Crusaders Rugby Club on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the
 The term "crusade" first referred to military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to the
The term "crusade" first referred to military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to the
 The Crusades to the Holy Land are the best known of the religious wars associated with the term, beginning in 1095 and lasting some two centuries. These Crusades began with the fervent desire to wrest the Holy Land from the Muslims, and ran through eight major numbered crusades and dozens of minor crusades over the period.
The Crusades to the Holy Land are the best known of the religious wars associated with the term, beginning in 1095 and lasting some two centuries. These Crusades began with the fervent desire to wrest the Holy Land from the Muslims, and ran through eight major numbered crusades and dozens of minor crusades over the period.
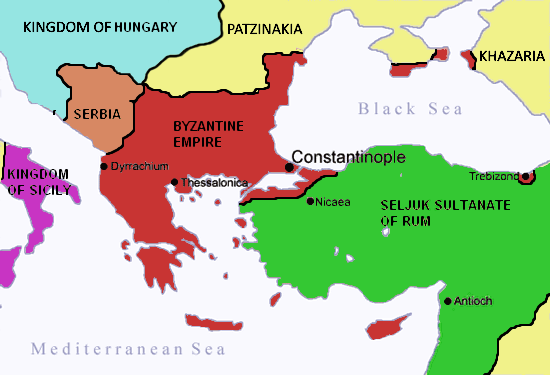 In 1074, just three years after Manzikert and the Seljuk takeover of Jerusalem, Gregory VII began planning to launch a military campaign for the liberation of the Holy Land. Twenty years later,
In 1074, just three years after Manzikert and the Seljuk takeover of Jerusalem, Gregory VII began planning to launch a military campaign for the liberation of the Holy Land. Twenty years later,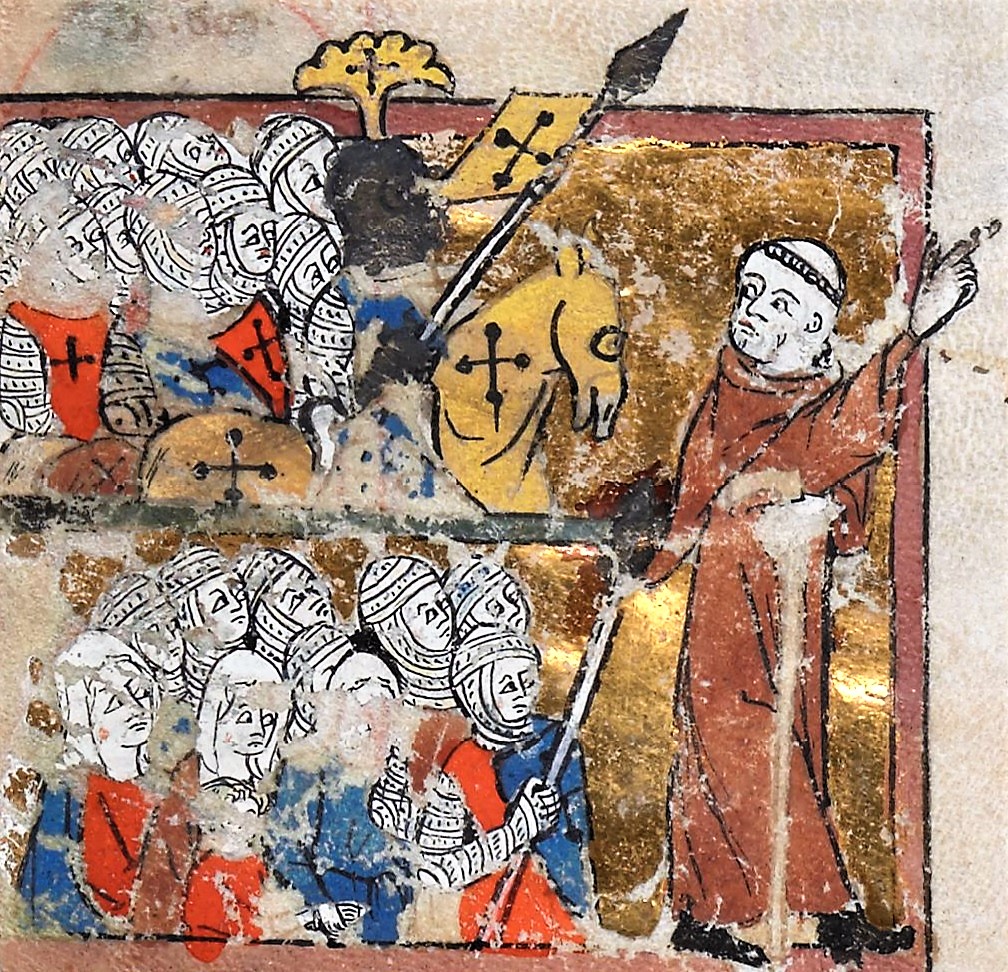  Immediately after Urban's proclamation, the French priest Peter the Hermit led thousands of mostly poor Christians out of Europe in what became known as the People's Crusade. In transit through Germany, these Crusaders spawned German bands who massacred Jewish communities in what became known as the Rhineland massacres. They were destroyed in 1096 when the main body of Crusaders was annihilated at the battle of Civetot.
In response to Urban's call, members of the high aristocracy from Europe took the cross. Foremost amongst these was the elder statesman Raymond IV of Toulouse, who with bishop Adhemar of Le Puy commanded southern French forces. Other armies included: one led by Godfrey of Bouillon and his brother
Immediately after Urban's proclamation, the French priest Peter the Hermit led thousands of mostly poor Christians out of Europe in what became known as the People's Crusade. In transit through Germany, these Crusaders spawned German bands who massacred Jewish communities in what became known as the Rhineland massacres. They were destroyed in 1096 when the main body of Crusaders was annihilated at the battle of Civetot.
In response to Urban's call, members of the high aristocracy from Europe took the cross. Foremost amongst these was the elder statesman Raymond IV of Toulouse, who with bishop Adhemar of Le Puy commanded southern French forces. Other armies included: one led by Godfrey of Bouillon and his brother 
Chapter XVII. The Latin States under Baldwin III and Amalric I, 1143-1174
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 528-563. Following John's death, the Byzantine army withdrew, leaving Zengi unopposed. Fulk's death later in the year left
Chapter XV. The Second Crusade
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 463-512. The aftermath of the Crusade saw the Muslim world united around Saladin, leading to the fall of Jerusalem. Gibb, Hamilton A. R. (1969).
Chapter XVIII. The Rise of Saladin, 1169-1189
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 563-589.
 After the Siege of Ascalon ended on 22 August 1153 with a Crusader victory and Damascus was taken by Nūr-ad-Din the next year, uniting all of Syria under Zengid rule. In 1156, Baldwin III was forced into a treaty with Nūr-ad-Din, and later entered into an alliance with the Byzantine Empire. On 18 May 1157, Nūr-ad-Din began a siege on the Knights Hospitaller contingent at Banias, with the Grand Master Bertrand de Blanquefort captured. Baldwin III was able to break the siege, only to be ambushed at Jacob's Ford in June. Reinforcements from Antioch and Tripoli were able to relieve the besieged Crusaders. Bertrand's captivity lasted until 1159, when emperor Manuel I negotiated an alliance with Nūr-ad-Din against the Seljuks.
Baldwin III died on 10 February 1163, and Amalric of Jerusalem was crowned as king of Jerusalem eight days later. He undertook a series of four
After the Siege of Ascalon ended on 22 August 1153 with a Crusader victory and Damascus was taken by Nūr-ad-Din the next year, uniting all of Syria under Zengid rule. In 1156, Baldwin III was forced into a treaty with Nūr-ad-Din, and later entered into an alliance with the Byzantine Empire. On 18 May 1157, Nūr-ad-Din began a siege on the Knights Hospitaller contingent at Banias, with the Grand Master Bertrand de Blanquefort captured. Baldwin III was able to break the siege, only to be ambushed at Jacob's Ford in June. Reinforcements from Antioch and Tripoli were able to relieve the besieged Crusaders. Bertrand's captivity lasted until 1159, when emperor Manuel I negotiated an alliance with Nūr-ad-Din against the Seljuks.
Baldwin III died on 10 February 1163, and Amalric of Jerusalem was crowned as king of Jerusalem eight days later. He undertook a series of four
Chapter XIX. The Decline and Fall of Jerusalem, 1174-1189
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 590-621.
 Frederick took the cross in March 1188.Johnson, Edgar N. (1977).
Frederick took the cross in March 1188.Johnson, Edgar N. (1977).
The Crusades of Frederick Barbarossa and Henry VI
". In Setton, K,. ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II.'' pp. 87-122. Frederick sent an ultimatum to Saladin, demanding the return of Palestine and challenging him to battle and in May 1189, Frederick's host departed for Byzantium. In March 1190, Frederick embarked to Asia Minor. The armies coming from western Europe pushed on through Anatolia, defeating the Turks and reaching as far as
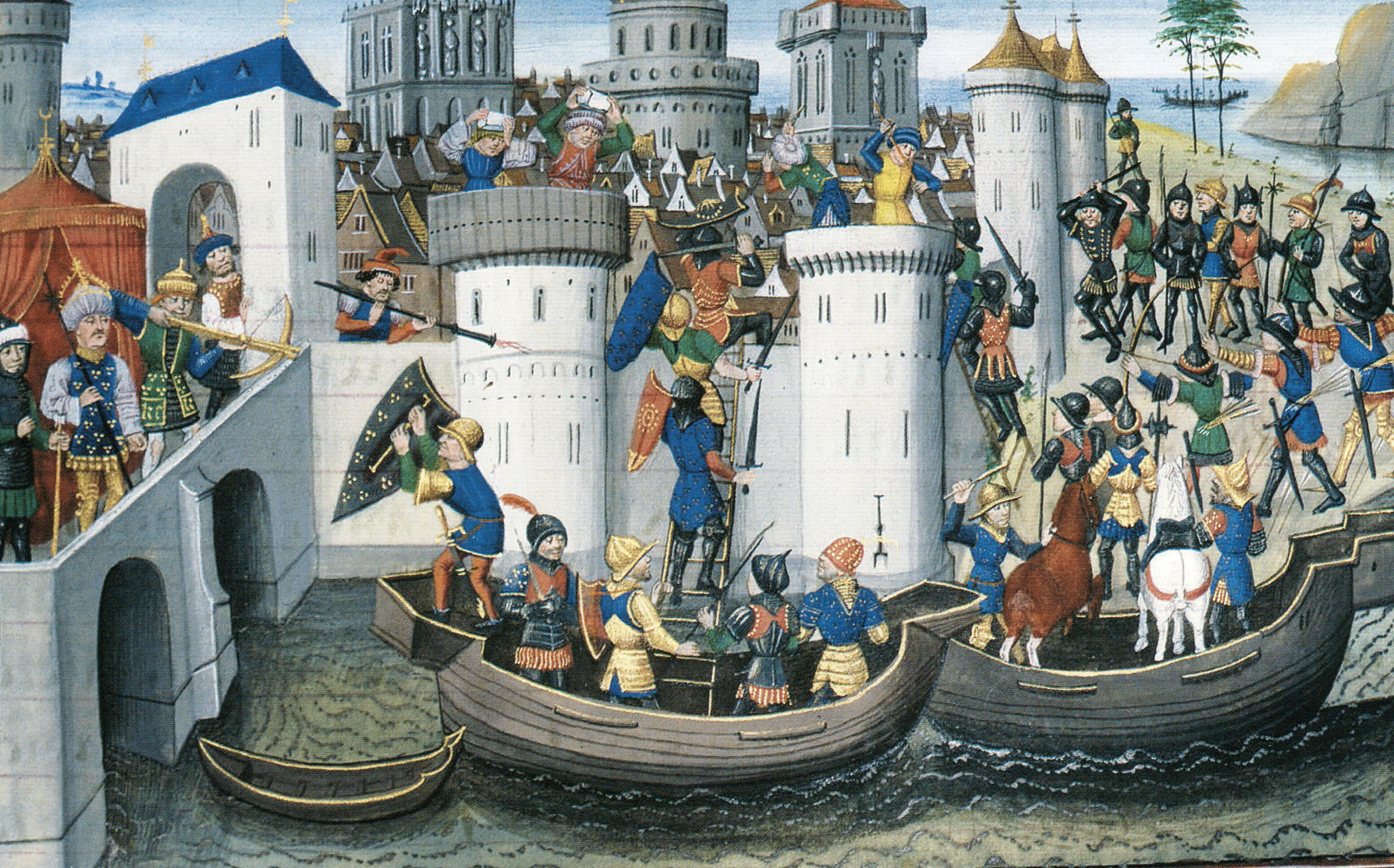 In 1198, the recently elected Pope Innocent III announced a new crusade, organised by three Frenchmen: Theobald of Champagne; Louis of Blois; and
In 1198, the recently elected Pope Innocent III announced a new crusade, organised by three Frenchmen: Theobald of Champagne; Louis of Blois; and
The Fifth Crusade
. In Setton, K., ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II''. pp. 343-376.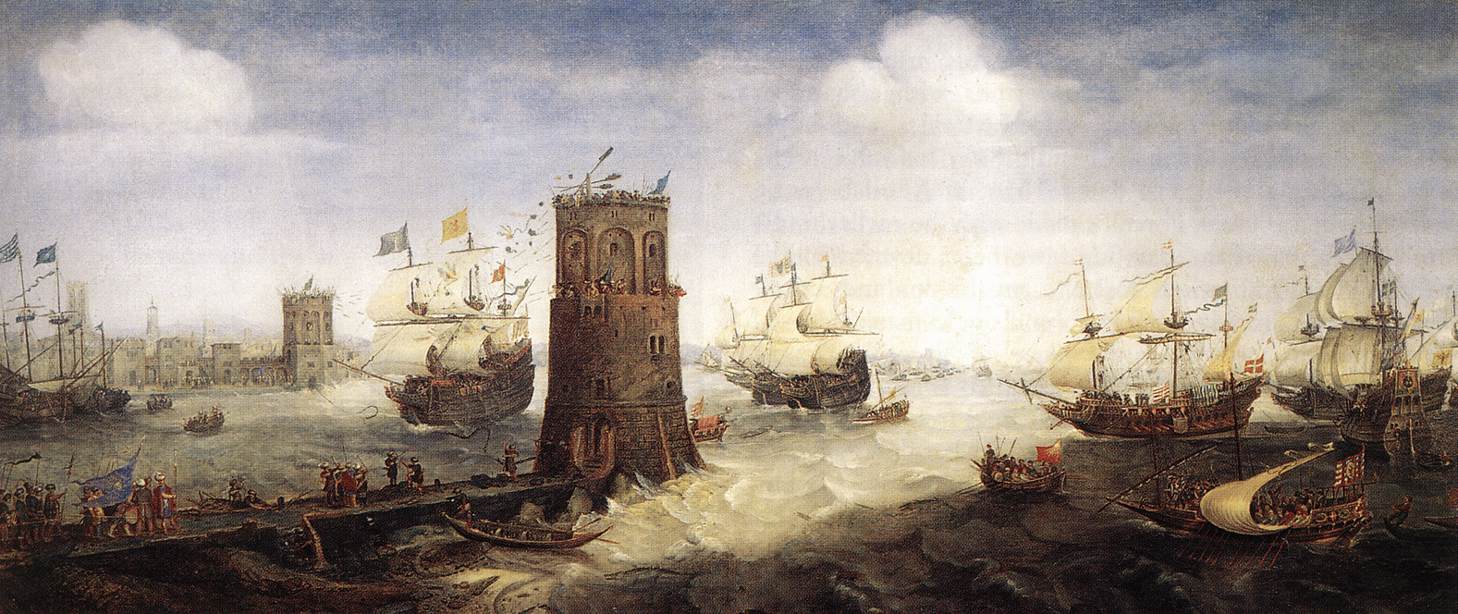 Andrew II left for Acre in August 1217, joining John of Brienne, king of Jerusalem. The initial plan of a two-prong attack in Syria and in Egypt was abandoned and instead the objective became limited operations in Syria. After accomplishing little, the ailing Andrew returned return to Hungary early in 1218. As it became clear that Frederick II was not coming to east, the remaining commanders began the planning to attack the Egyptian port of Damietta.
The fortifications of Damietta were impressive, and included the ''Burj al-Silsilah''the chain towerwith massive chains that could stretch across the Nile. The siege of Damietta began in June 1218 with a successful assault on the tower. The loss of the tower was a great shock to the Ayyubids, and the sultan al-Adil died soon thereafter. He was succeeded as sultan by his son al-Kamil. Further offensive action by the Crusaders would have to wait until the arrival of additional forces, including legate Pelagius with a contingent of Romans. A group from England arrived shortly thereafter.
By February 1219, the Crusaders now had Damietta surrounded, and al-Kamil opened negotiations with the Crusaders, asking for envoys to come to his camp. He offered to surrender the kingdom of Jerusalem, less the fortresses of al-Karak and Krak de Montréal, guarding the road to Egypt, in exchange for the evacuation of Egypt. John of Brienne and the other secular leaders were in favor of the offer, as the original objective of the Crusade was the recovery of Jerusalem. But Pelagius and the leaders of the Templars and Hospitallers refused. Later,
Andrew II left for Acre in August 1217, joining John of Brienne, king of Jerusalem. The initial plan of a two-prong attack in Syria and in Egypt was abandoned and instead the objective became limited operations in Syria. After accomplishing little, the ailing Andrew returned return to Hungary early in 1218. As it became clear that Frederick II was not coming to east, the remaining commanders began the planning to attack the Egyptian port of Damietta.
The fortifications of Damietta were impressive, and included the ''Burj al-Silsilah''the chain towerwith massive chains that could stretch across the Nile. The siege of Damietta began in June 1218 with a successful assault on the tower. The loss of the tower was a great shock to the Ayyubids, and the sultan al-Adil died soon thereafter. He was succeeded as sultan by his son al-Kamil. Further offensive action by the Crusaders would have to wait until the arrival of additional forces, including legate Pelagius with a contingent of Romans. A group from England arrived shortly thereafter.
By February 1219, the Crusaders now had Damietta surrounded, and al-Kamil opened negotiations with the Crusaders, asking for envoys to come to his camp. He offered to surrender the kingdom of Jerusalem, less the fortresses of al-Karak and Krak de Montréal, guarding the road to Egypt, in exchange for the evacuation of Egypt. John of Brienne and the other secular leaders were in favor of the offer, as the original objective of the Crusade was the recovery of Jerusalem. But Pelagius and the leaders of the Templars and Hospitallers refused. Later,
 The
The
The Crusade of Frederick II
. In Setton, K. ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II''. pp. 377-448. Of all the European sovereigns, only Frederick II, the Holy Roman Emperor, was in a position to regain Jerusalem. Frederick was, like many of the 13th-century rulers, a serial ''crucesignatus'', having taken the cross multiple times since 1215. After much wrangling, an onerous agreement between the emperor and Pope Honorius III was signed on 25 July 1225 at San Germano. Frederick promised to depart on the Crusade by August 1227 and remain for two years. During this period, he was to maintain and support forces in Syria and deposit escrow funds at Rome in gold. These funds would be returned to the emperor once he arrived at Acre. If he did not arrive, the money would be employed for the needs of the Holy Land. Frederick II would go on the Crusade as king of Jerusalem. He married John of Brienne's daughter Isabella II by proxy in August 1225 and they were formally married on 9 November 1227. Frederick claimed the kingship of Jerusalem despite John having been given assurances that he would remain as king. Frederick took the crown in December 1225. Frederick's first royal decree was to grant new privileges on the Teutonic Knights, placing them on equal footing as the Templars and Hospitallers. After the Fifth Crusade, the Ayyubid sultan al-Kamil became involved in civil war in Syria and, having unsuccessfully tried negotiations with the West beginning in 1219, again tried this approach, offering return of much of the Holy Land in exchange for military support. Becoming pope in 1227, Gregory IX was determined to proceed with the Crusade. The first contingents of Crusaders then sailed in August 1227, joining with forces of the kingdom and fortifying the coastal towns. The emperor was delayed while his ships were refitted. He sailed on 8 September 1227, but before they reached their first stop, Frederick was struck with the plague and disembarked to secure medical attention. Resolved to keep his oath, he sent his fleet on to Acre. He sent his emissaries to inform Gregory IX of the situation, but the pope did not care about Frederick's illness, just that he had not lived up to his agreement. Frederick was excommunicated on 29 September 1227, branded a wanton violator of his sacred oath taken many times. Frederick made his last effort to be reconciled with Gregory. It had no effect and Frederick sailed from
 In 1229, Frederick II and the Ayyubid sultan al-Kamil, had agreed to a ten-year truce. Nevertheless, Gregory IX, who had condemned this truce from the beginning, issued the papal bull ''
In 1229, Frederick II and the Ayyubid sultan al-Kamil, had agreed to a ten-year truce. Nevertheless, Gregory IX, who had condemned this truce from the beginning, issued the papal bull ''
 The Seventh Crusade (1248–1254) was the first of the two Crusades led by
The Seventh Crusade (1248–1254) was the first of the two Crusades led by
Chapter XIV. The Crusades of Louis IX
. In Wolff, Robert L. and Hazard, H. W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II, The Later Crusades 1187-1311''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 487-521. At the end of 1244, Louis was stricken with a severe malarial infection and he vowed that if he recovered he would set out for a Crusade. His life was spared, and as soon as his health permitted him, he took the cross and immediately began preparations.James Thomson Shotwell (1911). " Louis IX. of France". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 17. (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 37–38. The next year, the pope presided over On 28 February 1250, Turanshah arrived from Damascus and began an Egyptian offensive, intercepting the boats that brought food from Damietta. The Franks were quickly beset by famine and disease. The Battle of Fariskur fought on 6 April 1250 would be the decisive defeat of Louis' army. Louis knew that the army must be extricated to Damietta and they departed on the morning of 5 April, with the king in the rear and the Egyptians in pursuit. The next day, the Muslims surrounded the army and attacked in full force. On 6 April, Louis' surrender was negotiated directly with the sultan by Philip of Montfort. The king and his entourage were taken in chains to Mansurah and the whole of the army was rounded up and led into captivity.
The Egyptians were unprepared for the large number of prisoners taken, comprising most of Louis' force. The infirm were executed immediately and several hundred were decapitated daily. Louis and his commanders were moved to Mansurah, and negotiations for their release commenced. The terms agreed to were harsh. Louis was to ransom himself by the surrender of Damietta and his army by the payment of a million bezants (later reduced to 800,000). Latin patriarch
On 28 February 1250, Turanshah arrived from Damascus and began an Egyptian offensive, intercepting the boats that brought food from Damietta. The Franks were quickly beset by famine and disease. The Battle of Fariskur fought on 6 April 1250 would be the decisive defeat of Louis' army. Louis knew that the army must be extricated to Damietta and they departed on the morning of 5 April, with the king in the rear and the Egyptians in pursuit. The next day, the Muslims surrounded the army and attacked in full force. On 6 April, Louis' surrender was negotiated directly with the sultan by Philip of Montfort. The king and his entourage were taken in chains to Mansurah and the whole of the army was rounded up and led into captivity.
The Egyptians were unprepared for the large number of prisoners taken, comprising most of Louis' force. The infirm were executed immediately and several hundred were decapitated daily. Louis and his commanders were moved to Mansurah, and negotiations for their release commenced. The terms agreed to were harsh. Louis was to ransom himself by the surrender of Damietta and his army by the payment of a million bezants (later reduced to 800,000). Latin patriarch
 The military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to recover the Holy Land from Muslims provided a template for warfare in other areas that also interested the Latin Church. These included the 12th and 13thcentury conquest of Muslim Al-Andalus by Spanish Christian kingdoms; 12th to 15thcentury German Northern Crusades expansion into the pagan
The military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to recover the Holy Land from Muslims provided a template for warfare in other areas that also interested the Latin Church. These included the 12th and 13thcentury conquest of Muslim Al-Andalus by Spanish Christian kingdoms; 12th to 15thcentury German Northern Crusades expansion into the pagan  By the beginning of the 13thcentury Papal reticence in applying crusades against the papacy's political opponents and those considered heretics. Innocent III proclaimed a crusade against Catharism that failed to suppress the heresy itself but ruined the culture the Languedoc. This set a precedent that was followed in 1212 with pressure exerted on the city of Milan for tolerating Catharism, in 1234
By the beginning of the 13thcentury Papal reticence in applying crusades against the papacy's political opponents and those considered heretics. Innocent III proclaimed a crusade against Catharism that failed to suppress the heresy itself but ruined the culture the Languedoc. This set a precedent that was followed in 1212 with pressure exerted on the city of Milan for tolerating Catharism, in 1234
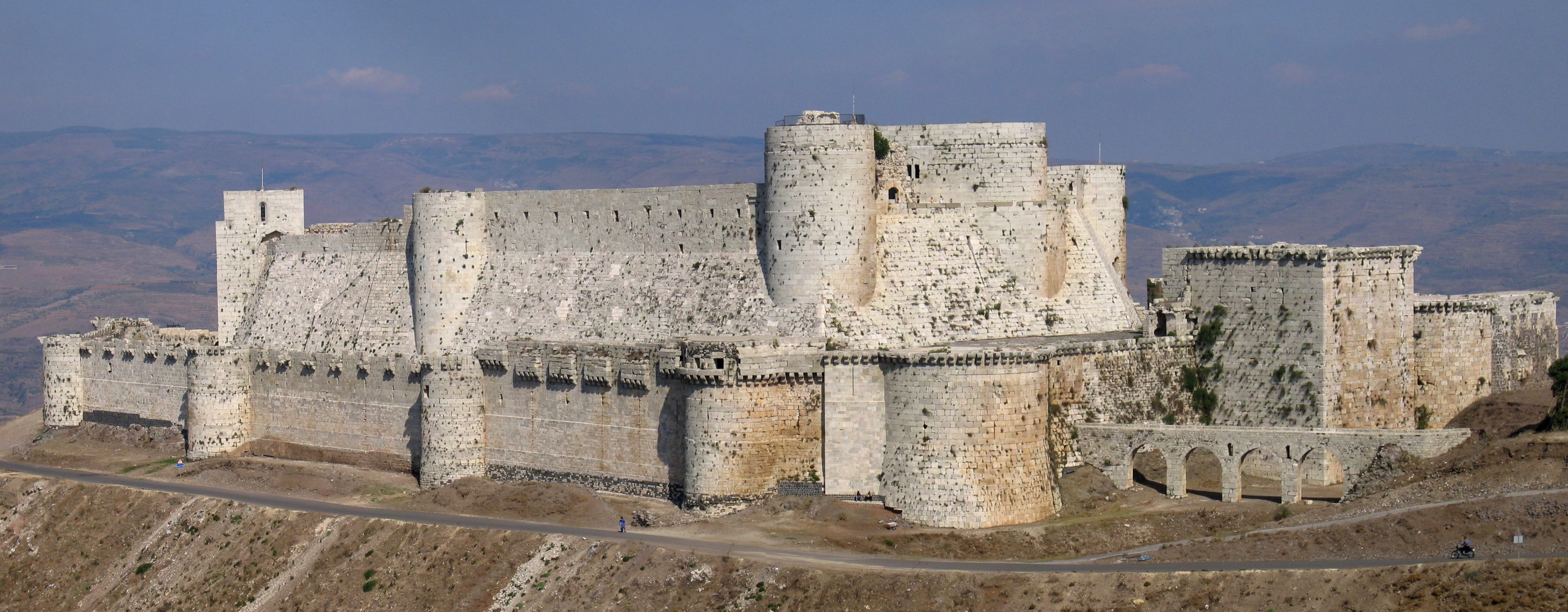 According to the historian Joshua Prawer no major European poet, theologian, scholar or historian settled in the crusader states. Some went on pilgrimage, and this is seen in new imagery and ideas in western poetry. Although they did not migrate east themselves, their output often encouraged others to journey there on pilgrimage.
Historians consider the crusader military architecture of the Middle East to demonstrate a synthesis of the European, Byzantine and Muslim traditions and to be the most original and impressive artistic achievement of the crusades. Castles were a tangible symbol of the dominance of a Latin Christian minority over a largely hostile majority population. They also acted as centres of administration. Modern historiography rejects the 19th-century consensus that Westerners learnt the basis of military architecture from the Near East, as Europe had already experienced rapid development in defensive technology before the First Crusade. Direct contact with Arab fortifications originally constructed by the Byzantines did influence developments in the east, but the lack of documentary evidence means that it remains difficult to differentiate between the importance of this design culture and the constraints of situation. The latter led to the inclusion of oriental design features such as large water reservoirs and the exclusion of occidental features such as moats.
According to the historian Joshua Prawer no major European poet, theologian, scholar or historian settled in the crusader states. Some went on pilgrimage, and this is seen in new imagery and ideas in western poetry. Although they did not migrate east themselves, their output often encouraged others to journey there on pilgrimage.
Historians consider the crusader military architecture of the Middle East to demonstrate a synthesis of the European, Byzantine and Muslim traditions and to be the most original and impressive artistic achievement of the crusades. Castles were a tangible symbol of the dominance of a Latin Christian minority over a largely hostile majority population. They also acted as centres of administration. Modern historiography rejects the 19th-century consensus that Westerners learnt the basis of military architecture from the Near East, as Europe had already experienced rapid development in defensive technology before the First Crusade. Direct contact with Arab fortifications originally constructed by the Byzantines did influence developments in the east, but the lack of documentary evidence means that it remains difficult to differentiate between the importance of this design culture and the constraints of situation. The latter led to the inclusion of oriental design features such as large water reservoirs and the exclusion of occidental features such as moats.
 Typically, crusader church design was in the
Typically, crusader church design was in the
 Primary sources. The primary sources for the Crusades are generally presented in the individual articles on each Crusade and summarized in the list of sources for the Crusades. For the First Crusade, the original Latin chronicles, including the ''
Primary sources. The primary sources for the Crusades are generally presented in the individual articles on each Crusade and summarized in the list of sources for the Crusades. For the First Crusade, the original Latin chronicles, including the ''
A history of the Crusades
The crusades
London. This edition also includes an essay on
''Histoire des croisades''
6. éd. Paris.Michaud, J. Fr., Robson, W. (1881)
The history of the crusades
New ed. London. was published by the French historian
Latin Church
, native_name_lang = la
, image = San Giovanni in Laterano - Rome.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, alt = Façade of the Archbasilica of St. John in Lateran
, caption = Archbasilica of Saint Joh ...
in the medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were intended to recover Jerusalem and its surrounding area from Islamic rule. Beginning with the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
, which resulted in the recovery of Jerusalem in 1099, dozens of Crusades were fought, providing a focal point of European history for centuries.
In 1095, Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
proclaimed the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Pope Urban's spee ...
. He encouraged military support for Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
AlexiosI against the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. The first Crusaders had a variety of motivations, including religious salvation, satisfying feudal obligations, opportunities for renown, and economic or political advantage. Later crusades were conducted by generally more organized armies, sometimes led by a king. All were granted papal indulgences
In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence (, from , 'permit') is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins". The '' Catechism of the Catholic Church'' describes an indulgence as "a remission before God o ...
. Initial successes established four Crusader states
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
: the County of Edessa
The County of Edessa (Latin: ''Comitatus Edessanus'') was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century. Ferdinandi, Sergio (2017). La Contea Franca di Edessa. Fondazione e Profilo Storico del Primo Principato Crociato nel Levante (1098-115 ...
; the Principality of Antioch
The Principality of Antioch was one of the crusader states created during the First Crusade which included parts of modern-day Turkey and Syria. The principality was much smaller than the County of Edessa or the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It extende ...
; the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establishe ...
; and the County of Tripoli
The County of Tripoli (1102–1289) was the last of the Crusader states. It was founded in the Levant in the modern-day region of Tripoli, northern Lebanon and parts of western Syria which supported an indigenous population of Christians, Druze ...
. The Crusader presence remained in the region in some form until the fall of Acre
The siege of Acre (also called the fall of Acre) took place in 1291 and resulted in the Crusaders losing control of Acre to the Mamluks. It is considered one of the most important battles of the period. Although the crusading movement continu ...
in 1291. After this, there were no further crusades to recover the Holy Land.
Concurrent military activities in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
against the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
and in northeastern Europe against pagan West Slav
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic lang ...
, Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
* Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originati ...
, and Finnic peoples (the Northern Crusades) have also been called crusades – sometimes retroactively, long after the event had ended – due to the facts that they also had central approval by the Roman Catholic Church and that the military campaigns were organized in comparable fashion, with often similar rhetoric, symbolism, and banners as applied during the campaigns in the Middle East. Other church-sanctioned campaigns called crusades were fought against heretical Christian sects (precursors of proto-Protestantism), against the Ottoman Empire, and for political reasons. Unsanctioned by the church, there were also several Popular Crusades of ordinary citizens.
Proclaimed a crusade in 1123, the struggle between the Christians and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula eventually became better known as the '' Reconquista'' in European historiography, and only ended in 1492 with the fall of the Muslim Emirate of Granada. From 1147, campaigns
Campaign or The Campaign may refer to:
Types of campaigns
* Campaign, in agriculture, the period during which sugar beets are harvested and processed
*Advertising campaign, a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme
*Bl ...
in Northern Europe against pagan tribes were considered crusades. In 1199, Pope Innocent III began the practice of proclaiming crusades against Christian heretics. In the 13th century, crusading was used against the Cathars in Languedoc and against Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
; this practice continued against the Waldensians in Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Savo ...
and the Hussites in Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
in the 15thcentury and against Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
in the 16th. From the mid-14thcentury, crusading rhetoric was used in response to the rise of the Ottoman Empire, and ended around 1699 with the War of the Holy League.
Terminology
 The term "crusade" first referred to military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to the
The term "crusade" first referred to military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
. The conflicts to which the term is applied have been extended to include other campaigns initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Roman Catholic Church against pagans and heretics, or for alleged religious ends. Crusades differed from other Christian religious wars in that they were considered a penitential exercise, and so earned participants forgiveness for all confessed sins. The term's usage can be misleading, particularly regarding the early Crusades, and the definition remains a matter of debate among contemporary historians.
At the time of the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
, , "journey", and , "pilgrimage", were used to describe the campaign. Crusader terminology remained largely indistinguishable from that of Christian pilgrimage during the 12th century. Only at the end of the century was a specific language of Crusading adopted in the form of "one signed by the cross"for a Crusader. This led to the French "the way of the cross". Bréhier, Louis René. (1908). " Crusades". In ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 4. New York. By the mid 13th century the cross became the major descriptor of the Crusades with "the cross overseas"used for crusades in the eastern Mediterranean, and "the cross this side of the sea"for those in Europe. The modern English "crusade" dates to the 17th century, with the work of Louis Malmbourg.' Strategic raiding was known as and more fundamental campaigns as .
The terms "Franks" () and "Latins" were used by the peoples of the Near East during the crusades for western Europeans, distinguishing them from the Byzantine Christians, who were known as "Greeks". " Saracen" was used for an Arab Muslim, derived from a Greek and Roman name for the nomadic peoples of the Syro-Arabian desert. Crusader sources used the term "Syrians" to describe local Christians who were members of the Greek Orthodox Church, and "Jacobites" for those who were members of the Syrian Orthodox Church. The Crusader states of Syria and Palestine were known as the " Outremer" from the French , or "the land beyond the sea".
Crusades and the Holy Land, 1095–1291
Background
The Arab-Byzantine wars from 629 to the 1050s resulted in the conquest of the Levant and Egypt by theMuslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
. Jerusalem was captured after a half-year siege in 637. In 1025, the Byzantine emperor Basil II was able to extend the empire's territorial recovery to its furthest extent in 1025, with frontiers stretching east to Iran. The empire's relationships with its Islamic neighbours were no more quarrelsome than its relationships with the Western Christians, after the East-West Schism of 1054. The political situation in the Middle East was changed by waves of Turkic migrationin particular, the arrival of the Seljuk Turks in the 10thcentury. Previously a minor ruling clan from Transoxiana, they were recent converts to Islam who migrated into Persia. They conquered Iran, Iraq and the Near East to the Seljuk Empire. Byzantium's attempted confrontation in 1071 to suppress the Seljuks' sporadic raiding led to the defeat at the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and th ...
, eventually the occupation of most of the Anatolian peninsula. In the same year, Jerusalem was taken from the Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
by the Turkish warlord Atsiz, who seized most of Syria and Palestine throughout the Middle East. The Seljuk hold on the city resulted in pilgrims reporting difficulties and the oppression of Christians.
First Crusade
 In 1074, just three years after Manzikert and the Seljuk takeover of Jerusalem, Gregory VII began planning to launch a military campaign for the liberation of the Holy Land. Twenty years later,
In 1074, just three years after Manzikert and the Seljuk takeover of Jerusalem, Gregory VII began planning to launch a military campaign for the liberation of the Holy Land. Twenty years later, Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
realized that dream, hosting the decisive Council of Piacenza and subsequent Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Pope Urban's spee ...
in November 1095, resulting in the mobilization of Western Europe to go to the Holy Land. Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos, worried about the continued advances of the Seljuks, sent envoys to these councils asking Urban for aid against the invading Turks. Urban talked of the violence of Europe and the necessity of maintaining the Peace of God; about helping Byzantium; about the crimes being committed against Christians in the east; and about a new kind of war, an armed pilgrimage, and of rewards in heaven, where remission of sins was offered to any who might die in the undertaking. The enthusiastic crowd responded with cries of '' Deus lo volt!''"God wills it!"
 Immediately after Urban's proclamation, the French priest Peter the Hermit led thousands of mostly poor Christians out of Europe in what became known as the People's Crusade. In transit through Germany, these Crusaders spawned German bands who massacred Jewish communities in what became known as the Rhineland massacres. They were destroyed in 1096 when the main body of Crusaders was annihilated at the battle of Civetot.
In response to Urban's call, members of the high aristocracy from Europe took the cross. Foremost amongst these was the elder statesman Raymond IV of Toulouse, who with bishop Adhemar of Le Puy commanded southern French forces. Other armies included: one led by Godfrey of Bouillon and his brother
Immediately after Urban's proclamation, the French priest Peter the Hermit led thousands of mostly poor Christians out of Europe in what became known as the People's Crusade. In transit through Germany, these Crusaders spawned German bands who massacred Jewish communities in what became known as the Rhineland massacres. They were destroyed in 1096 when the main body of Crusaders was annihilated at the battle of Civetot.
In response to Urban's call, members of the high aristocracy from Europe took the cross. Foremost amongst these was the elder statesman Raymond IV of Toulouse, who with bishop Adhemar of Le Puy commanded southern French forces. Other armies included: one led by Godfrey of Bouillon and his brother Baldwin of Boulogne
Baldwin I, also known as Baldwin of Boulogne (1060s – 2April 1118), was the first count of Edessa from 1098 to 1100, and king of Jerusalem from 1100 to his death in 1118. He was the youngest son of Eustace II, Count of Boulogne, and Ida of Lor ...
; forces led by Bohemond of Taranto and his nephew Tancred
Tancred or Tankred is a masculine given name of Germanic origin that comes from ''thank-'' (thought) and ''-rath'' (counsel), meaning "well-thought advice". It was used in the High Middle Ages mainly by the Normans (see French Tancrède) and espec ...
; and contingents under Robert Curthose, Stephen of Blois, Hugh of Vermandois, and Robert II of Flanders. The armies travelled to Byzantium where they were cautiously welcomed by the emperor.
Alexios persuaded many of the princes to pledge allegiance to him. He also convinced them their first objective should be Nicaea. Buoyed by their success at Civetot, the over-confident Seljuks left the city unprotected, thus enabling its capture after the siege of Nicaea in May–June 1097. The first experience of Turkish tactics occurred when a force led by Bohemond and Robert was ambushed at battle of Dorylaeum in July 1097. The Normans resisted for hours before the arrival of the main army caused a Turkish withdrawal.
The Crusader army marched to the former Byzantine city of Antioch, which had been in Muslim control since 1084. The Crusaders began the siege of Antioch in October 1097 and fought for eight months to a stalemate. Finally, Bohemond persuaded a guard in the city to open a gate. The Crusaders entered, massacring the Muslim inhabitants as well as many Christians. A force to recapture the city was raised by Kerbogha, the Seljuk atabeg of Mosul
This is a list of the rulers of the Iraqi city of Mosul.
Umayyad governors
* Muhammad ibn Marwan (ca. 685–705)
* Yusuf ibn Yahya ibn al-Hakam (ca. 685–705)
* Sa'id ibn Abd al-Malik (ca. 685–705)
* Yahya ibn Yahya al-Ghassani (719–720)
* ...
.
The discovery of the Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Lance of Longinus (named after Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his crucifixion.
Biblical references
The l ...
by mystic Peter Bartholomew may have boosted the morale of the Crusaders. The Byzantines did not march to the assistance of the Crusaders. Instead, Alexius retreated from Philomelium. The Greeks were never truly forgiven for this perceived betrayal. The Crusaders attempted to negotiate surrender but were rejected. Bohemond recognised that the only remaining option was open combat and launched a counterattack. Despite superior numbers, the Muslims retreated and abandoned the siege.
Raymond besieged Arqa in mid-February 1099 and the crusaders sent an embassy to the vizier of Egypt seeking a treaty. When Adhemar died after Antioch, there was no spiritual leader of the crusade and the discovery of the Holy Lance provoked accusations of fraud among the clerical factions. On 8 April 1099, Arnulf of Chocques, chaplain to Robert Curthose, challenged Bartholomew to an ordeal by fire. Peter underwent the ordeal and died after days of agony from his wounds, which discredited the Holy Lance as a fake. Raymond lifted the siege of Arqa in May without capturing the town and the crusade proceeded south along the Mediterranean coast. Bohemond remained in Antioch, retaining the city, despite his pledge to return it to Byzantine control, while Raymond led the remaining army. Local rulers offered little resistance. They opted for peace in return for providing provisions. The Frankish emissaries rejoined the army accompanied by representatives from Egypt. This brought added information: the Egyptians had recaptured Jerusalem from the Seljuks. The Franks offered to partition conquered territory in return for rights to the city. When the offer was refused, it became advantageous if the crusade could reach Jerusalem before the Egyptians reinforced its defences and raised a defensive army.
On 7 June 1099, the Crusaders reached Jerusalem. Many Crusaders wept upon seeing the city they had journeyed so long to reach. An initial attack on the city failed, and the siege of Jerusalem of 1099 became a stalemate, until they breached the walls on 15 July 1099. Iftikhar al-Dawla, the commander of the garrison, struck a deal with Raymond, surrendering the citadel in return for being granted safe passage to Ascalon. For two days the Crusaders massacred the inhabitants and pillaged the city. Jerusalem had been returned to Christian rule. Urban II died on 29 July 1099, fourteen days after the fall of Jerusalem to the Crusaders, but before news of the event had reached Italy. He was succeeded by Paschal II.
On July 22, 1099, a council was held in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
and Godfrey of Bouillon took the leadership, not called king but rather with the title '' Advocatus Sancti Sepulchri'' (Defender of the Holy Sepulchre). At this point, most Crusaders considered their pilgrimage complete and returned to Europe. Godfrey was left with a small forcea mere 300 knights and 2,000 foot soldiersto defend the kingdom. In August 1099, the Franks defeated an Egyptian relief force at the battle of Ascalon. The First Crusade thus ended successfully and resulted in the creation of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establishe ...
.The Kingdom of Jerusalem, 1099–1147
Godfrey of Bouillon died on 18 July 1100, likely from typhoid. The news of his death was met with mourning in Jerusalem. He was lying in state for five days, before his burial at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. The Jerusalem knights offered the kingdom to Godfrey's brother Baldwin I of Jerusalem, then Count of Edessa. Godfrey's last battle, the siege of Arsuf, would be completed by Baldwin in April 1101. Meanwhile, Dagobert of Pisa, nowLatin Patriarch of Jerusalem
The Latin Patriarchate of Jerusalem ( la, Patriarchatus Latinus Hierosolymitanus) is the Latin Catholic ecclesiastical patriarchate in Jerusalem, officially seated in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. It was originally established in 1099, wit ...
, made the same offer to Bohemond, and asking that he prevent Baldwin's expected travel to Jerusalem. But the letter was intercepted and Bohemond was captured with Richard of Salerno
Richard of Salerno ( 1060 – 1114), was a participant in the First Crusade and governor of the County of Edessa from 1104 to 1108. He was the cousin of Richard of Hauteville.
Biography
Richard was born around 1060, the third son of William of t ...
by the Danishmends after the battle of Melitene in August 1100. Baldwin I was crowned as the first king of Jerusalem on Christmas Day 1100 by Dagobert at the Church of the Nativity. Baldwin's cousin Baldwin of Bourcq, later his successor as Baldwin II, was named Count of Edessa, and Tancred became regent of Antioch during Bohemond's captivity, lasting through 1103.
Crusade of 1101
The Crusade of 1101 was initiated by Paschal II when he learned of the precarious position of the remaining forces in the Holy Land. The host consisted of four separate armies, sometimes regarded as a second wave following the First Crusade. The first army was Lombardy, led by Anselm, archbishop of Milan. They were joined by a force led by Conrad, constable to the German emperor, Henry IV. A second army, the Nivernois, was commanded by William II of Nevers. The third group from northern France was led by Stephen of Blois and Stephen of Burgundy. They were joined by Raymond of Saint-Gilles, now in the service of the emperor. The fourth army was led by William IX of Aquitaine and Welf IV of Bavaria. The Crusaders faced their old enemy Kilij Arslan and his Seljuk forces first met the Lombard and French contingents in August 1101 at the Battle of Mersivan, with the crusader camp captured. The Nivernois contingent was decimated that same month at Heraclea, with nearly the entire force wiped out, except for the count William and a few of his men. The Aquitainians and Bavarians reached Heraclea in September where again the Crusaders were massacred. The Crusade of 1101 was a total disaster both militarily and politically, showing the Muslims that the Crusaders were not invincible.Establishment of the kingdom
The reign of Baldwin I began in 1100 and oversaw the consolidation of the kingdom in the face of enemies to the north, the Seljuks, and the Fatimids to the south. Al-Afdal Shahanshah, the powerful Fatimid vizier, anxious to recover the lands lost to the Franks, initiated the First Battle of Ramla on 7 September 1101 in which his forces were narrowly defeated, by those of Baldwin I. On 17 May 1102, the Crusaders were not so lucky, suffering a major defeat at the hands of the Fatimids, under the command of al-Afdal's son Sharaf al-Ma'ali at the Second Battle of Ramla. Among the slain were veterans of the Crusade of 1101, Stephen of Blois and Stephen of Burgundy. Conrad of Germany fought so valiantly that his attackers offered to spare his life if he surrendered. The kingdom was on the verge of collapse after the defeat, recovering after the successful Battle of Jaffa on 27 May. In the north, the siege of Tripoli was begun, not to be resolved for seven years. Al-Afdal tried once more in the Third Battle of Ramla in August 1105 and was defeated. After the Crusader victory at the siege of Beirut in 1110, the Fatimid threat to the kingdom subsided for two decades. The Battle of Harran was fought in 1104, pitting the Crusader states ofEdessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene ...
and Antioch against Jikirmish
Jikirmish, also known as Jekermish, Chokurmish or Chökürmish (died in 1106), was the atabeg of Mosul from 1102 to 1106. After the death of his predecessor Kerbogha, he became the adoptive father of Imad ad-Din Zengi. Jikirmish and Sökmen of M ...
, who had replaced Kerbogha as atabeg of Mosul
This is a list of the rulers of the Iraqi city of Mosul.
Umayyad governors
* Muhammad ibn Marwan (ca. 685–705)
* Yusuf ibn Yahya ibn al-Hakam (ca. 685–705)
* Sa'id ibn Abd al-Malik (ca. 685–705)
* Yahya ibn Yahya al-Ghassani (719–720)
* ...
, and Sökmen, commander of the Seljuk forces. The ensuing Seljuk victory also resulted in the capture of Baldwin of Bourcq, then count of Edessa and later king of Jerusalem, and his cousin Joscelin of Courtenay. A Turkish adventurer Jawali Saqawa killed Jikirmish in 1106, seizing Mosul and his hostage Baldwin. Separately freed, Joscelin began negotiations with Jawali for Baldwin's release. Expelled from Mosul by Mawdud, Jawali fled with his hostage to the fortress of Qal'at Ja'bar. Jawali, in need of allies against Mawdud, accepted Joscelin's offer, releasing Baldwin in the summer of 1108.
After Bohemond was ransomed in 1103, he had resumed control of Antioch and continued the conflict with the Byzantine empire. The Byzantines had taken advantage of Bohemond's absence, retaking lands lost. Bohemond returned to Italy on late 1104 to recruit allies and gather supplies. Tancred again assumed leadership in Antioch, successfully defeating the Seljuks at the Battle of Artah in 1105, threatening Aleppo. In the meantime, his uncle began what is known as Bohemond's Crusade (or the Crusade of 1107–1108). Bohemond crossed into the Balkans and began the failed siege of Dyrrhachium. The subsequent Treaty of Devol of 1108 forced Bohemond to become vassal to the emperor, restore taken lands and other onerous terms. Bohemond never returned. He died in 1111, leaving Tancred as regent to his son Bohemond II
Bohemond II (1107/1108 – February 1130) was Prince of Taranto from 1111 to 1128 and Prince of Antioch from 1111/1119 to 1130. He was the son of Bohemond I of Antioch, Bohemond I, who in 1108 was forced to submit to the authority of the Byzantin ...
, who ignored the treaty.
The Norwegian Crusade also known as the Crusade of Sigurd Jorsalfar, king of Norway, took place from 1107 to 1110. More of a pilgrimage than a crusade, it did include the participation in military action at the siege of Sidon
The siege of Sidon was an event in the aftermath of the First Crusade. The coastal city of Sidon was captured by the forces of Baldwin I of Jerusalem and Sigurd I of Norway, with assistance from the Ordelafo Faliero, Doge of Venice.
Background ...
of 1110. Baldwin's army besieged the city by land, while the Norwegians came by sea, and the victorious Crusaders gave similar terms of surrender as given to previous victories at Arsuf in 1102 and at the siege of Acre of 1100–1104, freeing the major port of the kingdom. This Crusade marked the first time a European king visited the Holy Land.
Beginning in 1110, the Seljuks launched a series of attacks on the Crusader states, in particular Edessa, led by Mawdud. These included the Battle of Shaizar in 1111, a stalemate. At the Battle of al-Sannabra of 1113, a Crusader army led by Baldwin I was defeated by a Muslim army led by Mawdud and Toghtekin, atabeg of Damascus, whose ultimate objective was Edessa. Mawdud was unable to annihilate the Crusader forces and was soon murdered by Assassins
An assassin is a person who commits targeted murder.
Assassin may also refer to:
Origin of term
* Someone belonging to the medieval Persian Ismaili order of Assassins
Animals and insects
* Assassin bugs, a genus in the family ''Reduviid ...
. Bursuq ibn Bursuq took command of the failed attempt against Edessa in 1114. Finally, Roger of Salerno routed the last Seljuk invading army at the First Battle of Tell Danith on 14 September 1115.
Baldwin I died on 2 April 1118 after an attack on the city of Pelusium
Pelusium ( Ancient Egyptian: ; cop, /, romanized: , or , romanized: ; grc, Πηλουσιον, Pēlousion; la, Pēlūsium; Arabic: ; Egyptian Arabic: ) was an important city in the eastern extremes of Egypt's Nile Delta, 30 km to ...
on the Nile. He was buried in Jerusalem. Baldwin II of Jerusalem became king on 14 April 1118, but was there was not a formal coronation until Christmas Day 1119 due to issues concerning his wife Morphia of Melitene
Morphia of Melitene, or Morfia, or Moraphia (died c. 1126 or 1127) was queen of the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem as the wife of Baldwin II.
Marriage
Morphia was the daughter of an Armenian nobleman named Gabriel (or Khoril, in Armenian), the ...
. The early days of Baldwin II's reign included the Battle of Ager Sanguinis
In the Battle of ''Ager Sanguinis'', also known as the Battle of the Field of Blood, the Battle of Sarmada, or the Battle of Balat, Roger of Salerno's Crusader army of the Principality of Antioch was annihilated by the army of Ilghazi of Mardin, ...
, the Field of Blood, on 28 June 1119. At Ager Sanguinis, an army led by Ilghazi
Najm ad-Din Ilghazi ibn Artuq (died November 8, 1122) was the Turkmen Artukid ruler of Mardin from 1107 to 1122. He was born into the Oghuz tribe of Döğer.
Biography
His father Artuk Bey was the founder of the Artukid dynasty, and had be ...
annihilated the Antiochian forces led by Roger of Salerno who was killed during the battle. The Muslim victory was short-lived, with Baldwin II and Pons of Tripoli narrowly defeating Ilghazi's army at the Second Battle of Tell Danith on 14 August 1119.
On 16 January 1120, Baldwin II and the new patriarch Warmund of Jerusalem held the Council of Nablus, establishing a rudimentary set of rules for governing the kingdom now known as the ''assizes'' of Jerusalem. The formal establishment of the Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
was likely also granted by the council, complementing the military arm of the Knights Hospitaller that was protecting pilgrims to the Holy Land. Both military orders were accumulating holdings in the kingdom and Crusader states, with the Hospitallers eventually obtaining the famous Krak des Chevaliers, an important military and administrative center.
The Venetian Crusade
The Venetian Crusade of 1122–1124 was an expedition to the Holy Land launched by the Republic of Venice that succeeded in capturing Tyre.
It was an important victory at the start of a period when the Kingdom of Jerusalem would expand to it ...
, also known as the Crusade of Calixtus II, was conducted from 1122 to 1124. The Western participants included those from the Republic of Venice as well as Pons of Tripoli. The actions resulted in the successful siege of Tyre, taking the city from the Damascene atabeg Toghtekin. This marked a major victor for Baldwin II prior to his second captivity in 1123.
In 1123, Baldwin II led a raid to Sarūj in order to rescue hostages held by Belek Ghazi and was also captured. Belek died in May 1124 and Baldwin II was seized by Ilghazi's son, Timurtash, who commenced negotiations for Baldwin's release. After a portion of the ransom was paid, additional hostages, to include Baldwin's youngest daughter Jovetta, were provided secure the payment of the balance, Baldwin II was released from the Citadel of Aleppo on 29 August 1124. Jovetta was held by il-Bursuqi and were ransomed by Baldwin II in 1125 using his spoils from the Battle of Azaz of 1125.
Toghtekin died in February 1128, and Baldwin II began the Crusade of 1129, also known as the Damascus Crusade, shortly thereafter. The objective was Damascus, now led by the new atabeg Taj al-Muluk Buri, the son of Toghtekin. The Crusaders were able to capture the town of Banias, but were unable to take Damascus despite coming within six miles of the town.
Baldwin II and Morphia married their eldest daughter Melisende of Jerusalem
Melisende (1105 – 11 September 1161) was Queen of Jerusalem from 1131 to 1153, and regent for her son between 1153 and 1161, while he was on campaign. She was the eldest daughter of King Baldwin II of Jerusalem, and the Armenian princess M ...
to Fulk V of Anjou
Fulk ( la, Fulco, french: Foulque or ''Foulques''; c. 1089/1092 – 13 November 1143), also known as Fulk the Younger, was the count of Anjou (as Fulk V) from 1109 to 1129 and the king of Jerusalem with his wife from 1131 to his death. During t ...
in 1129 in anticipation of a royal succession. Baldwin II fell ill in Antioch and died on 21 August 1131. Fulk and Melisende were crowned joint rulers of Jerusalem on 14 September 1131 in the same church where Baldwin II had been laid to rest. Fulk assumed full control of the government, excluding Melisende, as he favored fellow Angevins to the native nobility.
The rise of Zengi
At the same time, the advent of Imad ad-Din Zengi saw the Crusaders threatened by a Muslim ruler who would introduce ''jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
'' to the conflict, joining the powerful Syrian emirates in a combined effort against the Franks. He became atabeg of Mosul
This is a list of the rulers of the Iraqi city of Mosul.
Umayyad governors
* Muhammad ibn Marwan (ca. 685–705)
* Yusuf ibn Yahya ibn al-Hakam (ca. 685–705)
* Sa'id ibn Abd al-Malik (ca. 685–705)
* Yahya ibn Yahya al-Ghassani (719–720)
* ...
in September 1127 and used this to expand his control to Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
in June 1128. In 1135, Zengi moved against Antioch and, when the Crusaders failed to put an army into the field to oppose him, he captured several important Syrian town. He defeated Fulk at the Battle of Ba'rin of 1137, seizing Ba'rin Castle.
In 1137, Zengi invaded Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
*Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in t ...
, killing the count Pons of Tripoli. Fulk intervened, but Zengi's troops captured Pons' successor Raymond II of Tripoli, and besieged Fulk in the border castle of Montferrand. Fulk surrendered the castle and paid Zengi a ransom for his and Raymond's freedom. John II Komnenos, emperor since 1118, reasserted Byzantine claims to Cilicia and Antioch, compelling Raymond of Poitiers to give homage. In April 1138, the Byzantines and Franks jointly besieged Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
and, with no success, began the Siege of Shaizar, abandoning it a month later.
On 13 November 1143, while the royal couple were in Acre, Fulk was killed in a hunting accident. On Christmas Day 1143, their son Baldwin III of Jerusalem was crowned co-ruler with his mother. That same year, having prepared his army for a renewed attack on Antioch, John II Komnenos went hunting wild boar, cutting himself with a poisoned arrow. He died on 8 April 1143 and was succeeded as emperor by his son Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos ( el, Μανουήλ Κομνηνός, translit=Manouíl Komnenos, translit-std=ISO; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Romanization of Greek, Latinized Comnenus, also called Porphyrogennetos (; "born in the purple"), w ...
.Baldwin, Marshall W. (1969).Chapter XVII. The Latin States under Baldwin III and Amalric I, 1143-1174
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 528-563. Following John's death, the Byzantine army withdrew, leaving Zengi unopposed. Fulk's death later in the year left
Joscelin II of Edessa
Joscelin II of Edessa (died 1159) was the fourth and last ruling count of Edessa. He was son of his predecessor Joscelin I of Edessa and Beatrice, daughter of Constantine I of Armenia.
Biography
In 1122, Joscelin I was captured by Belek Ghazi. ...
with no powerful allies to help defend Edessa. Zengi came north to begin the first siege of Edessa, arriving on 28 November 1144. The city had been warned of his arrival and was prepared for a siege, but there was little they could do. Zengi realized there was no defending force and surrounded the city. The walls collapsed on 24 December 1144. Zengi's troops rushed into the city, killing all those who were unable to flee. All the Frankish prisoners were executed, but the native Christians were allowed to live. The Crusaders were dealt their first major defeat.
Zengi was assassinated by a slave on 14 September 1146 and was succeeded in the Zengid dynasty by his son Nūr-ad-Din. The Franks recaptured the city during the Second Siege of Edessa of 1146 by stealth but could not take or even properly besiege the citadel. After a brief counter-siege, Nūr-ad-Din took the city. The men were massacred, with the women and children enslaved, and the walls razed.
Second Crusade
The fall of Edessa caused great consternation in Jerusalem and Western Europe, tampering the enthusiastic success of the First Crusade. Calls for a new crusadetheSecond Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusa ...
were immediate, and was the first to be led by European kings. Concurrent campaigns as part of the '' Reconquista'' and Northern Crusades are also sometimes associated with this Crusade.Berry, Virginia G. (1969).Chapter XV. The Second Crusade
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 463-512. The aftermath of the Crusade saw the Muslim world united around Saladin, leading to the fall of Jerusalem. Gibb, Hamilton A. R. (1969).
Chapter XVIII. The Rise of Saladin, 1169-1189
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 563-589.
The Second Crusade
Eugene III, recently elected pope, issued the bull '' Quantum praedecessores'' in December 1145 calling for a new crusade, one that would be more organized and centrally controlled than the First. The armies would be led by the strongest kings of Europe and a route that would be pre-planned. The pope called on Bernard of Clairvaux to preach the Second Crusade, granting the same indulgences which had accorded to the First Crusaders. Among those answering the call were by two European kings,Louis VII of France
Louis VII (1120 – 18 September 1180), called the Younger, or the Young (french: link=no, le Jeune), was King of the Franks from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI (hence the epithet "the Young") and married Duchess ...
and Conrad III of Germany
Conrad III (german: Konrad; it, Corrado; 1093 or 1094 – 15 February 1152) of the Hohenstaufen dynasty was from 1116 to 1120 Duke of Franconia, from 1127 to 1135 anti-king of his predecessor Lothair III and from 1138 until his death in 1152 k ...
. Louis, his wife, Eleanor of Aquitaine, and many princes and lords prostrated themselves at the feet of Bernard in order to take the cross. Conrad and his nephew Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
also received the cross from the hand of Bernard.
Conrad III and the German contingent planned to leave for the Holy Land at Easter, but did not depart until May 1147. When the German army began to cross Byzantine territory, emperor Manuel I had his troops posted to ensure against trouble. A brief Battle of Constantinople in September ensued, and their defeat at the emperor's hand convinced the Germans to move quickly to Asia Minor. Without waiting for the French contingent, Conrad III engaged the Seljuks of Rûm under sultan Mesud I, son and successor of Kilij Arslan Kilij Arslan, meaning ''Sword Lion'' in Turkish, was the name of four sultans of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm:
* Kilij Arslan I reigned as of 1092, died 1107
*Kilij Arslan II
Kilij Arslan II ( 1ca, قِلِج اَرسلان دوم) or ʿIzz ad-D� ...
, the nemesis of the First Crusade. Mesud and his forces almost totally destroyed Conrad's contingent at the Second Battle of Dorylaeum on 25 October 1147.
The French contingent departed in June 1147. In the meantime, Roger II of Sicily
Roger II ( it, Ruggero II; 22 December 1095 – 26 February 1154) was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily
Roger I ( it, Ruggero I, Arabic: ''رُجار'', ''Rujār''; Maltese: ''Ruġġieru'', – 22 June 1101), nicknamed Rog ...
, an enemy of Conrad's, had invaded Byzantine territory. Manuel I needed all his army to counter this force, and, unlike the armies of the First Crusade, the Germans and French entered Asia with no Byzantine assistance. The French met the remnants of Conrad's army in northern Turkey, and Conrad joined Louis's force. They fended off a Seljuk attack at the Battle of Ephesus on 24 December 1147. A few days later, they were again victorious at the Battle of the Meander
The Battle of the Meander took place in December 1147, during the Second Crusade. The French crusader army, led by Louis VII of France, successfully fended off an ambush by the Seljuks of Rum at the Meander River.
Background
King Louis VII ...
. Louis was not as lucky at the Battle of Mount Cadmus on 6 January 1148 when the army of Mesud inflicted heavy losses on the Crusaders. Shortly thereafter, they sailed for Antioch, almost totally destroyed by battle and sickness.
The Crusader army arrived at Antioch on 19 March 1148 with the intent on moving to retake Edessa, but Baldwin III of Jerusalem and the Knights Templar had other ideas. The Council of Acre was held on 24 June 1148, changing the objective of the Second Crusade to Damascus, a former ally of the kingdom that had shifted its allegiance to that of the Zengids. The Crusaders fought the Battle of Bosra with the Damascenes in the summer of 1147, with no clear winner. Bad luck and poor tactics of the Crusaders led to the disastrous five-day siege of Damascus from 24 to 28 July 1148. The barons of Jerusalem withdrew support and the Crusaders retreated before the arrival of a relief army led by Nūr-ad-Din. Morale fell, hostility to the Byzantines grew and distrust developed between the newly arrived Crusaders and those that had made the region their home after the earlier crusades. The French and German forces felt betrayed by the other, lingering for a generation due to the defeat, to the ruin of the Christian kingdoms in the Holy Land.
In the spring of 1147, Eugene III authorized the expansion of his mission into the Iberian peninsula, equating these campaigns against the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
with the rest of the Second Crusade. The successful Siege of Lisbon, from 1 July to 25 October 1147, was followed by the six-month siege of Tortosa, ending on 30 December 1148 with a defeat for the Moors. In the north, some Germans were reluctant to fight in the Holy Land while the pagan Wends were a more immediate problem. The resulting Wendish Crusade of 1147 was partially successful but failed to convert the pagans to Christianity.
The disastrous performance of this campaign in the Holy Land damaged the standing of the papacy, soured relations between the Christians of the kingdom and the West for many years, and encouraged the Muslims of Syria to even greater efforts to defeat the Franks. The dismal failures of this Crusade then set the stage for the fall of Jerusalem, leading to the Third Crusade.
Nūr-ad-Din and the rise of Saladin
In the first major encounter after the Second Crusade, Nūr-ad-Din's forces then destroyed the Crusader army at theBattle of Inab
The Battle of Inab, also called Battle of Ard al-Hâtim or Fons Muratus, was fought on 29 June 1149, during the Second Crusade. The Zengid army of Atabeg Nur ad-Din Zangi destroyed the combined army of Prince Raymond of Poitiers and the Assassi ...
on 29 June 1149. Raymond of Poitiers, as prince of Antioch, came to the aid of the besieged city. Raymond was killed and his head was presented to Nūr-ad-Din, who forwarded it to the caliph al-Muqtafi in Baghdad. In 1150, Nūr-ad-Din defeated Joscelin II of Edessa
Joscelin II of Edessa (died 1159) was the fourth and last ruling count of Edessa. He was son of his predecessor Joscelin I of Edessa and Beatrice, daughter of Constantine I of Armenia.
Biography
In 1122, Joscelin I was captured by Belek Ghazi. ...
for a final time, resulting in Joscelin being publicly blinded, dying in prison in Aleppo in 1159. Later that year, at the Battle of Aintab
In the Battle of Aintab in August 1150, a Crusader force commanded by King Baldwin III of Jerusalem repelled the attacks of Nur ad-Din Zangi of Aleppo and evacuated the Latin Christian residents of the County of Edessa. This was both a tactica ...
, he tried but failed to prevent Baldwin III's evacuation of the residents of Turbessel. The unconquered portions of the County of Edessa would nevertheless fall to the Zengids within a few years. In 1152, Raymond II of Tripoli became the first Frankish victim of the Assassins
An assassin is a person who commits targeted murder.
Assassin may also refer to:
Origin of term
* Someone belonging to the medieval Persian Ismaili order of Assassins
Animals and insects
* Assassin bugs, a genus in the family ''Reduviid ...
. Later that year, Nūr-ad-Din captured and burned Tortosa, briefly occupying the town, before it was taken by the Knights Templar as a military headquarters.
 After the Siege of Ascalon ended on 22 August 1153 with a Crusader victory and Damascus was taken by Nūr-ad-Din the next year, uniting all of Syria under Zengid rule. In 1156, Baldwin III was forced into a treaty with Nūr-ad-Din, and later entered into an alliance with the Byzantine Empire. On 18 May 1157, Nūr-ad-Din began a siege on the Knights Hospitaller contingent at Banias, with the Grand Master Bertrand de Blanquefort captured. Baldwin III was able to break the siege, only to be ambushed at Jacob's Ford in June. Reinforcements from Antioch and Tripoli were able to relieve the besieged Crusaders. Bertrand's captivity lasted until 1159, when emperor Manuel I negotiated an alliance with Nūr-ad-Din against the Seljuks.
Baldwin III died on 10 February 1163, and Amalric of Jerusalem was crowned as king of Jerusalem eight days later. He undertook a series of four
After the Siege of Ascalon ended on 22 August 1153 with a Crusader victory and Damascus was taken by Nūr-ad-Din the next year, uniting all of Syria under Zengid rule. In 1156, Baldwin III was forced into a treaty with Nūr-ad-Din, and later entered into an alliance with the Byzantine Empire. On 18 May 1157, Nūr-ad-Din began a siege on the Knights Hospitaller contingent at Banias, with the Grand Master Bertrand de Blanquefort captured. Baldwin III was able to break the siege, only to be ambushed at Jacob's Ford in June. Reinforcements from Antioch and Tripoli were able to relieve the besieged Crusaders. Bertrand's captivity lasted until 1159, when emperor Manuel I negotiated an alliance with Nūr-ad-Din against the Seljuks.
Baldwin III died on 10 February 1163, and Amalric of Jerusalem was crowned as king of Jerusalem eight days later. He undertook a series of four invasions of Egypt
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
from 1163 to 1169, taking advantage of weaknesses of the Fatimids. Nūr-ad-Din's intervention in the first invasion allowed his general Shirkuh, accompanied by his nephew Saladin, to enter Egypt. Shawar, the deposed vizier to the Fatimid caliph al-Adid, allied with Amalric I, attacking Shirkuh at the second siege of Bilbeis beginning in August 1164, following Amalric's unsuccessful first siege in September 1163. This action left the Holy Land lacking in defenses, and Nūr-ad-Din defeated a Crusader forces at the Battle of Harim in August 1164, capturing most of the Franks' leaders.
After the sacking of Bilbeis, the Crusader-Egyptian force was to meet Shirkuh's army in the indecisive Battle of al-Babein on 18 March 1167. In 1169, both Shawar and Shirkuh died, and al-Adid appointed Saladin as vizier. Saladin, with reinforcements from Nūr-ad-Din, defeated a massive Crusader-Byzantine force at the siege of Damietta in late October. This gained Saladin the attention of the Assassins, with attempts on his life in January 1175 and again on 22 May 1176.
Baldwin IV of Jerusalem became king on 5 July 1174 at the age of 13. As a leper he was not expected to live long, and served with a number of regents, and served as co-ruler with his cousin Baldwin V of Jerusalem
Baldwin V (1177 or 1178August 1186) was King of Jerusalem who reigned together with his uncle Baldwin IV from 1183 to 1185 and, after his uncle's death, as the sole king from 1185 to his death. Baldwin IV's leprosy meant that he could not hav ...
beginning in 1183. Baldwin IV, Raynald of Châtillon and the Knights Templar defeated Saladin at the celebrated Battle of Montgisard on 25 November 1177. In June 1179, the Crusaders were defeated at the Battle of Marj Ayyub, and in August the unfinished castle at Jacob's Ford fell to Saladin, with the slaughter of half its Templar garrison. However, the kingdom repelled his attacks at the Battle of Belvoir Castle in 1182 and later in the Siege of Kerak of 1183.
The fall of Jerusalem
Baldwin V became sole king upon the death of his uncle in 1185 under the regency of Raymond III of Tripoli. Raymond negotiated a truce with Saladin which went awry when the king died in the summer of 1186. His mother Sibylla of Jerusalem and her husband Guy of Lusignan were crowned as queen and king of Jerusalem in the summer of 1186, shortly thereafter. They immediately had to deal with the threat posed by Saladin. Despite his defeat at the Battle of al-Fule in the fall of 1183, Saladin increased his attacks against the Franks, leading to their defeat at the Battle of Cresson on 1 May 1187. Guy of Lusignan responded by raising the largest army that Jerusalem had ever put into the field. Saladin lured this force into inhospitable terrain without water supplies and routed them at theBattle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of t ...
on 4 July 1187. One of the major commanders was Raymond III of Tripoli who saw his force slaughtered, with some knights deserting to the enemy, and narrowly escaping, only to be regarded as a traitor and coward. Guy of Lusignan was one of the few captives of Saladin's after the battle, along with Raynald of Châtillon and Humphrey IV of Toron. Raynald was beheaded, settling an old score. Guy and Humphrey were imprisoned in Damascus and later released in 1188.
As a result of his victory, much of Palestine quickly fell to Saladin. The siege of Jerusalem began on 20 September 1187 and the Holy City was surrendered to Saladin by Balian of Ibelin on 2 October. According to some, on 19October 1187, Urban III died upon of hearing of the defeat. Jerusalem was once again in Muslim hands. Many in the kingdom fled to Tyre, and Saladin's subsequent attack at the siege of Tyre beginning in November 1187 was unsuccessful. The later siege of Safed in late 1188 completed Saladin's conquest of the Holy Land.Baldwin, Marshall W. (1969).Chapter XIX. The Decline and Fall of Jerusalem, 1174-1189
. In Setton, Kenneth M.; Baldwin, Marshall W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume One. The First Hundred Years''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 590-621.
Third Crusade
The years following the founding of the Kingdom of Jerusalem were met with multiple disasters. TheSecond Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusa ...
did not achieve its goals, and left the Muslim East in a stronger position with the rise of Saladin. A united Egypt–Syria led to the loss of Jerusalem itself, and Western Europe had no choice but to launch the Third Crusade, this time led by the kings of Europe.
The news of the disastrous defeat at the battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of t ...
and subsequent fall of Jerusalem gradually reached Western Europe. Urban III died shortly after hearing the news, and his successor Gregory VIII issued the bull '' Audita tremendi'' on 29 October 1187 describing the events in the East and urging all Christians to take up arms and go to the aid of those in the Kingdom of Jerusalem, calling for a new crusade to the Holy Landthe Third Crusadeto be led by Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
and Richard I of England.
The Crusades of Frederick Barbarossa and Henry VI
". In Setton, K,. ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II.'' pp. 87-122. Frederick sent an ultimatum to Saladin, demanding the return of Palestine and challenging him to battle and in May 1189, Frederick's host departed for Byzantium. In March 1190, Frederick embarked to Asia Minor. The armies coming from western Europe pushed on through Anatolia, defeating the Turks and reaching as far as
Cilician Armenia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, ...
. On 10 June 1190, Frederick drowned near Silifke Castle
Silifke Castle ( tr, Silifke kalesi) is a medieval castle in Turkey.
Geography
The castle is in Silifke district of Mersin Province. It is situated to the west of Silifke city center, to the south of Göksu River (''Calydanus'' of the antiquity) ...
. His death caused several thousand German soldiers to leave the force and return home. The remaining German army moved under the command of the English and French forces that arrived shortly thereafter.
Richard the Lionheart had already taken the cross as the Count of Poitou in 1187. His father Henry II of England and Philip II of France had done so on 21 January 1188 after receiving news of the fall of Jerusalem to Saladin. Richard I and Philip II of France agreed to go on the Crusade in January 1188. Arriving in the Holy Land, Richard led his support to the stalemated siege of Acre. The Muslim defenders surrendered on 12 July 1191. Richard remained in sole command of the Crusader force after the departure of Philip II on 31 July 1191. On 20 August 1191, Richard had more than 2000 prisoners beheaded at the massacre of Ayyadieh. Saladin subsequently ordered the execution of his Christian prisoners in retaliation.
Richard moved south, defeating Saladin's forces at the battle of Arsuf
The Battle of Arsuf took place on 7 September 1191, as part of the Third Crusade. It saw a multi-national force of Crusaders, led by Richard I of England, defeat a significantly larger army of the Ayyubid Sultanate, led by Saladin.
Followin ...
on 7 September 1191. Three days later, Richard took Jaffa
Jaffa, in Hebrew Yafo ( he, יָפוֹ, ) and in Arabic Yafa ( ar, يَافَا) and also called Japho or Joppa, the southern and oldest part of Tel Aviv-Yafo, is an ancient port city in Israel. Jaffa is known for its association with the b ...
, held by Saladin since 1187, and advanced inland towards Jerusalem. On 12 December 1191 Saladin disbanded the greater part of his army. Learning this, Richard pushed his army forward, to within 12 miles from Jerusalem before retreating back to the coast. The Crusaders made another advance on Jerusalem, coming within sight of the city in June before being forced to retreat again. Hugh III of Burgundy, leader of the Franks, was adamant that a direct attack on Jerusalem should be made. This split the Crusader army into two factions, and neither was strong enough to achieve its objective. Without a united command the army had little choice but to retreat back to the coast.
On 27 July 1192, Saladin's army began the battle of Jaffa, capturing the city. Richard's forces stormed Jaffa from the sea and the Muslims were driven from the city. Attempts to retake Jaffa failed and Saladin was forced to retreat. On 2 September 1192 Richard and Saladin entered into the Treaty of Jaffa Treaty of Jaffa may refer to:
*Treaty of Jaffa (1192)
The Treaty of Jaffa, more seldom referred to as the Treaty of Ramla or the treaty of 1192, was a truce agreed to during the Crusades. It was signed on 1 or 2 September 1192 A.D. (20th of Sha'b ...
, providing that Jerusalem would remain under Muslim control, while allowing unarmed Christian pilgrims and traders to freely visit the city. This treaty ended the Third Crusade.
Three years later, Henry VI launched the Crusade of 1197. While his forces were en route to the Holy Land, Henry VI died in Messina on 28 September 1197. The nobles that remained captured the Levant coast between Tyre and Tripoli before returning to Germany. The Crusade ended on 1 July 1198 after capturing Sidon and Beirut.
Fourth Crusade
 In 1198, the recently elected Pope Innocent III announced a new crusade, organised by three Frenchmen: Theobald of Champagne; Louis of Blois; and
In 1198, the recently elected Pope Innocent III announced a new crusade, organised by three Frenchmen: Theobald of Champagne; Louis of Blois; and Baldwin of Flanders
Baldwin I ( nl, Boudewijn; french: Baudouin; July 1172 – ) was the first Emperor of the Latin Empire of Constantinople; Count of Flanders (as Baldwin IX) from 1194 to 1205 and Count of Hainaut (as Baldwin VI) from 1195-1205. Baldwin was on ...
. After Theobald's premature death, the Italian Boniface of Montferrat replaced him as the new commander of the campaign. They contracted with the Republic of Venice for the transportation of 30,000 crusaders at a cost of 85,000 marks. However, many chose other embarkation ports and only around 15,000 arrived in Venice. The Doge of Venice Enrico Dandolo proposed that Venice would be compensated with the profits of future conquests beginning with the seizure of the Christian city of Zara. Pope Innocent III's role was ambivalent. He only condemned the attack when the siege started. He withdrew his legate to disassociate from the attack but seemed to have accepted it as inevitable. Historians question whether for him, the papal desire to salvage the crusade may have outweighed the moral consideration of shedding Christian blood. The crusade was joined by King Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208) was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of his older brother Emperor Henry VI in 1197 meant that the Hohenstaufen rule (whi ...
, who intended to use the Crusade to install his exiled brother-in-law, Alexios IV Angelos, as Emperor. This required the overthrow of Alexios III Angelos
Alexios III Angelos ( gkm, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνός Ἄγγελος, Alexios Komnēnos Angelos; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnen ...
, the uncle of AlexiosIV. Alexios IV offered the crusade 10,000 troops, 200,000 marks and the reunion of the Greek Church with Rome if they toppled his uncle Emperor Alexios III. When the crusade entered Constantinople, AlexiosIII fled and was replaced by his nephew. The Greek resistance prompted AlexiosIV to seek continued support from the crusade until he could fulfil his commitments. This ended with his murder in a violent anti-Latin revolt. The crusaders were without seaworthy ships, supplies or food. Their only escape route was through the city, taking by force what Alexios had promised and the new anti-westerner Byzantine ruler Alexios V Doukasdenied them. The Sack of Constantinople involved three days of pillaging churches and killing much of the Greek Orthodox Christian populace. This sack was not unusual considering the violent military standards of the time, but contemporaries such as Innocent III and Ali ibn al-Athir saw it as an atrocity against centuries of classical and Christian civilisation.
Fifth Crusade
The Fifth Crusade (1217–1221) was a campaign by Western Europeans to reacquire Jerusalem and the rest of the Holy Land by first conquering Egypt, ruled by the sultanal-Adil
Al-Adil I ( ar, العادل, in full al-Malik al-Adil Sayf ad-Din Abu-Bakr Ahmed ibn Najm ad-Din Ayyub, ar, الملك العادل سيف الدين أبو بكر بن أيوب, "Ahmed, son of Najm ad-Din Ayyub, father of Bakr, the Just K ...
, brother of Saladin. In 1213, Innocent III called for another Crusade at the Fourth Lateran Council, and in the papal bull '' Quia maior''. Innocent died in 1216 and was succeeded by Honorius III who immediately called on Andrew II of Hungary and Frederick II of Germany to lead a Crusade. Frederick had taken the cross in 1215, but hung back, with his crown still in contention, and Honorius delayed the expedition.Van Cleve, Thomas C. (1977).The Fifth Crusade
. In Setton, K., ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II''. pp. 343-376.
 Andrew II left for Acre in August 1217, joining John of Brienne, king of Jerusalem. The initial plan of a two-prong attack in Syria and in Egypt was abandoned and instead the objective became limited operations in Syria. After accomplishing little, the ailing Andrew returned return to Hungary early in 1218. As it became clear that Frederick II was not coming to east, the remaining commanders began the planning to attack the Egyptian port of Damietta.
The fortifications of Damietta were impressive, and included the ''Burj al-Silsilah''the chain towerwith massive chains that could stretch across the Nile. The siege of Damietta began in June 1218 with a successful assault on the tower. The loss of the tower was a great shock to the Ayyubids, and the sultan al-Adil died soon thereafter. He was succeeded as sultan by his son al-Kamil. Further offensive action by the Crusaders would have to wait until the arrival of additional forces, including legate Pelagius with a contingent of Romans. A group from England arrived shortly thereafter.
By February 1219, the Crusaders now had Damietta surrounded, and al-Kamil opened negotiations with the Crusaders, asking for envoys to come to his camp. He offered to surrender the kingdom of Jerusalem, less the fortresses of al-Karak and Krak de Montréal, guarding the road to Egypt, in exchange for the evacuation of Egypt. John of Brienne and the other secular leaders were in favor of the offer, as the original objective of the Crusade was the recovery of Jerusalem. But Pelagius and the leaders of the Templars and Hospitallers refused. Later,
Andrew II left for Acre in August 1217, joining John of Brienne, king of Jerusalem. The initial plan of a two-prong attack in Syria and in Egypt was abandoned and instead the objective became limited operations in Syria. After accomplishing little, the ailing Andrew returned return to Hungary early in 1218. As it became clear that Frederick II was not coming to east, the remaining commanders began the planning to attack the Egyptian port of Damietta.
The fortifications of Damietta were impressive, and included the ''Burj al-Silsilah''the chain towerwith massive chains that could stretch across the Nile. The siege of Damietta began in June 1218 with a successful assault on the tower. The loss of the tower was a great shock to the Ayyubids, and the sultan al-Adil died soon thereafter. He was succeeded as sultan by his son al-Kamil. Further offensive action by the Crusaders would have to wait until the arrival of additional forces, including legate Pelagius with a contingent of Romans. A group from England arrived shortly thereafter.
By February 1219, the Crusaders now had Damietta surrounded, and al-Kamil opened negotiations with the Crusaders, asking for envoys to come to his camp. He offered to surrender the kingdom of Jerusalem, less the fortresses of al-Karak and Krak de Montréal, guarding the road to Egypt, in exchange for the evacuation of Egypt. John of Brienne and the other secular leaders were in favor of the offer, as the original objective of the Crusade was the recovery of Jerusalem. But Pelagius and the leaders of the Templars and Hospitallers refused. Later, Francis of Assisi
Giovanni di Pietro di Bernardone, better known as Saint Francis of Assisi ( it, Francesco d'Assisi; – 3 October 1226), was a mystic Italian Catholic friar, founder of the Franciscans, and one of the most venerated figures in Christianit ...
arrived to negotiate unsuccessfully with the sultan.
In November 1219, the Crusaders entered Damietta and found it abandoned, al-Kamil having moved his army south. In the captured city, Pelagius was unable to prod the Crusaders from their inactivity, and many returned home, their vow fulfilled. Al-Kamil took advantage of this lull to reinforce his new camp at Mansurah, renewing his peace offering to the Crusaders, which was again refused. Frederick II sent troops and word that he would soon follow, but they were under orders not to begin offensive operations until he had arrived.
In July 1221, Pelagius began to advance to the south. John of Brienne argued against the move, but was powerless to stop it. Already deemed a traitor for opposing the plans and threatened with excommunication, John joined the force under the command of the legate. In the ensuing Battle of Mansurah in late August, al-Kamil had the sluices along the right bank of the Nile opened, flooding the area and rendering battle impossible. Pelagius had no choice but to surrender.
The Crusaders still had some leverage as Damietta was well-garrisoned. They offered the sultan a withdrawal from Damietta and an eight-year truce in exchange for allowing the Crusader army to pass, the release of all prisoners, and the return of the relic of the True Cross. Prior to the formal surrender of Damietta, the two sides would maintain hostages, among them John of Brienne and Hermann of Salza for the Franks side and a son of al-Kamil for Egypt. The masters of the military orders were dispatched to Damietta, where the forces were resistant to giving up, with the news of the surrender, which happened on 8 September 1221. The Fifth Crusade was over, a dismal failure, unable to even gain the return of the piece of the True Cross.
Sixth Crusade
 The
The Sixth Crusade
The Sixth Crusade (1228–1229), also known as the Crusade of Frederick II, was a military expedition to recapture Jerusalem and the rest of the Holy Land. It began seven years after the failure of the Fifth Crusade and involved very little actua ...
(1228–1229) was a military expedition to recapture the city of Jerusalem. It began seven years after the failure of the Fifth Crusade and involved very little actual fighting. The diplomatic maneuvering of Frederick IIFranz Kampers (1909). " Frederick II". In ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 6. New York: Robert Appleton Company. resulted in the Kingdom of Jerusalem regaining some control over Jerusalem for much of the ensuing fifteen years. The Sixth Crusade is also known as the Crusade of Frederick II.Van Cleve, Thomas C. (1977).The Crusade of Frederick II
. In Setton, K. ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II''. pp. 377-448. Of all the European sovereigns, only Frederick II, the Holy Roman Emperor, was in a position to regain Jerusalem. Frederick was, like many of the 13th-century rulers, a serial ''crucesignatus'', having taken the cross multiple times since 1215. After much wrangling, an onerous agreement between the emperor and Pope Honorius III was signed on 25 July 1225 at San Germano. Frederick promised to depart on the Crusade by August 1227 and remain for two years. During this period, he was to maintain and support forces in Syria and deposit escrow funds at Rome in gold. These funds would be returned to the emperor once he arrived at Acre. If he did not arrive, the money would be employed for the needs of the Holy Land. Frederick II would go on the Crusade as king of Jerusalem. He married John of Brienne's daughter Isabella II by proxy in August 1225 and they were formally married on 9 November 1227. Frederick claimed the kingship of Jerusalem despite John having been given assurances that he would remain as king. Frederick took the crown in December 1225. Frederick's first royal decree was to grant new privileges on the Teutonic Knights, placing them on equal footing as the Templars and Hospitallers. After the Fifth Crusade, the Ayyubid sultan al-Kamil became involved in civil war in Syria and, having unsuccessfully tried negotiations with the West beginning in 1219, again tried this approach, offering return of much of the Holy Land in exchange for military support. Becoming pope in 1227, Gregory IX was determined to proceed with the Crusade. The first contingents of Crusaders then sailed in August 1227, joining with forces of the kingdom and fortifying the coastal towns. The emperor was delayed while his ships were refitted. He sailed on 8 September 1227, but before they reached their first stop, Frederick was struck with the plague and disembarked to secure medical attention. Resolved to keep his oath, he sent his fleet on to Acre. He sent his emissaries to inform Gregory IX of the situation, but the pope did not care about Frederick's illness, just that he had not lived up to his agreement. Frederick was excommunicated on 29 September 1227, branded a wanton violator of his sacred oath taken many times. Frederick made his last effort to be reconciled with Gregory. It had no effect and Frederick sailed from
Brindisi
Brindisi ( , ) ; la, Brundisium; grc, Βρεντέσιον, translit=Brentésion; cms, Brunda), group=pron is a city in the region of Apulia in southern Italy, the capital of the province of Brindisi, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea.
Histo ...
in June 1228. After a stop at Cyprus, Frederick II arrived in Acre on 7 September 1228 and was received warmly by the military orders, despite his excommunication. Frederick's army was not large, mostly German, Sicilian and English. Of the troops he had sent in 1227 had mostly returned home. He could neither afford nor mount a lengthening campaign in the Holy Land given the ongoing War of the Keys with Rome. The Sixth Crusade would be one of negotiation.
After resolving the internecine struggles in Syria, al-Kamil's position was stronger than it was a year before when he made his original offer to Frederick. For unknown reasons, the two sides came to an agreement. The resultant Treaty of Jaffa Treaty of Jaffa may refer to:
*Treaty of Jaffa (1192)
The Treaty of Jaffa, more seldom referred to as the Treaty of Ramla or the treaty of 1192, was a truce agreed to during the Crusades. It was signed on 1 or 2 September 1192 A.D. (20th of Sha'b ...
was concluded on 18 February 1229, with al-Kamil surrendering Jerusalem, with the exception of some Muslim holy sites, and agreeing to a ten-year truce. Frederick entered Jerusalem on 17 March 1229 and received the formal surrender of the city by al-Kamil's agent and the next day, crowned himself. On 1 May 1229, Frederick departed from Acre and arrived in Sicily a month before the pope knew that he had left the Holy Land. Frederick obtained from the pope relief from his excommunication on 28 August 1230 at the Treaty of Ceprano.
The results of the Sixth Crusade were not universally acclaimed. Two letters from the Christian side tell differing stories, with Frederick touting the great success of the endeavor and the Latin patriarch painting a darker picture of the emperor and his accomplishments. On the Muslim side, al-Kamil himself was pleased with the accord, but other regarded the treaty as a disastrous event. In the end, the Sixth Crusade successfully returned Jerusalem to Christian rule and had set a precedent, in having achieved success on crusade without papal involvement.
The Crusades of 1239–1241
The Crusades of 1239–1241, also known as theBarons' Crusade
The Barons' Crusade (1239–1241), also called the Crusade of 1239, was a crusade to the Holy Land that, in territorial terms, was the most successful crusade since the First Crusade. Called by Pope Gregory IX, the Barons' Crusade broadly embod ...
, were a series of crusades to the Holy Land that, in territorial terms, were the most successful since the First Crusade. The major expeditions were led separately by Theobald I of Navarre and Richard of Cornwall. These crusades are sometimes discussed along with that of Baldwin of Courtenay to Constantinople.
 In 1229, Frederick II and the Ayyubid sultan al-Kamil, had agreed to a ten-year truce. Nevertheless, Gregory IX, who had condemned this truce from the beginning, issued the papal bull ''
In 1229, Frederick II and the Ayyubid sultan al-Kamil, had agreed to a ten-year truce. Nevertheless, Gregory IX, who had condemned this truce from the beginning, issued the papal bull ''Rachel suum videns
''Rachel suum videns'' is a papal bull issued by Pope Gregory IX on 17 November 1234 calling for a crusade to the Holy Land and ordering Dominicans and Franciscans to preach in favour of it. It was issued before the truce between Frederick II, H ...
'' in 1234 calling for a new crusade once the truce expired. A number of English and French nobles took the cross, but the crusade's departure was delayed because Frederick, whose lands the crusaders had planned to cross, opposed any crusading activity before the expiration of this truce. Frederick was again excommunicated in 1239, causing most crusaders to avoid his territories on their way to the Holy Land.
The French expedition was led by Theobald I of Navarre and Hugh of Burgundy, joined by Amaury of Montfort and Peter of Dreux. Jackson, Peter. "The Crusades of 1239–1241 and Their Aftermath". ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', Vol. 50, No. 1 (1987). pp. 32–60. . On 1 September 1239, Theobald arrived in Acre, and was soon drawn into the Ayyubid civil war, which had been raging since the death of al-Kamil in 1238. At the end of September, al-Kamil's brother as-Salih Ismail
As-Salih Ismail may refer to:
*As-Salih Ismail, Emir of Damascus, the Ayyubid ruler of Damascus in the mid-13th century
*As-Salih Ismail, Sultan of Egypt, the Mamluk sultan of Egypt between 1342 and 1345
*As-Salih Ismail al-Malik
As-Salih Isma ...
seized Damascus from his nephew, as-Salih Ayyub
Al-Malik as-Salih Najm al-Din Ayyub (5 November 1205 – 22 November 1249), nickname: Abu al-Futuh ( ar, أبو الفتوح), also known as al-Malik al-Salih, was the Ayyubid Kurdish ruler of Egypt from 1240 to 1249.
Early life
In 1221, as-S ...
, and recognized al-Adil II as sultan of Egypt. Theobald decided to fortify Ascalon to protect the southern border of the kingdom and to move against Damascus later. While the Crusaders were marching from Acre to Jaffa, Egyptian troops moved to secure the border in what became the Battle at Gaza.Burgturf, Jochen. "Gaza, Battle of (1239)". ''The Crusades: An Encyclopedia''. pp. 498–499. Contrary to Theobald's instructions and the advice of the military orders, a group decided to move against the enemy without further delay, but they were surprised by the Muslims who inflicted a devasting defeat on the Franks. The masters of the military orders then convinced Theobald to retreat to Acre rather than pursue the Egyptians and their Frankish prisoners. A month after the battle at Gaza, an-Nasir Dā'ūd, emir of Kerak
Al-Karak ( ar, الكرك), is a city in Jordan known for its medieval castle, the Kerak Castle. The castle is one of the three largest castles in the region, the other two being in Syria. Al-Karak is the capital city of the Karak Governorate.
...
, seized Jerusalem, virtually unguarded. The internal strife among the Ayyubids allowed Theobald to negotiate the return of Jerusalem. In September 1240, Theobald departed for Europe, while Hugh of Burgundy remained to help fortify Ascalon.
On 8 October 1240, the English expedition arrived, led by Richard of Cornwall. The force marched to Jaffa, where they completed the negotiations for a truce with Ayyubid leaders begun by Theobald just a few months prior. Richard consented, the new agreement was ratified by Ayyub by 8 February 1241, and prisoners from both sides were released on 13 April. Meanwhile, Richard's forces helped to work on Ascalon's fortifications, which were completed by mid-March 1241. Richard entrusted the new fortress to an imperial representative, and departed for England on 3 May 1241.
In July 1239, Baldwin of Courtenay, the young heir to the Latin Empire, travelled to Constantinople with a small army. In the winter of 1239, Baldwin finally returned to Constantinople, where he was crowned emperor around Easter of 1240, after which he launched his crusade. Baldwin then besieged and captured Tzurulum, a Nicaean stronghold seventy-five miles west of Constantinople.
Although the Barons' Crusade returned the kingdom to its largest size since 1187, the gains would be dramatically reversed a few years later. On 15 July 1244, the city was reduced to ruins during the siege of Jerusalem and its Christians massacred by the Khwarazmian army. A few months later, the Battle of La Forbie permanently crippled Christian military power in the Holy Land. The sack of the city and the massacre which accompanied it encouraged Louis IX of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the ...
to organize the Seventh Crusade.
The Seventh Crusade
 The Seventh Crusade (1248–1254) was the first of the two Crusades led by
The Seventh Crusade (1248–1254) was the first of the two Crusades led by Louis IX of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the ...
. Also known as the Crusade of Louis IX to the Holy Land, its objective was to reclaim the Holy Land by attacking Egypt, the main seat of Muslim power in the Middle East, then under as-Salih Ayyub
Al-Malik as-Salih Najm al-Din Ayyub (5 November 1205 – 22 November 1249), nickname: Abu al-Futuh ( ar, أبو الفتوح), also known as al-Malik al-Salih, was the Ayyubid Kurdish ruler of Egypt from 1240 to 1249.
Early life
In 1221, as-S ...
, son of al-Kamil. The Crusade was conducted in response to setbacks in the Kingdom of Jerusalem, beginning with the loss of the Holy City in 1244, and was preached by Innocent IV in conjunction with a crusade against emperor Frederick II, the Prussian crusades and Mongol incursions.Strayer, Joseph R. (1977).Chapter XIV. The Crusades of Louis IX
. In Wolff, Robert L. and Hazard, H. W. (eds.). ''A History of the Crusades: Volume II, The Later Crusades 1187-1311''. Madison: The University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 487-521. At the end of 1244, Louis was stricken with a severe malarial infection and he vowed that if he recovered he would set out for a Crusade. His life was spared, and as soon as his health permitted him, he took the cross and immediately began preparations.James Thomson Shotwell (1911). " Louis IX. of France". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 17. (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 37–38. The next year, the pope presided over
First Council of Lyon
The First Council of Lyon (Lyon I) was the thirteenth ecumenical council, as numbered by the Catholic Church, taking place in 1245.
The First General Council of Lyon was presided over by Pope Innocent IV. Innocent IV, threatened by Holy Roman ...
, directing a new Crusade under the command of Louis. With Rome under siege by Frederick, the pope also issued his '' Ad Apostolicae Dignitatis Apicem'', formally renewing the sentence of excommunication on the emperor, and declared him deposed from the imperial throne and that of Naples.Michael Ott (1910). " Pope Innocent IV". In ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 8. New York.
The recruiting effort under cardinal Odo of Châteauroux was difficult, and the Crusade finally began on 12 August 1248 when Louis IX left Paris under the insignia of a pilgrim, the '' Oriflamme''.Goldsmith, Linda (2006). ''Crusade of Louis IX to the East (1248–1254)''. In The Crusades–An Encyclopedia. pp. 321–324. With him were queen Margaret of Provence
Margaret of Provence (french: Marguerite; 1221 – 20 December 1295) was Queen of France by marriage to King Louis IX.
Early life
Margaret was born in the spring of 1221 in Forcalquier. She was the eldest of four daughters of Ramon Berenguer IV ...
and two of Louis' brothers, Charles I of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the Capetian House of Anjou, second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and County of Fo ...
and Robert I of Artois. Their youngest brother Alphonse of Poitiers departed the next year. They were followed by Hugh IV of Burgundy, Peter Maulcerc, Hugh XI of Lusignan, royal companion and chronicler Jean de Joinville, and an English detachment under William Longespée, grandson of Henry II of England.
The first stop was Cyprus, arriving in September 1248 where they experienced a long wait for the forces to assemble. Many of the men were lost ''en route'' or to disease. The Franks were soon met by those from Acre including the masters of the Orders Jean de Ronay and Guillaume de Sonnac. The two eldest sons of John of Brienne, Alsonso of Brienne and Louis of Brienne Louis of Brienne, also known as Louis of Acre (died in 1297), was viscount of Beaumont-sur-Sarthe in Maine, France.
Early life
Louis was the second son of John of Brienne and his third wife, Berengaria of León. Louis and his two brothers, ...
, would also join as would John of Ibelin, nephew to the Old Lord of Beirut. William of Villehardouin also arrived with ships and Frankish soldiers from the Morea. It was agreed that Egypt was the objective and many remembered how the sultan's father had been willing to exchange Jerusalem itself for Damietta in the Fifth Crusade. Louis was not willing to negotiate with the infidel Muslims, but he did unsuccessfully seek a Franco-Mongol alliance, reflecting what the pope had sought in 1245.
As-Salih Ayyub conducting a campaign in Damascus when the Franks invaded as he had expected the Crusaders to land in Syria. Hurrying his forces back to Cairo , he turned to his vizier Fakhr ad-Din ibn as-Shaikh to command the army that fortified Damietta in anticipation of the invasion. On 5 June 1249 the Crusader fleet began the landing and subsequent siege of Damietta. After a short battle, the Egyptian commander decided to evacuate the city. Remarkably, Damietta had been seized with only one Crusader casualty. The city became a Frankish city and Louis waited until the Nile floods abated before advancing, remembering the lessons of the Fifth Crusade. The loss of Damietta was a shock to the Muslim world, and as-Salih Ayyub offered to trade Damietta for Jerusalem as his father had thirty years before. The offer was rejected. By the end of October 1249 the Nile had receded and reinforcements had arrived. It was time to advance, and the Frankish army set out towards Mansurah.
The sultan died in November 1249, his widow Shajar al-Durr concealing the news of her husband's death. She forged a document which appointed his son al-Muazzam Turanshah, then in Syria, as heir and Fakhr ad-Din as viceroy. But the Crusade continued, and by December 1249, Louis was encamped on the river banks opposite to Mansurah. For six weeks, the armies of the West and Egypt faced each other on opposite sides of the canal, leading to the Battle of Mansurah that would end on 11 February 1250 with an Egyptian defeat. Louis had his victory, but a cost of the loss of much of his force and their commanders. Among the survivors were the Templar master Guillaume de Sonnac, losing an eye, Humbert V de Beaujeu, constable of France, John II of Soissons, and the duke of Brittany, Peter Maulcerc. Counted with the dead were the king's brother Robert I of Artois, William Longespée and most of his English followers, Peter of Courtenay, and Raoul II of Coucy. But the victory would be short-lived. On 11 February 1250, the Egyptians attacked again. Templar master Guillaume de Sonnac and acting Hospitaller master Jean de Ronay were killed. Alphonse of Poitiers, guarding the camp was encircled and was rescued by the camp followers. At nightfall, the Muslims gave up the assault.
 On 28 February 1250, Turanshah arrived from Damascus and began an Egyptian offensive, intercepting the boats that brought food from Damietta. The Franks were quickly beset by famine and disease. The Battle of Fariskur fought on 6 April 1250 would be the decisive defeat of Louis' army. Louis knew that the army must be extricated to Damietta and they departed on the morning of 5 April, with the king in the rear and the Egyptians in pursuit. The next day, the Muslims surrounded the army and attacked in full force. On 6 April, Louis' surrender was negotiated directly with the sultan by Philip of Montfort. The king and his entourage were taken in chains to Mansurah and the whole of the army was rounded up and led into captivity.
The Egyptians were unprepared for the large number of prisoners taken, comprising most of Louis' force. The infirm were executed immediately and several hundred were decapitated daily. Louis and his commanders were moved to Mansurah, and negotiations for their release commenced. The terms agreed to were harsh. Louis was to ransom himself by the surrender of Damietta and his army by the payment of a million bezants (later reduced to 800,000). Latin patriarch
On 28 February 1250, Turanshah arrived from Damascus and began an Egyptian offensive, intercepting the boats that brought food from Damietta. The Franks were quickly beset by famine and disease. The Battle of Fariskur fought on 6 April 1250 would be the decisive defeat of Louis' army. Louis knew that the army must be extricated to Damietta and they departed on the morning of 5 April, with the king in the rear and the Egyptians in pursuit. The next day, the Muslims surrounded the army and attacked in full force. On 6 April, Louis' surrender was negotiated directly with the sultan by Philip of Montfort. The king and his entourage were taken in chains to Mansurah and the whole of the army was rounded up and led into captivity.
The Egyptians were unprepared for the large number of prisoners taken, comprising most of Louis' force. The infirm were executed immediately and several hundred were decapitated daily. Louis and his commanders were moved to Mansurah, and negotiations for their release commenced. The terms agreed to were harsh. Louis was to ransom himself by the surrender of Damietta and his army by the payment of a million bezants (later reduced to 800,000). Latin patriarch Robert of Nantes
Robert of Nantes (died 8 June 1254) was the Latin patriarch of Jerusalem from 1240 to 1254.
Early life and career
Robert was a native of the Saintonge. He was a bishop in Apulia, but was expelled by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II. In 1236, Pop ...
went under safe-conduct to complete the arrangements for the ransom. Arriving in Cairo, he found Turanshah dead, murdered in a coup instigated by his stepmother Shajar al-Durr. On 6 May, Geoffrey of Sergines handed Damietta over to the Moslem vanguard. Many wounded soldiers had been left behind at Damietta, and contrary to their promise, the Muslims massacred them all. In 1251, the Shepherds' Crusade, a popular crusade formed in 1251, with the objective to free Louis, engulfed France. After his release, Louis went to Acre where he remained until 1254. This is regarded as the end of the Seventh Crusade.
The Last Crusades
After the defeat of the Crusaders in Egypt, Louis remained in Syria until 1254 to consolidate the crusader states. A brutal power struggle developed in Egypt between various Mamluk leaders and the remaining weak Ayyubid rulers. The threat presented by an invasion by the Mongols led to one of the competing Mamluk leaders, Qutuz, seizing the sultanate in 1259 and uniting with another faction led byBaibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
to defeat the Mongols at Ain Jalut. The Mamluks then quickly gained control of Damascus and Aleppo before Qutuz was assassinated and Baibers assumed control.
Between 1265 and 1271, Baibars drove the Franks to a few small coastal outposts. Baibars had three key objectives: to prevent an alliance between the Latins and the Mongols, to cause dissension among the Mongols (particularly between the Golden Horde and the Persian Ilkhanate), and to maintain access to a supply of slave recruits from the Russian steppes. He supported Manfred of Sicily's failed resistance to the attack of Charles and the papacy. Dissension in the crusader states led to conflicts such as the War of Saint Sabas. Venice drove the Genoese from Acre to Tyre where they continued to trade with Egypt. Indeed, Baibars negotiated free passage for the Genoese with MichaelVIII Palaiologos, Emperor of Nicaea, the newly restored ruler of Constantinople. In 1270 Charles turned his brother King LouisIX's crusade, known as the Eighth Crusade, to his own advantage by persuading him to attack Tunis. The crusader army was devastated by disease, and Louis himself died at Tunis on 25August. The fleet returned to France. Prince Edward, the future king of England, and a small retinue arrived too late for the conflict but continued to the Holy Land in what is known as Lord Edward's Crusade. Edward survived an assassination attempt, negotiated a ten-year truce, and then returned to manage his affairs in England. This ended the last significant crusading effort in the eastern Mediterranean.
Decline and fall of the Crusader States
The years 1272–1302 include numerous conflicts throughout the Levant as well as the Mediterranean and Western European regions, and many crusades were proposed to free the Holy Land from Mamluk control. These include ones of Gregory X,Charles I of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the Capetian House of Anjou, second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and County of Fo ...
and Nicholas IV, none of which came to fruition. The major players fighting the Muslims included the kings of England and France, the kingdoms of Cyprus and Sicily, the three Military Orders and Mongol Ilkhanate. The end of Western European presence in the Holy Land was sealed with the fall of Tripoli and their subsequent defeat at the siege of Acre in 1291. The Christian forces managed to survive until the final fall of Ruad
The fall of Ruad in 1302 was one of the culminating events of the Crusades in the Eastern Mediterranean. When the garrison on the tiny Isle of Ruad fell, it marked the loss of the last Crusader outpost on the coast of the Levant. In 1291, the C ...
in 1302.
The Holy Land would no longer be the focus of the West even though various crusades were proposed in the early years of the fourteenth century. The Knights Hospitaller would conquer Rhodes from Byzantium, making it the center of their activity for a hundred years. The Knights Templar, the elite fighting force in the kingdom, would be disbanded and its knights imprisoned or executed. The Mongols converted to Islam, but disintegrated as a fighting force. The Mamluk sultanate would continue for another century. The Crusades to liberate Jerusalem and the Holy Land were over.
Other crusades
 The military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to recover the Holy Land from Muslims provided a template for warfare in other areas that also interested the Latin Church. These included the 12th and 13thcentury conquest of Muslim Al-Andalus by Spanish Christian kingdoms; 12th to 15thcentury German Northern Crusades expansion into the pagan
The military expeditions undertaken by European Christians in the 11th, 12th, and 13thcenturies to recover the Holy Land from Muslims provided a template for warfare in other areas that also interested the Latin Church. These included the 12th and 13thcentury conquest of Muslim Al-Andalus by Spanish Christian kingdoms; 12th to 15thcentury German Northern Crusades expansion into the pagan Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
; the suppression of non-conformity, particularly in Languedoc during what has become called the Albigensian Crusade
The Albigensian Crusade or the Cathar Crusade (; 1209–1229) was a military and ideological campaign initiated by Pope Innocent III to eliminate Catharism in Languedoc, southern France. The Crusade was prosecuted primarily by the French crown ...
and for the Papacy's temporal advantage in Italy and Germany that are now known as political crusades. In the 13th and 14th centuries there were also unsanctioned, but related popular uprisings to recover Jerusalem known variously as Shepherds' or Children's crusades.
Urban II equated the crusades for Jerusalem with the ongoing Catholic invasion of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
and crusades were preached in 1114 and 1118, but it was Pope Callixtus II
Pope Callixtus II or Callistus II ( – 13 December 1124), born Guy of Burgundy, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 February 1119 to his death in 1124. His pontificate was shaped by the Investiture Controversy, ...
who proposed dual fronts in Spain and the Middle East in 1122. In the spring of 1147, Eugene authorized the expansion of his mission into the Iberian peninsula, equating these campaigns against the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct or ...
with the rest of the Second Crusade. The successful siege of Lisbon, from 1 July to 25 October 1147, was followed by the six-month siege of Tortosa, ending on 30 December 1148 with a defeat for the Moors. In the north, some Germans were reluctant to fight in the Holy Land while the pagan Wends were a more immediate problem. The resulting Wendish Crusade of 1147 was partially successful but failed to convert the pagans to Christianity. By the time of the Second Crusade the three Spanish kingdoms were powerful enough to conquer Islamic territory Castile, Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
, and Portugal. In 1212 the Spanish were victorious at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa with the support of foreign fighters responding to the preaching of Innocent III. Many of these deserted because of the Spanish tolerance of the defeated Muslims, for whom the Reconquista was a war of domination rather than extermination. In contrast the Christians formerly living under Muslim rule called Mozarabs had the Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while dist ...
relentlessly imposed on them and were absorbed into mainstream Catholicism. Al-Andalus, Islamic Spain, was completely suppressed in 1492 when the Emirate of Granada surrendered.
In 1147, Pope Eugene III extended Calixtus's idea by authorising a crusade on the German north-eastern frontier against the pagan Wends from what was primarily economic conflict. From the early 13thcentury, there was significant involvement of military orders, such as the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and the Order of Dobrzyń. The Teutonic Knights diverted efforts from the Holy Land, absorbed these orders and established the State of the Teutonic Order. This evolved the Duchy of Prussia and Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia ( la, Ducatus Curlandiæ et Semigalliæ; german: Herzogtum Kurland und Semgallen; lv, Kurzemes un Zemgales hercogiste; lt, Kuršo ir Žiemgalos kunigaikštystė; pl, Księstwo Kurlandii i Semigalii) was ...
in 1525 and 1562, respectively.
 By the beginning of the 13thcentury Papal reticence in applying crusades against the papacy's political opponents and those considered heretics. Innocent III proclaimed a crusade against Catharism that failed to suppress the heresy itself but ruined the culture the Languedoc. This set a precedent that was followed in 1212 with pressure exerted on the city of Milan for tolerating Catharism, in 1234
By the beginning of the 13thcentury Papal reticence in applying crusades against the papacy's political opponents and those considered heretics. Innocent III proclaimed a crusade against Catharism that failed to suppress the heresy itself but ruined the culture the Languedoc. This set a precedent that was followed in 1212 with pressure exerted on the city of Milan for tolerating Catharism, in 1234 against
Against may refer to:
* ''Against'' (album), 1998 album by Brazilian metal band Sepultura
** "Against" (song) the title track song from the Sepultura album
*Against (American band), 2006 American thrash band
*Against (Australian band)
Again ...
the Stedinger peasants of north-western Germany, in 1234 and 1241 Hungarian crusades against Bosnian heretics. The historian Norman Housley notes the connection between heterodoxy
In religion, heterodoxy (from Ancient Greek: , "other, another, different" + , "popular belief") means "any opinions or doctrines at variance with an official or orthodox position". Under this definition, heterodoxy is similar to unorthodoxy, wh ...
and anti-papalism in Italy. Indulgence was offered to anti-heretical groups such as the Militia of Jesus Christ and the Order of the Blessed Virgin Mary. Innocent III declared the first political crusade against Frederick II's regent, Markward von Annweiler
Markward von Annweiler (died 1202) was Imperial Seneschal and Regent of the Kingdom of Sicily.
Biography
Markward was a ministerialis, that is, he came not from the free nobility, but from a class of unfree knights and administrators whose purpose ...
, and when Frederick later threatened Rome in 1240, Gregory IX used crusading terminology to raise support against him. On Frederick II's death the focus moved to Sicily. In 1263, Pope Urban IV offered crusading indulgences to Charles of Anjou in return for Sicily's conquest. However, these wars had no clear objectives or limitations, making them unsuitable for crusading. The 1281 election of a French pope, MartinIV, brought the power of the papacy behind Charles. Charles's preparations for a crusade against Constantinople were foiled by the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos, who instigated an uprising called the Sicilian Vespers. Instead, Peter III of Aragon
Peter III of Aragon ( November 1285) was King of Aragon, King of Valencia (as ), and Count of Barcelona (as ) from 1276 to his death. At the invitation of some rebels, he conquered the Kingdom of Sicily and became King of Sicily in 1282, pres ...
was proclaimed king of Sicily, despite his excommunication and an unsuccessful Aragonese Crusade. Political crusading continued against Venice over Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream ...
; Louis IV, King of Germany when he marched to Rome for his imperial coronation; and the free companies of mercenaries.
The Latin states established were a fragile patchwork of petty realms threatened by Byzantine successor statesthe Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claim ...
, the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse ...
and the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to t ...
. Thessaloniki fell to Epirus in 1224, and Constantinople to Nicaea in 1261. Achaea and Athens survived under the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
after the Treaty of Viterbo. The Venetians endured a long-standing conflict with the Ottoman Empire until the final possessions were lost in the Seventh Ottoman–Venetian War in the 18thcentury. This period of Greek history
The history of Greece encompasses the history of the territory of the modern nation-state of Greece as well as that of the Greek people and the areas they inhabited and ruled historically. The scope of Greek habitation and rule has varied throu ...
is known as the ''Frankokratia
The ''Frankokratia'' ( el, Φραγκοκρατία, la, Francocratia, sometimes anglicized as Francocracy, "rule of the Franks"), also known as ''Latinokratia'' ( el, Λατινοκρατία, la, Latinocratia, "rule of the Latins") and ...
'' or ''Latinokratia'' ("Frankish or Latin rule") and designates a period when western European Catholics ruled Orthodox Byzantine Greeks.
The threat of the expanding Ottoman Empire prompted further campaigns. In 1389, the Ottomans defeated the Serbs at the Battle of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo ( tr, Kosova Savaşı; sr, Косовска битка) took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan ...
, won control of the Balkans from the Danube to the Gulf of Corinth
The Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf ( el, Κορινθιακός Kόλπος, ''Korinthiakόs Kόlpos'', ) is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea, separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. It is bounded in the east by the Isth ...
, in 1396 defeated French crusaders and King Sigismund of Hungary at the Nicopolis, in 1444 destroyed a crusading Polish and Hungarian force at Varna, four years later again defeated the Hungarians at Kosovo and in 1453 captured Constantinople. The 16thcentury saw growing rapprochement. The Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
, French, Spanish and Venetians and Ottomans all signed treaties. Francis I of France allied with all quarters, including from German Protestant princes and Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
Anti-Christian crusading declined in the 15thcentury, the exceptions were the six failed crusades against the religiously radical Hussites in Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and attacks on the Waldensians in Savoy. Crusading became a financial exercise; precedence was given to the commercial and political objectives. The military threat presented by the Ottoman Turks diminished, making anti-Ottoman crusading obsolete in 1699 with the final Holy League
Commencing in 1332 the numerous Holy Leagues were a new manifestation of the Crusading movement in the form of temporary alliances between interested Christian powers. Successful campaigns included the capture of Smyrna in 1344, at the Battle of ...
.
Crusading movement
Origins
The First Crusade was an unexpected event for contemporary chroniclers, but historical analysis demonstrates it had its roots in developments earlier in the 11thcentury. Clerics andlaity
In religious organizations, the laity () consists of all members who are not part of the clergy, usually including any non-ordained members of religious orders, e.g. a nun or a lay brother.
In both religious and wider secular usage, a layperson ...
increasingly recognised Jerusalem as worthy of penitential pilgrimage. The desire of Christians for a more effective church was evident in increased piety
Piety is a virtue which may include religious devotion or spirituality. A common element in most conceptions of piety is a duty of respect. In a religious context piety may be expressed through pious activities or devotions, which may vary among ...
. Pilgrimage to the Holy Land expanded after safer routes through Hungary developed from 1000. There was an increasingly articulate piety within the knighthood and the developing devotional and penitential practises of the aristocracy created a fertile ground for crusading appeals. The papacy's decline in power and influence had left it as little more than a localised bishopric, but its assertion grew under the influence of the Gregorian Reform in the period from the 1050s until the 1080s. The doctrine of papal supremacy
Papal supremacy is the doctrine of the Catholic Church that the Pope, by reason of his office as Vicar of Christ, the visible source and foundation of the unity both of the bishops and of the whole company of the faithful, and as pastor of the ...
conflicted with the view of the Eastern church that considered the pope as only one of the five patriarchs of the Christian Church, alongside the Patriarchates of Alexandria, Antioch, Constantinople and Jerusalem. In 1054 differences in custom, creed, and practice spurred Pope Leo IX to send a delegation to the Patriarch of Constantinople, which ended in mutual excommunication and an East–West Schism
The East–West Schism (also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054) is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. It is estimated that, immediately after the schism occurred, a ...
.
Military orders
The military orders were forms of a religious order first established early in the twelfth century with the function of defending Christians, as well as observing monastic vows. The Knights Hospitaller had a medical mission in Jerusalem since before theFirst Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
, later becoming a formidable military force supporting the crusades in the Holy Land and Mediterranean. The Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
were founded in 1119 by a band of knights who dedicated themselves to protecting pilgrims enroute to Jerusalem. The Teutonic Knights were formed in 1190 to protect pilgrims in both the Holy Land and Baltic region.
The Hospitallers and the Templars became supranational organisations as papal support led to rich donations of land and revenue across Europe. This, in turn, led to a steady flow of new recruits and the wealth to maintain multiple fortifications in the crusader states. In time, they developed into autonomous powers in the region. After the fall of Acre the Hospitallers relocated to Cyprus, then ruled Rhodes until the island was taken by the Ottomans in 1522. While there was talk of merging the Templars and Hospitallers in by Clement V, but ultimately the Templars were charged with heresy and disbanded. The Teutonic Knights supported the later Prussian campaigns into the fifteenth century.
Art and architecture
 According to the historian Joshua Prawer no major European poet, theologian, scholar or historian settled in the crusader states. Some went on pilgrimage, and this is seen in new imagery and ideas in western poetry. Although they did not migrate east themselves, their output often encouraged others to journey there on pilgrimage.
Historians consider the crusader military architecture of the Middle East to demonstrate a synthesis of the European, Byzantine and Muslim traditions and to be the most original and impressive artistic achievement of the crusades. Castles were a tangible symbol of the dominance of a Latin Christian minority over a largely hostile majority population. They also acted as centres of administration. Modern historiography rejects the 19th-century consensus that Westerners learnt the basis of military architecture from the Near East, as Europe had already experienced rapid development in defensive technology before the First Crusade. Direct contact with Arab fortifications originally constructed by the Byzantines did influence developments in the east, but the lack of documentary evidence means that it remains difficult to differentiate between the importance of this design culture and the constraints of situation. The latter led to the inclusion of oriental design features such as large water reservoirs and the exclusion of occidental features such as moats.
According to the historian Joshua Prawer no major European poet, theologian, scholar or historian settled in the crusader states. Some went on pilgrimage, and this is seen in new imagery and ideas in western poetry. Although they did not migrate east themselves, their output often encouraged others to journey there on pilgrimage.
Historians consider the crusader military architecture of the Middle East to demonstrate a synthesis of the European, Byzantine and Muslim traditions and to be the most original and impressive artistic achievement of the crusades. Castles were a tangible symbol of the dominance of a Latin Christian minority over a largely hostile majority population. They also acted as centres of administration. Modern historiography rejects the 19th-century consensus that Westerners learnt the basis of military architecture from the Near East, as Europe had already experienced rapid development in defensive technology before the First Crusade. Direct contact with Arab fortifications originally constructed by the Byzantines did influence developments in the east, but the lack of documentary evidence means that it remains difficult to differentiate between the importance of this design culture and the constraints of situation. The latter led to the inclusion of oriental design features such as large water reservoirs and the exclusion of occidental features such as moats.
 Typically, crusader church design was in the
Typically, crusader church design was in the French Romanesque
Romanesque architecture appeared in France at the end of the 10th century, with the development of feudal society and the rise and spread of monastic orders, particularly the Benedictines, which built many important abbeys and monasteries in the ...
style. This can be seen in the 12th-century rebuilding of the Holy Sepulchre. It retained some of the Byzantine details, but new arches and chapels were built to northern French, Aquitanian, and Provençal patterns. There is little trace of any surviving indigenous influence in sculpture, although in the Holy Sepulchre the column capitals of the south facade follow classical Syrian patterns.
In contrast to architecture and sculpture, it is in the area of visual culture that the assimilated nature of the society was demonstrated. Throughout the 12thand 13thcenturies the influence of indigenous artists was demonstrated in the decoration of shrines, paintings and the production of illuminated manuscripts. Frankish practitioners borrowed methods from the Byzantines and indigenous artists and iconographical practice leading to a cultural synthesis, illustrated by the Church of the Nativity. Wall mosaics were unknown in the west but in widespread use in the crusader states. Whether this was by indigenous craftsmen or learnt by Frankish ones is unknown, but a distinctive original artistic style evolved.
Manuscripts were produced and illustrated in workshops housing Italian, French, English and local craftsmen leading to a cross-fertilisation of ideas and techniques. An example of this is the Melisende Psalter, created by several hands in a workshop attached to the Holy Sepulchre. This style could have both reflected and influenced the taste of patrons of the arts. But what is seen is an increase in stylised, Byzantine-influenced content. This extended to the production of icons, unknown at the time to the Franks, sometimes in a Frankish style and even of western saints. This is seen as the origin of Italian panel painting. While it is difficult to track illumination of manuscripts and castle design back to their origins, textual sources are simpler. The translations made in Antioch are notable, but they are considered of secondary importance to the works emanating from Muslim Spain and from the hybrid culture of Sicily.
Female involvement
Until the requirement was abolished by InnocentIII, married men needed to obtain their wives' consent before taking the cross, which was not always readily forthcoming. Muslim and Byzantine observers viewed with disdain the many women who joined the armed pilgrimages, including female fighters. Western chroniclers indicated that female crusaders were wives, merchants, servants and sex workers. Attempts were made to control the women's behaviour in ordinances of 1147 and 1190. Aristocratic women had a significant impact: Ida of Formbach-Ratelnberg led her own force in 1101; Eleanor of Aquitaine conducted her own political strategy; andMargaret of Provence
Margaret of Provence (french: Marguerite; 1221 – 20 December 1295) was Queen of France by marriage to King Louis IX.
Early life
Margaret was born in the spring of 1221 in Forcalquier. She was the eldest of four daughters of Ramon Berenguer IV ...
negotiated her husband LouisIX's ransom with an opposing womanthe Egyptian sultana Shajar al-Durr. Misogyny meant that there was male disapproval; chroniclers tell of immorality and Jerome of Prague blamed the failure of the Second Crusade on the presence of women. Even though they often promoted crusading, preachers would typecast them as obstructing recruitment, despite their donations, legacies and vow redemptions. The wives of crusaders shared their plenary indulgences.
Finance of the Crusades
Crusade finance and taxation left a legacy of social, financial, and legal institutions. Property became available while coinage and precious materials circulated more readily within Europe. Crusading expeditions created immense demands for food supplies, weapons, and shipping that benefited merchants and artisans. Levies for crusades contributed to the development of centralised financial administrations and the growth of papal and royal taxation. This aided development of representative bodies whose consent was required for many forms of taxation. The Crusades strengthened exchanges between oriental and occidental economic spheres. The transport of pilgrims and crusaders notably benefitted Italian maritime cities, such as the trio of Venice, Pisa, and Genoa. Having obtained commercial privileges in the fortified places of Syria, they became the favoured intermediaries for trade in goods such as silk, spices, as well as other raw alimentary goods and mineral products. Trade with the Muslim world was thus extended beyond existing limits. Merchants were further advantaged by technological improvements, and long-distance trade as a whole expanded. The increased volume of goods being traded through ports of the Latin Levant and the Muslim world made this the cornerstone of a wider middle-eastern economy, as manifested in important cities along the trade routes, such as Aleppo, Damascus and Acre. It became increasingly common for European merchants to venture further east, and business was conducted fairly despite religious differences, and continued even in times of political and military tensions.Legacy
The Crusades created national mythologies, tales of heroism, and a few place names. Historical parallelism and the tradition of drawing inspiration from the Middle Ages have become keystones of political Islam encouraging ideas of a modern jihad and a centuries-long struggle against Christian states, while secular Arab nationalism highlights the role of western imperialism. Modern Muslim thinkers, politicians and historians have drawn parallels between the crusades and political developments such as the establishment of Israel in 1948. Right-wing circles in the western world have drawn opposing parallels, considering Christianity to be under an Islamic religious and demographic threat that is analogous to the situation at the time of the crusades. Crusader symbols and anti-Islamic rhetoric are presented as an appropriate response. These symbols and rhetoric are used to provide a religious justification and inspiration for a struggle against a religious enemy.Historiography
The historiography of the Crusades is concerned with their "history of the histories" during the Crusader period. The subject is a complex one, with overviews provided in ''Select Bibliography of the Crusades, Modern Historiography'',Tyerman, Christopher (2006). "Historiography, Modern". ''The Crusades: An Encyclopedia''. pp. 582–588. and ''Crusades (Bibliography and Sources'').Bréhier, Louis René (1908). " Crusades (Sources and Bibliography)". In Herbermann, Charles (ed.). ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 4. New York: Robert Appleton Company. The histories describing the Crusades are broadly of three types: (1) The primary sources of the Crusades, which include works written in the medieval period, generally by participants in the Crusade or written contemporaneously with the event, letters and documents in archives, and archaeological studies; (2)secondary source
In Scholarly method, scholarship, a secondary sourcePrimary, secondary and tertiary ...
s, beginning with early consolidated works in the 16th century and continuing to modern times; and (3) tertiary sources, primarily encyclopedias, bibliographies and genealogies.
 Primary sources. The primary sources for the Crusades are generally presented in the individual articles on each Crusade and summarized in the list of sources for the Crusades. For the First Crusade, the original Latin chronicles, including the ''
Primary sources. The primary sources for the Crusades are generally presented in the individual articles on each Crusade and summarized in the list of sources for the Crusades. For the First Crusade, the original Latin chronicles, including the ''Gesta Francorum
The ''Gesta Francorum'' (Deeds of the Franks), or ''Gesta Francorum et aliorum Hierosolimitanorum'' (Deeds of the Franks and the other pilgrims to Jerusalem), is a Latin chronicle of the First Crusade by an anonymous author connected with Bohemon ...
'', works by Albert of Aachen and Fulcher of Chartres, '' The Alexiad'' by Byzantine princess Anna Komnene, the ''Complete Work of History'' by Muslim historian Ali ibn al-Athir, and the ''Chronicle'' of Armenian historian Matthew of Edessa, provide for a starting point for the study of the Crusades' historiography. Many of these and related texts are found in the collections ''Recueil des historiens des croisades'' (RHC) and Crusade Texts in Translation. The work of William of Tyre, ''Historia Rerum in Partibus Transmarinis Gestarum,'' and its continuations by later historians complete the foundational work of the traditional Crusade. Some of these works also provide insight into the later Crusades and Crusader states. Other works of note include:
* Eyewitness accounts of the Second Crusade by Odo of Deuil and Otto of Freising. The Arab view from Damascus is provided by ibn al-Qalanisi.
* Works on the Third Crusade such as ''Libellus de Expugnatione Terrae Sanctae per Saladinum expeditione'', the '' Itinerarium Regis Ricardi,'' and the works of Crusaders Tageno and Roger of Howden, and the narratives of Richard of Devizes, Ralph de Diceto, Ralph of Coggeshall and Arnold of Lübeck. The Arabic works by al-Isfahani and al-Maqdisi as well as the biography of Saladin by Baha ad-Din ibn Shaddad
Bahāʾ al-Dīn Abū al-Maḥāsin Yūsuf ibn Rāfiʿ ibn Tamīm ( ar, بهاء الدين ابن شداد; the honorific title "Bahā' ad-Dīn" means "splendor of the faith"; sometimes known as Bohadin or Boha-Eddyn) (6 March 1145 – 8 Novem ...
are also of interest.
* The Fourth Crusade is described in the ''Devastatio Constantinopolitana
The ''Devastatio Constantinopolitana'' ("Devastation of Constantinople") is a short anonymous Latin eyewitness account of the Fourth Crusade. It covers the period from the preaching of Peter of Capua in France in 1198 until 16 May 1204, shortly a ...
'' and works of Geoffrey of Villehardouin, in his chronicle ''De la Conquête de Constantinople
''De la Conquête de Constantinople'' (''On the Conquest of Constantinople''), is the oldest surviving example of historical French prose, and considered to be one of the most important historical sources on the Fourth Crusade. It was written by ...
,'' Robert de Clari and Gunther of Pairis. The view of Byzantium is provided by Niketas Choniates
Niketas or Nicetas Choniates ( el, Νικήτας Χωνιάτης; c. 1155 – 1217), whose actual surname was Akominatos (Ἀκομινάτος), was a Byzantine Greek government official and historian – like his brother Michael Akominatos, wh ...
and the Arab perspective is given by Abū Shāma and Abu'l-Fida
Ismāʿīl b. ʿAlī b. Maḥmūd b. Muḥammad b. ʿUmar b. Shāhanshāh b. Ayyūb b. Shādī b. Marwān ( ar, إسماعيل بن علي بن محمود بن محمد بن عمر بن شاهنشاه بن أيوب بن شادي بن مروان ...
.
* The history of the Fifth and Sixth Crusades is well represented in the works of Jacques de Vitry
Jacques de Vitry (''Jacobus de Vitriaco'', c. 1160/70 – 1 May 1240) was a French canon regular who was a noted theologian and chronicler of his era.
He was elected bishop of Acre in 1214 and made cardinal in 1229.
His ''Historia Oriental ...
, Oliver of Paderborn and Roger of Wendover, and the Arabic works of Badr al-Din al-Ayni
Abū Muḥammad Maḥmūd ibn Aḥmad ibn Mūsā Badr al-Dīn al-ʿAynī, often quoted simply as al-'Ayni ( ar, بدر الدين العيني, Badr al-ʿAynī; born 762 AH/1360 CE, died 855 AH/1453 CE) was a Sunni Islamic scholar of the Hanafi m ...
.
* Key sources for the later Crusades include '' Gestes des Chiprois'', Jean de Joinville's ''Life of Saint Louis,'' as well as works by Guillaume de Nangis, Matthew Paris, Fidentius of Padua and al-Makrizi.
After the fall of Acre, the crusades continued in through the 16th century. Principal references on this subject are the Wisconsin Collaborative History of the CrusadesSetton, K. M. (Kenneth Meyer). (1969)A history of the Crusades
d ed.
D, or d, is the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''dee'' (pronounced ), plural ''dees''.
History
The ...
Madison: University of Wisconsin Press. and Norman Housley's ''The Later Crusades, 1274-1580: From Lyons to Alcazar.'' Complete bibliographies are also given in these works.
Secondary sources. The secondary sources of the Crusades began in the 16th century, with the first use of the term ''crusades'' was by 17th century French historian Louis Maimbourg in his ''Histoire des Croisades pour la délivrance de la Terre Sainte.'' Notable works of the 18th century include Voltaire's ''Histoire des Croisades'', and Edward Gibbon's Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, excerpted as ''The Crusades, A.D. 1095–1261'' and published in 1870.Gibbon, E., Kaye, J., Scott, W., Caoursin, G. (1870)The crusades
London. This edition also includes an essay on
chivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is an informal and varying code of conduct developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It was associated with the medieval Christianity, Christian institution of knighthood; knights' and gentlemen's behaviours we ...
by Sir Walter Scott, whose works helped popularize the Crusades. Early in the 19th century, the monumental ''Histoire des Croisades''Michaud, J. Fr. (Joseph Fr.). (1841)''Histoire des croisades''
6. éd. Paris.Michaud, J. Fr., Robson, W. (1881)
The history of the crusades
New ed. London. was published by the French historian
Joseph François Michaud
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
, a major new narrative based on original sources.
These histories have provided evolving views of the Crusades as discussed in detail in the Historiography writeup in Crusading movement. Modern works that serve as secondary source material are listed in the Bibliography section below and need no further discussion here.
Tertiary sources. Three such works are: Louis Bréhier's multiple works on the Crusades in the Catholic Encyclopedia; the works of Ernest Barker
Sir Ernest Barker (23 September 1874 – 17 February 1960) was an English political scientist who served as Principal of King's College London from 1920 to 1927.
Life and career
Ernest Barker was born in Woodley, Cheshire, and educated at Ma ...
Ernest Barker (1874–1960) (1911). In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Index (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press. in the Encyclopædia Britannica (11th edition), later expanded into a separate publication; and ''The Crusades: An Encyclopedia'' (2006), edited by historian Alan V. Murray.
See also
*Criticism of crusading In the Middle Ages, criticism of crusading was a minority opinion in western Europe. By contrast, the crusades in general were roundly criticized in the Byzantine Empire and unanimously condemned in the Islamic world.
Criticism of crusading could ...
* History of Christianity
* History of the Knights Hospitaller in the Levant
* History of the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and the Temple of Jerusalem, or Templars, was a military order founded in 1119.
The Crusades and the Knights Templar
The Knights Templar were an elite fighting force of their day, highly trained, well-equip ...
* List of Crusades to Europe and the Holy Land
* Military history of the Crusader states
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Catholicism and Islam Catholicism-related controversies Christianity-related controversies Islam-related controversies Judaism-related controversies Medieval Asia Medieval Africa Medieval European scribes Medieval history of the Middle East