Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cornelius "Sonny" Vanderbilt Whitney (February 20, 1899 – December 13, 1992) was an American businessman, film producer, government official, writer and philanthropist. He was also a polo player and the owner of a significant stable of
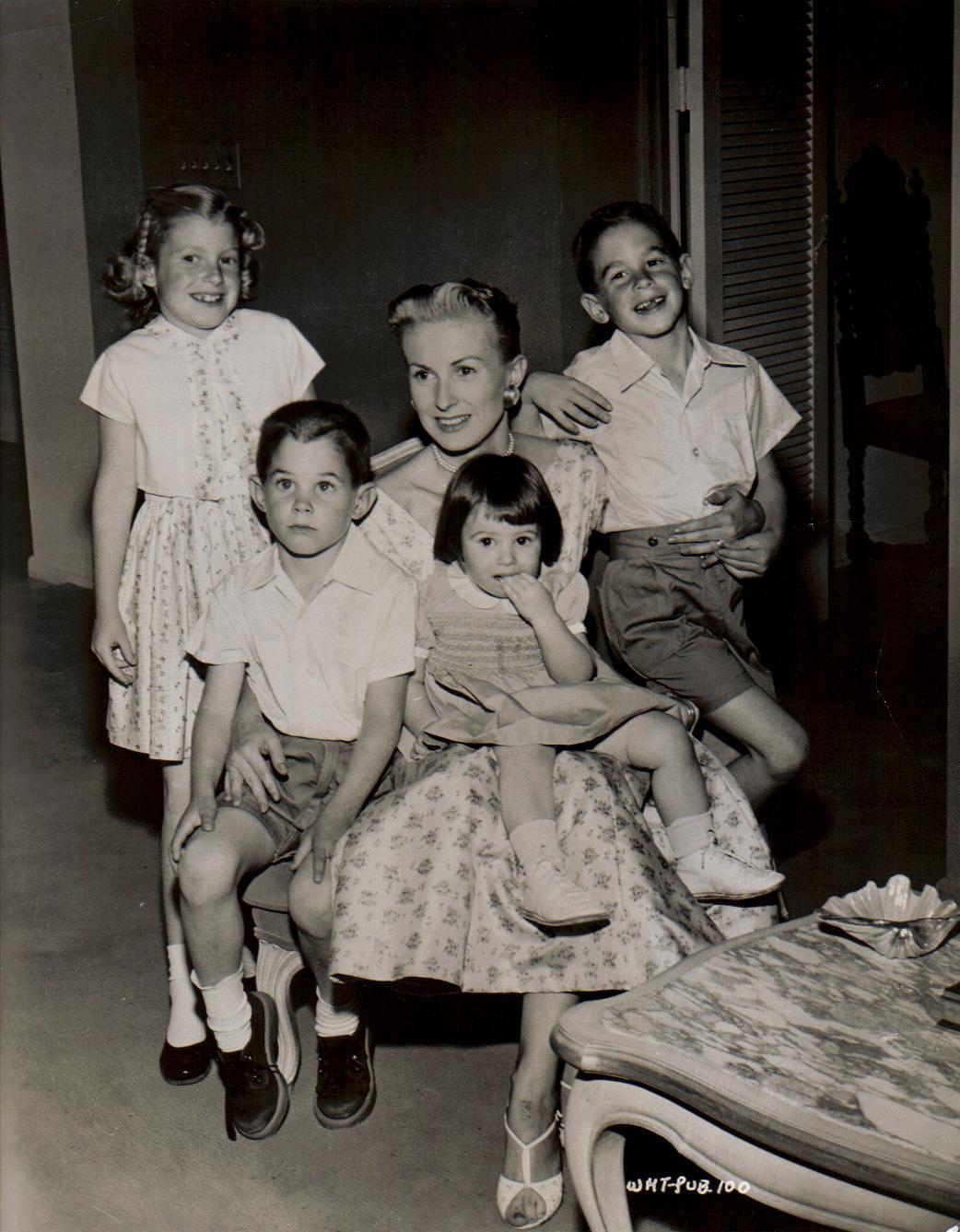
 Whitney habitually married:
On March 5, 1923, Whitney married for the first time to
Whitney habitually married:
On March 5, 1923, Whitney married for the first time to
Gulfbase.org Info
In addition, he donated Whitney Hall to the university, a building that serves as a conference center and contains dormitories and apartments. In 1963, his estate at
Thoroughbred
The Thoroughbred is a horse breed best known for its use in horse racing. Although the word ''thoroughbred'' is sometimes used to refer to any breed of purebred horse, it technically refers only to the Thoroughbred breed. Thoroughbreds are c ...
racehorses.
Early life
Born inOld Westbury, New York
Old Westbury is a village in the Towns of North Hempstead and Oyster Bay in Nassau County, on the North Shore of Long Island, in New York, United States. The population was 4,671 at the 2010 census.
The Incorporated Village of Old Westbury ...
, he was the only son of the wealthy and socially prominent Harry Payne Whitney
Harry Payne Whitney (April 29, 1872 – October 26, 1930) was an American businessman, thoroughbred horse breeder, and member of the prominent Whitney family.
Early years
Whitney was born in New York City on April 29, 1872, as the eldest son ...
(1872–1932) and his wife, Gertrude Vanderbilt (1875–1942). He had a younger sister, Barbara Vanderbilt Whitney (1903-1982), and an elder sister, Flora Payne Whitney
Flora Payne Whitney, also known as Flora Whitney Miller (July 27, 1897 – July 18, 1986), was an American artist and socialite, art collector, and patron of the arts.
Early life
Flora Payne Whitney was born on July 27, 1897 and raised in Manhatt ...
(1897–1986). As a member of both the Whitney Whitney may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Whitney'' (2015 film), a Whitney Houston biopic starring Yaya DaCosta
* ''Whitney'' (2018 film), a documentary about Whitney Houston
* ''Whitney'' (TV series), an American sitcom that premiered i ...
and Vanderbilt families, he inherited a substantial fortune. He also proved to be a very capable businessman in his own right.
Career
After graduating fromYale University
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wo ...
in 1922, he went to work at a Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
mine owned by his father. Whitney's paternal grandfather, William Collins Whitney
William Collins Whitney (July 5, 1841February 2, 1904) was an American political leader and financier and a prominent descendant of the John Whitney family. He served as Secretary of the Navy in the first administration of President Grover Clev ...
, was a co-founder and director of the Guaranty Trust Company of New York
J.P. Morgan & Co. is a commercial and investment banking institution founded by J. P. Morgan in 1871. Through a series of mergers and acquisitions, the company is now a subsidiary of JPMorgan Chase, one of the largest banking institutions in t ...
, and in 1926, Whitney was appointed a director, serving on the bank's board until 1940. In 1927, Whitney joined with William Avery Rockefeller III and other investors to back Juan Trippe
Juan Terry Trippe (June 27, 1899 – April 3, 1981) was an American commercial aviation pioneer, entrepreneur and the founder of Pan American World Airways, one of the iconic airlines of the 20th century. He was involved in the introduction of t ...
in establishing the Aviation Corporation of America, which a year later would become Pan American World Airways
Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and commonly known as Pan Am, was an American airline that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas flag carrier of the United States ...
.
In 1931, Whitney founded the Hudson Bay Mining and Smelting Co., Limited in Canada. The company became a major zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
mining operation, and Whitney served as chairman of the board until 1964.
Equine sports
His father,Harry Payne Whitney
Harry Payne Whitney (April 29, 1872 – October 26, 1930) was an American businessman, thoroughbred horse breeder, and member of the prominent Whitney family.
Early years
Whitney was born in New York City on April 29, 1872, as the eldest son ...
, had been an avid polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ...
player and thoroughbred racehorse owner, and C.V. Whitney followed in his footsteps, winning the U.S. Open polo title three times. Since 1979, the Greenwich Polo Club at Conyers Farm in Greenwich, Connecticut
Greenwich (, ) is a New England town, town in southwestern Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. At the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the town had a total population of 63,518. The largest town on Connecticut's Gold Coast (Conne ...
, has awarded the C.V. Whitney Cup to the winner of an annual polo tournament.
He was the third generation of Whitneys to be heavily involved in thoroughbred horse racing
Thoroughbred racing is a sport and industry involving the racing of Thoroughbred horses. It is governed by different national bodies. There are two forms of the sport – flat racing and jump racing, the latter known as National Hunt racing in t ...
. The Grade 1
First grade (also called Grade One, called ''Year 2'' in England or Primary 2 in Scotland) is the first grade in elementary school and the first school year after kindergarten. Children are usually 6–7 years old in this grade.
Examples by re ...
Whitney Handicap
The Whitney Stakes (run as the Whitney Handicap through 2013 and still sometimes referred to as such) is an American Grade 1 stakes race for Thoroughbred racehorses three years of age and older run at a distance of miles. The current purse is $1 ...
at Saratoga Race Course
Saratoga Race Course is a Thoroughbred horse racing track located on Union Avenue in Saratoga Springs, New York, United States. Opened in 1863, it is often considered to be the oldest major sporting venue of any kind in the country, but is actua ...
was inaugurated in his family's honor in 1928. C.V. Whitney acquired his father's stable in 1930 and on May 17, his two-year-old colt
Colt(s) or COLT may refer to:
*Colt (horse), an intact (uncastrated) male horse under four years of age
People
* Colt (given name)
*Colt (surname)
Places
*Colt, Arkansas, United States
*Colt, Louisiana, an unincorporated community, United States ...
Equipoise
Equipoise may refer to:
* Clinical equipoise, or the principle of equipoise, a medical research term
* Equilibrioception, the state of being balanced or in equilibrium
* Boldenone undecylenate, an anabolic steroid, by the trade name ''Equipoise''
* ...
gave him his first stakes race
Glossary of North American horse racing:
Additional glossaries at:
*Glossary of Australian and New Zealand punting
*Glossary of equestrian terms
This is a basic glossary of equestrian terms that includes both technical terminology and jargon ...
victory when he won the Keene Memorial Stakes at Belmont Park
Belmont Park is a major thoroughbred horse racing facility in the northeastern United States, located in Elmont, New York, just east of the New York City limits. It was opened on May 4, 1905.
It is operated by the non-profit New York Racin ...
. Equipoise would go on to become a success on the racetrack and as a leading sire, and would be inducted into racing's Hall of Fame
A hall, wall, or walk of fame is a list of individuals, achievements, or other entities, usually chosen by a group of electors, to mark their excellence or Wiktionary:fame, fame in their field. In some cases, these halls of fame consist of actu ...
in 1957. Among Whitney's other outstanding horses, Top Flight
Top Flight (April 15, 1929 – 1949) was an American U.S. Hall of Fame Thoroughbred racehorse. She was the leading American filly of her generation at two and three years of age.
Background
Bred in Kentucky by the very prominent horseman Harry ...
was the 1931 American Champion Two-Year-Old Filly
The American Champion Two-Year-Old Filly is an American Thoroughbred horse racing honor awarded annually to a female horse in Thoroughbred flat racing. It became part of the Eclipse Awards program in 1971.
The award originated in 1936 when both t ...
and the 1932 American Champion Three-Year-Old Filly The American Champion Three-Year-Old Filly is an American Thoroughbred horse racing honor awarded annually to a female horse in Thoroughbred flat racing. It became part of the Eclipse Awards program in 1971.
The award originated in 1936 when both ...
, and was also voted into the U.S. Racing Hall of Fame, in 1966.
Although he had fifteen horses compete in the Kentucky Derby
The Kentucky Derby is a horse race held annually in Louisville, Kentucky, United States, almost always on the first Saturday in May, capping the two-week-long Kentucky Derby Festival. The competition is a Grade I stakes race for three-year ...
, Whitney never won the prestigious race. Silver Spoon
The English language expression silver spoon is synonymous with wealth, especially inherited wealth; someone born into a wealthy family is said to have "been born with a silver spoon in their mouth". As an adjective, "silver spoon" describes s ...
was the only filly
A filly is a female horse that is too young to be called a mare. There are two specific definitions in use:
*In most cases, a ''filly'' is a female horse under four years old.
*In some nations, such as the United Kingdom and the United States, t ...
entered in the Derby between the years 1945 and 1980, coming in a credible fifth in 1959. Ridden by jockey Eddie Arcaro
George Edward Arcaro (February 19, 1916 – November 14, 1997), was an American Thoroughbred horse racing Hall of Fame jockey who won more American classic races than any other jockey in history and is the only rider to have won the U.S. Tripl ...
and trained by Sylvester Veitch, Whitney's horse Phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly use ...
won the first division of the 1947 Wood Memorial Stakes
The Wood Memorial Stakes is an American flat Thoroughbred horse race for three-year-olds held annually in April at Aqueduct Racetrack in Ozone Park, Queens, New York. It is run over a distance of 1 1/8 miles (9 furlongs) on dirt. The Wood Memori ...
, finished second in the 1947 Kentucky Derby, took third in the ensuing Preakness Stakes
The Preakness Stakes is an American thoroughbred horse race held on Armed Forces Day which is also the third Saturday in May each year at Pimlico Race Course in Baltimore, Maryland. It is a Grade I race run over a distance of 9.5 furlongs () on ...
, then won the Belmont Stakes
The Belmont Stakes is an American Grade I stakes race for three-year-old Thoroughbreds run at Belmont Park in Elmont, New York. It is run over 1.5 miles (2,400 m). Colts and geldings carry a weight of ; fillies carry . The race, nicknamed Th ...
. In the 1951 Kentucky Derby, Whitney's Veitch-trained colt Counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradi ...
was still developing after an injury as a yearling that almost ended its career and tired badly, finishing 11th. However, Counterpoint came back to take second place in the Preakness Stakes and subsequently gave Whitney his second win in the Belmont Stakes and then went on to earn 1951 Horse of the Year honors. Among other successful horses from his stables, Career Boy
Career Boy (foaled 1953 in Kentucky) was an American Champion Thoroughbred racehorse.
Background
He was bred and raced by Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney, a member of the prominent horse-racing Whitney family. Out of the mare Swanky, whose damsire ...
won the United Nations Handicap
The United Nations Stakes is a Grade I American Thoroughbred horse race for three-year-olds and older run over a distance of one and three-eighth miles on the turf held annually in July at Monmouth Park Racetrack in Oceanport, New Jersey. The event ...
and was voted the Champion Grass Horse for 1956. First Flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets.
The maiden flight of a new aircraft type is alwa ...
was one of his best fillies
A filly is a female horse that is too young to be called a mare. There are two specific definitions in use:
*In most cases, a ''filly'' is a female horse under four years old.
*In some nations, such as the United Kingdom and the United States, t ...
, winning the Matron Stakes and beating males in Belmont's Futurity Stakes in 1946.
In 1972 the Keeneland Association honored Whitney with its Mark of Distinction for his contribution to Keeneland and the Thoroughbred industry.
Film production
Whitney became involved in the motion picture industry, notably with his cousinJohn Hay Whitney
John Hay Whitney (August 17, 1904 – February 8, 1982) was U.S. Ambassador to the United Kingdom, publisher of the ''New York Herald Tribune'', and president of the Museum of Modern Art. He was a member of the Whitney family.
Early life
Whit ...
as a major shareholder backing the Technicolor Corporation
Technicolor is a series of color motion picture processes, the first version dating back to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.
Definitive Technicolor movies using three black and white films running through a special ...
. The two were also financiers for the 1939 film classic ''Gone with the Wind
Gone with the Wind most often refers to:
* ''Gone with the Wind'' (novel), a 1936 novel by Margaret Mitchell
* ''Gone with the Wind'' (film), the 1939 adaptation of the novel
Gone with the Wind may also refer to:
Music
* ''Gone with the Wind'' ...
''. Seventeen years later, C.V. Whitney served as a producer through his own "C.V. Whitney Pictures". His company made three films, the first being the acclaimed 1956 production, ''The Searchers
''The Searchers'' is a 1956 American Technicolor VistaVision epic Western film directed by John Ford and written by Frank S. Nugent, based on the 1954 novel by Alan Le May. It is set during the Texas-Native American wars, and stars John Wa ...
'', directed by John Ford
John Martin Feeney (February 1, 1894 – August 31, 1973), known professionally as John Ford, was an American film director and naval officer. He is widely regarded as one of the most important and influential filmmakers of his generation. He ...
. The second was ''The Missouri Traveler
''The Missouri Traveler'' is a 1958 American coming-of-age period piece drama film directed by Jerry Hopper starring Brandon deWilde and Lee Marvin. It is based on the novel of the same name by John Burress. The cinematography was by Technicolo ...
'' in 1958 with Brandon deWilde
Andre Brandon deWilde (April 9, 1942 – July 6, 1972) was an American theater, film, and television actor. Born into a theatrical family in Brooklyn, he debuted on Broadway at the age of seven and became a national phenomenon by the time he comp ...
and Lee Marvin
Lee Marvin (born Lamont Waltman Marvin Jr.; February 19, 1924August 29, 1987) was an American film and television actor. Known for his bass voice and premature white hair, he is best remembered for playing hardboiled "tough guy" characters. Alth ...
, and the third was ''The Young Land
''The Young Land'' is a 1959 American Western film directed by Ted Tetzlaff and starring Patrick Wayne, Yvonne Craig, Dennis Hopper and Dan O'Herlihy. The cinematography was by Technicolor developer Winton C. Hoch and Henry Sharp. The film was ...
'' in 1959 with Patrick Wayne
Patrick John Morrison (born July 15, 1939), better known by his stage name Patrick Wayne, is an American actor. He is the second son of movie star John Wayne and his first wife, Josephine Alicia Saenz. He made over 40 films, including eleven w ...
and Dennis Hopper
Dennis Lee Hopper (May 17, 1936 – May 29, 2010) was an American actor, filmmaker and photographer. He attended the Actors Studio, made his first television appearance in 1954, and soon after appeared in ''Giant'' (1956). In the next ten years ...
.
Whitney was a major financial partner in the development of Marine Studios
Marineland of Florida (usually just called Marineland), one of Florida's first marine mammal parks, is billed as "the world's first oceanarium". Marineland functions as an entertainment and swim-with-the-dolphins facility, and reopened to the pu ...
, designed as an underwater motion picture studio located on the ocean south of St. Augustine, Florida. The Studios opened on June 23, 1938, with an estimated 30,000 visitors and eventually evolved into a major marine attraction. It was billed as "the world's original marine attraction". Whitney sold the attraction and its amenities to a group of St. Augustine businessmen, and Whitney's legacy continues at the Whitney Laboratory nearby.
Government and military service
Having spent considerable time in France, Whitney's mother Gertrude became involved supporting the Allied forces duringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. She dedicated a great deal of her time and money to various relief efforts, establishing and maintaining a hospital in France for wounded soldiers. Eighteen-year-old C.V. Whitney joined the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
, serving as an aviation cadet in the Signal Corps, rising to the rank of second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
and becoming a military pilot. During the war, Whitney served as a flight instructor in Texas.
In 1932 Whitney unsuccessfully ran for Congress against fellow wealthy long islander Robert L. Bacon.
With the onset of American involvement in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Whitney volunteered again for service, rising to the rank of colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
with the United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
. He was awarded the Distinguished Service Medal Distinguished Service Medal (DSM) is a high award of a nation.
Examples include:
*Distinguished Service Medal (Australia) (established 1991), awarded to personnel of the Australian Defence Force for distinguished leadership in action
* Distinguishe ...
and Legion of Merit
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements. The decoration is issued to members of the eight ...
.
At the end of the war, Whitney served under U.S. President Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
as Assistant Secretary of the Air Force
Assistant Secretary of the Air Force is the title of five civilian officials in the United States Department of the Air Force. They report to and assist the United States Secretary of the Air Force and the United States Under Secretary of the Air ...
from 1947 to 1949, and United States Under Secretary of Commerce
A United States Under Secretary of Commerce is one of several positions in the United States Department of Commerce, serving under the United States Secretary of Commerce.
History
In June 1939, Edward J. Noble was appointed the first Under Secreta ...
from 1949 to 1950. He was also appointed President Truman's special envoy to the United Kingdom, Luxembourg, Spain and Italy in 1950.
Estates
One of Whitney's homes was the "Cady Hill" estate atSaratoga Springs, New York
Saratoga Springs is a city in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The population was 28,491 at the 2020 census. The name reflects the presence of mineral springs in the area, which has made Saratoga a popular resort destination for over 2 ...
, not far from the Saratoga Race Course
Saratoga Race Course is a Thoroughbred horse racing track located on Union Avenue in Saratoga Springs, New York, United States. Opened in 1863, it is often considered to be the oldest major sporting venue of any kind in the country, but is actua ...
. It was there in 1950 that he founded the National Museum of Racing and Hall of Fame
The National Museum of Racing and Hall of Fame was founded in 1950 in Saratoga Springs, New York, to honor the achievements of American Thoroughbred race horses, jockeys, and trainers. In 1955, the museum moved to its current location on Union Av ...
and served as its first president. A former director of Churchill Downs
Churchill Downs is a horse racing complex located on Central Avenue in south Louisville, Kentucky, United States, famed for hosting the annual Kentucky Derby. It officially opened in 1875 and was named for Samuel Churchill, whose family was ...
, he was given an Eclipse Special Award in 1984 in recognition of his lifetime contribution to thoroughbred horse racing in the United States. The C.V. Whitney Farm in Lexington, Kentucky
Lexington is a city in Kentucky, United States that is the county seat of Fayette County, Kentucky, Fayette County. By population, it is the List of cities in Kentucky, second-largest city in Kentucky and List of United States cities by popul ...
, bred more than 175 stakes winners until age forced him to sell off a large part of the property in the 1980s to Gainesway Farm. After his death in 1992, his widow, Marylou Whitney
Marie Louise "Marylou" Whitney ( née Schroeder; December 24, 1925 – July 19, 2019) was an American socialite and philanthropist. A prominent owner and breeder of thoroughbred racehorses, Whitney was notable for "reigning for decades as the so ...
, continued breeding and racing operations on a smaller scale. A much respected figure in racing, her "Marylou Whitney Stables" owned Birdstone
Birdstone (foaled May 16, 2001, in Kentucky) is an American Thoroughbred racehorse best known for winning the 2004 Belmont Stakes and has become a successful sire.
On August 28, 2020 Birdstone was pensioned from stud duty to Old Friends Retirem ...
, the 2004 Belmont Stakes winner.
Upon his death, Whitney owned over 51,000 acres (210 km2) in the Adirondacks
The Adirondack Mountains (; a-də-RÄN-dak) form a massif in northeastern New York with boundaries that correspond roughly to those of Adirondack Park. They cover about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The mountains form a roughly circular d ...
along with a great camp
__NOTOC__
The Great Camps of the Adirondack Mountains refers to the grandiose family compounds of cabins that were built in the latter half of the nineteenth century on lakes in the Adirondacks such as Spitfire Lake and Rainbow Lake. The ca ...
called ''Deerlands''. Located within the Oswegatchie Great Forest, the Whitney estate is home to more than 40 lakes and ponds, as well as the headwaters of the Beaver, Raquette and Bog rivers. In 1997, New York State bought 14,700 acres (59 km2) of the 51,000-acre (210 km2) Whitney tract from Marylou Whitney's "Whitney Industries" for $17.1 million.
Personal life
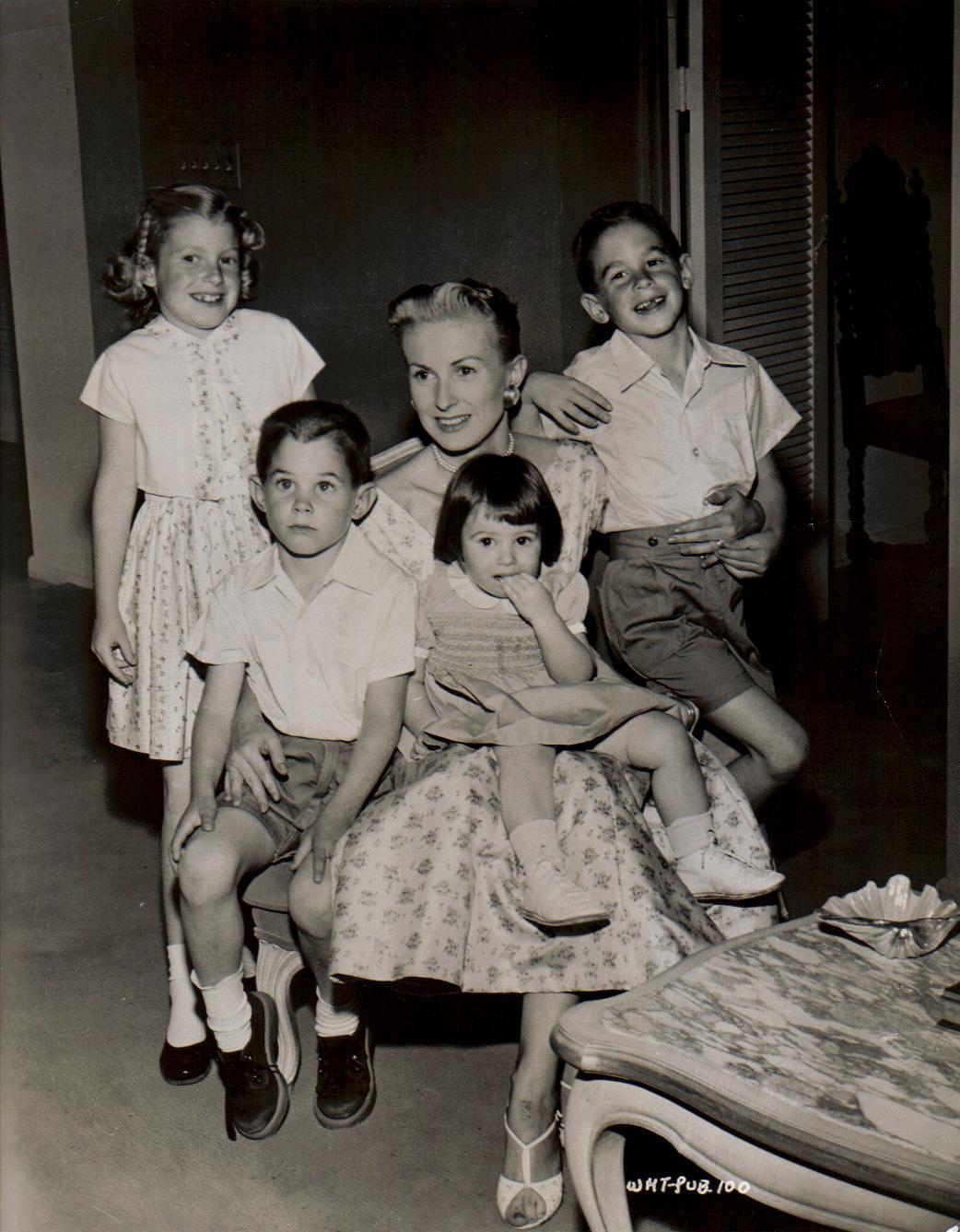
 Whitney habitually married:
On March 5, 1923, Whitney married for the first time to
Whitney habitually married:
On March 5, 1923, Whitney married for the first time to Marie Norton
Marie Harriman ( ''née'' Norton, formerly Whitney; April 12, 1903September 26, 1970) was an American art collector and First Lady of New York from 1955 to 1958. She was the second wife of former New York Governor and diplomat Averell Harriman. ...
(1903–1970), daughter of Sheridan Nook Norton, an attorney, and Beulah Sanfield Einstein, in Paris. They divorced in 1929. Marie later married New York Governor
The governor of New York is the head of government of the U.S. state of New York. The governor is the head of the executive branch of New York's state government and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor has a ...
and diplomat Averell Harriman
William Averell Harriman (November 15, 1891July 26, 1986), better known as Averell Harriman, was an American Democratic politician, businessman, and diplomat. The son of railroad baron E. H. Harriman, he served as Secretary of Commerce un ...
, and she was First Lady of New York from January 1, 1955, to December 31, 1958. She and Whitney had two children together:
* Harry Payne Whitney II (1924–1985), who married Alexandra Ewing (1927–2014), daughter of Gifford Cochran Ewing and Frances Riker, and later Andrea R. Whitney
* Nancy Marie Whitney (1926–2006), who married four times and divorced three times:
** in 1949 to Edwin Denison Morgan III (1921–2001), by whom she had two children:
*** Alida Morgan
*** Pamela Morgan
** on August 26, 1957, to (Charles) Russell Hurd
** on July 1, 1958, to his widowed elder brother, Edward Augustus Hurd Jr.
** and finally, to well known water colorist Pierre Lutz (1923–1991).
C.V. Whitney's second marriage was to Gwladys Crosby "Gee" Hopkins, from 1931 to 1940. They had one daughter:
* Gail Whitney (1939–1963), who married Richard Cox Cowell in 1958. They were divorced a year later. In 1961, she married Louis S. Stur. Gail died at the age of 24.
In 1941, in Plymouth, Ohio
Plymouth is a village in Huron and Richland counties in the U.S. state of Ohio. The population was 1,857 at the 2010 census.
The Richland County portion of Plymouth is part of the Mansfield Metropolitan Statistical Area, while the Huron County ...
, he married for the third time to Eleanor Searle (c. 1908–2002), daughter of Dr. and Mrs. George James Searle. Before their divorce in 1957, they had one son:
* Cornelius Searle Whitney (1944–2015), an economist, psychologist and philanthropist.
On January 25, 1958, he married for the fourth, and final, time to Marie Louise Schroeder (1925–2019), universally known as "Marylou". She was an actress in a movie he produced, called ''The Missouri Traveler
''The Missouri Traveler'' is a 1958 American coming-of-age period piece drama film directed by Jerry Hopper starring Brandon deWilde and Lee Marvin. It is based on the novel of the same name by John Burress. The cinematography was by Technicolo ...
''. They remained married until his death. Together, they had one daughter:
* Cornelia Whitney, an art instructor and divorced mother of one who lives in Ithaca, New York
Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, Ithaca is the seat of Tompkins County and the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. It is named a ...
.
Over the 1920s, Whitney successfully fended off several million-dollar lawsuits filed by former Ziegfeld Follies dancer Evan-Burrows Fontaine
Evan-Burrows Fontaine (October 3, 1898 – December 27, 1984) was an American Denishawn-trained interpretive dancer and actress whose career suffered after she became entangled in a breach of promise lawsuit with a member of one of America's ...
charging him with breach of promise
Breach of promise is a common law tort, abolished in many jurisdictions. It was also called breach of contract to marry,N.Y. Civil Rights Act article 8, §§ 80-A to 84. and the remedy awarded was known as heart balm.
From at least the Middle ...
and paternity of her son.
Whitney died in 1992 in Saratoga Springs, New York
Saratoga Springs is a city in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The population was 28,491 at the 2020 census. The name reflects the presence of mineral springs in the area, which has made Saratoga a popular resort destination for over 2 ...
, at the age of 93 and is buried there in the Greenridge Cemetery
Greenridge Cemetery is a historic cemetery in Saratoga Springs, New York.
Notable burials
* Seymour Ainsworth (1821–1890)
* George Sherman Batcheller (1837–1908)
* George S. Bolster (1913–1989)
* Charles Brackett (1892–1969)
* Edgar T. ...
. In 1994, a portion of New York State Route 50
New York State Route 50 (NY 50) is a state highway in the Capital District of New York in the United States. The southern terminus of the route is at an intersection with NY 5 in Scotia. Its northern terminus is at a junction with ...
in the City of Saratoga Springs was designated "C.V. Whitney Memorial Highway."
Philanthropy and arts patronage
Whitney was raised in an artistic environment. His mother, Gertrude, was an accomplished sculptor who studied in Paris underAuguste Rodin
François Auguste René Rodin (12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor, generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a uniqu ...
. She was also the founder of the Whitney Museum of American Art
The Whitney Museum of American Art, known informally as "The Whitney", is an art museum in the Meatpacking District and West Village neighborhoods of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1930 by Gertrude Vanderbilt Whitney (1875–1942), ...
in New York City. As an adult, C.V. Whitney played a role in establishing the Saratoga Performing Arts Center
Saratoga Performing Arts Center (SPAC) is a large amphitheatre located in Saratoga Springs, New York, on the grounds of Saratoga Spa State Park. It presents summer performances of classical music, jazz, pop and rock, country, comedy, dance, opera, ...
in Saratoga Springs, New York
Saratoga Springs is a city in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The population was 28,491 at the 2020 census. The name reflects the presence of mineral springs in the area, which has made Saratoga a popular resort destination for over 2 ...
, was a supporter of the American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 inter ...
in New York City, and was a founder of the Whitney Gallery of Western Art in Cody, Wyoming
Cody is a city in Northwest Wyoming and the seat of government of Park County, Wyoming, United States. It is named after Colonel William Frederick " Buffalo Bill" Cody for his part in the founding of Cody in 1896.
The population was 10,066 at ...
. The "Mr. and Mrs. Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney Hall of Fame" collection was provided in 1987 to the National Museum of Dance
The National Museum of Dance and Hall of Fame, in the Saratoga Spa State Park, Saratoga Springs, New York, was established in 1986. It contains photographs, videos, artifacts, costumes, and biographies. The museum is located in the former Washi ...
in Saratoga Springs, New York. It is the only museum in the world dedicated to professional dance.
Whitney donated important artworks to various museums. Notable donations include the gift of a 1634 Anthony van Dyck
Sir Anthony van Dyck (, many variant spellings; 22 March 1599 – 9 December 1641) was a Brabantian Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Southern Netherlands and Italy.
The seventh c ...
painting of Henri II de Lorraine, 5e Duc de Guise
Henry II de Lorraine, 5th Duke of Guise (4 April 1614, in Paris – 2 June 1664, in Paris) was a French aristocrat and archbishop, the second son of Charles, Duke of Guise and Henriette Catherine de Joyeuse.
Life
At the age of fifteen, he became ...
, which had been in the Whitney family for three generations, to the National Gallery of Art
The National Gallery of Art, and its attached Sculpture Garden, is a national art museum in Washington, D.C., United States, located on the National Mall, between 3rd and 9th Streets, at Constitution Avenue NW. Open to the public and free of char ...
in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
In 1953, Whitney donated the 1872 Thomas Eakins
Thomas Cowperthwait Eakins (; July 25, 1844 – June 25, 1916) was an American realist painter, photographer, sculptor, and fine arts educator. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the most important American artists.
For the length ...
painting ''The Biglin Brothers Racing'' to the National Gallery of Art.
Whitney's interest in the natural history of marine animals resulted in the 1938 founding of the world's first oceanarium. Marineland, near St. Augustine, Florida, included a small research laboratory that drew academic biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
s. Eventually, Whitney provided the University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
with an adjacent parcel of land plus half of the construction capital required to build a full-scale academic center, the C.V. Whitney Laboratory for Experimental Marine Biology and Medicine (now called The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience).In addition, he donated Whitney Hall to the university, a building that serves as a conference center and contains dormitories and apartments. In 1963, his estate at
Old Westbury, New York
Old Westbury is a village in the Towns of North Hempstead and Oyster Bay in Nassau County, on the North Shore of Long Island, in New York, United States. The population was 4,671 at the 2010 census.
The Incorporated Village of Old Westbury ...
, was subdivided and offered to the New York Institute of Technology
The New York Institute of Technology (NYIT or New York Tech) is a private research university founded in 1955. It has two main campuses in New York—one in Old Westbury, on Long Island, and one in Manhattan. Additionally, it has a cybersecu ...
for use as part of its Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
campus.
In 2000, his widow helped finance the publication of ''Legend of Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney'' by Jeffrey L. Rodengen.
Written works
Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney wrote five books: *''Lone and Level Sands'' (1951) – a personal narrative ofAllied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
aerial operations during World War II
*''High Peaks'' (1977) – autobiography
*''Live a Year with a Millionaire'' (1981)
*''Owl Hoots Again'' (1988) – a collection of short stories for children
*''First Flight: The Diary of a Cadet in the Signal Corps in World War I'' (1989)
See also
*Whitney Marine Lab
The Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience or Whitney Marine Lab at the University of Florida is a research and teaching facility, that conducts research pertaining to Marine Bioscience.
The Marine lab can be traced back to the benefactor Cornel ...
References
Further reading
*http://www.nytimes.com/1985/09/26/nyregion/harry-payne-whitney-is-dead-yachtsman-from-manhattan.html *http://www.independent.co.uk/news/people/obituary-cornelius-vanderbilt-whitney-1480302.html *http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/642886/Cornelius-Vanderbilt-Whitney *https://vault.si.com/vault/1961/09/04/sonny-whitney-a-success-in-spite-of-his-money {{DEFAULTSORT:Whitney, Cornelius Vanderbilt 20th-century American essayists 1899 births 1992 deaths American art collectors American children's writers 20th-century American memoirists United States Army Air Service pilots of World War I United States Army Air Forces personnel of World War II American polo players American racehorse owners and breeders United States Under Secretaries of Commerce Burials at Greenridge Cemetery Eclipse Award winners Military personnel from New York (state) New York Institute of Technology People from Old Westbury, New York People from Roslyn, New York Philanthropists from New York (state) Private equity and venture capital investors Sportspeople from Saratoga Springs, New York United States Army Air Forces officersCornelius Vanderbilt Whitney
Cornelius "Sonny" Vanderbilt Whitney (February 20, 1899 – December 13, 1992) was an American businessman, film producer, government official, writer and philanthropist. He was also a polo player and the owner of a significant stable of Thorough ...
Cornelius Vanderbilt Whitney
Cornelius "Sonny" Vanderbilt Whitney (February 20, 1899 – December 13, 1992) was an American businessman, film producer, government official, writer and philanthropist. He was also a polo player and the owner of a significant stable of Thorough ...
Writers from New York (state)
Yale University alumni