Cracked tooth syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cracked tooth syndrome (CTS) is where a tooth has incompletely cracked but no part of the tooth has yet broken off. Sometimes it is described as a
 The reported symptoms are very variable, and frequently have been present for many months before the condition is diagnosed. Reported symptoms may include some of the following:
* Sharp pain when biting on a certain tooth, which may get worse if the applied biting force is increased. Sometimes the pain on biting occurs when the food being chewed is soft with harder elements, e.g. seeded bread.
* "Rebound pain" i.e. sharp, fleeting pain occurring when the biting force is released from the tooth, which may occur when eating fibrous foods.
* Pain on biting
* Pain when grinding the teeth backward and forward and side to side.
* Sharp pain when drinking cold beverages or eating cold foods, lack of pain with heat stimuli.
* Pain when eating or drinking sugary substances.
*Sometimes the pain is well localized, and the individual is able to determine the exact tooth from which the symptoms are originating, but not always.
If the crack propagates into the pulp, irreversible
The reported symptoms are very variable, and frequently have been present for many months before the condition is diagnosed. Reported symptoms may include some of the following:
* Sharp pain when biting on a certain tooth, which may get worse if the applied biting force is increased. Sometimes the pain on biting occurs when the food being chewed is soft with harder elements, e.g. seeded bread.
* "Rebound pain" i.e. sharp, fleeting pain occurring when the biting force is released from the tooth, which may occur when eating fibrous foods.
* Pain on biting
* Pain when grinding the teeth backward and forward and side to side.
* Sharp pain when drinking cold beverages or eating cold foods, lack of pain with heat stimuli.
* Pain when eating or drinking sugary substances.
*Sometimes the pain is well localized, and the individual is able to determine the exact tooth from which the symptoms are originating, but not always.
If the crack propagates into the pulp, irreversible
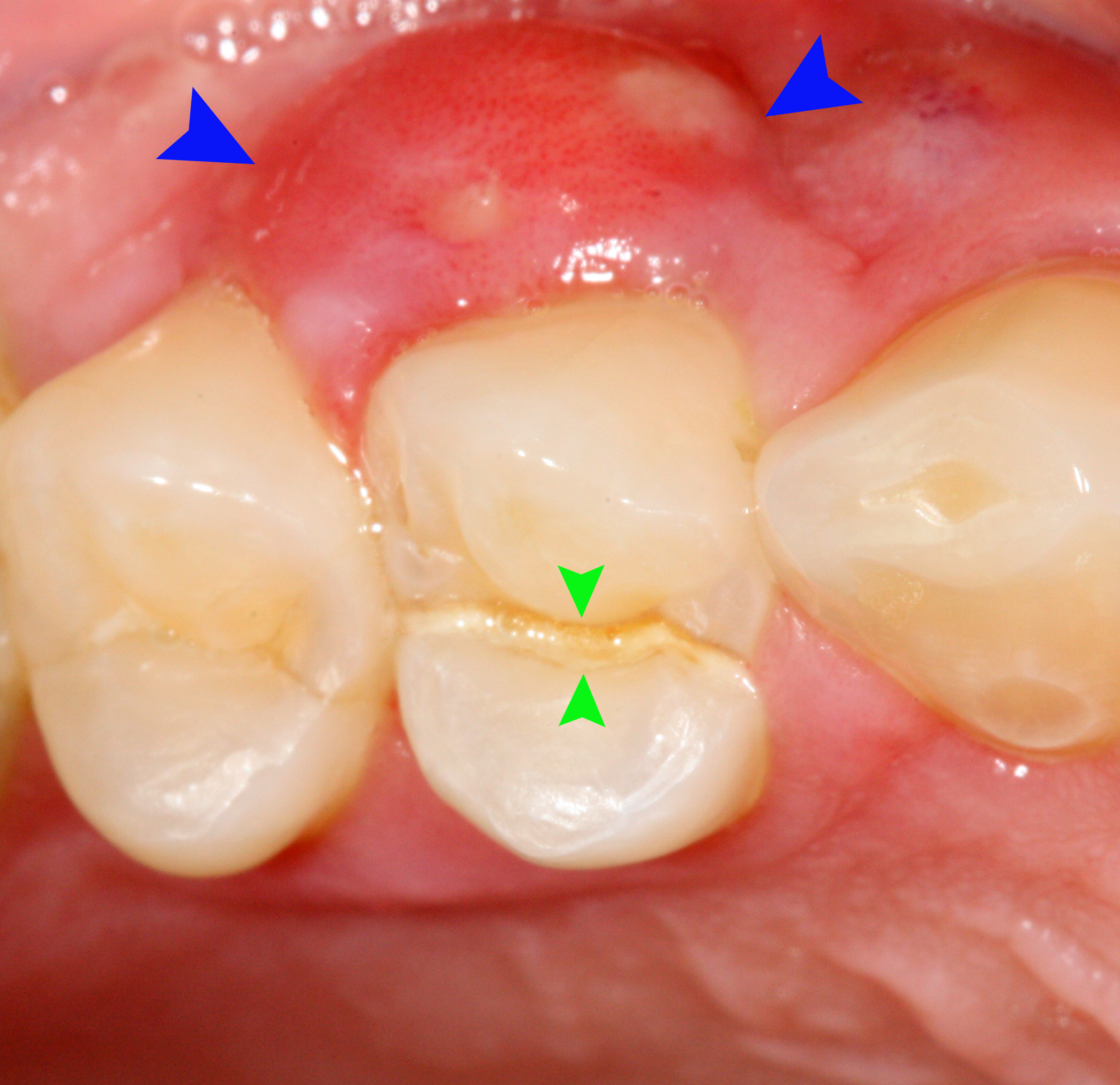 CTS is typically characterized by pain when releasing biting pressure on an object. This is because when biting down the segments are usually moving apart and thereby reducing the pressure in the nerves in the dentin of the tooth. When the bite is released the "segments" snap back together sharply increasing the pressure in the intradentin nerves causing pain. The pain is often inconsistent, and frequently hard to reproduce. Pain associated with CTS has been reported to occur more commonly on biting, rather than on release of pressure after biting. If untreated, CTS can lead to severe pain, possible pulpal death, abscess, and even the loss of the tooth.
If the fracture propagates into the pulp, this is termed a complete fracture, and pulpitis and pulp death may occur.
If the crack propagates further into the root, a periodontal defect may develop, or even a vertical root fracture.
According to one theory, the pain on biting is caused by the 2 fractured sections of the tooth moving independently of each other, triggering sudden movement of fluid within the dentinal tubules. This activates A-type
CTS is typically characterized by pain when releasing biting pressure on an object. This is because when biting down the segments are usually moving apart and thereby reducing the pressure in the nerves in the dentin of the tooth. When the bite is released the "segments" snap back together sharply increasing the pressure in the intradentin nerves causing pain. The pain is often inconsistent, and frequently hard to reproduce. Pain associated with CTS has been reported to occur more commonly on biting, rather than on release of pressure after biting. If untreated, CTS can lead to severe pain, possible pulpal death, abscess, and even the loss of the tooth.
If the fracture propagates into the pulp, this is termed a complete fracture, and pulpitis and pulp death may occur.
If the crack propagates further into the root, a periodontal defect may develop, or even a vertical root fracture.
According to one theory, the pain on biting is caused by the 2 fractured sections of the tooth moving independently of each other, triggering sudden movement of fluid within the dentinal tubules. This activates A-type
 Transillumination is best performed by placing a fibre optic light source directly onto the tooth and optimal results can be achieved with the aid of magnification. Cracks involving dentine interrupt the light transmission. However, transillumination may cause cracks to appear enlarged as well as causing colour changes to become invisible.
Transillumination is best performed by placing a fibre optic light source directly onto the tooth and optimal results can be achieved with the aid of magnification. Cracks involving dentine interrupt the light transmission. However, transillumination may cause cracks to appear enlarged as well as causing colour changes to become invisible.
 There is no universally accepted treatment strategy, but, generally, treatments aim to prevent movement of the segments of the involved tooth so they do not move or flex independently during biting and grinding (stabilisation of the crack) to prevent propagation of the crack. Provisionally, a band may be placed around the tooth or a direct composite splint can be placed in supra-occlusion to minimize flexing. Definitive options include:
* Bonded intra-coronal restoration
* Onlay restoration, either direct or indirectly placed (currently the recommended technique)
* Crown restoration (though this is associated with a high incidence of loss of vitality in teeth with CTS)
Teeth originally presenting with CTS may subsequently require
There is no universally accepted treatment strategy, but, generally, treatments aim to prevent movement of the segments of the involved tooth so they do not move or flex independently during biting and grinding (stabilisation of the crack) to prevent propagation of the crack. Provisionally, a band may be placed around the tooth or a direct composite splint can be placed in supra-occlusion to minimize flexing. Definitive options include:
* Bonded intra-coronal restoration
* Onlay restoration, either direct or indirectly placed (currently the recommended technique)
* Crown restoration (though this is associated with a high incidence of loss of vitality in teeth with CTS)
Teeth originally presenting with CTS may subsequently require
greenstick fracture
A greenstick fracture is a fracture in a young, soft bone in which the bone bends and breaks. Greenstick fractures occur most often during infancy and childhood when bones are soft. The name is by analogy with green (i.e., fresh) wood which simil ...
. The symptoms are very variable, making it a notoriously difficult condition to diagnose.
Classification and definition
Cracked tooth syndrome could be considered a type ofdental trauma
Dental trauma refers to trauma (injury) to the teeth and/or periodontium (gums, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone), and nearby soft tissues such as the lips, tongue, etc. The study of dental trauma is called dental traumatology.''Textbook and C ...
and also one of the possible causes of dental pain
Toothache, also known as dental pain,Segen JC. (2002). ''McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine''. The McGraw-Hill Companies. is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the te ...
. One definition of cracked tooth syndrome is "a fracture plane of unknown depth and direction passing through tooth structure that, if not already involving, may progress to communicate with the pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
...
and/or periodontal ligament
The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits. It inserts into root cementum one side and onto alveolar b ...
."
Signs and symptoms
 The reported symptoms are very variable, and frequently have been present for many months before the condition is diagnosed. Reported symptoms may include some of the following:
* Sharp pain when biting on a certain tooth, which may get worse if the applied biting force is increased. Sometimes the pain on biting occurs when the food being chewed is soft with harder elements, e.g. seeded bread.
* "Rebound pain" i.e. sharp, fleeting pain occurring when the biting force is released from the tooth, which may occur when eating fibrous foods.
* Pain on biting
* Pain when grinding the teeth backward and forward and side to side.
* Sharp pain when drinking cold beverages or eating cold foods, lack of pain with heat stimuli.
* Pain when eating or drinking sugary substances.
*Sometimes the pain is well localized, and the individual is able to determine the exact tooth from which the symptoms are originating, but not always.
If the crack propagates into the pulp, irreversible
The reported symptoms are very variable, and frequently have been present for many months before the condition is diagnosed. Reported symptoms may include some of the following:
* Sharp pain when biting on a certain tooth, which may get worse if the applied biting force is increased. Sometimes the pain on biting occurs when the food being chewed is soft with harder elements, e.g. seeded bread.
* "Rebound pain" i.e. sharp, fleeting pain occurring when the biting force is released from the tooth, which may occur when eating fibrous foods.
* Pain on biting
* Pain when grinding the teeth backward and forward and side to side.
* Sharp pain when drinking cold beverages or eating cold foods, lack of pain with heat stimuli.
* Pain when eating or drinking sugary substances.
*Sometimes the pain is well localized, and the individual is able to determine the exact tooth from which the symptoms are originating, but not always.
If the crack propagates into the pulp, irreversible pulpitis
Pulpitis is inflammation of dental pulp tissue. The pulp contains the blood vessels, the nerves, and connective tissue inside a tooth and provides the tooth’s blood and nutrients. Pulpitis is mainly caused by bacterial infection which itself is ...
, pulpal necrosis and periapical periodontitis
Periapical periodontitis or apical periodontitis (AP) is an acute or chronic inflammatory lesion around the apex of a tooth root, most commonly caused by bacterial invasion of the pulp of the tooth. It is a likely outcome of untreated dental ca ...
may develop, with the respective associated symptoms.
Pathophysiology
 CTS is typically characterized by pain when releasing biting pressure on an object. This is because when biting down the segments are usually moving apart and thereby reducing the pressure in the nerves in the dentin of the tooth. When the bite is released the "segments" snap back together sharply increasing the pressure in the intradentin nerves causing pain. The pain is often inconsistent, and frequently hard to reproduce. Pain associated with CTS has been reported to occur more commonly on biting, rather than on release of pressure after biting. If untreated, CTS can lead to severe pain, possible pulpal death, abscess, and even the loss of the tooth.
If the fracture propagates into the pulp, this is termed a complete fracture, and pulpitis and pulp death may occur.
If the crack propagates further into the root, a periodontal defect may develop, or even a vertical root fracture.
According to one theory, the pain on biting is caused by the 2 fractured sections of the tooth moving independently of each other, triggering sudden movement of fluid within the dentinal tubules. This activates A-type
CTS is typically characterized by pain when releasing biting pressure on an object. This is because when biting down the segments are usually moving apart and thereby reducing the pressure in the nerves in the dentin of the tooth. When the bite is released the "segments" snap back together sharply increasing the pressure in the intradentin nerves causing pain. The pain is often inconsistent, and frequently hard to reproduce. Pain associated with CTS has been reported to occur more commonly on biting, rather than on release of pressure after biting. If untreated, CTS can lead to severe pain, possible pulpal death, abscess, and even the loss of the tooth.
If the fracture propagates into the pulp, this is termed a complete fracture, and pulpitis and pulp death may occur.
If the crack propagates further into the root, a periodontal defect may develop, or even a vertical root fracture.
According to one theory, the pain on biting is caused by the 2 fractured sections of the tooth moving independently of each other, triggering sudden movement of fluid within the dentinal tubules. This activates A-type nociceptor
A nociceptor ("pain receptor" from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is a sensory neuron that responds to damaging or potentially damaging stimuli by sending "possible threat" signals to the spinal cord and the brain. The brain creates the sens ...
s in the dentin-pulp complex, reported by the pulp-dentin complex as pain. Another theory is that the pain upon cold stimuli results from leak of noxious substances via the crack, irritating the pulp.
Diagnosis
Cracked tooth syndrome (CTS) was defined as 'an incomplete fracture of a vital posterior tooth that involves the dentine and occasionally extends to the pulp' by Cameron in 1964 and more recently has included 'a fracture plane of unknown depth and direction passing through tooth structure that, if not already involving, may progress to communicate with the pulp and/or periodontal ligament'. The diagnosis of cracked tooth syndrome is notoriously difficult even for experienced clinicians. The features are highly variable and may mimicsinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the nasal mucosa, mucous membranes that line the paranasal sinuses, sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick Mucus#Respiratory system, nasal mucus, a nasal congestion, plugg ...
, temporomandibular disorder
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD, TMJD) is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication (the muscles that move the jaw) and the temporomandibular joints (the joints which connect the mandible to the skul ...
s, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
s, ear pain
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain i ...
, or atypical facial pain
Atypical facial pain (AFP) is a type of chronic facial pain which does not fulfill any other diagnosis. There is no consensus as to a globally accepted definition, and there is even controversy as to whether the term should be continued to be use ...
/atypical odontalgia
Atypical facial pain (AFP) is a type of chronic facial pain which does not fulfill any other diagnosis. There is no consensus as to a globally accepted definition, and there is even controversy as to whether the term should be continued to be use ...
(persistent idiopathic facial pain). When diagnosing cracked tooth syndrome, a dentist takes many factors into consideration. Effective management and good prognosis of cracked teeth is linked to prompt diagnosis. A detailed history may reveal pain on release of pressure when eating or sharp pain when consuming cold food and drink. There are a variety of habits which predispose patients to CTS including chewing ice, pens and hard sweets etc. Recurrent occlusal adjustment of restorations due to discomfort may also be indicative of CTS, alongside a history of extensive dental treatment. Below different techniques used for diagnosing CTS are discussed.
Clinical examination
Cracks are difficult to see during a clinical exam which may limit diagnosis. However other clinical signs which may lead to the diagnosis of CTS includes wear faceting indicating excessive forces perhaps from clenching or grinding or the presence of an isolated deep periodontal pocket which may symbolise a split tooth. Removing restorations may help to visualise fracture lines but should only be carried out after gaining informed consent from the patient, as removing a restoration may prove to be of little diagnostic benefit. Tactile examination with a sharp probe may also aid diagnosis.Gentian Violet or Methylene Blue Stains
Dyes may be used to aid visualisation of fractures. The technique requires 2–5 days to be effective and a temporary restoration may be required. The structural integrity can be weakened by this method, leading to crack propagation.Transillumination
 Transillumination is best performed by placing a fibre optic light source directly onto the tooth and optimal results can be achieved with the aid of magnification. Cracks involving dentine interrupt the light transmission. However, transillumination may cause cracks to appear enlarged as well as causing colour changes to become invisible.
Transillumination is best performed by placing a fibre optic light source directly onto the tooth and optimal results can be achieved with the aid of magnification. Cracks involving dentine interrupt the light transmission. However, transillumination may cause cracks to appear enlarged as well as causing colour changes to become invisible.
Radiographs
Radiographs offer little benefit in visualising cracks. This is due to the fact that cracks propagate in a direction which is parallel to the plane of the film (Mesiodistal) however radiographs can be useful when examining the periodontal and pulpal status.Bite Test
Different tools can be used when carrying out a bite test which produce symptoms associated with cracked tooth syndrome. Patients bite down followed by sudden release of pressure. CTS diagnosis is confirmed by pain on release of pressure. The involved cusp can be determined by biting on individual cusps separately. Tooth Slooth II (Professional Results Inc., Laguna Niguel, CA, USA) and Fractfinder (Denbur, Oak Brook, IL, USA) are commercially available tools.Epidemiology
Aetiology of CTS is multifactorial, the causative factors include: * previous restorative procedures. * occlusal factors; patients who suffer frombruxism
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; reports of prevalence range from 8% to 31% in the gene ...
, or clenching are prone to have cracked teeth.
* developmental conditions/anatomical considerations.
* trauma
* others, e.g., aging dentition or presence of lingual tongue studs.
Most commonly involved teeth are mandibular molars followed by maxillary premolars, maxillary molars and maxillary premolars. in a recent audit, mandibular first molar thought to be most affected by CTS possibly due to the wedging effect of opposing pointy, protruding maxillary mesio-palatal cusp onto the mandibular molar central fissure. Studies have also found signs of cracked teeth following the cementation of porcelain inlays; it is suggested that the debonding of intracoronal restorations may be caused by unrecognized cracks in the tooth.
Treatments
 There is no universally accepted treatment strategy, but, generally, treatments aim to prevent movement of the segments of the involved tooth so they do not move or flex independently during biting and grinding (stabilisation of the crack) to prevent propagation of the crack. Provisionally, a band may be placed around the tooth or a direct composite splint can be placed in supra-occlusion to minimize flexing. Definitive options include:
* Bonded intra-coronal restoration
* Onlay restoration, either direct or indirectly placed (currently the recommended technique)
* Crown restoration (though this is associated with a high incidence of loss of vitality in teeth with CTS)
Teeth originally presenting with CTS may subsequently require
There is no universally accepted treatment strategy, but, generally, treatments aim to prevent movement of the segments of the involved tooth so they do not move or flex independently during biting and grinding (stabilisation of the crack) to prevent propagation of the crack. Provisionally, a band may be placed around the tooth or a direct composite splint can be placed in supra-occlusion to minimize flexing. Definitive options include:
* Bonded intra-coronal restoration
* Onlay restoration, either direct or indirectly placed (currently the recommended technique)
* Crown restoration (though this is associated with a high incidence of loss of vitality in teeth with CTS)
Teeth originally presenting with CTS may subsequently require Root Canal therapy
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of ...
(if pain persists after above) or Extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pro ...
History
The term "cuspal fracture odontalgia" was suggested in 1954 by Gibbs. Subsequently, the term "cracked tooth syndrome" was coined in 1964 by Cameron, who defined the condition as "an incomplete fracture of a vital posterior tooth that involves the dentin and occasionally extends into the pulp."References
External links
{{Oral pathology Orofacial pain Acquired tooth pathology Syndromes affecting teeth