Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) is a space-based system developed by the
''University of Michigan.'' Retrieved: August 15, 2015 CYGNSS will measure the ocean surface wind field using a bi-static
''University of Michigan.'' Retrieved: September 27, 2015. Using a network of eight small satellites enables frequent observations: the mean revisit time is predicted to be 7 hours. The eight microsatellites orbit at an inclination of 35°, and are each capable of measuring 4 simultaneous reflections, resulting in 32 wind measurements per second across the globe. CYGNSS is the first of NASA's Earth Venture-class spaceborne missions, part of NASA's Earth Science System Pathfinder program; the previous EV selections were divided among five airborne remote sensing missions. The two-year mission launched on December 15, 2016, after postponements from November 2016, and December 12, 2016.
 Early mission operations focused on engineering commissioning of the satellites and adjustments to the spacing between them. Their relative spacing is important for achieving the desired spatial and temporal sampling. Inter-satellite spacing is controlled by adjusting spacecraft orientation and, as a result, the difference in atmospheric drag between satellites. This technique is referred to as differential drag. An increase in drag lowers a satellite's altitude and increases its orbital velocity. The distance between spacecraft changes as a result of their relative velocities. This is an alternate way of managing the spacing between a constellation of satellites, as opposed to using traditional active propulsion, and is significantly lower cost. It allows for more satellites to be built for the same net cost, resulting in more frequent sampling of short lived, extreme weather events like tropical cyclones. Differential drag maneuvers were conducted throughout the first year and a half of on-orbit operations, and have resulted in a well-dispersed constellation that is able to make measurements with the desired sampling properties.
Early mission operations focused on engineering commissioning of the satellites and adjustments to the spacing between them. Their relative spacing is important for achieving the desired spatial and temporal sampling. Inter-satellite spacing is controlled by adjusting spacecraft orientation and, as a result, the difference in atmospheric drag between satellites. This technique is referred to as differential drag. An increase in drag lowers a satellite's altitude and increases its orbital velocity. The distance between spacecraft changes as a result of their relative velocities. This is an alternate way of managing the spacing between a constellation of satellites, as opposed to using traditional active propulsion, and is significantly lower cost. It allows for more satellites to be built for the same net cost, resulting in more frequent sampling of short lived, extreme weather events like tropical cyclones. Differential drag maneuvers were conducted throughout the first year and a half of on-orbit operations, and have resulted in a well-dispersed constellation that is able to make measurements with the desired sampling properties.
Numerical data files of ocean wind speed measurements are available a
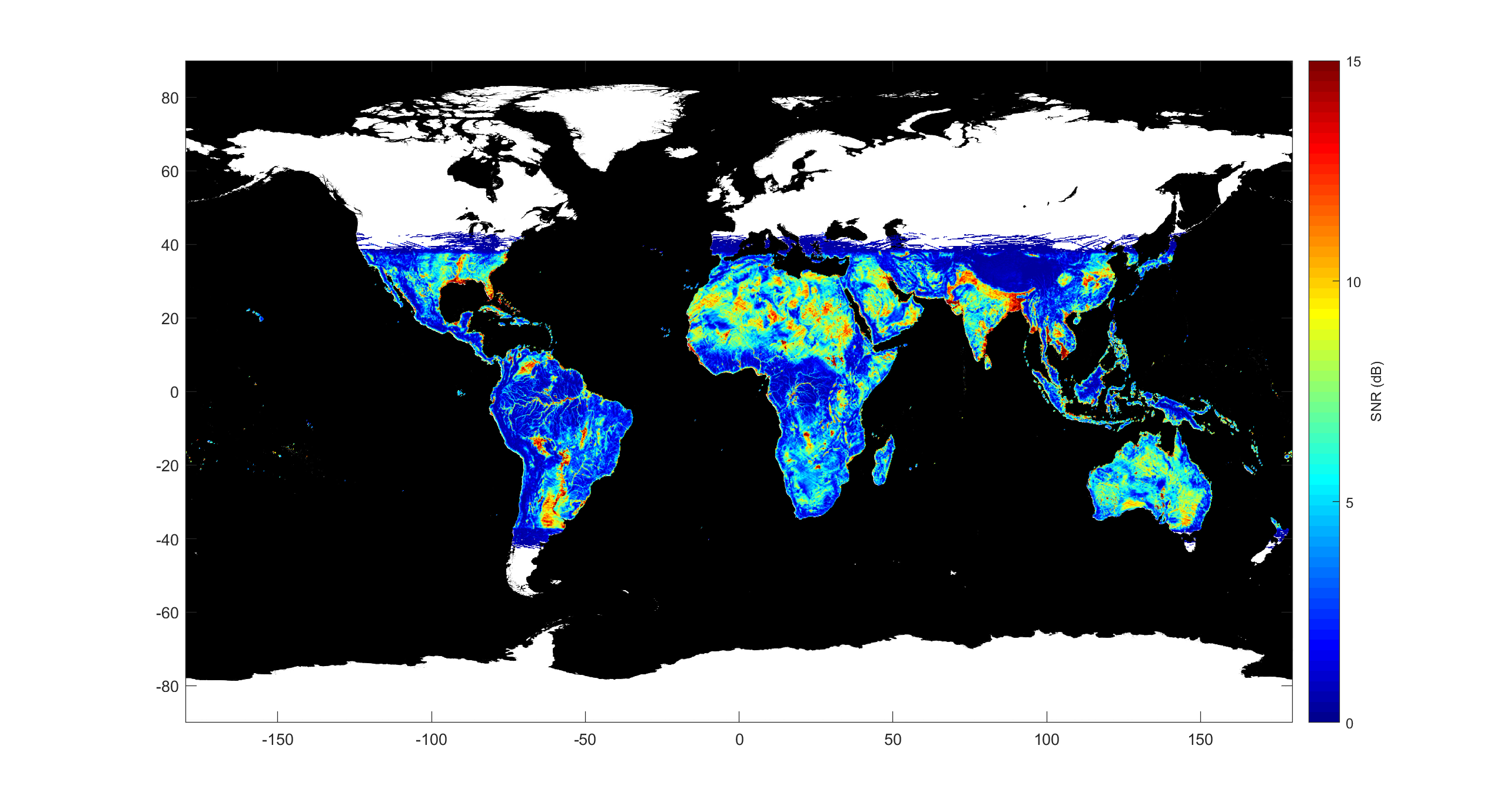 CYGNSS operates continuously, over both ocean and land, and the land measurements also contain useful information. The measurements are sensitive to surface soil moisture and to the presence and extent of inland water bodies. Soil moisture has been estimated using CYGNSS data at numerous sites in the continental U.S. and is found to be in close agreement with independent measurements made by ground sensors and by another satellite. Numerical data files of soil moisture measurements are available a
CYGNSS operates continuously, over both ocean and land, and the land measurements also contain useful information. The measurements are sensitive to surface soil moisture and to the presence and extent of inland water bodies. Soil moisture has been estimated using CYGNSS data at numerous sites in the continental U.S. and is found to be in close agreement with independent measurements made by ground sensors and by another satellite. Numerical data files of soil moisture measurements are available a
The ability of CYGNSS land data to detect and map the extent of flood inundation under dense forest canopies has also been demonstrated and this capability has been used to produce time lapse images of flooding in and around Houston and Havana after landfalls by Hurricanes Harvey and Irma, respectively.
University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
and Southwest Research Institute
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, is an independent and nonprofit applied research and development (R&D) organization. Founded in 1947 by oil businessman Tom Slick, it provides contract research and develo ...
with the aim of improving hurricane forecasting by better understanding the interactions between the sea and the air near the core of a storm.
In June 2012, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedi ...
sponsored the project for $152 million with the University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
leading its development. Other participants in CYGNSS' development include the Southwest Research Institute
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, is an independent and nonprofit applied research and development (R&D) organization. Founded in 1947 by oil businessman Tom Slick, it provides contract research and develo ...
, Sierra Nevada Corporation
Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) is an American, privately held aerospace and national security contractor specializing in aircraft modification and integration, space components and systems, and related technology products for cybersecurity and ...
, and Surrey Satellite Technology
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd, or SSTL, is a company involved in the manufacture and operation of small satellites. A spin-off company of the University of Surrey, it is presently wholly owned by Airbus Defence and Space.
The company began ...
.
The plan was to build a constellation of eight micro-satellites
A small satellite, miniaturized satellite, or smallsat is a satellite of low mass and size, usually under . While all such satellites can be referred to as "small", different classifications are used to categorize them based on mass. Satellites ...
to be launched simultaneously in a single launch vehicle into low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
,
at 500 km altitude. The program was scheduled to launch December 12, 2016, and then observe two hurricane seasons. Problems with a pump on the launching aircraft prevented this first launch, but a second launch attempt took place successfully on December 15, 2016.
Overview
Forecasting the tracks oftropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
s since 1990 has improved by approximately 50%; however, in the same time period there has not been a corresponding improvement in forecasting the intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
* Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
*Level (disambiguation)
*Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
* Field strength of electric, ma ...
of these storms. A better understanding of the inner core of tropical storms could lead to better forecasts; however, current sensors are unable to gather a sufficient quality of data on the inner core due to obscuration from rain bands surrounding it and to infrequent sampling. In order to improve the models used in intensity forecasts, better data are required."CYGNSS."''University of Michigan.'' Retrieved: August 15, 2015 CYGNSS will measure the ocean surface wind field using a bi-static
scatterometry
A scatterometer or diffusionmeter is a scientific instrument to measure the return of a beam of light or radar waves Scattering, scattered by diffusion in a medium such as air. Diffusionmeters using visible light are found in airports or along road ...
technique based on Global Navigation Satellite Systems
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high pre ...
(GNSS) signals, primarily GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
. Each satellite receives both direct GPS signals and signals reflected from the Earth's surface; the direct signals pinpoint the microsatellite position and provide a timing reference, while the reflected or "scattered" signals provide information about the condition of the sea's surface. Sea surface roughness corresponds to wind speed."CYGNSS Factsheet October 2014".''University of Michigan.'' Retrieved: September 27, 2015. Using a network of eight small satellites enables frequent observations: the mean revisit time is predicted to be 7 hours. The eight microsatellites orbit at an inclination of 35°, and are each capable of measuring 4 simultaneous reflections, resulting in 32 wind measurements per second across the globe. CYGNSS is the first of NASA's Earth Venture-class spaceborne missions, part of NASA's Earth Science System Pathfinder program; the previous EV selections were divided among five airborne remote sensing missions. The two-year mission launched on December 15, 2016, after postponements from November 2016, and December 12, 2016.
Science goal
The CYGNSS science goal is to understand the coupling between ocean surface properties, moist atmospheric thermodynamics, radiation, and convective dynamics in the inner core of a tropical cyclone. To achieve this goal, the system will measure ocean surface wind speed in all precipitating conditions, including those experienced in theeyewall
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weat ...
. The mission will also measure ocean surface wind speed in the storm's inner core with sufficient frequency to resolve genesis and rapid intensification. As secondary goal, the project will support the operational hurricane forecast community by producing and providing ocean surface wind speed data products.
Instruments
Each CYGNSS satellite carries a Delay Doppler Mapping Instrument (DDMI), consisting of: *a Delay Mapping Receiver (DMR) *two nadir-pointing antennas *one zenith-pointing antenna The instrument receivesGPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
signals scattered by the ocean surface for the purposes of bi-static scatterometry
A scatterometer or diffusionmeter is a scientific instrument to measure the return of a beam of light or radar waves Scattering, scattered by diffusion in a medium such as air. Diffusionmeters using visible light are found in airports or along road ...
.
Launch and early orbit operations
The CYGNSS mission was launched on December 15, 2016, at 13:37:21 UTC from a singlePegasus XL
Pegasus is an air-launched launch vehicle developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC) and now built and launched by Northrop Grumman. Capable of carrying small payloads of up to into low Earth orbit, Pegasus first flew in 1990 and remai ...
air-launched rocket. The rocket was deployed from a customized Lockheed L-1011
The Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, also known as the L-1011 (pronounced "El-ten-eleven") and TriStar, is an American medium-to-long-range, wide-body trijet airliner built by the Lockheed Corporation. It was the third wide-body airliner to enter comme ...
aircraft, Orbital ATK
Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems (NGIS) was a sector (business segment) of Northrop Grumman from 2018 through 2019. It was formed from Orbital ATK Inc. a company which resulted from the merger of Orbital Sciences Corporation and parts of Alli ...
''Stargazer
Stargazer may refer to:
* an observational astronomer, particularly an amateur
Aerospace
* Stargazer (aircraft), a Lockheed L-1011 airliner used to launch the Pegasus rocket
* Orbiting Astronomical Observatory 2, nicknamed Stargazer, the first ...
'', from a position off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida
Cape Canaveral ( es, Cabo Cañaveral, link=) is a city in Brevard County, Florida. The population was 9,912 at the 2010 United States Census. It is part of the Palm Bay–Melbourne– Titusville Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
After ...
. A launch attempt on December 12 was aborted due to problems with the hydraulic system that separates the Pegasus rocket from the carrier aircraft. After launch, the eight microsats were released into orbit beginning at 13:50 UTC and ending at 13:52 UTC by a deployment module attached to the Pegasus third stage. Successful radio contact with the first microsat was made at 16:42 UTC. The eighth microsat was successfully contacted at 20:30 UTC. By the end of the day on December 15, all eight microsats had their solar arrays deployed and were sun-pointed with batteries charging in safe condition, ready to begin engineering commissioning.
Use of Differential Drag to Adjust Satellite Spacing
 Early mission operations focused on engineering commissioning of the satellites and adjustments to the spacing between them. Their relative spacing is important for achieving the desired spatial and temporal sampling. Inter-satellite spacing is controlled by adjusting spacecraft orientation and, as a result, the difference in atmospheric drag between satellites. This technique is referred to as differential drag. An increase in drag lowers a satellite's altitude and increases its orbital velocity. The distance between spacecraft changes as a result of their relative velocities. This is an alternate way of managing the spacing between a constellation of satellites, as opposed to using traditional active propulsion, and is significantly lower cost. It allows for more satellites to be built for the same net cost, resulting in more frequent sampling of short lived, extreme weather events like tropical cyclones. Differential drag maneuvers were conducted throughout the first year and a half of on-orbit operations, and have resulted in a well-dispersed constellation that is able to make measurements with the desired sampling properties.
Early mission operations focused on engineering commissioning of the satellites and adjustments to the spacing between them. Their relative spacing is important for achieving the desired spatial and temporal sampling. Inter-satellite spacing is controlled by adjusting spacecraft orientation and, as a result, the difference in atmospheric drag between satellites. This technique is referred to as differential drag. An increase in drag lowers a satellite's altitude and increases its orbital velocity. The distance between spacecraft changes as a result of their relative velocities. This is an alternate way of managing the spacing between a constellation of satellites, as opposed to using traditional active propulsion, and is significantly lower cost. It allows for more satellites to be built for the same net cost, resulting in more frequent sampling of short lived, extreme weather events like tropical cyclones. Differential drag maneuvers were conducted throughout the first year and a half of on-orbit operations, and have resulted in a well-dispersed constellation that is able to make measurements with the desired sampling properties.
Wind Observations over the Ocean
Wind speed measurements are made by CYGNSS in a manner analogous to that of previous spaceborne ocean wind sensing radars, by detecting changes in surface roughness caused by near surface wind stress. The quality of the measurements is determined by comparisons to nearly coincident observations by other wind sensors. Comparisons at low to moderate wind speeds (below ) are made to the NOAA Global Data Assimilation System numerical reanalysis wind product and indicate an uncertainty in CYGNSS winds of , with higher uncertainty at high wind speeds. Above 45 mph, and in particular for measurements made within tropical cyclones, comparisons are made to nearly coincident observations by wind sensing instruments on NOAA P-3 hurricane hunter aircraft which were flown into hurricanes in coordination with satellite overpasses by CYGNSS. The comparisons indicate an uncertainty in CYGNSS winds of 11%. As was the case at lower wind speeds, the uncertainty increases with wind speed. CYGNSS ocean wind speed measurements are currently being incorporated into hurricane numerical forecast models and storm surge models to assess the improvement in their performance. Images of recent and archival ocean wind measurements, both globally and centered on individual storms, are available aNumerical data files of ocean wind speed measurements are available a
Observations over Land
 CYGNSS operates continuously, over both ocean and land, and the land measurements also contain useful information. The measurements are sensitive to surface soil moisture and to the presence and extent of inland water bodies. Soil moisture has been estimated using CYGNSS data at numerous sites in the continental U.S. and is found to be in close agreement with independent measurements made by ground sensors and by another satellite. Numerical data files of soil moisture measurements are available a
CYGNSS operates continuously, over both ocean and land, and the land measurements also contain useful information. The measurements are sensitive to surface soil moisture and to the presence and extent of inland water bodies. Soil moisture has been estimated using CYGNSS data at numerous sites in the continental U.S. and is found to be in close agreement with independent measurements made by ground sensors and by another satellite. Numerical data files of soil moisture measurements are available aThe ability of CYGNSS land data to detect and map the extent of flood inundation under dense forest canopies has also been demonstrated and this capability has been used to produce time lapse images of flooding in and around Houston and Havana after landfalls by Hurricanes Harvey and Irma, respectively.
See also
*Tropical cyclone forecasting
Tropical cyclone forecasting is the science of forecasting where a tropical cyclone's center, and its effects, are expected to be at some point in the future. There are several elements to tropical cyclone forecasting: track forecasting, intensi ...
*Tropical cyclone scales
Tropical cyclones are ranked on one of five tropical cyclone intensity scales, according to their maximum sustained winds and which tropical cyclone basins they are located in. Only a few scales of classifications are used officially by the met ...
References
{{orbital launches in 2016 Weather forecasting Tropical cyclone meteorology NASA satellites orbiting Earth Weather satellites of the United States Spacecraft launched in 2016 2016 in the United States Spacecraft launched by Pegasus rockets