Cyclone Waste Heat Engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Cyclone Waste Heat Engine (WHE) is a small steam engine developed to produce power from steam created from
The Cyclone Waste Heat Engine (WHE) is a small steam engine developed to produce power from steam created from
 The timing on the admission valve(s) is arranged so that no matter what position the engine is in when it stopped last, the valve to at least one cylinder will always be open. This allows the engine to start by itself whenever steam is supplied to it, without other means such as an electric starter motor to cause the engine to initially rotate.
The fraction of the stroke in which the admission valve is open on a steam engine is termed the cutoff. On the WHE-25 it is 34% of the stroke.Cyclone Waste Heat Engine Specification Sheet. Retrieved from From top dead center to 34% of stroke, the crank turns through an angle of about 71°. In the six cylinder engine, one piston reaches top dead center every 360°/6 = 60°. The three cylinder WHE-DR engine only has a piston reach TDC every 120°, so its admission valve must be open over a much larger angle to ensure the engine is self-starting. If the valve is open for 130° of crankshaft rotation, the cutoff value would be about 64%.
The expansion stroke of the steam engine covers piston travel from
The timing on the admission valve(s) is arranged so that no matter what position the engine is in when it stopped last, the valve to at least one cylinder will always be open. This allows the engine to start by itself whenever steam is supplied to it, without other means such as an electric starter motor to cause the engine to initially rotate.
The fraction of the stroke in which the admission valve is open on a steam engine is termed the cutoff. On the WHE-25 it is 34% of the stroke.Cyclone Waste Heat Engine Specification Sheet. Retrieved from From top dead center to 34% of stroke, the crank turns through an angle of about 71°. In the six cylinder engine, one piston reaches top dead center every 360°/6 = 60°. The three cylinder WHE-DR engine only has a piston reach TDC every 120°, so its admission valve must be open over a much larger angle to ensure the engine is self-starting. If the valve is open for 130° of crankshaft rotation, the cutoff value would be about 64%.
The expansion stroke of the steam engine covers piston travel from
 No independent tests of any WHE model have been reported, but an indication comes from information published regarding the test waste heat recovery system for Bent Glass Design of Hatboro, PA.Press release "Bent Glass Design Purchases Engine System From Cyclone Power Technologies" Retrieved from http://www.marketwired.com/press-release/Bent-Glass-Design-Purchases-Engine-System-From-Cyclone-Power-Technologies-921147.htm The system was described as providing up to 10 kW electrical output using a WHE-25 model engine and "will convert over 500,000 BTUs of exhaust heat from the customer's glass manufacturing furnaces into electric power." A heat flow rate 500,000 BTU/hr equals 146.5 kW.
The WHE-25 engine has a 34% cutoff. This allows for the remaining 66% of the piston stroke to expand the steam, extracting work from it and causing the pressure to drop. The figure to the right shows how pressure in the cylinder of a steam engine drops after the cutoff point. The WHE-DR must have a much later cutoff to allow it to self-start. The later cutoff leads to a larger
No independent tests of any WHE model have been reported, but an indication comes from information published regarding the test waste heat recovery system for Bent Glass Design of Hatboro, PA.Press release "Bent Glass Design Purchases Engine System From Cyclone Power Technologies" Retrieved from http://www.marketwired.com/press-release/Bent-Glass-Design-Purchases-Engine-System-From-Cyclone-Power-Technologies-921147.htm The system was described as providing up to 10 kW electrical output using a WHE-25 model engine and "will convert over 500,000 BTUs of exhaust heat from the customer's glass manufacturing furnaces into electric power." A heat flow rate 500,000 BTU/hr equals 146.5 kW.
The WHE-25 engine has a 34% cutoff. This allows for the remaining 66% of the piston stroke to expand the steam, extracting work from it and causing the pressure to drop. The figure to the right shows how pressure in the cylinder of a steam engine drops after the cutoff point. The WHE-DR must have a much later cutoff to allow it to self-start. The later cutoff leads to a larger
 Expander: A steam engine is just one component in a
Expander: A steam engine is just one component in a
Cyclone Power Technologies Official WebsiteQ2Power, Inc. Official Website
Steam engines
 The Cyclone Waste Heat Engine (WHE) is a small steam engine developed to produce power from steam created from
The Cyclone Waste Heat Engine (WHE) is a small steam engine developed to produce power from steam created from waste heat
Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utilit ...
. It is an offshoot of the development of the Cyclone Mark V Engine
The Cyclone Mark V Engine is a steam engine in which the engine, steam generator, condenser and feed pump are integrated into a single compact unit. The company Cyclone Power Technologies of Pompano Beach, Florida was founded by inventor Harry ...
by the company Cyclone Power Technologies of Pompano Beach, Florida. The original versions were designed by inventor Harry Schoell, founder of Cyclone Power Technologies and the later versions have been designed by the Ohio State University
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best pu ...
Center for Automotive Research (OSU-CAR).
In July 2014, Cyclone Power Technologies separated its waste heat engine product into the separate WHE Generation Corporation,Quarterly Report for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2014, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against mark ...
. Retrieved from https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1442711/000139843214000332/cypw20140630_10q.htm which does business under the trade name Q2Power, Inc., of Lancaster, Ohio.
Engine construction and operation
The Cyclone Waste Heat Engine (WHE) is a single-acting,Uniflow steam engine
The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder an ...
. The two main variations are the WHE-25, a six-cylinder radial engine that was under development until November 2013, and the 3-cylinder WHE-DR that has been under development since.Press release "Cyclone Power Technologies completes build of next generation waste heat engine with The Ohio State University's Center for Automotive Research", November 5, 2013. Retrieved from http://car.osu.edu/news/cyclone-power-technologies-completes-build-next-generation-waste-heat-engine-ohio-state A display model of a 12-cylinder radial engine was built,Curtis Ellzey interviews Harry Schoell about Waste Heat Engine. Retrieved from http://www.engineeringtv.com/video/Cyclone-Waste-Heat-Engine but it is not known if any working engines were built in this configuration.
Operation
 The timing on the admission valve(s) is arranged so that no matter what position the engine is in when it stopped last, the valve to at least one cylinder will always be open. This allows the engine to start by itself whenever steam is supplied to it, without other means such as an electric starter motor to cause the engine to initially rotate.
The fraction of the stroke in which the admission valve is open on a steam engine is termed the cutoff. On the WHE-25 it is 34% of the stroke.Cyclone Waste Heat Engine Specification Sheet. Retrieved from From top dead center to 34% of stroke, the crank turns through an angle of about 71°. In the six cylinder engine, one piston reaches top dead center every 360°/6 = 60°. The three cylinder WHE-DR engine only has a piston reach TDC every 120°, so its admission valve must be open over a much larger angle to ensure the engine is self-starting. If the valve is open for 130° of crankshaft rotation, the cutoff value would be about 64%.
The expansion stroke of the steam engine covers piston travel from
The timing on the admission valve(s) is arranged so that no matter what position the engine is in when it stopped last, the valve to at least one cylinder will always be open. This allows the engine to start by itself whenever steam is supplied to it, without other means such as an electric starter motor to cause the engine to initially rotate.
The fraction of the stroke in which the admission valve is open on a steam engine is termed the cutoff. On the WHE-25 it is 34% of the stroke.Cyclone Waste Heat Engine Specification Sheet. Retrieved from From top dead center to 34% of stroke, the crank turns through an angle of about 71°. In the six cylinder engine, one piston reaches top dead center every 360°/6 = 60°. The three cylinder WHE-DR engine only has a piston reach TDC every 120°, so its admission valve must be open over a much larger angle to ensure the engine is self-starting. If the valve is open for 130° of crankshaft rotation, the cutoff value would be about 64%.
The expansion stroke of the steam engine covers piston travel from top dead center
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC).
...
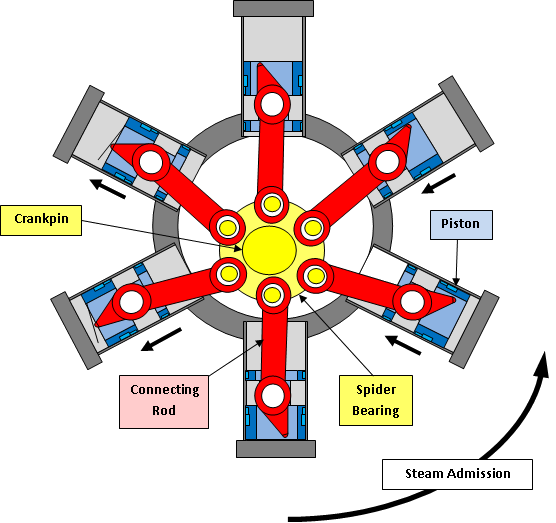
to bottom dead center. When the piston reverses to return to top dead center, an exhaust valve needs to open so that the expanded steam from the previous stroke can be released from the cylinder. The WHE engine has an exhaust valve in each piston actuated by a protrusion on the connecting rod (see figure to right). On the exhaust stroke the angle of the connecting rod causes it to open the piston valve, allowing expanded steam to exhaust into the crankcase.
The WHE-25 design used a reed valve, which is a piece of thin metal covering the top of the piston (as shown in the figure). The WHE-DR design replaced the reed with a ball resting in a valve seat in the piston crown.
'Spider bearing'
The WHE-25 is designed with six connecting rods sharing onecrankpin
A crankpin or crank pin, also known as a rod bearing journal, is a mechanical device in an engine which connects the crankshaft to the connecting rod for each cylinder. It has a cylindrical surface, to allow the crankpin to rotate relative to the ...
on the crankshaft. The standard design for such connection is with a master connecting rod connected to one piston and the remaining rods connected to pins in the big end of the master rod. Harry Schoell, inventor of the WHE, also invented what he called a 'spider bearing',US Patent 7900454, "Connecting rod journals and crankshaft spider bearing in an engine". Retrieved from http://www.google.com/patents/US7900454 which is a disk that can rotate around the crankpin, and has one bearing journal around its periphery for each of the six connecting rods. While this design eliminates the need for a separate master rod, it introduces one uncontrolled degree of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
, i.e., the spider bearing itself can rotate in one direction until its motion is stopped by impacting with the connecting rods, then rotate in the other direction through some angle before it is stopped by again impacting connecting rods.
The WHE-DR design eliminated the spider bearing by having each cylinder offset from the others longitudinally so that the connecting rod big ends can fit on a shared crankpin side by side. It has been reported that "Initial testing has demonstrated significantly smoother and quieter operation." Elimination of the spider bearing was the only design change that would have led to this improvement.
Water lubrication
The Waste Heat Engine's design requires the use of water to lubricate the moving parts because exhaust steam goes into the engine crankcase. Any oil used to lubricate crankshaft and connecting rod bearings would soon form anemulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Althou ...
of oil and water that would have very poor lubricating properties.
Journal bearings on the crankshaft and connecting rods and the pistons sliding in their cylinders operate in the hydrodynamic
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and ...
lubrication regime. The carrying capacity of a journal bearing is a direct function of the dynamic viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
of the lubricating fluid. Water at 20 °C has a viscosity of 0.001002 Pa·s, while a typical motor oil could have a viscosity of about 0.250 Pa·s. Thus, water is about 250 times less effective of a lubricant than oil.
Cyclone Power Technologies had contracted with the Ohio State University
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best pu ...
Center for Automotive Research (OSU-CAR) for engineering analysis. A March 8, 2014 presentationENGINEERING ANALYSIS OF CYCLONE POWER TECHNOLOGIES’ WASTE HEAT ENGINE. Retrieved from by OSU-CAR described the engine bearings as a "critical path issue" and stated:
* "Little or no data exists outside Cyclone’s own experience for the use of water lubrication for either ball bearings or roller bearings in our environment and under our loadings. Calculated life using just the bearing load and the scaling factors for the viscosity of the lubricant indicate that very high ratio of load capacity to applied load is required." * "Minimal data exists for the use of water lubricated polymer journal bearings in our environment and under our loadings. Factors of a 4:1 increase in life have been shown with submerged operation, but little long term wear data is available with pressurized water lubrication."The contract between Cyclone Power Technologies and Phoenix Power Group for the WHEAmended and Restated Systems Application License Agreement, September 30, 2013, filed as Exhibit 10.25 with the
Securities and Exchange Commission
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against mark ...
. Retrieved from https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1442711/000139843213000687/ex10-25.htm states that Phoenix Power Group will make a $150,000 progress payment "Upon the completion of 200 hours of durability testing of WHE version 5.0 as conducted and/or overseen by OSU. The durability testing shall consist of the WHE engine operating, without failure, and producing 10hp to 20hp". As of March 25, 2015 there has been no indication they have made a water lubricated engine pass this 200-hour endurance test.
Efficiency
mean effective pressure
The mean effective pressure (MEP) is a quantity relating to the operation of a reciprocating engine and is a measure of an engine's capacity to do work that is independent of engine displacement.Heywood, J. B., "Internal Combustion Engine Fundam ...
that will give a larger power output for an engine of a given size operating at a given speed, but also leads to a decrease in efficiency since steam is at a higher pressure when exhausted from the cylinder and less of its energy has been converted to mechanical work.
Auxiliary equipment
 Expander: A steam engine is just one component in a
Expander: A steam engine is just one component in a Rankine cycle
The Rankine cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle describing the process by which certain heat engines, such as steam turbines or reciprocating steam engines, allow mechanical work to be extracted from a fluid as it moves between a heat sou ...
power system. The figure of the Rankine cycle at the right shows a turbine rather than a reciprocating piston engine between states 3 and 4, but either device acts as the expander stage in the cycle.
Condenser: The device between states 4 and 1 is the condenser. It removes heat from the engine exhaust steam to condense it back into water. In the case of the WHE-25 engine in the previous sub-section, of the 146.5 kW of heat energy supplied in the initial steam, 10 kW was converted into electricity. That leaves 146.5 - 10 = 136.5 kW of heat energy to be removed by the condenser. As a point of comparison, a Caterpillar C13 diesel engine that is commonly used in tractor-trailer trucks has a heat rejection to coolant rating of 128 kW. Thus, a condenser for the WHE-25 engine producing 10 kW of power would be about the size of the radiator on a semi-truck. The newer WHE-DR is likely less efficient, so would need an even bigger condenser for the same output power.
The condenser requires enough airflow to take away the heat. A fan is usually used to create this airflow, and its power consumption reduces the net power available from the system.
Feed water pump: The condensed water is stored in a tank, then pumped to high pressure by the feed water pump, states 1 to 2 in the figure. This pump requires a source of power, as well as a control system so that it pumps the proper amount of water to compensate for the amount of steam put into the engine.
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centr ...
: Heat is added to the water in the boiler to create the steam, states 2 to 3 in the figure. Boilers are sometimes called steam generators, and Cyclone Power Technologies has used the term "Combustion Chamber/Heat Exchanger" or "CCHX".Press release "Cyclone Power Technologies and Phoenix Power Group Successfully Integrate Waste Oil Co-Generation System". Retrieved from http://www.marketwired.com/press-release/cyclone-power-technologies-phoenix-power-group-successfully-integrate-waste-oil-co-generation-otcqb-cypw-1706457.htm Regardless of the name used, if the system pressure is greater than 15 psi (1 bar) and heat is added, the device is legally a boiler. All states in the United States except Idaho and Wyoming and all provinces in Canada have legally adopted the requirement for boilers to be registered with the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors
The National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors (NBBI) is composed of chief boiler and pressure vessel inspectors representing states, cities, and provinces enforcing pressure equipment laws and regulations. Created to prevent death, i ...
.National Board Synopsis Map 2015. Retrieved from Registration includes the requirements that the boiler's design be approved as meeting the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) The ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) is an American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard that regulates the design and construction of boilers and pressure vessels. The document is written and maintained by volunteers chosen for ...
, must be constructed in a facility currently authorized by ASME to construct such boilers, must be installed and tested to the approval of a National Board inspector, and, is required to undergo periodic inspections at the owner's expense.
The jurisdiction may also require the installation be operated by a licensed stationary engineer
A stationary engineer (also called an operating engineer, power engineer or process operator) is a technically trained professional who operates, troubleshoots and oversees industrial machinery and equipment that provide and utilize energy in vari ...
, as well as be covered by sufficient liability insurance.
The reason for such scrutiny is because of the catastrophic losses that can occur due to a boiler explosion
A boiler explosion is a catastrophic failure of a boiler. There are two types of boiler explosions. One type is a failure of the pressure parts of the steam and water sides. There can be many different causes, such as failure of the safety val ...
.
A system will also require an approved steam safety valve
A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceed ...
and water level control as well as valves for water into the boiler and steam to the engine. If the system is intended to run without supervision, then sensors and automatic safety shutdown systems are needed.
Thus, the waste heat engine may be one of the least expensive components of a complete waste heat recovery system.
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Cyclone Power Technologies Official Website
Steam engines