Crochet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crochet (; ) is a process of creating
 Knitted textiles survive from as early as the 11th century CE, but the first substantive evidence of crocheted fabric emerges in Europe during the 19th century. Earlier work identified as crochet was commonly made by
Knitted textiles survive from as early as the 11th century CE, but the first substantive evidence of crocheted fabric emerges in Europe during the 19th century. Earlier work identified as crochet was commonly made by  The first known published instructions for crochet explicitly using that term to describe the craft in its present sense appeared in the Dutch magazine ''Penélopé'' in 1823. This includes a colour plate showing five styles of purse, of which three were intended to be crocheted with silk thread. The first is "simple open crochet" (''crochet simple ajour''), a mesh of chain-stitch arches. The second (illustrated here) starts in a semi-open form (''demi jour''), where chain-stitch arches alternate with equally long segments of slip-stitch crochet, and closes with a star made with "double-crochet stitches" (''dubbelde hekelsteek'': double-crochet in British terminology; single-crochet in US). The third purse is made entirely in double-crochet. The instructions prescribe the use of a tambour
The first known published instructions for crochet explicitly using that term to describe the craft in its present sense appeared in the Dutch magazine ''Penélopé'' in 1823. This includes a colour plate showing five styles of purse, of which three were intended to be crocheted with silk thread. The first is "simple open crochet" (''crochet simple ajour''), a mesh of chain-stitch arches. The second (illustrated here) starts in a semi-open form (''demi jour''), where chain-stitch arches alternate with equally long segments of slip-stitch crochet, and closes with a star made with "double-crochet stitches" (''dubbelde hekelsteek'': double-crochet in British terminology; single-crochet in US). The third purse is made entirely in double-crochet. The instructions prescribe the use of a tambour 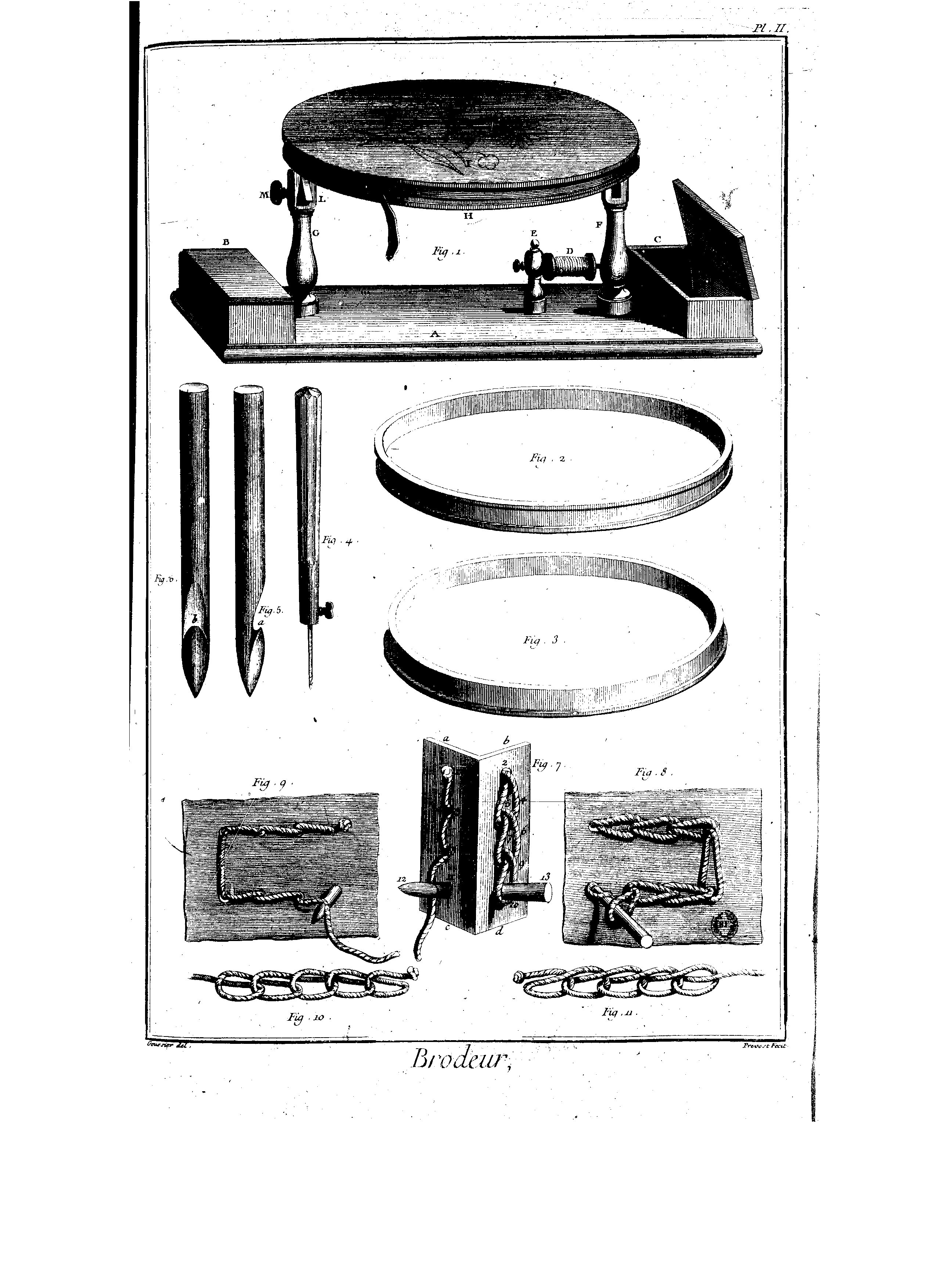 Notwithstanding the categorical assertion of a purely British origin, there is solid evidence of a connection between French tambour
Notwithstanding the categorical assertion of a purely British origin, there is solid evidence of a connection between French tambour 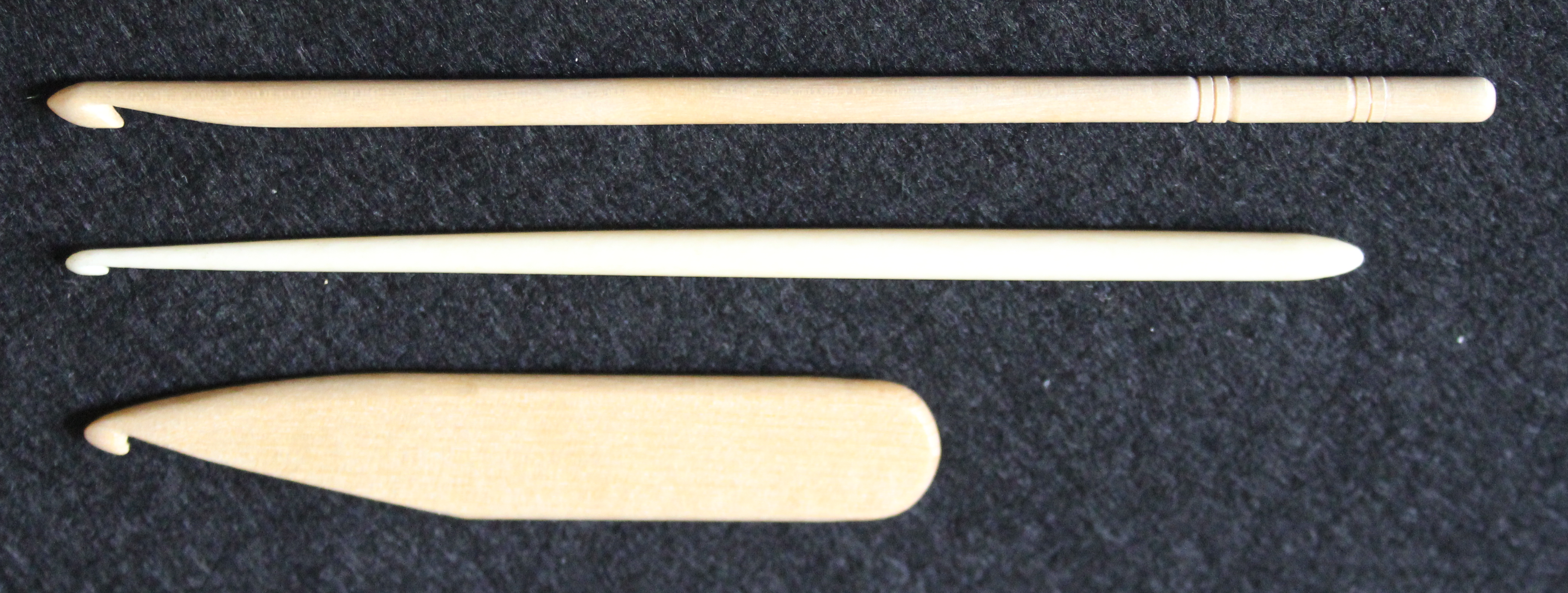 The strong taper of the shepherd's hook eases the production of slip-stitch crochet but is less amenable to stitches that require multiple loops on the hook at the same time. Early yarn hooks were also continuously tapered but gradually enough to accommodate multiple loops. The design with a cylindrical shaft that is commonplace today was largely reserved for tambour-style steel needles. Both types gradually merged into the modern form that appeared toward the end of the 19th century, including both tapered and cylindrical segments, and the continuously tapered bone hook remained in industrial production until World War II.
The early instruction books make frequent reference to the alternative use of 'ivory, bone, or wooden hooks' and 'steel needles in a handle', as appropriate to the stitch being made. Taken with the synonymous labeling of shepherd's- and single crochet, and the similar equivalence of French- and double crochet, there is a strong suggestion that crochet is rooted both in tambour embroidery and shepherd's knitting, leading to thread and yarn crochet respectively; a distinction that is still made. The locus of the fusion of all these elements—the "invention" noted above—has yet to be determined, as does the origin of shepherd's knitting.
Shepherd's hooks are still being made for local slip-stitch crochet traditions. The form in the accompanying photograph is typical for contemporary production. A longer continuously tapering design intermediate between it and the 19th-century tapered hook was also in earlier production, commonly being made from the handles of forks and spoons.
The strong taper of the shepherd's hook eases the production of slip-stitch crochet but is less amenable to stitches that require multiple loops on the hook at the same time. Early yarn hooks were also continuously tapered but gradually enough to accommodate multiple loops. The design with a cylindrical shaft that is commonplace today was largely reserved for tambour-style steel needles. Both types gradually merged into the modern form that appeared toward the end of the 19th century, including both tapered and cylindrical segments, and the continuously tapered bone hook remained in industrial production until World War II.
The early instruction books make frequent reference to the alternative use of 'ivory, bone, or wooden hooks' and 'steel needles in a handle', as appropriate to the stitch being made. Taken with the synonymous labeling of shepherd's- and single crochet, and the similar equivalence of French- and double crochet, there is a strong suggestion that crochet is rooted both in tambour embroidery and shepherd's knitting, leading to thread and yarn crochet respectively; a distinction that is still made. The locus of the fusion of all these elements—the "invention" noted above—has yet to be determined, as does the origin of shepherd's knitting.
Shepherd's hooks are still being made for local slip-stitch crochet traditions. The form in the accompanying photograph is typical for contemporary production. A longer continuously tapering design intermediate between it and the 19th-century tapered hook was also in earlier production, commonly being made from the handles of forks and spoons.
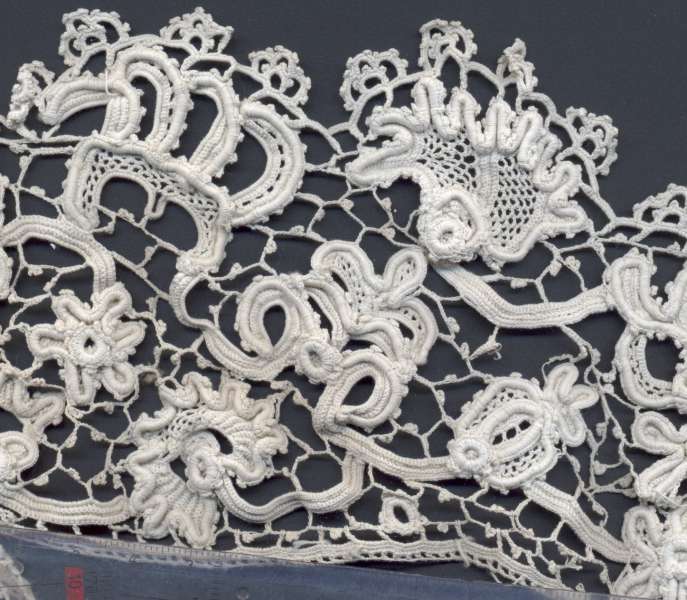
 In the 19th century, as Ireland was facing the Great Irish Famine (1845–1849), crochet lace work was introduced as a form of famine relief (the production of crocheted lace being an alternative way of making money for impoverished Irish workers).Irish Crochet Lace Exhibit Catalog
In the 19th century, as Ireland was facing the Great Irish Famine (1845–1849), crochet lace work was introduced as a form of famine relief (the production of crocheted lace being an alternative way of making money for impoverished Irish workers).Irish Crochet Lace Exhibit Catalog
Lacis Museum of Lace and Textiles. 2005. Men, women, children joined a cooperative in order to crochet and produce products to help with famine relief during the Great Irish Famine. Schools to teach crocheting were started. Teachers were trained and sent across Ireland to teach this craft. When the Irish immigrated to the Americas, they were able to take with them crocheting. Mademoiselle Riego de la Branchardiere is generally credited with the invention of
 The strong Victorian colours disappeared, though, and new publications called for white or pale threads, except for fancy purses, which were often crocheted of brightly colored silk and elaborately beaded. After World War I, far fewer crochet patterns were published, and most of them were simplified versions of the early 20th-century patterns. After
The strong Victorian colours disappeared, though, and new publications called for white or pale threads, except for fancy purses, which were often crocheted of brightly colored silk and elaborately beaded. After World War I, far fewer crochet patterns were published, and most of them were simplified versions of the early 20th-century patterns. After  Although crochet underwent a subsequent decline in popularity, the early 21st century has seen a revival of interest in handcrafts and
Although crochet underwent a subsequent decline in popularity, the early 21st century has seen a revival of interest in handcrafts and  Crochet has experienced a revival on the
Crochet has experienced a revival on the
 Yarn for crochet is usually sold as balls, or skeins (hanks), although it may also be wound on spools or cones. Skeins and balls are generally sold with a ''yarn band'', a label that describes the yarn's
Yarn for crochet is usually sold as balls, or skeins (hanks), although it may also be wound on spools or cones. Skeins and balls are generally sold with a ''yarn band'', a label that describes the yarn's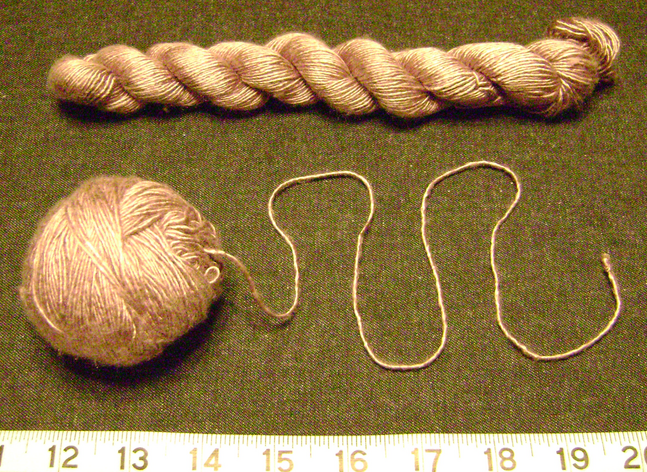  Before use, hanks are wound into balls in which the yarn emerges from the center, making crocheting easier by preventing the yarn from becoming easily tangled. The winding process may be performed by hand or done with a ballwinder and
Before use, hanks are wound into balls in which the yarn emerges from the center, making crocheting easier by preventing the yarn from becoming easily tangled. The winding process may be performed by hand or done with a ballwinder and  Although crochet may be done with ribbons, metal wire or more exotic filaments, most yarns are made by
Although crochet may be done with ribbons, metal wire or more exotic filaments, most yarns are made by
 Crocheted fabric is begun by placing a slip-knot loop on the hook (though other methods, such as a magic ring or simple folding over of the yarn may be used), pulling another loop through the first loop, and repeating this process to create a chain of a suitable length. The chain is either turned and worked in rows, or joined to the beginning of the row with a slip stitch and worked in rounds. Rounds can also be created by working many stitches into a single loop. Stitches are made by pulling one or more loops through each loop of the chain. At any one time at the end of a stitch, there is only one loop left on the hook. Tunisian crochet, however, draws all of the loops for an entire row onto a long hook before working them off one at a time. Like knitting, crochet can be worked either flat (back and forth in rows) or in the round (in spirals, such as when making tubular pieces).
Crocheted fabric is begun by placing a slip-knot loop on the hook (though other methods, such as a magic ring or simple folding over of the yarn may be used), pulling another loop through the first loop, and repeating this process to create a chain of a suitable length. The chain is either turned and worked in rows, or joined to the beginning of the row with a slip stitch and worked in rounds. Rounds can also be created by working many stitches into a single loop. Stitches are made by pulling one or more loops through each loop of the chain. At any one time at the end of a stitch, there is only one loop left on the hook. Tunisian crochet, however, draws all of the loops for an entire row onto a long hook before working them off one at a time. Like knitting, crochet can be worked either flat (back and forth in rows) or in the round (in spirals, such as when making tubular pieces).
 In the English-speaking crochet world, basic stitches have different names that vary by country. The differences are usually referred to as UK/US or British/American. Crochet is traditionally worked off a written pattern in which stitches and placement are communicated using textual abbreviations. To help counter confusion when reading patterns, a diagramming system using a standard international notation has come into use (illustration, left). In the United States, crochet terminology and sizing guidelines, as well as standards for yarn and hook labeling, are primarily regulated by the Craft Yarn Council.
Another terminological difference is known as ''tension'' (UK) and ''gauge'' (US). Individual crocheters work yarn with a loose or a tight hold and, if unmeasured, these differences can lead to significant size changes in finished garments that have the same number of stitches. In order to control for this inconsistency, printed crochet instructions include a standard for the number of stitches across a standard swatch of fabric. An individual crocheter begins work by producing a test swatch and compensating for any discrepancy by changing to a smaller or larger hook. North Americans call this ''gauge'', referring to the result of these adjustments; British crocheters speak of ''tension'', which refers to the crafter's grip on the yarn while producing stitches.
In the English-speaking crochet world, basic stitches have different names that vary by country. The differences are usually referred to as UK/US or British/American. Crochet is traditionally worked off a written pattern in which stitches and placement are communicated using textual abbreviations. To help counter confusion when reading patterns, a diagramming system using a standard international notation has come into use (illustration, left). In the United States, crochet terminology and sizing guidelines, as well as standards for yarn and hook labeling, are primarily regulated by the Craft Yarn Council.
Another terminological difference is known as ''tension'' (UK) and ''gauge'' (US). Individual crocheters work yarn with a loose or a tight hold and, if unmeasured, these differences can lead to significant size changes in finished garments that have the same number of stitches. In order to control for this inconsistency, printed crochet instructions include a standard for the number of stitches across a standard swatch of fabric. An individual crocheter begins work by producing a test swatch and compensating for any discrepancy by changing to a smaller or larger hook. North Americans call this ''gauge'', referring to the result of these adjustments; British crocheters speak of ''tension'', which refers to the crafter's grip on the yarn while producing stitches.
File:Crochet-round.jpg, Most crochet uses one hook and works upon one stitch at a time. Crochet may be worked in circular rounds without any specialized tools, as shown here.
File:Pink knitting in front of pink sweatshirt.JPG, Knitting uses two or more straight needles that carry multiple stitches.
File:Doublepoints2.JPG, Unlike crochet, knitting requires specialized needles to create circular rounds.
 Examples in nature of organisms that show hyperbolic structures include lettuces, sea slugs, flatworms and coral.
Examples in nature of organisms that show hyperbolic structures include lettuces, sea slugs, flatworms and coral.
Yarn Weight
Yarn weight to crochet hook size guide
The Antique Pattern Library
Virtual Museum of Textile Arts
Ancient Crochet Lace {{Authority control Crafts Figured fabrics Needlework Articles containing video clips
textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not t ...
s by using a crochet hook
A crochet hook (or crochet needle) is an implement used to make loops in thread or yarn and to interlock them into crochet stitches. It is a round shaft pointed on one end, with a lateral groove behind it. The point eases the insertion of the hook ...
to interlock loops of yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufac ...
, thread
Thread may refer to:
Objects
* Thread (yarn), a kind of thin yarn used for sewing
** Thread (unit of measurement), a cotton yarn measure
* Screw thread, a helical ridge on a cylindrical fastener
Arts and entertainment
* ''Thread'' (film), 2016 ...
, or strands of other materials. The name is derived from the French term ''crochet'', meaning 'hook'. Hooks can be made from a variety of materials, such as metal, wood, bamboo, or plastic. The key difference between crochet and knitting
Knitting is a method by which yarn is manipulated to create a textile, or fabric. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine.
Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row, either flat o ...
, beyond the implements used for their production, is that each stitch in crochet is completed before the next one is begun, while knitting
Knitting is a method by which yarn is manipulated to create a textile, or fabric. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine.
Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row, either flat o ...
keeps many stitches open at a time. Some variant forms of crochet, such as Tunisian crochet
Tunisian crochet or Afghan crochet is a type of crochet that uses an elongated hook, often with a stopper on the handle end, called an Afghan hook. It is sometimes considered to be a mixture of crocheting and knitting. As such, some techniques ...
and broomstick lace
Broomstick lace, also known as jiffy lace and peacock eye crochet, is a historic crochet technique from the 19th century made using a crochet hook and another long slender item such as a knitting needle. Traditionally a broomstick was used, hen ...
, do keep multiple crochet stitches open at a time.
Etymology
The word crochet is derived from theOld French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligi ...
''crochet'', a diminutive of ''croche'', in turn from the Germanic ''croc'', both meaning "hook". It was used in 17th-century French lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted o ...
-making, where the term ''crochetage'' designated a stitch used to join separate pieces of lace. The word ''crochet'' subsequently came to describe both the specific type of textile, and the hooked needle used to produce it.
Origins
 Knitted textiles survive from as early as the 11th century CE, but the first substantive evidence of crocheted fabric emerges in Europe during the 19th century. Earlier work identified as crochet was commonly made by
Knitted textiles survive from as early as the 11th century CE, but the first substantive evidence of crocheted fabric emerges in Europe during the 19th century. Earlier work identified as crochet was commonly made by nålebinding
Nålebinding (Danish: literally 'binding with a needle' or 'needle-binding', also naalbinding, nålbinding, nålbindning or naalebinding) is a fabric creation technique predating both knitting and crochet. Also known in English as "knotless nett ...
, a different looped yarn technique.
 The first known published instructions for crochet explicitly using that term to describe the craft in its present sense appeared in the Dutch magazine ''Penélopé'' in 1823. This includes a colour plate showing five styles of purse, of which three were intended to be crocheted with silk thread. The first is "simple open crochet" (''crochet simple ajour''), a mesh of chain-stitch arches. The second (illustrated here) starts in a semi-open form (''demi jour''), where chain-stitch arches alternate with equally long segments of slip-stitch crochet, and closes with a star made with "double-crochet stitches" (''dubbelde hekelsteek'': double-crochet in British terminology; single-crochet in US). The third purse is made entirely in double-crochet. The instructions prescribe the use of a tambour
The first known published instructions for crochet explicitly using that term to describe the craft in its present sense appeared in the Dutch magazine ''Penélopé'' in 1823. This includes a colour plate showing five styles of purse, of which three were intended to be crocheted with silk thread. The first is "simple open crochet" (''crochet simple ajour''), a mesh of chain-stitch arches. The second (illustrated here) starts in a semi-open form (''demi jour''), where chain-stitch arches alternate with equally long segments of slip-stitch crochet, and closes with a star made with "double-crochet stitches" (''dubbelde hekelsteek'': double-crochet in British terminology; single-crochet in US). The third purse is made entirely in double-crochet. The instructions prescribe the use of a tambour needle
Needle may refer to:
Crafting
* Crochet needle, a tool for making loops in thread or yarn
* Knitting needle, a tool for knitting, not as sharp as a sewing needle
* Sewing needle, a long slender tool with a pointed tip
* Trussing needle, a long sl ...
(as illustrated below) and introduce a number of decorative techniques.
The earliest dated reference in English to garments made of cloth produced by looping yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufac ...
with a hook—''shepherd's knitting''—is in ''The Memoirs of a Highland Lady'' by Elizabeth Grant (1797–1830). The journal entry, itself, is dated 1812 but was not recorded in its subsequently published form until some time between 1845 and 1867, and the actual date of publication was first in 1898. Nonetheless, the 1833 volume of ''Penélopé'' describes and illustrates a shepherd's hook, and recommends its use for crochet with coarser yarn.
In 1844, one of the numerous books discussing crochet that began to appear in the 1840s states:
Two years later, the same author writes:
An instruction book from 1846 describes ''Shepherd or single crochet'' as what in current British usage is either called single crochet or slip-stitch crochet, with U.S. American terminology always using the latter (reserving single crochet for use as noted above). It similarly equates "Double" and "French crochet".
 Notwithstanding the categorical assertion of a purely British origin, there is solid evidence of a connection between French tambour
Notwithstanding the categorical assertion of a purely British origin, there is solid evidence of a connection between French tambour embroidery
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen ...
and crochet. French tambour embroidery was illustrated in detail in 1763 in Diderot's Encyclopedia. The tip of the needle shown there is indistinguishable from that of a present-day inline crochet hook and the chain stitch separated from a cloth support is a fundamental element of the latter technique. The 1823 ''Penélopé'' instructions unequivocally state that the tambour tool was used for crochet and the first of the 1840s instruction books uses the terms ''tambour'' and ''crochet'' as synonyms. This equivalence is retained in the 4th edition of that work, 1847.
 The strong taper of the shepherd's hook eases the production of slip-stitch crochet but is less amenable to stitches that require multiple loops on the hook at the same time. Early yarn hooks were also continuously tapered but gradually enough to accommodate multiple loops. The design with a cylindrical shaft that is commonplace today was largely reserved for tambour-style steel needles. Both types gradually merged into the modern form that appeared toward the end of the 19th century, including both tapered and cylindrical segments, and the continuously tapered bone hook remained in industrial production until World War II.
The early instruction books make frequent reference to the alternative use of 'ivory, bone, or wooden hooks' and 'steel needles in a handle', as appropriate to the stitch being made. Taken with the synonymous labeling of shepherd's- and single crochet, and the similar equivalence of French- and double crochet, there is a strong suggestion that crochet is rooted both in tambour embroidery and shepherd's knitting, leading to thread and yarn crochet respectively; a distinction that is still made. The locus of the fusion of all these elements—the "invention" noted above—has yet to be determined, as does the origin of shepherd's knitting.
Shepherd's hooks are still being made for local slip-stitch crochet traditions. The form in the accompanying photograph is typical for contemporary production. A longer continuously tapering design intermediate between it and the 19th-century tapered hook was also in earlier production, commonly being made from the handles of forks and spoons.
The strong taper of the shepherd's hook eases the production of slip-stitch crochet but is less amenable to stitches that require multiple loops on the hook at the same time. Early yarn hooks were also continuously tapered but gradually enough to accommodate multiple loops. The design with a cylindrical shaft that is commonplace today was largely reserved for tambour-style steel needles. Both types gradually merged into the modern form that appeared toward the end of the 19th century, including both tapered and cylindrical segments, and the continuously tapered bone hook remained in industrial production until World War II.
The early instruction books make frequent reference to the alternative use of 'ivory, bone, or wooden hooks' and 'steel needles in a handle', as appropriate to the stitch being made. Taken with the synonymous labeling of shepherd's- and single crochet, and the similar equivalence of French- and double crochet, there is a strong suggestion that crochet is rooted both in tambour embroidery and shepherd's knitting, leading to thread and yarn crochet respectively; a distinction that is still made. The locus of the fusion of all these elements—the "invention" noted above—has yet to be determined, as does the origin of shepherd's knitting.
Shepherd's hooks are still being made for local slip-stitch crochet traditions. The form in the accompanying photograph is typical for contemporary production. A longer continuously tapering design intermediate between it and the 19th-century tapered hook was also in earlier production, commonly being made from the handles of forks and spoons.
Irish crochet

 In the 19th century, as Ireland was facing the Great Irish Famine (1845–1849), crochet lace work was introduced as a form of famine relief (the production of crocheted lace being an alternative way of making money for impoverished Irish workers).Irish Crochet Lace Exhibit Catalog
In the 19th century, as Ireland was facing the Great Irish Famine (1845–1849), crochet lace work was introduced as a form of famine relief (the production of crocheted lace being an alternative way of making money for impoverished Irish workers).Irish Crochet Lace Exhibit CatalogLacis Museum of Lace and Textiles. 2005. Men, women, children joined a cooperative in order to crochet and produce products to help with famine relief during the Great Irish Famine. Schools to teach crocheting were started. Teachers were trained and sent across Ireland to teach this craft. When the Irish immigrated to the Americas, they were able to take with them crocheting. Mademoiselle Riego de la Branchardiere is generally credited with the invention of
Irish Crochet
Irish lace has always been an important part of the Irish needlework tradition. Both needlepoint and bobbin laces were made in Ireland before the middle of the eighteenth century, but never, apparently, on a commercial scale. It was promoted by Ir ...
, publishing the first book of patterns in 1846. Irish lace became popular in Europe and America, and was made in quantity until the first World War.
Modern practice and culture
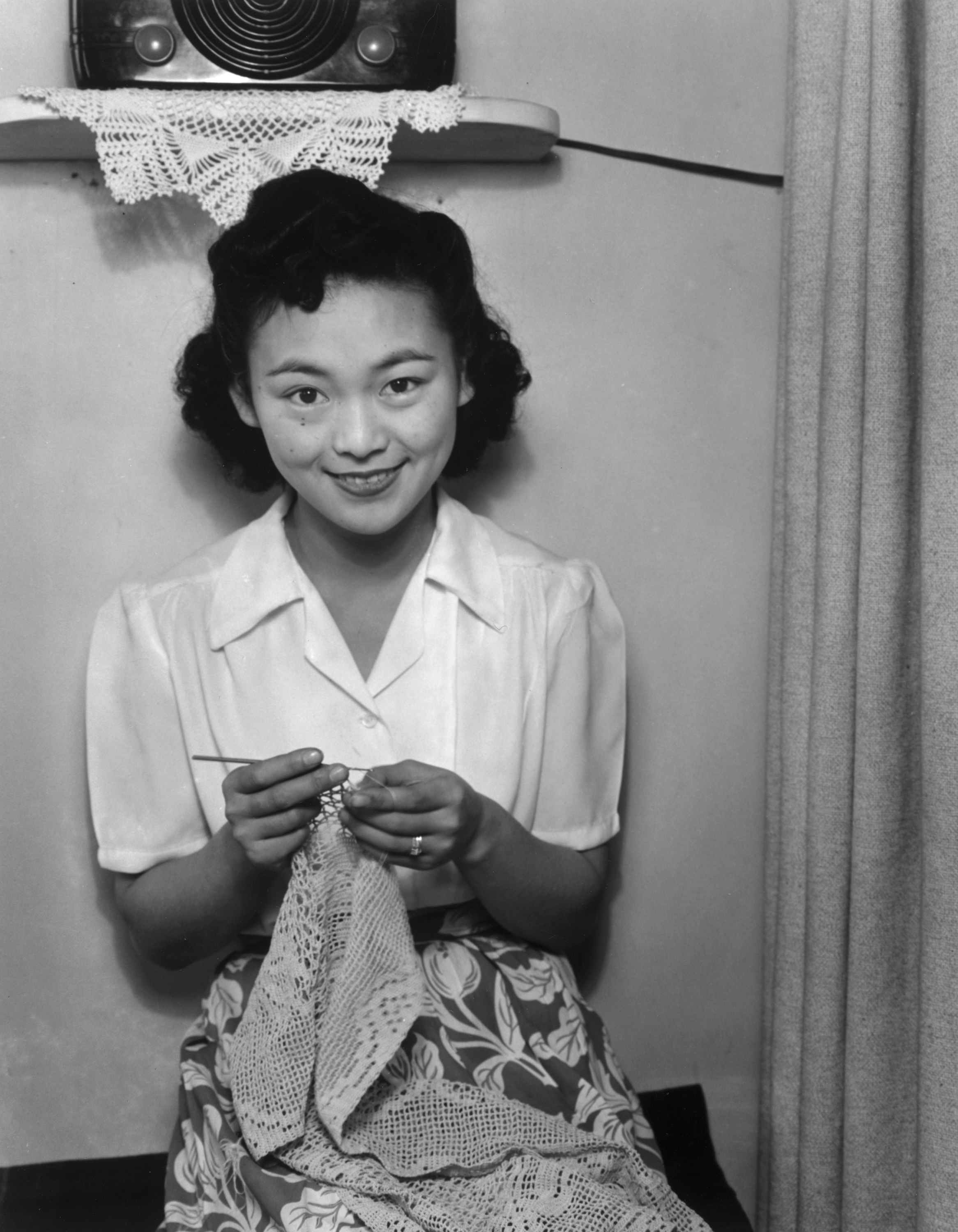
Fashions in crochet changed with the end of the Victorian era in the 1890s. Crocheted laces in the new Edwardian era, peaking between 1910 and 1920, became even more elaborate in texture and complicated stitching. The strong Victorian colours disappeared, though, and new publications called for white or pale threads, except for fancy purses, which were often crocheted of brightly colored silk and elaborately beaded. After World War I, far fewer crochet patterns were published, and most of them were simplified versions of the early 20th-century patterns. After
The strong Victorian colours disappeared, though, and new publications called for white or pale threads, except for fancy purses, which were often crocheted of brightly colored silk and elaborately beaded. After World War I, far fewer crochet patterns were published, and most of them were simplified versions of the early 20th-century patterns. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, from the late 1940s until the early 1960s, there was a resurgence in interest in home crafts, particularly in the United States, with many new and imaginative crochet designs published for colorful doilies, potholders, and other home items, along with updates of earlier publications. These patterns called for thicker threads and yarns than in earlier patterns and included variegated colors. The craft remained primarily a homemaker's art until the late 1960s and early 1970s, when the new generation picked up on crochet and popularized granny squares, a motif worked in the round and incorporating bright colors.
 Although crochet underwent a subsequent decline in popularity, the early 21st century has seen a revival of interest in handcrafts and
Although crochet underwent a subsequent decline in popularity, the early 21st century has seen a revival of interest in handcrafts and DIY
"Do it yourself" ("DIY") is the method of building, modifying, or repairing things by oneself without the direct aid of professionals or certified experts. Academic research has described DIY as behaviors where "individuals use raw and sem ...
, as well as improvement of the quality and varieties of yarn. As well as books and classes, there are YouTube tutorials and tiktok videos to help people who may need a clearer explanation to learn how to crochet.
Filet crochet, Tunisian crochet
Tunisian crochet or Afghan crochet is a type of crochet that uses an elongated hook, often with a stopper on the handle end, called an Afghan hook. It is sometimes considered to be a mixture of crocheting and knitting. As such, some techniques ...
, tapestry crochet, broomstick lace, hairpin lace, cro-hooking, and Irish crochet are all variants of the basic crochet method.
 Crochet has experienced a revival on the
Crochet has experienced a revival on the catwalk
A fashion show (French ''défilé de mode'') is an event put on by a fashion designer to showcase their upcoming line of clothing and/or accessories during a fashion week. Fashion shows debut every season, particularly the Spring/Summer and Fal ...
as well. Christopher Kane
Christopher John Kane (born 26 July 1982) is a Scottish fashion designer based in London.
Biography
Kane was born as the youngest of five children in Newarthill, North Lanarkshire, to an engineer and draughtsman father and housewife mother.
K ...
's Fall 2011 Ready-to-Wear collection makes intensive use of the granny square
A granny square is a piece of square fabric produced in crochet by working in rounds from the center outward. Granny squares are traditionally handmade as crochet cannot be manufactured by machine. They resemble coarse lace. Although there is ...
, one of the most basic of crochet motifs. In addition, crochet has been utilized many times by designers on the reality show ''Project Runway
''Project Runway'' is an American reality television series that premiered on Bravo on December 1, 2004. The series focuses on fashion design.
The contestants compete with each other to create the best clothes and are restricted by time, mate ...
''. Websites such as Etsy
Etsy, Inc. is an American e-commerce company focused on handmade or vintage items and craft supplies. These items fall under a wide range of categories, including jewelry, bags, clothing, home décor and furniture, toys, art, as well as craft ...
and Ravelry
Ravelry is a free social networking service and website that beta-launched in May 2007. It functions as an organizational tool for a variety of fiber arts, including knitting, crocheting, spinning and weaving. Members share projects, ideas, and ...
have made it easier for individual hobbyists to sell and distribute their patterns or projects across the internet.
Materials
Basic materials required for crochet are a hook and some type of material that will be crocheted, most commonly yarn or thread. Yarn, one of the most commonly used materials for crocheting, has varying weights which need to be taken into consideration when following patterns. Acrylic can also be used when crocheting, as it is synthetic and an alternative for wool. Additional tools are convenient for making related accessories. Examples of such tools include cardboard cutouts, which can be used to make tassels,fringe
Fringe may refer to:
Arts
* Edinburgh Festival Fringe, the world's largest arts festival, known as "the Fringe"
* Adelaide Fringe, the world's second-largest annual arts festival
* Fringe theatre, a name for alternative theatre
* The Fringe, the ...
, and many other items; a pom-pom circle, used to make pom-poms; a tape measure
A tape measure or measuring tape is a flexible ruler used to measure length or distance.
It consists of a ribbon of cloth, plastic, fibre glass, or metal strip with linear measurement markings. It is a common measuring tool. Its design all ...
and a gauge measure, both used for measuring crocheted work and counting stitches; a row counter; and occasionally plastic rings, which are used for special projects.
In recent years, yarn selections have moved beyond synthetic and plant and animal-based fibers to include bamboo, qiviut, hemp, and banana stalks, to name a few. Many advanced crocheters have also incorporated recycled materials into their work in an effort to "go green" and experiment with new textures by using items such as plastic bags, old t-shirts or sheets, VCR or Cassette tape, and ribbon.
Crochet hook
The crochet hook comes in many sizes and materials, such as bone, bamboo, aluminium, plastic, and steel. Because sizing is categorized by the diameter of the hook's shaft, a crafter aims to create stitches of a certain size in order to reach a particular gauge specified in a given pattern. If gauge is not reached with one hook, another is used until the stitches made are the needed size. Crafters may have a preference for one type of hook material over another due to aesthetic appeal, yarn glide, or hand disorders such as arthritis, where bamboo or wood hooks are favored over metal for the perceived warmth and flexibility during use. Hook grips and ergonomic hook handles are also available to assist crafters. Steel crochet hooks range in size from 0.4 to 3.5 millimeters, or from 00 to 16 in American sizing. These hooks are used for fine crochet work such as doilies and lace. Aluminium, bamboo, and plastic crochet hooks are available from 2.5 to 19 millimeters in size, or from B to S in American sizing. Artisan-made hooks are often made of hand-turned woods, sometimes decorated with semi-precious stones or beads. Crochet hooks used for Tunisian crochet are elongated and have a stopper at the end of the handle, while double-ended crochet hooks have a hook on both ends of the handle. There is also a double hooked apparatus called a Cro-hook that has become popular. A hairpin loom is often used to create lacy and long stitches, known as hairpin lace. While this is not in itself a hook, it is a device used in conjunction with a crochet hook to produce stitches. See : List of United States standard crochet hook and knitting needle sizesYarn
 Yarn for crochet is usually sold as balls, or skeins (hanks), although it may also be wound on spools or cones. Skeins and balls are generally sold with a ''yarn band'', a label that describes the yarn's
Yarn for crochet is usually sold as balls, or skeins (hanks), although it may also be wound on spools or cones. Skeins and balls are generally sold with a ''yarn band'', a label that describes the yarn's weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar q ...
, length, dye lot, fiber content, washing instructions, suggested needle size, likely gauge, etc. It is a common practice to save the yarn band for future reference, especially if additional skeins must be purchased. Crocheters generally ensure that the yarn for a project comes from a single dye lot. The dye lot specifies a group of skeins that were dyed together and thus have precisely the same color; skeins from different dye lots, even if very similar in color, are usually slightly different and may produce a visible stripe when added onto existing work. If insufficient yarn of a single dye lot is bought to complete a project, additional skeins of the same dye lot can sometimes be obtained from other yarn stores or online.
The thickness or weight of the yarn is a significant factor in determining how many stitches and rows are required to cover a given area for a given stitch pattern. This is also termed the gauge. Thicker yarns generally require large-diameter crochet hooks, whereas thinner yarns may be crocheted with thick or thin hooks. Hence, thicker yarns generally require fewer stitches, and therefore less time, to work up a given project. The recommended gauge for a given ball of yarn can be found on the label that surrounds the skein when buying in stores. Patterns and motifs are coarser with thicker yarns and produce bold visual effects, whereas thinner yarns are best for refined or delicate pattern-work. Yarns are standardly grouped by thickness into six categories: superfine, fine, light, medium, bulky and superbulky. Quantitatively, thickness is measured by the number of wraps per inch (WPI). The related ''weight per unit length'' is usually measured in tex or denier.
 Before use, hanks are wound into balls in which the yarn emerges from the center, making crocheting easier by preventing the yarn from becoming easily tangled. The winding process may be performed by hand or done with a ballwinder and
Before use, hanks are wound into balls in which the yarn emerges from the center, making crocheting easier by preventing the yarn from becoming easily tangled. The winding process may be performed by hand or done with a ballwinder and swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT ...
.
A yarn's usefulness is judged by several factors, such as its ''loft'' (its ability to trap air), its ''resilience'' (elasticity under tension), its washability and colorfastness, its ''hand'' (its feel, particularly softness vs. scratchiness), its durability against abrasion, its resistance to pilling, its ''hairiness'' (fuzziness), its tendency to twist or untwist, its overall weight and drape, its blocking and felting
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile or wood pu ...
qualities, its comfort (breathability, moisture absorption, wicking properties) and its appearance, which includes its color, sheen, smoothness and ornamental features. Other factors include allergenicity, speed of drying, resistance to chemicals, moths, and mildew, melting point and flammability, retention of static electricity, and the propensity to accept dyes. Desirable properties may vary for different projects, so there is no one "best" yarn.
 Although crochet may be done with ribbons, metal wire or more exotic filaments, most yarns are made by
Although crochet may be done with ribbons, metal wire or more exotic filaments, most yarns are made by spinning
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thread by twisting fibers together, traditionally by hand spinning
* Spin, the rotation of an object around a central axis
* Spin (propaganda), an intentionally b ...
fibers. In spinning, the fibers are twisted so that the yarn resists breaking under tension; the twisting may be done in either direction, resulting in a Z-twist or S-twist yarn. If the fibers are first aligned by combing them and the spinner uses a worsted type drafting method such as the short forward draw, the yarn is smoother and called a ''worsted''; by contrast, if the fibers are carded but not combed and the spinner uses a woolen drafting method such as the long backward draw, the yarn is fuzzier and called ''woolen-spun''. The fibers making up a yarn may be continuous ''filament'' fibers such as silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
and many synthetics, or they may be '' staples'' (fibers of an average length, typically a few inches); naturally filament fibers are sometimes cut up into staples before spinning. The strength of the spun yarn against breaking is determined by the amount of twist, the length of the fibers and the thickness of the yarn. In general, yarns become stronger with more twist (also called ''worst''), longer fibers and thicker yarns (more fibers); for example, thinner yarns require more twist than do thicker yarns to resist breaking under tension. The thickness of the yarn may vary along its length; a '' slub'' is a much thicker section in which a mass of fibers is incorporated into the yarn.
The spun fibers are generally divided into animal fiber
Animal fibers are natural fibers that consist largely of certain proteins. Examples include silk, hair/ fur (including wool) and feathers. The animal fibers used most commonly both in the manufacturing world as well as by the hand spinners are ...
s, plant and synthetic fiber
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants (like cotton ...
s. These fiber types are chemically different, corresponding to protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s, carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s and synthetic polymer
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and ...
s, respectively. Animal fibers include silk, but generally are long hairs of animals such as sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sh ...
(wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
...
), goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of ...
( angora, or cashmere goat), rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
( angora), llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a meat and pack animal by Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with others as a herd. Their wool is so ...
, alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can success ...
, dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relativ ...
, cat
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
, camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. ...
, yak
The domestic yak (''Bos grunniens''), also known as the Tartary ox, grunting ox or hairy cattle, is a species of long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Kachin St ...
, and muskox
The muskox (''Ovibos moschatus'', in Latin "musky sheep-ox"), also spelled musk ox and musk-ox, plural muskoxen or musk oxen (in iu, ᐅᒥᖕᒪᒃ, umingmak; in Woods Cree: ), is a hoofed mammal of the family Bovidae. Native to the Arctic, ...
( qiviut). Plants used for fibers include cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor p ...
, flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. Textiles made from flax are known i ...
(for linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
), bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
, ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ) is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is a herbaceous perennial growing to tall;
, hemp, jute
Jute is a long, soft, shiny bast fiber that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', which is in the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is ''Corchorus olit ...
, nettle, raffia
Raffia palms (''Raphia'') are a genus of about twenty species of palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species (''R. taedigera'') also occurring in Central and South America. ''R. taedigera'' is the sou ...
, yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish ...
, coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or ...
husk, banana trees, soy and corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
. Rayon
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. It is also called viscose. Many types and grades of viscose ...
and acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called ...
fibers are also produced from cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
mainly derived from tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
s. Common synthetic fibers include acrylic
Acrylic may refer to:
Chemicals and materials
* Acrylic acid, the simplest acrylic compound
* Acrylate polymer, a group of polymers (plastics) noted for transparency and elasticity
* Acrylic resin, a group of related thermoplastic or thermosett ...
s, polyesters such as dacron
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and food ...
and ingeo, nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides ( repeating units linked by amide links).The polyamides may be aliphatic or semi-aromatic.
Nylon is a silk-like thermoplastic, generally made from pet ...
and other polyamides, and olefin
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, an ...
s such as polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins an ...
. Of these types, wool is generally favored for crochet, chiefly owing to its superior elasticity, warmth and (sometimes) felt
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile or w ...
ing; however, wool is generally less convenient to clean and some people are allergic to it. It is also common to blend different fibers in the yarn, e.g., 85% alpaca and 15% silk. Even within a type of fiber, there can be great variety in the length and thickness of the fibers; for example, Merino
The Merino is a breed or group of breeds of domestic sheep, characterised by very fine soft wool. It was established in Spain near the end of the Middle Ages, and was for several centuries kept as a strict Spanish monopoly; exports of the bree ...
wool and Egyptian cotton
''Gossypium barbadense'' (''gos-SIP-pee-um bar-ba-DEN-see'') is one of several species of cotton. It is in the mallow family. It has been cultivated since antiquity, but has been especially prized since a form with particularly long fibers was ...
are favored because they produce exceptionally long, thin (fine) fibers for their type.
A single spun yarn may be crochet as is, or braid
A braid (also referred to as a plait) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing two or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair.
The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-strande ...
ed or plied
In the textile arts, plying (from the French verb ''plier'', "to fold", from the Latin verb ''plico'', from the ancient Greek verb .) is a process of twisting one or more strings (called strands) of yarn together to create a stronger yarn. Stran ...
with another. In plying, two or more yarns are spun together, almost always in the opposite sense from which they were spun individually; for example, two Z-twist yarns are usually plied with an S-twist. The opposing twist relieves some of the yarns' tendency to curl up and produces a thicker, ''balanced'' yarn. Plied yarns may themselves be plied together, producing ''cabled yarns'' or ''multi-stranded yarns''. Sometimes, the yarns being plied are fed at different rates, so that one yarn loops around the other, as in bouclé. The single yarns may be dyed separately before plying, or afterwards to give the yarn a uniform look.
The dyeing of yarns is a complex art. Yarns need not be dyed; or they may be dyed one color, or a great variety of colors. Dyeing may be done industrially, by hand or even hand-painted onto the yarn. A great variety of synthetic dyes have been developed since the synthesis of indigo dye
Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the ''Indigofera'' genus, in particular '' Indigofera tinctoria''; dye-bearing ''Indigofera'' p ...
in the mid-19th century; however, natural dye
Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.
Archae ...
s are also possible, although they are generally less brilliant. The color-scheme of a yarn is sometimes called its colorway. Variegated yarns can produce interesting visual effects, such as diagonal stripes.
Process
 Crocheted fabric is begun by placing a slip-knot loop on the hook (though other methods, such as a magic ring or simple folding over of the yarn may be used), pulling another loop through the first loop, and repeating this process to create a chain of a suitable length. The chain is either turned and worked in rows, or joined to the beginning of the row with a slip stitch and worked in rounds. Rounds can also be created by working many stitches into a single loop. Stitches are made by pulling one or more loops through each loop of the chain. At any one time at the end of a stitch, there is only one loop left on the hook. Tunisian crochet, however, draws all of the loops for an entire row onto a long hook before working them off one at a time. Like knitting, crochet can be worked either flat (back and forth in rows) or in the round (in spirals, such as when making tubular pieces).
Crocheted fabric is begun by placing a slip-knot loop on the hook (though other methods, such as a magic ring or simple folding over of the yarn may be used), pulling another loop through the first loop, and repeating this process to create a chain of a suitable length. The chain is either turned and worked in rows, or joined to the beginning of the row with a slip stitch and worked in rounds. Rounds can also be created by working many stitches into a single loop. Stitches are made by pulling one or more loops through each loop of the chain. At any one time at the end of a stitch, there is only one loop left on the hook. Tunisian crochet, however, draws all of the loops for an entire row onto a long hook before working them off one at a time. Like knitting, crochet can be worked either flat (back and forth in rows) or in the round (in spirals, such as when making tubular pieces).
Types of stitches
There are six main types of basic stitches (the following description uses US crochet terminology which differs from the terminology used in the UK and Europe). #''Chain stitch'' – the most basic of all stitches and used to begin most projects. #''Slip stitch'' – used to join chain stitch to form a ring. #''Single crochet stitch'' (called ''double crochet stitch'' in the UK) – easiest stitch to master #''Half-double crochet stitch'' (called ''half treble stitch'' in the UK) – the 'in-between' stitch, sometimes called ''short double crochet'' in vintage publications #''Double crochet stitch'' (called ''treble stitch'' in the UK) (yarn over once) – many uses for this unlimited use stitch #''Treble'' (or ''triple'') ''crochet stitch'' (called ''double treble stitch'' in the UK) (yarn over twice) While the horizontal distance covered by these basic stitches is the same, they differ in height and thickness. The more advanced stitches are often combinations of these basic stitches, or are made by inserting the hook into the work in unusual locations. More advanced stitches include the ''shell stitch'', ''V stitch'', ''spike stitch'', ''Afghan stitch'', ''butterfly stitch'', ''popcorn stitch'', ''cluster stitch'', and ''crocodile stitch''.International crochet terms and notations
 In the English-speaking crochet world, basic stitches have different names that vary by country. The differences are usually referred to as UK/US or British/American. Crochet is traditionally worked off a written pattern in which stitches and placement are communicated using textual abbreviations. To help counter confusion when reading patterns, a diagramming system using a standard international notation has come into use (illustration, left). In the United States, crochet terminology and sizing guidelines, as well as standards for yarn and hook labeling, are primarily regulated by the Craft Yarn Council.
Another terminological difference is known as ''tension'' (UK) and ''gauge'' (US). Individual crocheters work yarn with a loose or a tight hold and, if unmeasured, these differences can lead to significant size changes in finished garments that have the same number of stitches. In order to control for this inconsistency, printed crochet instructions include a standard for the number of stitches across a standard swatch of fabric. An individual crocheter begins work by producing a test swatch and compensating for any discrepancy by changing to a smaller or larger hook. North Americans call this ''gauge'', referring to the result of these adjustments; British crocheters speak of ''tension'', which refers to the crafter's grip on the yarn while producing stitches.
In the English-speaking crochet world, basic stitches have different names that vary by country. The differences are usually referred to as UK/US or British/American. Crochet is traditionally worked off a written pattern in which stitches and placement are communicated using textual abbreviations. To help counter confusion when reading patterns, a diagramming system using a standard international notation has come into use (illustration, left). In the United States, crochet terminology and sizing guidelines, as well as standards for yarn and hook labeling, are primarily regulated by the Craft Yarn Council.
Another terminological difference is known as ''tension'' (UK) and ''gauge'' (US). Individual crocheters work yarn with a loose or a tight hold and, if unmeasured, these differences can lead to significant size changes in finished garments that have the same number of stitches. In order to control for this inconsistency, printed crochet instructions include a standard for the number of stitches across a standard swatch of fabric. An individual crocheter begins work by producing a test swatch and compensating for any discrepancy by changing to a smaller or larger hook. North Americans call this ''gauge'', referring to the result of these adjustments; British crocheters speak of ''tension'', which refers to the crafter's grip on the yarn while producing stitches.
Differences from and similarities to knitting
One of the more obvious differences is that crochet uses one hook while muchknitting
Knitting is a method by which yarn is manipulated to create a textile, or fabric. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine.
Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row, either flat o ...
uses two needles. In most crochet, the artisan usually has only one live stitch on the hook (with the exception being Tunisian crochet), while a knitter keeps an entire row of stitches active simultaneously. Dropped stitches, which can unravel a knitted fabric, rarely interfere with crochet work, due to a second structural difference between knitting and crochet. In knitting, each stitch is supported by the corresponding stitch in the row above and it supports the corresponding stitch in the row below, whereas crochet stitches are only supported by and support the stitches on either side of it. If a stitch in a finished crocheted item breaks, the stitches above and below remain intact, and because of the complex looping of each stitch, the stitches on either side are unlikely to come loose unless heavily stressed.
Round or cylindrical patterns are simple to produce with a regular crochet hook, but cylindrical knitting requires either a set of circular needles or three to five special double-ended needles. Many crocheted items are composed of individual motifs which are then joined, either by sewing or crocheting, whereas knitting is usually composed of one fabric, such as entrelac.
Freeform crochet is a technique that can create interesting shapes in three dimensions because new stitches can be made independently of previous stitches almost anywhere in the crocheted piece. It is generally accomplished by building shapes or structural elements onto existing crocheted fabric at any place the crafter desires.
Knitting can be accomplished by machine, while many crochet stitches can only be crafted by hand. The height of knitted and crocheted stitches is also different: a single crochet stitch is twice the height of a knit stitch in the same yarn size and comparable diameter tools, and a double crochet stitch is about four times the height of a knit stitch.
While most crochet is made with a hook, there is also a method of crocheting with a knitting loom. This is called ''loomchet''. Slip stitch crochet is very similar to knitting. Each stitch in slip stitch crochet is formed the same way as a knit or purl stitch which is then bound off. A person working in slip stitch crochet can follow a knitted pattern with knits, purls, and cables, and get a similar result.
It is a common perception that crochet produces a thicker fabric than knitting, tends to have less "give" than knitted fabric, and uses approximately a third more yarn for a comparable project than knitted items. Although this is true when comparing a single crochet swatch with a stockinette swatch, both made with the same size yarn and needle/hook, it is not necessarily true for crochet in general. Most crochet uses far less than 1/3 more yarn than knitting for comparable pieces, and a crocheter can get similar feel and drape to knitting by using a larger hook or thinner yarn. Tunisian crochet and slip stitch crochet can in some cases use less yarn than knitting for comparable pieces. According to sources claiming to have tested the 1/3 more yarn assertion, a single crochet stitch (sc) uses approximately the same amount of yarn as knit garter stitch, but more yarn than stockinette stitch. Any stitch using yarnovers uses less yarn than single crochet to produce the same amount of fabric. Cluster stitches, which are in fact multiple stitches worked together, will use the most length.
Standard crochet stitches like sc and dc also produce a thicker fabric, more like knit garter stitch. This is part of why they use more yarn. Slip stitch can produce a fabric much like stockinette that is thinner and therefore uses less yarn.
Any yarn can be either knitted or crocheted, provided needles or hooks of the correct size are used, but the cord's properties should be taken into account. For example, lofty, thick woolen yarns tend to function better when knitted, which does not crush their airy structure, while thin and tightly spun yarn helps to achieve the firm texture required for Amigurumi crochet.
Charity and activism
It has been very common for people and groups to crochet clothing and other garments and then donate them to soldiers during war. People have also crocheted clothing and then donated it to hospitals, for sick patients and also for newborn babies. Sometimes groups will crochet for a specific charity purpose, such as crocheting forhomeless shelters
Homeless shelters are a type of homeless service agency which provide temporary residence for homeless individuals and families. Shelters exist to provide residents with safety and protection from exposure to the weather while simultaneously re ...
, nursing homes
A nursing home is a facility for the residential care of elderly or disabled people. Nursing homes may also be referred to as skilled nursing facility (SNF) or long-term care facilities. Often, these terms have slightly different meanings to i ...
, etc.
It is becoming increasingly popular to crochet hats (commonly referred to as "chemo caps") and donate them to cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
treatment centers, for those undergoing chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
and therefore losing hair. During October pink hats and scarves are made and proceeds are donated to breast cancer funds. Organizations dedicated to using crochet as a way to help others include Knots of Love, Crochet for Cancer, and Soldiers' Angels. These organizations offer warm useful items for people in need.
In 2020, people around the world banded together to help save the wildlife affected by the Australian bushfires by crocheting kangaroo pouches, koala mittens and wildlife nests. This was an international effort to help during the particularly bad bushfire season which devastated local ecological systems.
A group started in 2005 to create crochet versions of coral reefs grew by 2022 to over 20,000 contributors in what became the Crochet Coral Reef Project. To promote awareness of the effects of global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes ...
, their creations have been displayed in galleries and museums by an estimated 2 million people. Many creations apply hyperbolic (curved) geometric shapes—distinguished from Euclidean (flat) geometry—to emulate natural structures.
Mathematics and hyperbolic crochet
Crochet has been used to illustrate shapes in hyperbolic space that are difficult to reproduce using other media or are difficult to understand when viewed two-dimensionally. Mathematician Daina Taimiņa first used crochet in 1997 to create strong, durable models of hyperbolic space after finding paper models were delicate and hard to create. These models enable one to turn, fold, and otherwise manipulate space to more fully grasp ideas such as how a line can appear curved in hyperbolic space yet actually be straight. Her work received an exhibition by the Institute For Figuring. Examples in nature of organisms that show hyperbolic structures include lettuces, sea slugs, flatworms and coral.
Examples in nature of organisms that show hyperbolic structures include lettuces, sea slugs, flatworms and coral. Margaret Wertheim
Margaret Wertheim (born 20 August 1958) is an Australian-born science writer, curator, and artist based in the United States. She is the author of books on the cultural history of physics, and has written about science, including for the ''New Yo ...
and Christine Wertheim of the Institute For Figuring created a travelling art installation of a coral reef using Taimina's method. Local artists are encouraged to create their own "satellite reefs" to be included alongside the original display.
As hyperbolic and mathematics-based crochet has become more popular, there have been several events highlighting work from various fiber artists. Two shows were ''Sant Ocean Hall'' at the Smithsonian in Washington D.C. and ''Sticks, Hooks, and the Mobius: Knit and Crochet Go Cerebral'' at Lafayette College
Lafayette College is a private liberal arts college in Easton, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1826 by James Madison Porter and other citizens in Easton, the college first held classes in 1832. The founders voted to name the college after General La ...
in Pennsylvania.
Architecture
In ''Style in the technical arts'', Gottfried Semper looks at the textile with great promise and historical precedent. In Section 53, he writes of the "loop stitch, or Noeud Coulant: a knot that, if untied, causes the whole system to unravel." In the same section, Semper confesses his ignorance of the subject of crochet but believes strongly that it is a technique of great value as a textile technique and possibly something more. There are a small number of architects currently interested in the subject of crochet as it relates to architecture. The following publications, explorations and thesis projects can be used as a resource to see how crochet is being used within the capacity of architecture. * ''Emergent Explorations: Analog and Digital Scripting'' - Alexander Worden * ''Research and Design: The Architecture of variation'' - Lars Spuybroek * ''YurtAlert'' - Kate PokornyYarn bombing
In the past few years, a practice calledyarn bombing
Yarn bombing (or yarnbombing) is a type of graffiti or street art that employs colourful displays of knitted or crocheted yarn or fibre rather than paint or chalk. It is also called wool bombing, yarn storming, guerrilla knitting, kniffiti, ur ...
, or the use of knitted or crocheted cloth to modify and beautify one's (usually outdoor) surroundings, emerged in the US and spread worldwide. Yarn bombers sometimes target existing pieces of graffiti for beautification. In 2010, an entity dubbed "the Midnight Knitter" hit West Cape May. Residents awoke to find knit cozies hugging tree branches and sign poles. In September 2015, Grace Brett was named "The World's Oldest Yarn Bomber". She is part of a group of yarn graffiti-artists called the Souter Stormers, who beautify their local town in Scotland.
Styles in Crochet
* Mosaic Crochet *Granny square
A granny square is a piece of square fabric produced in crochet by working in rounds from the center outward. Granny squares are traditionally handmade as crochet cannot be manufactured by machine. They resemble coarse lace. Although there is ...
* Freeform Crochet
* Motifs
* Crocheted lace
* Tunisian Crochet
Tunisian crochet or Afghan crochet is a type of crochet that uses an elongated hook, often with a stopper on the handle end, called an Afghan hook. It is sometimes considered to be a mixture of crocheting and knitting. As such, some techniques ...
* Tapestry Crochet
* Amigurumi
* Filet Crochet
* Corner to Corner (C2C) Crochet
See also
* Crochet Guild of America * The Tempestry Project *Fiber art
Fiber art (fibre art in British spelling) refers to fine art whose material consists of natural or synthetic fiber and other components, such as fabric or yarn. It focuses on the materials and on the manual labor on the part of the artist as ...
* Macramé
Macramé is a form of textile produced using knotting (rather than weaving or knitting) techniques.
The primary knots of macramé are the square (or reef knot) and forms of "hitching": various combinations of half hitches. It was long crafted by ...
* Knitting
Knitting is a method by which yarn is manipulated to create a textile, or fabric. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine.
Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row, either flat o ...
References
Further reading
* * Hadley, Sara. "Irish Crochet Lace", ''The Lace Maker'', Vol. 4 3, New York: D.S. Bennet, 1911. * Kooler, Donna ''Donna Kooler's Encyclopedia of Crochet'', Leisure Arts, Inc., Little Rock, Arkansas * Lambert, Miss rances ''My Crochet Sampler'', London: John Murray, Albemarle Street, 1844. * Potter, Annie Louise. ''A living mystery: the international art & history of crochet'' * Riego de la Branchardiere, Eléanor. ''Crochet Book 4th Series'', London: Simpkin, Marshall, and Co., 1848. * Riego de la Branchardiere, Eléanor. ''Crochet Book 6th Series, containing D'Oyleys and Anti-Macassars'', London: Simpkin, Marshall, and Co., 1877. This is the 20th printing of this book; the original publishing date is probably about 1850. * Riego de la Branchardiere, Eléanor. ''Crochet Book, 9th Series or Third Winter Book'', London: Simpkin, Marshall and Co., 1850. * Warren, ''The Court Crochet Doyley Book'', London: Ackermann & Co, 1847. * Wildman, Emily. ''Step-By-Step Crochet'', 1972External links
Yarn Weight
Yarn weight to crochet hook size guide
The Antique Pattern Library
Virtual Museum of Textile Arts
Ancient Crochet Lace {{Authority control Crafts Figured fabrics Needlework Articles containing video clips