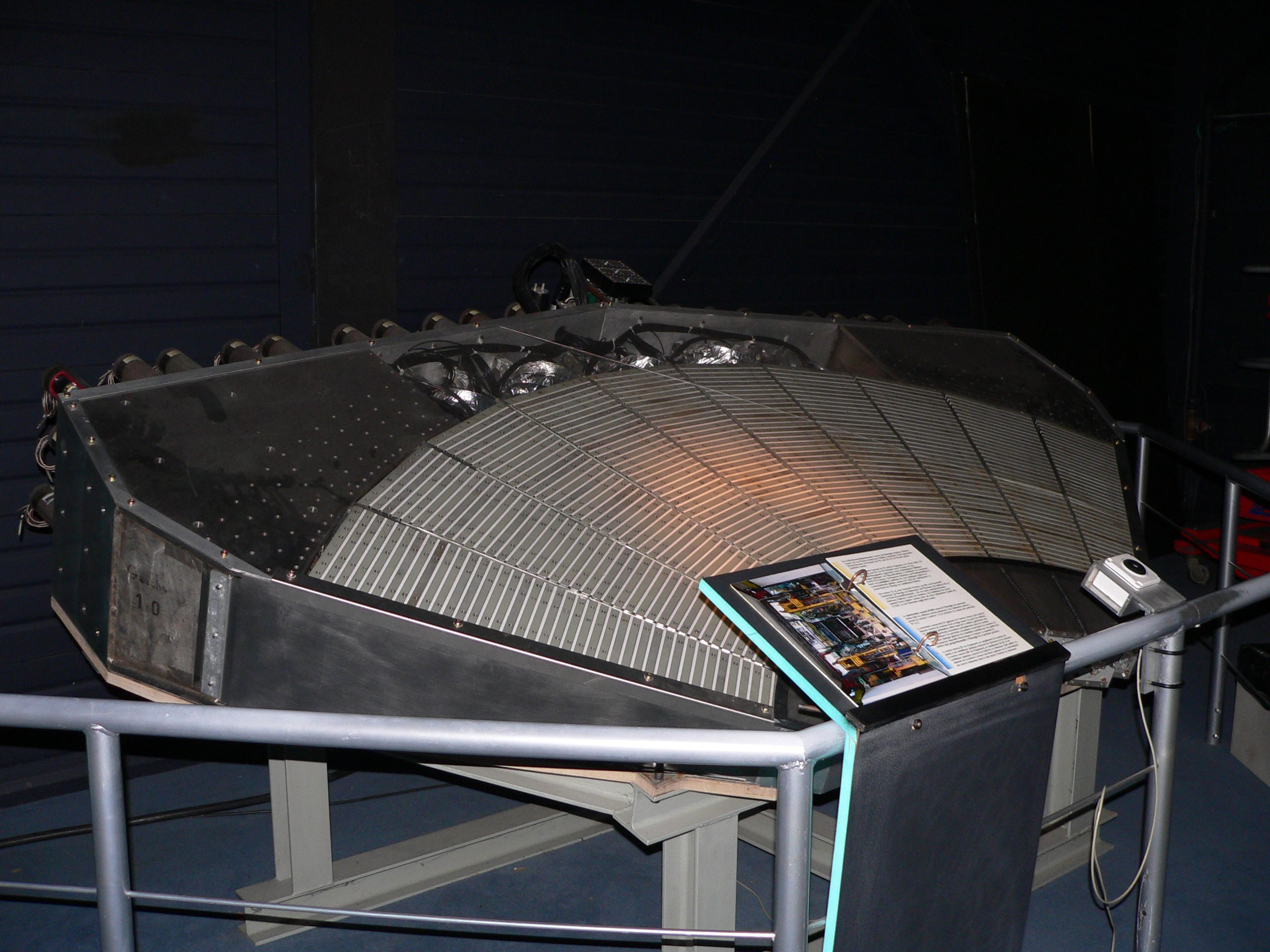 In experimental
In experimental
Calorimeter section of The Particle Detector BriefBook
Explanation of Calorimeters
on Quantumdiaries.org Particle detectors
 In experimental
In experimental particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
, a calorimeter is a type of detector that measures the energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
of particles
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from su ...
. Particles enter the calorimeter
A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorimete ...
and initiate a particle shower
In particle physics, a shower is a cascade of secondary particles produced as the result of a high-energy particle interacting with dense matter. The incoming particle interacts, producing multiple new particles with lesser energy; each of these t ...
in which their energy is deposited in the calorimeter, collected, and measured. The energy may be measured in its entirety, requiring total containment of the particle shower, or it may be sampled. Typically, calorimeters are segmented transversely to provide information about the direction of the particle or particles, as well as the energy deposited, and longitudinal segmentation can provide information about the identity of the particle based on the shape of the shower as it develops. Calorimetry
In chemistry and thermodynamics, calorimetry () is the science or act of measuring changes in ''state variables'' of a body for the purpose of deriving the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due, for example, to chemical reacti ...
design is an active area of research in particle physics.
Types of calorimeters
Electromagnetic versus hadronic
such as electrons, positrons and photons. A . (See types of particle showers for the differences between the two.) Calorimeters are characterized by the radiation length (for ECALs) and nuclear interaction length (for HCALs) of their active material. ECALs tend to be 15–30 radiation lengths deep while HCALs are 5–8nuclear interaction length
Nuclear interaction length is the mean distance travelled by a hadronic particle before undergoing an inelastic nuclear interaction.
See also
*Nuclear collision length
*Radiation length In physics, the radiation length is a characteristic of a mat ...
s deep.
Homogeneous versus sampling
An ECAL or an HCAL can be either a ''sampling calorimeter'' or a ''homogeneous calorimeter''. Particle Physics Booklet 2006 pg 272Calorimeters in high-energy physics experiments
Most particle physics experiments use some form of calorimetry. Often it is the most practical way to detect and measure neutral particles from an interaction. In addition, calorimeters are necessary for calculating "missing energy" which can be attributed to particles that rarely interact with matter and escape the detector, such as neutrinos. In most experiments the calorimeter works in conjunction with other components like a central tracker and amuon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As wi ...
detector. All the detector components work together to achieve the objective of reconstructing a physics event.
See also
*Calorimeter
A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorimete ...
(for other uses of the term)
* Total absorption spectroscopy
Total absorption spectroscopy is a measurement technique that allows the measurement of the gamma radiation emitted in the different nuclear gamma transitions that may take place in the daughter nucleus after its unstable parent has decayed by mean ...
, a technique whose main measuring device is a calorimeter
References
{{reflist, 1External links
Calorimeter section of The Particle Detector BriefBook
Explanation of Calorimeters
on Quantumdiaries.org Particle detectors