Cystathionine beta-lyase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cystathionine beta-lyase (), also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an  Thus, the substrate of this enzyme is L-cystathionine, whereas its 3
Thus, the substrate of this enzyme is L-cystathionine, whereas its 3



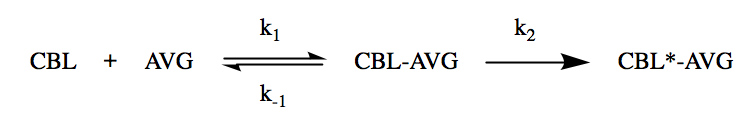 Excess addition of cystathionine prevented the inactivation of the enzyme, suggesting that AVG acts as a
Excess addition of cystathionine prevented the inactivation of the enzyme, suggesting that AVG acts as a
 Through kinetic methods and
Through kinetic methods and 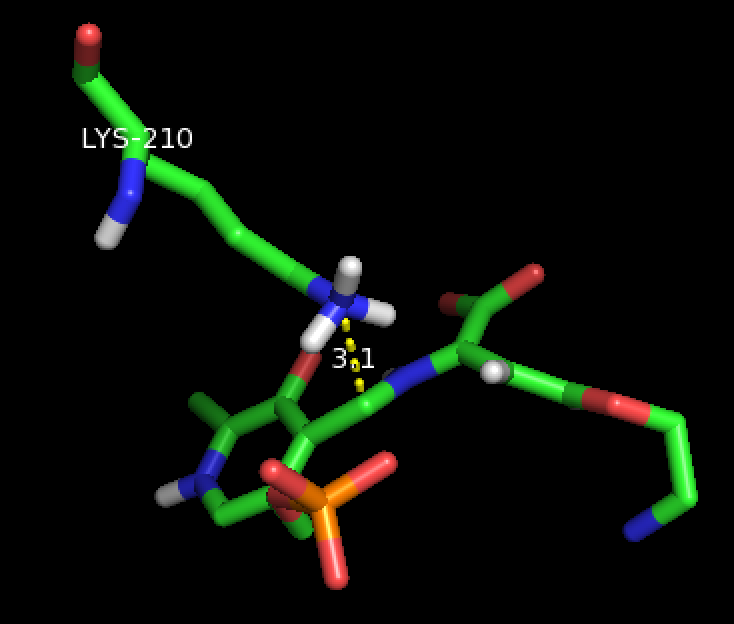
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
that primarily catalyzes
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
the following α,β-elimination reaction
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response to an action, event, or exposure:
Physics and chemistry
*Chemical reaction
*Nuclear reaction
*Reaction (physics), as defined by Newton's third law
*Chain reaction (disambiguation).
Biology and me ...
 Thus, the substrate of this enzyme is L-cystathionine, whereas its 3
Thus, the substrate of this enzyme is L-cystathionine, whereas its 3 products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
are homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene bridge (-CH2-). It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group. In the b ...
, pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic aci ...
, and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
.
Found in plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s, bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, and yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ...
, cystathionine beta-lyase is an essential part of the methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. ...
pathway as homocysteine can be directly converted into methionine by methionine synthase
Methionine synthase also known as MS, MeSe, MTR is responsible for the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine. In humans it is encoded by the ''MTR'' gene (5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase). Methionine synthase forms ...
. The enzyme belongs to the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes due to its use of a pyridoxal-5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent ac ...
(PLP) cofactor to cleave cystathionine. The enzyme also belongs to the family of lyase
In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking (an elimination reaction) of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis (a substitution reaction) and oxidation, often forming a new double bond or a new ring structure. ...
s, specifically the class of carbon-sulfur lyases. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature.
A semisystematic name or semitrivial ...
of this enzyme class is L-cystathionine L-homocysteine-lyase (deaminating; pyruvate-forming). This enzyme participates in 5 metabolic pathways
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reac ...
: methionine metabolism
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
, cysteine metabolism
Cysteine metabolism refers to the biological pathways that consume or create cysteine. The pathways of different amino acids and other metabolites interweave and overlap to creating complex systems.cysteine is metabolism creating complex systems
...
, selenoamino acid metabolism, nitrogen metabolism
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biologi ...
, and sulfur metabolism
Sulfur is metabolism, metabolized by all organisms, from bacteria and archaea to plants and animals. Sulfur is redox, reduced or redox, oxidized by organisms in a variety of forms. The chemical element, element is present in proteins, organosulfate ...
.
Structure
Cystathionine beta-lyase is atetramer
A tetramer () (''tetra-'', "four" + '' -mer'', "parts") is an oligomer formed from four monomers or subunits. The associated property is called ''tetramery''. An example from inorganic chemistry is titanium methoxide with the empirical formula Ti ...
composed of identical subunits, and is constructed as a dimer
Dimer may refer to:
* Dimer (chemistry), a chemical structure formed from two similar sub-units
** Protein dimer, a protein quaternary structure
** d-dimer
* Dimer model, an item in statistical mechanics, based on ''domino tiling''
* Julius Dimer ( ...
of dimers, each associated with one molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
of PLP bound to the catalytic site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where Enzyme substrate, substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid, amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with t ...
by a lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
residue
Residue may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
* An amino acid, within a peptide chain
* Crop residue, materials left after agricultural processes
* Pesticide residue, refers to the pesticides that may remain on or in food after they are applied ...
. The dimer is formed by two monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
Mo ...
s associated through several electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber ...
, hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
ing, and hydrophobic interactions
The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution and exclude water molecules. The word hydrophobic literally means "water-fearing", and it describes the segregation of water and nonpolar ...
, whereas the tetramer is stabilized through interactions between the N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
domains and key α-helices.
Most of the enzyme's catalytic site residues are conserved amongst the enzymes involved in the transsulfuration pathway
The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the ''forward'' and the ''reverse''.
The ''forward ...
. Other members include cystathionine gamma-synthase
In enzymology, a cystathionine gamma-synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cystathionine from cysteine and an activated derivative of homoserine, e.g.:
:''O''4-succinyl-L-homoserine + L-cysteine \longrightarrow L-cystathionine ...
, cystathionine gamma-lyase
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate ( α-ketobutyrate), and ...
, and methionine gamma lyase. Additionally, these structures exhibit a type I fold and belong to the aspartate aminotransferase
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT, SGOT), is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme () that was first described by Arthur ...
(AAT) family, characterized by homodimers with dihedral symmetry
In mathematics, a dihedral group is the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, which includes rotations and reflections. Dihedral groups are among the simplest examples of finite groups, and they play an important role in group theory, ge ...
and active sites composed of residues belonging to adjacent subunits.

Monomer
The cystathionine beta-lyase monomer consists of three functionally and structurally distinct domains:N-terminal domain
Composed of three α-helices and onebeta-strand
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common structural motif, motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone chain, backb ...
that contribute to the formation of the quaternary structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also refe ...
. This domain contains residues that interact with the active site of the neighboring subunit to facilitate substrate and cofactor binding.
PLP-binding domain
Contains most of the catalytically relevant residues on the enzyme. It is composed of α-helices and β-sheets with a distinct parallel seven-stranded β-sheet. These sheets form a curved structure around the PLP-binding helix. PLP is covalently attached to a lysine residue at theC-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
of the sheet.
C-terminal domain
Smallest domain on the enzyme, which is attached to the PLP-binding domain by a long, kinked α-helix. The domain is structured into four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet with neighboring helices.Catalytic site
Aside from being bound to a lysine residue, PLP is fixed within the substrate binding site of the enzyme through various interactions with catalytic residues.Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituen ...
- and hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
-containing residues are located in hydrogen bonding distance to the four phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
s. This phosphate group is considered to be the main contributor to securing PLP in the active site. Additionally, residues neighboring the pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a d ...
nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
in PLP help stabilize its positive charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectiv ...
, thereby increasing its electrophilic
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carri ...
character.
The aromatic ring
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturat ...
in PLP is fixed in place by an almost coplanar
In geometry, a set of points in space are coplanar if there exists a geometric plane that contains them all. For example, three points are always coplanar, and if the points are distinct and non-collinear, the plane they determine is unique. Howe ...
tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
residue. It is believed that this configuration increases the electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
sink character of the cofactor. These stacking interactions between PLP and aromatic side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a l ...
s can be found in most PLP-dependent enzymes as it plays an important role in catalyzing the reaction by facilitating transaldimination.

Mechanism
As shown in themechanism
Mechanism may refer to:
*Mechanism (engineering), rigid bodies connected by joints in order to accomplish a desired force and/or motion transmission
*Mechanism (biology), explaining how a feature is created
*Mechanism (philosophy), a theory that a ...
below, cystathionine beta-lyase facilitates the S-C bond
Bond or bonds may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bond (finance), a type of debt security
* Bail bond, a commercial third-party guarantor of surety bonds in the United States
* Chemical bond, the attraction of atoms, ions or molecules to form chemical ...
cleavage in cystathionine with the use of a PLP cofactor bounded to a catalytic lysine residue. Initially, a deprotonated
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu ...
amino group is needed to perform the transaldimination reaction. Given that the pH optimum for the enzyme is between 8.0 and 9.0, a tyrosine residue in the catalytic pocket exists as a phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it req ...
ate, which abstracts a proton from the α-amino group of the substrate. In the next step, the deprotonated amine undergoes a nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
attack and displaces the lysine to form a Schiff base
In organic chemistry, a Schiff base (named after Hugo Schiff) is a compound with the general structure ( = alkyl or aryl, but not hydrogen). They can be considered a sub-class of imines, being either secondary ketimines or secondary aldimine ...
, forming an internal aldimine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bon ...
.
The released lysine can now abstract the proton from the Cα and form a quinoid intermediate, which is facilitated by the delocalization
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref>
The term delocalization is general and can have slightly diff ...
of the negative charge over PLP's conjugated p-system. Subsequently, the protonation of Sγ induces Cβ-Sγ bond cleavage, thereby releasing homocysteine
The external aldimine is displaced by the nucleophilic attack of the lysine, regenerating the catalytically active internal aldimine and releasing dehydroalanine
Dehydroalanine (Cα,β-didehydroalanine, α,β-di-dehydroalanine, 2-aminoacrylate, or 2,3-didehydroalanine) is a dehydroamino acid. It does not exist in its free form, but it occurs naturally as a residue found in peptides of microbial origin. As ...
. Lastly, the enamine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine. Enamines are versatile intermediates.
:
The word "enamine" is derived from the affix ''en''-, used as the suffix of alkene, and th ...
tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydr ...
izes into an imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bo ...
that undergoes hydrolytic
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
deamination
Deamination is the removal of an amino group from a molecule. Enzymes that catalyse this reaction are called deaminases.
In the human body, deamination takes place primarily in the liver, however it can also occur in the kidney. In situations of e ...
to form pyruvate and ammonia.

Inhibition
Plant and bacterial cystathionine beta-lyases are inhibited by theantimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
amino acid, L-aminoethoxybinylglycine (AVG), and the antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
amino acid, rhizobitoxine.
Plants
Cystathionine beta-lyase in plants exhibits a two-step mechanism inactivation process with AVG, in which a reversible enzyme-inhibitor complex is formed before the irreversible inactivation of the enzyme: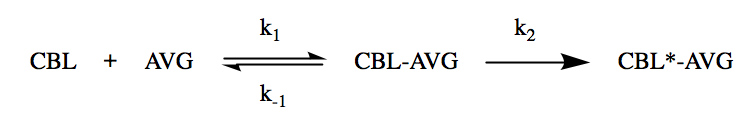 Excess addition of cystathionine prevented the inactivation of the enzyme, suggesting that AVG acts as a
Excess addition of cystathionine prevented the inactivation of the enzyme, suggesting that AVG acts as a competitive inhibitor
Competitive inhibition is interruption of a chemical pathway owing to one chemical substance inhibiting the effect of another by competing with it for binding or bonding. Any metabolic or chemical messenger system can potentially be affected b ...
with respect to cystathionine. Additionally, the enzyme has been shown to be sensitive to thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...
-blocking inhibitors, such as N-ethylmaleimide and idoacetamide.
Bacteria
Unlike in plants, Cystathionine beta-lyase in bacteria exhibits a one-step inhibition mechanism: Through kinetic methods and
Through kinetic methods and X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
, a time-dependent, slow-binding inhibition was observed. It is believed that the inhibitor binds to the enzyme in a similar way as the substrate; however, after the abstraction of the α-proton, the reaction proceeds to create an inactive ketimine PLP derivative.

Evolution
Arabidopsis
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organi ...
cystathionine beta-lyase possesses 22% homology
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
* Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
*Homologous chrom ...
with its Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
counterpart and even higher homology (between 28% to 36%) with cystathionine γ-synthase from plant and bacterial sources and cystathionine γ-lyase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been o ...
. All of these enzymes are involved in the Cys/Met biosynthetic pathway and belong to the same class of PLP-dependent enzymes, suggesting that these enzymes were derived from a common ancestor.
Industrial relevance
Cystathionine beta-lyase catalyzes the production of homocysteine, a direct precursor to methionine. Methionine is an essential amino acid for bacteria that is required for protein synthesis and the synthesis ofS-adenosylmethionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throug ...
; thus, the amino acid is directly linked to DNA replication. Because of its necessity in DNA replication, inhibition of cystathionine beta-lyase is an attractive antibiotic target. Furthermore, the enzyme is absent in humans, decreasing the chance of harmful and unwanted side effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
s.
Studies have linked the anti-fungal activity of several anti-fungal agents to the inhibition of cystathionine beta-lyase; however, other studies have not observed enzyme inhibition by these. Further research is needed to characterize the full extent cystathionine beta-lyase inhibition has on microbial and fungal growth.
References
{{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 4.4.1 Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes Enzymes of known structure