Convoy CU 1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas.


 The Highway Code of several European countries (Norway, Italy, Greece, Netherlands, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, possibly more) includes special rights for marked convoys. They have to be treated like a single vehicle. If the first vehicle has passed an intersection, all others may do so without interruption. If other road users overtake the convoy, they aren't allowed to split into the queue. Clear and uniform marking has been required in court decisions for these rights to apply. Operating such convoy usually needs special permission, but there are exemptions for emergency and catastrophe intervention. Common practice is, to operate with the same style of marking as NATO convoys: STANAG 2154 marking plus country-specific augmentation listed in Annex B to the STANAG.
During the
The Highway Code of several European countries (Norway, Italy, Greece, Netherlands, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, possibly more) includes special rights for marked convoys. They have to be treated like a single vehicle. If the first vehicle has passed an intersection, all others may do so without interruption. If other road users overtake the convoy, they aren't allowed to split into the queue. Clear and uniform marking has been required in court decisions for these rights to apply. Operating such convoy usually needs special permission, but there are exemptions for emergency and catastrophe intervention. Common practice is, to operate with the same style of marking as NATO convoys: STANAG 2154 marking plus country-specific augmentation listed in Annex B to the STANAG.
During the
abstract
* Herwig, Holger H., and David F. David. "The Failure of Imperial Germany's Undersea Offensive Against World Shipping, February 1917–October 1918." ''Historian'' (1971) 33#4 pp: 611–636
online
* Lewis, James Allen. ''The Spanish convoy of 1750: heaven's hammer and international diplomacy'' (Univ Press of Florida, 2009) * Syrett, David. "The Organization Of British Trade Convoys during the American War, 1775–1783." ''The Mariner's Mirror'' (1976) 62#2 pp: 169–181
abstract
* Thompson, F. J. "The Merchant Ship in Convoy." ''The RUSI Journal'' 79.513 (1934): 69–86.
online
– a comprehensive analysis of certain naval convoy routes
Aid Convoy
– a humanitarian aid charity running convoys {{Authority control Naval warfare Water transport Road transport Vehicle operation
Naval convoys
Age of Sail
Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effectivenaval
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral zone, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and ...
convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790.
When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer could cruise a shipping lane and capture ships as they passed. Ships sailing in convoy presented a much smaller target: a convoy was as hard to find as a single ship. Even if the privateer found a convoy and the wind was favourable for an attack, it could still hope to capture only a handful of ships before the rest managed to escape, and a small escort of warships could easily thwart it. As a result of the convoy system's effectiveness, wartime insurance premiums were consistently lower for ships that sailed in convoys.
Many naval battles
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large la ...
in the Age of Sail
The Age of Sail is a period that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid- 15th) to the mid- 19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the introduction of naval ...
were fought around convoys, including:
*The Battle of Portland
The naval Battle of Portland, or Three Days' Battle took place during 18–20 February 1653 (28 February – 2 March 1653 (Gregorian calendar)), during the First Anglo-Dutch War, when the fleet of the Commonwealth of England under General at ...
(1653)
*The Battle of Ushant (1781)
*The Battle of Dogger Bank (1781)
The Battle of Dogger Bank was a naval battle that took place on 5 August 1781 during the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War, contemporaneously related to the American Revolutionary War, in the North Sea. It was a bloody encounter between a British sq ...
* The Glorious First of June (1794)
*The Battle of Pulo Aura (1804)
By the end of the Napoleonic Wars the Royal Navy had in place a sophisticated convoy system to protect merchant ships. Losses of ships travelling out of convoy however were so high that no merchant ship was allowed to sail unescorted.
World War I
In the early 20th century, the dreadnought changed the balance of power in convoy battles. Steaming faster than merchant ships and firing at long ranges, a singlebattleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ...
could destroy many ships in a convoy before the others could scatter over the horizon. To protect a convoy against a capital ship required providing it with an escort of another capital ship, at very high opportunity cost
In microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a particular activity is the value or benefit given up by engaging in that activity, relative to engaging in an alternative activity. More effective it means if you chose one activity (for example ...
(i.e. potentially tying down multiple capital ships to defend different convoys against one opponent ship).
Battleships were the main reason that the British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of it ...
did not adopt convoy tactics at the start of the first Battle of the Atlantic in World War I. But the German capital ships had been bottled up in the North Sea, and the main threat to shipping came from U-boats. From a tactical point of view, World War I–era submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s were similar to privateers in the age of sail. These submarines were only a little faster than the merchant ships they were attacking, and capable of sinking only a small number of vessels in a convoy because of their limited supply of torpedoes and shells. The Admiralty took a long time to respond to this change in the tactical position, and in April 1917 convoys were trialled, before being officially introduced in the Atlantic in September 1917.
Other arguments against convoys were raised. The primary issue was the loss of productivity, as merchant shipping in convoy has to travel at the speed of the slowest vessel in the convoy and spent a considerable amount of time in ports waiting for the next convoy to depart. Further, large convoys were thought to overload port resources.
Actual analysis of shipping losses in World War I disproved all these arguments, at least so far as they applied to transatlantic and other long-distance traffic. Ships sailing in convoys were far less likely to be sunk, even when not provided with an escort. The loss of productivity due to convoy delays was small compared with the loss of productivity due to ships being sunk. Ports could deal more easily with convoys because they tended to arrive on schedule and so loading and unloading could be planned.
In his book '' On the Psychology of Military Incompetence'', Norman Dixon suggested that the hostility towards convoys in the naval establishment were in part caused by a (sub-conscious) perception of convoys as effeminating, due to warships having to care for civilian merchant ships. Convoy duty also exposes the escorting warships to the sometimes hazardous conditions of the North Atlantic, with only rare occurrences of visible achievement (i.e. fending off a submarine assault).
World War II

Atlantic
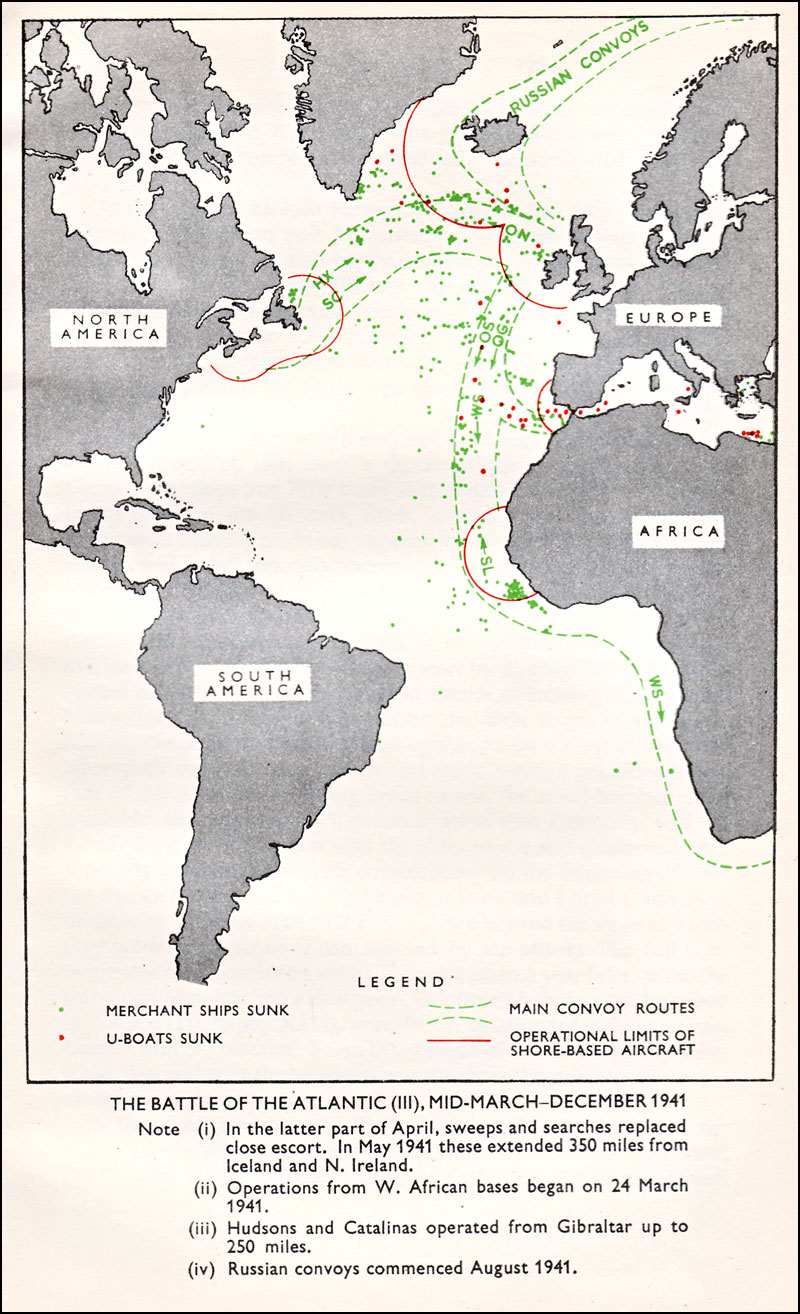
The British adopted a convoy system, initially voluntary and later compulsory for almost all merchant ships, the moment that World War II was declared. Each convoy consisted of between 30 and 70 mostly unarmed merchant ships. Canadian, and later American, supplies were vital for Britain to continue its war effort. The course of theBattle of the Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockade ...
was a long struggle as the Germans developed anti-convoy tactics and the British developed counter-tactics to thwart the Germans.
The capability of a heavily armed warship against a convoy was dramatically illustrated by the fate of Convoy HX 84. On November 5, 1940, the German heavy cruiser encountered the convoy. ''Maiden'', ''Trewellard'', and ''Kenbame Head'' were quickly destroyed, and ''Beaverford'' and ''Fresno City'' falling afterwards. Only the sacrifices of the armed merchant cruiser
An armed merchantman is a merchant ship equipped with guns, usually for defensive purposes, either by design or after the fact. In the days of sail, piracy and privateers, many merchantmen would be routinely armed, especially those engaging in lo ...
and the freighter ''Beaverford'' to stall the ''Scheer'', in addition to failing light, allowed the rest of the convoy to escape.
The deterrence value of a battleship in protecting a convoy was also dramatically illustrated when the German light battleships (referred by some as battlecruisers) and , mounting guns, came upon an eastbound British convoy ( HX 106, with 41 ships) in the North Atlantic on February 8, 1941. When the Germans detected the slow but well-protected battleship escorting the convoy, they fled the scene rather than risk damage from her guns.
The enormous number of vessels involved and the frequency of engagements meant that statistical techniques could be applied to evaluate tactics: an early use of operational research in war.
Prior to overt participation in World War II, the US was actively engaged in convoys with the British in the North Atlantic Ocean, primarily supporting British activities in Iceland.
After Germany declared war on the US, the US Navy decided not to organize convoys on the American eastern seaboard. US Fleet Admiral Ernest King ignored advice on this subject from the British, as he had formed a poor opinion of the Royal Navy early in his career. The result was what the U-boat crews called their Second Happy Time
The "Second Happy Time" (; officially Operation Paukenschlag ("Operation Drumbeat"), and also known among German submarine commanders as the "American Shooting Season") was a phase in the Battle of the Atlantic during which Axis submarines att ...
, which did not end until convoys were introduced.
Pacific
In the Pacific Theater of World War II,Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese merchant ships rarely traveled in convoys. Japanese destroyers were generally deficient in antisubmarine weaponry compared to their Allied counterparts, and the Japanese navy did not develop an inexpensive convoy escort like the Allies' destroyer escort/frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
until it was too late. In the early part of the conflict, American submarines in the Pacific were ineffective as they suffered from timid tactics, faulty torpedoes, and poor deployment, while there were only small numbers of British and Dutch boats. U.S. Admiral Charles A. Lockwood
Charles Andrews Lockwood (May 6, 1890 – June 6, 1967) was a vice-admiral and flag officer of the United States Navy. He is known in submarine history as the commander of ComSubPac, Submarine Force Pacific Fleet during World War II. He devised ...
's efforts, coupled with strenuous complaints from his captains, rectified these problems and U.S. submarines became much more successful by war's end. As a result, the Japanese merchant fleet was largely destroyed by the end of the war. Japanese submarines, unlike their U.S. and German equivalents, focused on U.S. battle fleets rather than merchant convoys, and while they did manage some early successes, sinking two U.S. carriers, they failed to significantly inhibit the invasion convoys carrying troops and equipment in support of the U.S. island-hopping campaign.
Several notable battles in the South Pacific involved Allied bombers interdicting Japanese troopship convoys which were often defended by Japanese fighters, notable Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the south-western Pacific, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomon Islands by area, and the seco ...
(13 November 1942), Rabaul
Rabaul () is a township in the East New Britain province of Papua New Guinea, on the island of New Britain. It lies about 600 kilometres to the east of the island of New Guinea. Rabaul was the provincial capital and most important settlement in ...
(5 January 1943), and the Battle of the Bismarck Sea (2–4 March 1943).
At the Battle off Samar, the effectiveness of the U.S. Navy's escorts was demonstrated when they managed to defend their troop convoy from a much larger and more powerful Japanese battle-fleet. The Japanese force comprised four battleships and numerous heavy cruisers, while the U.S. force consisted of escort carriers, destroyers, and destroyer escorts. Large numbers of American aircraft (albeit without much anti-ship ordnance other than torpedoes) and aggressive tactics of the destroyers (with their radar-directed gunfire) allowed the U.S. to sink three Japanese heavy cruisers at the cost of one escort carrier and three destroyers.
Tactics
The German anti-convoy tactics included: * long-range surveillance aircraft to find convoys; * strings of U-boats ( wolfpacks) that could be directed onto a convoy by radio; * breaking the British naval codes; * improved anti-ship weapons, including magnetic detonators and sonic homing torpedoes. The Allied responses included: * air raids on the U-boat bases at Brest and La Rochelle; * converted merchant ships, e.g.,Merchant aircraft carrier
A merchant aircraft carrier (also known as a MAC ship, the Admiralty's official 'short name') was a limited-purpose aircraft carrier operated under British and Dutch civilian registry during World War II. MAC ships were adapted by adding a flig ...
s, Catapult Aircraft Merchantman and armed merchant cruisers
* Q-ships, submarine-hunters disguised as unarmed merchant ships to lure submarines into an attack
* more convoy escorts, including cheaply produced yet effective destroyer escorts
Destroyer escort (DE) was the United States Navy mid-20th-century classification for a warship designed with the endurance necessary to escort mid-ocean convoys of merchant marine ships.
Development of the destroyer escort was promoted by th ...
/frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
s (as corvette
A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the slo ...
s were meant as a stopgap), and escort carrier
The escort carrier or escort aircraft carrier (U.S. hull classification symbol CVE), also called a "jeep carrier" or "baby flattop" in the United States Navy (USN) or "Woolworth Carrier" by the Royal Navy, was a small and slow type of aircraft ...
s;
* fighter aircraft (carried by escort carriers and merchant aircraft carriers) that would drive off German bombers and attack U-boats
* long-range aircraft patrols to find and attack U-boats;
* improved anti-submarine weapons such as the hedgehog;
* larger convoys, allowing more escorts per convoy as well as the extraction of enough escorts to form hunter-killer support groups that were not attached to a particular convoy
* allocating vessels to convoys according to speed, so that faster ships were less exposed.
They were also aided by
* improved sonar ( ASDIC) allowing escort vessels to better track U-boats;
* breaking the German naval cipher;
* improved radar and radio direction finding
Direction finding (DF), or radio direction finding (RDF), isin accordance with International Telecommunication Union (ITU)defined as radio location that uses the reception of radio waves to determine the direction in which a radio station ...
allowing planes to find and destroy U-boats;
Convoy battles
Many naval battles of World War II were fought around convoys, including: * Convoy PQ 16, May 1942 *Convoy PQ 17
PQ 17 was the code name for an Allied Arctic convoy during the Second World War. On 27 June 1942, the ships sailed from Hvalfjörður, Iceland, for the port of Arkhangelsk in the Soviet Union. The convoy was located by German forces on 1 July, aft ...
, June–July 1942
* Convoy PQ 18
Convoy PQ 18 was an Arctic convoy of forty Allied freighters from Scotland and Iceland to Arkhangelsk in the Soviet Union in the war against Nazi Germany. The convoy departed Loch Ewe, Scotland on 2 September 1942, rendezvoused with more ships an ...
, September 1942
* Operation Pedestal
Operation Pedestal ( it, Battaglia di Mezzo Agosto, Battle of mid-August), known in Malta as (), was a British operation to carry supplies to the island of Malta in August 1942, during the Second World War. Malta was a base from which British ...
, August 1942
* The Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, November 1942
* The Battle of the Barents Sea
The Battle of the Barents Sea was a World War II naval engagement on 31 December 1942 between warships of the German Navy (''Kriegsmarine'') and British ships escorting convoy JW 51B to Kola Inlet in the USSR. The action took place in the Bare ...
, December 1942
* The Battle of the Bismarck Sea, March 1943
The convoy prefix indicates the route of the convoy. For example, 'PQ' would be Iceland to Northern Russia and 'QP' the return route.
Analysis
The success of convoys as an anti-submarine tactic during the world wars can be ascribed to several reasons related to U-boat capabilities, the size of the ocean and convoy escorts. In practice,Type VII
Type VII U-boats were the most common type of German World War II U-boat. 703 boats were built by the end of the war. The lone surviving example, , is on display at the Laboe Naval Memorial located in Laboe, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
Conc ...
and Type IX U-boats were limited in their capabilities. Submerged speed and endurance was limited and not suited for overhauling many ships. Even a surfaced U-boat could take several hours to gain an attack position. Torpedo capacity was also restricted to around fourteen (Type VII) or 24 (Type IX), thus limiting the number of attacks that could be made, particularly when multiple firings were necessary for a single target. There was a real problem for the U-boats and their adversaries in finding each other; with a tiny proportion of the ocean in sight, without intelligence or radar, warships and even aircraft would be fortunate in coming across a submarine. The Royal Navy and later the United States Navy each took time to learn this lesson. Conversely, a U-boat's radius of vision was even smaller and had to be supplemented by regular long-range reconnaissance flights.
For both major allied navies, it had been difficult to grasp that, however large a convoy, its "footprint" (the area within which it could be spotted) was far smaller than if the individual ships had traveled independently. In other words, a submarine had less chance of finding a single convoy than if it were scattered as single ships. Moreover, once an attack had been made, the submarine would need to regain an attack position on the convoy. If, however, an attack were thwarted by escorts, even if the submarine had escaped damage, it would have to remain submerged for its own safety and might only recover its position after many hours' hard work. U-boats patrolling areas with constant and predictable flows of sea traffic, such as the United States Atlantic coast in early 1942, could dismiss a missed opportunity in the certain knowledge that another would soon present itself.
The destruction of submarines required their discovery, an improbable occurrence on aggressive patrols, by chance alone. Convoys, however, presented irresistible targets and could not be ignored. For this reason, the U-boats presented themselves as targets to the escorts with increasing possibility of destruction. In this way, the Ubootwaffe suffered severe losses, for little gain, when pressing pack attacks on well-defended convoys.
Post-World War II
The largest convoy effort since World War II was Operation Earnest Will, theU.S. Navy's
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the worl ...
1987–88 escort of reflagged Kuwaiti tanker
Tanker may refer to:
Transportation
* Tanker, a tank crewman (US)
* Tanker (ship), a ship designed to carry bulk liquids
** Chemical tanker, a type of tanker designed to transport chemicals in bulk
** Oil tanker, also known as a petroleum ta ...
s in the Persian Gulf during the Iran–Iraq War.
In the present day, convoys are used as a tactic by navies to deter pirates off the coast of Somalia from capturing unarmed civilian freighters who would otherwise pose easy targets if they sailed alone.
Road convoys
Humanitarian aid convoys
The word "convoy" is also associated with groups of road vehicles being driven, mostly by volunteers, to deliverhumanitarian aid
Humanitarian aid is material and logistic assistance to people who need help. It is usually short-term help until the long-term help by the government and other institutions replaces it. Among the people in need are the homeless, refugees, and ...
, supplies, and—a stated objective in some cases—"solidarity".
In the 1990s these convoys became common traveling from Western Europe to countries of the former Yugoslavia, in particular Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
and Kosovo, to deal with the aftermath of the wars there. They also travel to countries where standards of care in institutions such as orphanages are considered low by Western European standards, such as Romania; and where other disasters have led to problems, such as around the Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
in Belarus and Ukraine.
The convoys are made possible partly by the relatively small geographic distances between the stable and affluent countries of Western Europe, and the areas of need in Eastern Europe and, in a few cases, North Africa and even Iraq. They are often justified because although less directly cost-effective than mass freight transport, they emphasise the support of large numbers of small groups, and are quite distinct from multinational organisations such as United Nations humanitarian efforts.

Truckers' convoys
Truckers' convoys consisting of semi-trailer trucks and/or petrol tankers are more similar to acaravan
Caravan or caravans may refer to:
Transport and travel
*Caravan (travellers), a group of travellers journeying together
**Caravanserai, a place where a caravan could stop
*Camel train, a convoy using camels as pack animals
*Convoy, a group of veh ...
than a military convoy.
Truckers' convoys were created as a byproduct of the USA's national 55 mph speed limit and 18-wheelers becoming the prime targets of speed traps. Most truckers had difficult schedules to keep and as a result had to maintain a speed above the posted speed limit to reach their destinations on time. Convoys were started so that multiple trucks could run together at a high speed with the rationale being that if they passed a speed trap the police would only be able to pull over one of the trucks in the convoy. When driving on a highway, convoys are also useful to conserve fuel by drafting
Drafting or draughting may refer to:
* Campdrafting, an Australian equestrian sport
* Drafting (aerodynamics), slipstreaming
* Drafting (writing), writing something that is likely to be amended
* Technical drawing, the act and discipline of compo ...
.
The film ''Convoy'', inspired by a 1975 song of the same name, explores the camaraderie between truck drivers, where the culture of the CB radio encourages truck drivers to travel in convoys.

Special convoy rights
 The Highway Code of several European countries (Norway, Italy, Greece, Netherlands, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, possibly more) includes special rights for marked convoys. They have to be treated like a single vehicle. If the first vehicle has passed an intersection, all others may do so without interruption. If other road users overtake the convoy, they aren't allowed to split into the queue. Clear and uniform marking has been required in court decisions for these rights to apply. Operating such convoy usually needs special permission, but there are exemptions for emergency and catastrophe intervention. Common practice is, to operate with the same style of marking as NATO convoys: STANAG 2154 marking plus country-specific augmentation listed in Annex B to the STANAG.
During the
The Highway Code of several European countries (Norway, Italy, Greece, Netherlands, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, possibly more) includes special rights for marked convoys. They have to be treated like a single vehicle. If the first vehicle has passed an intersection, all others may do so without interruption. If other road users overtake the convoy, they aren't allowed to split into the queue. Clear and uniform marking has been required in court decisions for these rights to apply. Operating such convoy usually needs special permission, but there are exemptions for emergency and catastrophe intervention. Common practice is, to operate with the same style of marking as NATO convoys: STANAG 2154 marking plus country-specific augmentation listed in Annex B to the STANAG.
During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
with its high number of military exercises, the military was the main user of convoy rights. Today, catastrophes like large-scale flooding might bring a high number of flagged convoys to the roads. Large-scale evacuations for the disarming of World War II bombs are another common reason for non-governmental organization (NGO) unit movements under convoy rights.
Storm convoys
In Norway, "convoy driving" ( no, kolonnekjøring) is used during winter in case weather is too bad for vehicles to pass on their own. Convoy driving is initiated when the strong wind quickly fills the road with snow behind snowplows, particularly on mountain passes. Only a limited number of vehicles are allowed for each convoy and convoy leader is obliged to decline vehicles not fit for the drive. Storm convoys are prone to multiple-vehicle collision. Convoy driving is used through Hardangervidda pass on road 7 during blizzards. Convoy is sometimes used on road E134 at the highest and most exposed sections during bad weather. OnEuropean route E6
European route E6 ( no, Europavei 6, sv, Europaväg 6, or simply E6) is the main north-south thoroughfare through Norway as well as the west coast of Sweden. It is long and runs from the southern tip of Sweden at Trelleborg, into Norway and t ...
through Saltfjellet pass convoy driving is often used when wind speed is over 15–20 m/s ( fresh or strong gale) in winter conditions. During the winter of 1990 there was convoy driving for almost 500 hours at Saltfjellet
See also
* Camel train *Motorcade
A motorcade, or autocade, is a procession of vehicles.
Etymology
The term ''motorcade'' was coined by Lyle Abbot (in 1912 or 1913 when he was automobile editor of the ''Arizona Republican''), and is formed after ''cavalcade'', playing off of ...
* Road train
* Shoaling and schooling
* Wagon train
References
Further reading
* Allard, Dean C. "Anglo-American Naval Differences During World War I." ''Military Affairs: The Journal of Military History, Including Theory and Technology'' (1980): 75–81. in JSTOR * Crowhurst, R. Patrick. "The Admiralty and the Convoy System in the Seven Years War." ''The Mariner's Mirror'' (1971) 57#2 pp: 163–173. * Gasslander, Olle. "The convoy affair of 1798." ''Scandinavian Economic History Review'' 2.1 (1954): 22–30abstract
* Herwig, Holger H., and David F. David. "The Failure of Imperial Germany's Undersea Offensive Against World Shipping, February 1917–October 1918." ''Historian'' (1971) 33#4 pp: 611–636
online
* Lewis, James Allen. ''The Spanish convoy of 1750: heaven's hammer and international diplomacy'' (Univ Press of Florida, 2009) * Syrett, David. "The Organization Of British Trade Convoys during the American War, 1775–1783." ''The Mariner's Mirror'' (1976) 62#2 pp: 169–181
abstract
* Thompson, F. J. "The Merchant Ship in Convoy." ''The RUSI Journal'' 79.513 (1934): 69–86.
Primary sources
* Connor, Guy, and Jeffrey L. Patrick. "On Convoy Duty in World War I: The Diary of Hoosier Guy Connor." ''Indiana Magazine of History'' (1993)online
World War II
* Edwards, Bernard. ''The road to Russia: Arctic convoys 1942'' (Leo Cooper Books, 2002) * Forczyk, Robert. ''Fw 200 Condor Vs Atlantic Convoy, 1941-1943'' (Osprey Publishing, 2010) * Hague, Arnold. ''The allied convoy system, 1939-1945: its Organization, Defence and Operation'' (Naval Institute Press, 2000) * Kaplan, Philip, and Jack Currie. ''Convoy: merchant sailors at war, 1939-1945'' (Aurum Press, 1998) * Middlebrook, Martin. ''Convoy: the Battle for Convoys SC. 122 and HX. 229'' (Allen Lane, 1976) * Milner, Marc. "Convoy Escorts: Tactics, Technology and Innovation in the Royal Canadian Navy, 1939-1943." Military Affairs: The Journal of Military History, Including Theory and Technology (1984): 19–25. * O'Hara, Vincent P. ''In Passage Perilous: Malta and the Convoy Battles of June 1942'' (Indiana University Press, 2012) * Smith, Peter Charles. ''Arctic Victory: The Story of Convoy PQ 18'' (Kimber, 1975) * Winton, John. ''Convoy, The Defense of Sea Trade 1890–1990'', 1983.Official history
* Commander in Chief, United States Fleet, "Convoy and Routing." Washington, 1945. 147 pp.External links
– a comprehensive analysis of certain naval convoy routes
Aid Convoy
– a humanitarian aid charity running convoys {{Authority control Naval warfare Water transport Road transport Vehicle operation