Cul-de-sac To Honeycomb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A dead end, also known as a cul-de-sac (, from French for 'bag-bottom'), no through road or no exit road, is a street with only one inlet or outlet.
The term "dead end" is understood in all varieties of English, but the official terminology and traffic signs include many different alternatives. Some of these are used only regionally. In the United States and other countries, ''cul-de-sac'' is often not an exact synonym for ''dead end'' and refers to dead ends with a circular end, allowing for easy turning at the end of the road. In Australia and Canada, they are usually referred to as a ''court'' when they have a bulbous end.
Dead ends are added to road layouts in urban planning to limit through-traffic in residential areas. While some dead ends provide no possible passage except in and out of their road entry, others allow cyclists,
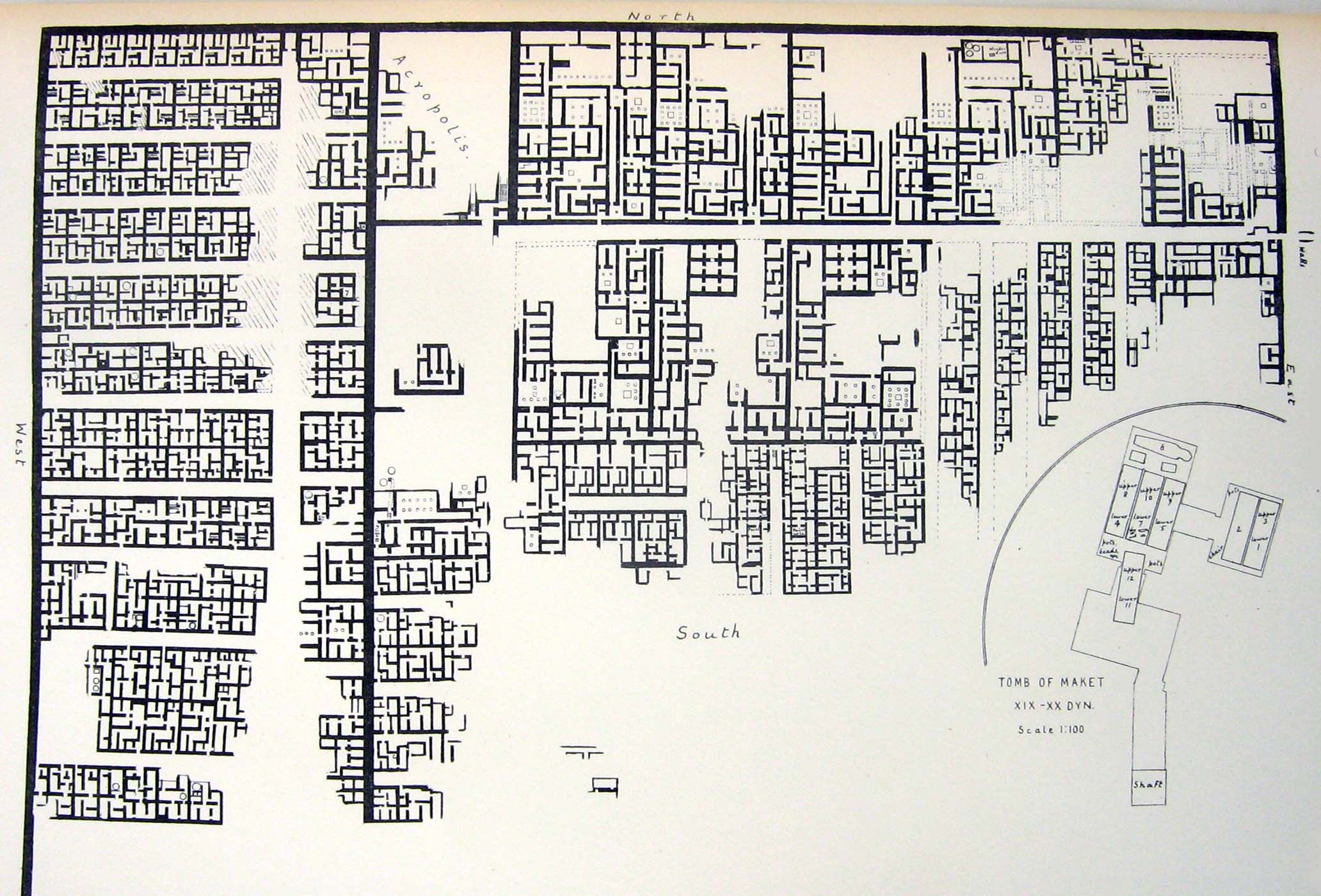 The earliest examples of dead ends were unearthed in the
The earliest examples of dead ends were unearthed in the
 Originally-unplanned dead ends have been added in city centers that are laid out on a grid by blocking through-traffic. Whole neighbourhood street reconfigurations emerged in several cities, mainly concentrated in North America and the UK, which include Berkeley, California; Seattle, Washington; and Vancouver, British Columbia. The transformation of
Originally-unplanned dead ends have been added in city centers that are laid out on a grid by blocking through-traffic. Whole neighbourhood street reconfigurations emerged in several cities, mainly concentrated in North America and the UK, which include Berkeley, California; Seattle, Washington; and Vancouver, British Columbia. The transformation of
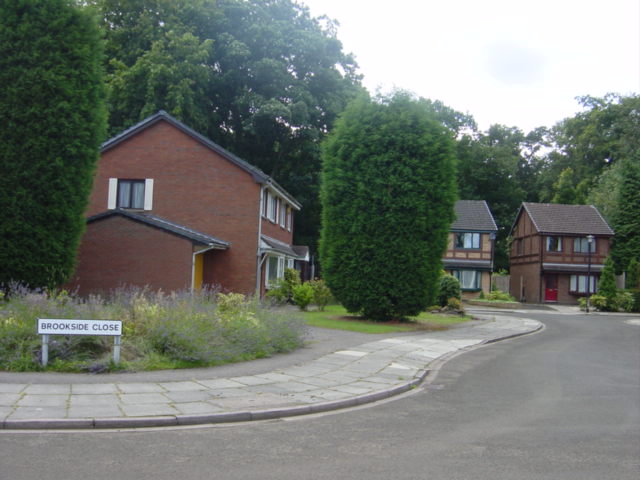 The use of culs-de-sac reduces the amount of car traffic on residential streets within the subdivision, thus reducing noise, air pollution and the probability of accidents. Ben-Joseph (1995), and Lovegrove and Sayed (2006), indicate a substantially lower collision rate for
The use of culs-de-sac reduces the amount of car traffic on residential streets within the subdivision, thus reducing noise, air pollution and the probability of accidents. Ben-Joseph (1995), and Lovegrove and Sayed (2006), indicate a substantially lower collision rate for  Similar studies in Europe and Australia found that children's outdoor play is significantly reduced on through roads where traffic is, or perceived by parents to be, a risk. In addition, they confirmed the results of the seminal Donald Appleyard 1982 study, which showed the negative correlation between amount of traffic and social networks. The inverse correlation between amounts of traffic and sociability of streets was reconfirmed by a newer study that repeated Appleyard's San Francisco analysis in Bristol, UK. It showed that the cul-de-sac street with the lowest traffic of the three streets had the highest level of social interaction.
The studies recommend the use of the cul-de-sac or strong traffic calming measures. When culs-de-sac are interconnected with foot and bike paths, as for example in Vauban, Freiburg and
Similar studies in Europe and Australia found that children's outdoor play is significantly reduced on through roads where traffic is, or perceived by parents to be, a risk. In addition, they confirmed the results of the seminal Donald Appleyard 1982 study, which showed the negative correlation between amount of traffic and social networks. The inverse correlation between amounts of traffic and sociability of streets was reconfirmed by a newer study that repeated Appleyard's San Francisco analysis in Bristol, UK. It showed that the cul-de-sac street with the lowest traffic of the three streets had the highest level of social interaction.
The studies recommend the use of the cul-de-sac or strong traffic calming measures. When culs-de-sac are interconnected with foot and bike paths, as for example in Vauban, Freiburg and



Charles: let’s kill off the cul-de-sac
' – '' The Sunday Times'', February 11, 2007 Related research in the United States by Richard Jackson has shown that people in car-based (cul-de-sac heavy) communities weigh on average more than those in traditional towns (with open grid networks). An extensive analysis of the research evidence by TRB, however, shows only an association between the built environment and physical activity levels, not causal connections. The evidence also does not identify with certainty which characteristics of the built environment are most closely associated with physical activity behaviour. The study also warns against confusing inadequate physical activity with obesity which is the outcome of an energy imbalance. Many contemporary lifestyle trends, some inevitable (sedentary work) and some avoidable (frequent energy-rich food consumption or the watching of television

 U.S. Federal Highway Administration rules state: "The ''Dead End'' sign may be used at the entrance of a single road or street that terminates in a dead end or cul-de-sac. The ''No Outlet'' sign may be used at the entrance to a road or road network from which there is no other exit." There is no federal regulation on "no exit".
The phrase "No Exit" is also preferred for Chicago signs, although "dead end" is still used there. New York City has favored "dead end" since at least the 1930s, when Sidney Kingsley used the phrase to title his Broadway play about poor, tough East Side youths with lives of little promise, in contrast to the dead-end streets of the nearby
U.S. Federal Highway Administration rules state: "The ''Dead End'' sign may be used at the entrance of a single road or street that terminates in a dead end or cul-de-sac. The ''No Outlet'' sign may be used at the entrance to a road or road network from which there is no other exit." There is no federal regulation on "no exit".
The phrase "No Exit" is also preferred for Chicago signs, although "dead end" is still used there. New York City has favored "dead end" since at least the 1930s, when Sidney Kingsley used the phrase to title his Broadway play about poor, tough East Side youths with lives of little promise, in contrast to the dead-end streets of the nearby
Image:Vienna Convention road sign G13-EA.svg, Vienna Convention sign (most countries use a variant of this sign)
Image:Philippines road sign S2-8A.svg, Australia & Philippines
Image:Hinweiszeichen 11.svg, Austria
Image:SADC road sign IN4.svg, Southern African Development Community countries ( BW, LS, MW, MZ, NA, ZA, SZ, TZ, ZM, ZW)
Image:Brasil A-45.svg, Brazil
Image:Ontario Wa-31.svg, Canada (Ontario)
Image:MUTCDC ID-31.svg, Canada (Prince Edward Island)
Image:Québec I-375-1.svg, Canada (Quebec)
Image:IE road sign F-350.svg, Ireland
Image:New Zealand road sign A40-1.svg, New Zealand
Image:UAE No Through Road.svg, United Arab Emirates
Image:Dead End sign.svg, United States
Image:MUTCD_W14-2.svg, United States
Image:NYCDOT W14-5.SVG, United States
Image:Not a through street.svg, United States
pedestrian
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In modern times, the term usually refers to someone walking on a road or pavement, but this was not the case historically.
The meaning of pedestrian is displayed with ...
s or other non-automotive traffic to pass through connecting easements or paths, an example of filtered permeability
Permeability or connectivity describes the extent to which urban forms permit (or restrict) movement of people or vehicles in different directions. The terms are often used interchangeably, although differentiated definitions also exist (see belo ...
. The International Federation of Pedestrians The International Federation of Pedestrians (IFP) is an umbrella federation for national pedestrian organisations, promoting and defending walking
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legg ...
proposed to call such streets "living end streets" and to provide signage at the entry of the streets that make this permeability for pedestrians and cyclists clear. Its application retains the dead end's primary function as a non-through road, but establishes complete pedestrian and bicycle network connectivity.
History
 The earliest examples of dead ends were unearthed in the
The earliest examples of dead ends were unearthed in the El Lahun
El Lahun ( ar, اللاهون ''El Lāhūn,'' alt. Illahun, Lahun, or Kahun (the latter being a neologism coined by archaeologist William Matthew Flinders Petrie) is a workmen's village in Faiyum, Egypt. El Lahun is associated with the Pyramid of ...
workers' village in Egypt, which was built circa 1885 BC. The village is laid out with straight streets that intersect at right angles, akin to a grid but irregular. The western part of the excavated village, where the workers lived, shows fifteen narrow and short dead-ends laid out perpendicularly on either side of a wider, straight street; all terminate at the enclosing walls.
Dead-end streets also appeared during the classical period of Athens and Rome. The 15th century architect and planner Leon Battista Alberti implies in his writings that dead-end streets may have been used intentionally in antiquity for defense purposes. He writes:
The same opinion is expressed by an earlier thinker, Aristotle, when he criticized the Hippodamian grid:
In the UK, their prior existence is implied by the Public Health Act 1875
The Public Health Act 1875c 55 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, one of the Public Health Acts, and a significant step in the advancement of public health in England.
Its purpose was to codify previous measures aimed at combatin ...
which banned their use in new developments.
Inferential evidence of their earlier use can also be drawn from the text of a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
architect, Rudolf Eberstadt, that explains their purpose and utility:
It was in the United Kingdom that the cul-de-sac street type was first legislated into use, with the Hampstead Garden Suburb Act 1906. The proponents of the Act, Raymond Unwin and Barry Parker, thus gained permission to introduce culs-de-sac in their subsequent site plans, and they promoted it as a suitable street type for Garden Suburbs. Unwin's applications of the cul-de-sac and the related crescent always included pedestrian paths independent of the road network. This design feature reflects the predominance of pedestrian movement for local trips at the turn of the 20th century, and presages the current planning priority for increased pedestrian accessibility. The 1906 Act defined the nature of the cul-de-sac as a non-through road and restricted its length to . Garden cities in the UK that followed Hampstead, such as Welwyn Garden City, all included culs-de-sac.
In the 1920s, the garden city movement became more popular in the United States and, with it, came its design elements, such as the cul-de-sac. Clarence Stein
Clarence Samuel Stein (June 19, 1882 – February 7, 1975) was an American urban planner, architect, and writer, a major proponent of the garden city movement in the United States.
Biography
Stein was born in Rochester, New York into an upwardly ...
, a main proponent of the movement, incorporated it in the Radburn, New Jersey
Radburn is an unincorporated community located within Fair Lawn in Bergen County, New Jersey, United States.
Radburn was founded in 1929 as "a town for the motor age".
subdivision, which was to become a model for subsequent neighborhood developments. The country's Federal Housing Authority (FHA) recommended and promoted their use through their 1936 guidelines and the power of lending development funds.
In Canada, a variation of Stein's Radburn 1929 plan that used crescents (loops) instead of culs-de-sac was built in 1947: Wildwood Park, Winnipeg, designed by Hubert Bird. In 1954, the Central Mortgage and Housing Corporation published its own guidelines in which the cul-de-sac was strongly recommended for local streets and, as the FHA in the US, used its lending power to see its inclusion in development plans. The Varsity Village and Braeside, subdivisions in Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
, Alberta also used the Radburn model in the late 1960s.
In the 1960s the cul-de-sac attained systematic international application in planned new cities such as Doxiadis' Islamabad (1960). In the UK, new towns such as Harlow
Harlow is a large town and local government district located in the west of Essex, England. Founded as a new town, it is situated on the border with Hertfordshire and London, Harlow occupies a large area of land on the south bank of the upp ...
(1947) by Sir Frederick Gibberd and Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
(1967) incorporated culs-de-sac and crescents in their layouts.
Planning theorists have suggested the use of alternatives to culs-de-sac. Most notably, Christopher Alexander et al., in his 1977 book " A Pattern Language" (pattern #49) suggests the use of looped local roads which do not abruptly stop. Although dead end streets (culs-de-sac), would fit his definition of looped local roads Alexander suggestions that "cul-de-sacs ic are very bad from a social standpoint—they force interaction and they feel claustrophobic, because there is only one entrance". Doxiadis has additionally argued their important role in separating man from machine.
Originally-unplanned dead ends
 Originally-unplanned dead ends have been added in city centers that are laid out on a grid by blocking through-traffic. Whole neighbourhood street reconfigurations emerged in several cities, mainly concentrated in North America and the UK, which include Berkeley, California; Seattle, Washington; and Vancouver, British Columbia. The transformation of
Originally-unplanned dead ends have been added in city centers that are laid out on a grid by blocking through-traffic. Whole neighbourhood street reconfigurations emerged in several cities, mainly concentrated in North America and the UK, which include Berkeley, California; Seattle, Washington; and Vancouver, British Columbia. The transformation of grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
s since the 1970s limits access to an existing road that is newly designated as a major artery, enabling traffic to move smoothly on it, alleviating residents' concerns.
This selective, sporadic transformation is continuing. As traffic volumes increase and as cities decide to remove or reduce traffic on specific streets of central areas, streets are closed off using bollards or landscaping thus making new, originally unplanned dead ends and producing a new, functional blend of the inherited grid with newer street types. A recent variation of limiting traffic is managed closure by using retractable bollards that are activated only by designated card-holders.
Suburban use and benefits
Since the end of World War II, new subdivisions in the United States and Canada, as well as New Towns in England and other countries have made extensive use of the cul-de-sac and crescent (loops) street types. Typically, there is one or several central roads in the subdivision with many cul-de-sac streets of varying length, branching out from the main roads, to fill the land in the subdivision, a dendrite orhierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
pattern. Since the 1960s, the pattern has been the dominant road network structure of suburbs and exurbs in the United States, Canada, and Australia. It is also increasingly popular in Latin America, Western Europe, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. In this pattern, there are only a few roads (relative to the number of cul-de-sac streets) leading out of the subdivision and into other subdivisions or onto major roads.
In the US, these changes can be attributed to real-estate developers' desire to meet FHA guidelines and make federal home loans available to their customers. In Canada, a similar incentive was provided to developers by CMHC. The incentives, which were discontinued in the 1970s, gave the initial impetus for the application of the hierarchical pattern. In other countries, such incentives do not exist, and adoption is motivated by customer preferences.
American urban planning, in the 19th and the early 20th centuries, emphasized a grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
, partly out of extensive reliance on foot, horse and trams for transportation. In such earlier urban development, alleys were included to allow for deliveries of soiled supplies, such as coal, to the rear of houses that are now heated by electricity, piped natural gas or oil.
 The use of culs-de-sac reduces the amount of car traffic on residential streets within the subdivision, thus reducing noise, air pollution and the probability of accidents. Ben-Joseph (1995), and Lovegrove and Sayed (2006), indicate a substantially lower collision rate for
The use of culs-de-sac reduces the amount of car traffic on residential streets within the subdivision, thus reducing noise, air pollution and the probability of accidents. Ben-Joseph (1995), and Lovegrove and Sayed (2006), indicate a substantially lower collision rate for street network A street network is a system of interconnecting lines and points (called ''edges'' and ''nodes'' in network science) that represent a system of streets or roads for a given area. A street network provides the foundation for network analysis; for exa ...
s based on the cul-de-sac street type. Dumbaugh and Rae (2009) suggest that land-use patterns play a significant role in traffic safety and should be considered in conjunction with the network pattern. While all intersection types in general increase the incidence of fatal crashes, four-way intersections, which rarely occur in a network with cul-de-sac or loop streets, increase total and injurious crashes significantly. The study recommends hybrid street networks with dense concentrations of T-intersections and concludes that a return to the 19th century gridiron is undesirable.
The decrease in traffic, in turn, is thought to lower the incidence of crime and increase desirability, because in most cases the people who traverse the cul-de-sac either live there or are guests of those who do. CPTED
Crime prevention through environmental design (CPTED) is an agenda for manipulating the built environment to create safer neighborhoods.
It originated in America around 1960, when urban renewal strategies were felt to be destroying the social fram ...
planning principles suggest increased natural surveillance and sense of ownership as a means of fostering security in a neighbourhood. Both of these phenomena occur naturally on a cul-de-sac street as does social networking. Design guidelines based on the CPTED perspective recommend its use for those reasons.
Cul-de-sac streets increase spontaneous outdoor activity by children. A study in California examined the amount of child play that occurred on the streets of neighbourhoods with different characteristics; grid pattern and culs-de-sac. The findings indicate that culs-de-sac showed substantial increase in play activity than the open grid street pattern. Culs-de-sac reduce perceived danger from traffic, thereby encouraging more outdoor play.
 Similar studies in Europe and Australia found that children's outdoor play is significantly reduced on through roads where traffic is, or perceived by parents to be, a risk. In addition, they confirmed the results of the seminal Donald Appleyard 1982 study, which showed the negative correlation between amount of traffic and social networks. The inverse correlation between amounts of traffic and sociability of streets was reconfirmed by a newer study that repeated Appleyard's San Francisco analysis in Bristol, UK. It showed that the cul-de-sac street with the lowest traffic of the three streets had the highest level of social interaction.
The studies recommend the use of the cul-de-sac or strong traffic calming measures. When culs-de-sac are interconnected with foot and bike paths, as for example in Vauban, Freiburg and
Similar studies in Europe and Australia found that children's outdoor play is significantly reduced on through roads where traffic is, or perceived by parents to be, a risk. In addition, they confirmed the results of the seminal Donald Appleyard 1982 study, which showed the negative correlation between amount of traffic and social networks. The inverse correlation between amounts of traffic and sociability of streets was reconfirmed by a newer study that repeated Appleyard's San Francisco analysis in Bristol, UK. It showed that the cul-de-sac street with the lowest traffic of the three streets had the highest level of social interaction.
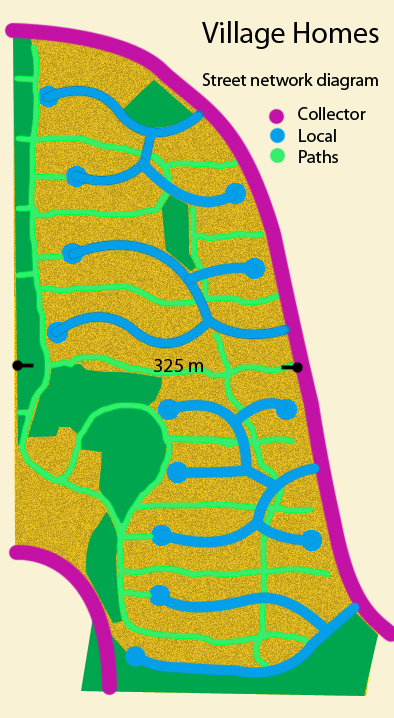
The studies recommend the use of the cul-de-sac or strong traffic calming measures. When culs-de-sac are interconnected with foot and bike paths, as for example in Vauban, Freiburg and Village Homes
Village Homes is a planned community in Davis, Yolo County, California. It is designed to be ecologically sustainable by harnessing the energies and natural resources that exist in the landscape, especially stormwater and solar energy.
History
Th ...
in Davis, California, they can increase active modes of mobility among their residents.
Real estate developers prefer culs-de-sac because they allow builders to fit more houses into oddly-shaped tracts of land and facilitate building to the edges of rivers and property lines. They also choose these discontinuous network patterns of cul-de-sac and loop streets because of the often significant economies in infrastructure costs compared to the grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
.
From an environmental perspective, culs-de-sac allow greater flexibility than the common grid in adapting to the natural grades of a site and to its ecologically sensitive features, such as streams, creeks, and mature forest growth.
The desirability of the cul-de-sac street type among home buyers is implied by the evidence that they often pay up to a 20% premium for a home on such a street, according to one study. That could be because there is considerably less passing traffic, resulting in less noise and reduced actual or perceived risk, increasing the sense of tranquility. A survey of residents on three types of streets: cul-de-sac, loop, and through (grid) recorded their preferences among these types. It found that 82% of cul-de-sac residents preferred their own street type, 18% preferred a loop, and 0% the grid. Only 13% of grid street residents preferred their own type and 54% would choose a cul-de-sac.
Two other studies, reported in 1990 and 2009 respectively, confirmed the upward trend and determined the premium that cul-de-sac streets command. The first found a 29% premium over the streets in a grid. The second, focused on trails and greenbelts, found that other amenities including cul-de-sac streets add significantly to the home value.
The positive feelings that a cul-de-sac street could evoke, that residents value, are expressed vividly by Allan Jacobs in describing Roslyn Place, a short (), narrow (), densely built (), and wood-paved cul-de-sac in the Shadyside neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: "Step into Roslyn Place and you are likely to sense, immediately, that you are in a ''place'', a special place, a handsome place, a safe place, a welcoming place, a place where you might wish to live." "narrowness and enclosure and intimacy bring a feeling of safety to Roslyn Place... 'Stay on our street' is all the kids have to know".
Gated communities, whose numbers steadily increase worldwide, use cul-de-sac and loop street networks because the dendrite structure reduces the number of through roads and thus the corresponding number of entries and exits that need to be controlled.
Criticisms and discussion




Traffic safety issues
Dead ends are traditionally considered safer traffic environments for children than normal streets, but research shows that areas with many dead ends in fact have higher rates of traffic accidents involving young children. This increased risk of death is due to multiple factors, including: * families living on dead-end streets drive longer distances to reach their destinations, * parents living on dead-end streets spend less time teaching their children to be as wary of traffic, and * an increased risk of the parents accidentally driving over the children in front of their own homes.Environmental, health, and crime issues
Culs-de-sac are criticised by urban designers like those of the Foundation for the Built Environment in the UK for encouraging car transport for even short distances, as more direct connections are precluded by the geometry, which necessitates long travel distances even to physically-nearby locations. This increases fuel consumption and vehicle emissions and has negative effects on health by reducing walking and cycling rates.Charles: let’s kill off the cul-de-sac
' – '' The Sunday Times'', February 11, 2007 Related research in the United States by Richard Jackson has shown that people in car-based (cul-de-sac heavy) communities weigh on average more than those in traditional towns (with open grid networks). An extensive analysis of the research evidence by TRB, however, shows only an association between the built environment and physical activity levels, not causal connections. The evidence also does not identify with certainty which characteristics of the built environment are most closely associated with physical activity behaviour. The study also warns against confusing inadequate physical activity with obesity which is the outcome of an energy imbalance. Many contemporary lifestyle trends, some inevitable (sedentary work) and some avoidable (frequent energy-rich food consumption or the watching of television
our hours per day
Our or OUR may refer to:
* The possessive form of " we"
* Our (river), in Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany
* Our, Belgium, a village in Belgium
* Our, Jura, a commune in France
* Office of Utilities Regulation (OUR), a government utility regulato ...
, contribute to the imbalance and must be considered in understanding and combating obesity.
The impermeability deficiency of the typical cul-de-sac street can be addressed by applying a modified, improved version of it, mentioned above, that enables pedestrian and bicycle through-movement. While this more permeable version can be applied in new developments easily, modifying existing impermeable cul-de-sac streets is problematic as it encounters property ownership issues. Efforts in that direction are, however, being made. Because of the complicated legal process and the sheer number of existing cul-de-sac streets, however, such efforts would be slow to produce results and may have little impact in changing the landscape of existing districts. Conversely, transforming existing streets that are part of a grid plan into permeable, linked culs-de-sac, as was done in Berkeley, California, and Vancouver, British Columbia, is physically and administratively easy due to the public ownership of the street right-of-way. However, residents on adjacent through roads may resent the potential traffic increase and delay the process. In Berkeley, the barriers used were permeable to both pedestrian and bicycle traffic and became the backbone of the bicycle boulevard system in that region.
Increases in pedestrian and bicycle permeability may result in a displacement of local car trips for short-distance destinations and consequently a reduction in neighbourhood vehicle emissions. The impermeable cul-de-sac not only discourages walking and biking but also increases the length of car trips by the circuitous geometry of the dendrite network structure of which it is a part. Research studies examined the influence of several variables on the amount of car travel that residents of several types of districts recorded. Results vary considerably among them, but there is general agreement on a number of key correlations:Taming the Flow—Better Traffic and Safer Neighbourhoods. Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation, July 2008 a) the wealthier and the larger the family is, the more cars they own, and the more they drive, b) the farther away a family lives from the city centre, and the fewer the jobs in the vicinity, plus a slow bus service, the more they drive, and c) street patterns may add a 10% length to local trips, but the total VKTs are affected more by the "macro" urban than the "micro" neighbourhood structure.
Culs-de-sac, especially those that also limit pedestrian routes instead of only road-traffic routes, have also been criticised for negative effects on safety because they decrease the amount of through-traffic (vehicular or pedestrian) that might notice an accident or crime victim in need of help. Proponents of culs-de-sac and gated communities have in turn countered that the reduction in through-traffic makes any "stranger" much more recognisable in the closed local environment and thus reduces crime danger. That view has in turn been characterized as unrealistic. It is argued that, since only very few of all non-locals passing through the area are potential criminals, increased traffic should increase rather than decrease safety.
Research has expanded the discussion on the disputed issue. A 2008 study did extensive spatial analysis and correlated several building, site plan and social factors with crime frequencies and identified subtle nuances to the contrasting positions. The study looked at, among others, a) dwelling types, b) unit density (site density) c) movement on the street, d) culs-de-sac or grids, and e) the permeability of a residential area. Among its conclusions are, respectively, that a) flats are always safer than houses and the wealth of inhabitants matters, b) density is generally beneficial but more so at ground level, c) local movement is beneficial but larger-scale movement not so, d) relative affluence and the number of neighbours has a greater effect than either being on a cul-de-sac or being on a through-street. It also established again that simple, linear culs-de-sac with good numbers of dwellings that are joined to through streets tend to be safe. As for permeability, it suggests that residential areas should be permeable enough to allow movement in all directions but no more. The overprovision of poorly-used permeability is a crime hazard.
More generally, the New Urbanism movement has offered criticism of the cul-de-sac and crescent (loop) street types not intended to network with each other. It has been suggested that such street layouts can cause increased traffic on the collector streets. It is recognized that culs-de-sac and looped streets inherently remove car traffic through them and restrict access to residents only. Resident traffic is naturally channelled to minor residential collectors and to arterials that provide inter-neighbourhood and inter-district connectivity. A study, reported in 1990, compared the traffic performance in a development that was laid out using two approaches, one with and the other without hierarchy or cul-de-sac streets. It concluded that the non-hierarchical, traditional layout generally shows lower peak speed and shorter, more frequent intersection delays than the hierarchical pattern. The traditional pattern is not as conducive to long trips as the hierarchical but more conducive to short trips. Local trips in it are shorter in distance but about equivalent in time with the hierarchical layout. A later similar comparative traffic study of about concluded that all types of layouts perform adequately in most land-use scenarios and that a refined hierarchical, dendrite network can improve traffic performance.
Anecdotal and research evidence suggests that navigation (especially on foot) in a disconnected network of cul-de-sac and looped streets is inconvenient and non-intuitive, particularly when combined with curvilinear geometry. Loss of orientation and sense of direction is also a common experience in older cities with cul-de-sac streets (Medina of Arab cities or Mediterranean hill towns) as well as in cities with highly-irregular block geometries and sizes and corresponding street alignments that produce a labyrinthine effect. The long history of such cities implies that an irregular, complicated street network that appears entirely illegible to a visitor is well understood and used by the inhabitants. More convincing about its workability for their permanent residents are the case histories of cities such as Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the f ...
that show a gradual transformation of an imported or imposed orthogonal, "legible" grid to the traditional "confusing" street networks.
Cul-de-sac and loop streets can reduce the size of any given neighbourhood to a single street. Neighbourhoods can be defined by geographic boundaries but more often it is shared ethnic, socioeconomic and cultural characteristics that produce social cohesion irrespective of apparent physical "boundaries". Mehaffy ''et al.'' (2010), who propose a model for structuring an urban network, suggest that neighbourhoods cannot be designed into being. "Community" is viewed as a dynamic social and cultural construct, especially in contemporary, open, multicultural cities. Residential area street configuration can assist its emergence only by reducing through-traffic and increasing local pedestrian movementa design goal for which connected cul-de-sac and looped streets are suited.
Issues of pedestrian trip length and isolation are very evident in the back-to-front housing arrangement where the front of the house fronts onto the cul-de-sac street while the rear fronts onto the main roads. Some of the problems can be mitigated by the newer practice of connecting the neighbouring roads and culs-de-sac with public pedestrian or cycle paths. In effect, this removes the discontinuity aspect for these modes of transport. Built examples of such connected culs-de-sac can be found in the United States (such as Radburn Radburn may refer to:
Places
*Radburn, New Jersey, an American suburb and the basis for later housing planning designs known as 'Radburn estates'
*Radburn (NJT station), railway station
People
*Jade Radburn, English football defender
*Will Radbur ...
, New Jersey, and Village Homes
Village Homes is a planned community in Davis, Yolo County, California. It is designed to be ecologically sustainable by harnessing the energies and natural resources that exist in the landscape, especially stormwater and solar energy.
History
Th ...
, California), England (such as Milton Keynes
Milton Keynes ( ) is a city and the largest settlement in Buckinghamshire, England, about north-west of London. At the 2021 Census, the population of its urban area was over . The River Great Ouse forms its northern boundary; a tributary ...
), and Greece (such as Papagou
Papagou ( el, Παπάγου or Παπάγος ''Papagos'') is a suburb and municipal unit in the eastern part of the Athens agglomeration, Greece. The town is named after Marshal Alexandros Papagos, a general who led the Greek Army in the Second ...
, a suburb of Athens). Acknowledging their use, Germany, under the 2009 amendment to the Road Traffic Act, introduced an additional sign for culs-de-sac that are permeable to pedestrians and cyclists (see under signage below). A new system for organizing connected, permeable culs-de-sac into complete neighbourhoods, the fused grid, has been developed by Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation.
In the development context and planning literature of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, culs-de-sac have been associated with low-density residential development. Sustainable development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The des ...
theorists and proponents claim that to be, in some undefined way, inefficient. The increased prevalence of cul-de-sac streets occurred in the 1960s and 1970s, a period of rapid economic and city expansion, when a detached house on a large lot meant an ideal form of habitation. The temporal coincidence of the wide adoption of a street type and an increasing demand for large lots and houses suggests a necessary relationship between street type and unit density. Historically, however, the earliest systematic application of the cul-de-sac street type by Raymond Unwin (1909) had a unit density between , considerably higher than mid-to-late 20th century. Even in the 21st century, developments rarely achieve densities above in the suburbs. Conversely, early 1950s suburban developments that were laid out on a grid exhibit similar low densities. Evidently, street, network type and density are not linked causally; other factors, such as land scarcity and income, influence the outcome as, for example, in cities that are landlocked or that have low average incomes.
Another concern is often voiced by emergency services, which can have difficulty locating streets when a community consists of a large number of similarly named culs-de-sac; also, large fire response vehicles, in particular, can have great difficulty with turning around in a cul-de-sac. However, confusing street naming is not a necessary outcome of street network design and can be improved. The practice of naming orthogonal networks by numbers and letters in the corresponding cardinal directions has been criticized by Camilo Sitte
Camillo Sitte (17 April 1843 – 16 November 1903) was an Austrian architect, painter and urban theorist whose work influenced urban planning and land use regulation. Today, Sitte is best remembered for his 1889 book, ''City Planning According to ...
as lacking imagination. Nonetheless, police and fire departments now use advanced GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of t ...
systems that quickly locate the destination and the shortest path to follow.
School buses can also have a hard time turning around, which means that children who live in a cul-de-sac must often walk to a bus stop on a main through-road. However, recent research on obesity and urban planning suggests that to be a possible advantage because it enables children to get daily physical activity. Longer walking distances, however, reduce interest to use buses especially when a car is available. This disincentive to walking to a school bus-stop can be overcome in planned cul-de-sac streets by regulating their maximum length to about , as was recommended and practiced by R. Unwin and others.
Weighing available evidence has led a few US cities including Austin, Texas; Charlotte, North Carolina; and Portland, Oregon, to restrict and regulate the inclusion of cul-de-sac streets in new suburbs. However, a 2010 study on sprawl in North America by a legal expert concludes that "neighborhoods dominated by culs-de-sac are less walkable than those that include street grids.... On the other hand, culs-de-sac do have a countervailing public benefit: because of their very inaccessibility, they tend to have less automobile traffic. Given the existence of important public policy goals on both sides, a city seeking to maximize walkability should not favor culs-de-sac over grids, but should also allow some culs-de-sac as a legitimate residential option.... In addition, there are "middle ground" alternatives between prohibiting culs-de-sac and mandating them. For example, a city could encourage culs-de-sac combined with pedestrian walkways." This design combination is shown in the Village Homes layout and is an integral part of the Fused Grid.
Terminology
George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was an English novelist, essayist, journalist, and critic. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to totalitar ...
wrote in his 1946 article " Politics and the English Language" that the term "cul de sac" is another foreign word used in English as pretentious diction and is unnecessary.
The word "cul-de-sac" and its synonyms or near synonyms "dead end" and "no exit" have inspired metaphorical uses in literature and in culture, often with the result that a word or phrase seeming to have a negative connotation is replaced in street signs with a new coinage ("no outlet" is another alternative name used on street signs).
The expression ''cul-de-sac'' comes from French, where it originally meant "bottom of a sack". It was first used in English in anatomy (since 1738). It was used for dead-end streets since 1800 in English (since the 14th century in French). The often-heard erroneous folk etymology "arse/ass uttocksof the sack" is based on the modern meaning of ''cul'' in French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
, and Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language
Occitan (; o ...
, but ''cul'' does not have that meaning in ''cul-de-sac'', which is still used to refer to dead ends in modern Frenchalthough the terms and are more common.
J. R. R. Tolkien used the name Bag End as a translation of "cul-de-sac" to poke fun at the British use of French terms.
Australia
In Australia, dead-end streets are signposted as and often referred to as a "No Through Road". Suffixes for these types of streets include "court", "close" or "place". The term "cul-de-sac" generally only refers to a reasonably short street with a bulbous end, or even only to the end portion. A long road that is a no-through road and terminates abruptly is usually called a dead end.Canada
In Canada, "cul-de-sac" is commonly used in speech but "no exit" or "no through road" is more common in road signs, especially in western Canada. In Quebec and Newfoundland, "Cul-de-Sac" is in far more common use, although Quebec is using "Impasse" too.France
Cul de sac isFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
for 'bag-bottom'.
New Zealand
In New Zealand, dead-end streets are sometimes signposted as "No Exit", but are often not signposted at all. The terms 'cul-de-sac' and 'dead end' have the same senses as in Australia. Similarly to Australia, residential cul-de-sacs with bulbous ends are often suffixed with "Place", abbreviated to "Pl" on street signs.United Kingdom
In British English, the phrase "close" is generally used as a prefix for residential cul-de-sac roads, although several variants exist similar to those used in Commonwealth countries.United States

 U.S. Federal Highway Administration rules state: "The ''Dead End'' sign may be used at the entrance of a single road or street that terminates in a dead end or cul-de-sac. The ''No Outlet'' sign may be used at the entrance to a road or road network from which there is no other exit." There is no federal regulation on "no exit".
The phrase "No Exit" is also preferred for Chicago signs, although "dead end" is still used there. New York City has favored "dead end" since at least the 1930s, when Sidney Kingsley used the phrase to title his Broadway play about poor, tough East Side youths with lives of little promise, in contrast to the dead-end streets of the nearby
U.S. Federal Highway Administration rules state: "The ''Dead End'' sign may be used at the entrance of a single road or street that terminates in a dead end or cul-de-sac. The ''No Outlet'' sign may be used at the entrance to a road or road network from which there is no other exit." There is no federal regulation on "no exit".
The phrase "No Exit" is also preferred for Chicago signs, although "dead end" is still used there. New York City has favored "dead end" since at least the 1930s, when Sidney Kingsley used the phrase to title his Broadway play about poor, tough East Side youths with lives of little promise, in contrast to the dead-end streets of the nearby Sutton Place Sutton Place may refer to:
Canada
* Sutton Place Hotel, a former hotel in Toronto, Ontario
* The Sutton Place, a hotel in Vancouver, British Columbia
England
* Sutton Place, Hackney, a Georgian terrace in London
* Sutton Place, Surrey, a country ...
neighborhood. (Similarly, French existentialist Jean-Paul Sartre titled a play about three damned sinners, ''Huis Clos
''No Exit'' (french: Huis clos, links=no, ) is a 1944 existentialist French play by Jean-Paul Sartre. The play was first performed at the Théâtre du Vieux-Colombier in May 1944. The play begins with three characters who find themselves waiting ...
'', translated into English as " No Exit".) Kingsley's play was later made into a movie, '' Dead End'', which proved so popular that it spawned similar movies, many starring a group of recurring characters known as the Dead End Kids. The play and movies produced such a strong image of bleak futures and an unfair society that some municipalities changed the sign terminology for culs-de-sac, often to "no outlet" or "no exit". (The "dead end" signs currently at Sutton Place are bright yellow with black lettering.)
In New York City, as of 2008, there were 4,659 "dead end" traffic signs, along with 160 "no outlet" signs. The city records, which go back to the 1960s, show only a couple of "no exit" signs once existing near the approaches to the Midtown Tunnel, and which are no longer there. New York City Commissioner of Transportation Janette Sadik-Khan
Janette Sadik-Khan (born April 28, 1961) is a former commissioner of the New York City Department of Transportation (2007–2013) and an advisor on transportation and urban issues. She works for Bloomberg Associates, a philanthropic consultancy es ...
said in 2008: "We hear that some towns use 'no outlet' instead of 'dead end' because they think it sounds less morbid." "We tell New Yorkers the truth: it's a 'dead end', and we think that motorists get the point quickly."
California uses the phrase ''Not a Through Street'' or ''Not a Through Road'' to mark roads or road systems that end in culs-de-sac. More recently, ''No Outlet'' has been shown on some signs as well (an example being Meyers Avenue south of Eureka Street in the Pine Hills area).
Other uses
In military parlance, a "cul-de-sac" refers to a situation where an army is ''"hemmed in on all sides but behind"''.OED, online edition, draft revision December 2007, entry for ''cul-de-sac, n2'' "Cul-de-sac" is also used metaphorically to mean a line of thought or action that leads nowhere. In medicine, the expression is used to refer to the recto-uterine pouch, also known as the Pouch of Douglas, the deepest point of the female peritoneal cavity.Signage
See also
* Fused Grid * Permeability (spatial and transport planning) *Turnaround (road) In the field of road transport, a turnaround is a type of junction that allows traffic traveling in one direction on a road to efficiently make a U-turn (to reverse course and travel the opposite direction) typically without backing up or making da ...
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Cul-De-Sac Types of streets