calcium channel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A calcium channel is an
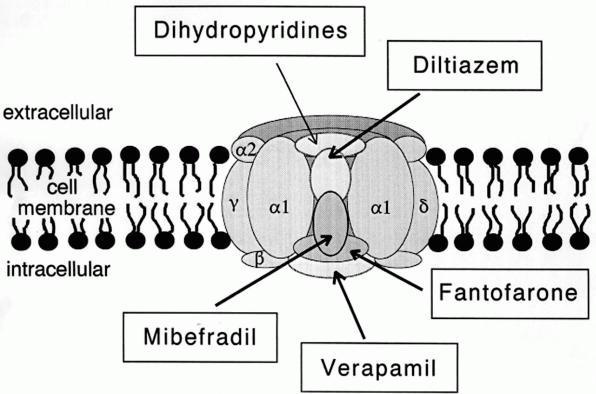 L-type
L-type
ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
which shows selective permeability to calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, although there are also ligand-gated calcium channels.
Comparison tables
The following tables explain gating, gene, location and function of different types of calcium channels, both voltage and ligand-gated.Voltage-gated
Ligand-gated
*the ''receptor-operated calcium channels'' (invasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vesse ...
)
**P2X receptor
The ATP-gated P2X receptor cation channel familyTC# 1.A.7, or simply P2X receptor family, consists of cation-permeable ligand-gated ion channels that open in response to the binding of extracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate ( ATP). They belong ...
s Page 479
Pharmacology
 L-type
L-type calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s are used to treat hypertension. In most areas of the body, depolarization is mediated by sodium influx into a cell; changing the calcium permeability has little effect on action potentials. However, in many smooth muscle tissues, depolarization is mediated primarily by calcium influx into the cell. L-type calcium channel blockers selectively inhibit these action potentials in smooth muscle which leads to dilation of blood vessels; this in turn corrects hypertension.
T-type calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s are used to treat epilepsy. Increased calcium conductance in the neurons leads to increased depolarization and excitability. This leads to a greater predisposition to epileptic episodes. Calcium channel blockers reduce the neuronal calcium conductance and reduce the likelihood of experiencing epileptic attacks.
See also
* .References
External links
* * * * {{Ion channels, g1 Ion channels Electrophysiology Integral membrane proteins Calcium channels