County Courthouses In Tennessee on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A county is a geographic
A county is a geographic
– Type details for ancient county. Retrieved 31 March 2012 many county names derive from the name of the county town (
 The ostans (provinces) of
The ostans (provinces) of
 A was a territory ruled by a
A was a territory ruled by a
 The island of
The island of
 The territorial administration of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The country is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, ''voivodeships'' (provinces); these are further divided into ''powiats'' (counties or districts). The term ''powiat'' is often translated into English as ''county'' (or sometimes ''district''). In historical contexts this may be confusing because the Polish term ''hrabstwo'' (a territorial unit administered/owned by a ''hrabia'' (
The territorial administration of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The country is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, ''voivodeships'' (provinces); these are further divided into ''powiats'' (counties or districts). The term ''powiat'' is often translated into English as ''county'' (or sometimes ''district''). In historical contexts this may be confusing because the Polish term ''hrabstwo'' (a territorial unit administered/owned by a ''hrabia'' (
 The Romanian word for county, , is not currently used for any Romanian administrative divisions. Romania is divided into a total of 41 counties ( ro, județe), which along with the
The Romanian word for county, , is not currently used for any Romanian administrative divisions. Romania is divided into a total of 41 counties ( ro, județe), which along with the
 The Swedish division into counties, , which literally means 'fief', was established in 1634, and was based on an earlier division into provinces of Sweden, provinces; Sweden is divided into 21 counties and 290 municipalities (''kommuner''). At the county level there is a county Administrative Boards of Sweden, county administrative board led by a governor appointed by the central government of Sweden, as well as an elected county councils of Sweden, county council that handles a separate set of issues, notably hospitals and public transportation for the municipalities of Sweden, municipalities within its borders.
Every county council corresponds to a county with a number of municipalities per county. County councils and municipalities have different roles and separate responsibilities relating to local government. Health care, public transport and certain cultural institutions are administered by county councils while general education, public water utilities, garbage disposal, elderly care and rescue services are administered by the municipalities. Gotland is a special case of being a county council with only one municipality and the functions of county council and municipality are performed by the same organisation.
The Swedish division into counties, , which literally means 'fief', was established in 1634, and was based on an earlier division into provinces of Sweden, provinces; Sweden is divided into 21 counties and 290 municipalities (''kommuner''). At the county level there is a county Administrative Boards of Sweden, county administrative board led by a governor appointed by the central government of Sweden, as well as an elected county councils of Sweden, county council that handles a separate set of issues, notably hospitals and public transportation for the municipalities of Sweden, municipalities within its borders.
Every county council corresponds to a county with a number of municipalities per county. County councils and municipalities have different roles and separate responsibilities relating to local government. Health care, public transport and certain cultural institutions are administered by county councils while general education, public water utilities, garbage disposal, elderly care and rescue services are administered by the municipalities. Gotland is a special case of being a county council with only one municipality and the functions of county council and municipality are performed by the same organisation.
 In England, in the Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period, ''shires'' were established as areas used for the raising of taxes, and usually had a fortified town at their centre. This became known as the ''shire town'' or later the county town. In many cases, the shires were named after their shire town (for example Bedford''shire''), but there are several exceptions, such as Cumberland, Norfolk and Suffolk. In several other cases, such as Buckinghamshire, the modern county town is different from the town after which the shire is named. (See Toponymical list of counties of the United Kingdom)
Most non-metropolitan counties in England are run by
In England, in the Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period, ''shires'' were established as areas used for the raising of taxes, and usually had a fortified town at their centre. This became known as the ''shire town'' or later the county town. In many cases, the shires were named after their shire town (for example Bedford''shire''), but there are several exceptions, such as Cumberland, Norfolk and Suffolk. In several other cases, such as Buckinghamshire, the modern county town is different from the town after which the shire is named. (See Toponymical list of counties of the United Kingdom)
Most non-metropolitan counties in England are run by
 In
In
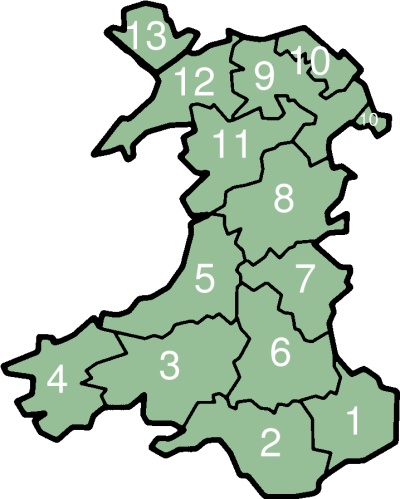
 The thirteen historic counties of Wales were fixed by statute in 1539 (although counties such as Pembrokeshire date from 1138) and most of the shires of Scotland are of at least this age. The Welsh word for county is ''sir'' which is derived from the English 'shire'. The word is officially used to signify counties in Wales. In the Gaelic form, Scottish traditional county names are generally distinguished by the designation —literally "sheriffdom", e.g. (Argyllshire). This term corresponds to the jurisdiction of the sheriff in the Scottish legal system.
The thirteen historic counties of Wales were fixed by statute in 1539 (although counties such as Pembrokeshire date from 1138) and most of the shires of Scotland are of at least this age. The Welsh word for county is ''sir'' which is derived from the English 'shire'. The word is officially used to signify counties in Wales. In the Gaelic form, Scottish traditional county names are generally distinguished by the designation —literally "sheriffdom", e.g. (Argyllshire). This term corresponds to the jurisdiction of the sheriff in the Scottish legal system.
 Counties in U.S. states are Administrative division, administrative or political subdivision of the state in which their boundaries are drawn. In addition, the United States Census Bureau uses the term "county equivalent" to describe places that are comparable to counties, but called by different names. Today, 3,142 counties and county equivalents carve up the United States, ranging in number from 3 for Delaware to 254 for Texas.
Forty-eight of the 50 U.S. states use the term "county", while Alaska and Louisiana use the terms "List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, borough" and "List of parishes in Louisiana, parish", respectively, for analogous jurisdictions. A ''consolidated city-county'' such as Philadelphia and San Francisco is formed when a city and county merge into one unified jurisdiction. Conversely, an ''Independent city (United States), independent city'' like Baltimore and St. Louis legally belongs to no county, i.e. no county even nominally exists in those places compared to a consolidated city-county where a county does legally exist in some form. The Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, outside the jurisdiction of any state, is viewed by the U.S. Census Bureau as a single county equivalent.
The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states. They are generally the intermediate tier of state government, between the statewide tier and the immediately local government tier (typically a city, town/borough or village/township). Some of the governmental functions that a county may offer include judiciary, county prisons, land registration, enforcement of building codes, and federally mandated services programs. Depending on the individual state, counties or their equivalents may be administratively subdivided into
Counties in U.S. states are Administrative division, administrative or political subdivision of the state in which their boundaries are drawn. In addition, the United States Census Bureau uses the term "county equivalent" to describe places that are comparable to counties, but called by different names. Today, 3,142 counties and county equivalents carve up the United States, ranging in number from 3 for Delaware to 254 for Texas.
Forty-eight of the 50 U.S. states use the term "county", while Alaska and Louisiana use the terms "List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, borough" and "List of parishes in Louisiana, parish", respectively, for analogous jurisdictions. A ''consolidated city-county'' such as Philadelphia and San Francisco is formed when a city and county merge into one unified jurisdiction. Conversely, an ''Independent city (United States), independent city'' like Baltimore and St. Louis legally belongs to no county, i.e. no county even nominally exists in those places compared to a consolidated city-county where a county does legally exist in some form. The Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, outside the jurisdiction of any state, is viewed by the U.S. Census Bureau as a single county equivalent.
The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states. They are generally the intermediate tier of state government, between the statewide tier and the immediately local government tier (typically a city, town/borough or village/township). Some of the governmental functions that a county may offer include judiciary, county prisons, land registration, enforcement of building codes, and federally mandated services programs. Depending on the individual state, counties or their equivalents may be administratively subdivided into
 A county is a geographic
A county is a geographic region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary
The ''Chambers Dictionary'' (''TCD'') was first published by William and Robert Chambers as ''Chambers's English Dictionary'' in 1872. It was an expanded version of ''Chambers's Etymological Dictionary'' of 1867, compiled by James Donald. A sec ...
, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intellig ...
denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
(earl
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form '' jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particula ...
) or a viscount
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status.
In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judicia ...
.The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology, C. W. Onions (Ed.), 1966, Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including , , , , , , , and ''zhupa'' in Slavic languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the ...
; terms equivalent to commune/community are now often instead used.
When the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
conquered England, they brought the term with them. The Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
had already established the districts that became the historic counties of England
The historic counties of England are areas that were established for administration by the Normans, in many cases based on earlier kingdoms and shires created by the Angles, Saxons, Jutes, Celts and others. They are alternatively known as an ...
, calling them shires;Vision of Britai– Type details for ancient county. Retrieved 31 March 2012 many county names derive from the name of the county town (
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
) with the word ''shire'' added on: for example, Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
and Worcestershire
Worcestershire ( , ; written abbreviation: Worcs) is a county in the West Midlands of England. The area that is now Worcestershire was absorbed into the unified Kingdom of England in 927, at which time it was constituted as a county (see H ...
. The Anglo-Saxon terms ''earl'' and ''earldom'' were taken as equivalent to the continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
terms "count" and "county" under the conquering Normans, and over time the two blended and became equivalent. Further, the later-imported term became a synonym for the native Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
word () or, in Modern English, ''shire'' – an equivalent administrative division of the kingdom. The term "county" evolved, consequently, to designate a level of local administration
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
that was immediately beneath a national government, within a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigrou ...
(non-federal) system of government. County later also became used differently in some federal systems of government, for a local administrative division subordinate to a primary subnational entity, such as a Province (e.g. Canada) or a level 3 territorial unit (NUTS 3).
In the United States and Canada, founded 600 years later on the British traditions, counties are usually an administrative division set by convenient geographical demarcations, which in governance have certain officeholders (for example sheriffs and their departments) as a part of the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
and provincial mechanisms, including geographically common court systems.
A county may be further subdivided into districts, hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to des ...
s, townships
A township is a kind of human settlement or administrative subdivision, with its meaning varying in different countries.
Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, that tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, C ...
or other administrative jurisdictions within the county. A county usually, but not always, contains cities, towns, townships
A township is a kind of human settlement or administrative subdivision, with its meaning varying in different countries.
Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, that tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, C ...
, village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred ...
s, or other municipal corporation
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally ...
s, which in most cases are somewhat subordinate or dependent upon county governments. Depending on the nation, municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
, and local geography, municipalities may or may not be subject to direct or indirect county control — the functions of both levels are often consolidated into a city government when the area is densely populated.
Outside English-speaking countries
The following is a list of English-speaking population by country, including information on both native speakers and second-language speakers.
List
* The European Union is a supranational union composed of 27 member states. The total En ...
, an equivalent of the term ''county'' is often used to describe subnational jurisdictions that are structurally equivalent to counties in the relationship they have with their national government; but which may not be administratively equivalent to counties in predominantly English-speaking countries.
Africa
Kenya
Counties are the current second-level political division in Kenya. Each county has an assembly where members of the county assembly (MCAs) sit. This assembly is headed by a governor. Each county is also represented in theSenate of Kenya
The Senate of the Republic of Kenya is one of the two Houses of the Parliament of Kenya, along with the National Assembly. The Senate was first established as part of Kenya's 1963 Constitution.
After being abolished in 1966, the Senate wa ...
by a senator. Additionally, a women's representative is elected from each county to the Parliament of Kenya
The Parliament of Kenya is the bicameral legislature of Kenya. It is based at Parliament Buildings in Nairobi and consists of two houses:
* Senate (upper house)
* The National Assembly ( lower house)
See also
*Politics of Kenya
* List of legisl ...
to represent women's interests. Counties replaced provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
as the second-level division after the promulgation of the 2010 Constitution of Kenya.
Liberia
Liberia has 15 counties, each of which elects two senators to theSenate of Liberia
The Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislative branch of Liberia, and together with the House of Representatives comprises the Legislature of Liberia. Each of the fifteen counties are equally represented by two senators, elected to ...
.
Asia
China
The English word ''county'' is used to translate the Chinese term ( or ). InMainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
, governed by the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(PRC), counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
and county-level division
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there ...
s are the third level of regional/local government, coming under the provincial level
Provincial may refer to:
Government & Administration
* Provincial capitals, an administrative sub-national capital of a country
* Provincial city (disambiguation)
* Provincial minister (disambiguation)
* Provincial Secretary, a position in Can ...
and the prefectural level, and above the township level and village level.
There are 1,464 so-named "counties" out of 2,862 county-level divisions in the PRC, and the number of counties has remained more or less constant since the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warr ...
(206 BC – AD 220). It remains one of the oldest titles of local-level government in China and significantly predates the establishment of provinces in the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fift ...
(1279–1368). The county government was particularly important in imperial China because this was the lowest level at which the imperial government is functionally involved, while below it the local people are managed predominantly by the gentries. The head of a county government during imperial China was the magistrate
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a '' magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judic ...
, who was often a newly ascended ''jinshi
''Jinshi'' () was the highest and final degree in the imperial examination in Imperial China. The examination was usually taken in the imperial capital in the palace, and was also called the Metropolitan Exam. Recipients are sometimes referr ...
''.
In older context, ''district'' was an older English translation of before the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC). The English nomenclature ''county'' was adopted following the establishment of the ROC. In addition, provincial cities have the same level of authority as counties. Above county, there are special municipalities (in effect) and province (suspended due to economical and political reasons). There are currently 13 counties in the ROC-controlled territories.
During most of the imperial era, there were no concepts like municipalities in China. All cities existed within counties, commanderies, prefectures, etc., and had no governments of their own. Large cities (must be imperial capitals or seats of prefectures) could be divided and administered by two or three counties. Such counties are called 倚郭縣 (, 'county leaning on the city walls') or (, 'county attached to the city walls'). The yamen
A ''yamen'' (''ya-men''; ; Manchu: ''yamun'') was the administrative office or residence of a local bureaucrat or mandarin in imperial China. A ''yamen'' can also be any governmental office or body headed by a mandarin, at any level of gover ...
or governmental houses of these counties exist in the same city. In other words, they share one county town. In this sense, a or is similar to a district of a city.
For example, the city of Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
(seat of the eponymous prefecture, also known as ''Canton'' in the Western world) was historically divided by Nanhai County
Nanhai County was a former county in Guangdong Province, China, named after the South China Sea.
Its former area now makes up Nanhai District in Foshan and Liwan District in Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and C ...
() and Panyu County
Panyu, alternately romanized as Punyu, is one of 11 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province, China. It was a separate county-level city before its incorporation into modern Guangzhou in 200 ...
(). When the first modern city government in China was established in Guangzhou, the urban area was separated from these two counties, with the rural areas left in the remaining parts of them. However, the county governments remained in the city for years, before moving into the respective counties. Similar processes happened in many Chinese cities.
Nowadays, most counties in mainland China, i.e. with "Xian" in their titles, are administered by prefecture-level cities
A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure.
During the Republican era, many of China' ...
and have mainly agricultural economies and rural populations.
Iran
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
are further subdivided into counties called ( fa, شهرستان). County consists of a city centre, a few ( fa, بخش), and many villages around them. There are usually a few cities ( fa, شهر, ) and rural agglomerations ( fa, دهستان, ) in each county. Rural agglomerations are a collection of a number of villages. One of the cities of the county is appointed as the capital of the county.
Each has a government office known as (), which coordinates different events and government offices. The , or the head of , is the governor of the .
Fars Province has the highest number of , with 36, while Qom uniquely has one, being coextensive with its namesake county. Iran had 324 in 2005 and 443 in 2021.
Korea
County is the common English translation for thecharacter
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to The ...
( or ) that denotes the current second level political division in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eas ...
. In North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
, the county is one type of municipal-level division.
Europe
Denmark
Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
was divided into counties ( da, amter) from 1662 to 2006. On 1 January 2007 the counties were replaced by five Regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
. At the same time, the number of municipalities was slashed to 98.
The counties were first introduced in 1662, replacing the 49 fiefs () in Denmark–Norway with the same number of counties. This number does not include the subdivisions of the Duchy of Schleswig, which was only under partial Danish control. The number of counties in Denmark (excluding Norway) had dropped to around 20 by 1793. Following the reunification of South Jutland with Denmark in 1920, four counties replaced the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n . Aabenraa
Aabenraa (; , ; Sønderjysk: ''Affenråe'') is a town in Southern Denmark, at the head of the Aabenraa Fjord, an arm of the Little Belt, north of the Denmark–Germany border and north of German town of Flensburg. It was the seat of Sønderjyl ...
and Sønderborg County
Sønderborg County ( da, Sønderborg Amt) is a former province in Denmark, located on the island of Als and the easternmost part of Southern Jutland. Sønderborg County was established in 1920 following the reunification of Denmark and South Jutl ...
merged in 1932 and Skanderborg
Skanderborg is a town in Skanderborg municipality, Denmark. It is situated on the north and north eastern brinks of Skanderborg Lake and there are several smaller ponds and bodies of water within the city itself, like Lillesø, Sortesø, Døj S ...
and Aarhus were separated in 1942. From 1942 to 1970, the number stayed at 22. The number was further decreased by the 1970 Danish municipal reform, leaving 14 counties plus two cities unconnected to the county structure; Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
and Frederiksberg
Frederiksberg () is a part of the Capital Region of Denmark. It is formally an independent municipality, Frederiksberg Municipality, separate from Copenhagen Municipality, but both are a part of the City of Copenhagen. It occupies an area of ...
.
In 2003, Bornholm County
Bornholms Amt () is a former county ( Danish, ''amt'') on the island of Bornholm in easternmost Denmark.
Short history
The county was established in 1662, replacing the former Hammershus Len. It was the only county unchanged by the administr ...
merged with the local five municipalities, forming the Bornholm Regional Municipality
Bornholm () is a Danish island in the Baltic Sea, to the east of the rest of Denmark, south of Sweden, northeast of Germany and north of Poland.
Strategically located, Bornholm has been fought over for centuries. It has usually been ruled ...
. The remaining 13 counties were abolished on 1 January 2007 where they were replaced by five new regions. In the same reform, the number of municipalities was slashed from 270 to 98 and all municipalities now belong to a region.
France
count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
() in medieval France. In modern France, the rough equivalent of a county as used in many English-speaking countries is a department (). Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
, and five are overseas departments
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainlan ...
, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 334 arrondissements
An arrondissement (, , ) is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
Europe
France
The 101 French departments are divided into 342 ''arrondissements'', ...
, but these have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections.
Germany
Each administrative district consists of an elected council and an executive, and whose duties are comparable to those of a county executive in the United States, supervising local government administration. Historically, counties in theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
were called .
The majority of German districts are "rural districts" (German: ), of which there are 294 . Cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants (and smaller towns in some states) do not usually belong to a district, but take on district responsibilities themselves, similar to the concept of independent cities and there are 107 of them, bringing the total number of districts to 401.
Hungary
The administrative unit ofHungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
is called (historically, they were also called ; in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
), which can be translated with the word ''county''. The 19 counties constitute the highest level of the administrative subdivisions of the country together with the capital city Budapest, although counties and the capital are grouped into seven statistical regions.
Counties are subdivided to municipalities, the two types of which are towns and villages, each one having their own elected mayor and council. 23 of the towns have the rights of a county although they do not form independent territorial units equal to counties. Municipalities are grouped within counties into subregions (), which have statistical and organizational functions only.
The was also the historic administrative unit in the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, which included areas of present-day neighbouring countries of Hungary. Its Latin name () is the equivalent of the French . Actual political and administrative role of counties changed much through history. Originally they were subdivisions of the royal administration, but from the 13th century they became self-governments of the nobles and kept this character until the 19th century when in turn they became modern local governments.
Ireland
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
was historically divided into 32 counties, of which 26 later formed the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern ...
and 6 made up Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
.
These counties are traditionally grouped into four provinces: Leinster
Leinster ( ; ga, Laighin or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, situated in the southeast and east of Ireland. The province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige. Following the 12th-century Norman invasion of ...
(12 counties), Munster (6), Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms ( Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Del ...
(5) and Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kin ...
(9). Historically, the counties of Meath and Westmeath
"Noble above nobility"
, image_map = Island of Ireland location map Westmeath.svg
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Ireland
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 =
, subdivis ...
and small parts of surrounding counties constituted the province of Mide
Meath (; Old Irish: ''Mide'' ; spelt ''Mí'' in Modern Irish) was a kingdom in Ireland from the 1st to the 12th century AD. Its name means "middle," denoting its location in the middle of the island.
At its greatest extent, it included all ...
, which was one of the "Five Fifths" of Ireland (in the Irish language the word for province, , means 'a fifth': from , 'five'); however, these have long since been absorbed into Leinster. In the Republic each county is administered by an elected "county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irel ...
", and the old provincial divisions are merely traditional names with no political significance.
The number and boundaries of administrative counties in the Republic of Ireland were reformed in the 1990s. For example, County Dublin
"Action to match our speech"
, image_map = Island_of_Ireland_location_map_Dublin.svg
, map_alt = map showing County Dublin as a small area of darker green on the east coast within the lighter green background of ...
was divided into three: Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Fingal, and South Dublin; the City of Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 cen ...
had existed for centuries before. The cities of Cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
and Galway
Galway ( ; ga, Gaillimh, ) is a city in the West of Ireland, in the province of Connacht, which is the county town of County Galway. It lies on the River Corrib between Lough Corrib and Galway Bay, and is the sixth most populous city on ...
have been separated from the town and rural areas of their counties. The cities of Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
and Waterford were merged with their respective counties in 2014. Thus, the Republic of Ireland now has 31 'county-level' authorities, although the borders of the original twenty-six counties are still officially in place.
In Northern Ireland, the six county councils and the smaller town councils were abolished in 1973 and replaced by a single tier of local government. However, in the north as well as in the south, the traditional 32 counties and 4 provinces remain in common usage for many sporting, cultural and other purposes. County identity is heavily reinforced in the local culture by allegiances to county teams in hurling and Gaelic football. Each Gaelic Athletic Association county has its own flag/colours (and often a nickname), and county allegiances are taken quite seriously. See the counties of Ireland and the Gaelic Athletic Association.
Italy
In Italy the word ''county'' is not used; the administrative sub-division of a region is called . Italy, Italian provinces are mainly named after their principal town and comprise several administrative subdivisions called ('communes'). There are currently 110 provinces in Italy. In the context of pre-modern Italy, the Italian word generally refers to the countryside surrounding, and controlled by, the city state. The provided natural resources and agricultural products to sustain the urban population. In contemporary usage, can refer to a metropolitan area, and in some cases large rural/suburban regions providing resources to distant cities.Lithuania
(plural ) is the Lithuanian word for county. Since 1994 Lithuania has 10 counties; before 1950 it had 20. The only purpose with the county is an office of a state governor who shall conduct law and order in the county.Norway
Norway has been divided into 11 counties of Norway, counties ( nb, fylker, nn, fylke; singular: ) since 2020; they previously numbered 19 following a local government reform in 1972. Until that year Bergen was a separate county, but today it is amunicipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
within the county of Vestland. All counties form administrative entities called county municipalities ( or ; singular: ), further subdivided into list of municipalities of Norway, municipalities ( or ; singular: ). One county, Oslo, is not divided into municipalities, rather it is equivalent to the municipality of Oslo.
Each county has its own county council (Norway), county council () whose representatives are elected every four years together with representatives to the municipal council (Norway), municipal councils. The counties handle matters such as high schools and local roads, and until 1 January 2002 hospitals as well. This last responsibility was transferred to the state-run regional health authority (Norway), health authorities and health trusts, and there is a debate on the future of the county municipality as an administrative entity. Some people, and parties, such as the Conservative Party (Norway), Conservative and Progress Party (Norway), Progress Party, call for the abolition of the county municipalities once and for all, while others, including the Labour Party (Norway), Labour Party, merely want to merge some of them into larger regions.
Poland
 The territorial administration of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The country is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, ''voivodeships'' (provinces); these are further divided into ''powiats'' (counties or districts). The term ''powiat'' is often translated into English as ''county'' (or sometimes ''district''). In historical contexts this may be confusing because the Polish term ''hrabstwo'' (a territorial unit administered/owned by a ''hrabia'' (
The territorial administration of Poland since 1999 has been based on three levels of subdivision. The country is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, ''voivodeships'' (provinces); these are further divided into ''powiats'' (counties or districts). The term ''powiat'' is often translated into English as ''county'' (or sometimes ''district''). In historical contexts this may be confusing because the Polish term ''hrabstwo'' (a territorial unit administered/owned by a ''hrabia'' (count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
) is also literally translated as "county" and it was subordinated under ''powiat''.
The 380 county-level entities in Poland include 314 "land counties" (powiaty ziemskie) and the 66 "city counties" (''miasta na prawach powiatu'' or ''powiaty grodzkie'') . They are subdivisions of the 16 voivodeship (Poland), ''voivodeship'', and are further subdivided into 2,477 gminas (also called commune or municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
).
Romania
 The Romanian word for county, , is not currently used for any Romanian administrative divisions. Romania is divided into a total of 41 counties ( ro, județe), which along with the
The Romanian word for county, , is not currently used for any Romanian administrative divisions. Romania is divided into a total of 41 counties ( ro, județe), which along with the municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
of Bucharest, constitute the official administrative divisions of Romania. They represent Romania, the country's NUTS-3 (Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics – Level 3) statistical subdivisions within the European Union and each of them serves as the local level of Government of Romania, government within its borders. Most counties are named after a major Rivers in Romania, river, while some are named after notable cities within them, such as the county seat.
Sweden
Ukraine
In Ukraine the county () was introduced in Ukrainian territories under Poland in the second half of the 14th century, and in the eighteenth century under the Russian Empire in the Cossack Hetmanate, Sloboda Ukraine, Southern Ukraine, and Right-bank Ukraine, Right-Bank Ukraine. In 1913 there were 126 counties in Ukrainian-inhabited territories of the Russian Empire. Under the Austrian Empire in 1914 there were 59 counties in Ukrainian-inhabited Galicia, 34 in Carpathian Ruthenia, Transcarpathia, and 10 in Bukovina. Counties were retained by the independent Ukrainian People's Republic of 1917–1921, and in Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Romania until the Soviet annexations at the start of World War II. 99 counties formed the Ukrainian SSR in 1919, where they were abolished in 1923–25 in favour of 53 Okruhas of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, okruhas (in turn replaced by Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts in 1930–32), although they existed in the Zakarpattia Oblast until 1953.United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is divided into a number of metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties of England, metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties. There are also ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial counties which group small non-metropolitan counties into geographical areas broadly based on thehistoric counties of England
The historic counties of England are areas that were established for administration by the Normans, in many cases based on earlier kingdoms and shires created by the Angles, Saxons, Jutes, Celts and others. They are alternatively known as an ...
. In 1974, the metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties replaced the system of administrative counties of England, administrative counties and county boroughs which was introduced in 1889. The counties generally belong to level 3 of the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics#Former EU state, NUTS 3).
In 1965 and 1974–1975, major reorganisations of local government in England and Wales created several new administrative counties such as Hereford and Worcester (abolished again in 1998 and reverted, with some transfers of territory, to the two separate historic counties of Herefordshire and Worcestershire) and also created several new metropolitan county, metropolitan counties based on large urban areas as a single administrative unit. In Scotland, county-level local government was replaced by larger local government areas of Scotland 1973 to 1996, regions, which lasted until 1996. Modern local government in Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and a large part of England is trending towards smaller unitary authorities: a system similar to that proposed in the 1960s by the Redcliffe-Maud Report for most of Britain.
The name "county" was introduced by the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
, and was derived from a Norman term for an area administered by a Count (lord). These Norman "counties" were simply the Saxon shires, and kept their Saxon names. Several traditional counties, including Essex, Sussex and Kent, predate the unification of England by Alfred the Great, and were originally more or less independent kingdoms (although the most important Saxon Kingdom on the island of Britain, Alfred's own Wessex, no longer survives in any form).
England
county council
A county council is the elected administrative body governing an area known as a county. This term has slightly different meanings in different countries.
Ireland
The county councils created under British rule in 1899 continue to exist in Irel ...
s and are divided into non-metropolitan districts, each with its own council. Local authorities in the UK are usually responsible for education, emergency services, planning, transport, social services, and a number of other functions.
Until 1974, the county boundaries of England changed little over time. In the medieval period, a number of important cities were granted the status of counties in their own right, such as London, Bristol and Coventry, and numerous small exclaves such as Islandshire were created. In 1844, most of these exclaves were transferred to their surrounding counties.
Northern Ireland
 In
In Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, the six county councils, if not their counties, were abolished in 1973 and replaced by 26 local government districts. The traditional six counties remain in common everyday use for many cultural and other purposes.
Scotland and Wales

 The thirteen historic counties of Wales were fixed by statute in 1539 (although counties such as Pembrokeshire date from 1138) and most of the shires of Scotland are of at least this age. The Welsh word for county is ''sir'' which is derived from the English 'shire'. The word is officially used to signify counties in Wales. In the Gaelic form, Scottish traditional county names are generally distinguished by the designation —literally "sheriffdom", e.g. (Argyllshire). This term corresponds to the jurisdiction of the sheriff in the Scottish legal system.
The thirteen historic counties of Wales were fixed by statute in 1539 (although counties such as Pembrokeshire date from 1138) and most of the shires of Scotland are of at least this age. The Welsh word for county is ''sir'' which is derived from the English 'shire'. The word is officially used to signify counties in Wales. In the Gaelic form, Scottish traditional county names are generally distinguished by the designation —literally "sheriffdom", e.g. (Argyllshire). This term corresponds to the jurisdiction of the sheriff in the Scottish legal system.
North America
Canada
In Ontario, Quebec and Nova Scotia, Canadian province, provinces that have a two-tier system of local government, the counties constitute the upper tier and local municipalities form the lower tier. Manitoba and Saskatchewan are divided into rural municipalities. The Northwest Territories and Nunavut are divided into regions; however, these regions only serve to streamline the delivery of territorial governmental services, and have no government of their own. Newfoundland and Labrador, and Yukon do not have any second-level administrative subdivision between the provincial/territorial government and their municipalities.New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island
The counties of list of counties of New Brunswick, New Brunswick and list of counties of Prince Edward Island, Prince Edward Island are historical and have no governments of their own today. However, they remain used as census divisions, census Census geographic units of Canada, divisions by Statistics Canada, and by locals as geographic identifiers.Ontario
The primary administrative Ontario#Administrative divisions, division of Southern Ontario is its 22 counties, which are upper-tier local governments providing limited municipal services to rural and moderately dense areas—within them, there are a variety of lower-tier towns, cities, villages, etc. that provide most municipal services. This contrasts with Northern Ontario's 10 districts, which are geographic divisions but not local governments—although some towns, etc. are within them that are local governments, the low population densities and much larger area have significant impacts on how government is organized and operates. In both Northern and Southern Ontario, urban densities in cities are one of two other local structures: regional municipalities (restructured former counties which are also upper tiers) or single-tier municipalities.Quebec
Quebec's counties are more properly called "list of regional county municipalities and equivalent territories in Quebec, Regional County Municipalities" (). The province's List of former counties of Quebec, former counties proper were supplanted in the early 1980s.Alberta
A ''county'' in Alberta used to be a type of designation in a single-tier municipal system; but this was nominally changed to "list of municipal districts in Alberta, municipal district" under the ''Municipal Government Act'', when the ''County Act'' was repealed in the mid-1990s. However, at the time the new "municipal districts" were also permitted to retain the usage of ''county'' in their official names. As a result, in Alberta, the term ''list of municipal districts in Alberta, county'' is synonymous with the term ''list of municipal districts in Alberta, municipal district'' – it is not its own incorporated municipal status that is different from that of a municipal district. As such, Alberta Municipal Affairs provides municipal districts with the opportunity to change to a ''county'' in their official names, but some have chosen to hold out with the ''municipal district'' title. The vast majority of "municipal districts" in Alberta are named as counties.British Columbia
British Columbia has counties of British Columbia, counties for the purposes of its justice system but otherwise they hold no governmental function. For the provision of all other governmental services, the province is divided into list of regional districts of British Columbia, regional districts that form the upper tier, which are further subdivided into list of municipalities in British Columbia, local municipalities that are partly autonomous, and unincorporated area, unincorporated list of regional district electoral areas in British Columbia, electoral areas that are governed directly by the regional districts.Manitoba
The province of Manitoba was divided into List of former counties of Manitoba, counties; however, these counties were abolished in 1890.Jamaica
Jamaica is divided into 14 parishes of Jamaica, parishes which are grouped together into 3 historic counties of Jamaica, counties: Cornwall County, Jamaica, Cornwall, Middlesex County, Jamaica, Middlesex, and Surrey County, Jamaica, Surrey.United States
townships
A township is a kind of human settlement or administrative subdivision, with its meaning varying in different countries.
Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, that tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, C ...
, borough, boroughs or boros, or towns (in the New England states, New York (state), New York and Administrative divisions of Wisconsin, Wisconsin). For independent cities and consolidated city-counties, those places report directly to the state.
New York City is a special case where the city is made up of Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs, each of which is territorially coterminous with a List of counties in New York, county of New York State. In the context of city government, the boroughs are subdivisions of the city but are still called "county" where state function is involved, e.g., "''New York County'' Courthouse".
County governments in Rhode Island and Connecticut have been completely abolished but the entities remain for administrative and statistical purposes. Alaska's Unorganized Borough, Alaska, Unorganized Borough also has no county equivalent government, but the U.S. Census Bureau further divides it into statistical county equivalent subdivisions called List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, census areas.
The areas of each county also vary widely between the states. For example, the territorially medium-sized state of Pennsylvania has 67 counties delineated in geographically convenient ways. By way of contrast, Massachusetts, with far less territory, has massively sized counties in comparison even to Pennsylvania's largest, yet each organizes their judicial and incarceration officials similarly.
Most counties have a county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
: a city, town, or other named place where its administrative functions are centered. Some New England states use the term shire town to mean "county seat". A handful of counties like Harrison County, Mississippi have two or more county seats, usually located on opposite sides of the county, dating back from the days when travel was difficult.
Oceania
Australia
In the eastern states of Australia, counties are lands administrative divisions of Australia, used in the administration of land titles. They do not generally correspond to a level of government, but are used in the identification of parcels of land. The local communities in Australia that share the same post code are usually referred to as suburbs and localities (Australia), suburbs or localities. Several neighboring suburbs are often serviced by the same local government in Australia, local government known as a council, whose jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction is officially known as the local government area (LGA). An LGA functions basically the same way as a county of other countries, although it is called instead as "city", "municipality", "shire", "borough", "town", "district" or simple "councils" depending on the states and territories of Australia, state/territory and subregion. It performs municipal services and regulates construction permit, permits for land uses, but lacks any legislative or law enforcement powers.New Zealand
After New Zealand abolished its provinces of New Zealand, provinces in 1876, a system of counties similar to other countries' systems was instituted, lasting until 1989. They had chairmen, not mayors as boroughs and cities had; many legislative provisions (such as burial and subdivision (land), land subdivision control) were different for the counties. During the second half of the 20th century, many counties received overflow population from nearby cities. The result was often a merger of the two into a ''district'' (e.g. Rotorua) or a change of name to either ''district'' (e.g. Waimairi) or ''city'' (e.g. Manukau City). The Local Government Act 1974 (New Zealand), Local Government Act 1974 began the process of bringing urban, mixed, and rural councils into the same legislative framework. Substantial reorganisations under that Act resulted in the 1989 shake-up, which covered the country in (non-overlapping) cities and districts and abolished all the counties except for the Chatham Islands County, which survived under that name for a further 6 years but then became a "Territory" under the "Chatham Islands Council".South America
Argentina
Provinces in Argentina are divided into departments of Argentina, departments ( es, departamentos), except in the Buenos Aires Province, where they are called . The Buenos Aires, Autonomous City of Buenos Aires is divided into communes ().Notes
References
External links
* {{Authority control Counties, Types of administrative division