Cornet à Bouquin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and
The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and
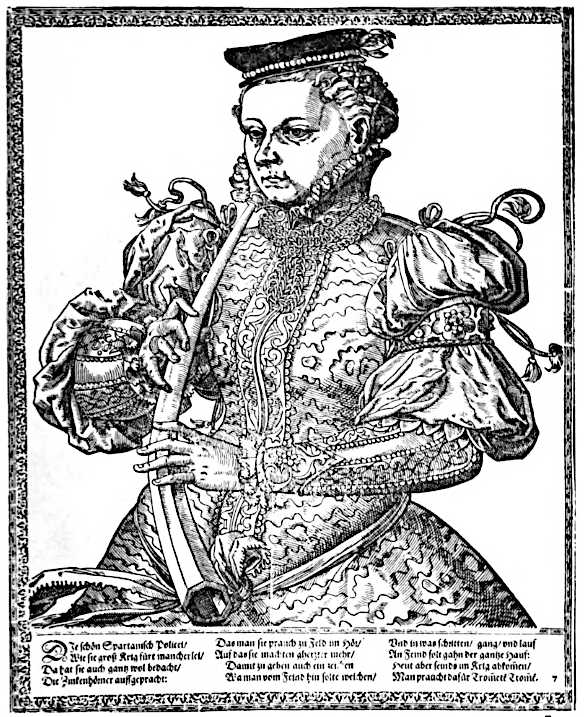 Historically, two cornetts were frequently used in consort with three sackbuts, often to double a church choir. This was particularly popular in
Historically, two cornetts were frequently used in consort with three sackbuts, often to double a church choir. This was particularly popular in
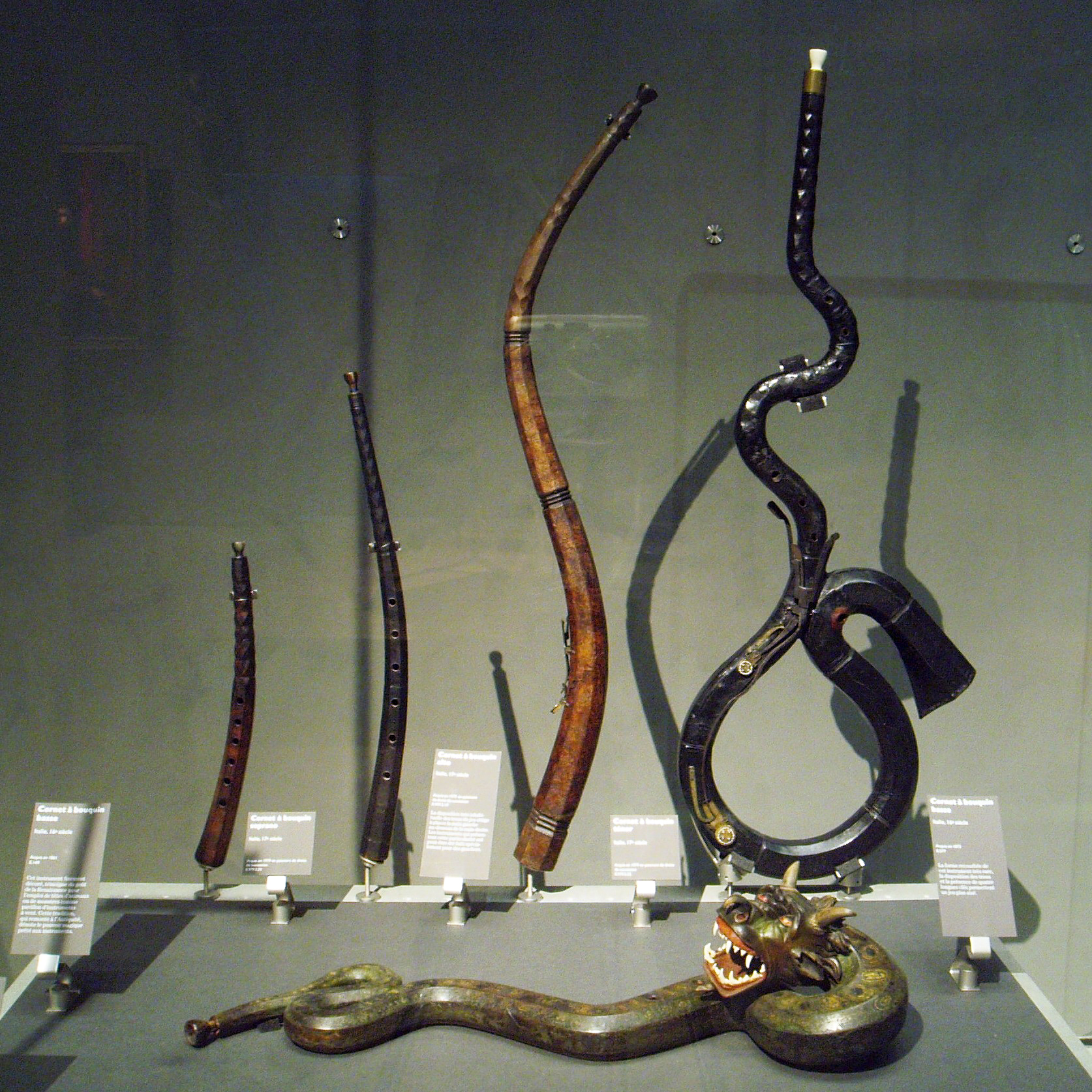 The cornett in its current form was developed in the late 15th or early 16th centuries, as an improvement over earlier designs of horn that had been around since at least the medieval era. These early instruments were played with one hand covering four or fewer fingerholes and the other stopping the bell to create additional tones, much like on a French horn. In Northern Europe, these horns, referred to in Scandinavian languages as
The cornett in its current form was developed in the late 15th or early 16th centuries, as an improvement over earlier designs of horn that had been around since at least the medieval era. These early instruments were played with one hand covering four or fewer fingerholes and the other stopping the bell to create additional tones, much like on a French horn. In Northern Europe, these horns, referred to in Scandinavian languages as
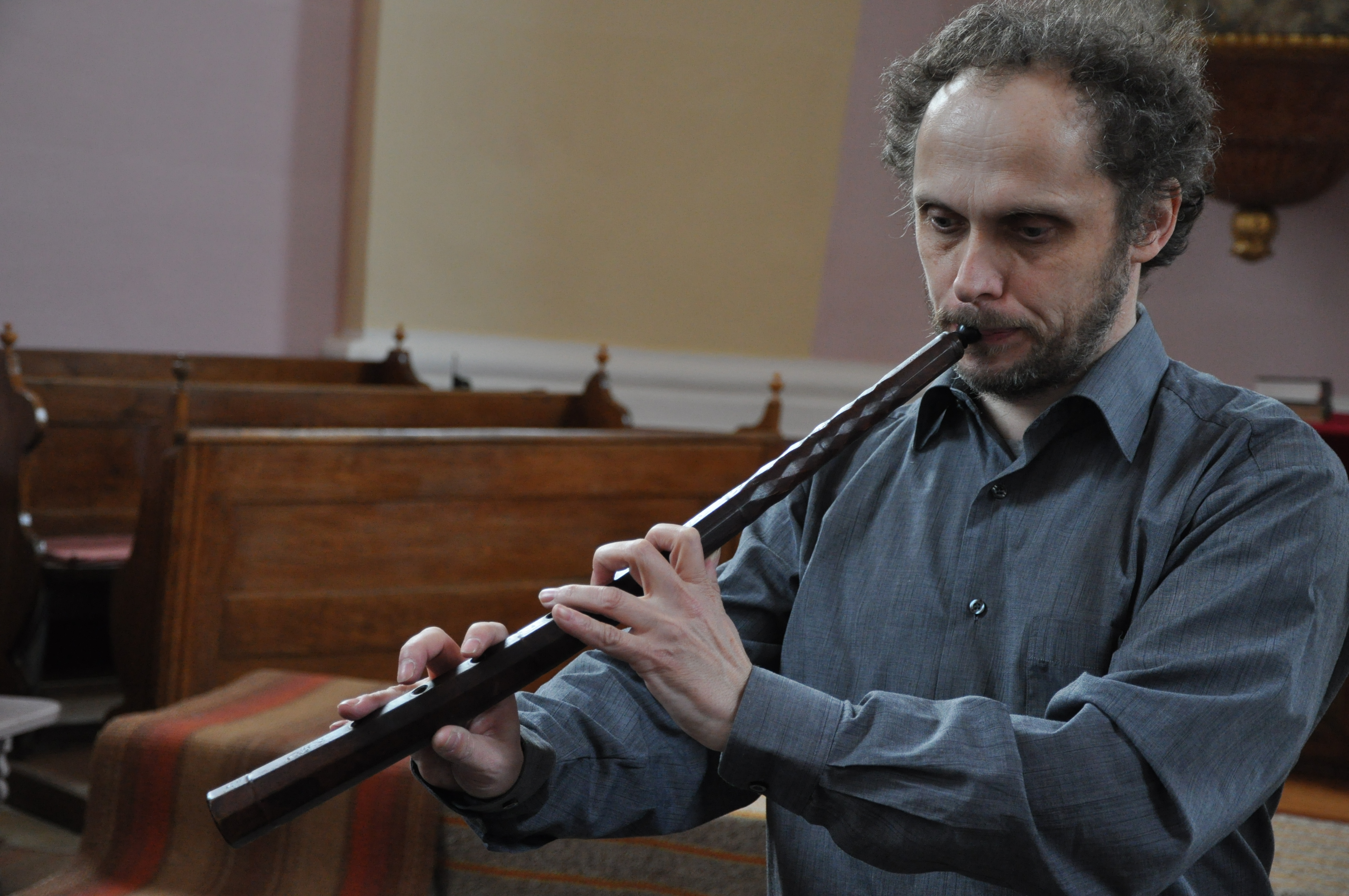 The cornett is generally regarded to be a difficult instrument to play, requiring a lot of practice. The instrument is similar in design to the Russian
The cornett is generally regarded to be a difficult instrument to play, requiring a lot of practice. The instrument is similar in design to the Russian
A third bass cornett in the collection of the Musée de la Musique, Paris
A page about the cornett
, one of the more well-known modern makers of cornetts Extant cornetts at The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ivory Cornetto, 1570–80, Germany
Tenor Cornetto, 17th century, France
Online sound recordings of modern performance, by ''Antiqua''L'Arpeggiata
with Christina Pluhar as conductor, (winner of the 2010 Dutch Edison) makes use of one or two cornetts
City of Lincoln Waites
''(The Mayor of Lincoln's own Band of Musick)''
Concerto Palatino
a leading ensemble centered on the cornetto and trombone and directed by Bruce Dickey and Charles Toet.
The English Cornett and Sackbut Ensemble
a performance group that makes use of the cornett
A French period performance group directed by cornettist Jean Tubery.
His Majestys Sagbutts & Cornetts
(est. 1982), the pre-eminent, internationally renowned British cornett and sackbut ensemble. * Johann Rosenmüller Ensemble, a performance group directed by the German cornetto player Arno Paduch
QuintEssential – Sackbut and Cornett ensemble
{{Authority control Baroque instruments Brass instruments Early musical instruments Horns Renaissance instruments
 The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and
The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
periods, popular from 1500 to 1650. It was used in what are now called alta capella
An alta cappella or alta musica (Italian), haute musique (French) or just alta was a kind of town wind band found throughout continental Europe from the thirteenth to the eighteenth centuries, which typically consisted of shawms and slide trumpets ...
s or wind ensembles. It is not to be confused with the modern cornet
The cornet (, ) is a brass instrument similar to the trumpet but distinguished from it by its conical bore, more compact shape, and mellower tone quality. The most common cornet is a transposing instrument in B, though there is also a sopr ...
.
The sound of the cornett is produced by lip vibrations against a cup mouthpiece, similar to modern brass instruments. A cornett consists of a conical wooden pipe covered in leather, is about long, and has finger holes and a small horn, ivory, or bone mouthpiece. The range is from A3 to A5, however the bottom note can be lipped as far as G3 and a good player can get up to E6.
Construction
The ordinary treble cornett is made by splitting a length of wood and gouging out the two halves to make the gently conical, curved bore. The halves are then glued together, and the outside planed to an octagonal cross section, the whole being bound in thin black leather. Six front finger holes and a thumb hole on the back (like on therecorder
Recorder or The Recorder may refer to:
Newspapers
* ''Indianapolis Recorder'', a weekly newspaper
* ''The Recorder'' (Massachusetts newspaper), a daily newspaper published in Greenfield, Massachusetts, US
* ''The Recorder'' (Port Pirie), a news ...
) are bored in the instrument, and are slightly undercut. The socket for the mouthpiece at the narrow end is reinforced with a brass collar, concealed by an ornamental silver or brass mount. The separate cup mouthpiece is usually made of horn, ivory, or bone, with a thin rim and thread-wrapped shank. Because it lacks a little-finger hole at the bottom, its lowest note is the A below middle C, though another tone lower could be produced by slackening the lips to flatten the note.
At least three existing specimens of bass cornett reside in the collection of the Musée de la Musique, Paris.
Music for the cornett
 Historically, two cornetts were frequently used in consort with three sackbuts, often to double a church choir. This was particularly popular in
Historically, two cornetts were frequently used in consort with three sackbuts, often to double a church choir. This was particularly popular in Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
churches such as the Basilica San Marco, where extensive instrumental accompaniment was encouraged, particularly in use with antiphonal choirs. Giovanni Bassano was a virtuoso early player of the cornett, and Giovanni Gabrieli wrote much of his polychoral music with Bassano in mind. Heinrich Schütz also used the instrument extensively, especially in his earlier work; he had studied in Venice with Gabrieli and was acquainted with Bassano's playing.
The cornett was, like almost all Renaissance and Baroque instruments, made in a complete family; the different sizes being the high cornettino, the cornett (or curved cornett), the tenor cornett (or lizard) and the rare bass cornett
The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods, popular from 1500 to 1650. It was used in what are now called alta capellas or wind ensembles. It is not to be confused w ...
. The serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
largely supplanted the bass cornett in the 17th century. Other versions include the mute cornett, which is a straight narrow-bore instrument with integrated mouthpiece, quiet enough to be used in a consort of viols or even recorders.
The cornett was also used as a virtuoso solo instrument, and a relatively large amount of solo music for the cornetto (and/or violin) survives. The use of the instrument had declined by 1700, although the instrument was still common in Europe until the late 18th century. Johann Sebastian Bach, Georg Philipp Telemann and their German contemporaries used both the cornett and cornettino in cantatas to play in unison with the soprano voices of the choir. Occasionally, these composers allocated a solo part to the cornetto (see Bach's cantata '' O Jesu Christ, meins Lebens Licht, BWV 118''). Alessandro Scarlatti
Pietro Alessandro Gaspare Scarlatti (2 May 1660 – 22 October 1725) was an Italian Baroque composer, known especially for his operas and chamber cantatas. He is considered the most important representative of the Neapolitan school of opera.
...
used the cornetto or pairs of cornetts in a number of his operas. Johann Joseph Fux used a pair of mute cornetts in a Requiem.
It was scored for by Gluck, in his opera ''Orfeo ed Euridice
' (; French: '; English: ''Orpheus and Eurydice'') is an opera composed by Christoph Willibald Gluck, based on Orpheus, the myth of Orpheus and set to a libretto by Ranieri de' Calzabigi. It belongs to the genre of the ''azione teatrale'', mea ...
'' (he suggested the soprano trombone as an alternative) and features in the TV theme music ''Testament'' by Nigel Hess, released in 1983.
History
 The cornett in its current form was developed in the late 15th or early 16th centuries, as an improvement over earlier designs of horn that had been around since at least the medieval era. These early instruments were played with one hand covering four or fewer fingerholes and the other stopping the bell to create additional tones, much like on a French horn. In Northern Europe, these horns, referred to in Scandinavian languages as
The cornett in its current form was developed in the late 15th or early 16th centuries, as an improvement over earlier designs of horn that had been around since at least the medieval era. These early instruments were played with one hand covering four or fewer fingerholes and the other stopping the bell to create additional tones, much like on a French horn. In Northern Europe, these horns, referred to in Scandinavian languages as bukkehorn
A bukkehorn (Norwegian) or bockhorn (Swedish), also called ″Billy Goat Horn″ in English, is an ancient Scandinavian musical instrument, made from the horn of a ram or a goat. The horn is usually made from a goat horn harvested 5 to 7 years ...
s, were made from natural animal horns, whereas similar instruments from central Europe were made from wood turned on a lathe
A lathe () is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to c ...
; the fusion of these two instrument-building traditions as the cornett advanced in melodic capability explains the coexistence of the straight and curved cornetts, with the form of the latter most likely being a skeuomorphic trait derived from animal horns.
Playing the cornett
 The cornett is generally regarded to be a difficult instrument to play, requiring a lot of practice. The instrument is similar in design to the Russian
The cornett is generally regarded to be a difficult instrument to play, requiring a lot of practice. The instrument is similar in design to the Russian Vladimir horn
The rozhok (russian: рожок) is an ancient Russian wooden trumpet, a relative of the cornett, which has remained in continuous use until the present day. It is also known as Vladimirskiy rozhok, (russian: Владимирский рожок ...
or rozhok. The main tube of the cornett is around the length of a modern clarinet or oboe, but the mouthpiece is that of a brass instrument, relying on a combination of the player's lips and the alteration of the length of the sound column via the opening and closing of the finger holes to alter the pitch.
Baroque theorist Marin Mersenne
Marin Mersenne, OM (also known as Marinus Mersennus or ''le Père'' Mersenne; ; 8 September 1588 – 1 September 1648) was a French polymath whose works touched a wide variety of fields. He is perhaps best known today among mathematicians for ...
described the sound of the cornett as "a ray of sunshine piercing the shadows". The instrument's upper register sounds somewhat like a modern trumpet or cornet, the lower register more closely resembling a trombone. Cornett intonation is flexible, which enables it to be played perfectly in tune in a range of tonalities and temperaments.
As a result of its design, the cornett requires a specialized embouchure that is, initially, tiring to play for any length of time. Violins often replaced cornetts in consort music, and cornetts similarly substituted for violins in consort music and sacred music. Like its successor, the serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
, the cornett was also used to reinforce the human voice in choirs. Due to their similarities, cornettists frequently also play trumpets or recorders.
The cornett and authentic performance
As a result of the recenthistorically informed performance
Historically informed performance (also referred to as period performance, authentic performance, or HIP) is an approach to the performance of Western classical music, classical music, which aims to be faithful to the approach, manner and style of ...
movement the cornett has been rediscovered, and modern works for the instrument have been written.
See also
Cornettino, Tenor cornett, Mute Cornett, Alto Cornett,Serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
,
Sackbut.
References
External links
* The French Wikipedia cornett page shows photos of two existing specimens of the bass cornettA third bass cornett in the collection of the Musée de la Musique, Paris
A page about the cornett
, one of the more well-known modern makers of cornetts Extant cornetts at The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ivory Cornetto, 1570–80, Germany
Tenor Cornetto, 17th century, France
Modern performance
Online sound recordings of modern performance, by ''Antiqua''
with Christina Pluhar as conductor, (winner of the 2010 Dutch Edison) makes use of one or two cornetts
City of Lincoln Waites
''(The Mayor of Lincoln's own Band of Musick)''
Concerto Palatino
a leading ensemble centered on the cornetto and trombone and directed by Bruce Dickey and Charles Toet.
The English Cornett and Sackbut Ensemble
a performance group that makes use of the cornett
A French period performance group directed by cornettist Jean Tubery.
His Majestys Sagbutts & Cornetts
(est. 1982), the pre-eminent, internationally renowned British cornett and sackbut ensemble. * Johann Rosenmüller Ensemble, a performance group directed by the German cornetto player Arno Paduch
QuintEssential – Sackbut and Cornett ensemble
{{Authority control Baroque instruments Brass instruments Early musical instruments Horns Renaissance instruments