Cystic Lung Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A focal lung pneumatosis, is an enclosed pocket of air or gas in the

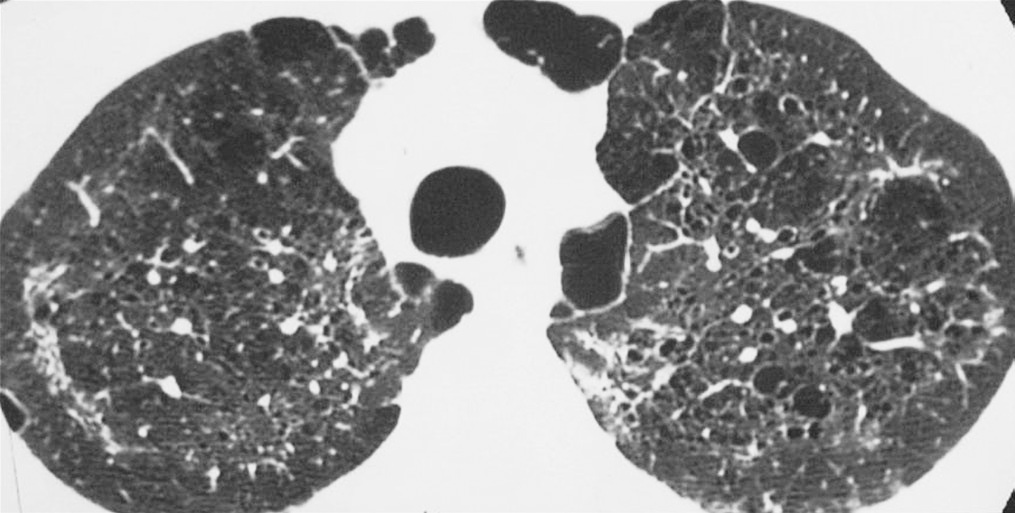 Cystic lung diseases include:
*
Cystic lung diseases include:
*
 Two
Two
lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
and includes blebs, bullae, pulmonary cysts, and lung cavities. Blebs and bullae can be classified by their wall thickness.
* A bleb has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm. By radiology definition, it is up to 1 cm in total size. By pathology definition, it originates in the pleurae (rather than in the lung parenchyma).
*A bulla has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm. By radiology definition, it has a total size of greater than 1 cm. By pathology definition, it originates in the lung parenchyma (rather than in the pleurae).
* A lung cyst has a wall thickness of up to 4 mm. A minimum wall thickness of 1 mm has been suggested, but thin-walled pockets may be included in the definition as well.
* A cavity has a wall thickness of more than 4 mm.
The terms above, when referring to sites other than the lungs, often imply fluid content.
Lung cysts are seen in about 8% of the general population, with an increased prevalence in older people, and are not associated with emphysema
Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces ( pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alve ...
. They may be part of the aging changes of the lungs, and cause a slight decrease in their diffusing capacity. The presence of multiple pulmonary cysts may indicate a need to evaluate the possibility of bullous or cystic lung diseases. Cavitation indicates workup for serious infection or lung cancer.
Bleb or bulla
The most common disease causing blebs or bullae isparaseptal emphysema
Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces ( pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alv ...
though centrilobular emphysema may sometimes be involved.
Other conditions associated with lung bullae are:
* Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an inc ...
Updated: Feb 21, 2019
* Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a ...
* Ehlers–Danlos syndromes
* Cocaine smoking
* Sarcoidosis
* HIV/AIDS
* Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
Cyst
A pulmonary cyst is not necessarily the same type of cyst seen in many cystic lung diseases. The cyst for example in pneumocystis pneumonia is not the same as the pulmonary cyst.
 Cystic lung diseases include:
*
Cystic lung diseases include:
* Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is an abnormal clonal proliferation of Langerhans cells, abnormal cells deriving from bone marrow and capable of migrating from skin to lymph nodes.
Symptoms range from isolated bone lesions to multisystem dise ...
(LCH)
* Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM)
* Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
* Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome
* ''Pneumocystis'' pneumonia
* Pulmonary amyloidosis
* Light chain deposition disease
Light chain deposition disease (LCDD) is a rare blood cell disease which is characterized by deposition of fragments of infection-fighting immunoglobulins, called light chains (LCs), in the body. LCs are normally cleared by the kidneys, but in ...
* Lung metastases
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
rarely cause multiple cystic lung lesions. This form of presentation has been described in metastatic sarcomas.
Incidental blebs and cysts
A focal lung pneumatosis that is an incidental imaging finding such as on aCT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
, without suspicious findings (such as findings indicating any of the diseases listed above), generally does not indicate further follow-up.
Cavity
 Two
Two infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
that are commonly associated with cavities of lung tissue are ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its c ...
'' and '' Klebsiella pneumoniae''. The formation of cavities is due to tissue necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
and creates an environment that allows the pathogen to expand in numbers and spread further.
In the absence of infectious symptoms, a lung nodule with cavitation is a suspected lung cancer.
References
{{reflist Lung disorders