Cybele (band) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian
Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian
 No contemporary text or myth survives to attest the original character and nature of Cybele's Phrygian cult. She may have evolved from a statuary type found at Çatalhöyük in Anatolia, of a "corpulent and fertile" female figure accompanied by large felines, dated to the
No contemporary text or myth survives to attest the original character and nature of Cybele's Phrygian cult. She may have evolved from a statuary type found at Çatalhöyük in Anatolia, of a "corpulent and fertile" female figure accompanied by large felines, dated to the
 Cybele's early Greek images are small votive representations of her monumental rock-cut images in the Phrygian highlands. She stands alone within a
Cybele's early Greek images are small votive representations of her monumental rock-cut images in the Phrygian highlands. She stands alone within a  Their cults shared several characteristics: the foreigner-deity arrived in a chariot, drawn by exotic big cats (Dionysus by tigers or panthers, Cybele by lions), accompanied by wild music and an ecstatic entourage of exotic foreigners and people from the lower classes. At the end of the 1st century BC
Their cults shared several characteristics: the foreigner-deity arrived in a chariot, drawn by exotic big cats (Dionysus by tigers or panthers, Cybele by lions), accompanied by wild music and an ecstatic entourage of exotic foreigners and people from the lower classes. At the end of the 1st century BC
 Cybele's major mythographic narratives attach to her relationship with Attis, who is described by ancient Greek and Roman sources and cults as her youthful consort, and as a Phrygian deity. In Phrygia, "Attis" was not a deity, but both a commonplace and priestly name, found alike in casual graffiti, the dedications of personal monuments, as well as at several of Cybele's Phrygian shrines and monuments. His divinity may therefore have begun as a Greek invention based on what was known of Cybele's Phrygian cult. His earliest certain image as deity appears on a 4th-century BC Greek
Cybele's major mythographic narratives attach to her relationship with Attis, who is described by ancient Greek and Roman sources and cults as her youthful consort, and as a Phrygian deity. In Phrygia, "Attis" was not a deity, but both a commonplace and priestly name, found alike in casual graffiti, the dedications of personal monuments, as well as at several of Cybele's Phrygian shrines and monuments. His divinity may therefore have begun as a Greek invention based on what was known of Cybele's Phrygian cult. His earliest certain image as deity appears on a 4th-century BC Greek
 Romans knew Cybele as ''Magna Mater'' ("Great Mother"), or as ''Magna Mater deorum Idaea'' ("great Idaean mother of the gods"), equivalent to the Greek title ''Meter Theon Idaia'' ("Mother of the Gods, from Mount Ida"). Rome officially adopted her cult during the
Romans knew Cybele as ''Magna Mater'' ("Great Mother"), or as ''Magna Mater deorum Idaea'' ("great Idaean mother of the gods"), equivalent to the Greek title ''Meter Theon Idaia'' ("Mother of the Gods, from Mount Ida"). Rome officially adopted her cult during the  Most modern scholarship agrees that Cybele's consort, Attis, and her eunuch Phrygian priests (
Most modern scholarship agrees that Cybele's consort, Attis, and her eunuch Phrygian priests (
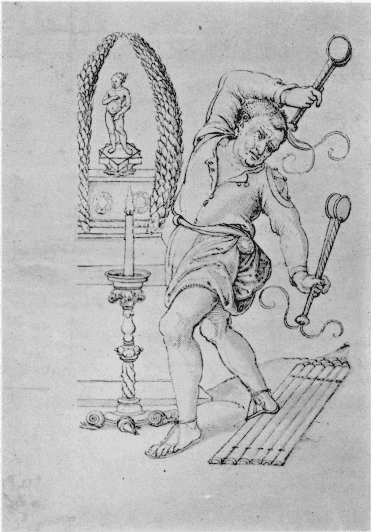 The ''Megalesia'' festival to Magna Mater commenced on April 4, the anniversary of her arrival in Rome. The festival structure is unclear, but it included ludi scaenici (plays and other entertainments based on religious themes), probably performed on the deeply stepped approach to her temple; some of the plays were commissioned from well-known playwrights. On April 10, her image was taken in public procession to the Circus Maximus, and chariot races were held there in her honour; a statue of Magna Mater was permanently sited on the racetrack's dividing barrier, showing the goddess seated on a lion's back.
Roman bystanders seem to have perceived Megalesia as either characteristically " Greek"; or Phrygian. At the cusp of Rome's transition to Empire, the Greek
The ''Megalesia'' festival to Magna Mater commenced on April 4, the anniversary of her arrival in Rome. The festival structure is unclear, but it included ludi scaenici (plays and other entertainments based on religious themes), probably performed on the deeply stepped approach to her temple; some of the plays were commissioned from well-known playwrights. On April 10, her image was taken in public procession to the Circus Maximus, and chariot races were held there in her honour; a statue of Magna Mater was permanently sited on the racetrack's dividing barrier, showing the goddess seated on a lion's back.
Roman bystanders seem to have perceived Megalesia as either characteristically " Greek"; or Phrygian. At the cusp of Rome's transition to Empire, the Greek
 Rome's strictures against castration and citizen participation in Magna Mater's cult limited both the number and kind of her initiates. From the 160s AD, citizens who sought initiation to her mysteries could offer either of two forms of bloody animal sacrifice – and sometimes both – as lawful substitutes for self-castration. The
Rome's strictures against castration and citizen participation in Magna Mater's cult limited both the number and kind of her initiates. From the 160s AD, citizens who sought initiation to her mysteries could offer either of two forms of bloody animal sacrifice – and sometimes both – as lawful substitutes for self-castration. The
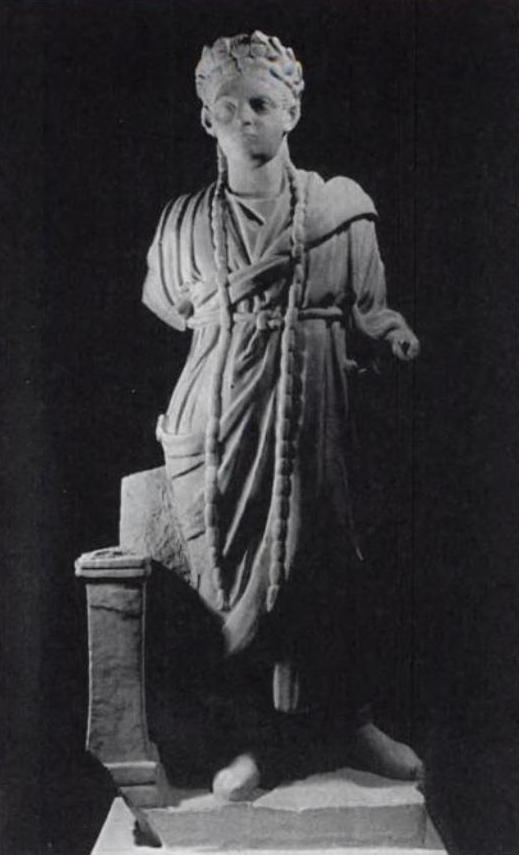 Pessinus, site of the temple whence the Magna Mater was brought to Rome, was a theocracy whose leading Galli may have been appointed via some form of adoption, to ensure "dynastic" succession. The highest ranking Gallus was known as "Attis", and his junior as "Battakes". The Galli of Pessinus were politically influential; in 189 BC, they predicted or prayed for Roman victory in Rome's imminent war against the Galatians. The following year, perhaps in response to this gesture of goodwill, the Roman senate formally recognised Illium as the ancestral home of the Roman people, granting it extra territory and tax immunity. In 103, a Battakes traveled to Rome and addressed its senate, either for the redress of impieties committed at his shrine, or to predict yet another Roman military success. He would have cut a remarkable figure, with "colourful attire and headdress, like a crown, with regal associations unwelcome to the Romans". Yet the senate supported him; and when a plebeian tribune who had violently opposed his right to address the senate died of a fever (or, in the alternative scenario, when the prophesied Roman victory came) Magna Mater's power seemed proven.
In Rome, the Galli and their cult fell under the supreme authority of the pontifices, who were usually drawn from Rome's highest ranking, wealthiest citizens. The Galli themselves, although imported to serve the day-to-day workings of their goddess's cult on Rome's behalf, represented an inversion of Roman priestly traditions in which senior priests were citizens, expected to raise families, and personally responsible for the running costs of their temples, assistants, cults, and festivals. As eunuchs, incapable of reproduction, the Galli were forbidden Roman citizenship and rights of inheritance; like their eastern counterparts, they were technically mendicants whose living depended on the pious generosity of others. For a few days of the year, during the Megalesia, Cybele's laws allowed them to leave their quarters, located within the goddess' temple complex, and roam the streets to beg for money. They were outsiders, marked out as Galli by their regalia, and their notoriously effeminate dress and demeanour, but as priests of a state cult, they were sacred and inviolate. From the start, they were objects of Roman fascination, scorn, and religious awe. No Roman, not even a slave, could castrate himself "in honour of the Goddess" without penalty; in 101 BC, a slave who had done so was exiled. Augustus selected priests from among his own freedmen to supervise Magna Mater's cult, and brought it under Imperial control.
Pessinus, site of the temple whence the Magna Mater was brought to Rome, was a theocracy whose leading Galli may have been appointed via some form of adoption, to ensure "dynastic" succession. The highest ranking Gallus was known as "Attis", and his junior as "Battakes". The Galli of Pessinus were politically influential; in 189 BC, they predicted or prayed for Roman victory in Rome's imminent war against the Galatians. The following year, perhaps in response to this gesture of goodwill, the Roman senate formally recognised Illium as the ancestral home of the Roman people, granting it extra territory and tax immunity. In 103, a Battakes traveled to Rome and addressed its senate, either for the redress of impieties committed at his shrine, or to predict yet another Roman military success. He would have cut a remarkable figure, with "colourful attire and headdress, like a crown, with regal associations unwelcome to the Romans". Yet the senate supported him; and when a plebeian tribune who had violently opposed his right to address the senate died of a fever (or, in the alternative scenario, when the prophesied Roman victory came) Magna Mater's power seemed proven.
In Rome, the Galli and their cult fell under the supreme authority of the pontifices, who were usually drawn from Rome's highest ranking, wealthiest citizens. The Galli themselves, although imported to serve the day-to-day workings of their goddess's cult on Rome's behalf, represented an inversion of Roman priestly traditions in which senior priests were citizens, expected to raise families, and personally responsible for the running costs of their temples, assistants, cults, and festivals. As eunuchs, incapable of reproduction, the Galli were forbidden Roman citizenship and rights of inheritance; like their eastern counterparts, they were technically mendicants whose living depended on the pious generosity of others. For a few days of the year, during the Megalesia, Cybele's laws allowed them to leave their quarters, located within the goddess' temple complex, and roam the streets to beg for money. They were outsiders, marked out as Galli by their regalia, and their notoriously effeminate dress and demeanour, but as priests of a state cult, they were sacred and inviolate. From the start, they were objects of Roman fascination, scorn, and religious awe. No Roman, not even a slave, could castrate himself "in honour of the Goddess" without penalty; in 101 BC, a slave who had done so was exiled. Augustus selected priests from among his own freedmen to supervise Magna Mater's cult, and brought it under Imperial control.

 Rome characterised the Phrygians as barbaric, effeminate orientals, prone to excess. While some Roman sources explained Attis' death as punishment for his excess devotion to Magna Mater, others saw it as punishment for his lack of devotion, or outright disloyalty. Only one account of Attis and Cybele (related by Pausanias) omits any suggestion of a personal or sexual relationship between them; Attis achieves divinity through his support of ''Meters cult, is killed by a boar sent by Zeus, who is envious of the cult's success, and is rewarded for his commitment with godhood.
The most complex, vividly detailed, and lurid accounts of Magna Mater and Attis were produced as anti-pagan polemic in the late 4th century by the Christian apologist Arnobius, who presented their cults as a repulsive combination of blood-bath, incest, and sexual orgy, derived from the myths of Agdistis. This has been presumed the most ancient, violent, and authentically Phrygian version of myth and cult, closely following an otherwise lost orthodox, approved version preserved by the priest-kings at Pessinous and imported to Rome. Arnobius claimed several scholarly sources as his authority; but the oldest versions are also the most fragmentary and, during an interval of several centuries, apt to diverge into whatever version suited a new audience, or potentially, new acolytes. Greek versions of the myth recall those concerning the mortal Adonis and his divine lovers, - Aphrodite, who had some claim to cult as a 'Mother of all", or her rival for Adonis' love, Persephone - showing the grief and anger of a powerful goddess, mourning the helpless loss of her mortal beloved.
The emotionally charged literary version presented in
Rome characterised the Phrygians as barbaric, effeminate orientals, prone to excess. While some Roman sources explained Attis' death as punishment for his excess devotion to Magna Mater, others saw it as punishment for his lack of devotion, or outright disloyalty. Only one account of Attis and Cybele (related by Pausanias) omits any suggestion of a personal or sexual relationship between them; Attis achieves divinity through his support of ''Meters cult, is killed by a boar sent by Zeus, who is envious of the cult's success, and is rewarded for his commitment with godhood.
The most complex, vividly detailed, and lurid accounts of Magna Mater and Attis were produced as anti-pagan polemic in the late 4th century by the Christian apologist Arnobius, who presented their cults as a repulsive combination of blood-bath, incest, and sexual orgy, derived from the myths of Agdistis. This has been presumed the most ancient, violent, and authentically Phrygian version of myth and cult, closely following an otherwise lost orthodox, approved version preserved by the priest-kings at Pessinous and imported to Rome. Arnobius claimed several scholarly sources as his authority; but the oldest versions are also the most fragmentary and, during an interval of several centuries, apt to diverge into whatever version suited a new audience, or potentially, new acolytes. Greek versions of the myth recall those concerning the mortal Adonis and his divine lovers, - Aphrodite, who had some claim to cult as a 'Mother of all", or her rival for Adonis' love, Persephone - showing the grief and anger of a powerful goddess, mourning the helpless loss of her mortal beloved.
The emotionally charged literary version presented in
Britannica Online Encyclopædia
*
* ttps://iconographic.warburg.sas.ac.uk/category/vpc-taxonomy-000208 The Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (images of Cybele) {{Authority control Hellenistic Anatolian deities Phrygian goddesses Greek goddesses Roman goddesses Mountain goddesses Mother goddesses Life-death-rebirth goddesses Metamorphoses characters Lion goddesses
 Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian
Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian mother goddess
A mother goddess is a goddess who represents a personified deification of motherhood, fertility goddess, fertility, creation, destruction, or the earth goddess who embodies the bounty of the earth or nature. When equated with the earth or th ...
; she may have a possible forerunner in the earliest neolithic at Çatalhöyük. She is Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
's only known goddess, and was probably its national deity
A national god is a guardian divinity whose special concern is the safety and well-being of an ethnic group (''nation''), and of that group's leaders. This is contrasted with other guardian figures such as family gods responsible for the well-be ...
. Greek colonists in Asia Minor adopted and adapted her Phrygian cult and spread it to mainland Greece and to the more distant western Greek colonies around the 6th century BC.
In Greece, Cybele met with a mixed reception. She became partially assimilated to aspects of the Earth-goddess Gaia
In Greek mythology, Gaia (; from Ancient Greek , a poetical form of , 'land' or 'earth'),, , . also spelled Gaea , is the personification of the Earth and one of the Greek primordial deities. Gaia is the ancestral mother—sometimes parthenog ...
, of her possibly Minoan
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
equivalent Rhea, and of the harvest–mother goddess Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
. Some city-states, notably Athens, evoked her as a protector, but her most celebrated Greek rites and processions show her as an essentially foreign, exotic mystery-goddess who arrives in a lion-drawn chariot to the accompaniment of wild music, wine, and a disorderly, ecstatic following. Uniquely in Greek religion, she had a eunuch mendicant priesthood. Many of her Greek cults included rites to a divine Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
n castrate shepherd-consort Attis, who was probably a Greek invention. In Greece, Cybele became associated with mountains, town and city walls, fertile nature, and wild animals, especially lions.
In Rome, Cybele became known as Magna Mater ("Great Mother"). The Roman state adopted and developed a particular form of her cult after the Sibylline oracle in 205 BC recommended her conscription as a key religious ally in Rome's second war against Carthage (218 to 201 BC). Roman mythographers reinvented her as a Trojan goddess, and thus an ancestral goddess of the Roman people by way of the Trojan prince Aeneas. As Rome eventually established hegemony over the Mediterranean world, Romanized forms of Cybele's cults spread throughout Rome's empire. Greek and Roman writers debated and disputed the meaning and morality of her cults and priesthoods, which remain controversial subjects in modern scholarship.
Anatolia
 No contemporary text or myth survives to attest the original character and nature of Cybele's Phrygian cult. She may have evolved from a statuary type found at Çatalhöyük in Anatolia, of a "corpulent and fertile" female figure accompanied by large felines, dated to the
No contemporary text or myth survives to attest the original character and nature of Cybele's Phrygian cult. She may have evolved from a statuary type found at Çatalhöyük in Anatolia, of a "corpulent and fertile" female figure accompanied by large felines, dated to the 6th millennium BC
The 6th millennium BC spanned the years 6000 BC to 5001 BC (c. 8 ka to c. 7 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological an ...
and identified by some as a mother goddess
A mother goddess is a goddess who represents a personified deification of motherhood, fertility goddess, fertility, creation, destruction, or the earth goddess who embodies the bounty of the earth or nature. When equated with the earth or th ...
. In Phrygian art of the 8th century BC, the cult attributes of the Phrygian mother-goddess include attendant lions, a bird of prey, and a small vase for her libations or other offerings.
The inscription ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya''R. S. P. Beekes
Robert Stephen Paul Beekes (; 2 September 1937 – 21 September 2017) was a Dutch linguist who was emeritus professor of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics at Leiden University and an author of many monographs on the Proto-Indo-European lang ...
, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 794 (''s.v.'' "Κυβέλη"). at a Phrygian rock-cut shrine, dated to the first half of the 6th century BC, is usually read as "Mother of the mountain", a reading supported by ancient classical sources, and consistent with Cybele as any of several similar tutelary goddesses
Tutelary may refer to:
* Patron saint, or tutelary saint
* Tutelary deity
See also
* Tutoring
{{Disambiguation ...
, each known as "mother" and associated with specific Anatolian mountains or other localities: a goddess thus "born from stone". She is ancient Phrygia's only known goddess, the divine companion or consort of its mortal rulers, and was probably the highest deity of the Phrygian state. Her name, and the development of religious practices associated with her, may have been influenced by the Kubaba
Kubaba (in the ''Weidner'' or ''Esagila Chronicle''), sux, , , is the only queen on the ''Sumerian King List'', which states she reigned for 100 years – roughly in the Early Dynastic III period (ca. 2500–2330 BC) of Sumerian history. A co ...
cult of the deified Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian queen Kubaba
Kubaba (in the ''Weidner'' or ''Esagila Chronicle''), sux, , , is the only queen on the ''Sumerian King List'', which states she reigned for 100 years – roughly in the Early Dynastic III period (ca. 2500–2330 BC) of Sumerian history. A co ...
.
In the 2nd century AD, the geographer Pausanias attests to a Magnesian (Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
n) cult to "the mother of the gods", whose image was carved into a rock-spur of Mount Sipylus. This was believed to be the oldest image of the goddess, and was attributed to the legendary Broteas
In Greek mythology, Broteas (Ancient Greek: Βροτέας), a hunter, was the son of Tantalus (by Dione, Euryanassa or Eurythemista), whose other offspring were Niobe and Pelops.
Broteas was also one of the Lapiths, killed at the battle of the La ...
. At Pessinos
Pessinus ( el, Πεσσινούς or Πισσινούς) was an Ancient city and archbishopric in Asia Minor, a geographical area roughly covering modern Anatolia (Asian Turkey). The site of the city is now the modern Turkish village of Ballıhisa ...
in Phrygia, the mother goddess—identified by the Greeks as Cybele—took the form of an unshaped stone of black meteoric iron, and may have been associated with or identical to Agdistis
Agdistis ( grc, Ἄγδιστις) is a deity of Greek, Roman, and Anatolian mythology who possesses both male and female sexual organs. They were closely associated with the Phrygian goddess Cybele.
Their androgyny was seen as a symbol of ...
, Pessinos' mountain deity. This was the aniconic stone that was removed to Rome in 204 BC.
Images and iconography in funerary contexts, and the ubiquity of her Phrygian name ''Matar'' ("Mother"), suggest that she was a mediator between the "boundaries of the known and unknown": the civilized and the wild, the worlds of the living and the dead. Her association with hawks, lions, and the stone of the mountainous landscape of the Anatolian wilderness, seem to characterize her as mother of the land in its untrammeled natural state, with power to rule, moderate or soften its latent ferocity, and to control its potential threats to a settled, civilized life. Anatolian elites sought to harness her protective power to forms of ruler-cult; in Phrygia, the Midas monument connects her with king Midas, as her sponsor, consort, or co-divinity. As protector of cities, or city states, she was sometimes shown wearing a mural crown, representing the city walls. At the same time, her power "transcended any purely political usage and spoke directly to the goddess' followers from all walks of life".
Some Phrygian shaft monuments are thought to have been used for libations and blood offerings to Cybele, perhaps anticipating by several centuries the pit used in her taurobolium
In the Roman Empire of the second to fourth centuries, ''taurobolium'' referred to practices involving the sacrifice of a bull, which after mid-second century became connected with the worship of the Great Mother of the Gods; though not previo ...
and criobolium Criobolium is the ritual sacrifice of a ram in the cult of Attis
Attis (; grc-gre, Ἄττις, also , , ) was the consort of Cybele, in Phrygian and Greek mythology.
His priests were eunuchs, the ''Galli'', as explained by origin myths per ...
sacrifices during the Roman imperial era. Over time, her Phrygian cults and iconography were transformed, and eventually subsumed, by the influences and interpretations of her foreign devotees, at first Greek and later Roman.
Greek Cybele
From around the 6th century BC, cults to the Anatolian mother-goddess were introduced from Phrygia into the ethnically Greek colonies of western Anatolia, mainland Greece, the Aegean islands and the westerly colonies ofMagna Graecia
Magna Graecia (, ; , , grc, Μεγάλη Ἑλλάς, ', it, Magna Grecia) was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these re ...
. The Greeks called her ''Mātēr'' or ''Mētēr'' ("Mother"), or from the early 5th century ''Kubelē''; in Pindar, she is "Mistress Cybele the Mother". In Homeric Hymn
The ''Homeric Hymns'' () are a collection of thirty-three anonymous ancient Greek hymns celebrating individual gods. The hymns are "Homeric" in the sense that they employ the same epic meter—dactylic hexameter—as the ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'', ...
14 she is "the Mother of all gods and all human beings." Cybele was readily assimilated with several Greek goddesses, especially Rhea, as ''Mētēr theōn'' ("Mother of the gods"), whose raucous, ecstatic rites she may have acquired. As an exemplar of devoted motherhood, she was partly assimilated to the grain-goddess Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
, whose torchlight procession recalled her search for her lost daughter, Persephone; but she also continued to be identified as a foreign deity, with many of her traits reflecting Greek ideas about barbarians and the wilderness, as ''Mētēr oreia'' ("Mother of the Mountains"). She is depicted as a Potnia Theron ("Mistress of animals"), with her mastery of the natural world expressed by the lions that flank her, sit in her lap, or draw her chariot. This schema may derive from a goddess figure from Minoan religion. Walter Burkert places her among the "foreign gods" of Greek religion, a complex figure combining a putative Minoan-Mycenaean tradition with the Phrygian cult imported directly from Asia Minor.
 Cybele's early Greek images are small votive representations of her monumental rock-cut images in the Phrygian highlands. She stands alone within a
Cybele's early Greek images are small votive representations of her monumental rock-cut images in the Phrygian highlands. She stands alone within a naiskos
The naiskos (pl.: naiskoi; el, ναΐσκος, diminutive of ναός "temple") is a small temple in classical order with columns or pillars and pediment.
Ancient Greece
Often applied as an artificial motif, it is common in ancient art. It al ...
, which represents her temple or its doorway, and is crowned with a ''polos'', a high, cylindrical hat. A long, flowing chiton
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora (), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.
They are also sometimes known as gumboots or sea cradles or coat-of-mail s ...
covers her shoulders and back. She is sometimes shown with lions in attendance. Around the 5th century BC, Agoracritos
Agoracritus (Greek ''Agorákritos''; fl. late 5th century BC) was a famous sculptor in ancient Greece.
Life
Agoracritus was born on the island of Paros, and was active from about Olympiad 85 to 88, that is, from about 436 to 424 BC.Pliny, ''Nat ...
created a fully Hellenised and influential image of Cybele that was set up in the Metroon in the Athenian agora
The ancient Agora of Athens (also called the Classical Agora) is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill ...
. It showed her enthroned, with a lion attendant, holding a '' phiale'' (a dish for making libations to the gods) and a ''tympanon
The hammered dulcimer (also called the hammer dulcimer) is a percussion-stringed instrument which consists of strings typically stretched over a trapezoidal resonant sound board. The hammered dulcimer is set before the musician, who in more trad ...
'' (a hand drum). Both were Greek innovations to her iconography and reflect key features of her ritual worship introduced by the Greeks which would be salient in the cult's later development.
For the Greeks, the tympanon was a marker of foreign cults, suitable for rites to Cybele, her close equivalent Rhea, and Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
; of these, only Cybele holds the tympanon. She appears with Dionysus, as a secondary deity in Euripides' '' Bacchae'', 64 – 186, and Pindar's ''Dithyramb'' II.6 – 9. In the ''Bibliotheca'' formerly attributed to Apollodorus, Cybele is said to have cured Dionysus of his madness.
 Their cults shared several characteristics: the foreigner-deity arrived in a chariot, drawn by exotic big cats (Dionysus by tigers or panthers, Cybele by lions), accompanied by wild music and an ecstatic entourage of exotic foreigners and people from the lower classes. At the end of the 1st century BC
Their cults shared several characteristics: the foreigner-deity arrived in a chariot, drawn by exotic big cats (Dionysus by tigers or panthers, Cybele by lions), accompanied by wild music and an ecstatic entourage of exotic foreigners and people from the lower classes. At the end of the 1st century BC Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
notes that Rhea-Cybele's popular rites in Athens were sometimes held in conjunction with Dionysus' procession. Both were regarded with caution by the Greeks, as being foreign, to be simultaneously embraced and "held at arm's length".
Cybele was also the focus of mystery cult
Mystery religions, mystery cults, sacred mysteries or simply mysteries, were religious schools of the Greco-Roman world for which participation was reserved to initiates ''(mystai)''. The main characterization of this religion is the secrecy ass ...
, private rites with a chthonic
The word chthonic (), or chthonian, is derived from the Ancient Greek word ''χθών, "khthon"'', meaning earth or soil. It translates more directly from χθόνιος or "in, under, or beneath the earth" which can be differentiated from Γῆ ...
aspect connected to hero cult and exclusive to those who had undergone initiation, although it is unclear who Cybele's initiates were. Reliefs show her alongside young female and male attendants with torches, and with vessels for purification. Literary sources describe joyous abandonment to the loud, percussive music of tympanon, castanets, clashing cymbals, and flutes, and to the frenzied "Phrygian dancing", perhaps a form of circle-dancing by women, to the roar of "wise and healing music of the gods".
In literary sources, the spread of Cybele's cult is presented as a source of conflict and crisis. Herodotus says that when Anacharsis returned to Scythia after traveling and acquiring knowledge among the Greeks in the 6th century BC, his brother, the Scythian king, put him to death for celebrating Cybele's mysteries. The historicity of this account and that of Anacharsis himself are widely questioned. In Athenian tradition, the city's Metroon was founded to placate Cybele, who had visited a plague on Athens when one of her wandering priests was killed for his attempt to introduce her cult. The earliest source is the ''Hymn to the Mother of the Gods'' (362 AD) by the Roman emperor Julian
Julian may refer to:
People
* Julian (emperor) (331–363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363
* Julian (Rome), referring to the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots
* Saint Julian (disambiguation), several Christian saints
* Julian (give ...
, but references to it appear in scholia from an earlier date. The account may reflect real resistance to Cybele's cult, but Lynne Roller sees it as a story intended to demonstrate Cybele's power, similar to myth of Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
' arrival in Thebes recounted in '' The Bacchae''. Many of Cybele's cults were funded privately, rather than by the polis, but she also had publicly established temples in many Greek cities, including Athens and Olympia. Her "vivid and forceful character" and association with the wild, set her apart from the Olympian deities
Olympian or Olympians may refer to:
Religion
* Twelve Olympians, the principal gods and goddesses in ancient Greek religion
* Olympian spirits, spirits mentioned in books of ceremonial magic
Fiction
* ''Percy Jackson & the Olympians'', fiction ...
. Her association with Phrygia led to particular unease in Greece after the Persian Wars, as Phrygian symbols and costumes were increasingly associated with the Achaemenid empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
.
Conflation
Conflation is the merging of two or more sets of information, texts, ideas, opinions, etc., into one, often in error. Conflation is often misunderstood. It originally meant to fuse or blend, but has since come to mean the same as equate, treati ...
with Rhea led to Cybele's association with various male demigods who served Rhea as attendants, or as guardians of her son, the infant Zeus, as he lay in the cave of his birth. In cult terms, they seem to have functioned as intercessors or intermediaries between goddess and mortal devotees, through dreams, waking trance, or ecstatic dance and song. They include the armed Curetes, who danced around Zeus and clashed their shields to amuse him; their supposedly Phrygian equivalents, the youthful Corybantes
According to Greek mythology, the Korybantes or Corybantes (also Corybants) (; grc-gre, Κορύβαντες) were the armed and crested dancers who worshipped the Phrygian goddess Cybele with drumming and dancing. They are also called the ''Ku ...
, who provided similarly wild and martial music, dance and song; and the dactyls and Telchines, magicians associated with metalworking.
Cybele and Attis
 Cybele's major mythographic narratives attach to her relationship with Attis, who is described by ancient Greek and Roman sources and cults as her youthful consort, and as a Phrygian deity. In Phrygia, "Attis" was not a deity, but both a commonplace and priestly name, found alike in casual graffiti, the dedications of personal monuments, as well as at several of Cybele's Phrygian shrines and monuments. His divinity may therefore have begun as a Greek invention based on what was known of Cybele's Phrygian cult. His earliest certain image as deity appears on a 4th-century BC Greek
Cybele's major mythographic narratives attach to her relationship with Attis, who is described by ancient Greek and Roman sources and cults as her youthful consort, and as a Phrygian deity. In Phrygia, "Attis" was not a deity, but both a commonplace and priestly name, found alike in casual graffiti, the dedications of personal monuments, as well as at several of Cybele's Phrygian shrines and monuments. His divinity may therefore have begun as a Greek invention based on what was known of Cybele's Phrygian cult. His earliest certain image as deity appears on a 4th-century BC Greek stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
from Piraeus, near Athens. It shows him as the Hellenised stereotype of a rustic, eastern barbarian; he sits at ease, sporting the Phrygian cap and shepherd's crook of his later Greek and Roman cults. Before him stands a Phrygian goddess (identified by the inscription as Agdistis
Agdistis ( grc, Ἄγδιστις) is a deity of Greek, Roman, and Anatolian mythology who possesses both male and female sexual organs. They were closely associated with the Phrygian goddess Cybele.
Their androgyny was seen as a symbol of ...
) who carries a tympanon in her left hand. With her right, she hands him a jug, as if to welcome him into her cult with a share of her own libation. Later images of Attis show him as a shepherd, in similar relaxed attitudes, holding or playing the syrinx
In classical Greek mythology, Syrinx (Greek Σύριγξ) was a nymph and a follower of Artemis, known for her chastity. Pursued by the amorous god Pan, she ran to a river's edge and asked for assistance from the river nymphs. In answer, sh ...
(panpipes). In Demosthenes' '' On the Crown'' (330 BC), ''attes'' is "a ritual cry shouted by followers of mystic rites".
Attis seems to have accompanied the diffusion of Cybele's cult through Magna Graecia; there is evidence of their joint cult at the Greek colonies of Marseilles
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Franc ...
(Gaul) and Lokroi (southern Italy) from the 6th and 7th centuries BC. After Alexander the Great's conquests, "wandering devotees of the goddess became an increasingly common presence in Greek literature and social life; depictions of Attis have been found at numerous Greek sites". When shown with Cybele, he is always the younger, lesser deity, or perhaps her priestly attendant. In the mid 2nd century, letters from the king of Pergamum to Cybele's shrine at Pessinos consistently address its chief priest as "Attis".
Roman Cybele
Republican era
 Romans knew Cybele as ''Magna Mater'' ("Great Mother"), or as ''Magna Mater deorum Idaea'' ("great Idaean mother of the gods"), equivalent to the Greek title ''Meter Theon Idaia'' ("Mother of the Gods, from Mount Ida"). Rome officially adopted her cult during the
Romans knew Cybele as ''Magna Mater'' ("Great Mother"), or as ''Magna Mater deorum Idaea'' ("great Idaean mother of the gods"), equivalent to the Greek title ''Meter Theon Idaia'' ("Mother of the Gods, from Mount Ida"). Rome officially adopted her cult during the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
(218 to 201 BC), after dire prodigies, including a meteor shower, a failed harvest, and famine, seemed to warn of Rome's imminent defeat. The Roman Senate and its religious advisers consulted the Sibylline oracle and decided that Carthage might be defeated if Rome imported the ''Magna Mater'' ("Great Mother") of Phrygian Pessinos. As this cult object belonged to a Roman ally, the Kingdom of Pergamum, the Roman Senate sent ambassadors to seek the king's consent; en route, a consultation with the Greek oracle at Delphi confirmed that the goddess should be brought to Rome. The goddess arrived in Rome in the form of Pessinos' black meteoric stone. Roman legend connects this voyage, or its end, to the matron Claudia Quinta, who was accused of unchastity but proved her innocence with a miraculous feat on behalf of the goddess. Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica Scipio Nasica was the name of several members of the Scipiones, a branch of the patrician Roman gens Cornelia. Metellus Scipio was born into this family, but was later adopted out to the gens Caecilia. He still retained his former name by combini ...
, supposedly the "best man" in Rome, was chosen to meet the goddess at Ostia
Ostia may refer to:
Places
*Ostia (Rome), a municipio (also called ''Ostia Lido'' or ''Lido di Ostia'') of Rome
*Ostia Antica, a township and port of ancient Rome
*Ostia Antica (district), a district of the commune of Rome
Arts and entertainment ...
; and Rome's most virtuous matrons (including Claudia Quinta) conducted her to the temple of Victoria, to await the completion of her temple on the Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; la, Collis Palatium or Mons Palatinus; it, Palatino ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." ...
. Pessinos' stone was later used as the face of the statue of the goddess. In due course, the famine ended and Hannibal was defeated.
 Most modern scholarship agrees that Cybele's consort, Attis, and her eunuch Phrygian priests (
Most modern scholarship agrees that Cybele's consort, Attis, and her eunuch Phrygian priests (Galli
A ''gallus'' (pl. ''galli'') was a eunuch priest of the Phrygian goddess Cybele (Magna Mater in Rome) and her consort Attis, whose worship was incorporated into the state religious practices of ancient Rome.
Origins
Cybele's cult may have orig ...
) would have arrived with the goddess, along with at least some of the wild, ecstatic features of her Greek and Phrygian cults. The histories of her arrival deal with the piety, purity, and status of the Romans involved, the success of their religious stratagem, and power of the goddess herself; she has no consort or priesthood, and seems fully Romanised from the first. Some modern scholars assume that Attis must have followed much later; or that the Galli, described in later sources as shockingly effeminate and flamboyantly "un-Roman", must have been an unexpected consequence of bringing the goddess in blind obedience to the Sibyl; a case of "biting off more than one can chew". Others note that Rome was well versed in the adoption (or sometimes, the "calling forth", or seizure) of foreign deities, and the diplomats who negotiated Cybele's move to Rome would have been well-educated, and well-informed.
Romans believed that Cybele, considered a Phrygian outsider even within her Greek cults, was the mother-goddess of ancient Troy (Ilium). Some of Rome's leading patrician families claimed Trojan ancestry; so the "return" of the Mother of all Gods to her once-exiled people would have been particularly welcome, even if her spouse and priesthood were not; its accomplishment would have reflected well on the principals involved and, in turn, on their descendants. The upper classes who sponsored the Magna Mater's festivals delegated their organisation to the plebeian aediles, and honoured her and each other with lavish, private festival banquets from which her Galli would have been conspicuously absent. Whereas in most of her Greek cults she dwelt outside the ''polis'', in Rome she was the city's protector, contained within her Palatine precinct, along with her priesthood, at the geographical heart of Rome's most ancient religious traditions. She was promoted as patrician property; a Roman matron – albeit a strange one, "with a stone for a face" – who acted for the clear benefit of the Roman state.

Imperial era
Augustan ideology identified Magna Mater with Imperial order and Rome's religious authority throughout the empire. Augustus claimed a Trojan ancestry through his adoption byJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
and the divine favour of Venus; in the iconography of Imperial cult, the empress Livia
Livia Drusilla (30 January 59 BC – 28 September AD 29) was a Roman empress from 27 BC to AD 14 as the wife of Roman emperor, Emperor Augustus Caesar. She was known as Julia Augusta after her formal Adoption in ancient Rome, adoption into the J ...
was Magna Mater's earthly equivalent, Rome's protector and symbolic "Great Mother"; the goddess is portrayed with Livia's face on cameos and statuary. By this time, Rome had absorbed the goddess's Greek and Phrygian homelands, and the Roman version of Cybele as Imperial Rome's protector was introduced there.
Imperial Magna Mater protected the empire's cities and agriculture — Ovid "stresses the barrenness of the earth before the Mother's arrival. Virgil's '' Aeneid'' (written between 29 and 19 BC) embellishes her "Trojan" features; she is ''Berecyntian Cybele'', mother of Jupiter himself, and protector of the Trojan prince Aeneas in his flight from the destruction of Troy. She gives the Trojans her sacred tree for shipbuilding, and begs Jupiter to make the ships indestructible. These ships become the means of escape for Aeneas and his men, guided toward Italy and a destiny as ancestors of the Roman people by Venus Genetrix Venus Genetrix may refer to:
* Venus Genetrix, epithet of the goddess Venus
* Venus Genetrix (sculpture), the name for a type of sculptural depiction of the goddess
* Temple of Venus Genetrix, a ruined temple in the Forum of Caesar, Rome
See a ...
. Once arrived in Italy, these ships have served their purpose and are transformed into sea nymphs.
Stories of Magna Mater's arrival were used to promote the fame of its principals, and thus their descendants. Claudia Quinta's role as Rome's ''castissima femina'' (purest or most virtuous woman) became "increasingly glorified and fantastic"; she was shown in the costume of a Vestal Virgin, and Augustan ideology represented her as the ideal of virtuous Roman womanhood. The emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
claimed her among his ancestors. Claudius promoted Attis to the Roman pantheon and placed his cult under the supervision of the quindecimviri (one of Rome's priestly colleges).
Festivals and cults
Megalesia in April
 The ''Megalesia'' festival to Magna Mater commenced on April 4, the anniversary of her arrival in Rome. The festival structure is unclear, but it included ludi scaenici (plays and other entertainments based on religious themes), probably performed on the deeply stepped approach to her temple; some of the plays were commissioned from well-known playwrights. On April 10, her image was taken in public procession to the Circus Maximus, and chariot races were held there in her honour; a statue of Magna Mater was permanently sited on the racetrack's dividing barrier, showing the goddess seated on a lion's back.
Roman bystanders seem to have perceived Megalesia as either characteristically " Greek"; or Phrygian. At the cusp of Rome's transition to Empire, the Greek
The ''Megalesia'' festival to Magna Mater commenced on April 4, the anniversary of her arrival in Rome. The festival structure is unclear, but it included ludi scaenici (plays and other entertainments based on religious themes), probably performed on the deeply stepped approach to her temple; some of the plays were commissioned from well-known playwrights. On April 10, her image was taken in public procession to the Circus Maximus, and chariot races were held there in her honour; a statue of Magna Mater was permanently sited on the racetrack's dividing barrier, showing the goddess seated on a lion's back.
Roman bystanders seem to have perceived Megalesia as either characteristically " Greek"; or Phrygian. At the cusp of Rome's transition to Empire, the Greek Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary sty ...
describes this procession as wild Phrygian "mummery" and "fabulous clap-trap", in contrast to the Megalesian sacrifices and games, carried out in what he admires as a dignified "traditional Roman" manner; Dionysius also applauds the wisdom of Roman religious law, which forbids the participation of any Roman citizen in the procession, and in the goddess's mysteries; Slaves are forbidden to witness any of this. In the late republican era, Lucretius vividly describes the procession's armed "war dancers" in their three-plumed helmets, clashing their shields together, bronze on bronze, "delighted by blood"; yellow-robed, long-haired, perfumed Galli waving their knives, wild music of thrumming tympanons and shrill flutes. Along the route, rose petals are scattered, and clouds of incense arise. The goddess's sculpted image wears the Mural Crown and is seated within a sculpted, lion-drawn chariot, carried high on a bier. The Roman display of Cybele's Megalesia procession as an exotic, privileged public pageant offers signal contrast to what is known of the private, socially inclusive Phrygian-Greek mysteries on which it was based.
'Holy week' in March
The Principate brought the development of an extended festival or "holy week" for Cybele and Attis in March (Latin ''Martius
Martius may refer to:
* Martius (month) the month of March on the ancient Roman calendar
* Campus Martius, the "Field of Mars" in ancient Rome
* Telo Martius, an ancient name for Toulon, France
People
* Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius (1794–1 ...
)'', from the Ides to nearly the end of the month. Citizens and freedmen were allowed limited forms of participation in rites pertaining to Attis, through their membership of two colleges
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offerin ...
, each dedicated to a specific task; the ''Cannophores'' ("reed bearers") and the ''Dendrophores'' ("tree bearers").
* March 15 (Ides): ''Canna intrat'' ("The Reed enters"), marking the birth of Attis and his exposure in the reeds along the Phrygian river Sangarius
The Sakarya (Sakara River, tr, Sakarya Irmağı; gr, Σαγγάριος, translit=Sangarios; Latin: ''Sangarius'') is the third longest river in Turkey. It runs through the region known in ancient times as Phrygia. It was considered one of t ...
, where he was discovered—depending on the version—by either shepherds or Cybele herself. The reed was gathered and carried by the ''cannophores''.
* March 22: ''Arbor intrat'' ("The Tree enters"), commemorating the death of Attis under a pine tree. The ''dendrophores'' ("tree bearers") cut down a tree, suspended from it an image of Attis, and carried it to the temple with lamentations. The day was formalized as part of the official Roman calendar under Claudius. A three-day period of mourning followed.
* March 23: on the Tubilustrium
In Ancient Rome the month of March was the traditional start of the campaign season, and the Tubilustrium was a ceremony to make the army fit for war. The ceremony involved sacred trumpets called ''tubae''.
Johannes Quasten, however, argues t ...
, an archaic holiday to Mars, the tree was laid to rest at the temple of the Magna Mater, with the traditional beating of the shields by Mars' priests the Salii and the lustration of the trumpets perhaps assimilated to the noisy music of the Corybantes.
* March 24: ''Sanguem'' or ''Dies Sanguinis'' ("Day of Blood"), a frenzy of mourning when the devotees whipped themselves to sprinkle the altars and effigy of Attis with their own blood; some performed the self-castrations of the Galli. The "sacred night" followed, with Attis placed in his ritual tomb.
* March 25 (vernal equinox Spring equinox or vernal equinox or variations may refer to:
* March equinox, the spring equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* September equinox, the spring equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Nowruz, Persian/Iranian new year which be ...
on the Roman calendar): '' Hilaria'' ("Rejoicing"), when Attis was reborn. Some early Christian sources associate this day with the resurrection of Jesus. Damascius attributed a "liberation from Hades" to the Hilaria.
* March 26: ''Requietio'' ("Day of Rest").
* March 27: ''Lavatio'' ("Washing"), noted by Ovid and probably an innovation under Augustus, Literary references indicate that the ''lavatio'' was "well established" by the Flavian period
The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known as ...
; when Cybele's sacred stone was taken in procession from the Palatine temple to the Porta Capena and down the Appian Way to the stream called Almo Almo may refer to:
* Almo (god), a river deity from Roman mythology
* Almo, the ancient name for the River Almone near Rome (whence the name of the above deity)
*Almo, Idaho, a town in the United States
*Almo, Kentucky, a town in the United States
...
, a tributary of the Tiber. There the stone and sacred iron implements were bathed "in the Phrygian manner" by a red-robed priest. The ''quindecimviri'' attended. The return trip was made by torchlight, with much rejoicing. The ceremony alluded to, but did not reenact, Cybele's original reception in the city, and seems not to have involved Attis.
* March 28: ''Initium Caiani'', sometimes interpreted as initiations into the mysteries of the Magna Mater and Attis at the Gaianum The Gaianum was an area in the Transtiberim in ancient Rome. It is located in Regio XIV, about 300m northwest of the Mausoleum of Hadrian, south of the Naumachia Vaticana built by Trajan, and east of the Via Triumphalis. The historian Cassius Dio ...
, near the Phrygianum sanctuary at the Vatican Hill
Vatican Hill (; la, Mons Vaticanus; it, Colle Vaticano) is a hill located across the Tiber river from the traditional seven hills of Rome, that also gave the name of Vatican City. It is the location of St. Peter's Basilica.
Etymology
The anc ...
.
Scholars are divided as to whether the entire series was more or less put into place under Claudius, or whether the festival grew over time. The Phrygian character of the cult would have appealed to the Julio-Claudians as an expression of their claim to Trojan ancestry. It may be that Claudius established observances mourning the death of Attis, before he had acquired his full significance as a resurrected god of rebirth, expressed by rejoicing at the later ''Canna intrat'' and by the Hilaria. The full sequence at any rate is thought to have been official in the time of Antoninus Pius (reigned 138–161), but among extant '' fasti'' appears only in the Calendar of Philocalus
The ''Chronograph of 354'' (or "Chronography"), also known as the ''Calendar of 354'', is a compilation of chronological and calendrical texts produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus by the calligrapher and illustrator ...
(354 AD).
Minor cults
Significant anniversaries, stations, and participants in the 204 arrival of the goddess – including her ship, which would have been thought a sacred object – may have been marked from the beginning by minor, local, or private rites and festivals at Ostia, Rome, and Victoria's temple. Cults to Claudia Quinta are likely, particularly in the Imperial era. Rome seems to have introduced evergreen cones (pine or fir) to Cybele's iconography, based at least partly on Rome's "Trojan ancestor" myth, in which the goddess gave Aeneas her sacred tree for shipbuilding. The evergreen cones probably symbolised Attis' death and rebirth. Despite the archaeological evidence of early cult to Attis at Cybele's Palatine precinct, no surviving Roman literary or epigraphic source mentions him until Catullus, whose poem 63 places him squarely within Magna Mater's mythology, as the hapless leader and prototype of her Galli.Taurobolium and Criobolium
 Rome's strictures against castration and citizen participation in Magna Mater's cult limited both the number and kind of her initiates. From the 160s AD, citizens who sought initiation to her mysteries could offer either of two forms of bloody animal sacrifice – and sometimes both – as lawful substitutes for self-castration. The
Rome's strictures against castration and citizen participation in Magna Mater's cult limited both the number and kind of her initiates. From the 160s AD, citizens who sought initiation to her mysteries could offer either of two forms of bloody animal sacrifice – and sometimes both – as lawful substitutes for self-castration. The Taurobolium
In the Roman Empire of the second to fourth centuries, ''taurobolium'' referred to practices involving the sacrifice of a bull, which after mid-second century became connected with the worship of the Great Mother of the Gods; though not previo ...
sacrificed a bull, the most potent and costly victim in Roman religion; the Criobolium Criobolium is the ritual sacrifice of a ram in the cult of Attis
Attis (; grc-gre, Ἄττις, also , , ) was the consort of Cybele, in Phrygian and Greek mythology.
His priests were eunuchs, the ''Galli'', as explained by origin myths per ...
used a lesser victim, usually a ram.
A late, melodramatic and antagonistic account by the Christian apologist Prudentius has a priest stand in a pit beneath a slatted wooden floor; his assistants or junior priests dispatch a bull, using a sacred spear. The priest emerges from the pit, drenched with the bull's blood, to the applause of the gathered spectators. This description of a Taurobolium as blood-bath is, if accurate, an exception to usual Roman sacrificial practice; it may have been no more than a bull sacrifice in which the blood was carefully collected and offered to the deity, along with its organs of generation, the testicles.
The Taurobolium and Criobolium are not tied to any particular date or festival, but probably draw on the same theological principles as the life, death, and rebirth cycle of the March "holy week". The celebrant personally and symbolically took the place of Attis, and like him was cleansed, renewed or, in emerging from the pit or tomb, "reborn". These regenerative effects were thought to fade over time, but they could be renewed by further sacrifice. Some dedications transfer the regenerative power of the sacrifice to non-participants, including emperors, the Imperial family and the Roman state; some mark a ''dies natalis'' (birthday or anniversary) for the participant or recipient. Dedicants and participants could be male or female.
The sheer expense of the Taurobolium ensured that its initiates were from Rome's highest class, and even the lesser offering of a Criobolium would have been beyond the means of the poor. Among the Roman masses, there is evidence of private devotion to Attis, but virtually none for initiations to Magna Mater's cult.
In the religious revivalism of the later Imperial era, Magna Mater's notable initiates included the deeply religious, wealthy, and erudite praetorian prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders be ...
Praetextatus; the quindecimvir Volusianus
Gaius Vibius Volusianus (died August 253) was a Roman emperor from 251 to 253, ruling with his father Trebonianus Gallus.
After Emperor Decius and his son and co-ruler Herennius Etruscus died in battle in June 251, Trebonianus Gallus was el ...
, who was twice consul; and possibly the Emperor Julian. Taurobolium dedications to Magna Mater tend to be more common in the Empire's western provinces than elsewhere, attested by inscriptions in (among others) Rome and Ostia
Ostia may refer to:
Places
*Ostia (Rome), a municipio (also called ''Ostia Lido'' or ''Lido di Ostia'') of Rome
*Ostia Antica, a township and port of ancient Rome
*Ostia Antica (district), a district of the commune of Rome
Arts and entertainment ...
in Italy, Lugdunum in Gaul, and Carthage in Africa.
Priesthoods
"Attis" may have been a name or title of Cybele's priests or priest-kings in ancient Phrygia. Most myths of the deified Attis present him as founder of Cybele's Galli priesthood but in Servius' account, written during the Roman Imperial era, Attis castrates a king to escape his unwanted sexual attentions, and is castrated in turn by the dying king. Cybele's priests find Attis at the base of a pine tree; he dies and they bury him, emasculate themselves in his memory, and celebrate him in their rites to the goddess. This account might attempt to explain the nature, origin, and structure of Pessinus' theocracy. A Hellenistic poet refers to Cybele's priests in the feminine, as ''Gallai''. The Roman poet Catullus refers to Attis in the masculine until his emasculation, and in the feminine thereafter. Various Roman sources refer to the Galli as a middle or third gender (''medium genus'' or ''tertium sexus''). The Galli's voluntary emasculation in service of the goddess was thought to give them powers of prophecy. Pessinus, site of the temple whence the Magna Mater was brought to Rome, was a theocracy whose leading Galli may have been appointed via some form of adoption, to ensure "dynastic" succession. The highest ranking Gallus was known as "Attis", and his junior as "Battakes". The Galli of Pessinus were politically influential; in 189 BC, they predicted or prayed for Roman victory in Rome's imminent war against the Galatians. The following year, perhaps in response to this gesture of goodwill, the Roman senate formally recognised Illium as the ancestral home of the Roman people, granting it extra territory and tax immunity. In 103, a Battakes traveled to Rome and addressed its senate, either for the redress of impieties committed at his shrine, or to predict yet another Roman military success. He would have cut a remarkable figure, with "colourful attire and headdress, like a crown, with regal associations unwelcome to the Romans". Yet the senate supported him; and when a plebeian tribune who had violently opposed his right to address the senate died of a fever (or, in the alternative scenario, when the prophesied Roman victory came) Magna Mater's power seemed proven.
In Rome, the Galli and their cult fell under the supreme authority of the pontifices, who were usually drawn from Rome's highest ranking, wealthiest citizens. The Galli themselves, although imported to serve the day-to-day workings of their goddess's cult on Rome's behalf, represented an inversion of Roman priestly traditions in which senior priests were citizens, expected to raise families, and personally responsible for the running costs of their temples, assistants, cults, and festivals. As eunuchs, incapable of reproduction, the Galli were forbidden Roman citizenship and rights of inheritance; like their eastern counterparts, they were technically mendicants whose living depended on the pious generosity of others. For a few days of the year, during the Megalesia, Cybele's laws allowed them to leave their quarters, located within the goddess' temple complex, and roam the streets to beg for money. They were outsiders, marked out as Galli by their regalia, and their notoriously effeminate dress and demeanour, but as priests of a state cult, they were sacred and inviolate. From the start, they were objects of Roman fascination, scorn, and religious awe. No Roman, not even a slave, could castrate himself "in honour of the Goddess" without penalty; in 101 BC, a slave who had done so was exiled. Augustus selected priests from among his own freedmen to supervise Magna Mater's cult, and brought it under Imperial control.
Pessinus, site of the temple whence the Magna Mater was brought to Rome, was a theocracy whose leading Galli may have been appointed via some form of adoption, to ensure "dynastic" succession. The highest ranking Gallus was known as "Attis", and his junior as "Battakes". The Galli of Pessinus were politically influential; in 189 BC, they predicted or prayed for Roman victory in Rome's imminent war against the Galatians. The following year, perhaps in response to this gesture of goodwill, the Roman senate formally recognised Illium as the ancestral home of the Roman people, granting it extra territory and tax immunity. In 103, a Battakes traveled to Rome and addressed its senate, either for the redress of impieties committed at his shrine, or to predict yet another Roman military success. He would have cut a remarkable figure, with "colourful attire and headdress, like a crown, with regal associations unwelcome to the Romans". Yet the senate supported him; and when a plebeian tribune who had violently opposed his right to address the senate died of a fever (or, in the alternative scenario, when the prophesied Roman victory came) Magna Mater's power seemed proven.
In Rome, the Galli and their cult fell under the supreme authority of the pontifices, who were usually drawn from Rome's highest ranking, wealthiest citizens. The Galli themselves, although imported to serve the day-to-day workings of their goddess's cult on Rome's behalf, represented an inversion of Roman priestly traditions in which senior priests were citizens, expected to raise families, and personally responsible for the running costs of their temples, assistants, cults, and festivals. As eunuchs, incapable of reproduction, the Galli were forbidden Roman citizenship and rights of inheritance; like their eastern counterparts, they were technically mendicants whose living depended on the pious generosity of others. For a few days of the year, during the Megalesia, Cybele's laws allowed them to leave their quarters, located within the goddess' temple complex, and roam the streets to beg for money. They were outsiders, marked out as Galli by their regalia, and their notoriously effeminate dress and demeanour, but as priests of a state cult, they were sacred and inviolate. From the start, they were objects of Roman fascination, scorn, and religious awe. No Roman, not even a slave, could castrate himself "in honour of the Goddess" without penalty; in 101 BC, a slave who had done so was exiled. Augustus selected priests from among his own freedmen to supervise Magna Mater's cult, and brought it under Imperial control. Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
introduced the senior priestly office of Archigallus
A ''gallus'' (pl. ''galli'') was a eunuch priest of the Phrygian goddess Cybele (Magna Mater in Rome) and her consort Attis, whose worship was incorporated into the state religious practices of ancient Rome.
Origins
Cybele's cult may have ori ...
, who was not a eunuch and held full Roman citizenship.
The religiously lawful circumstances for a Gallus's self-castration remain unclear; some may have performed the operation on the Dies Sanguinis ("Day of Blood") in Cybele and Attis' March festival. Pliny describes the procedure as relatively safe, but it is not known at what stage in their career the Galli performed it, or exactly what was removed, or even whether all Galli performed it. Some Galli devoted themselves to their goddess for most of their lives, maintained relationships with relatives and partners throughout, and eventually retired from service. Galli remained a presence in Roman cities well into the Empire's Christian era. Some decades after Christianity became the sole Imperial religion, St. Augustine saw Galli "parading through the squares and streets of Carthage, with oiled hair and powdered faces, languid limbs and feminine gait, demanding even from the tradespeople the means of continuing to live in disgrace".
Temples
Greece
The earliest known temple for Cybele in the Greek world is theDaskalopetra monument
The Daskalopetra monument is a rock-cut shrine to the goddess Cybele at Daskalopetra, near Vrontados on Chios, in Greece, dating to the late sixth or early fifth century BC. It is probably the earliest known cult site of the Cybele in the Greek w ...
on Chios, which dates to the sixth or early fifth centuries BC. In Greek, a temple to Cybele was often called a '' Metroon''. Several Metroa were established in Greek cities from the fifth century BC onward. The Metroon at Athens was established in the early fifth century BC on the west side of the Athenian Agora
The ancient Agora of Athens (also called the Classical Agora) is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, located to the northwest of the Acropolis and bounded on the south by the hill of the Areopagus and on the west by the hill ...
, next to the Boule (town council). It was a rectangular building with three rooms and an altar in front. It was destroyed during the Persian sack of Athens
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of th ...
in 480 BC, but repaired around 460 BC. The cult was deeply integrated into civic life; the Metroon was used as the state archive and Cybele was one of the four main deities, to whom serving councillors sacrificed, along with Zeus, Athena, and Apollo. The highly influential fifth-century BC statue of Cybele enthroned by Agoracritus was located in this building. The building was rebuilt around 150 BC, with separate rooms for cult worship and archival storage, and it remained in use until Late Antiquity. A second Metroon in the Athenian suburb of Agrae was associated with the Eleusinian Mysteries. At the end of the fifth century BC, a Metroon was established at Olympia
The name Olympia may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Olympia'' (1938 film), by Leni Riefenstahl, documenting the Berlin-hosted Olympic Games
* ''Olympia'' (1998 film), about a Mexican soap opera star who pursues a career as an athlet ...
. It is a small hexastyle temple, the third to be built on the site after the archaic Heraion and the mid-fifth century Temple of Zeus
Temple of Zeus may refer to:
Greece
* Temple of Zeus, Olympia
* Temple of Olympian Zeus, Athens
* Sanctuary of Zeus Polieus, Athens
Italy
* Temple of Olympian Zeus, Agrigento
* Temple G, Selinunte
Selinunte (; grc, Σελῑνοῦς, Sel� ...
. In the Roman period it was used for the Imperial cult. In the fourth century, further Metroa are attested at Smyrna and Colophon, where they also served as state archives, as in Athens.
Rome and its provinces
Magna Mater's temple stood high on the slope of the Palatine, overlooking the valley of the Circus Maximus and facing the temple ofCeres
Ceres most commonly refers to:
* Ceres (dwarf planet), the largest asteroid
* Ceres (mythology), the Roman goddess of agriculture
Ceres may also refer to:
Places
Brazil
* Ceres, Goiás, Brazil
* Ceres Microregion, in north-central Goiás st ...
on the slopes of the Aventine. It was accessible via a long upward flight of steps from a flattened area or proscenium below, where the goddess's festival games and plays were staged. At the top of the steps was a statue of the enthroned goddess, wearing a mural crown and attended by lions. Her altar stood at the base of the steps, at the proscenium's edge. The first temple was damaged by fire in 111 BC, and was repaired or rebuilt. It burnt down in the early Imperial era, and was restored by Augustus; it burned down again soon after, and Augustus rebuilt it in more sumptuous style; the Ara Pietatis
ARA may refer to:
Media and the arts
* American-Romanian Academy of Arts and Sciences
* '' Artistička Radna Akcija'', compilation album released in former Yugoslavia
* Associate of the Royal Academy, denoting membership in the British Royal Acad ...
relief shows its pediment. The goddess is represented by her empty throne and crown, flanked by two figures of Attis reclining on tympanon
The hammered dulcimer (also called the hammer dulcimer) is a percussion-stringed instrument which consists of strings typically stretched over a trapezoidal resonant sound board. The hammered dulcimer is set before the musician, who in more trad ...
s; and by two lions who eat from bowls, as if tamed by her unseen presence. The scene probably represents a ''sellisternium The sellisternium or ''solisternium'' was a ritual banquet for goddesses in the Ancient Roman religion. It was based on a variant of the Greek ''theoxenias'', and was considered an appropriately "greek" form of rite for some Roman goddesses tho ...
'', a form of banquet usually reserved for goddesses, in accordance with "Greek rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
The canonical hours are ...
" as practiced in Rome. This feast was probably held within the building, with attendance reserved for the aristocratic sponsors of the goddesses rites; the flesh of her sacrificial animal provided their meat.
From at least 139 AD, Rome's port at Ostia
Ostia may refer to:
Places
*Ostia (Rome), a municipio (also called ''Ostia Lido'' or ''Lido di Ostia'') of Rome
*Ostia Antica, a township and port of ancient Rome
*Ostia Antica (district), a district of the commune of Rome
Arts and entertainment ...
, the site of the goddess's arrival, had a fully developed sanctuary to Magna Mater and Attis, served by a local Archigallus and college of ''dendrophores'' (the ritual tree-bearers of "Holy Week").
Ground preparations for the building of St. Peter's basilica on the Vatican Hill uncovered a shrine, known as the Phrygianum, with some 24 dedications to Magna Mater and Attis. Many are now lost, but most that survive were dedicated by high-status Romans after a taurobolium sacrifice to Magna Mater. None of these dedicants were priests of the Magna Mater or Attis, and several held priesthoods of one or more different cults.
Near Setif (Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, ...
), the ''dendrophores'' and the faithful (''religiosi'') restored their temple of Cybele and Attis after a disastrous fire in 288 AD. Lavish new fittings paid for by the private group included the silver statue of Cybele and her processional chariot; the latter received a new canopy with tassels in the form of fir
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family (biology), family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North America, North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The ...
cones. Cybele drew ire from Christians throughout the Empire; when St. Theodore of Amasea was granted time to recant his beliefs, he spent it by burning a temple of Cybele instead.
Myths, theology, and cosmology
 Rome characterised the Phrygians as barbaric, effeminate orientals, prone to excess. While some Roman sources explained Attis' death as punishment for his excess devotion to Magna Mater, others saw it as punishment for his lack of devotion, or outright disloyalty. Only one account of Attis and Cybele (related by Pausanias) omits any suggestion of a personal or sexual relationship between them; Attis achieves divinity through his support of ''Meters cult, is killed by a boar sent by Zeus, who is envious of the cult's success, and is rewarded for his commitment with godhood.
The most complex, vividly detailed, and lurid accounts of Magna Mater and Attis were produced as anti-pagan polemic in the late 4th century by the Christian apologist Arnobius, who presented their cults as a repulsive combination of blood-bath, incest, and sexual orgy, derived from the myths of Agdistis. This has been presumed the most ancient, violent, and authentically Phrygian version of myth and cult, closely following an otherwise lost orthodox, approved version preserved by the priest-kings at Pessinous and imported to Rome. Arnobius claimed several scholarly sources as his authority; but the oldest versions are also the most fragmentary and, during an interval of several centuries, apt to diverge into whatever version suited a new audience, or potentially, new acolytes. Greek versions of the myth recall those concerning the mortal Adonis and his divine lovers, - Aphrodite, who had some claim to cult as a 'Mother of all", or her rival for Adonis' love, Persephone - showing the grief and anger of a powerful goddess, mourning the helpless loss of her mortal beloved.
The emotionally charged literary version presented in
Rome characterised the Phrygians as barbaric, effeminate orientals, prone to excess. While some Roman sources explained Attis' death as punishment for his excess devotion to Magna Mater, others saw it as punishment for his lack of devotion, or outright disloyalty. Only one account of Attis and Cybele (related by Pausanias) omits any suggestion of a personal or sexual relationship between them; Attis achieves divinity through his support of ''Meters cult, is killed by a boar sent by Zeus, who is envious of the cult's success, and is rewarded for his commitment with godhood.
The most complex, vividly detailed, and lurid accounts of Magna Mater and Attis were produced as anti-pagan polemic in the late 4th century by the Christian apologist Arnobius, who presented their cults as a repulsive combination of blood-bath, incest, and sexual orgy, derived from the myths of Agdistis. This has been presumed the most ancient, violent, and authentically Phrygian version of myth and cult, closely following an otherwise lost orthodox, approved version preserved by the priest-kings at Pessinous and imported to Rome. Arnobius claimed several scholarly sources as his authority; but the oldest versions are also the most fragmentary and, during an interval of several centuries, apt to diverge into whatever version suited a new audience, or potentially, new acolytes. Greek versions of the myth recall those concerning the mortal Adonis and his divine lovers, - Aphrodite, who had some claim to cult as a 'Mother of all", or her rival for Adonis' love, Persephone - showing the grief and anger of a powerful goddess, mourning the helpless loss of her mortal beloved.
The emotionally charged literary version presented in Catullus 63
The poetry of Gaius Valerius Catullus was written towards the end of the Roman Republic. It describes the lifestyle of the poet and his friends, as well as, most famously, his love for the woman he calls Lesbia.
Sources and organization
Catull ...
follows Attis' initially ecstatic self-castration into exhausted sleep, and a waking realisation of all he has lost through his emotional slavery to a domineering and utterly self-centered goddess; it is narrated with a rising sense of isolation, oppression, and despair, virtually an inversion of the liberation promised by Cybele's Anatolian cult. Contemporaneous with this, more or less, Dionysius of Halicarnassos pursues the idea that the "Phrygian degeneracy" of the Galli, personified in Attis, be removed from the Megalensia to reveal the dignified, "truly Roman" festival rites of the Magna Mater. Somewhat later, Vergil expresses the same deep tension and ambivalence regarding Rome's claimed Phrygian, Trojan ancestors, when he describes his hero Aeneas as a perfumed, effeminate Gallus, a half-man who would, however, "rid himself of the effeminacy of the Oriental in order to fulfill his destiny as the ancestor of Rome." This would entail him and his followers shedding their Phrygian language and culture, to follow the virile example of the Latins. In Lucretius' description of the goddess and her acolytes in Rome, her priests provide an object lesson in the self-destruction wrought when passion and devotion exceed rational bounds; a warning, rather than an offer.
For Lucretius, Roman Magna Mater "symbolised the world order": her image held reverentially aloft in procession signifies the Earth, which "hangs in the air". She is the mother of all, ultimately the Mother of humankind, and the yoked lions that draw her chariot show an otherwise ferocious offspring's duty of obedience to the parent. She herself is uncreated, and thus essentially separate from and independent of her creations.
In the early Imperial era, the Roman poet Manilius
The gens Manilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are frequently confused with the Manlii, Mallii, and Mamilii. Several of the Manilii were distinguished in the service of the Republic, with Manius Manilius obtaining ...
inserts Cybele as the thirteenth deity of an otherwise symmetrical, classic Greco-Roman zodiac, in which each of twelve zodiacal houses (represented by particular constellations) is ruled by one of twelve deities, known in Greece as the Twelve Olympians and in Rome as the Di Consentes
The ''Dii Consentes'', also known as ''Di'' or ''Dei Consentes'' (once ''Dii Complices''), is an ancient list of twelve major deities, six gods and six goddesses, in the pantheon of Ancient Rome. Their gilt statues stood in the Roman Forum, an ...
. Manilius has Cybele and Jupiter as co-rulers of Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
(the Lion), in astrological opposition to Juno
Juno commonly refers to:
*Juno (mythology), the Roman goddess of marriage and queen of the gods
*Juno (film), ''Juno'' (film), 2007
Juno may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
*Juno, in the film ''Jenny, Juno''
*Ju ...
, who rules Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainment ...
. Modern scholarship remarks that as Cybele's Leo rises above the horizon, Taurus (the Bull) sets; the lion thus dominates the bull. Some of the possible Greek models for Cybele's Megalensia festival include representations of lions attacking and dominating bulls. The festival date coincided, more or less, with events of the Roman agricultural calendar (around April 12) when farmers were advised to dig their vineyards, break up the soil, sow millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
, "and – curiously apposite, given the nature of the Mother's priests – castrate cattle and other animals."Hannah, p. 872, citing Varro, ''De Re Rustica'', 1. 30; Columella, ''De Re Rustica'', 11. 2. 32 – 35; Pliny the Elder, Historia Naturalis, 18. 246 – 249.
See also
*Agdistis
Agdistis ( grc, Ἄγδιστις) is a deity of Greek, Roman, and Anatolian mythology who possesses both male and female sexual organs. They were closely associated with the Phrygian goddess Cybele.
Their androgyny was seen as a symbol of ...
* Atargatis
* Attis
* Mother goddess
A mother goddess is a goddess who represents a personified deification of motherhood, fertility goddess, fertility, creation, destruction, or the earth goddess who embodies the bounty of the earth or nature. When equated with the earth or th ...
* Rhea
* Temple of Cybele (Palatine)
The Temple of Cybele or Temple of Magna Mater was Rome's first and most important temple to the Magna Mater ("Great Mother"), who was known to the Greeks as Cybele. It was built to house a particular image or form of the goddess, a meteoric sto ...
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * * * . * * .Further reading
* D’Andria, Francesco, MAHMUT BILGE BAŞTÜRK, and JAMES HARGRAVE. "THE CULT OF CYBELE IN HIERAPOLIS OF PHRYGIA". In: ''Phrygia in Antiquity: From the Bronze Age to the Byzantine Period: Proceedings of an International Conference "The Phrygian Lands over Time: From Prehistory to the Middle of the 1st Millennium AD", Held at Anadolu University, Eskisehir, Turkey, 2nd-8th November, 2015''. Edited by GOCHA R. TSETSKHLADZE, 24. Peeters Publishers, 2019. pp. 479–500. http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctv1q26v1n.28. * Knauer, Elfried R. (2006). "The Queen Mother of the West: A Study of the Influence of Western Prototypes on the Iconography of the Taoist Deity." In: ''Contact and Exchange in the Ancient World''. Ed. Victor H. Mair. University of Hawai'i Press. Pp. 62–115. ; (An article showing the probable derivation of the Daoist goddess, Xi Wangmu, from Kybele/Cybele) * * Munn, Mark. "Kybele as Kubaba in a Lydo-Phrygian Context". In: ''Anatolian Interfaces: Hittites, Greeks and Their Neighbours''. Edited by Collins Billie Jean, Bachvarova Mary R., and Rutherford Ian C., Oxford, UK: Oxbow Books, 2008. pp. 159-64. Accessed July 11, 2020. www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt1cd0nsg.22. * Roller, Lynne E. "THE PHRYGIAN CHARACTER OF KYBELE: THE FORMATION OF AN ICONOGRAPHY AND CULT ETHOS IN THE IRON AGE". In: ''Anatolian Iron Ages 3: The Proceedings of the Third Anatolian Iron Ages Colloquium Held at Van, 6-12 August 1990''. Edited by Çilingiroğlu A. and French D.H.. London: British Institute at Ankara, 1994. pp. 189-98. Accessed July 11, 2020. www.jstor.org/stable/10.18866/j.ctt1pc5gxc.29. * * Vermaseren, Maarten Jozef. ''Cybele and Attis: The Myth and the Cult'' trans. from Dutch by A. M. H. Lemmers (Thames and Hudson, 1977) * Virgil. ''The Aeneid'' trans from Latin by West, David (Penguin Putnam Inc. 2003)External links
Britannica Online Encyclopædia
*
* ttps://iconographic.warburg.sas.ac.uk/category/vpc-taxonomy-000208 The Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (images of Cybele) {{Authority control Hellenistic Anatolian deities Phrygian goddesses Greek goddesses Roman goddesses Mountain goddesses Mother goddesses Life-death-rebirth goddesses Metamorphoses characters Lion goddesses