Council Of The District Of Columbia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Council of the District of Columbia is the legislative branch of the local government of the District of Columbia, the capital of the United States. As permitted in the
 When Congress passed the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, they called for a new permanent capital of the United States to be located on the Potomac River. The federal district originally comprised land in the form of a square measuring on each side donated by the states of Maryland and Virginia. The Residence Act also provided for the selection of a three-member board of commissioners, appointed by the president, charged with overseeing the construction of the new capital. Two other incorporated cities that predated the establishment of the district were also included within the new federal territory: Georgetown, founded in 1751, and the City of Alexandria, Virginia, founded in 1749. A new "federal city" called the City of Washington was then constructed on the north bank of the Potomac, to the east of the established settlement at Georgetown.
In 1800, Congress created a joint commission to recommend the governance for what was then called the Territory of Columbia. The joint commission recommended a governorship and a 25-member legislative assembly. This would have been the federal district's first legislature. However, the Organic Act of 1801 officially organized the entire federal territory under the control of Congress but did not establish an overarching government for the entire district as recommended. In 1802, the original board of commissioners was disbanded, and the City of Washington was officially incorporated. The city's incorporation allowed for a local municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the president and an elected six-member council. The local governments of Georgetown and Alexandria were also left intact. In 1820, the Congress granted the City of Washington a new charter, which allowed for an elected mayor.
This piecemeal governmental structure remained essentially intact until the passage of the Organic Act of 1871, which created a new government for the entire District of Columbia. This Act effectively combined the City of Washington, Georgetown, and the unincorporated area then known as Washington County – the portion south of the Potomac River had been returned to Virginia in the late 1840s – into a single municipality as Washington, D.C., exists today. In the same Organic Act, Congress created a territorial government which consisted of a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven council members appointed by the president and a 22-member house of delegates elected by the people, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city. In 1873, President Ulysses S. Grant appointed the board's most influential member, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the new post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale projects to modernize Washington but overspent three times the approved budget, bankrupting the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the district's local government in favor of a direct rule.
A three-member Board of Commissioners replaced the territorial government; two members were appointed by the president after approval by the Senate and a third member was selected from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. One of the three members would be selected to act as President of the Board. This form of government continued for nearly a century. Between 1948 and 1966, six bills were introduced in Congress to provide some form of home rule, but none ever passed. The commissioner form of government was replaced in 1967 by a mayor-commissioner and a nine-member city council appointed by the president.
Due to public pressure and the demands of handling the district's complex day-to-day affairs, Congress eventually agreed to devolve certain powers over the district to an elected local government. However, lawmakers in Congress during the early 1970s had originally sought to re-institute the post of governor and create a 25-member legislative assembly. Local officials opposed this form of government, insisting that the district's status as a municipality be respected. On December 24, 1973, Congress obliged the demands of local residents and enacted the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, providing for an elected mayor and the 13-member Council of the District of Columbia. The council has the ability to pass local laws and ordinances. However, pursuant to the Home Rule Act all legislation passed by the D.C. government, including the district's local budget, remains subject to the approval of Congress. After signing the bill, President Richard Nixon said, "I believe the legislation skillfully balances the local interest and the national interest in the way the District of Columbia is governed."
When Congress passed the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, they called for a new permanent capital of the United States to be located on the Potomac River. The federal district originally comprised land in the form of a square measuring on each side donated by the states of Maryland and Virginia. The Residence Act also provided for the selection of a three-member board of commissioners, appointed by the president, charged with overseeing the construction of the new capital. Two other incorporated cities that predated the establishment of the district were also included within the new federal territory: Georgetown, founded in 1751, and the City of Alexandria, Virginia, founded in 1749. A new "federal city" called the City of Washington was then constructed on the north bank of the Potomac, to the east of the established settlement at Georgetown.
In 1800, Congress created a joint commission to recommend the governance for what was then called the Territory of Columbia. The joint commission recommended a governorship and a 25-member legislative assembly. This would have been the federal district's first legislature. However, the Organic Act of 1801 officially organized the entire federal territory under the control of Congress but did not establish an overarching government for the entire district as recommended. In 1802, the original board of commissioners was disbanded, and the City of Washington was officially incorporated. The city's incorporation allowed for a local municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the president and an elected six-member council. The local governments of Georgetown and Alexandria were also left intact. In 1820, the Congress granted the City of Washington a new charter, which allowed for an elected mayor.
This piecemeal governmental structure remained essentially intact until the passage of the Organic Act of 1871, which created a new government for the entire District of Columbia. This Act effectively combined the City of Washington, Georgetown, and the unincorporated area then known as Washington County – the portion south of the Potomac River had been returned to Virginia in the late 1840s – into a single municipality as Washington, D.C., exists today. In the same Organic Act, Congress created a territorial government which consisted of a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven council members appointed by the president and a 22-member house of delegates elected by the people, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city. In 1873, President Ulysses S. Grant appointed the board's most influential member, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the new post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale projects to modernize Washington but overspent three times the approved budget, bankrupting the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the district's local government in favor of a direct rule.
A three-member Board of Commissioners replaced the territorial government; two members were appointed by the president after approval by the Senate and a third member was selected from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. One of the three members would be selected to act as President of the Board. This form of government continued for nearly a century. Between 1948 and 1966, six bills were introduced in Congress to provide some form of home rule, but none ever passed. The commissioner form of government was replaced in 1967 by a mayor-commissioner and a nine-member city council appointed by the president.
Due to public pressure and the demands of handling the district's complex day-to-day affairs, Congress eventually agreed to devolve certain powers over the district to an elected local government. However, lawmakers in Congress during the early 1970s had originally sought to re-institute the post of governor and create a 25-member legislative assembly. Local officials opposed this form of government, insisting that the district's status as a municipality be respected. On December 24, 1973, Congress obliged the demands of local residents and enacted the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, providing for an elected mayor and the 13-member Council of the District of Columbia. The council has the ability to pass local laws and ordinances. However, pursuant to the Home Rule Act all legislation passed by the D.C. government, including the district's local budget, remains subject to the approval of Congress. After signing the bill, President Richard Nixon said, "I believe the legislation skillfully balances the local interest and the national interest in the way the District of Columbia is governed."
 The council is composed of thirteen members, each elected by district residents to a four-year term. One member is elected from each of the district's eight
The council is composed of thirteen members, each elected by district residents to a four-year term. One member is elected from each of the district's eight
". ''Council of the District of Columbia''. Retrieved August 13, 2011. Commentators have questioned the legislature's structure noting that with 13 members nearly any piece of legislation can pass with just seven votes, leading to accusations that the council can too easily overreach in its powers. However, this unique governing structure has also allowed the council to operate more efficiently in comparison to some state legislatures with regard to consideration and passage of laws.
Official website
District of Columbia City Council Records
Special Collections Research Center, Estelle and Melvin Gelman Library, The George Washington University. {{DEFAULTSORT:Council Of The District Of Columbia District of Columbia Government of the District of Columbia District of Columbia Washington, D.C., government officials
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
, the district is not part of any U.S. state and is overseen directly by the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
.
Since 1975, the United States Congress has devolved to the Council certain powers that are typically exercised by city councils elsewhere in the country, as well as many powers normally held by state legislatures
A state legislature is a legislative branch or body of a political subdivision in a federal system.
Two federations literally use the term "state legislature":
* The legislative branches of each of the fifty state governments of the United Stat ...
. However, the Constitution vests Congress with ultimate authority over the federal district, and therefore all acts of the council are subject to congressional review. They may be overturned by Congress and the president. Congress also has the power to legislate for the district and even revoke the home rule charter altogether.
The council meets in the John A. Wilson Building in downtown Washington.
History
Under the Constitution, Congress has the power to legislate for the district "in all cases whatsoever," which has long been interpreted to vest Congress with ultimate authority over the capital. However, the Founding Fathers envisioned that Congress would delegate this authority to local officials. At various times in the district's history, Congress has devolved some of its authority to district residents and their elected representatives. When Congress passed the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, they called for a new permanent capital of the United States to be located on the Potomac River. The federal district originally comprised land in the form of a square measuring on each side donated by the states of Maryland and Virginia. The Residence Act also provided for the selection of a three-member board of commissioners, appointed by the president, charged with overseeing the construction of the new capital. Two other incorporated cities that predated the establishment of the district were also included within the new federal territory: Georgetown, founded in 1751, and the City of Alexandria, Virginia, founded in 1749. A new "federal city" called the City of Washington was then constructed on the north bank of the Potomac, to the east of the established settlement at Georgetown.
In 1800, Congress created a joint commission to recommend the governance for what was then called the Territory of Columbia. The joint commission recommended a governorship and a 25-member legislative assembly. This would have been the federal district's first legislature. However, the Organic Act of 1801 officially organized the entire federal territory under the control of Congress but did not establish an overarching government for the entire district as recommended. In 1802, the original board of commissioners was disbanded, and the City of Washington was officially incorporated. The city's incorporation allowed for a local municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the president and an elected six-member council. The local governments of Georgetown and Alexandria were also left intact. In 1820, the Congress granted the City of Washington a new charter, which allowed for an elected mayor.
This piecemeal governmental structure remained essentially intact until the passage of the Organic Act of 1871, which created a new government for the entire District of Columbia. This Act effectively combined the City of Washington, Georgetown, and the unincorporated area then known as Washington County – the portion south of the Potomac River had been returned to Virginia in the late 1840s – into a single municipality as Washington, D.C., exists today. In the same Organic Act, Congress created a territorial government which consisted of a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven council members appointed by the president and a 22-member house of delegates elected by the people, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city. In 1873, President Ulysses S. Grant appointed the board's most influential member, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the new post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale projects to modernize Washington but overspent three times the approved budget, bankrupting the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the district's local government in favor of a direct rule.
A three-member Board of Commissioners replaced the territorial government; two members were appointed by the president after approval by the Senate and a third member was selected from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. One of the three members would be selected to act as President of the Board. This form of government continued for nearly a century. Between 1948 and 1966, six bills were introduced in Congress to provide some form of home rule, but none ever passed. The commissioner form of government was replaced in 1967 by a mayor-commissioner and a nine-member city council appointed by the president.
Due to public pressure and the demands of handling the district's complex day-to-day affairs, Congress eventually agreed to devolve certain powers over the district to an elected local government. However, lawmakers in Congress during the early 1970s had originally sought to re-institute the post of governor and create a 25-member legislative assembly. Local officials opposed this form of government, insisting that the district's status as a municipality be respected. On December 24, 1973, Congress obliged the demands of local residents and enacted the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, providing for an elected mayor and the 13-member Council of the District of Columbia. The council has the ability to pass local laws and ordinances. However, pursuant to the Home Rule Act all legislation passed by the D.C. government, including the district's local budget, remains subject to the approval of Congress. After signing the bill, President Richard Nixon said, "I believe the legislation skillfully balances the local interest and the national interest in the way the District of Columbia is governed."
When Congress passed the Residence Act on July 16, 1790, they called for a new permanent capital of the United States to be located on the Potomac River. The federal district originally comprised land in the form of a square measuring on each side donated by the states of Maryland and Virginia. The Residence Act also provided for the selection of a three-member board of commissioners, appointed by the president, charged with overseeing the construction of the new capital. Two other incorporated cities that predated the establishment of the district were also included within the new federal territory: Georgetown, founded in 1751, and the City of Alexandria, Virginia, founded in 1749. A new "federal city" called the City of Washington was then constructed on the north bank of the Potomac, to the east of the established settlement at Georgetown.
In 1800, Congress created a joint commission to recommend the governance for what was then called the Territory of Columbia. The joint commission recommended a governorship and a 25-member legislative assembly. This would have been the federal district's first legislature. However, the Organic Act of 1801 officially organized the entire federal territory under the control of Congress but did not establish an overarching government for the entire district as recommended. In 1802, the original board of commissioners was disbanded, and the City of Washington was officially incorporated. The city's incorporation allowed for a local municipal government consisting of a mayor appointed by the president and an elected six-member council. The local governments of Georgetown and Alexandria were also left intact. In 1820, the Congress granted the City of Washington a new charter, which allowed for an elected mayor.
This piecemeal governmental structure remained essentially intact until the passage of the Organic Act of 1871, which created a new government for the entire District of Columbia. This Act effectively combined the City of Washington, Georgetown, and the unincorporated area then known as Washington County – the portion south of the Potomac River had been returned to Virginia in the late 1840s – into a single municipality as Washington, D.C., exists today. In the same Organic Act, Congress created a territorial government which consisted of a legislative assembly with an upper-house composed of eleven council members appointed by the president and a 22-member house of delegates elected by the people, as well as an appointed Board of Public Works charged with modernizing the city. In 1873, President Ulysses S. Grant appointed the board's most influential member, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the new post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale projects to modernize Washington but overspent three times the approved budget, bankrupting the city. In 1874, Congress abolished the district's local government in favor of a direct rule.
A three-member Board of Commissioners replaced the territorial government; two members were appointed by the president after approval by the Senate and a third member was selected from the United States Army Corps of Engineers. One of the three members would be selected to act as President of the Board. This form of government continued for nearly a century. Between 1948 and 1966, six bills were introduced in Congress to provide some form of home rule, but none ever passed. The commissioner form of government was replaced in 1967 by a mayor-commissioner and a nine-member city council appointed by the president.
Due to public pressure and the demands of handling the district's complex day-to-day affairs, Congress eventually agreed to devolve certain powers over the district to an elected local government. However, lawmakers in Congress during the early 1970s had originally sought to re-institute the post of governor and create a 25-member legislative assembly. Local officials opposed this form of government, insisting that the district's status as a municipality be respected. On December 24, 1973, Congress obliged the demands of local residents and enacted the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, providing for an elected mayor and the 13-member Council of the District of Columbia. The council has the ability to pass local laws and ordinances. However, pursuant to the Home Rule Act all legislation passed by the D.C. government, including the district's local budget, remains subject to the approval of Congress. After signing the bill, President Richard Nixon said, "I believe the legislation skillfully balances the local interest and the national interest in the way the District of Columbia is governed."
Composition
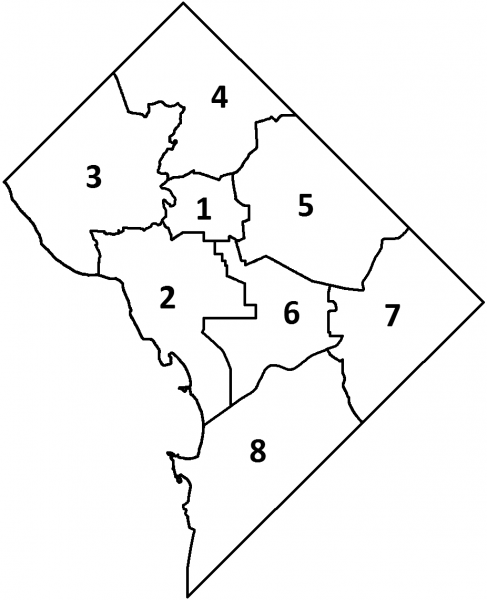
 The council is composed of thirteen members, each elected by district residents to a four-year term. One member is elected from each of the district's eight
The council is composed of thirteen members, each elected by district residents to a four-year term. One member is elected from each of the district's eight wards
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a priso ...
. Four at-large members represent the district as a whole. The chairman of the council is likewise elected at an at-large basis. The terms of the at-large members are staggered so that two are elected every two years, and each D.C. resident may vote for two different at-large candidates in each general election.
According to the Home Rule Act, of the chair and the at-large members, a maximum of three may be affiliated with the majority political party. In the council's electoral history, of the elected members who were not affiliated with the majority party, most were elected as at-large members. In 2008 and 2012, Democrats such as David Grosso, Elissa Silverman, and Michael A. Brown changed their party affiliation to Independent when running for council.
To become a candidate for council an individual must be resident of the District of Columbia for at least one year prior to the general election, a registered voter, and hold no other public office for which compensation beyond expenses is received. Candidates running for a ward position must be a resident of that ward.
Like other legislatures, the council has several standing committees and a full-time staff, including a council secretary, auditor, and general counsel. Given the limited number of council members, nearly every member of the council has, in effect, the opportunity to chair a committee.Organizational Structure". ''Council of the District of Columbia''. Retrieved August 13, 2011. Commentators have questioned the legislature's structure noting that with 13 members nearly any piece of legislation can pass with just seven votes, leading to accusations that the council can too easily overreach in its powers. However, this unique governing structure has also allowed the council to operate more efficiently in comparison to some state legislatures with regard to consideration and passage of laws.
Committees
Committees of the council consider legislation relevant to specific policy matters and are responsible for oversight on relevant local government agencies. Special committees are convened to consider investigations, ethics, and other matters. The members are nominated by the chairperson of the committee at the start of the council period and are voted on by the existing committee members. If a vacancy of a member occurs, the seat is filled by a vote on a nomination by the chairperson. If a vacancy of a councilperson occurs,Members

Salaries
As of December 2018, the eight ward and four at-large council members receive an annual salary of $140,161, while the council chairman receives an annual salary of $210,000. According to a 2011 article in '' The Washington Post'', the DC council were the second-highest-paid local representatives of large cities in the United States.See also
* List of members of the Council of the District of Columbia * Political party strength in Washington, D.C. *Neighborhoods in Washington, D.C.
Neighborhoods in Washington, D.C., are distinguished by their history, culture, architecture, demographics, and geography. The names of 131 neighborhoods are unofficially defined by the D.C. Office of Planning. Neighborhoods can be defined by t ...
References
External links
Official website
District of Columbia City Council Records
Special Collections Research Center, Estelle and Melvin Gelman Library, The George Washington University. {{DEFAULTSORT:Council Of The District Of Columbia District of Columbia Government of the District of Columbia District of Columbia Washington, D.C., government officials