cyclic nucleotides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) is a single-
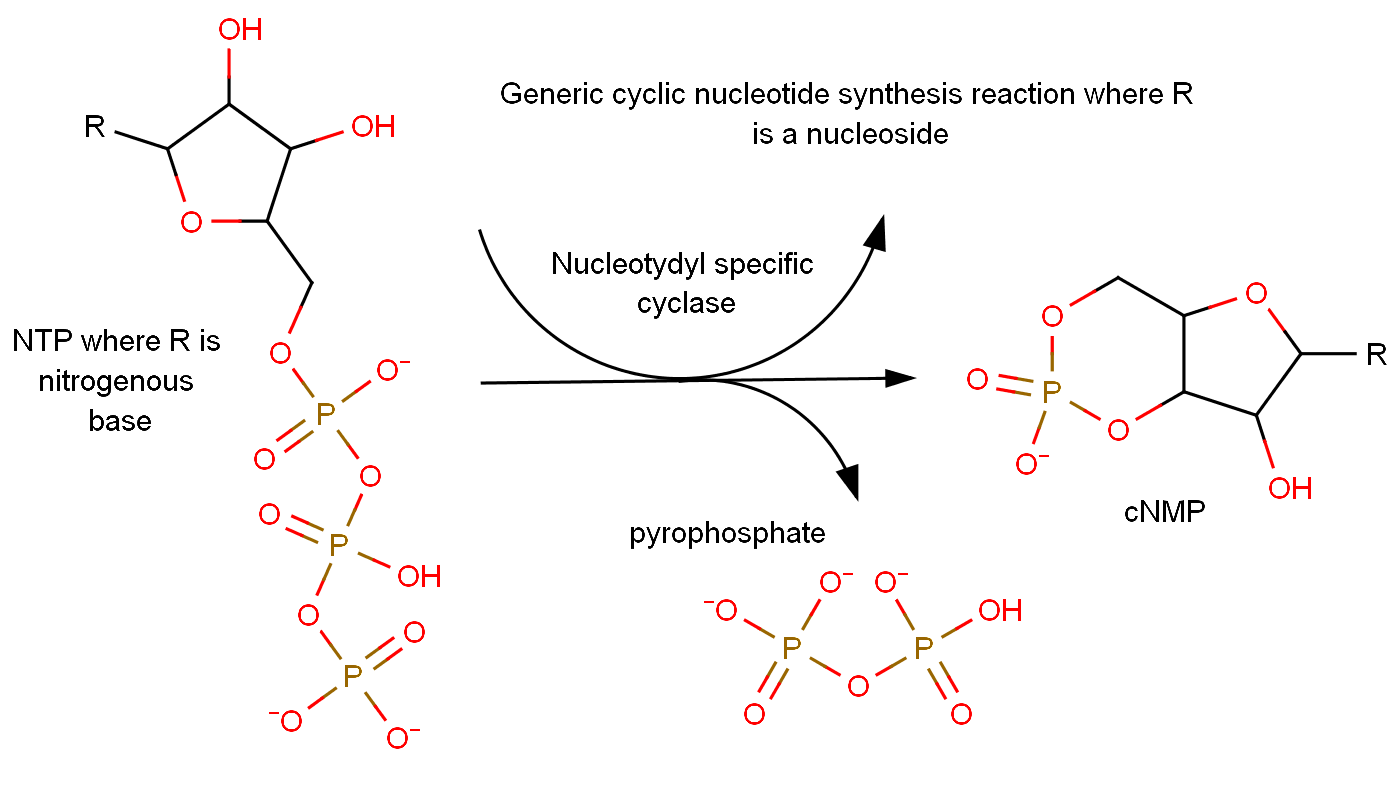 Cyclic nucleotides are produced from the generic reaction NTP → cNMP + PPi, where N represents a nitrogenous base. The reaction is catalyzed by specific nucleotidyl cyclases, such that production of cAMP is catalyzed by
Cyclic nucleotides are produced from the generic reaction NTP → cNMP + PPi, where N represents a nitrogenous base. The reaction is catalyzed by specific nucleotidyl cyclases, such that production of cAMP is catalyzed by
phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
with a cyclic bond arrangement between the sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecul ...
and phosphate groups. Like other nucleotides, cyclic nucleotides are composed of three functional groups: a sugar, a nitrogenous base
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
, and a single phosphate group. As can be seen in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine tri ...
(cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in ...
(cGMP) images, the 'cyclic' portion consists of two bonds between the phosphate group and the 3' and 5' hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
groups of the sugar, very often a ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
.
Their biological significance includes a broad range of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
-ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
interactions. They have been identified as secondary messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
s in both hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
and ion-channel signalling in eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
cells, as well as allosteric effector
In biology, an effector is a general term that can refer to several types of molecules or cells. In the context of biological system regulation, an effector is an element of a regulation loop controlling a regulated quantity.
Small molecule e ...
compounds of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
binding proteins in prokaryotic
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' ...
cells. cAMP and cGMP are currently the most well documented cyclic nucleotides, however there is evidence that cCMP (with cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
) is also involved in eukaryotic cellular messaging. The role of cyclic uridine monophosphate (cUMP) is even less well known.
Discovery of cyclic nucleotides has contributed greatly to the understanding of kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
and phosphatase
In biochemistry, a phosphatase is an enzyme that uses water to cleave a phosphoric acid Ester, monoester into a phosphate ion and an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. Because a phosphatase enzyme catalysis, catalyzes the hydrolysis of its Substrate ...
mechanisms, as well as protein regulation in general. Although more than 50 years have passed since their initial discovery, interest in cyclic nucleotides and their biochemical and physiological significance continues.
History
The understanding of the concept of second messengers, and in particular the role of cyclic nucleotides and their ability to relay physiological signals to a cell, has its origins in the research ofglycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
metabolism by Carl and Gerty Cori
Gerty Theresa Cori (; August 15, 1896 – October 26, 1957) was a Bohemian-Austrian and American biochemist who in 1947 was the third woman to win a Nobel Prize in science, and the first woman to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Me ...
, for which they were awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
in 1947. A number of incremental but important discoveries through the 1950s added to their research, primarily focusing on the activity of glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes (). Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphor ...
in dog liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
. Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the first step in glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanis ...
, the process of breaking glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
into its substituent glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
parts. Earl Sutherland investigated the effect of the hormones adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a Glucagon (medic ...
on glycogen phosphorylase, earning him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971.
In 1956 Edwin Krebs and Edmond Fischer discovered that adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP) is required for the conversion of glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes (). Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphor ...
b to glycogen phosphorylase a. While investigating the action of adrenaline on glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase.
Mechanis ...
the next year, Sutherland and Walter Wosilait reported that inorganic phosphate is released when the enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
liver phosphorylase is inactivated; but when it is activated, it incorporates a phosphate. The “active factor” that the hormones produced was finally purified in 1958, and then identified as containing a ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
, a phosphate, and an adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
in equal ratios. Further, it was proved that this factor reverted to 5’-AMP when it was inactivated.
Evgeny Fesenko, Stanislav Kolesnikov, and Arkady Lyubarsky discovered in 1985 that cyclic guanosine monophosphate
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) is a cyclic nucleotide derived from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). cGMP acts as a second messenger much like cyclic AMP. Its most likely mechanism of action is activation of intracellular protein kinases in ...
(cGMP) can initiate the photoresponse in rods. Soon after, the role of cNMP in gated ion channels of chemosensitive cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
of olfactory sensory neurons was reported by Tadashi Nakamura and Geoffrey Gold. In 1992 Lawrence Haynes and King-Wai Yau uncovered cNMP’s role in the light-dependent cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel of cone photoreceptors. By the end of the decade, the presence of two types of intramembrane receptors was understood: Rs (which stimulates cyclase) and Ri (which inhibits cyclase). Wei-Jen Tang and James Hurley reported in 1998 that adenylyl cyclase, which synthesizes cAMP, is regulated not only by hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s and neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s, but also by phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, forskolin, and guanine nucleotide-binding proteins ( G proteins).
Chemistry of cNMPs
Structure
The two most well-studied cyclic nucleotides are cyclic AMP (cAMP) and cyclic GMP (cGMP), while cyclic CMP (cCMP) and cyclic UMP (cUMP) are less understood. cAMP is 3’5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cGMP is 3’5’-cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cCMP is cytidine 3',5'-monophosphate, and cUMP is uridine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Each cyclic nucleotide has three components. It contains a nitrogenous base (meaning it contains nitrogen): for example,adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
in cAMP and guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
in cGMP. It also contains a sugar, specifically the five-carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
ribose. And finally, a cyclic nucleotide contains a phosphate. A double-ring purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted puri ...
is the nitrogenous base for cAMP and cGMP, while cytosine, thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
, and uracil
Uracil () (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via ...
each have a single-ring nitrogenous base (pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The oth ...
).
These three components are connected so that the nitrogenous base is attached to the first carbon of ribose (1’ carbon), and the phosphate group is attached to the 5’ carbon of ribose. While all nucleotides have this structure, the phosphate group makes a second connection to the ribose ring at the 3’ carbon in cyclic nucleotides. Because the phosphate group has two separate bonds to the ribose sugar, it forms a cyclic ring.
The atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
numbering convention is used to identify the carbons and nitrogens within a cyclic nucleotide. In the pentose, the carbon closest to the carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
group is labeled C-1. When a pentose is connected to a nitrogenous base, carbon atom numbering is distinguished with a prime (') notation, which differentiates these carbons from the atom numbering of the nitrogenous base.
Therefore, for cAMP, 3’5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate indicates that a single phosphate group forms a cyclic structure with the ribose group at its 3’ and 5’ carbons, while the ribose group is also attached to adenosine (this bond is understood to be at the 1’ position of the ribose).
Biochemistry
Cyclic nucleotides are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Control of intracellular concentrations is maintained through a series of enzymatic reactions involving several families of proteins. In higher order mammals, cNMPs are present in many types of tissue.Synthesis and Degradation
 Cyclic nucleotides are produced from the generic reaction NTP → cNMP + PPi, where N represents a nitrogenous base. The reaction is catalyzed by specific nucleotidyl cyclases, such that production of cAMP is catalyzed by
Cyclic nucleotides are produced from the generic reaction NTP → cNMP + PPi, where N represents a nitrogenous base. The reaction is catalyzed by specific nucleotidyl cyclases, such that production of cAMP is catalyzed by adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
and production of cGMP is catalyzed by guanylyl cyclase
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5′-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid ( conjugate base guanylate), is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of th ...
. Adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
has been found in both a transmembrane and cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
ic form, representing distinct protein classes and different sources of cAMP.
Both cAMP and cGMP are degraded by hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of the 3' phosphodiester bond
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is d ...
, resulting in a 5'NMP. Degradation is carried out primarily by a class of enzymes known as phosphodiesterase
A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, ''phosphodiesterase'' refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many oth ...
s (PDEs). In mammalian cells, there are 11 known PDE families with varying isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have uniqu ...
of each protein expressed based on the cell's regulatory needs. Some phosphodiesterases are cNMP-specific, while others can hydrolyze non-specifically. However, the cAMP and cGMP degradation pathways are much more understood than those for either cCMP or cUMP. The identification of specific PDEs for cCMP and cUMP has not been as thoroughly established.
Target Binding
Cyclic nucleotides can be found in many different types of eukaryotic cells, including photo-receptor rods and cones,smooth muscle cells
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal muscle, skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non-striated ...
and liver cells. Cellular concentrations of cyclic nucleotides can be very low, in the 10−7 M range, because metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
and function are often localized in particular parts of the cell. A highly conserved cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (CNB) is present in all proteins that bind cNMPs, regardless of their biological function. The domain consists of a beta sandwich architecture, with the cyclic nucleotide binding pocket between the beta sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gene ...
s. The binding of cNMP causes a conformational change that affects the protein's activity. There is also data to support a synergistic binding effect amongst multiple cyclic nucleotides, with cCMP lowering the effective concentration (EC50) of cAMP for activation of protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of serine-threonine kinases whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, in ...
(PKA).
Biology
Cyclic nucleotides are integral to a communication system that acts within cells. They act as "second messengers" by relaying the signals of many first messengers, such as hormones and neurotransmitters, to their physiological destinations. Cyclic nucleotides participate in many physiological responses, including receptor-effector coupling, down-regulation of drug responsiveness, protein-kinase cascades, and transmembrane signal transduction. Cyclic nucleotides act as second messengers when first messengers, which cannot enter the cell, instead bind to receptors in the cellular membrane. The receptor changes conformation and transmits a signal that activates an enzyme in the cell membrane interior called adenylyl cyclase. This releases cAMP into the cell interior, where it stimulates a protein kinase called cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. By phosphorylating proteins, cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase alters protein activity. cAMP's role in this process terminates upon hydrolysis to AMP by phosphodiesterase. Cyclic nucleotides are well-suited to act as second messengers for several reasons. Their synthesis is energetically favorable, and they are derived from common metabolic components (ATP and GTP). When they break down into AMP/GMP and inorganic phosphate, these components are non-toxic. Finally, cyclic nucleotides can be distinguished from non-cyclic nucleotides because they are smaller and less polar.Biological significance
The involvement of cyclic nucleotides on biological functions is varied, while an understanding of their role continues to grow. There are several examples of their biological influence. They are associated with long-term and short-term memory. They also work in the liver to coordinate various enzymes that controlblood glucose
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly blood sugar regulation, regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis ...
and other nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s. In bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, cyclic nucleotides bind to catabolite gene activator protein (CAP), which acts to increase metabolic enzymatic activity by increasing the rate of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
transcription. They also facilitate relaxation of smooth muscle cells in vascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
tissue, and activate cyclic CNG channels in retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
l photoreceptors and olfactory sensory neurons. In addition, they potentially activate cyclic CNG channels in: pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
light sensitivity, sensory neurons of the vomeronasal organ
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) in various tetrapods ...
(which is involved in the detection of pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
s), taste receptor
A taste receptor or tastant is a type of cellular receptor that facilitates the sensation of taste. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locat ...
cells, cellular signaling in sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
, airway epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
cells, gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and rele ...
(GnRH)-secreting neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
al cell line, and renal
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retrop ...
inner medullary collecting duct
The collecting duct system of the kidney consists of a series of tubules and ducts that physically connect nephrons to a minor calyx or directly to the renal pelvis. The collecting duct participates in electrolyte and fluid balance through rea ...
.
Pathway mutations and related diseases
Examples of disruptions of cNMP pathways include: mutations in CNG channelgene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s are associated with degeneration of the retina and with color blindness
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color percept ...
; and overexpression of cytosolic or soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC) has been linked to human prostate carcinoma. Inhibition of sAC, or knockdown by RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by ...
(RNAi) transfection
Transfection is the process of deliberately introducing naked or purified nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. It may also refer to other methods and cell types, although other terms are often preferred: " transformation" is typically used to des ...
has been shown to prevent the proliferation of the prostate carcinoma cells. The regulatory pathway appears to be part of the EPAC pathway and not the PKA pathway.
Phosphodiesterases, principle regulators of cNMP degradation, are often targets for therapeutics. Caffeine is a known PDE inhibitor, while drugs used for the treatment of erectile dysfunction like sildenafil
Sildenafil, sold under the brand name Viagra among others, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is also sometimes used off-label for the treatment of certain sym ...
and tadalafil also act through inhibiting the activity of phosphodiesterases.
References
External links
* {{Nucleobases, nucleosides, and nucleotides Nucleotides